engine coolant BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1985, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 62 of 228
detach them. Pieces of masking tape with
numbers or letters written on them work well
(see illustration).
6Label and detach all coolant hoses from the
engine (see Chapter 3).
7Remove the cooling fan, shroud and
radiator (see Chapter 3). Note:On the M40
engine, it is only necessary to remove the
cooling fan and shroud; however, prevent
damage to the radiator by covering it with a
piece of wood or cardboard.
8Remove the drivebelts (see Chapter 1).
9Disconnect the fuel lines from the fuel rail
(see Chapter 4).
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area, and don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance (such as a water heater or
clothes dryer) with a pilot light is present.
If you spill any fuel on your skin, rinse it off
immediately with soap and water. When
you perform any kind of work on the fuel
system, wear safety glasses, and have a
fire extinguisher on hand.
10Disconnect the accelerator cable (see
Chapter 4) and kickdown linkage/speed
control cable (see Chapter 7B), if applicable,
from the engine.
11Where fitted, unbolt the power steering
pump (see Chapter 10). Leave the lines/hoses
attached, and make sure the pump is kept in
an upright position in the engine compartment
(use wire or rope to restrain it out of the way).
12On air-conditioned models, unbolt the
compressor (see Chapter 3) and set it aside,
or tie it up out of the way. Do not disconnect
the hoses.
13Drain the engine oil (see Chapter 1) and
remove the filter. Remove the engine splash
guard from under the engine.
14Remove the starter motor (see Chapter 5).15Remove the alternator (see Chapter 5).
This is not essential on all models, but it is a
good idea in any case to avoid accidental
damage.
16Unbolt the exhaust system from the
engine (see Chapter 4).
17If you’re working on a vehicle with an
automatic transmission, remove the torque
converter-to-driveplate fasteners (see
Chapter 7B). On the M40 engine, unbolt the
automatic transmission fluid coolant pipes
from the sump.
18Support the transmission with a jack.
Position a block of wood between them, to
prevent damage to the transmission. Special
transmission jacks with safety chains are
available - use one if possible.
19Attach an engine sling or a length of chain
to the lifting brackets on the engine. If the
brackets have been removed, the chain can
be bolted directly to the intake manifold studs,
but place a flat washer between the chain and
the nut, and tighten the nut all the way up to
the chain, to avoid the possibility of the studs
bending.
20Roll the hoist into position and connect
the sling to it. Take up the slack in the sling or
chain, but don’t lift the engine.
Warning: DO NOT place any part
of your body under the engine
when it’s supported only by a
hoist or other lifting device.
21On M10, M20 and M30 engines, remove
the transmission rear crossmember, and
slightly lower the rear of the transmission.
22Remove the transmission-to-engine block
bolts using a Torx socket. Note:The bolts
holding the bellhousing to the engine block
will require a swivel at the socket, and a very
long extension going back towards the
transmission.
23Remove the engine mounting-to-frame
bracket nuts. On the M40 engine, unbolt the
dampers from the mountings.
24Recheck to be sure nothing is still
connecting the engine to the transmission or
vehicle. Disconnect anything still remaining.
25Raise the engine slightly. Carefully work it
forwards to separate it from the transmission.
If you’re working on a vehicle with an
automatic transmission, you may find the
torque converter comes forward with theengine. If it stays with the transmission, leave
it, but you may find it easier to let it come
forward until it can be grasped easier and be
pulled from the crankshaft. Note:When
refitting the torque converter to the
transmission before the engine is refitted, be
sure to renew the transmission front pump
seal, which will probably be damaged when
the converter comes out with the engine.
Either method is acceptable, but be prepared
for some fluid to leak from the torque
converter if it comes out of the transmission. If
you’re working on a vehicle with a manual
transmission, draw the engine forwards until
the input shaft is completely disengaged from
the clutch. Slowly raise the engine out of the
engine compartment. Check carefully to make
sure everything is disconnected.
26Remove the flywheel/driveplate (and
where applicable, the engine rear plate), and
mount the engine on an engine stand (see
illustration). Do not turn the M40 engine
upside-down (see Cautionin Section 4).
Refitting
27Check the engine and transmission
mountings. If they’re worn or damaged, renew
them.
28Refit the flywheel or driveplate (see
Chapter 2A). If you’re working on a manual
transmission vehicle, refit the clutch and
pressure plate (see Chapter 7A). Now is a
good time to fit a new clutch.
29If the torque converter came out with the
engine during removal, carefully refit the
converter into the transmission before the
engine is lowered into the vehicle.
30Carefully lower the engine into the engine
compartment - make sure the engine
mountings line up.
31If you’re working on an automatic
transmission vehicle, guide the torque
converter onto the crankshaft following the
procedure outlined in Chapter 7B.
32If you’re working on a manual
transmission vehicle, apply a dab of high-
melting-point grease to the input shaft, and
guide it into the clutch and crankshaft pilot
bearing until the bellhousing is flush with the
engine block.. Do not allow the weight of the
engine to hang on the input shaft.
33Refit the transmission-to-engine bolts,
and tighten them securely.
Caution: DO NOT use the bolts to
force the transmission and
engine together.
34Refit the remaining components in the
reverse order of removal.
35Add coolant, oil, power steering and
transmission fluid as needed.
2B•6 General engine overhaul procedures
5.26 Removing the engine rear plate -
M40 engine5.5 Label each wire before unplugging the
connector
If there’s any possibility of
confusion, make a sketch of
the engine compartment and
clearly label the lines, hoses
and wires.
It may be necessary to rock
the engine slightly, or to turn
the crankshaft, to allow the
input shaft splines to mate
with the clutch plate
Page 66 of 228
24Repeat the procedure for the remaining
valves. Remember to keep all the parts for
each valve together, so they can be refitted in
the same locations.
25Once the valves and related components
have been removed and stored in an
organised manner, the head should be
thoroughly cleaned and inspected. If a
complete engine overhaul is being done,
finish the engine dismantling procedures
before beginning the cylinder head cleaning
and inspection process.
9 Cylinder head and
components-
cleaning and inspection
4
1Thorough cleaning of the cylinder head(s)
and related valve train components, followed
by a detailed inspection, will enable you to
decide how much valve service work must be
done during the engine overhaul. Note: If the
engine was severely overheated, the cylinder
head is probably warped (see paragraph 10).
Cleaning
2Scrape all traces of old gasket material and
sealing compound off the cylinder head,
intake manifold and exhaust manifold sealing
surfaces. Be very careful not to gouge the
cylinder head. Special gasket removal
solvents are available at motor factors.
3Remove all built-up scale from the coolant
passages.
4Run a stiff brush through the various holes
to remove deposits that may have formed in
them.
5Run an appropriate-size tap into each of the
threaded holes, to remove corrosion and
thread sealant that may be present. If
compressed air is available, use it to clear the
holes of debris produced by this operation.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
6Clean the cylinder head with solvent, and
dry it thoroughly. Compressed air will speed
the drying process, and ensure that all holesand recessed areas are clean. Note:
Decarbonising chemicals are available, and
may prove very useful when cleaning cylinder
heads and valve train components. They are
very caustic, however, and should be used
with caution. Be sure to follow the instructions
on the container.
7Clean all the rocker shafts/arms/followers,
springs, valve springs, spring seats, keepers
and retainers with solvent, and dry them
thoroughly. Clean the components from one
valve at a time, to avoid mixing up the parts.
Caution: DO NOT clean the
hydraulic tappets of the M40
engine; leave them completely
immersed in oil.
8Scrape off any heavy deposits that may
have formed on the valves, then use a
motorised wire brush to remove deposits from
the valve heads and stems. Again, make sure
the valves don’t get mixed up.
Inspection
Note: Be sure to perform all of the following
inspection procedures before concluding that
machine shop work is required. Make a list of
the items that need attention.
Cylinder head
9Inspect the head very carefully for cracks,
evidence of coolant leakage, and other
damage. If cracks are found, check with an
machine shop concerning repair. If repair isn’t
possible, a new cylinder head should be
obtained.
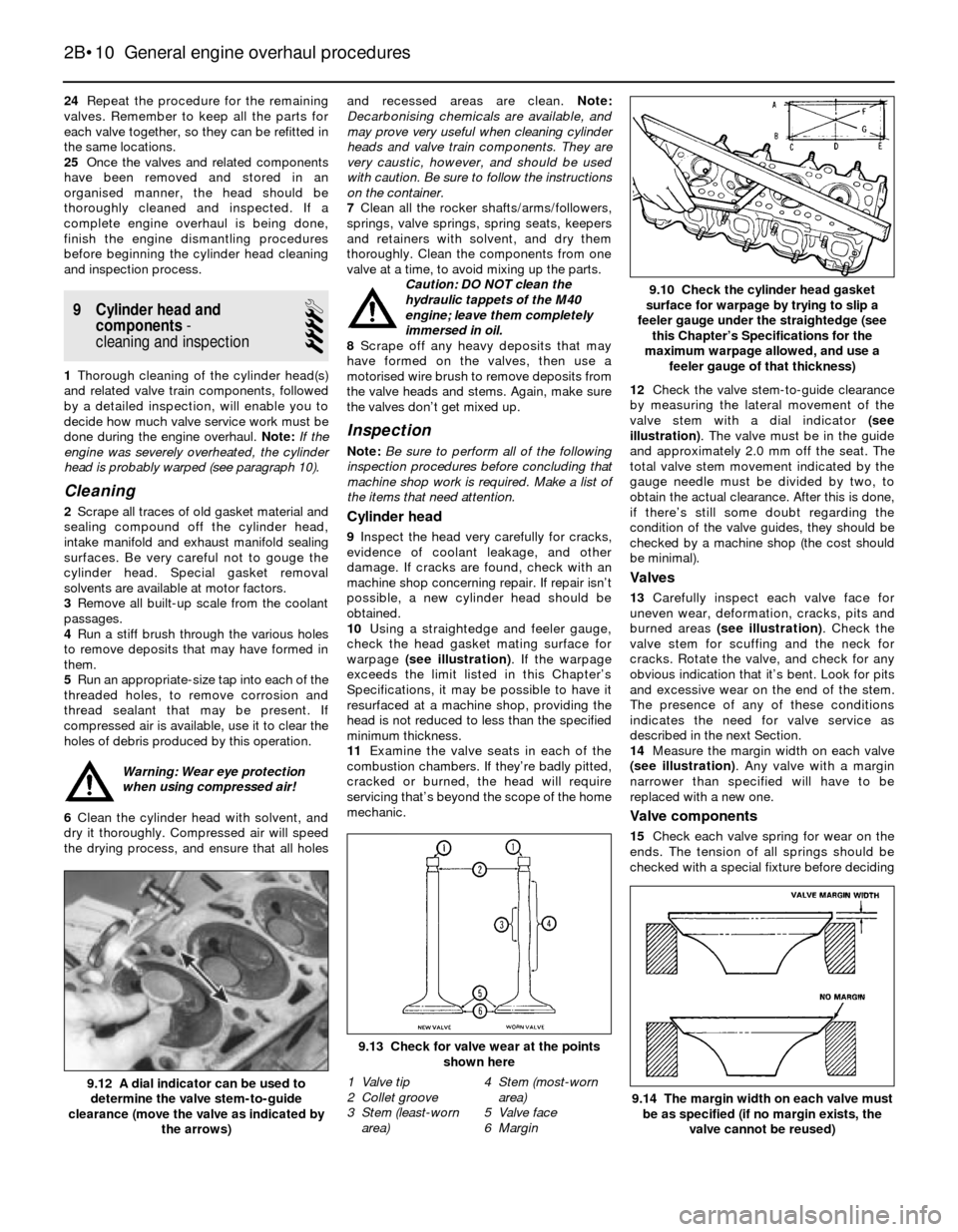
10Using a straightedge and feeler gauge,
check the head gasket mating surface for
warpage (see illustration). If the warpage
exceeds the limit listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications, it may be possible to have it
resurfaced at a machine shop, providing the
head is not reduced to less than the specified
minimum thickness.
11Examine the valve seats in each of the
combustion chambers. If they’re badly pitted,
cracked or burned, the head will require
servicing that’s beyond the scope of the home
mechanic.12Check the valve stem-to-guide clearance
by measuring the lateral movement of the
valve stem with a dial indicator (see
illustration). The valve must be in the guide
and approximately 2.0 mm off the seat. The
total valve stem movement indicated by the
gauge needle must be divided by two, to
obtain the actual clearance. After this is done,
if there’s still some doubt regarding the
condition of the valve guides, they should be
checked by a machine shop (the cost should
be minimal).
Valves
13Carefully inspect each valve face for
uneven wear, deformation, cracks, pits and
burned areas (see illustration). Check the
valve stem for scuffing and the neck for
cracks. Rotate the valve, and check for any
obvious indication that it’s bent. Look for pits
and excessive wear on the end of the stem.
The presence of any of these conditions
indicates the need for valve service as
described in the next Section.
14Measure the margin width on each valve
(see illustration). Any valve with a margin
narrower than specified will have to be
replaced with a new one.
Valve components
15Check each valve spring for wear on the
ends. The tension of all springs should be
checked with a special fixture before deciding
2B•10 General engine overhaul procedures
9.14 The margin width on each valve must
be as specified (if no margin exists, the
valve cannot be reused)
9.13 Check for valve wear at the points
shown here
9.12 A dial indicator can be used to
determine the valve stem-to-guide
clearance (move the valve as indicated by
the arrows)
9.10 Check the cylinder head gasket
surface for warpage by trying to slip a
feeler gauge under the straightedge (see
this Chapter’s Specifications for the
maximum warpage allowed, and use a
feeler gauge of that thickness)
1 Valve tip
2 Collet groove
3 Stem (least-worn
area)4 Stem (most-worn
area)
5 Valve face
6 Margin
Page 70 of 228

5Gently tap the caps with a soft-faced
hammer, then separate them from the engine
block. If necessary, use the bolts as levers to
remove the caps. Try not to drop the bearing
shells if they come out with the caps.
6Carefully lift the crankshaft out of the
engine. It may be a good idea to have an
assistant available, since the crankshaft is
quite heavy (see illustration). With the
bearing shells in place in the engine block and
main bearing caps, return the caps to their
respective locations on the engine block, and
tighten the bolts finger-tight.
14 Intermediate shaft-
removal and inspection
5
Note:The intermediate shaft is used on the
M20 engine only. The shaft rotates in the
engine block parallel to the crankshaft. It is
driven by the timing belt, and its only purpose
is to drive the oil pump.
1Remove the timing belt (see Chapter 2A).
2With the belt removed, unbolt the gear from
the intermediate shaft and unbolt the front
cover.
3Remove the oil pump driveshaft (see
Chapter 2A).
4The shaft is held in the cylinder block by a
retaining plate with two bolts. Remove the
bolts, and pull the shaft forwards and out of
the block.
5Look for any signs of abnormal wear on the
bearing surfaces or the gear at the back end
of the shaft, which drives the oil pump shaft. If
the bearing surfaces in the engine block show
wear, they’ll have to be attended to by a
machine shop.
15 Engine block- cleaning
2
Caution: The core plugs may be
difficult or impossible to retrieve
if they’re driven into the block
coolant passages.
1Remove the core plugs from the engine
block. To do this, knock one side of each plug
into the block with a hammer and punch,
grasp the other side by its edge with large
pliers, and pull it out.
2Using a gasket scraper, remove all traces of
gasket material from the engine block. Be very
careful not to nick or gouge the gasket sealing
surfaces.
3Remove the main bearing caps, and
separate the bearing shells from the caps and
the engine block. Tag the bearings, indicating
which cylinder they were removed from and
whether they were in the cap or the block,
then set them aside.
4Remove all of the threaded oil gallery plugs
from the block. The plugs are usually very
tight - they may have to be drilled out and theholes retapped. Use new plugs when the
engine is reassembled.
5If the engine is extremely dirty, it should be
taken to a machine shop to be steam-
cleaned.
6After the block is returned, clean all oil
holes and oil galleries one more time. Brushes
specifically designed for this purpose are
available at most motor factors. Flush the
passages with warm water until the water runs
clear, dry the block thoroughly, and wipe all
machined surfaces with a light, rust-
preventive oil. If you have access to
compressed air, use it to speed the drying
process and to blow out all the oil holes and
galleries.
Warning: Wear eye protection
when using compressed air!
7If the block isn’t extremely dirty or sludged
up, you can do an adequate cleaning job with
hot soapy water and a stiff brush. Take plenty
of time, and do a thorough job. Regardless of
the cleaning method used, be sure to clean all
oil holes and galleries very thoroughly, dry the
block completely, and coat all machined
surfaces with light oil.
8The threaded holes in the block must be
clean to ensure accurate torque readingsduring reassembly. Run the proper-size tap
into each of the holes to remove rust,
corrosion, thread sealant or sludge, and to
restore damaged threads (see illustration). If
possible, use compressed air to clear the
holes of debris produced by this operation. Be
sure also that the holes are dry- any oil or
other fluid present could cause the block to
be cracked by hydraulic pressure when the
bolts are tightened. Now is a good time to
clean the threads on all bolts. Note that BMW
recommend that the cylinder head bolts and
main bearing bolts are renewed as a matter of
course.
9Refit the main bearing caps, and tighten the
bolts finger-tight.
10After coating the sealing surfaces of the
new core plugs with a suitable sealant, refit
them in the engine block (see illustration).
Make sure they’re driven in straight and
seated properly, or leakage could result.
Special tools are available for this purpose,
but a large socket, with an outside diameter
that will just slip into the core plug, a 1/2-inch
drive extension, and a hammer, will work just
as well.
11Apply non-hardening sealant to the new
oil gallery plugs, and thread them into the
holes in the block. Make sure they’re
tightened securely.
12If the engine isn’t going to be
reassembled right away, cover it with a large
plastic bag to keep it clean.
2B•14 General engine overhaul procedures
15.10 A large socket on an extension can
be used to drive the new core plugs into
the block
15.8 All bolt holes in the block -
particularly the main bearing cap and head
bolt holes - should be cleaned and
restored with a tap (be sure to remove
debris from the holes after this is done)
13.6 Remove the crankshaft by lifting
straight up. Be very careful when removing
the crankshaft - it is very heavy13.4 Use a centre-punch or number-
stamping dies to mark the main bearing
caps to ensure refitting in their original
locations on the block (make the punch
marks near one of the bolt heads)
Page 72 of 228

7Wipe the oil out of the cylinder, and repeat
the procedure for the remaining cylinders.
8After the honing job is complete, chamfer
the top edges of the cylinder bores with a
small file, so the rings won’t catch when the
pistons are refitted. Be very careful not to nick
the cylinder walls with the end of the file.
9The entire engine block must be washed
again very thoroughly with warm, soapy
water, to remove all traces of the abrasive grit
produced during the honing operation. Note:
The bores can be considered clean when a
lint-free white cloth - dampened with clean
engine oil - used to wipe them out doesn’t
pick up any more honing residue, which will
show up as grey areas on the cloth.Be sure to
run a brush through all oil holes and galleries,
and flush them with running water.
10After rinsing, dry the block, and apply a
coat of light rust-preventive oil to all machined
surfaces. Wrap the block in a plastic bag to
keep it clean, and set it aside until
reassembly.
18 Pistons/connecting rods-
inspection
3
1Before the inspection process can be
carried out, the piston/connecting rod
assemblies must be cleaned and the original
piston rings removed from the pistons.Note:
Always use new piston rings when the engine
is reassembled.
2Using a piston ring refitting tool, carefully
remove the rings from the pistons. Be careful
not to nick or gouge the pistons in the
process (see illustration).
3Scrape all traces of carbon from the top of
the piston. A hand-held wire brush or a piece
of fine emery cloth can be used once the
majority of the deposits have been scraped
away. Do not, under any circumstances, use a
wire brush mounted in a drill motor to remove
deposits from the pistons. The piston material
is soft, and may be damaged by the wire
brush.
4Use a piston ring groove cleaning tool to
remove carbon deposits from the ring
grooves. Be very careful to remove only thecarbon deposits - don’t remove any metal,
and do not nick or scratch the sides of the
ring grooves (see illustration).
5Once the deposits have been removed,
clean the piston/rod assemblies with solvent,
and dry them with compressed air (if
available). Make sure the oil return holes in the
back sides of the ring grooves are clear.
6If the pistons and cylinder walls aren’t
damaged or worn excessively, and if the
engine block is not rebored, new pistons
won’t be necessary. Normal piston wear
appears as even vertical wear on the piston
thrust surfaces (90° to the gudgeon pin bore),
and slight looseness of the top ring in its
groove. New piston rings, however, should
always be used when an engine is rebuilt.
7Carefully inspect each piston for cracks
around the skirt, at the pin bosses, and at the
ring lands.
8Look for scoring and scuffing on the thrust
faces of the skirt, holes in the piston crown,
and burned areas at the edge of the crown. If
the skirt is scored or scuffed, the engine may
have been suffering from overheating and/or
abnormal combustion, which caused
excessively high operating temperatures. The
cooling and lubrication systems should be
checked thoroughly. A hole in the piston crown
is an indication that abnormal combustion (pre-
ignition) was occurring. Burned areas at the
edge of the piston crown are usually evidence
of spark knock (detonation). If any of the aboveproblems exist, the causes must be corrected,
or the damage will occur again. The causes
may include intake air leaks, incorrect fuel/air
mixture, or incorrect ignition timing. On later
vehicles with high levels of exhaust emission
control, including catalytic converters, the
problem may be with the EGR (exhaust gas
recirculation) system, where applicable.
9Corrosion of the piston, in the form of small
pits, indicates that coolant is leaking into the
combustion chamber and/or the crankcase.
Again, the cause must be corrected or the
problem may persist in the rebuilt engine.
10Measure the piston ring side clearance by
laying a new piston ring in each ring groove
and slipping a feeler gauge in beside it(see
illustration). Check the clearance at three or
four locations around each groove. Be sure to
use the correct ring for each groove - they are
different. If the side clearance is greater than
the figure listed in this Chapter’s Specifi-
cations, new pistons will have to be used.
11Check the piston-to-bore clearance by
measuring the bore (see Section 16) and the
piston diameter. Make sure the pistons and
bores are correctly matched. Measure the
piston across the skirt, at 90° to, and in line
with, the gudgeon pin (see illustration). (Any
difference between these two measurements
indicates that the piston is no longer perfectly
round.) Subtract the piston diameter from the
bore diameter to obtain the clearance. If it’s
greater than specified, the block will have to
be rebored, and new pistons and rings fitted.
2B•16 General engine overhaul procedures
18.11 Measure the piston diameter at a
90-degree angle to the gudgeon pin, at the
same height as the gudgeon pin
18.10 Check the ring side clearance with a
feeler gauge at several points around the
groove18.4 The piston ring grooves can be
cleaned with a special tool, as shown
here18.2 Removing the compression rings with
a ring expander - note the mark (arrowed)
facing up
If a groove cleaning tool isn’t available,
a piece broken off the old ring will do
the job, but protect your hands - piston
rings can be sharp
Page 78 of 228
the bearing - use your fingernail or the edge of
a credit card.
20Make sure the bearing faces are perfectly
clean, then apply a uniform layer of
molybdenum disulphide (“moly”) grease or
engine assembly oil to both of them. You’ll
have to push the piston into the cylinder to
expose the face of the bearing shell in the
connecting rod - be sure to slip the protective
hoses over the rod bolts first, where
applicable.
21Slide the connecting rod back into place
on the journal, and remove the protective
hoses from the rod cap bolts. Refit the rod
cap, and tighten the nuts/bolts to the
specified torque.
22Repeat the entire procedure for the
remaining pistons/connecting rods.
23The important points to remember are:
a) Keep the back sides of the bearing shells
and the insides of the connecting rods
and caps perfectly clean when
assembling them.
b) Make sure you have the correct
piston/rod assembly for each cylinder.
c) The notch or mark on the piston must
face the front of the engine.
d) Lubricate the cylinder walls with clean oil.
e) Lubricate the bearing faces when refitting
the rod caps after the oil clearance has
been checked.
24After all the piston/connecting rod
assemblies have been properly fitted, rotate
the crankshaft a number of times by hand to
check for any obvious binding.25Check the connecting rod side play (see
Section 13).
26Compare the measured side play to the
Specifications to make sure it’s correct. If it
was correct before dismantling, and the
original crankshaft and rods were refitted, it
should still be right. If new rods or a new
crankshaft were fitted, the side play may be
incorrect. If so, the rods will have to be
removed and taken to a machine shop for
attention.
27 Initial start-up and running-
in after overhaul
1
Warning:Have a fire extinguisher
handy when starting the engine
for the first time.
1Once the engine has been refitted in the
vehicle, double-check the engine oil and
coolant levels.
2With the spark plugs removed and the
ignition system disabled (see Section 3), crank
the engine until oil pressure registers on the
gauge, or until the oil pressure warning light
goes out.
3Refit the spark plugs, connect the HT leads,
and restore the ignition system functions (see
Section 3).
4Start the engine. It may take a few
moments for the fuel system to build uppressure, but the engine should start without
a great deal of effort. Note: If backfiring
occurs through the throttle body or
carburettor, check the valve timing (check that
the timing chain/belt has been correctly fitted),
the firing order (check the fitted order of the
spark plug HT leads), and the ignition timing.
5After the engine starts, it should be allowed
to warm up to normal operating temperature.
While the engine is warming up, make a
thorough check for fuel, oil and coolant leaks.
6Shut the engine off and recheck the engine
oil and coolant levels.
7Drive the vehicle to an area with minimum
traffic, accelerate at full throttle from 30 to
50 mph, then lift off the throttle completely,
and allow the vehicle to slow to 30 mph with
the throttle closed. Repeat the procedure
10 or 12 times. This will load the piston rings,
and cause them to seat properly against the
cylinder walls. Check again for oil and coolant
leaks.
8Drive the vehicle gently for the first
500 miles (no sustained high speeds) and
keep a constant check on the oil level. It is not
unusual for an engine to use oil during the
running-in period.
9At approximately 500 to 600 miles, change
the oil and filter.
10For the next few hundred miles, drive the
vehicle normally - don’t nurse it, but don’t
abuse it, either.
11After 2000 miles, change the oil and filter
again. The engine may now be considered to
be fully run-in.
2B•22 General engine overhaul procedures
Page 79 of 228

3General
Coolant capacity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Thermostat rating
Opening temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80°C (176°F)
Fully open at . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100°C (212°F)
Cooling fan thermo-switch - switching temperatures
Low-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91°C (196°F)
High-speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99°C (210°F)
Torque wrench settingsNm
Mechanical cooling fan clutch-to-water pump securing
nut (left-hand thread) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Mechanical cooling fan-to-clutch bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Water pump bolts
Small bolts (M6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Large bolts (M8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Thermostat housing bolts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Chapter 3
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
Air conditioner receiver-drier - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Air conditioning blower motor (E28/”old-shape” 5-series
models) - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Air conditioning compressor - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Air conditioning condenser - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Air conditioning system - precautions and maintenance . . . . . . . . . 12
Antifreeze - general information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Coolant level check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Coolant temperature sender unit - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Cooling system check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Chapter 1
Cooling system servicing (draining, flushing and refilling)See Chapter 1Engine cooling fan(s) and clutch - check, removal and refitting . . . . 5
Evaporator matrix - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
General information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Heater and air conditioner control assembly - removal and refitting 10
Heater and air conditioning blower motor - removal,testing and
refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Heater matrix - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Radiator - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Thermostat - check and renewal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Water pump - check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Water pump - removal and refitting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3•1
Easy,suitable for
novice with little
experienceFairly easy,suitable
for beginner with
some experienceFairly difficult,
suitable for competent
DIY mechanic
Difficult,suitable for
experienced DIY
mechanicVery difficult,
suitable for expert
DIY or professional
Degrees of difficulty
Specifications Contents
1 General information
Engine cooling system
All vehicles covered by this manual employ
a pressurised engine cooling system, with
thermostatically-controlled coolant circulation.
An impeller-type water pump mounted on
the front of the block pumps coolant through
the engine. The coolant flows around each
cylinder, and towards the rear of the engine.
Cast-in coolant passages direct coolantaround the intake and exhaust ports, near the
spark plug areas, and in close proximity to the
exhaust valve guides.
A wax-pellet-type thermostat is located in-
line in the bottom hose on M10 engines, in a
housing near the front of the engine on M20
and M30 engines, or behind an elbow under
the timing belt upper cover (on the front of the
cylinder head) on M40 engines. During warm-
up, the closed thermostat prevents coolant
from circulating through the radiator. As the
engine nears normal operating temperature,
the thermostat opens and allows hot coolant
to travel through the radiator, where it’s
cooled before returning to the engine.The pressure in the system raises the
boiling point of the coolant, and increases the
cooling efficiency of the radiator. The cooling
system is sealed by a pressure-type cap. If
the system pressure exceeds the cap
pressure relief value, the excess pressure in
the system forces the spring-loaded valve
inside the cap off its seat, and allows the
coolant to escape through the overflow tube.
The pressure cap on four-cylinder models is
on the top of the radiator; on six-cylinder models,
it’s on top of a translucent plastic expansion
tank. The cap pressure rating is moulded into the
top of the cap. The pressure rating is either
1.0 bar (14 psi) or 1.2 bars (17 psi).
Page 80 of 228

Warning: Do not remove the
pressure cap from the radiator or
expansion tank until the engine
has cooled completely and
there’s no pressure remaining in the
cooling system. Removing the cap from a
hot engine risks personal injury by
scalding.
Heating system
The heating system consists of a blower fan
and heater matrix located in the heater box,
with hoses connecting the heater matrix to the
engine cooling system, and the heater/air
conditioning control head on the dashboard.
Hot engine coolant is circulated through the
heater matrix passages all the time the engine
is running. Switching the heater on opens a
flap door to direct air through the heater
matrix, and the warmed air enters the
passenger compartment. A fan switch on the
control head activates the blower motor,
which forces more air through the heater
matrix, giving additional heater output for
demisting, etc.
Air conditioning system
The air conditioning system consists of a
condenser mounted in front of the radiator, an
evaporator mounted adjacent to the heater
matrix, a compressor mounted on the engine,
a filter-drier (receiver-drier) which contains a
high-pressure relief valve, and the plumbing
connecting all of the above components.
A blower fan forces the warmer air of the
passenger compartment through the
evaporator matrix (a radiator-in-reverse),
transferring the heat from the air to the
refrigerant. The liquid refrigerant boils off into
low-pressure vapour, taking the heat with it
when it leaves the evaporator.
Note: Refer to the precautions at the start
of Section 12 concerning the potential
dangers associated with the air conditioning
system.
2 Antifreeze-
general information
Warning: Do not allow antifreeze
to come in contact with your skin
or painted surfaces of the
vehicle. Rinse off spills
immediately with plenty of water. If
consumed, antifreeze can be fatal;
children and pets are attracted by its
sweet taste, so wipe up garage floor and
drip pan coolant spills immediately. Keep
antifreeze containers covered, and repair
leaks in your cooling system as soon as
they are noticed.
The cooling system should be filled with a
60/40% water/ethylene-glycol-based anti-
freeze solution, which will prevent freezing
down to approximately -27°C (-17°F). The
antifreeze also raises the boiling point of thecoolant, and (if of good quality) provides
protection against corrosion.
The cooling system should be drained,
flushed and refilled at the specified intervals
(see Chapter 1). Old or contaminated
antifreeze solutions are likely to cause
damage, and encourage the formation of rust
and scale in the system. Use distilled water
with the antifreeze, if available, or clean
rainwater. Tap water will do, but not if the
water in your area is at all “hard”.
Before adding antifreeze, check all hose
connections, because antifreeze tends to
search out and leak through very minute
openings. Engines don’t normally consume
coolant, so if the level goes down, find the
cause and correct it.
The antifreeze mixture should be
maintained at its correct proportions; adding
too much antifreeze reduces the efficiency of
the cooling system. If necessary, consult the
mixture ratio chart on the antifreeze container
before adding coolant. Hydrometers are
available at most car accessory shops to test
the coolant. Use antifreeze which meets the
vehicle manufacturer’s specifications.
3 Thermostat-
check and renewal
1
Warning: Do not remove the
radiator cap, drain the coolant, or
renew the thermostat until the
engine has cooled completely.
Check
1Before assuming the thermostat is to blame
for a cooling system problem, check the
coolant level, drivebelt tension (see Chapter 1)
and temperature gauge (or warning light)
operation.
2If the engine seems to be taking a long time
to warm up (based on heater output or
temperature gauge operation), the thermostat
is probably stuck open. Renew the
thermostat.
3If the engine runs hot, use your hand to
check the temperature of the upper radiator
hose. If the hose isn’t hot, but the engine is,
the thermostat is probably stuck closed,preventing the coolant inside the engine from
circulating to the radiator. Renew the
thermostat.
Caution: Don’t drive the vehicle
without a thermostat. The engine
will be very slow to warm-up in
cold conditions, resulting in poor
fuel economy and driveability. A new
thermostat is normally an inexpensive
component anyway.
4If the upper radiator hose is hot, it means
that the coolant is flowing and the thermostat
is at least partly open. Consult the “Fault
finding” Section at the rear of this manual for
cooling system diagnosis.
Renewal
All models
5Disconnect the negative cable from the
battery.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
6Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new or in good
condition, save it and re-use it.
M10 engines
7The thermostat is located in the bottom
hose. First remove the cooling fan.
8Note the fitted position of the thermostat,
then unscrew the hose clamps and withdraw
the thermostat from the hose connections
(see illustration).
9Refit the thermostat-to-hose connections,
and tighten the hose clamps.
10Refit the cooling fan.
M20 and M30 engines
11Loosen the hose clamp (see illustration),
then detach the hose(s) from the thermostat
cover.
3•2 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
3.11 On M20 and M30 engine models,
loosen the hose clamp (A) and disconnect
the hose from the thermostat housing
cover - note that the coolant temperature
sender unit (barely visible behind the fuel
pressure regulator) is located at the top of
the thermostat housing (B)
3.8 On the M10 (four-cylinder) engine, the
thermostat (arrowed) is connected in-line
in the radiator hose
Page 81 of 228
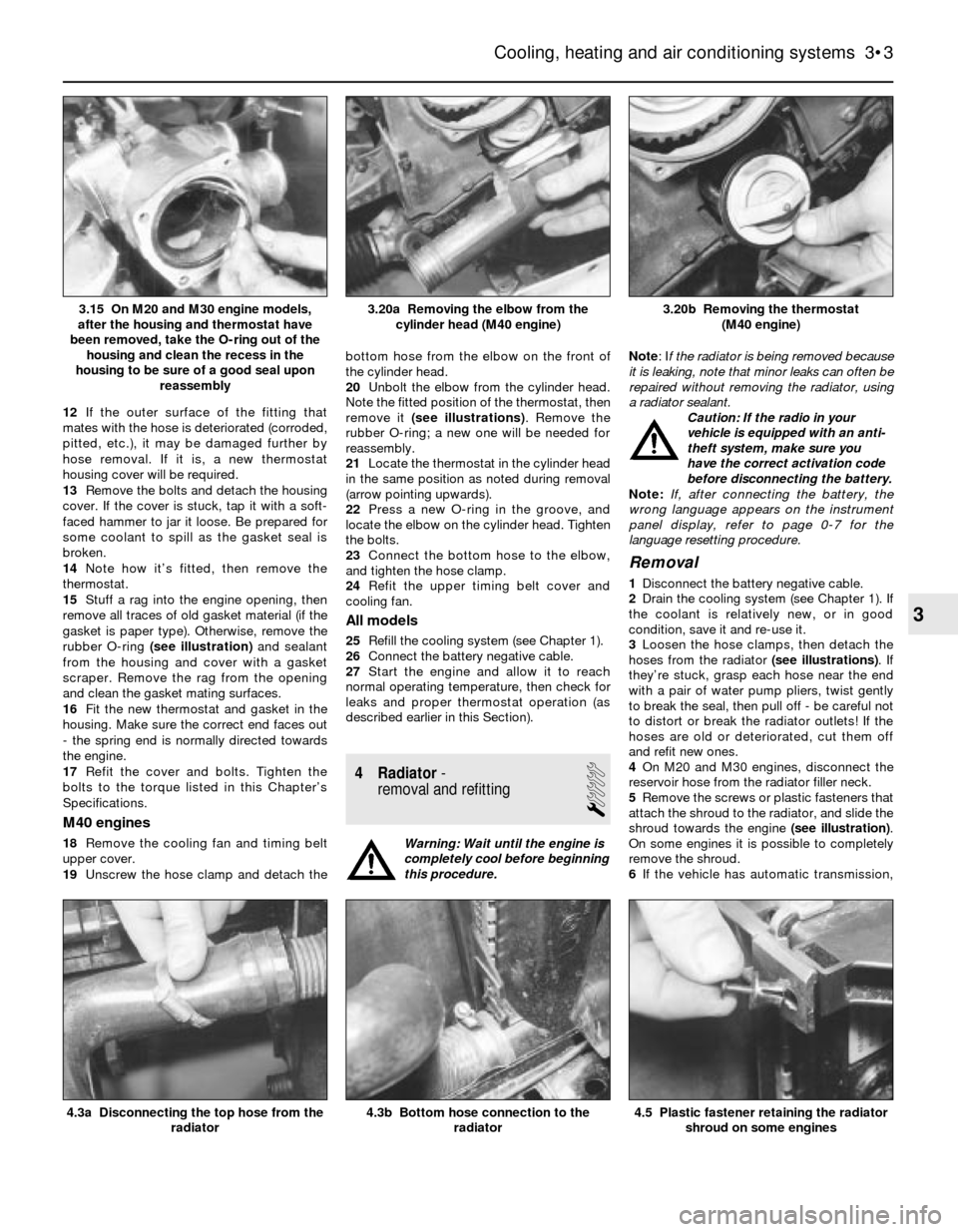
12If the outer surface of the fitting that
mates with the hose is deteriorated (corroded,
pitted, etc.), it may be damaged further by
hose removal. If it is, a new thermostat
housing cover will be required.
13Remove the bolts and detach the housing
cover. If the cover is stuck, tap it with a soft-
faced hammer to jar it loose. Be prepared for
some coolant to spill as the gasket seal is
broken.
14Note how it’s fitted, then remove the
thermostat.
15Stuff a rag into the engine opening, then
remove all traces of old gasket material (if the
gasket is paper type). Otherwise, remove the
rubber O-ring (see illustration)and sealant
from the housing and cover with a gasket
scraper. Remove the rag from the opening
and clean the gasket mating surfaces.
16Fit the new thermostat and gasket in the
housing. Make sure the correct end faces out
- the spring end is normally directed towards
the engine.
17Refit the cover and bolts. Tighten the
bolts to the torque listed in this Chapter’s
Specifications.
M40 engines
18Remove the cooling fan and timing belt
upper cover.
19Unscrew the hose clamp and detach thebottom hose from the elbow on the front of
the cylinder head.
20Unbolt the elbow from the cylinder head.
Note the fitted position of the thermostat, then
remove it (see illustrations). Remove the
rubber O-ring; a new one will be needed for
reassembly.
21Locate the thermostat in the cylinder head
in the same position as noted during removal
(arrow pointing upwards).
22Press a new O-ring in the groove, and
locate the elbow on the cylinder head. Tighten
the bolts.
23Connect the bottom hose to the elbow,
and tighten the hose clamp.
24Refit the upper timing belt cover and
cooling fan.
All models
25Refill the cooling system (see Chapter 1).
26Connect the battery negative cable.
27Start the engine and allow it to reach
normal operating temperature, then check for
leaks and proper thermostat operation (as
described earlier in this Section).
4 Radiator-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.Note: If the radiator is being removed because
it is leaking, note that minor leaks can often be
repaired without removing the radiator, using
a radiator sealant.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new, or in good
condition, save it and re-use it.
3Loosen the hose clamps, then detach the
hoses from the radiator (see illustrations). If
they’re stuck, grasp each hose near the end
with a pair of water pump pliers, twist gently
to break the seal, then pull off - be careful not
to distort or break the radiator outlets! If the
hoses are old or deteriorated, cut them off
and refit new ones.
4On M20 and M30 engines, disconnect the
reservoir hose from the radiator filler neck.
5Remove the screws or plastic fasteners that
attach the shroud to the radiator, and slide the
shroud towards the engine (see illustration).
On some engines it is possible to completely
remove the shroud.
6If the vehicle has automatic transmission,
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•3
3.20b Removing the thermostat
(M40 engine)3.20a Removing the elbow from the
cylinder head (M40 engine)3.15 On M20 and M30 engine models,
after the housing and thermostat have
been removed, take the O-ring out of the
housing and clean the recess in the
housing to be sure of a good seal upon
reassembly
4.5 Plastic fastener retaining the radiator
shroud on some engines4.3b Bottom hose connection to the
radiator4.3a Disconnecting the top hose from the
radiator
3
Page 82 of 228

disconnect the fluid cooler lines from the
radiator. Use a drip tray to catch spilled fluid.
Plug the fluid cooler lines and fittings.
7Disconnect the coolant sensors located on
the radiator (see illustration). The thermo-
statically-controlled switches for high- and
low-speed operation of the auxiliary fan are
located in the radiator tanks, in various
locations depending on engine and model.
8Remove the radiator mounting bolt(s). The
mountings are either on the top or sides of the
radiator (see illustration).
9Carefully lift out the radiator from the
bottom mountings, taking care not to damage
the cooling fins. Don’t spill coolant on the
vehicle, or scratch the paint.
10With the radiator removed, it can be
inspected for leaks and damage. If it needs
repair, have a specialist perform the work, as
special techniques are required.
11Flies and dirt can be removed from the
radiator with compressed air and a soft brush.
Don’t bend the cooling fins as this is done.
12Check the radiator mountings for
deterioration, and renew if necessary (see
illustration).
Refitting
13Refitting is the reverse of the removal
procedure.
14After refitting, fill the cooling system with
the proper mixture of antifreeze and water.
Refer to Chapter 1 if necessary.15Start the engine and check for leaks.
Allow the engine to reach normal operating
temperature, indicated by the upper radiator
hose becoming hot. Recheck the coolant
level, and add more if required.
16If you’re working on an automatic
transmission model, check and add
transmission fluid as needed.
5 Engine cooling fan(s) and
clutch- check, removal and
refitting
1
Warning: To avoid possible injury
or damage, DO NOT operate the
engine with a damaged fan. Do
not attempt to repair fan blades -
fit a new fan. Also, the electric auxiliary fan
in front of the radiator or air conditioning
condenser can come on without the
engine running or ignition being on. It is
controlled by the coolant temperature of
the thermo-switches located in the
radiator.
Check
Electric auxiliary fan
Note: This fan on most models is controlled
by two thermo-switches placed in the radiator:
one for low-speed/low-temperature operation,
and one for high-speed/high-temperature
operation. Each switch comes on at a different
coolant temperature (refer to the Specifica-
tions at the beginning of this Chapter).
1The thermostatically-controlled switches for
high- and low-speed operation of the auxiliary
fan are fitted in various locations in the
radiator (see illustration 4.7), depending on
engine or model. Two single switches, or one
dual switch, may be fitted.
2Insert a small screwdriver into the
connector to lift the lock tab, and unplug the
fan wire harness.
3To test the fan motor, unplug the electrical
connector at the motor, and use jumper wires
to connect the fan directly to the battery. If the
fan doesn’t work when connected directly to
the battery, the motor is proved faulty, and
must be renewed. If the fan works, there’s agood chance the switch is malfunctioning. To
more accurately diagnose the problem, follow
the steps that apply to your model. Note: Spin
the auxiliary fan motor by hand, to check that
the motor or fan isn’t binding. Make sure,
however, that the engine is sufficiently cool
that there is no danger of the fan cutting-in on
its own when this is done.
4To test the low-speed and high-speed
circuits, disconnect the electrical connector
from one of the fan switches, and bridge the
terminals of the switch’s electrical connector
with a short piece of wire. The fan should run
at low or high speed, depending on which
switch has been disconnected. On some
models the ignition must be on before the fan
will run.
5Repeat the test at the other switch so that
both high and low speeds are tested.
6If the low-speed and high-speed circuits
are OK, but there has been a problem with the
fan not operating correctly in service, renew
the switch (or switches). To remove a switch,
drain the coolant below the level of the switch
(see Chapter 1), then unscrew the switch and
screw in the new one. Refill the system with
coolant.
7If the switches are satisfactory, but the
motor still does not operate, the problem lies
in the fuse, the relay, the wiring which
connects the components (or the fan motor
itself). Carefully check the fuse, relay, all
wiring and connections. See Chapter 12 for
more information on how to carry out these
checks.
Mechanical fan with viscous clutch
8Disconnect the battery negative cable, and
rock the fan back and forth by hand to check
for excessive bearing play.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
9With the engine cold, turn the fan blades by
hand. The fan should turn with slight
resistance.
10Visually inspect for substantial fluid
leakage from the fan clutch assembly. If
problems are noted, renew the fan clutch
assembly.
11With the engine completely warmed up,
turn off the ignition switch and disconnect the
battery negative cable. Turn the fan by hand.
Heavier resistance should be evident. If the
fan turns easily, a new fan clutch may be
needed.
Removal and refitting
Electric auxiliary fan
12Disconnect the battery negative cable.
13To remove the auxiliary fan follow the
procedure that applies to your vehicle.
3•4 Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems
4.12 When the radiator is out, the radiator
mountings can be inspected - check for
signs of deterioration, and renew them, if
needed
4.8 The radiator is bolted to the front
panel at either the sides or the top of the
radiator4.7 Sensors that control the high- and
low-speed operation of the auxiliary
cooling fan are located in various places in
the radiator tanks
Page 83 of 228
3-Series models
14Remove the radiator grille assembly (see
Chapter 11).
15Unbolt and remove the fan bracket and
shroud assembly from the radiator (see
Section 5).
16Remove the radiator (see Section 4).
17Unbolt the air conditioning condenser
mounting bolts, where applicable. Do not
remove the condenser or disconnect any
refrigerant lines from the condenser.
18Carefully pull the condenser back towards
the engine, slightly, to gain access to lift the
auxiliary fan.
19Disconnect the fan motor electrical
connection and remove the auxiliary fan.
20Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5-Series models
21Remove the screws and trim panel in front
of the radiator.
22Unbolt the fan assembly from the
condenser mounting points.
23Disconnect the fan electrical connector.
24Remove the fan and housing from the car,
being careful not to damage the air
conditioning condenser (when applicable)
while removing the fan.
25Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Mechanical fan with viscous clutch
26Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Remove the fan shroud mounting screws or
plastic fasteners, and detach the shroud (see
Section 4).
27 Use a 32 mm open-ended spanner to
remove the fan/clutch assembly. Place the
spanner on the large nut ahead of the pulley
(see illustrations), and tap the end of the
spanner to loosen the nut.
Caution: The nut has left-handed
threads, so it loosens by being
turned clockwise, as viewed from
the front of the vehicle.
28Lift the fan/clutch assembly (and shroud,
if necessary) out of the engine compartment.
29If necessary, remove the four bolts
attaching the pulley to the water pump hub.
The pulley can then be removed after
removing the drivebelt(s) (see illustration).30Carefully inspect the fan blades for
damage and defects. Renew it if necessary.
31At this point, the fan may be unbolted
from the clutch, if necessary. If the fan clutch
is stored, position it with the radiator side
facing down.
32Refitting is the reverse of removal.
6 Water pump- check
1
1A failure in the water pump can cause
serious engine damage due to overheating.
2There are two ways to check the operation
of the water pump while it’s fitted on the
engine. If either of the following checks
suggest that the pump is defective, a new one
should be fitted.
3Water pumps are equipped with “weep” or
“vent” holes. If a failure occurs in the pump
seal, coolant will leak from the hole. In most
cases, you’ll need a torch to find the hole on
the water pump from underneath to check for
leaks.
4If the water pump shaft bearings fail, there
may be a howling sound at the front of the
engine while it’s running. Shaft wear can be
felt if the water pump pulley is rocked up and
down (with the drivebelt removed). Don’t
mistake drivebelt slippage, which causes a
squealing sound, for water pump bearing
failure. Alternator bearing failure can also
cause a howling sound, but after removing the
drivebelt(s) it should be easy enough to tell
which component is responsible.
7 Water pump-
removal and refitting
2
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Drain the cooling system (see Chapter 1). If
the coolant is relatively new, or in good
condition, save it and re-use it.
3Remove the cooling fan shroud (see
Section 5).
4Remove the drivebelts (see Chapter 1).
5Where applicable, loosen the clamps and
detach the hoses from the water pump. If
they’re stuck, grasp each hose near the end
with a pair of water pump pliers and gently
twist it to break the seal, then pull it off. If the
hoses are deteriorated, cut them off and refit
new ones.
6Remove the fan and clutch assembly and
the pulley at the end of the water pump shaft
(see Section 5).
7To remove the water pump, follow the
specific steps that apply to your engine.
M10 engine
8Unscrew the mounting bolts and remove
the water pump (see illustration).
Cooling, heating and air conditioning systems 3•5
5.29 Removing the water pump pulley
(M40 engine)5.27b . . . to loosen the nut, place a 32 mm
open-ended spanner on the nut, and
sharply strike the spanner (A) with a metal
drift (B) and hammer; this will loosen the
nut and allow it to be turned easily so the
fan can be removed5.27a The cooling fan on the water pump
is attached to the shaft by a left-hand-
threaded nut located directly behind the
fan . . .
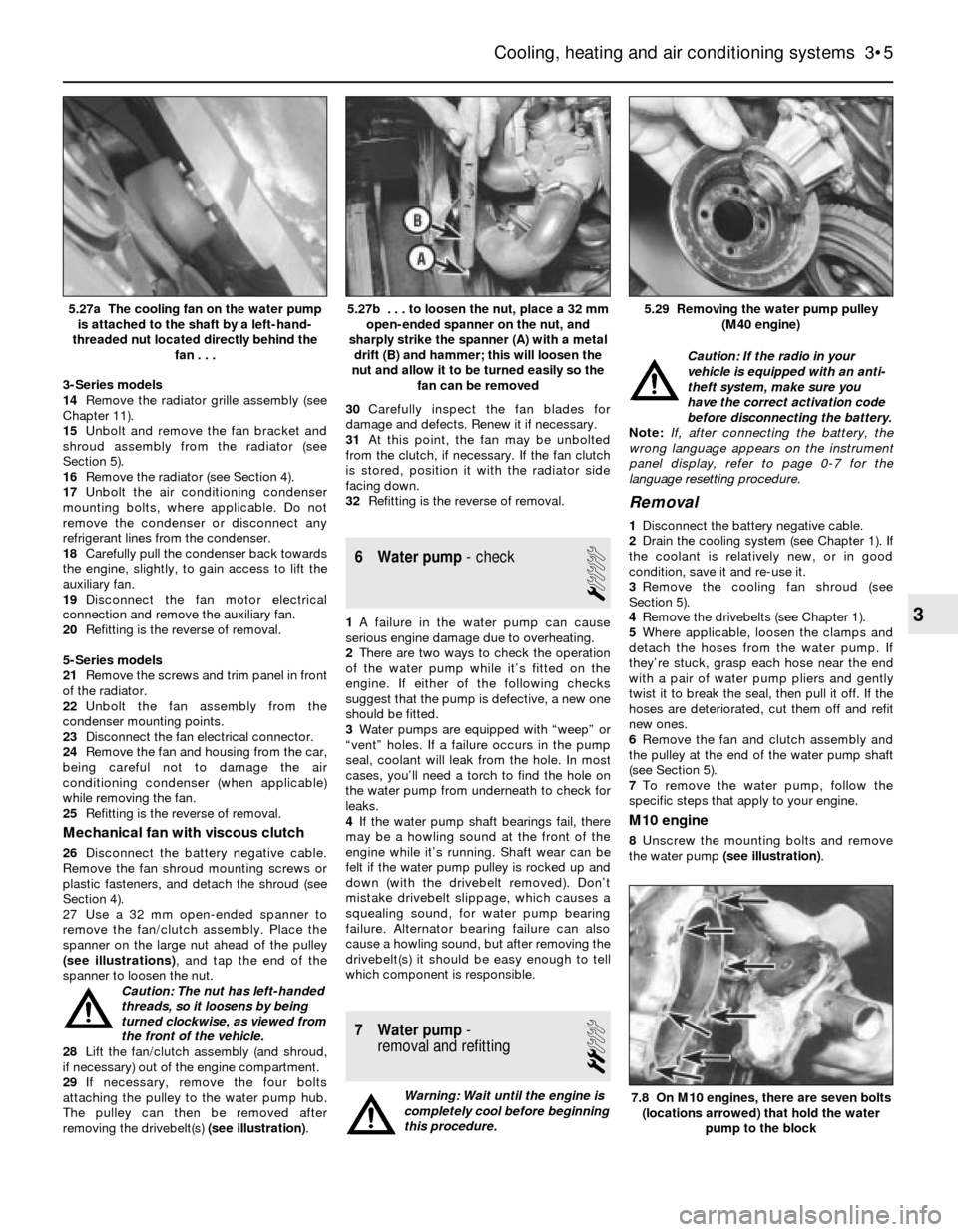
7.8 On M10 engines, there are seven bolts
(locations arrowed) that hold the water
pump to the block
3