Port BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30 Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1985, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 164 of 228
remove the pin (see illustrations). Be sure to
support the bonnet while doing this.
4Have an assistant hold onto the bonnet on
one side while you hold the other side.
5Remove the bonnet-to-hinge assembly
bolts on your side of the bonnet, then hold
your side of the bonnet while your assistant
removes the bonnet-to-hinge bolts on the
other side.
6Remove the bonnet. Place it somewhere
safe where it will not be knocked over, with
rags to protect the paintwork where it rests on
the ground or against a wall.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5-Series models
8Open the bonnet. On some later models, it
may be necessary to prise out the plastic clips
and remove the insulation pad for access tothe bonnet light connector and windscreen
washer hoses (see illustrations). Having
done this, disconnect the wires and hoses.
9Detach the clips and withdraw the bonnet
support pins (see illustration).
10Remove the pins from the hinges (see
illustration).
11Have an assistant hold onto the bonnet on
one side while you hold the other side.
12Remove the bonnet-to-hinge through-bolt
on your side of the bonnet, then hold your
side of the bonnet while your assistant
removes the through-bolt on the other side
(see illustration).
13Remove the bonnet. Place it somewhere
safe where it will not be knocked over, with
rags to protect the paintwork where it rests on
the ground or against a wall.
14Refitting is the reverse of the removal.
Adjustment
15The bonnet can be adjusted to obtain a
flush fit between the bonnet and wings after
loosening the bonnet hinge bolts. On some 5-
Series models, it will be necessary to remove the
side grille sections for access to the hinge bolts.
16Move the bonnet from side to side, or
front to rear, until the bonnet is properly
aligned with the wings at the front. Tighten the
bolts securely.
17The rear height of the bonnet can be
adjusted by loosening the bolts, and raising or
lowering the catch (see illustration). After
adjustment, tighten the bolts securely.
18Side-to-side adjustment of the bonnet can
be made by loosening the roller guide bolt
nuts, and moving the guide position until it
slides into the catch properly (see illustration).
Bodywork and fittings 11•5
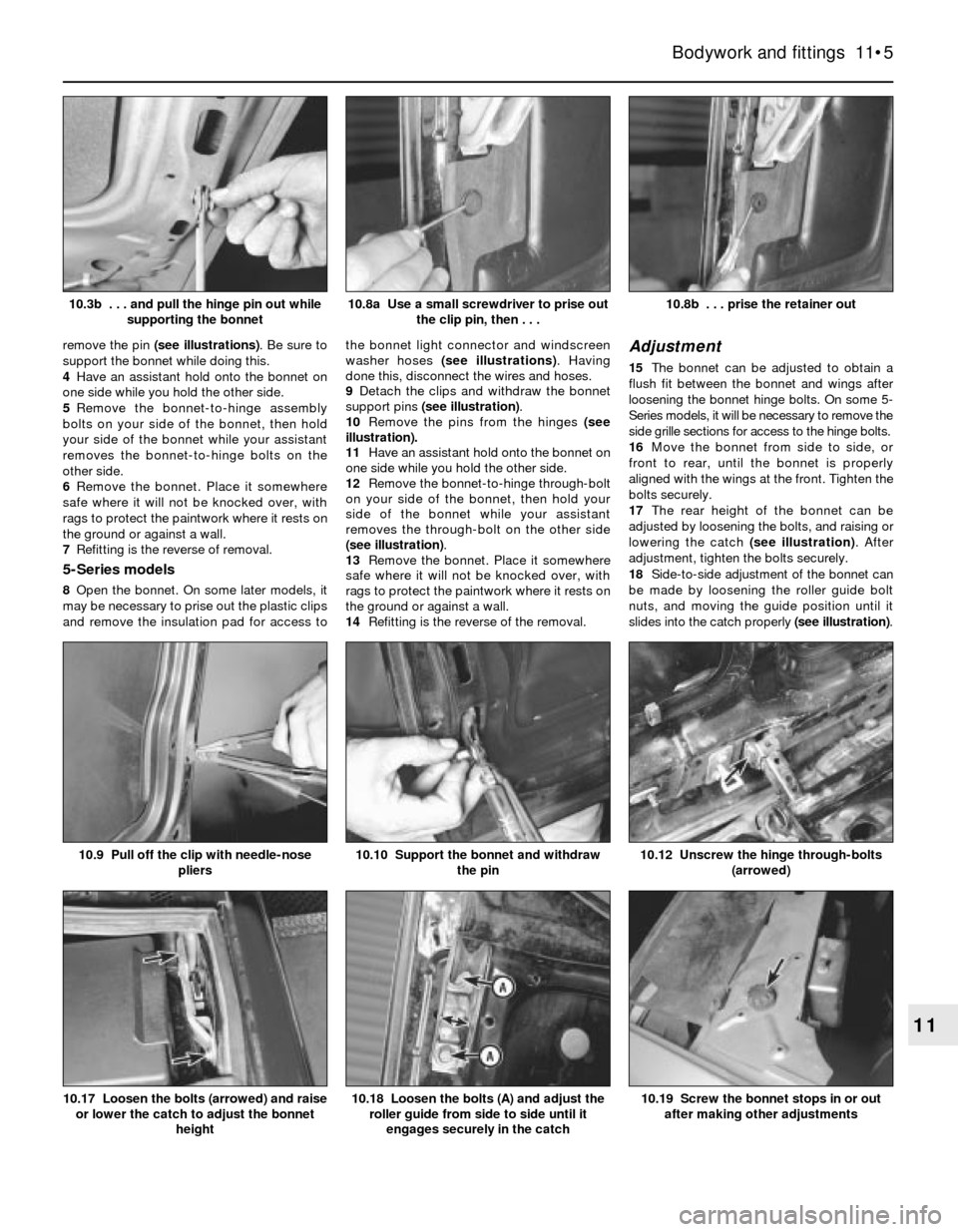
10.8b . . . prise the retainer out10.8a Use a small screwdriver to prise out
the clip pin, then . . .10.3b . . . and pull the hinge pin out while
supporting the bonnet
10.19 Screw the bonnet stops in or out
after making other adjustments10.18 Loosen the bolts (A) and adjust the
roller guide from side to side until it
engages securely in the catch10.17 Loosen the bolts (arrowed) and raise
or lower the catch to adjust the bonnet
height
10.12 Unscrew the hinge through-bolts
(arrowed)10.10 Support the bonnet and withdraw
the pin10.9 Pull off the clip with needle-nose
pliers
11
Page 165 of 228

19After adjustment, screw the stop pads in
or out to support the bonnet in its new
position (see illustration).
20The bonnet mechanism should be
lubricated periodically with grease, to prevent
sticking or jamming.
11 Bumpers-
removal and refitting
1
Removal
1Detach the bumper cover (if applicable) and
where necessary the front spoiler.
2Disconnect any wiring or other components
that would interfere with bumper removal.
3Support the bumper with a jack or axle
stand. Alternatively, have an assistant support
the bumper as the bolts are removed.
4Remove the retaining bolts and detach the
bumper.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal. Tighten
the retaining bolts securely, then refit the
bumper cover and any other components that
were removed.
12 Door trim panel-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code before
disconnecting the battery, Refer to the
information on page 0-7 at the front of this
manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove all door trim panel retaining screws
and door pull/armrest assemblies.3On models with manual (non-electric)
windows, remove the window regulator
handle (see illustration). On models with
electric windows, prise off the control switch
assembly and unplug it.
4Disengage the trim panel-to-door retaining
clips. Work around the outer edge until the
panel is free.
5Once all of the clips are disengaged, detach
the trim panel, unplug any electrical
connectors, and remove the trim panel from
the vehicle.
6For access to the inner door, carefully peel
back the plastic water shield.
Refitting
7Prior to refitting the door trim panel, be sure
to renew any clips in the panel which may
have come out (or got broken) during the
removal procedure.
8Plug in the electrical connectors (where
applicable) and place the panel in position in
the door. Press the door panel into place until
the clips are seated, then refit the
armrest/door pulls. Refit the window regulator
handle, where applicable.
13 Door- removal, refitting and
adjustment
1
Removal
1Remove the door trim panel (see Section
12). Disconnect any electrical connectors, andpush them through the door opening so they
won’t interfere with door removal.
2Place a trolley jack or axle stand under the
door, or have an assistant on hand to support
it when the hinge bolts are removed. Note: If a
jack or axle stand is used, place a rag between
it and the door, to protect the door’s painted
surfaces.
3Scribe or mark around the door hinges.
4Disconnect the door check strap by prising
the circlip out of the end of the pin, then slide
the pin out (see illustration). A roll pin is fitted
to some models; this is removed by driving it
out with a pin punch.
5Remove the hinge-to-door nuts, and
carefully lift off the door (see illustration).
Refitting and adjustment
6Refitting is the reverse of removal.
7Following refitting of the door, check the
alignment and adjust it if necessary as
follows:
a) Up-and-down and fore-and-aft
adjustments are made by loosening the
hinge-to-body nuts and moving the door
as necessary.
b) The door lock striker can also be adjusted
both up and down and sideways, to
provide positive engagement with the lock
mechanism. This is done by loosening the
mounting bolts and moving the striker as
necessary (see illustration).
14 Boot lid/tailgate- removal,
refitting and adjustment
1
Boot lid
1Open the boot lid, and cover the edges of
the boot compartment with pads or cloths to
protect the painted surfaces when the lid is
removed.
2Disconnect any cables or electrical
connectors attached to the boot lid that would
interfere with removal.
3Make alignment marks around the hinge
bolts (see illustration).
4Have an assistant support the lid, then
remove the lid-to-hinge bolts on both sides
and lift it off.
11•6 Bodywork and fittings
13.7 The door lock striker position can be
adjusted after loosening the screws
(arrowed)13.5 Remove the nuts (arrowed) and
detach the door from the hinges
13.4 Detach the circlip (arrowed) from the
tapered end of the pin12.3 On models without electric windows,
prise off the window regulator handle trim
piece for access to the retaining screw
Page 166 of 228

5Refitting is the reverse of removal. Align the
lid-to-hinge bolts with the marks made during
removal.
6After refitting, close the lid and make sure
it’s in proper alignment with the surrounding
panels. Fore-and-aft and side-to-side
adjustments are controlled by the position of
the hinge bolts in the slots. To make an
adjustment, loosen the hinge bolts, reposition
the lid, and retighten the bolts.
7The height of the lid in relation to the
surrounding body panels when closed can be
changed by loosening the lock and/or striker
bolts, repositioning the striker and/or lock,
and tightening the bolts (see illustrations).
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Tailgate
8Disconnect the battery negative cable.
9Open the tailgate and cover the rear edge
of the roof with pads or cloths to protect the
painted surfaces when the tailgate isremoved. On 5-Series models, the window
may be removed separately by disconnecting
the wiring and unscrewing the mounting
screws - have an assistant hold the window
while the screws are being loosened (see
illustration).
10Remove the trim from the inside of the
tailgate. Also where necessary on 5-Series
models, remove the edge covers for access to
the strut mountings.
11Disconnect the wiring loom and the
washer tubing. On some models, it will be
necessary to pull the wiring loom out of the
rear pillar and then disconnect the plug (see
illustration).
12While an assistant holds the tailgate open,disconnect the struts on both sides by
unscrewing the mounting screws. Where
applicable, pull out the retaining pin or spring
clip, and remove the strut from the ball (see
illustrations).
13Mark the position of the hinge arms on the
tailgate with a pencil.
14Unscrew the bolts and withdraw the
tailgate from the hinge arms. On 5-Series
models, it will be necessary to use an Allen
key or bit (see illustration).
15Refitting is the reverse of removal, but
make sure that the previously-made marks
are correctly aligned. Check that the tailgate
closes centrally between the rear pillars and
enters the lock correctly.
Bodywork and fittings 11•7
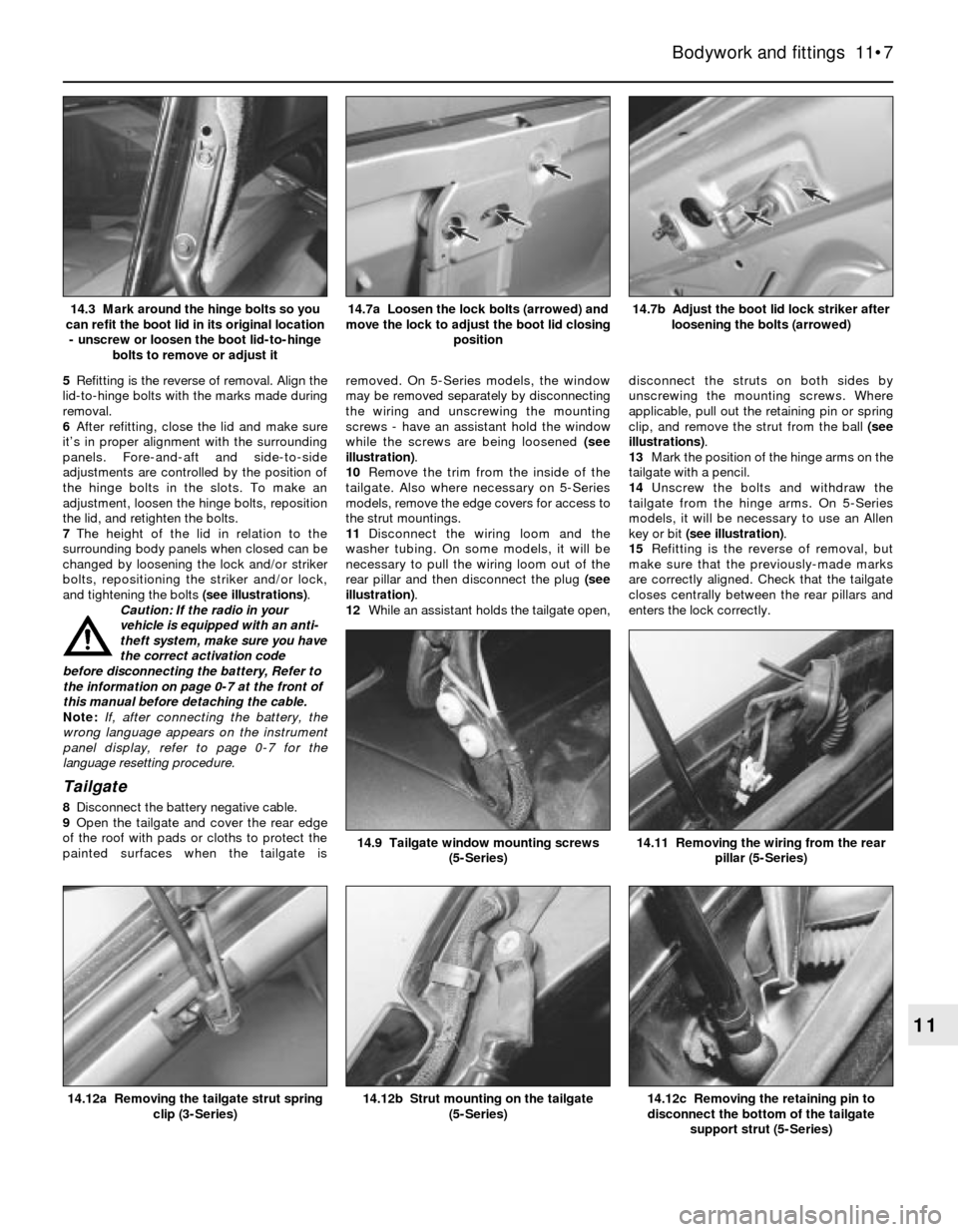
14.7b Adjust the boot lid lock striker after
loosening the bolts (arrowed)14.7a Loosen the lock bolts (arrowed) and
move the lock to adjust the boot lid closing
position14.3 Mark around the hinge bolts so you
can refit the boot lid in its original location
- unscrew or loosen the boot lid-to-hinge
bolts to remove or adjust it
14.12c Removing the retaining pin to
disconnect the bottom of the tailgate
support strut (5-Series)14.12b Strut mounting on the tailgate
(5-Series)14.12a Removing the tailgate strut spring
clip (3-Series)
14.11 Removing the wiring from the rear
pillar (5-Series)14.9 Tailgate window mounting screws
(5-Series)
11
Page 167 of 228

15 Latch, lock cylinder and
handles- removal, refitting
and adjustment
1
1Remove the trim panel(s) and, on the door,
the plastic shield (see Section 12).
Latch
2Disconnect the operating rods from the
latch (see illustration).
3Remove the latch retaining screws.
4Detach the latch assembly and withdraw it.
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Lock cylinder
6Detach the linkage.
7Use a screwdriver to slide the retaining clip
off, and withdraw the lock cylinder.
8Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Interior handle
9Disconnect the operating rod from the
handle.
10Remove the retaining screws and lift the
handle from the door.
11Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Exterior handle
12Lift up the handle for access, remove the
two retaining screws, then detach the handle
from the door.
13Refitting is the reverse of removal.
16 Door window glass-
removal and refitting
3
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Remove the door trim panel and the plastic
water shield (see Section 12).
3Prise the door inner and outer weatherstrips
from the door.
Front door
4Raise the window so that the mounting
bolts can be reached through the access hole.
If electric windows are fitted, temporarily
reconnect the battery cable to accomplish
this.
5Support the glass, and remove the retaining
bolts securing the glass to the regulator.
6Lift the window glass up and out of the door
window slot, then tilt it and remove it from the
door.
7Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Rear door
8Carry out the operations described in
paragraphs 1 to 5.
3-Series models
9Disengage the glass from the front guide
roller, and prise out the rubber window
guides.
10Remove the door handle screws, and
allow the handle assembly to hang out of the
way.
11Remove the rear window frame bolts,
push the frame into the door, and remove the
window glass.
12Refitting is the reverse of removal.
5-Series models
13Loosen the rear window guide mounting
bolt.14Detach the glass from the front guide
roller, disengage the glass from the guide
rails, then slide the glass to the rear and
remove by lifting from above.
15The fixed glass can be removed by
removing the guide rail bolts, then pulling the
rail down to the rear and detaching the glass.
16Refitting is the reverse of removal. The
rear window glass can be adjusted by
loosening the adjustment bolts, then raising
the glass to within one inch of the top of the
door opening. Adjust the glass-to-
opening gap evenly, then tighten the bolts
securely.
17 Door window regulator-
removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Remove the door window glass (Sec-
tion 16).
2Remove the securing bolts or nuts, and lift
the window regulator assembly out of the
door (withdraw the regulator mechanism
through the access hole). On models with
electric windows, unplug the electrical
connector.
Refitting
3Refitting is the reverse of removal.
18 Exterior mirror-
removal and refitting
1
Removal
1If it is required to renew the mirror glass
only, insert a small screwdriver through the
hole in the bottom of the exterior mirror, and
carefully lever clockwise the plastic holder on
the rear of the glass (ie move the bottom of
the screwdriver to the right). This will release
the glass, which can then be withdrawn. If
electric mirrors are fitted, it will be necessary
to disconnect the wiring before completely
removing the glass.
2To remove the complete mirror, prise off
the cover panel (and/or the tweeter speaker,
where applicable).
3Unplug the electrical connector.
4Remove the retaining screws and lift the
mirror off
Refitting
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
11•8 Bodywork and fittings
15.2 Typical door latch, lock cylinder and
handle details
14.14 Unscrewing the hinge mounting
bolts (5-Series)
Page 174 of 228
13 Headlights- adjustment
2
Note:The headlights must be aimed correctly.
If adjusted incorrectly, they could momentarily
blind the driver of an oncoming vehicle and
cause a serious accident, or seriously reduce
your ability to see the road. The headlights
should be checked for proper aim every
12 months (as is done during the MOT test),
and any time a new headlight is fitted or front-
end body work is performed. It should be
emphasised that the following procedure will
only provide a temporary setting until the
headlights can be adjusted by a properly-
equipped garage.
1Each headlight has two adjusting screws,
one controlling up-and-down movement and
one controlling left-and-right movement (see
illustration). It may be necessary to remove
the grille (see Chapter 11) for access to these
screws.
2There are several methods of adjusting the
headlights. The simplest method requires a
blank wall (or garage door) 25 feet in front of
the vehicle, and a level floor.
3Position masking tape vertically on the wall,
to mark the vehicle centreline and the
centreline of both headlights. Note:It may be
easier to position the tape on the wall with the
vehicle parked only a few inches away, and
then move the vehicle back the required
distance when all marks have been made.
4Make a horizontal line on the wall to mark
the centreline of all headlights.
5Move the vehicle back so that it is 25 feet
away from the marked wall (keep the front end
of the vehicle square to the wall). Adjustment
should be made with the vehicle sitting level,
the fuel tank half-full, and with no unusually
heavy loads in the vehicle.
6Switch on the dipped beam. The bright
spots on the wall should be two inches below
the horizontal line, and two inches to the left
of the headlight vertical lines. Adjustment is
made by turning the adjusting screw to raise
or lower the beam. The other adjusting screwshould be used in the same manner to move
the beam left or right.
7With main beam on, the bright spots on the
wall should be exactly on the vertical lines,
and just below the horizontal line. Note:It may
not be possible to position the headlight aim
exactly for both main and dipped beams. If a
compromise must be made, keep in mind that
the dipped beam is most used, and will have
the greatest effect on driver safety.
8Have the headlights adjusted by a dealer
service department or qualified garage at the
earliest opportunity.
14 Headlight housing-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you have
the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery, Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.2Remove the side grille (see Chapter 11),
then remove the rear cover(s) where
necessary.
3Unplug the headlight (sealed beam-type) or
remove the bulb (halogen bulb-type).
4Remove the screws and detach the housing
(see illustration).
Refitting
5Refitting is the reverse of removal.
15 Bulb renewal
1
1The lenses of many lights are held in place
by screws, which makes it a simple procedure
to gain access to the bulbs.
2On some lights, the lenses are held in place
by clips. The lenses can be removed by using
a small screwdriver to prise them off.
3Several bulbs are mounted in self-earthing
holders, and are removed by pushing in and
turning them anti-clockwise (see illustration).
The bulbs can then be removed (see
illustrations).
4The tail lights on 3-Series models are
accessible after removing the housing, then
removing the bulbs (see illustrations).
5To gain access to the facia lights, the
instrument cluster will have to be removed
first (see illustration).
12•6 Body electrical systems
15.3c . . . then pull the bulb from the
holder15.3b On models with high-mounted
centre brake lights, the self-earthing
holder is accessible from the luggage area
- pull the holder out . . .15.3a The tail light bulbs on later 5-Series
models are in self-earthing holders which
can be simply pulled out of the housing -
the bulb is then removed from the holder
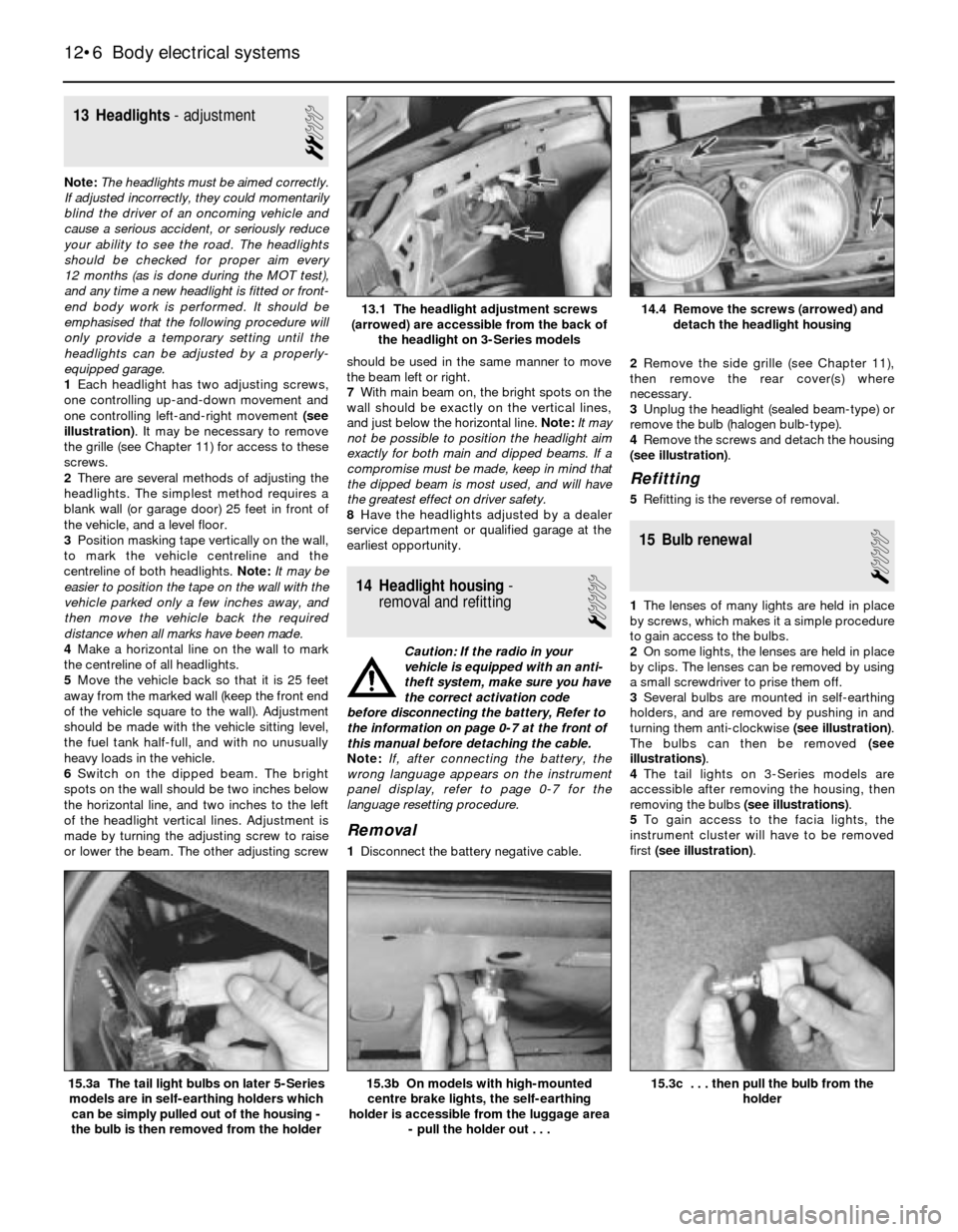
14.4 Remove the screws (arrowed) and
detach the headlight housing13.1 The headlight adjustment screws
(arrowed) are accessible from the back of
the headlight on 3-Series models
Page 202 of 228

REF•1
REF
MOT Test Checks
This is a guide to getting your vehicle through the MOT test.
Obviously it will not be possible to examine the vehicle to the same
standard as the professional MOT tester. However, working through
the following checks will enable you to identify any problem areas
before submitting the vehicle for the test.
Where a testable component is in borderline condition, the tester
has discretion in deciding whether to pass or fail it. The basis of such
discretion is whether the tester would be happy for a close relative or
friend to use the vehicle with the component in that condition. If the
vehicle presented is clean and evidently well cared for, the tester may
be more inclined to pass a borderline component than if the vehicle is
scruffy and apparently neglected.
It has only been possible to summarise the test requirements here,
based on the regulations in force at the time of printing. Test standards
are becoming increasingly stringent, although there are some
exemptions for older vehicles. For full details obtain a copy of the Haynes
publication Pass the MOT! (available from stockists of Haynes manuals).
An assistant will be needed to help carry out some of these checks.
The checks have been sub-divided into four categories, as follows:
HandbrakeMTest the operation of the handbrake.
Excessive travel (too many clicks) indicates
incorrect brake or cable adjustment.
MCheck that the handbrake cannot be
released by tapping the lever sideways. Check
the security of the lever mountings.
Footbrake
MDepress the brake pedal and check that it
does not creep down to the floor, indicating a
master cylinder fault. Release the pedal, wait
a few seconds, then depress it again. If the
pedal travels nearly to the floor before firm
resistance is felt, brake adjustment or repair is
necessary. If the pedal feels spongy, there is
air in the hydraulic system which must be
removed by bleeding.MCheck that the brake pedal is secure and in
good condition. Check also for signs of fluid
leaks on the pedal, floor or carpets, which
would indicate failed seals in the brake master
cylinder.
MCheck the servo unit (when applicable) by
operating the brake pedal several times, then
keeping the pedal depressed and starting the
engine. As the engine starts, the pedal will
move down slightly. If not, the vacuum hose or
the servo itself may be faulty.
Steering wheel and column
MExamine the steering wheel for fractures or
looseness of the hub, spokes or rim.
MMove the steering wheel from side to side
and then up and down. Check that the
steering wheel is not loose on the column,
indicating wear or a loose retaining nut.
Continue moving the steering wheel as before,
but also turn it slightly from left to right.
MCheck that the steering wheel is not loose
on the column, and that there is no abnormalmovement of the steering wheel, indicating
wear in the column support bearings or
couplings.
Windscreen and mirrors
MThe windscreen must be free of cracks or
other significant damage within the driver’s
field of view. (Small stone chips are
acceptable.) Rear view mirrors must be
secure, intact, and capable of being adjusted.
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S SEAT
1Checks carried out
FROM THE DRIVER’S
SEAT2Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
ON THE GROUND3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE
RAISED AND THE
WHEELS FREE TO
TURN4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S
EXHAUST EMISSION
SYSTEM
Page 204 of 228
REF•3
REF
MOT Test Checks
Exhaust system
MStart the engine. With your assistant
holding a rag over the tailpipe, check the
entire system for leaks. Repair or renew
leaking sections.
Jack up the front and rear of the vehicle,
and securely support it on axle stands.
Position the stands clear of the suspension
assemblies. Ensure that the wheels are
clear of the ground and that the steering
can be turned from lock to lock.
Steering mechanism
MHave your assistant turn the steering from
lock to lock. Check that the steering turns
smoothly, and that no part of the steering
mechanism, including a wheel or tyre, fouls
any brake hose or pipe or any part of the body
structure.
MExamine the steering rack rubber gaiters
for damage or insecurity of the retaining clips.
If power steering is fitted, check for signs of
damage or leakage of the fluid hoses, pipes or
connections. Also check for excessive
stiffness or binding of the steering, a missing
split pin or locking device, or severe corrosion
of the body structure within 30 cm of any
steering component attachment point.
Front and rear suspension and
wheel bearings
MStarting at the front right-hand side, grasp
the roadwheel at the 3 o’clock and 9 o’clock
positions and shake it vigorously. Check for
free play or insecurity at the wheel bearings,
suspension balljoints, or suspension mount-
ings, pivots and attachments.
MNow grasp the wheel at the 12 o’clock and
6 o’clock positions and repeat the previous
inspection. Spin the wheel, and check for
roughness or tightness of the front wheel
bearing.
MIf excess free play is suspected at a
component pivot point, this can be confirmed
by using a large screwdriver or similar tool and
levering between the mounting and the
component attachment. This will confirm
whether the wear is in the pivot bush, its
retaining bolt, or in the mounting itself (the bolt
holes can often become elongated).
MCarry out all the above checks at the other
front wheel, and then at both rear wheels.
Springs and shock absorbers
MExamine the suspension struts (when
applicable) for serious fluid leakage, corrosion,
or damage to the casing. Also check the
security of the mounting points.
MIf coil springs are fitted, check that the
spring ends locate in their seats, and that the
spring is not corroded, cracked or broken.
MIf leaf springs are fitted, check that all
leaves are intact, that the axle is securely
attached to each spring, and that there is no
deterioration of the spring eye mountings,
bushes, and shackles.MThe same general checks apply to vehicles
fitted with other suspension types, such as
torsion bars, hydraulic displacer units, etc.
Ensure that all mountings and attachments are
secure, that there are no signs of excessive
wear, corrosion or damage, and (on hydraulic
types) that there are no fluid leaks or damaged
pipes.
MInspect the shock absorbers for signs of
serious fluid leakage. Check for wear of the
mounting bushes or attachments, or damage
to the body of the unit.
Driveshafts
(fwd vehicles only)
MRotate each front wheel in turn and inspect
the constant velocity joint gaiters for splits or
damage. Also check that each driveshaft is
straight and undamaged.
Braking system
MIf possible without dismantling, check
brake pad wear and disc condition. Ensure
that the friction lining material has not worn
excessively, (A) and that the discs are not
fractured, pitted, scored or badly worn (B).
MExamine all the rigid brake pipes
underneath the vehicle, and the flexible
hose(s) at the rear. Look for corrosion, chafing
or insecurity of the pipes, and for signs of
bulging under pressure, chafing, splits or
deterioration of the flexible hoses.
MLook for signs of fluid leaks at the brake
calipers or on the brake backplates. Repair or
renew leaking components.
MSlowly spin each wheel, while your
assistant depresses and releases the
footbrake. Ensure that each brake is operating
and does not bind when the pedal is released.
3Checks carried out
WITH THE VEHICLE RAISED
AND THE WHEELS FREE TO
TURN
Page 205 of 228

REF•4MOT Test Checks
MExamine the handbrake mechanism,
checking for frayed or broken cables,
excessive corrosion, or wear or insecurity of
the linkage. Check that the mechanism works
on each relevant wheel, and releases fully,
without binding.
MIt is not possible to test brake efficiency
without special equipment, but a road test can
be carried out later to check that the vehicle
pulls up in a straight line.
Fuel and exhaust systems
MInspect the fuel tank (including the filler
cap), fuel pipes, hoses and unions. All
components must be secure and free from
leaks.
MExamine the exhaust system over its entire
length, checking for any damaged, broken or
missing mountings, security of the retaining
clamps and rust or corrosion.
Wheels and tyres
MExamine the sidewalls and tread area of
each tyre in turn. Check for cuts, tears, lumps,
bulges, separation of the tread, and exposure
of the ply or cord due to wear or damage.
Check that the tyre bead is correctly seated
on the wheel rim, that the valve is sound andproperly seated, and that the wheel is not
distorted or damaged.
MCheck that the tyres are of the correct size
for the vehicle, that they are of the same size
and type on each axle, and that the pressures
are correct.
MCheck the tyre tread depth. The legal
minimum at the time of writing is 1.6 mm over
at least three-quarters of the tread width.
Abnormal tread wear may indicate incorrect
front wheel alignment.
Body corrosion
MCheck the condition of the entire vehicle
structure for signs of corrosion in load-bearing
areas. (These include chassis box sections,
side sills, cross-members, pillars, and all
suspension, steering, braking system and
seat belt mountings and anchorages.) Any
corrosion which has seriously reduced the
thickness of a load-bearing area is likely to
cause the vehicle to fail. In this case
professional repairs are likely to be needed.
MDamage or corrosion which causes sharp
or otherwise dangerous edges to be exposed
will also cause the vehicle to fail.
Petrol models
MHave the engine at normal operating
temperature, and make sure that it is in good
tune (ignition system in good order, air filter
element clean, etc).
MBefore any measurements are carried out,
raise the engine speed to around 2500 rpm,
and hold it at this speed for 20 seconds. Allowthe engine speed to return to idle, and watch
for smoke emissions from the exhaust
tailpipe. If the idle speed is obviously much
too high, or if dense blue or clearly-visible
black smoke comes from the tailpipe for more
than 5 seconds, the vehicle will fail. As a rule
of thumb, blue smoke signifies oil being burnt
(engine wear) while black smoke signifies
unburnt fuel (dirty air cleaner element, or other
carburettor or fuel system fault).
MAn exhaust gas analyser capable of
measuring carbon monoxide (CO) and
hydrocarbons (HC) is now needed. If such an
instrument cannot be hired or borrowed, a
local garage may agree to perform the check
for a small fee.
CO emissions (mixture)
MAt the time of writing, the maximum CO
level at idle is 3.5% for vehicles first used after
August 1986 and 4.5% for older vehicles.
From January 1996 a much tighter limit
(around 0.5%) applies to catalyst-equipped
vehicles first used from August 1992. If the
CO level cannot be reduced far enough to
pass the test (and the fuel and ignition
systems are otherwise in good condition) then
the carburettor is badly worn, or there is some
problem in the fuel injection system or
catalytic converter (as applicable).
HC emissionsMWith the CO emissions within limits, HC
emissions must be no more than 1200 ppm
(parts per million). If the vehicle fails this test
at idle, it can be re-tested at around 2000 rpm;
if the HC level is then 1200 ppm or less, this
counts as a pass.
MExcessive HC emissions can be caused by
oil being burnt, but they are more likely to be
due to unburnt fuel.
Diesel models
MThe only emission test applicable to Diesel
engines is the measuring of exhaust smoke
density. The test involves accelerating the
engine several times to its maximum
unloaded speed.
Note: It is of the utmost importance that the
engine timing belt is in good condition before
the test is carried out.
M
Excessive smoke can be caused by a dirty
air cleaner element. Otherwise, professional
advice may be needed to find the cause.
4Checks carried out on
YOUR VEHICLE’S EXHAUST
EMISSION SYSTEM
Page 209 of 228

REF•8General Repair Procedures
Whenever servicing, repair or overhaul work
is carried out on the car or its components,
observe the following procedures and
instructions. This will assist in carrying out the
operation efficiently and to a professional
standard of workmanship.
Joint mating faces and gaskets
When separating components at their
mating faces, never insert screwdrivers or
similar implements into the joint between the
faces in order to prise them apart. This can
cause severe damage which results in oil
leaks, coolant leaks, etc upon reassembly.
Separation is usually achieved by tapping
along the joint with a soft-faced hammer in
order to break the seal. However, note that
this method may not be suitable where
dowels are used for component location.
Where a gasket is used between the mating
faces of two components, a new one must be
fitted on reassembly; fit it dry unless otherwise
stated in the repair procedure. Make sure that
the mating faces are clean and dry, with all
traces of old gasket removed. When cleaning a
joint face, use a tool which is unlikely to score
or damage the face, and remove any burrs or
nicks with an oilstone or fine file.
Make sure that tapped holes are cleaned
with a pipe cleaner, and keep them free of
jointing compound, if this is being used,
unless specifically instructed otherwise.
Ensure that all orifices, channels or pipes
are clear, and blow through them, preferably
using compressed air.
Oil seals
Oil seals can be removed by levering them
out with a wide flat-bladed screwdriver or
similar implement. Alternatively, a number of
self-tapping screws may be screwed into the
seal, and these used as a purchase for pliers or
some similar device in order to pull the seal free.
Whenever an oil seal is removed from its
working location, either individually or as part
of an assembly, it should be renewed.
The very fine sealing lip of the seal is easily
damaged, and will not seal if the surface it
contacts is not completely clean and free from
scratches, nicks or grooves. If the original
sealing surface of the component cannot be
restored, and the manufacturer has not made
provision for slight relocation of the seal
relative to the sealing surface, the component
should be renewed.
Protect the lips of the seal from any surface
which may damage them in the course of
fitting. Use tape or a conical sleeve where
possible. Lubricate the seal lips with oil before
fitting and, on dual-lipped seals, fill the space
between the lips with grease.
Unless otherwise stated, oil seals must be
fitted with their sealing lips toward the
lubricant to be sealed.
Use a tubular drift or block of wood of the
appropriate size to install the seal and, if the
seal housing is shouldered, drive the seal
down to the shoulder. If the seal housing isunshouldered, the seal should be fitted with
its face flush with the housing top face (unless
otherwise instructed).
Screw threads and fastenings
Seized nuts, bolts and screws are quite a
common occurrence where corrosion has set
in, and the use of penetrating oil or releasing
fluid will often overcome this problem if the
offending item is soaked for a while before
attempting to release it. The use of an impact
driver may also provide a means of releasing
such stubborn fastening devices, when used
in conjunction with the appropriate
screwdriver bit or socket. If none of these
methods works, it may be necessary to resort
to the careful application of heat, or the use of
a hacksaw or nut splitter device.
Studs are usually removed by locking two
nuts together on the threaded part, and then
using a spanner on the lower nut to unscrew
the stud. Studs or bolts which have broken off
below the surface of the component in which
they are mounted can sometimes be removed
using a stud extractor. Always ensure that a
blind tapped hole is completely free from oil,
grease, water or other fluid before installing
the bolt or stud. Failure to do this could cause
the housing to crack due to the hydraulic
action of the bolt or stud as it is screwed in.
When tightening a castellated nut to accept
a split pin, tighten the nut to the specified
torque, where applicable, and then tighten
further to the next split pin hole. Never slacken
the nut to align the split pin hole, unless stated
in the repair procedure.
When checking or retightening a nut or bolt
to a specified torque setting, slacken the nut
or bolt by a quarter of a turn, and then
retighten to the specified setting. However,
this should not be attempted where angular
tightening has been used.
For some screw fastenings, notably
cylinder head bolts or nuts, torque wrench
settings are no longer specified for the latter
stages of tightening, “angle-tightening” being
called up instead. Typically, a fairly low torque
wrench setting will be applied to the
bolts/nuts in the correct sequence, followed
by one or more stages of tightening through
specified angles.
Locknuts, locktabs and washers
Any fastening which will rotate against a
component or housing during tightening
should always have a washer between it and
the relevant component or housing.
Spring or split washers should always be
renewed when they are used to lock a critical
component such as a big-end bearing
retaining bolt or nut. Locktabs which are
folded over to retain a nut or bolt should
always be renewed.
Self-locking nuts can be re-used in non-
critical areas, providing resistance can be felt
when the locking portion passes over the bolt
or stud thread. However, it should be noted
that self-locking stiffnuts tend to lose theireffectiveness after long periods of use, and
should then be renewed as a matter of course.
Split pins must always be replaced with
new ones of the correct size for the hole.
When thread-locking compound is found
on the threads of a fastener which is to be re-
used, it should be cleaned off with a wire
brush and solvent, and fresh compound
applied on reassembly.
Special tools
Some repair procedures in this manual
entail the use of special tools such as a press,
two or three-legged pullers, spring com-
pressors, etc. Wherever possible, suitable
readily-available alternatives to the manu-
facturer’s special tools are described, and are
shown in use. In some instances, where no
alternative is possible, it has been necessary
to resort to the use of a manufacturer’s tool,
and this has been done for reasons of safety
as well as the efficient completion of the repair
operation. Unless you are highly-skilled and
have a thorough understanding of the
procedures described, never attempt to
bypass the use of any special tool when the
procedure described specifies its use. Not
only is there a very great risk of personal
injury, but expensive damage could be
caused to the components involved.
Environmental considerations
When disposing of used engine oil, brake
fluid, antifreeze, etc, give due consideration to
any detrimental environmental effects. Do not,
for instance, pour any of the above liquids
down drains into the general sewage system,
or onto the ground to soak away. Many local
council refuse tips provide a facility for waste
oil disposal, as do some garages. If none of
these facilities are available, consult your local
Environmental Health Department, or the
National Rivers Authority, for further advice.
With the universal tightening-up of legis-
lation regarding the emission of environmen-
tally-harmful substances from motor vehicles,
most vehicles have tamperproof devices fitted
to the main adjustment points of the fuel
system. These devices are primarily designed
to prevent unqualified persons from adjusting
the fuel/air mixture, with the chance of a
consequent increase in toxic emissions. If
such devices are found during servicing or
overhaul, they should, wherever possible, be
renewed or refitted in accordance with the
manufacturer’s requirements or current
legislation.
Note: It is
antisocial and
illegal to dump
oil down the
drain. To find
the location of
your local oil
recycling
bank, call this
number free.
Page 211 of 228

REF•10Fault Finding
Engine will not rotate when attempting to start
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mBattery discharged or faulty (Chapter 1).
m mAutomatic transmission not completely engaged in Park (Chap-
ter 7B) or (on models with a clutch switch) clutch not completely
depressed (Chapter 8).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapters 5 and 12).
m mStarter motor pinion jammed in flywheel ring gear (Chapter 5).
m mStarter solenoid faulty (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor faulty (Chapter 5).
m mIgnition switch faulty (Chapter 12).
m mStarter pinion or flywheel teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mEngine internal problem (Chapter 2B).
Engine rotates, but will not start
m
mFuel tank empty.
m mBattery discharged (engine rotates slowly) (Chapter 5).
m mBattery terminal connections loose or corroded (Chapter 1).
m mLeaking fuel injector(s), faulty fuel pump, pressure regulator, etc
(Chapter 4).
m mFuel not reaching fuel injection system or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mIgnition components damp or damaged (Chapter 5).
m mFuel injector stuck open (Chapter 4).
m mWorn, faulty or incorrectly-gapped spark plugs (Chapter 1).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wiring in the starting circuit
(Chapter 5).
m mLoose distributor mounting bolts causing ignition timing to wander
(Chapters 1 and 5).
m mBroken, loose or disconnected wires at the ignition coil, or faulty
coil (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when cold
m mBattery discharged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel system malfunctioning (Chapter 4).
m mInjector(s) leaking or carburettor automatic choke faulty (Chap-
ter 4).
m mDistributor rotor carbon-tracked (Chapter 5).
Engine hard to start when hot
m
mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel not reaching the fuel injection system or carburettor (Chap-
ter 4).
m mCorroded battery connections, especially earth (negative)
connection (Chapter 1).
Starter motor noisy or excessively-rough in
engagement
m mPinion or flywheel gear teeth worn or broken (Chapter 5).
m mStarter motor mounting bolts loose or missing (Chapter 5).
Engine starts, but stops immediately
m
mLoose or faulty electrical connections at distributor, coil or
alternator (Chapter 5).
m mInsufficient fuel reaching the fuel injector(s) or carburettor
(Chapters 1 and 4).
m mDamaged fuel injection system speed sensors (Chapter 5).
m mFaulty fuel injection relays (Chapter 5).
Oil puddle under engine
m
mOil sump gasket and/or sump drain plug seal leaking (Chapter 2).
m mOil pressure sender unit leaking (Chapter 2).
m mValve cover gaskets leaking (Chapter 2).
m mEngine oil seals leaking (Chapter 2).
Engine idles erratically
m
mVacuum leakage (Chapter 4).
m mAir filter element clogged (Chapter 1).
m mFuel pump not delivering sufficient fuel to the fuel injection system
or carburettor (Chapter 4).
m mLeaking head gasket (Chapter 2).
m mTiming belt/chain and/or sprockets worn (Chapter 2).
m mCamshaft lobes worn (Chapter 2).
m mFaulty charcoal canister, where fitted (Chapter 6). This Section provides an easy-reference guide to the more
common problems which may occur during the operation of your
vehicle. These problems and their possible causes are grouped under
headings denoting various components or systems, such as Engine,
Cooling system, etc. They also refer you to the Chapter and/or
Section which deals with the problem.
Remember that successful fault diagnosis is not a mysterious
black art practised only by professional mechanics. It is simply the
result of the right knowledge combined with an intelligent, systematic
approach to the problem. Always work by a process of elimination,
starting with the simplest solution and working through to the mostcomplex - and never overlook the obvious. Anyone can run the fuel
tank dry or leave the lights on overnight, so don’t assume that you are
exempt from such oversights.
Finally, always establish a clear idea of why a problem has
occurred, and take steps to ensure that it doesn’t happen again. If the
electrical system fails because of a poor connection, check all other
connections in the system to make sure that they don’t fail as well. If a
particular fuse continues to blow, find out why - don’t just renew one
fuse after another. Remember, failure of a small component can often
be indicative of potential failure or incorrect functioning of a more
important component or system.
Engine