Lambda AUDI S4 1998 B5 / 1.G Engine Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: AUDI, Model Year: 1998, Model line: S4, Model: AUDI S4 1998 B5 / 1.GPages: 72, PDF Size: 3.25 MB
Page 18 of 72
19
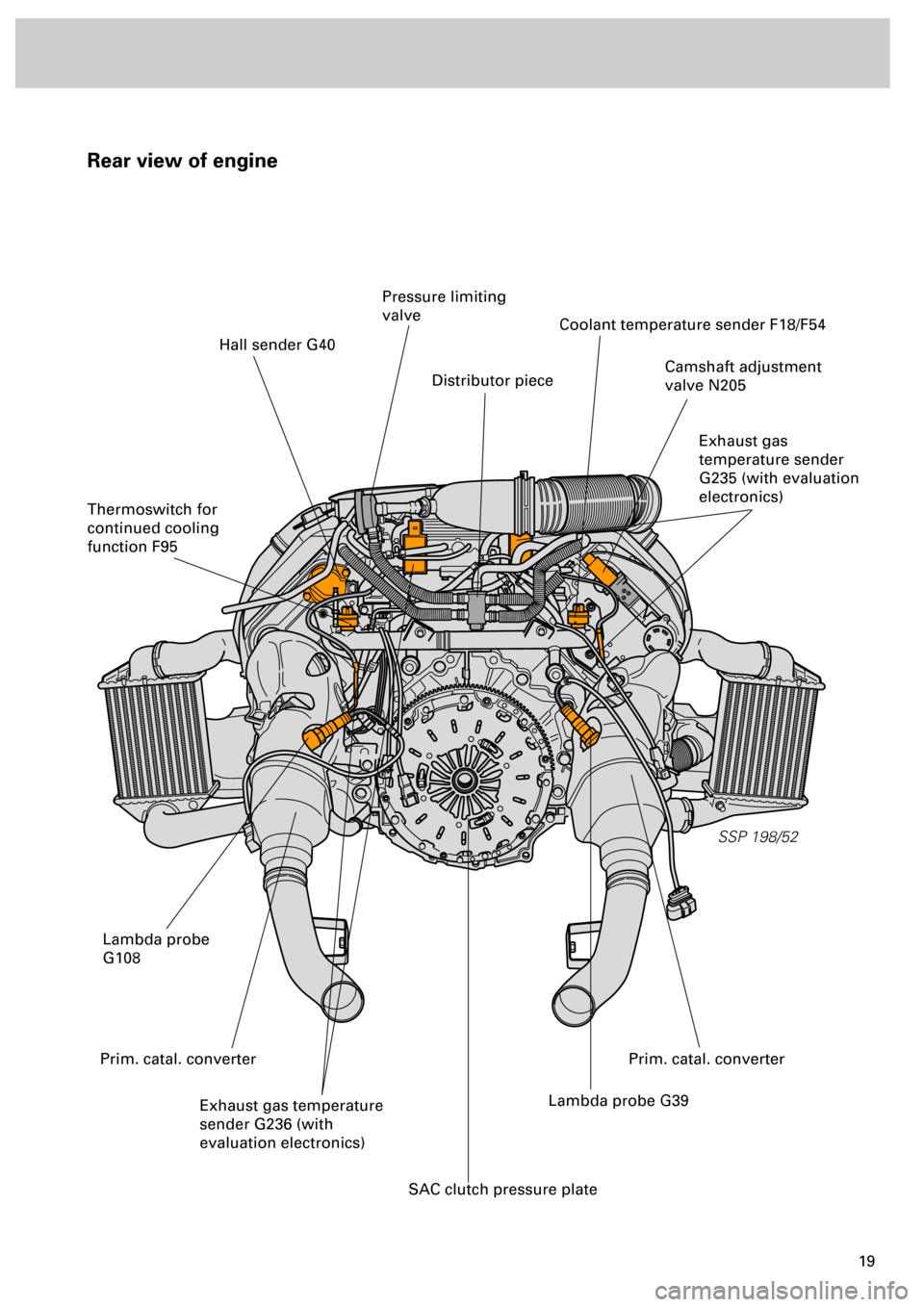
Rear view of engine
SSP 198/52
Hall sender G40
Thermoswitch for
continued cooling
function F95
Pressure limiting
valve
Distributor piece
Coolant temperature sender F18/F54
Camshaft adjustment
valve N205
Exhaust gas
temperature sender
G235 (with evaluation
electronics)
Lambda probe
G108
Exhaust gas temperature
sender G236 (with
evaluation electronics)Lambda probe G39
SAC clutch pressure plate
Prim. catal. converterPrim. catal. converter
Page 23 of 72
24
SSP 198/33
Engine
A new generation of probes is used
in this engine.
The “planar lambda probe“ is an
improvement on the finger-type
lambda probe (refer to chapter on
“Sensors”).
Advantage:
•
Short warm-up time
•
Less heating energy demand
•
Long service life
•
More stable control
characteristic
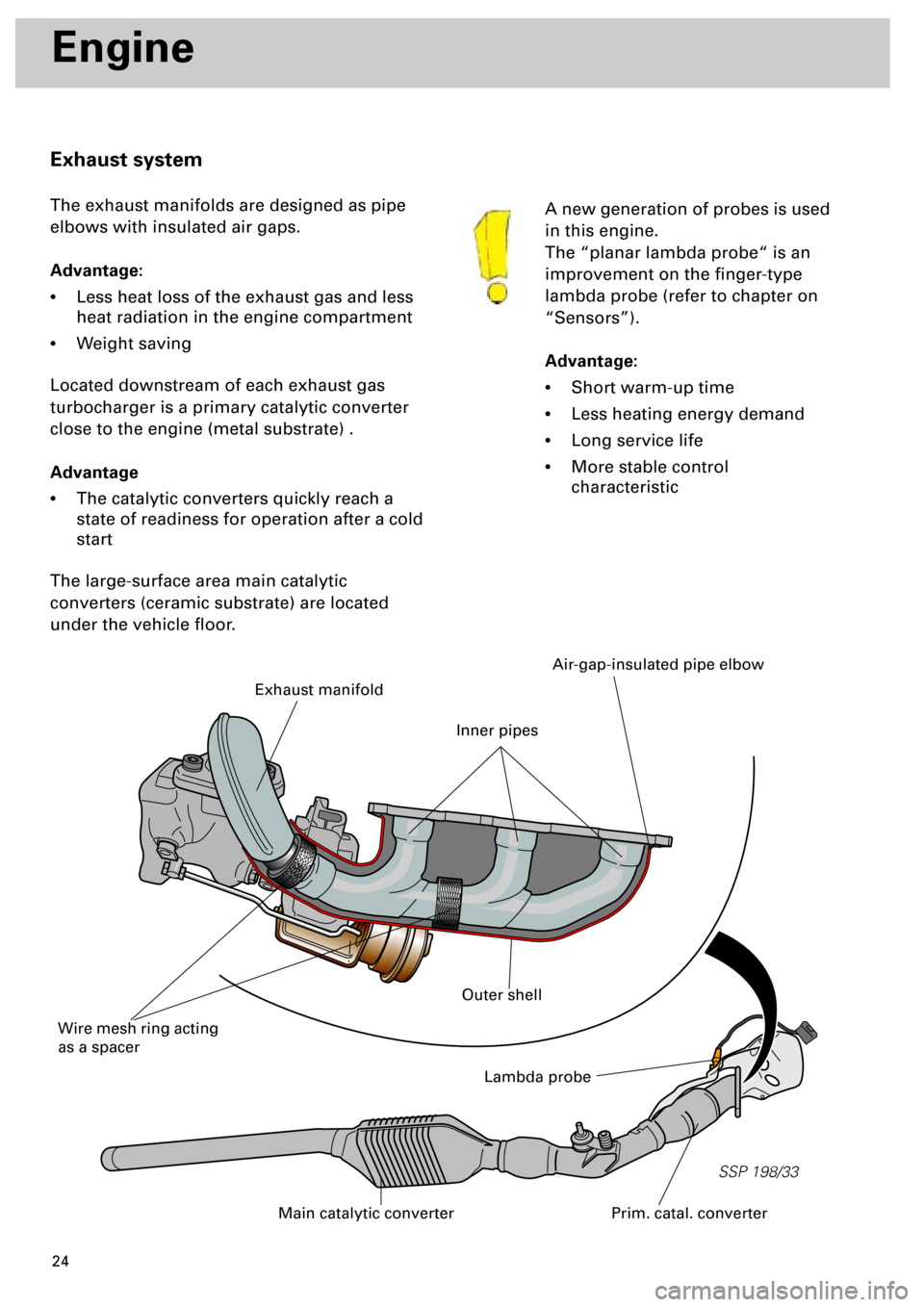
Exhaust system
The exhaust manifolds are designed as pipe
elbows with insulated air gaps.
Advantage:
•
Less heat loss of the exhaust gas and less
heat radiation in the engine compartment
•
Weight saving
Located downstream of each exhaust gas
turbocharger is a primary catalytic converter
close to the engine (metal substrate) .
Advantage
•
The catalytic converters quickly reach a
state of readiness for operation after a cold
start
The large-surface area main catalytic
converters (ceramic substrate) are located
under the vehicle floor.
Lambda probe
Prim. catal. converterMain catalytic converter
Exhaust manifold
Wire mesh ring acting
as a spacer
Air-gap-insulated pipe elbow
Outer shell
Inner pipes
Page 30 of 72
31
Motronic ME 7.1
Subfunctions of the Motronic
The Motronic consists of known and new subfunctions:
Sequential injection
Charge pressure control
(see chapter on “Engine” pp. 26 and 27)
Stereo lambda control
Mapped ignition
Cylinder-selective knock control
Static high-tension distribution with 6 individual ignition coils
ACF system
Torque-oriented engine management
Electrically actuated throttle valve (Electronic accelerator)
Cylinder bank-specific exhaust gas temperature control
Mapped variable valve timing (intake camshaft adjustment)
(see chapter on “Engine” p. 8)
New
New
New
New
l
SSP 198/44
Page 31 of 72
32
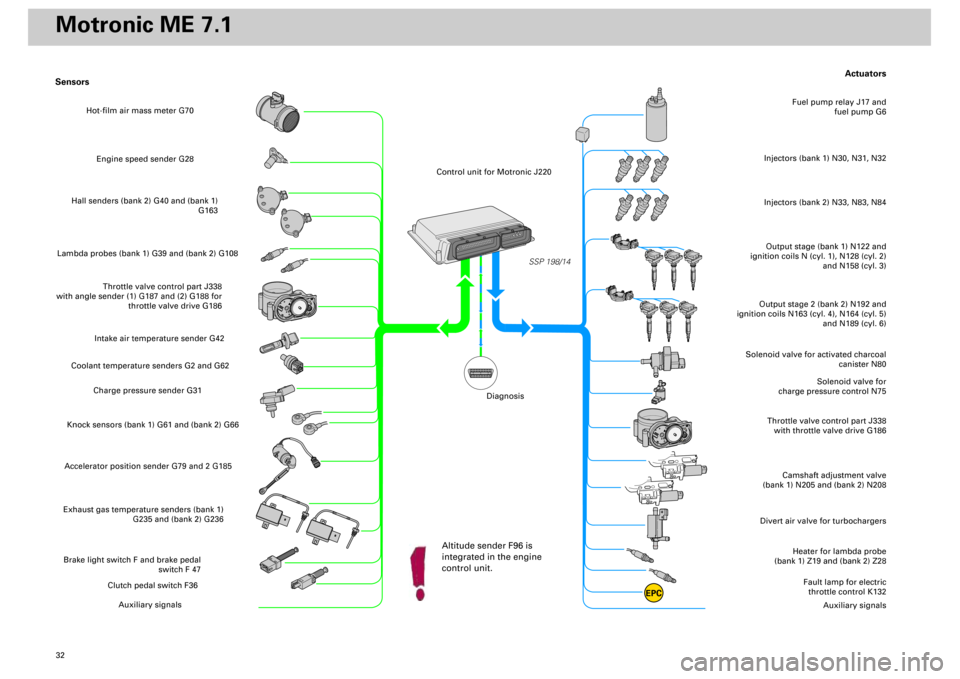
Actuators
Heater for lambda probe
(bank 1) Z19 and (bank 2) Z28
Divert air valve for turbochargers
Camshaft adjustment valve
(bank 1) N205 and (bank 2) N208
Throttle valve control part J338
with throttle valve drive G186
Solenoid valve for
charge pressure control N75
Solenoid valve for activated charcoal
canister N80
Output stage (bank 1) N122 and
ignition coils N (cyl. 1), N128 (cyl. 2)
and N158 (cyl. 3)Injectors (bank 1) N30, N31, N32
Fuel pump relay J17 and
fuel pump G6
Output stage 2 (bank 2) N192 and
ignition coils N163 (cyl. 4), N164 (cyl. 5)
and N189 (cyl. 6)
Fault lamp for electric
throttle control K132
Auxiliary signals
Sensors
Engine speed sender G28
Hall senders (bank 2) G40 and (bank 1)
G163
Lambda probes (bank 1) G39 and (bank 2) G108
Throttle valve control part J338
with angle sender (1) G187 and (2) G188 for
throttle valve drive G186
Intake air temperature sender G42
Coolant temperature senders G2 and G62
Charge pressure sender G31
Knock sensors (bank 1) G61 and (bank 2) G66Accelerator position sender G79 and 2 G185Exhaust gas temperature senders (bank 1)
G235 and (bank 2) G236Brake light switch F and brake pedal
switch F 47
Clutch pedal switch F36
Auxiliary signals
SSP 198/14
EPC
Injectors (bank 2) N33, N83, N84
Hot-film air mass meter G70
Control unit for Motronic J220
Altitude sender F96 is
integrated in the engine
control unit.
Diagnosis
Motronic ME 7.1
Page 45 of 72
46
SSP 198/26
Subsystems of the Motronic
Exhaust gas temperature control
A new feature of Audi automobiles
is a function which monitors
exhaust gas temperature over the
entire engine speed range.
For turbocharged engines, the maximum
permissible exhaust gas temperature is a key
design criterion.
To protect the exhaust gas turbocharger and
the exhaust manifold, the exhaust gas
temperature should not exceed 1000 °C for a
lengthy period of time.
Since many of the components which
influence the exhaust gas temperature have
tolerances, thermodynamic adaptation
previously took place at 950 °C for safety’s
sake.
This was achieved by enriching the air/fuel
mixture.
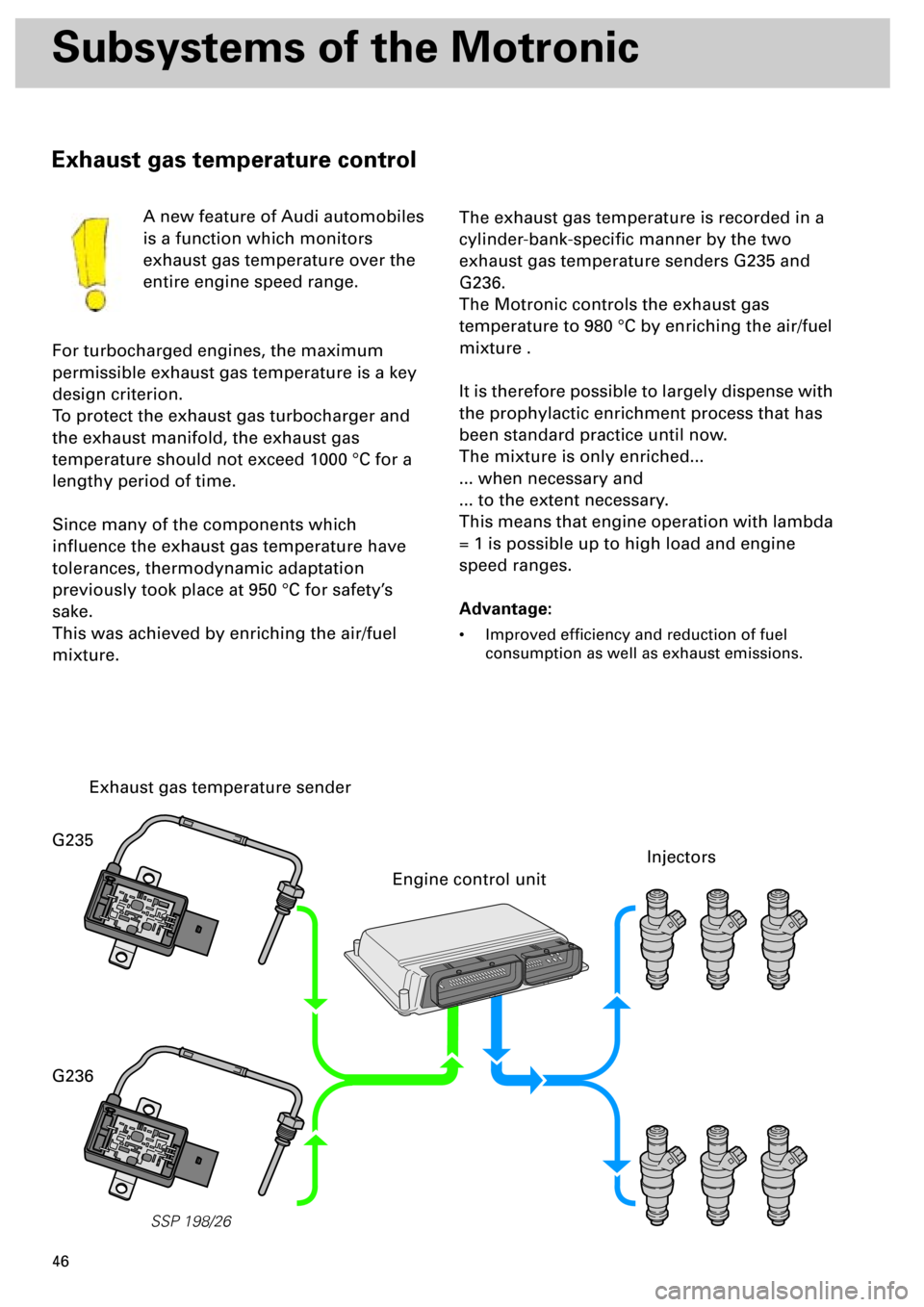
The exhaust gas temperature is recorded in a
cylinder-bank-specific manner by the two
exhaust gas temperature senders G235 and
G236.
The Motronic controls the exhaust gas
temperature to 980 °C by enriching the air/fuel
mixture .
It is therefore possible to largely dispense with
the prophylactic enrichment process that has
been standard practice until now.
The mixture is only enriched...
... when necessary and
... to the extent necessary.
This means that engine operation with lambda
= 1 is possible up to high load and engine
speed ranges.
Advantage:
• Improved efficiency and reduction of fuel
consumption as well as exhaust emissions.
Exhaust gas temperature sender
Engine control unit
Injectors
G235
G236
Page 51 of 72
52
Sensors
Lambda probes G39 and G108
The planar lambda probe is a further
development of the finger-type lambda probe
and has a transient response at lambda = 1.
There is a single lambda probe in the exhaust
pipe running to each of the primary catalytic
converters.
To ensure that the exhaust gases are treated
efficiently, it is important that the lambda
probe should react quickly. The lambda probe
should therefore reach its operating
temperature within as short a space of time as
possible. Its planar (= flat, elongated) design
makes this possible.
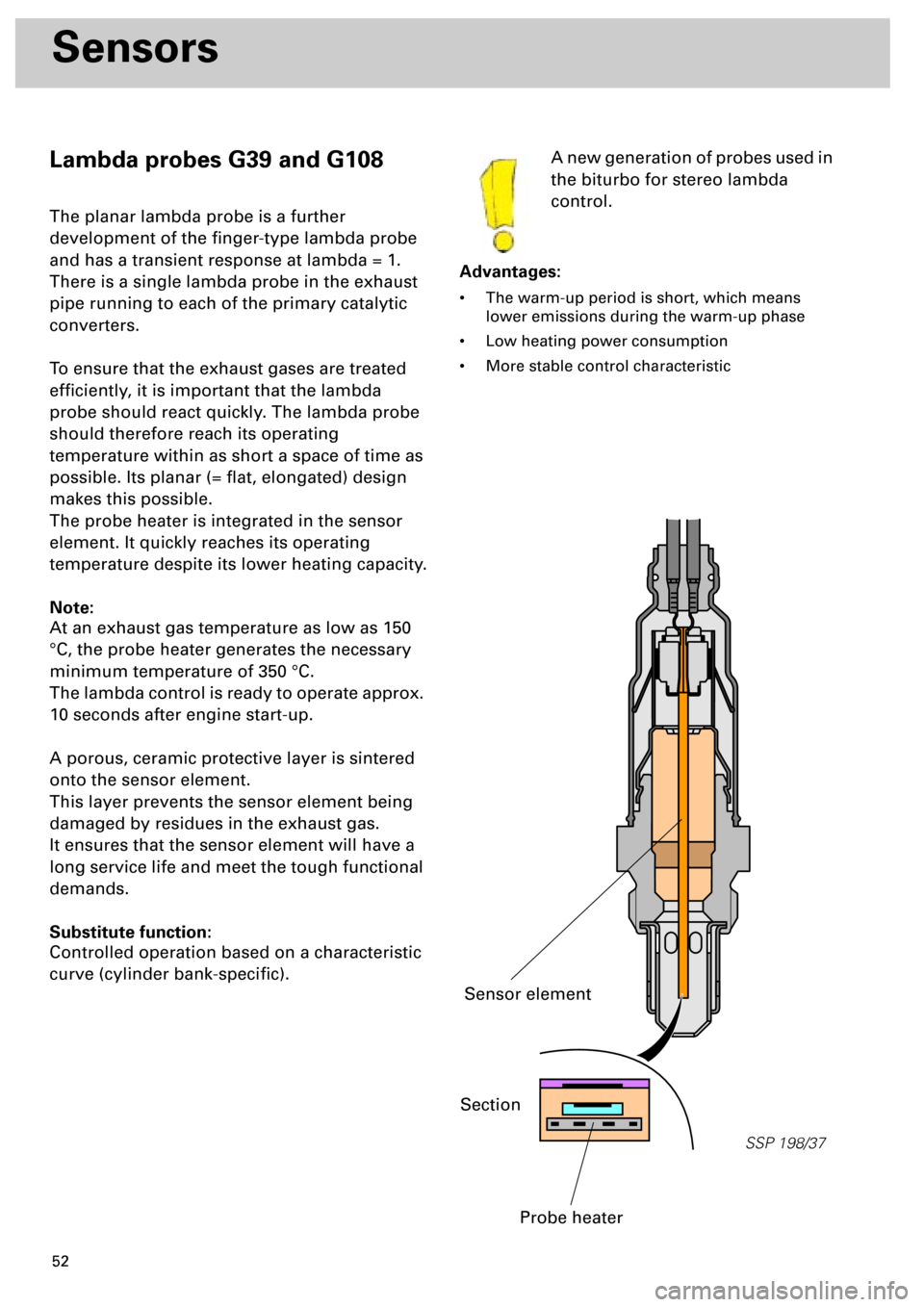
The probe heater is integrated in the sensor
element. It quickly reaches its operating
temperature despite its lower heating capacity.
Note:
At an exhaust gas temperature as low as 150
°C, the probe heater generates the necessary
minimum temperature of 350 °C.
The lambda control is ready to operate approx.
10 seconds after engine start-up.
A porous, ceramic protective layer is sintered
onto the sensor element.
This layer prevents the sensor element being
damaged by residues in the exhaust gas.
It ensures that the sensor element will have a
long service life and meet the tough functional
demands.
Substitute function:
Controlled operation based on a characteristic
curve (cylinder bank-specific).A new generation of probes used in
the biturbo for stereo lambda
control.
Advantages:
• The warm-up period is short, which means
lower emissions during the warm-up phase
• Low heating power consumption
• More stable control characteristic
SSP 198/37
Section
Probe heater
Sensor element
Page 61 of 72
62
Functional diagram
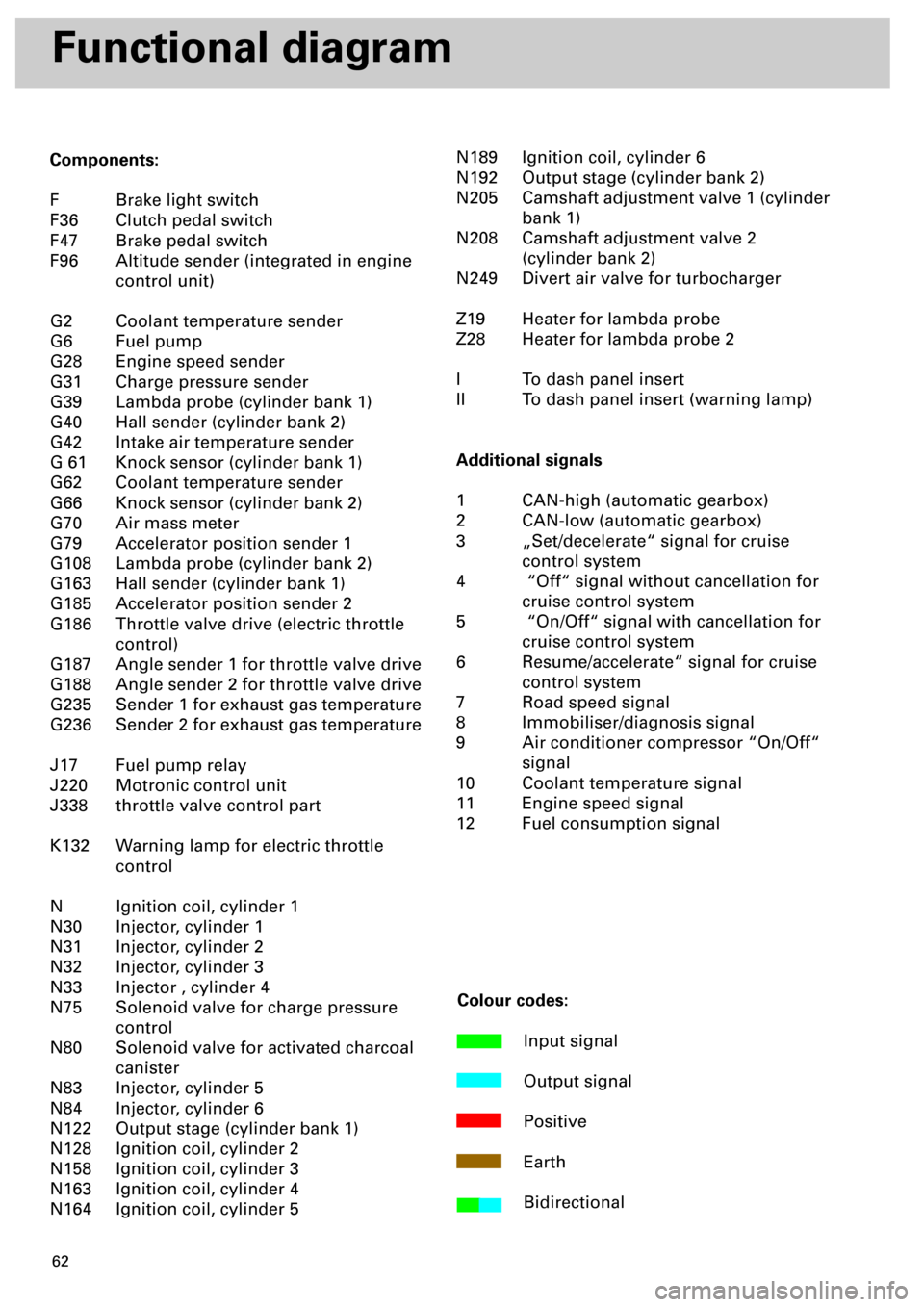
Components:
F Brake light switch
F36 Clutch pedal switch
F47 Brake pedal switch
F96 Altitude sender (integrated in engine
control unit)
G2 Coolant temperature sender
G6 Fuel pump
G28 Engine speed sender
G31 Charge pressure sender
G39 Lambda probe (cylinder bank 1)
G40 Hall sender (cylinder bank 2)
G42 Intake air temperature sender
G 61 Knock sensor (cylinder bank 1)
G62 Coolant temperature sender
G66 Knock sensor (cylinder bank 2)
G70 Air mass meter
G79 Accelerator position sender 1
G108 Lambda probe (cylinder bank 2)
G163 Hall sender (cylinder bank 1)
G185 Accelerator position sender 2
G186 Throttle valve drive (electric throttle
control)
G187 Angle sender 1 for throttle valve drive
G188 Angle sender 2 for throttle valve drive
G235 Sender 1 for exhaust gas temperature
G236 Sender 2 for exhaust gas temperature
J17 Fuel pump relay
J220 Motronic control unit
J338 throttle valve control part
K132 Warning lamp for electric throttle
control
N Ignition coil, cylinder 1
N30 Injector, cylinder 1
N31 Injector, cylinder 2
N32 Injector, cylinder 3
N33 Injector , cylinder 4
N75 Solenoid valve for charge pressure
control
N80 Solenoid valve for activated charcoal
canister
N83 Injector, cylinder 5
N84 Injector, cylinder 6
N122 Output stage (cylinder bank 1)
N128 Ignition coil, cylinder 2
N158 Ignition coil, cylinder 3
N163 Ignition coil, cylinder 4
N164 Ignition coil, cylinder 5N189 Ignition coil, cylinder 6
N192 Output stage (cylinder bank 2)
N205 Camshaft adjustment valve 1 (cylinder
bank 1)
N208 Camshaft adjustment valve 2
(cylinder bank 2)
N249 Divert air valve for turbocharger
Z19 Heater for lambda probe
Z28 Heater for lambda probe 2
I To dash panel insert
II To dash panel insert (warning lamp)
Additional signals
1 CAN-high (automatic gearbox)
2 CAN-low (automatic gearbox)
3 „Set/decelerate“ signal for cruise
control system
4 “Off“ signal without cancellation for
cruise control system
5 “On/Off“ signal with cancellation for
cruise control system
6 Resume/accelerate“ signal for cruise
control system
7 Road speed signal
8 Immobiliser/diagnosis signal
9 Air conditioner compressor “On/Off“
signal
10 Coolant temperature signal
11 Engine speed signal
12 Fuel consumption signal
Colour codes:
Input signal
Output signal
Positive
Earth
Bidirectional