ECO mode BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1983, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1983 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 1 of 228

BMW 3- & 5-Series
Service and Repair Manual
A K Legg LAE MIMI and Larry Warren
Models covered
3-Series (E30)
316 (83 to 88), 316i (88 to 91), 318i (83 to 91), 320i (87 to 91), 325i (87 to 91).
Also Touring and Convertible versions of these models
5-Series (E28)
518 (81 to 85), 518i (85 to 88), 525i (81 to 88), 528i (81 to 88), 535i (85 to 88), M535i (85 to 88)
5-Series (E34)
518i (90 to 91), 520i (88 to 91), 525i (88 to 91), 530i (88 to 91), 535i (88 to 91)
Engines covered
1596 cc, 1766 cc, 1795 cc, 1990 cc, 2494 cc, 2788 cc, 2986 cc & 3430 cc
Does not cover Diesel, dohc or V8 engines, or four-wheel-drive models
© Haynes Publishing 1997
A book in the Haynes Service and Repair Manual Series
All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted
in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including
photocopying, recording or by any information storage or retrieval system,
without permission in writing from the copyright holder.
ISBN1 85960 236 3
British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data
A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library.Printed by J H Haynes & Co. Ltd, Sparkford, Nr Yeovil,Somerset
BA22 7JJ, England
Haynes Publishing
Sparkford, Nr Yeovil, Somerset BA22 7JJ, England
Haynes North America, Inc
861 Lawrence Drive, Newbury Park, California 91320, USA
Editions Haynes S.A.
147/149, rue Saint Honoré, 75001 PARIS, France
Haynes Publishing Nordiska AB
Box 1504, 751 45 Uppsala, Sweden
(1948-256-11AA3)
ABCDE
FGHIJ
KLMNO
PQRST
1 2 3
Page 7 of 228

0•7Anti-theft audio system
Anti-theft audio system
General information
Some models are equipped with an audio
system having an anti-theft feature that will
render the stereo inoperative if stolen. If the
power source to the stereo is cut, the stereo
won’t work even if the power source is
immediately re-connected. If your vehicle is
equipped with this anti-theft system, do not
disconnect the battery or remove the stereo
unless you have the individual code number
for the stereo.
Refer to the owner’s handbook suppliedwith the vehicle for more complete
information on this audio system and its anti-
theft feature.
Unlocking procedure
1Turn on the radio. The word “CODE” should
appear on the display.
2Using the station preset selector buttons,
enter the five-digit code. If you make a
mistake when entering the code, continue
the five-digit sequence anyway. If you hear
a “beep,” however, stop immediately andstart the sequence over again. Note: Yo u
have three attempts to enter the correct
code. If the correct code isn’t entered in
three tries, you’ll have to wait one hour, with
the radio on, before you enter the codes
again.
5Once the code has been entered correctly,
the word “CODE” should disappear from the
display, and the radio should play (you’ll have
to tune-in and enter your preset stations,
however).
6If you have lost your code number, contact
a BMW dealer service department.
Instrument panel language display
On some later models, disconnecting the
battery may cause the instrument panel
display to default to the German language
(this does not usually apply to UK models). If
it is necessary to reset the correct language
after the battery is reconnected, proceed as
follows. With all the doors shut and theignition on (engine not running), press the trip
reset button until the panel displays the
desired language. There are eight languages
available. If you wish to bypass a particular
selection, release the reset button and press
again - this will cause the display to advance
to the next language. Once the correctlanguage has been selected, continue holding
the reset button until the display reads “I.O.
Version 2.0”. Continue holding the button until
it reads “H.P. Version 3.4”, then release the
button.
Page 12 of 228

Fuel system
Idle speed
3-Series, E30
316 with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 50 rpm
316i with M40/B16 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 40 rpm
318i with M10/B18 engine (manual transmission) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 50 rpm
318i with M10/B18 engine (automatic transmission) . . . . . . . . . . . 750 ± 50 rpm
318i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 40 rpm
320i with M20/B20 engine (L-Jetronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 50 rpm
320i with M20/B20 engine (Motronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760 ± 40 rpm
325i with M20/B25 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760 ± 40 rpm
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”)
518 and 518i with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 50 rpm
All other models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 50 rpm
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”)
518i with M40/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 40 rpm
520i with M20/B20M engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760 ± 40 rpm
525i with M20/B25M engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 760 ± 40 rpm
530i with M30/B30M engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 800 ± 50 rpm
535i with M30/B35M engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 850 ± 50 rpm
CO% at 3000 rpm
3-Series, E30
316 with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.5 to 1.0
316i and 318i with M40/B16 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.7 ± 0.5
318i with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 maximum
320i with M20/B20 engine (L-Jetronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 ± 0.5
320i with M20/B20 engine (Motronic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.7 ± 0.5
325i with M20/B25 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 ± 0.5
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”)
518 and 518i with M10/B18 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 maximum
525i with M30/B25 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.0 ± 0.5
528i with M30/B28 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.5 maximum
535i with M30/B34 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.3 to 1.5
M535i with M30/B34 engine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.3 to 1.5
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”)
All models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.7 ± 0.5
Air filter element
M10 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion W155 (round) or U504 (square)
M20 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion U504 or U527
M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion U504 or U527
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion U527
Fuel filter (all fuel injection engines) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion L206
Ignition system
Spark plug type
M10, M20 and M30 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion N9YCC
M40 engines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion C9YCC
Spark plug gap* . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0.8 mm
Spark plug (HT) leads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
* The spark plug gap quoted is that recommended by Champion for their specified plugs listed above. If spark plugs of any other type are to be
fitted, refer to their manufacturer’s spark plug gap recommendations.
Brakes
Disc brake pad thickness (minimum) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 mm
Drum brake shoe lining thickness (minimum) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2.0 mm
Wiper blades
Windscreen
3-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-5103
3-Series passenger side from 1991 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-5103 (20 inch) or Champion X-5303 (21 inch)
5-Series, E28 (“old-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-4503
5-Series, E34 (“new-shape”) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
Tailgate
3-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion X-4503
5-Series . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Champion type not available
1•2Servicing Specifications
Page 18 of 228

engine damage. Conversely, overfilling the
engine (adding oil above the upper mark) may
cause oil-fouled spark plugs, oil leaks, or oil
seal failures.
6To add oil, remove the filler cap located on
the valve cover (see illustrations). After
adding oil, wait a few minutes to allow the
level to stabilise, then pull the dipstick out and
check the level again. Add more oil if required.
Refit the filler cap, tightening it by hand only.
7Checking the oil level is an important
preventive maintenance step. A consistently
low oil level indicates oil leakage through
damaged seals or defective gaskets, or oil
burning (internal leakage past worn rings or
valve guides). The condition of the oil should
also be noted. If the oil looks milky in colour or
has water droplets in it, the cylinder head
gasket may be blown, or the head or block
may be cracked. The engine should be
repaired immediately. Whenever you check
the oil level, slide your thumb and index finger
up the dipstick before wiping off the oil. If you
see small dirt or metal particles clinging to the
dipstick, the oil should be changed (see
Section 6).
Engine coolant
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your
skin, or with the vehiclepaintwork. Rinse off spills immediately
with plenty of water. Antifreeze is highly
toxic if ingested. Never leave antifreeze
lying around in an open container, or in
puddles on the floor; children and pets are
attracted by its sweet smell, and may drink
it. Check with local authorities about
disposing of used antifreeze. Local
collection centres may exist, to see that
antifreeze is disposed of safely.
8All vehicles covered by this manual are
equipped with a pressurised coolant recovery
system. On most models, a white plastic
expansion tank (or coolant reservoir) located
in the engine compartment is connected by a
hose to the radiator. As the engine heats up
during operation, the expanding coolant fills
the tank. As the engine cools, the coolant is
automatically drawn back into the cooling
system, to maintain the correct level.
9The coolant level in the reservoir (see
illustrations)should be checked regularly.
Add a 40%/60% mixture of ethylene glycol-
based antifreeze to water (see illustration).
Warning: Do not remove the
expansion tank cap or radiator
cap to check the coolant level,
unless the engine is completely
cold! The level in the reservoir varies with
the temperature of the engine. When the
engine is cold, the coolant level should beabove the LOW mark on the reservoir.
Once the engine has warmed up, the level
should be at or near the FULL mark. If it
isn’t, allow the engine to cool, then remove
the cap from the reservoir.
10Drive the vehicle and recheck the coolant
level. If only a small amount of coolant is
required to bring the system up to the proper
level, plain water can be used. However,
repeated additions of water will dilute the
antifreeze. In order to maintain the proper
ratio of antifreeze and water, always top-up
the coolant level with the correct mixture.
11If the coolant level drops consistently,
there must be a leak in the system. Inspect
the radiator, hoses, filler cap, drain plugs and
water pump (see Section 29). If no leaks are
noted, have the expansion tank cap or
radiator cap pressure-tested by a BMW
dealer.
12If you have to remove the cap, wait until
the engine has cooled completely, then wrap
a thick cloth around the cap and turn it to the
first stop. If coolant or steam escapes, let the
engine cool down longer, then remove the
cap.
13Check the condition of the coolant as
well. It should be relatively clear. If it’s brown
or rust-coloured, the system should be
drained, flushed and refilled. Even if the
coolant appears to be normal, the corrosion
1•8
4.9d Adding antifreeze mixture4.9c On some 5-Series models, the
expansion tank (coolant reservoir) is
located on the bulkhead4.9b On other models, the expansion tank
(coolant reservoir) is located on the side of
the engine compartment - remove the cap
to add coolant
4.9a On some models, the expansion tank
(coolant reservoir) is mounted on the
radiator - make sure the level is kept at or
near the FULL mark (arrowed)4.6b Topping-up the engine oil4.6a The threaded oil filler cap is located
in the valve cover - always make sure the
area around the opening is clean before
unscrewing the cap
Weekly Checks
Page 19 of 228

inhibitors wear out, so it must be renewed at
the specified intervals.
Brake and clutch fluid
Warning: Brake fluid can harm
your eyes and damage painted
surfaces, so use extreme caution
when handling or pouring it. Do
not use brake fluid that has been standing
open or is more than one year old. Brake
fluid absorbs moisture from the air, which
can cause a dangerous loss of brake
effectiveness. Use only the specified type
of brake fluid. Mixing different types (such
as DOT 3 or 4 and DOT 5) can cause brake
failure.
14The brake master cylinder is mounted at
the left rear corner of the engine
compartment. The clutch fluid reservoir
(manual transmission models) is mounted on
the right-hand side.
15To check the clutch fluid level, observe
the level through the translucent reservoir.
The level should be at or near the step
moulded into the reservoir. If the level is low,
remove the reservoir cap to add the specified
fluid (see illustration).
16The brake fluid level is checked by looking
through the plastic reservoir mounted on the
master cylinder (see illustration). The fluid
level should be between the MAX and MIN
lines on the reservoir. If the fluid level is low,
first wipe the top of the reservoir and the cap
with a clean rag, to prevent contamination of
the system as the cap is unscrewed. Top-up
with the recommended brake fluid, but do not
overfill.
17While the reservoir cap is off, check the
master cylinder reservoir for contamination. If
rust deposits, dirt particles or water droplets
are present, the system should be drained
and refilled.
18After filling the reservoir to the proper
level, make sure the cap is seated correctly, to
prevent fluid leakage and/or contamination.
19The fluid level in the master cylinder will
drop slightly as the disc brake pads wear.
There is no need to top up to compensate for
this fall provided that the level stays above the
MIN line; the level will rise again when new
pads are fitted. A very low level may indicateworn brake pads. Check for wear (see Sec-
tion 26).
20If the brake fluid level drops consistently,
check the entire system for leaks immediately.
Examine all brake lines, hoses and
connections, along with the calipers, wheel
cylinders and master cylinder (see Sec-
tion 26).
21When checking the fluid level, if you
discover one or both reservoirs empty or
nearly empty, the brake or clutch hydraulic
system should be checked for leaks and bled
(see Chapters 8 and 9).
Windscreen washer fluid
22Fluid for the windscreen washer system is
stored in a plastic reservoir in the engine
compartment (see illustration).
23In milder climates, plain water can be
used in the reservoir, but it should be kept no
more than two-thirds full, to allow for
expansion if the water freezes. In colder
climates, use windscreen washer system
antifreeze, available at any car accessory
shop, to lower the freezing point of the fluid.
This comes in concentrated or pre-mixed
form. If you purchase concentrated antifreeze,
mix the antifreeze with water in accordance
with the manufacturer’s directions on the
container.
Caution: Do not use cooling
system antifreeze - it will damage
the vehicle’s paint.
5 Tyre and tyre pressure
checks
1
1Periodic inspection of the tyres may save
you the inconvenience of being stranded with
a flat tyre. It can also provide you with vital
information regarding possible problems in
the steering and suspension systems before
major damage occurs.
2Tyres are equipped with bands that will
appear when tread depth reaches 1.6 mm, at
which time the tyres can be considered worn
out. This represents the legal minimum tread
depth; most authorities recommend renewing
any tyre on which the tread depth is 2 mm or
less. Tread wear can be monitored with a
simple, inexpensive device known as a tread
depth indicator (see illustration).
3Note any abnormal tyre wear (see
illustration overleaf). Tread pattern irregular-
ities such as cupping, flat spots and more
wear on one side than the other are
indications of front end alignment and/or
wheel balance problems. If any of these
conditions are noted, take the vehicle to a tyre
specialist to correct the problem.
4Look closely for cuts, punctures and
embedded nails or tacks. Sometimes, after a
nail has embedded itself in the tread, a tyre
will hold air pressure for a short time, or may
1•9
4.22 The windscreen washer fluid reservoir
is located in the right front corner of the
engine compartment on most models4.16 The brake fluid level should be kept
above the MIN mark on the translucent
reservoir - unscrew the cap to add fluid4.15 Adding hydraulic fluid to the clutch
fluid reservoir
5.4a If a slow puncture is suspected,
check the valve core first to make sure it’s
tight5.2 Use a tyre tread depth indicator to
monitor tyre wear - they are available at
car accessory shops and service stations,
and cost very little
1
Weekly Checks
Page 20 of 228
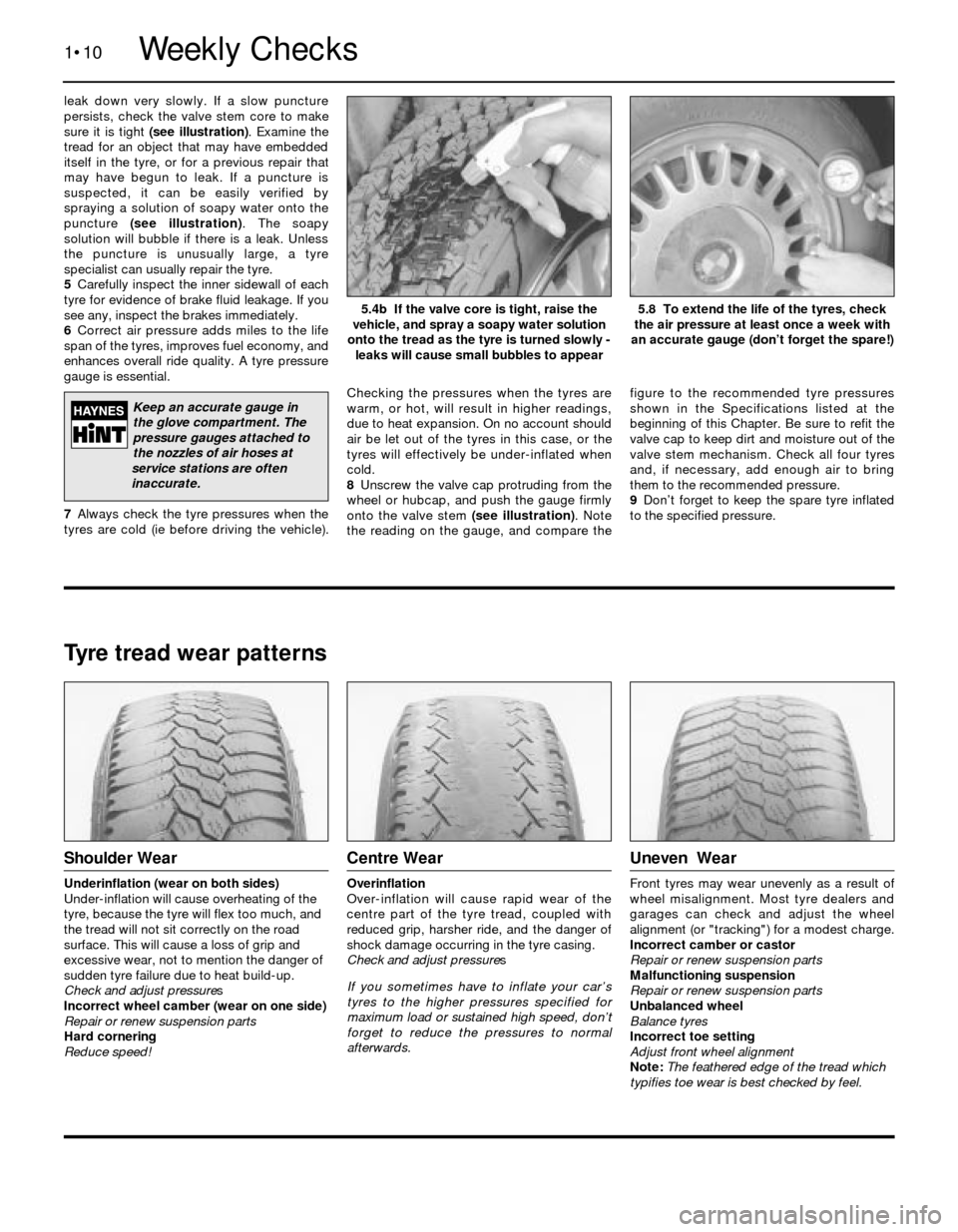
leak down very slowly. If a slow puncture
persists, check the valve stem core to make
sure it is tight (see illustration). Examine the
tread for an object that may have embedded
itself in the tyre, or for a previous repair that
may have begun to leak. If a puncture is
suspected, it can be easily verified by
spraying a solution of soapy water onto the
puncture (see illustration). The soapy
solution will bubble if there is a leak. Unless
the puncture is unusually large, a tyre
specialist can usually repair the tyre.
5Carefully inspect the inner sidewall of each
tyre for evidence of brake fluid leakage. If you
see any, inspect the brakes immediately.
6Correct air pressure adds miles to the life
span of the tyres, improves fuel economy, and
enhances overall ride quality. A tyre pressure
gauge is essential.
7Always check the tyre pressures when the
tyres are cold (ie before driving the vehicle).Checking the pressures when the tyres are
warm, or hot, will result in higher readings,
due to heat expansion. On no account should
air be let out of the tyres in this case, or the
tyres will effectively be under-inflated when
cold.
8Unscrew the valve cap protruding from the
wheel or hubcap, and push the gauge firmly
onto the valve stem (see illustration). Note
the reading on the gauge, and compare thefigure to the recommended tyre pressures
shown in the Specifications listed at the
beginning of this Chapter. Be sure to refit the
valve cap to keep dirt and moisture out of the
valve stem mechanism. Check all four tyres
and, if necessary, add enough air to bring
them to the recommended pressure.
9Don’t forget to keep the spare tyre inflated
to the specified pressure.
1•10
5.8 To extend the life of the tyres, check
the air pressure at least once a week with
an accurate gauge (don’t forget the spare!)5.4b If the valve core is tight, raise the
vehicle, and spray a soapy water solution
onto the tread as the tyre is turned slowly -
leaks will cause small bubbles to appear
Tyre tread wear patterns
Shoulder Wear
Underinflation (wear on both sides)
Under-inflation will cause overheating of the
tyre, because the tyre will flex too much, and
the tread will not sit correctly on the road
surface. This will cause a loss of grip and
excessive wear, not to mention the danger of
sudden tyre failure due to heat build-up.
Check and adjust pressures
Incorrect wheel camber (wear on one side)
Repair or renew suspension parts
Hard cornering
Reduce speed!
Centre Wear
Overinflation
Over-inflation will cause rapid wear of the
centre part of the tyre tread, coupled with
reduced grip, harsher ride, and the danger of
shock damage occurring in the tyre casing.
Check and adjust pressures
If you sometimes have to inflate your car’s
tyres to the higher pressures specified for
maximum load or sustained high speed, don’t
forget to reduce the pressures to normal
afterwards.
Uneven Wear
Front tyres may wear unevenly as a result of
wheel misalignment. Most tyre dealers and
garages can check and adjust the wheel
alignment (or "tracking") for a modest charge.
Incorrect camber or castor
Repair or renew suspension parts
Malfunctioning suspension
Repair or renew suspension parts
Unbalanced wheel
Balance tyres
Incorrect toe setting
Adjust front wheel alignment
Note: The feathered edge of the tread which
typifies toe wear is best checked by feel.
Weekly Checks
Keep an accurate gauge in
the glove compartment. The
pressure gauges attached to
the nozzles of air hoses at
service stations are often
inaccurate.
Page 22 of 228

Cartridge-type oil filter
17Some models are equipped with a
cartridge-type oil filter. Unscrew the bolt,
remove the cover, and lift the filter out (see
illustrations).
18Compare the new cartridge with the old
one, to make sure they are the same type,
then lower it into the housing.
19Using a clean rag, wipe off the mounting
surface of the housing and cover. If necessary,
renew the rubber O-ring (see illustration).
Smear some clean oil on the O-ring and refit
the cover and bolt. Tighten the bolt securely.
All models
20Remove all tools and materials from under
the vehicle, being careful not to spill the oil
from the drain pan, then lower the vehicle.
21Add new oil to the engine through the oil
filler cap in the valve cover. Use a funnel to
prevent oil from spilling onto the top of the
engine. Pour the specified quantity of fresh oil
into the engine. Wait a few minutes to allow the
oil to drain into the sump, then check the level
on the dipstick (see Section 4 if necessary). If
the oil level is correct, refit the filler cap.
22Start the engine and run it for about a
minute. The oil pressure warning light may
take a few seconds to go out while the new
filter fills with oil; don’t rev the engine while
the light is on. While the engine is running,
look under the vehicle, and check for leaks at
the sump drain plug and around the oil filter. Ifeither one is leaking, stop the engine and
tighten the plug or filter slightly.
23Wait a few minutes, then recheck the level
on the dipstick. Add oil as necessary.
24During the first few days after an oil
change, make it a point to check frequently
for leaks and proper oil level.
25The old oil drained from the engine cannot
be re-used in its present state, and should be
discarded. Oil reclamation centres and some
service stations will accept the oil, which can
be recycled. After the oil has cooled, it can be
transferred into a container for transport to a
disposal site.
7 Power steering fluid level
check
1
1Check the power steering fluid level
periodically to avoid steering system
problems, such as damage to the pump.
Proceed as follows.Caution: Do not hold the steering
wheel against either stop (full-left
or full-right lock) for more than
five seconds. If you do, the power
steering pump could be damaged.
2On some models, the power steering fluid
reservoir is located on the left side of the
engine compartment, and has a twist-off cap
with an integral fluid level dipstick (see
illustration). Other models use a hydraulic
power steering and brake servo system which
combines the fluid in one reservoir, located at
the right rear corner of the engine
compartment.
3Park the vehicle on level ground, and apply
the handbrake.
4On models with a fluid dipstick, run the
engine until it has reached normal operating
temperature. With the engine at idle, turn the
steering wheel back and forth several times to
get any air out of the steering system. Switch
off the engine, remove the cap by turning it
anti-clockwise, wipe the dipstick clean, and
refit the cap. Remove the cap again, and note
the fluid level. It must be between the two
lines (see illustration).
5On hydraulic servo models, pump the brake
pedal about ten times or until the pedal is firm.
Remove the nut, lift the cap off, and make
sure the fluid is within 6.0 mm of the top of the
reservoir.
6Add small amounts of fluid until the level is
correct (see illustration).
1•12
7.6 Adding fluid to the power steering
reservoir7.4 The power steering fluid level should
be kept between the two arrows near the
upper step on the dipstick7.2 The power steering fluid reservoir
(arrowed) is located on the left side of the
engine compartment
6.19 Renewing the rubber O-ring in the
cover6.17c . . . and lift out the cartridge
Every 6000 miles
6.17b . . . remove the cover . . .
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling
bank, call this
number free.
Page 23 of 228

Caution: Do not overfill the
reservoir. If too much fluid is
added, remove the excess with a
clean syringe. Refit the cap.
7If frequent topping-up is needed, check the
power steering hoses and connections for
leaks and wear (see Section 10).
8Check the condition and tension of the
drivebelt (see Section 11).
8 Automatic transmission fluid
level check
1
Caution: The use of transmission
fluid other than the type listed in
this Chapter’s Specifications
could result in transmission
malfunctions or failure.
1The automatic transmission fluid should be
carefully maintained. Low fluid level can lead
to slipping or loss of drive, while overfilling
can cause foaming and loss of fluid. Either
condition can cause transmission damage.
2Since transmission fluid expands as it heats
up, the fluid level should only be checked
when the transmission is warm (at normal
operating temperature). If the vehicle has just
been driven over 20 miles (32 km), the
transmission can be considered warm. You
can also check the fluid level when the
transmission is cold. If the vehicle has not
been driven for over five hours and the fluid is
about room temperature (20°C), the
transmission is cold. However, the fluid level
is normally checked with the transmission
warm, to ensure accurate results.
Caution: If the vehicle has just
been driven for a long time at
high speed or in city traffic, in hot
weather, or if it has been pulling
a trailer, an accurate fluid level reading
cannot be obtained. Allow the trans-
mission to cool down for about 30 minutes.
3Immediately after driving the vehicle, park it
on a level surface, apply the handbrake and
start the engine. While the engine is idling,
depress the brake pedal and move theselector lever through all the gear ranges,
beginning and ending in Park.
4The automatic transmission dipstick tube is
located in the left rear corner of the engine
compartment.
5With the engine still idling, pull the dipstick
out of the tube (see illustration), wipe it off
with a clean rag, push it all the way back into
the tube and withdraw it again, then note the
fluid level.
6The level should be between the two marks
(see illustration). If the level is low, add the
specified automatic transmission fluid through
the dipstick tube - use a clean funnel,
preferably equipped with a fine mesh filter, to
prevent spills.
Caution: Be careful not to
introduce dirt into the
transmission when topping up.
7Add just enough of the recommended fluid
to fill the transmission to the proper level. It
takes about half a litre to raise the level from
the low mark to the high mark when the fluid
is hot, so add the fluid a little at a time, and
keep checking the level until it’s correct.
8The condition of the fluid should also be
checked along with the level. If the fluid is
black or a dark reddish-brown colour, or if it
smells burned, it should be changed (see
Section 28). If you are in doubt about its
condition, purchase some new fluid, and
compare the two for colour and smell.
9 Tyre rotation
1
1The tyres can be rotated at the specified
intervals, or whenever uneven wear is noticed.
However, bear in mind that if rotation
succeeds in making all the tyres wear evenly,
you will eventually have to renew all four at
once. Since the vehicle will be raised and the
wheels removed anyway, check the brakes
also (see Section 26). Note: Even if you don’t
rotate the tyres, at least check the wheel bolt
tightness.
2It is recommended that the tyres be rotatedin a specific pattern (see illustration)so that
their direction of rotation remains the same.
3Refer to the information in “Jacking and
towing”at the front of this manual for the
proper procedure to follow when raising the
vehicle and changing a tyre.
4The vehicle must be raised on a hoist or
supported on axle stands to get all four tyres
off the ground. Make sure the vehicle is safely
supported!
5After the rotation procedure is finished,
check and adjust the tyre pressures as
necessary, and be sure to check the wheel
bolt tightness.
10 Underbonnet hose check
and renewal
3
Warning: Renewal of air
conditioning hoses must be left
to a dealer service department or
air conditioning specialist having
the equipment to depressurise the system
safely. Never disconnect air conditioning
hoses or components until the system has
been depressurised.
General
1High temperatures under the bonnet can
cause deterioration of the rubber and plastic
hoses used for various systems. Periodic
inspection should be made for cracks, loose
clamps, material hardening, and leaks.
2Information specific to the cooling system
can be found in Section 22, while the braking
system is covered in Section 26.
3Most (but not all) hoses are secured with
clamps. Where clamps are used, check to be
sure they haven’t lost their tension, allowing
the hose to leak. If clamps aren’t used, make
sure the hose has not expanded and/or
hardened where it slips over the fitting,
allowing it to leak.
Vacuum hoses
4It’s quite common for vacuum hoses,
especially those in the emissions system, to
be colour-coded or identified by coloured
1•13
9.2 The tyre rotation pattern for these
models8.6 With the fluid hot, the level should be
kept between the two dipstick notches,
preferably near the upper one8.5 The automatic transmission fluid
dipstick (arrowed) is located near the
bulkhead on the left side of the engine
compartment
1
Every 6000 miles
Page 26 of 228

13 Battery check, maintenance
and charging
2
Check and maintenance
Warning: Certain precautions
must be followed when checking
and servicing the battery.
Hydrogen gas, which is highly
flammable, is always present in the battery
cells, so keep lighted tobacco and all other
flames and sparks away from it. The
electrolyte inside the battery is actually
dilute sulphuric acid, which will cause
injury if splashed on your skin or in youreyes. It will also ruin clothes and painted
surfaces. When disconnecting the battery
cables, always detach the negative cable
first, and connect it last!
1Battery maintenance is an important
procedure, which will help ensure that you are
not stranded because of a dead battery.
Several tools are required for this procedure
(see illustration).
2Before servicing the battery, always switch
off the engine and all accessories, and
disconnect the cable from the negative
terminal of the battery.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code before
disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3A low-maintenance battery is standard
equipment. The cell caps can be removed and
distilled water can be added, if necessary.
Later models may be fitted with a
“maintenance-free” battery, which is sealed.
4Remove the caps and check the electrolyte
level in each of the battery cells. It must be
above the plates. There’s usually a split-ring
indicator in each cell to indicate the correct
level. If the level is low, add distilled water
only, then refit the cell caps.Caution: Overfilling the cells may
cause electrolyte to spill over
during periods of heavy charging,
causing corrosion and damage to
nearby components.
5If the positive terminal and cable clamp on
your vehicle’s battery is equipped with a
rubber protector, make sure that it’s not torn
or damaged. It should completely cover the
terminal.
6The external condition of the battery should
be checked periodically. Look for damage
such as a cracked case.
7Check the tightness of the battery cable
clamps to ensure good electrical connections.
Check the entire length of each cable, looking
for cracked or abraded insulation and frayed
conductors.
8If corrosion (visible as white, fluffy deposits)
is evident, remove the cables from the
terminals, clean them with a battery brush,
and reconnect them (see illustrations).
Corrosion can be kept to a minimum by fitting
specially treated washers available at car
accessory shops, or by applying a layer of
petroleum jelly or suitable grease to the
Every 12 000 miles or 12 months, whichever comes first
1•16
13.8d When cleaning the cable clamps, all
corrosion must be removed (the inside of
the clamp is tapered to match the taper on
the post, so don’t remove too much
material)
13.8c Regardless of the type of tool used
on the battery posts, a clean, shiny surface
should be the result
13.1 Tools and materials required for
battery maintenance
1 Face shield/safety goggles- When
removing corrosion with a brush, the acidic
particles can easily fly up into your eyes
2 Baking soda - A solution of baking soda and
water can be used to neutralise corrosion
3 Petroleum jelly- A layer of this on the
battery posts will help prevent corrosion
4 Battery post/cable cleaner- This wire-
brush cleaning tool will remove all traces of
corrosion from the battery posts and cable
clamps
5 Treated felt washers- Placing one of
these on each post, directly under the
cable clamps, will help prevent corrosion
6 Puller- Sometimes the cable clamps are
very difficult to pull off the posts, even after
the nut/bolt has been completely loosened.
This tool pulls the clamp straight up and off
the post without damage
7 Battery post/cable cleaner - Here is
another cleaning tool which is a slightly
different version of No 4 above, but it does
the same thing
8 Rubber gloves- Another safety item to
consider when servicing the battery;
remember that’s acid inside the battery!
13.8b Removing a cable from the battery
post with a spanner - sometimes special
battery pliers are required for this
procedure, if corrosion has caused
deterioration of the nut (always remove the
earth cable first, and connect it last!)
13.8a Battery terminal corrosion usually
appears as light, fluffy powder
Every 12 000 miles
Page 27 of 228

terminals and cable clamps after they are
assembled.
9Make sure that the battery carrier is in good
condition, and that the hold-down clamp bolt
is tight. If the battery is removed (see Chap-
ter 5 for the removal and refitting procedure),
make sure that no parts remain in the bottom
of the carrier when it’s refitted. When refitting
the hold-down clamp, don’t overtighten the
bolt.
10Corrosion on the carrier, battery case and
surrounding areas can be removed with a
solution of water and baking soda. Apply the
mixture with a small brush, let it work, then
rinse it off with plenty of clean water.
11Any metal parts of the vehicle damaged
by corrosion should be coated with a zinc-
based primer, then painted.
12Additional information on the battery and
jump starting can be found in Chapter 5 and
the front of this manual.
Charging
Note: The manufacturer recommends the
battery be removed from the vehicle for
charging, because the gas which escapes
during this procedure can damage the paint or
interior, depending on the location of the
battery. Fast charging with the battery cables
connected can result in damage to the
electrical system.
13Remove all of the cell caps (if applicable),
and cover the holes with a clean cloth to
prevent spattering electrolyte. Disconnect thebattery negative cable, and connect the
battery charger leads to the battery posts
(positive to positive, negative to negative),
then plug in the charger. Make sure it is set at
12 volts if it has a selector switch.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Note: If,
after connecting the battery, the wrong
language appears on the instrument panel
display, refer to page 0-7 for the language
resetting procedure.
14If you’re using a charger with a rate higher
than two amps, check the battery regularly
during charging to make sure it doesn’t
overheat. If you’re using a trickle charger, you
can safely let the battery charge overnight
after you’ve checked it regularly for the first
couple of hours. Where a maintenance-free
battery is fitted, special precautions may be
necessary when charging it (for example, the
charge rate is normally very low). There may
be a warning label on the battery, but if not,
consult a BMW dealer or auto-electrician.
15If the battery has removable cell caps,
measure the specific gravity with a
hydrometer every hour during the last few
hours of the charging cycle. Hydrometers are
available inexpensively from car accessory
shops - follow the instructions that come with
the hydrometer. Consider the battery charged
when there’s no change in the specific gravity
reading for two hours, and the electrolyte in
the cells is gassing (bubbling) freely. The
specific gravity reading from each cell should
be very close to the others. If not, the battery
probably has a bad cell(s), and a new one
should be fitted.
16Some maintenance-free (sealed) batteries
have built-in hydrometers on the top,
indicating the state of charge by the colour
displayed in the hydrometer window.
Normally, a bright-coloured hydrometer
indicates a full charge, and a dark hydrometer
indicates the battery still needs charging.
Check the battery manufacturer’s instructions
to be sure you know what the colours mean.17If the battery is sealed and has no built-in
hydrometer, you can connect a digital
voltmeter across the battery terminals to
check the charge. A fully-charged battery
should read 12.6 volts or higher.
18Further information on the battery and
jump starting can be found in Chapter 5 and
at the front of this manual.
14 Spark plug check and
renewal
1
1Before beginning, obtain the necessary
tools, which will include a spark plug socket
and a set of feeler blades. Special spark plug
gap gauges can be obtained from certain
spark plug manufacturers (see illustration).
2The best procedure to follow when
renewing the spark plugs is to purchase the
new spark plugs beforehand, adjust them to
the proper gap, and then renew each plug one
at a time. When buying the new spark plugs, it
is important to obtain the correct plugs for
your specific engine. This information can be
found in the Specifications section in the front
of this Chapter.
3With the new spark plugs at hand, allow the
engine to cool completely before attempting
plug removal. During this time, each of the
new spark plugs can be inspected for defects
and the gaps can be checked.
4The gap is checked by inserting the proper
thickness gauge between the electrodes at the
tip of the plug (see illustration). The gap
between the electrodes should be the same as
that given in the Specifications. The wire
should just touch each of the electrodes. If the
gap is incorrect, use the notched adjuster to
bend the curved side of the electrode slightly
until the proper gap is achieved (see
illustration). Note: When adjusting the gap of a
new plug, bend only the base of the earth
electrode, do not touch the tip. If the earth
electrode is not exactly over the centre
electrode, use the notched adjuster to align the
two. Check for cracks in the porcelain insulator,
indicating the spark plug should not be used.
1•17
14.4b To change the gap, bend the earth
electrode only, as indicated by the arrows,
and be very careful not to crack or chip the
porcelain insulator surrounding the centre
electrode14.4a Spark plug manufacturers
recommend using a wire-type gauge when
checking the gap - if the wire does not
slide between the electrodes with a slight
drag, adjustment is required
14.1 Tools required for changing spark
plugs
1 Spark plug socket- This will have special
padding inside to protect the spark plug’s
porcelain insulator
2 Torque wrench - Although not mandatory,
using this tool is the best way to ensure the
plugs are tightened properly
3 Ratchet - Standard hand tool to fit the
spark plug socket
4 Extension - Depending on model and
accessories, you may need special
extensions and universal joints to reach one
or more of the plugs
5 Spark plug gap gauge- This gauge for
checking the gap comes in a variety of
styles. Make sure the gap for your engine is
included. Feeler blades may be used
instead
1
Every 12 000 miles