clutch ASTON MARTIN DB7 1997 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: ASTON MARTIN, Model Year: 1997, Model line: DB7, Model: ASTON MARTIN DB7 1997Pages: 421, PDF Size: 9.31 MB
Page 314 of 421
^?
Air Conditioning
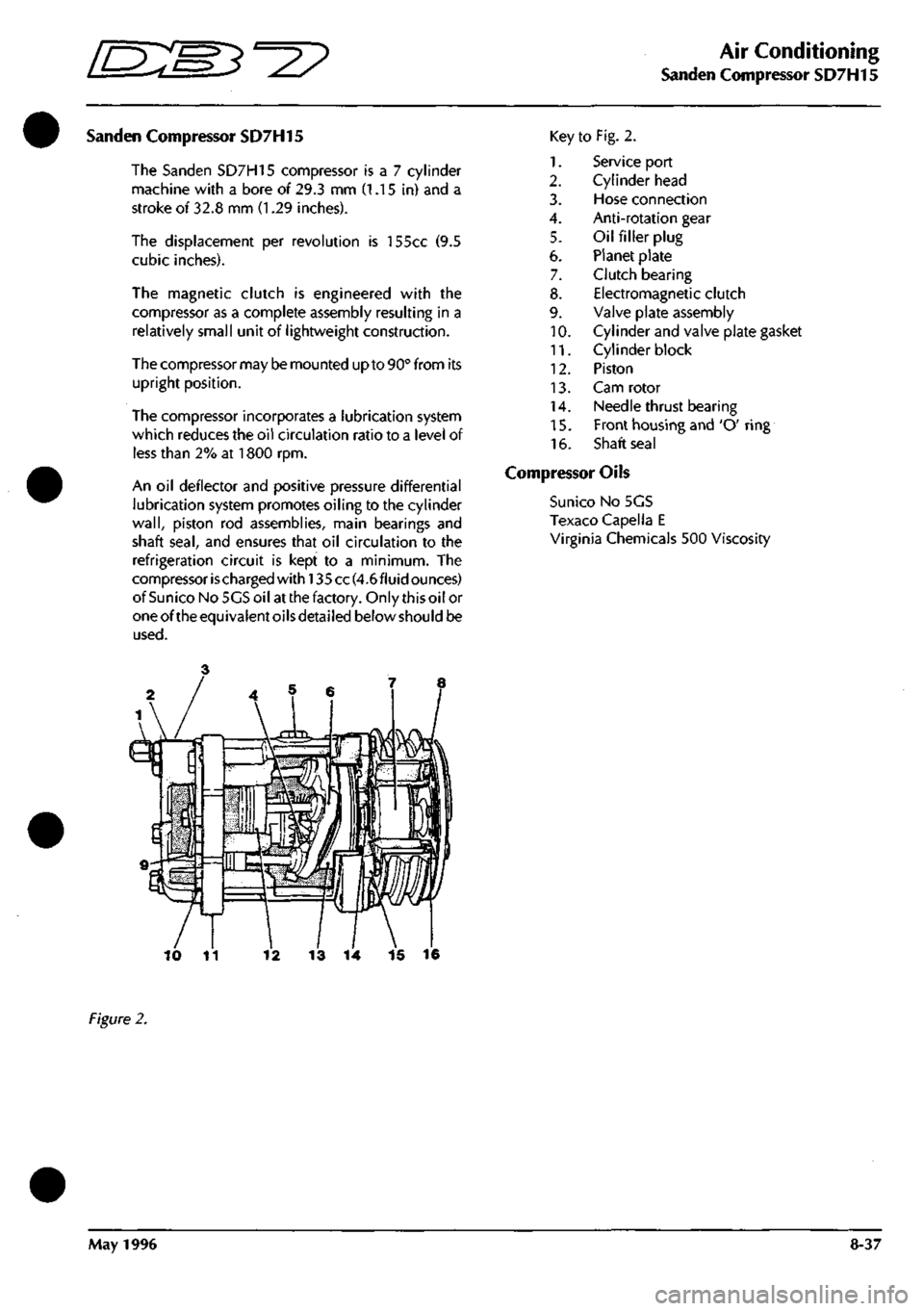
Sanden Compressor SD7H15
Sanden Compressor SD7H15
The Sanden SD7H15 compressor
is a 7
cylinder
machine with
a
bore
of
29.3
mm (1.15 in) and a
stroke
of
32.8
mm (1.29
inches).
The displacement
per
revolution
is
155cc
(9.5
cubic inches).
The magnetic clutch
is
engineered with
the
compressor
as a
complete assembly resulting
in a
relatively small unit
of
lightweight construction.
The compressor may be mounted up to 90° from
its
upright position.
The compressor incorporates
a
lubrication system
which reduces the
oil
circulation ratio
to a
level
of
less than
2% at 1800 rpm.
An
oil
deflector
and
positive pressure differential
lubrication system promotes oiling
to the
cylinder
wall,
piston
rod
assemblies, main bearings
and
shaft
seal,
and
ensures that
oil
circulation
to the
refrigeration circuit
is
kept
to a
minimum.
The
compressor ischarged
with!
35 cc(4.6fluid ounces)
ofSunico NoSGSoil at the factory. Only this oil
or
oneoftheequivalentoilsdetailed below should
be
used.
Key
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
to Fig. 2.
Service port
Cylinder head
Hose connection
Anti-rotation gear
Oil filler plug
Planet plate
Clutch bearing
Electromagnetic clutch
Valve plate assembly
Cylinder and valve plate gasket
Cylinder block
Piston
Cam rotor
Needle thrust bearing
Front housing and 'O' ring
Shaft seal
Compressor Oils
Suni
CO
No 5GS
Texaco Capella E
Virginia Chemicals 500 Viscosity
13
14 15 16
Figure
2.
May
1996
8-37
Page 326 of 421

^2?
Air Conditioning
System Recharging / Compressor Oil Check
Recharging the System
1.
Open the high side valve on the unit control panel.
If the messages PROGRAM and CHARGE are not
displayed press the CHG key to enter PROGRAM
mode.
2.
Key in the amount of refrigerant needed to recharge
the system and press ENTER.
3. Press the CHG key; the message AUTOMATIC and
the entered amount of refrigerant wi
11
be displayed.
The display counts down to zero as the charging
process proceeds. When the charging is complete
the message CPL is displayed.
If the refrigerant transfer is too slow the charging
unit emits a signal. If the message CHECK
REFRIGERANT is not displayed, close the high side
valve,
open the low side valve and start the air
conditioning system to pull the remainder of the
charge into the system.
If the refrigerant transfer will not complete and the
message CHECK REFRIGERANT is displayed, press
the HOLD/CONT key to interrupt the cycle then
reset the unit by pressing the RESET key. Recover
the refrigerant already charged into the system by
following the procedure for recovering the
refrigerant, add new refrigerant to the tank and
return to Step 1 to recharge the system.
4.
If the air conditioning system is not running start it
and let it run until the gauge pressure readings
stabilize (compare the gauge readings with the
system manufacturer's specifications).
Note:
Ensure
that the
readings
are accurate by closing
both the high and low side
valves
on the unit's control
panel.
5. Check the evaporator outlet temperature to make
sure that the air conditioning system is operating
properly (refer to the system manufacturer's
specifications for the proper temperature).
Compressor Oil Checic
Data
Special Tools
Sanden oil dipstick JD 149
Torque Figures
Oil filler plug 8-12 Nm
Procedure
Whenever a component has been replaced in the
refrigerator system or there is an obvious oil leak, the
following procedure should be carried out.
A Sanden oil dipstick and angle gauge are required in
order to carry out the check.
1.
Run the compressor for 10 minutes at engine idle
speed.
2.
Depressurise the system.
3. Lay the angle gauge across the flat surfaces of the
two front mounting lobes. Centre the bubble and
note the mounting angle.
4.
Remove the compressor from the vehicle.
3. Remove the plug from the oil filler hole
(1
Fig. 1).
4.
Rotate the counter weight (3 Fig. 1) on the front of
theclutchtoallowthedipstick(2 Fig. 1)to penetrate
to its fullest extent.
Figure 1.
5. Insert the dipstick to its stop position (4 Fig. 1). The
point of dipstick angle should be facing left.
6. Removethedipstickandchecktheoil levelagainst
the figures quoted in the chart below.
May 1996 8-49
Page 329 of 421

Air Conditioning Repair Procedures
Field Coil Renewal
/
Gasket Kit Renewal ffi^e^'^^
8.1.02.1 Field Coil Renewal 8.1.03.1 Renew Gasket
Kit
Procedure
1.
Open
the
bonnet
and fit a
wing cover.
2.
Depressurise
the air
conditioning system.
3. Remove
the
compressor.
4.
Remove
the
compressor drive clutch.
5. Remove
the
compressor pulley.
6. Slacken
the
field coil wire clamp screw
(Fig.
1) and
release
the
wire from
the
clamp.
10.
Remove
the
field coil retaining snap ring
and
detach
the
field
coil.
Clean
the
mating face
of the
compressor with
a
cloth moistened with
an
approved cleaning
fluid.
Position
the new
field coil
on the
compressor
and
fit
the
retaining snap
ring.
Route
the
wire
to the
compressor
and fit the
wire
clamp, tighten
the
securing screw.
11.
Fit the
compressor pulley.
12.
Fit the
compressor drive clutch.
13.
Fit the
compressor.
14.
Recharge
the air
conditioning system.
15.
Remove
the
wing cover
and
close
the
bonnet.
Data
Torque Figures
Cylinder head bolts 29.83
to 33.9 Nm.
Procedure
1.
Open
the
bonnet
and fit a
wing cover.
2.
Depressurise
the air
conditioning system.
3. Remove
the
compressor.
4.
Position
the
compressor
in a
vice, tighten
the
vice
onto
the
compressor body lugs.
5. Remove the outlet port blanking plate securing bolt
and detach
the
plate.
6. Remove
and
discard
the 'O'
ring seals from
the
outlet port.
7. Remove
the
compressor cylinder head securing
bolts,
detach
the
cylinder head.
8. Detach
the
valve plate from
the
compressor.
9. Remove
the
gaskets from
the
compressor.
10.
Remove
all
traces
of
gasket material from
the
mating surfaces
of the
cylinder head, valve plate
and cylinder block.
Figure
1.
11.
Position
new
gaskets (Fig.
1 -1
and 3) on the
valve
plate
(Fig. 1-2) and
then place
it on the
cylinder
block.
8-52 May
1996
Page 343 of 421

Air Conditioning
Portable Diagnostic Unit - Signal Monitoring 3^^?
Air Conditioning Signal Monitoring
The following signals can be monitored using the PDU. The abbreviated name of the signal is shown on the PDU
display.
Display Name Full Signal Name
AMBTEMP Ambient temperature sensor
ARECIP Auto-Recirculation input
ARECOP Auto-Recirculation output
AUX+ Auxiliary battery positive
CLUREL Clutch relay drive output
CVSOL Centre vent solenoid
DEFSOL Defrost solenoid
DIFF Temperature differential
EVSEN Evaporator sensor
FANDEF Fanspeed defrost
FANHIG Fanspeed high
FAN LOW Fanspeed low
FANMED Fanspeed medium
FIVEV Five volt supply voltage
FORSERL Lower servo forward drive
FORSERU Upper servo forward drive
GND10 Ground voltage
GND2 Ground voltage
GND38 Ground voltage
GND45 Ground voltage
GND6 Ground voltage
HSREL High speed relay drive
ICSEN In-Car sensor
LBLOFB Left blower feedback voltage
LBLOWOP Left blower output voltage
LSERFB Lower servo feedback potentiometer
MPROBE Measurement probe
POWIN+ Switched power input
POWOP+ Power output
RBLOFB Right blower feedback voltage
RBLOWOP Right blower output voltage
REF Reference signal
REVSERL Lower servo reverse drive
REVSERU Upper servo reverse drive
TEMPDEM Temperature demand
USERFB Upper servo feedback potentiometer
WATSW Water switch
WATVAL Water valve
8-66 May 1996
Page 344 of 421

^=2?
Air Conditioning
Portable Diagnostic Unit - Signal Definitions
ThefollowingsignalsaresupportedontheAir-ConditioningControlModule. For each signal. The signal name, mnemonic
and background information are detailed.
Ambient Temperature Sensor
(AMBTEMP)
Auto-Recircuiation Input
(ARECIP)
Auto-Recirculation Output
(ARECOP)
Auxiliary Battery Positive
(AUX+)
Clutch Relay Drive Output
(CLUREL)
A/CCM Pin 34 ref Pin 6
This sensor is located in the right hand blower motor. This signal is used to enable
the A/C system to compensate for changes in ambient air temperature. The output
to pin 34 is 2.732 volts at 0 degrees Celsius and changes by 0.01 volts for each
degree Celsius above or below zero.
A/CCM Pin 9 ref Pin 6
This is effectively an On/Off switch for the A/C system and forms part of the fan
control switch.
Switch Off - Pin 9 should be at ground
Switch On - Pin 9 should be at 10+ volts.
When pin 9 is at ground, pin 3 will be at 10+ volts causing the recirculation flaps
to open.
A/CCM Pin 3 ref Pin 6
This signal will cause the recirculation flaps to close. Operating conditions should
be:
A/C Off - 10+ volts at pin 3, flaps open.
Temp demand minimum - 10+ volts at pin 3, flaps open.
Defrost - 0 volts at pin 3, flaps closed.
Temp demand max - 0 volts at pin 3, flaps closed.
A/CCM Pin 1 ref Vehicle Battery -ve
This signal istheauxiliary supply to the A/CCM. Pin
1
should read battery voltage
if the ignition switch is in the auxiliary or ignition on positions. Pin
1
should read
0 volts when the ignition switch is in the Off position or in position III whilst
cranking the engine. Loss of this supply will cause total failureof the A/C system.
A/CCM Pin 20 ref Pin 6
This signal responds to the input at pin 5 (evaporator sensor). When pin 5 is
between 2.715 and 2.725 volts, pin 20 should read below 1 volt, and the
compressor clutch will be switched off. When pin 5 is between 2.735 and 2.745
volts,
pin 20 will rise to 10+ volts and the compressor will re-engage.
Centre Vent Solenoid
(CVSOL) A/CCM Pin 18 ref Pin 6
The centre vent solenoid controls the operation of the centre vent flap. The centre
vent will open to increase the cooling capabilities of the vehicle when cooling is
selected.
In all other conditions, the centre vent will be closed.
Solenoid energised: pin 18 should read 10+volts and the centre vent will be open.
Solenoid de-energised; pin 18 should read below 0.5 volts and the centre vent
should be closed.
May 1996 8-67
Page 392 of 421

^^?
The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide
Transmission Diagnostics
Selecting 'Transmission from the vehicle area menu will
present the technician with the following transmission
diagnostic tools menu:
Transmission Diagnostic
• Datalogger
• Diagnostic Trouble Codes
o
The Datalogger function is fully described in the worked
example at the rear of this PDU Users Guide.
Transmission Datalogger
The PDU datalogger function may be used to monitor the
following transmission controller signals
DIGS Number of DTCs Logged
The Diagnostics status manager (DSM) receives and
processes fault information and decides when a DTC
should be logged and the MIL turned on (if enabled). The
actual total stored is indicated by the parameter DTCS.
FBRAKE Brake Switch
The footbrake switch signal is input to the
TCM.
The input
is normally at ground potential and goes open circuit
when the brakes are applied. If the torque converter
clutch is applied it will disengage when this signal is
detected.
FMA Actual Force Motor Current
The force motor regulates the transmission fluid pressure.
It is a variable force solenoid whose coil current is
determined by the TCM. Range 0 -1.245 amps. A driver
circuit limits excessive current flow and performs a
ratiometric comparison of Desired (commanded) Force
Motor Current and Actual Force Motor current. The
parameter monitors the Actual Force Motor current 1 Bit
= l/204.8amps.
HOT Hot Mode
The signal from the transmission temperature sensor is
used to control TCC and line pressure. It is also used in
many diagnostic signals and is a critical component for
OBD II. Above 120°C the TCC is on in 2nd, 3rd and 4th
gears.
This reduces transmission temperature by decreasing
the heat generated by the torque converter. It also
provides maximum cooling by routing transmission fluid
directly to the transmission cooler in the radiator. When
the Hot Mode is ON the bit is set to 1.
IGN+ Ignition Feed Positive
The TCM receives ignition voltage through TCM pin 53.
MD Desired Force Motor Current
The force motor regulates the transmission fluid pressure.
It is a variable force solenoid whose coil current is
determined by the TCM. Range 0 -1.245 amps. A driver
circuit limits excessive current flow and performs a
ratiometric comparison of Desired (commanded) Force
Motor Current. The parameter mon itors the Desired Force
Motor current 1 Bit = 1/204.8amps.
RATIO Actual Gear Ratio
The diagnostic detects malfunction in the transmission
output components by monitoring the actual gear ratio.
The actual gear ratio is calculated using input (Ni) and
output speed (No): Ratio = Ni/No. This is compared with
the standard gear ratio for each gear. Malfunction can be
defined as: actual gear ratio is not equal to any of the
standard gear ratios.
RPM Engine Speed
The engine speed signal is input from the instrument pack.
The
signal
origi
nates
at the crankshaft
sensor.
The crankshaft
sensor signal is modified by the PCM and the instrument
pack before being input to the TCM.
SSA Shift Solenoid A
Shift solenoid A is attached to the valve body and its outlet
is open to exhaust when it is switched off. A OFF - outlet
open - 2nd and 3rd gears selected. The solenoid is
energised by the TCM providing an internal ground to
close the outlet. A ON - outlet closed -1 st and 4th gears
selected.
SSB Shift Solenoid B
Shift solenoid B is attached to the valve body and its outlet
is open to exhaust when it is switched off. B OFF - outlet
open - 1st and 2nd gears selected. The solenoid is
energised by the TCM providing an internal ground to
close the outlet. B ON - outlet closed - 3rd and 4th gears
selected.
September 1996 9-41
Page 393 of 421

The Aston Martin Lagonda Diagnostic System
Users Guide ^7
TCCS Torque Convertor Clutch Solenoid
The torque converter clutch solenoid is mounted on the
valve body. The signal is Pulse Width Modulated at 32Hz
to provide closed loop control of the pressure across the
converter clutch plates. 1 bit = 0.39% Range 0 to 100%
TP Throttle Position
This is provided by the EECV Engine Management System
as a Pulse Width Modulated signal derived from the
throttle position signal read by that module from the
throttle position sensor.
TCS Torque Convertor Slip
Torque converter slip is defined
as
the difference between
the Input/turbine (ni) speed and the Engine speed (Ne):
Slip = Ne-Ni. The PWM duty cycle may increase from 0
to 100% when TCC is fully applied. In practice a 100%
duty cycle will be achieved only if
a
large slip is detected.
Normal ly only a 50 to 95% duty cycle will be required for
full application of the TCC. Slip is expressed in rpm. 1 Bit
- 1/8 rpm. Range -4096 to +4096 rpm.
TCSW Transmission Control Switch
A three position switch allows the driver to select Sport,
Normal or 1st Gear Inhibit mode. When 'Sport' is selected
gearshifts take place at higher engine revs. When '1st
Gear Inhibit' is selected, the transmission only operates in
the higher forward ratios to prevent wheel slip in icy
conditions.
TISSA Turbine Input Shaft Speed
Turbine speed is the speed of the input shaft of the
transmission measured by the input speed sensor mounted
on the transmission. An alternating waveform is induced
in the sensor by 31 serrations on the forward clutch
housing as it rotates. The waveform frequency and
amplitude is low at low speeds and high at high speeds.
The TCM changes this signal into a digital signal. 1 bit =
1/8 RPM. Range: 0 - 8192 RPM.
TOS+ Transmission Output Speed
The output speed sensor is mounted on the transmission
case and measures the speed of the output shaft. As the
shaft rotates an alternating waveform is induced in the
sensor which varies in frequency and voltage. The wave
form is converted into
a
digital signal by the TCM and used
to control TCC, line pressure, shift timing and torque
management. 1 bit = 1/8 RPM. Range 0-8192 RPM
TRX Transmission Control Switch X
TRY Transmission Control Switch Y
TRZ Transmission Control Switch Z
The transmission range is detected by the pressure switch
manifold (PSM) and input to the
TCM.
The signal consists
of three discrete lines X, Y, Z which transmit a 3 bit binary
code as shown in the table below.
0 = open circuit
1 = short circuit to ground
X Y Z
p
R
N
D
3
2
Error
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
VS Vehicle Speed
Veh icie speed
is
derived from
a pu Ised
wave form generated
by the speed sensor in the hypoid unit. There are 40 pulses
per shaft rotation and the TCM converts this to vehicle
speed and applies correction for axle ratio and road wheel
diameter. 1 bit -
1
kph. Range 0 - 255kph
Transmission Diagnostic Trouble Codes
The diagnostic trouble codes supported by the CM 4L80-
E
Transmission Control Module are covered indetail inthe
DB7 OBD II Diagnostics Manual.
TOT Transmission Oil Temperature
The transmission temperature sensor signal is used to
control TCC and line
pressure.
It
has a
negative temperature
coefficient so when the temperature is cold its resistance
is high and the TCM sees
a
high voltage. Asthe temperature
warms the volts drop across the sensor decreases and the
signal voltage becomes lower. The TCM converts this
analogue input into a digital signal.
1 bit =
1
°C Range -55°C to +200°C.
9-42 September 1996