air flow sensor BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1985, Model line: 3 SERIES, Model: BMW 3 SERIES 1985 E30Pages: 228, PDF Size: 7.04 MB
Page 40 of 228
12After the No 1 piston has been positioned
at TDC on the compression stroke, TDC for
any of the remaining pistons can be located
by turning the crankshaft and following the
firing order. Mark the remaining spark plug
lead terminal locations just like you did for the
No 1 terminal, then number the marks to
correspond with the cylinder numbers. As you
turn the crankshaft, the rotor will also turn.
When it’s pointing directly at one of the marks
on the distributor, the piston for that particular
cylinder is at TDC on the compression stroke.
4 Valve cover-
removal and refitting
1
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2Detach the breather hose from the valve
cover.
3On M20 engines, unbolt and remove the
intake manifold support bracket and, if
applicable, the bracket for the engine sensors
or idle air stabiliser (it will probably be
necessary to disconnect the electrical
connectors from the sensors and stabiliser).
4On M30 engines, disconnect the electrical
connector for the airflow sensor. Unclip the
electrical harness, moving it out of the way.
5Where necessary on M30 engines, remove
the hoses and fittings from the intake air hose,
then loosen the clamp and separate the hose
from the throttle body. Unscrew the mounting
nuts for the air cleaner housing, and remove
the housing together with the air hose and
airflow sensor.
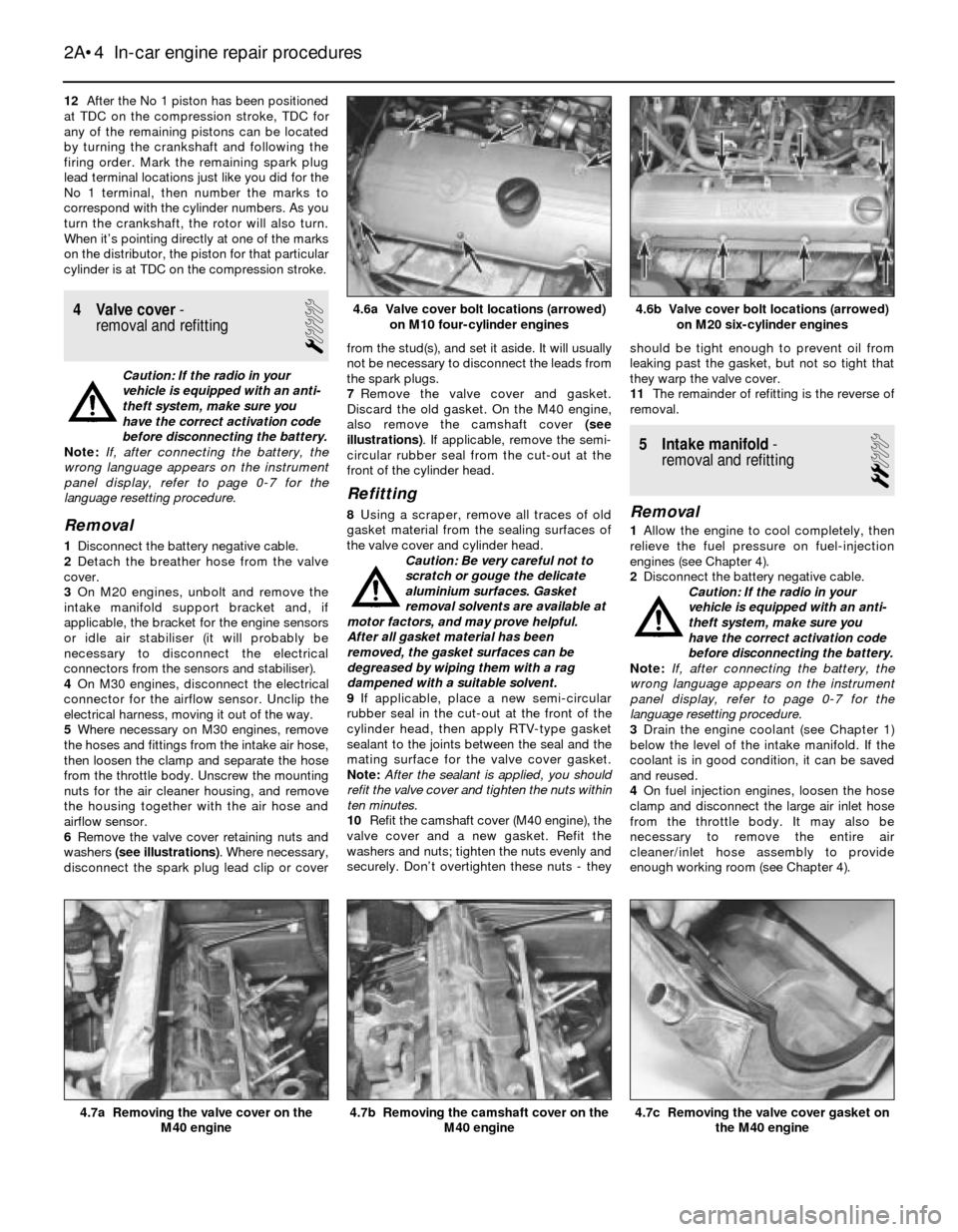
6Remove the valve cover retaining nuts and
washers (see illustrations). Where necessary,
disconnect the spark plug lead clip or coverfrom the stud(s), and set it aside. It will usually
not be necessary to disconnect the leads from
the spark plugs.
7Remove the valve cover and gasket.
Discard the old gasket. On the M40 engine,
also remove the camshaft cover (see
illustrations). If applicable, remove the semi-
circular rubber seal from the cut-out at the
front of the cylinder head.
Refitting
8Using a scraper, remove all traces of old
gasket material from the sealing surfaces of
the valve cover and cylinder head.
Caution: Be very careful not to
scratch or gouge the delicate
aluminium surfaces. Gasket
removal solvents are available at
motor factors, and may prove helpful.
After all gasket material has been
removed, the gasket surfaces can be
degreased by wiping them with a rag
dampened with a suitable solvent.
9If applicable, place a new semi-circular
rubber seal in the cut-out at the front of the
cylinder head, then apply RTV-type gasket
sealant to the joints between the seal and the
mating surface for the valve cover gasket.
Note:After the sealant is applied, you should
refit the valve cover and tighten the nuts within
ten minutes.
10Refit the camshaft cover (M40 engine), the
valve cover and a new gasket. Refit the
washers and nuts; tighten the nuts evenly and
securely. Don’t overtighten these nuts - theyshould be tight enough to prevent oil from
leaking past the gasket, but not so tight that
they warp the valve cover.
11The remainder of refitting is the reverse of
removal.
5 Intake manifold-
removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Allow the engine to cool completely, then
relieve the fuel pressure on fuel-injection
engines (see Chapter 4).
2Disconnect the battery negative cable.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3Drain the engine coolant (see Chapter 1)
below the level of the intake manifold. If the
coolant is in good condition, it can be saved
and reused.
4On fuel injection engines, loosen the hose
clamp and disconnect the large air inlet hose
from the throttle body. It may also be
necessary to remove the entire air
cleaner/inlet hose assembly to provide
enough working room (see Chapter 4).
2A•4 In-car engine repair procedures
4.7b Removing the camshaft cover on the
M40 engine4.7a Removing the valve cover on the
M40 engine4.7c Removing the valve cover gasket on
the M40 engine
4.6b Valve cover bolt locations (arrowed)
on M20 six-cylinder engines4.6a Valve cover bolt locations (arrowed)
on M10 four-cylinder engines
Page 42 of 228
6 Exhaust manifold-
removal and refitting
1
Warning: Make sure the engine is
completely cool before beginning
work on the exhaust system.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2On models where the air cleaner is on the
exhaust manifold side of the engine, remove
the air cleaner housing assembly and/or
airflow sensor to provide sufficient working
area (see Chapter 4, if necessary).
3Unplug the HT leads and set the spark plug
lead harness aside (see Chapter 1).
4Clearly label, then disconnect or remove, all
wires, hoses, fittings, etc. that are in the way.
Be sure to disconnect the oxygen sensor,
where fitted.
5Raise the vehicle, and support it securely
on axle stands. Working from under the
vehicle, separate the exhaust downpipe from
the manifold. Use penetrating oil on the
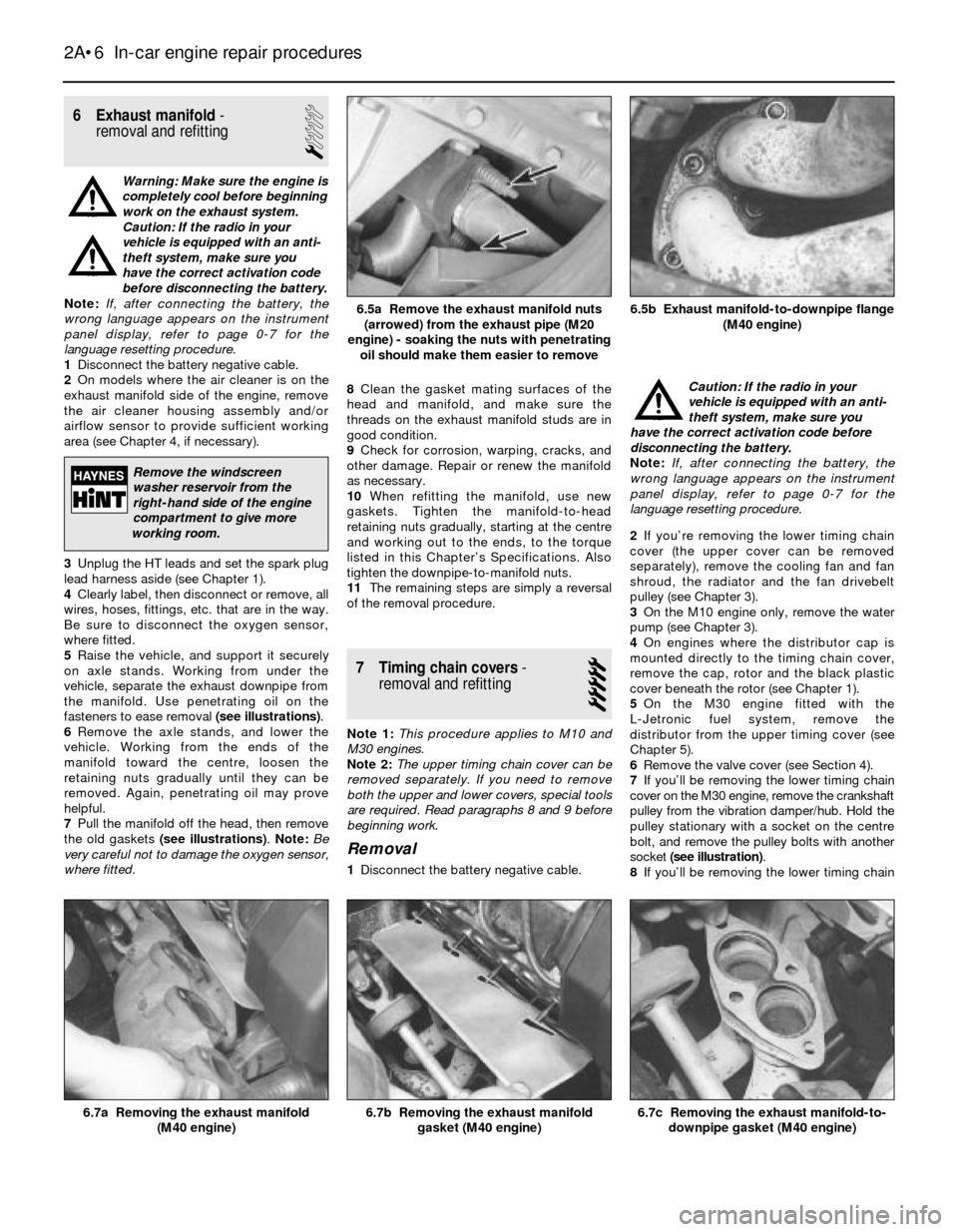
fasteners to ease removal (see illustrations).
6Remove the axle stands, and lower the
vehicle. Working from the ends of the
manifold toward the centre, loosen the
retaining nuts gradually until they can be
removed. Again, penetrating oil may prove
helpful.
7Pull the manifold off the head, then remove
the old gaskets (see illustrations). Note:Be
very careful not to damage the oxygen sensor,
where fitted.8Clean the gasket mating surfaces of the
head and manifold, and make sure the
threads on the exhaust manifold studs are in
good condition.
9Check for corrosion, warping, cracks, and
other damage. Repair or renew the manifold
as necessary.
10When refitting the manifold, use new
gaskets. Tighten the manifold-to-head
retaining nuts gradually, starting at the centre
and working out to the ends, to the torque
listed in this Chapter’s Specifications. Also
tighten the downpipe-to-manifold nuts.
11The remaining steps are simply a reversal
of the removal procedure.
7 Timing chain covers-
removal and refitting
5
Note 1:This procedure applies to M10 and
M30 engines.
Note 2:The upper timing chain cover can be
removed separately. If you need to remove
both the upper and lower covers, special tools
are required. Read paragraphs 8 and 9 before
beginning work.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative cable.Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code before
disconnecting the battery.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
2If you’re removing the lower timing chain
cover (the upper cover can be removed
separately), remove the cooling fan and fan
shroud, the radiator and the fan drivebelt
pulley (see Chapter 3).
3On the M10 engine only, remove the water
pump (see Chapter 3).
4On engines where the distributor cap is
mounted directly to the timing chain cover,
remove the cap, rotor and the black plastic
cover beneath the rotor (see Chapter 1).
5On the M30 engine fitted with the
L-Jetronic fuel system, remove the
distributor from the upper timing cover (see
Chapter 5).
6Remove the valve cover (see Section 4).
7If you’ll be removing the lower timing chain
cover on the M30 engine, remove the crankshaft
pulley from the vibration damper/hub. Hold the
pulley stationary with a socket on the centre
bolt, and remove the pulley bolts with another
socket (see illustration).
8If you’ll be removing the lower timing chain
2A•6 In-car engine repair procedures
6.7c Removing the exhaust manifold-to-
downpipe gasket (M40 engine)6.7b Removing the exhaust manifold
gasket (M40 engine)6.7a Removing the exhaust manifold
(M40 engine)
6.5b Exhaust manifold-to-downpipe flange
(M40 engine)6.5a Remove the exhaust manifold nuts
(arrowed) from the exhaust pipe (M20
engine) - soaking the nuts with penetrating
oil should make them easier to remove
Remove the windscreen
washer reservoir from the
right-hand side of the engine
compartment to give more
working room.
Page 91 of 228

information on removing and refitting the
intake manifold, refer to Chapter 2A.
The throttle valve inside the throttle body or
carburettor is actuated by the accelerator
cable. When you depress the accelerator
pedal, the throttle plate opens and airflow
through the intake system increases.
On fuel injection systems, a flap inside the
airflow meter opens wider as the airflow
increases. A throttle position switch attached
to the pivot shaft of the flap detects the angle
of the flap (how much it’s open) and converts
this to a voltage signal, which it sends to the
computer.
Fuel system
On carburettor models, the fuel pump
supplies fuel under pressure to the
carburettor. A needle valve in the float
chamber maintains the fuel at a constant
level. A fuel return system channels excess
fuel back to the fuel tank.
On fuel injection models, an electric fuel
pump supplies fuel under constant pressure
to the fuel rail, which distributes fuel to the
injectors. The electric fuel pump is located
inside the fuel tank on later models, or beside
the fuel tank on early models. Early models
also have a transfer pump located in the fuel
tank. The transfer pump acts as an aid to the
larger main pump for delivering the necessary
pressure. A fuel pressure regulator controls
the pressure in the fuel system. The fuel
system also has a fuel pulsation damper
located near the fuel filter. The damper
reduces the pressure pulsations caused by
fuel pump operation, and the opening and
closing of the injectors. The amount of fuel
injected into the intake ports is precisely
controlled by an Electronic Control Unit (ECU
or computer). Some later 5-Series models
have a fuel cooler in the return line.
Electronic control system (fuel
injection system)
Besides altering the injector opening
duration as described above, the electronic
control unit performs a number of other tasks
related to fuel and emissions control. It
accomplishes these tasks by using data
relayed to it by a wide array of information
sensors located throughout the enginecompartment, comparing this information to
its stored map, and altering engine operation
by controlling a number of different actuators.
Since special equipment is required, most
fault diagnosis and repair of the electronic
control system is beyond the scope of the
home mechanic. Additional information and
testing procedures for the emissions system
components (oxygen sensor, coolant
temperature sensor, EVAP system, etc.) is
contained in Chapter 6.
2 Fuel injection system-
depressurising
1
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
1Remove the fuel pump fuse from the main
fuse panel (see illustrations). Note:Consult
your owner’s handbook for the exact location
of the fuel pump fuse, if the information is not
stamped onto the fusebox cover.
2Start the engine, and wait for it to stall.
Switch off the ignition.
3Remove the fuel filler cap to relieve the fuel
tank pressure.
4The fuel system is now depressurised.
Note:Place a rag around fuel lines before
disconnecting, to prevent any residual fuel
from spilling onto the engine(see
illustration).
5Disconnect the battery negative cable
before working on any part of the system.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
3 Fuel pump/fuel pressure-
check
3
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Also, don’t work
in a garage where a natural gas-type
appliance with a pilot light is present.
Carburettor engines
1To test the fuel pump, it will be necessary to
connect a suitable pressure gauge between
the fuel pump outlet, and the carburettor
supply pipe. For this particular test, the fuel
return valve, which is normally connected in
the fuel line from the fuel pump to the
carburettor, mustbe bypassed.
2With the engine running at idle speed, the
pump pressure should be between 0.1 and
0.3 bars.
3Should a pressure gauge not be available, a
simpler (but less accurate) method of testing
the fuel pump is as follows.
4Disconnect the outlet hose from the fuel
pump.
5Disconnect the LT lead from the coil, to
prevent the engine firing, then turn the engine
over on the starter. Well-defined spurts of fuel
should be ejected from the outlet hose.
Fuel injection engines
Note 1:The electric fuel pump is located
inside the fuel tank on later models, or beside
the fuel tank on early models. Early models are
also equipped with a transfer pump located in
the fuel tank. The transfer pump feeds the
main pump, but can’t generate the high
pressure required by the system.
Note 2:The fuel pump relay on Motronic
systems is activated by an earth signal from
the Motronic control unit (ECU). The fuel
pump operates for a few seconds when the
ignition is first switched on, and then
continues to operate only when the engine is
actually running.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•3
2.4 Be sure to place a rag under and
around any fuel line when disconnecting2.1b Removing the fuel pump fuse on
5-Series models2.1a Removing the fuel pump fuse on
3-Series models
4
Page 102 of 228

Throttle positioner (2BE)
24Special tools are required to carry out a
comprehensive adjustment on the 2BE
carburettor. This work should therefore be left
to a BMW dealer.
13 Fuel injection -
general information
The fuel injection system is composed of
three basic sub-systems: fuel system, air
intake system and electronic control system.
Fuel system
An electric fuel pump, located inside the
fuel tank or beside the fuel tank, supplies fuel
under constant pressure to the fuel rail, which
distributes fuel evenly to all injectors. From
the fuel rail, fuel is injected into the intake
ports, just above the intake valves, by the fuel
injectors. The amount of fuel supplied by the
injectors is precisely controlled by an
Electronic Control Unit (ECU). An additional
injector, known as the cold start injector (L-
Jetronic and early Motronic systems only),
supplies extra fuel into the intake manifold for
starting. A pressure regulator controls system
pressure in relation to intake manifold
vacuum. A fuel filter between the fuel pump
and the fuel rail filters the fuel, to protect the
components of the system.
Air intake system
The air intake system consists of an air filter
housing, an airflow meter, a throttle body, the
intake manifold, and the associated ducting.
The airflow meter is an information-gathering
device for the ECU. These models are
equipped with the vane-type airflow meter. A
potentiometer measures intake airflow, and a
temperature sensor measures intake air
temperature. This information helps the ECU
determine the amount of fuel to be injected by
the injectors (injection duration). The throttle
plate inside the throttle body is controlled by
the driver. As the throttle plate opens, the
amount of air that can pass through the
system increases, so the potentiometer opens
further and the ECU signals the injectors to
increase the amount of fuel delivered to the
intake ports.
Electronic control system
The computer control system controls the
fuel system and other systems by means of
an Electronic Control Unit (ECU). The ECU
receives signals from a number of information
sensors which monitor such variables as
intake air volume, intake air temperature,
coolant temperature, engine rpm,
acceleration/deceleration, and exhaust
oxygen content. These signals help the ECU
determine the injection duration necessary for
the optimum air/fuel ratio. These sensors and
their corresponding ECU-controlled outputactuators are located throughout the engine
compartment. For further information
regarding the ECU and its relationship to the
engine electrical systems and ignition system,
refer to Chapters 5 and 6.
Either an L-Jetronic system or a Motronic
system is fitted. Later models have an
updated version of the original Motronic
system.
14 Fuel injection systems
L-Jetronic fuel injection system
The Bosch L-Jetronic fuel injection system
is used on most 3-Series models up to 1987,
and on most E28 (“old-shape”) 5-Series
models. It is an electronically-controlled fuel
injection system that utilises one solenoid-
operated fuel injector per cylinder. The system
is governed by an Electronic Control Unit
(ECU) which processes information sent by
various sensors, and in turn precisely
meters the fuel to the cylinders by
adjusting the amount of time that the injectors
are open.
An electric fuel pump delivers fuel under
high pressure to the injectors, through the fuel
feed line and an in-line filter. A pressure
regulator keeps fuel available at an optimum
pressure, allowing pressure to rise or fall
depending on engine speed and load. Any
excess fuel is returned to the fuel tank by a
separate line.
A sensor in the air intake duct constantly
measures the mass of the incoming air, and
the ECU adjusts the fuel mixture to provide an
optimum air/fuel ratio.
Other components incorporated in the
system are the throttle valve (which controls
airflow to the engine), the coolant temperature
sensor, the throttle position switch, idle
stabiliser valve (which bypasses air around
the throttle plate to control idle speed) and
associated relays and fuses.
Motronic fuel injection system
The Motronic system combines the fuel
control of the L-Jetronic fuel injection system
with the control of ignition timing, idle speed
and emissions into one control unit.
The fuel injection and idle speed control
functions are similar to those used on the L-
Jetronic system described above. For more
information on the Motronic system, see
Chapter 6.
An oxygen sensor is mounted in the
exhaust system on later models with a
catalytic converter. This sensor continually
reads the oxygen content of the exhaust gas.
The information is used by the ECU to adjust
the duration of injection, making it possible to
adjust the fuel mixture for optimum converter
efficiency and minimum emissions.
15 Fuel injection system-
check
2
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
1Check the earth wire connections. Check
all wiring harness connectors that are related
to the system. Loose connectors and poor
earths can cause many problems that
resemble more serious malfunctions.
2Make sure the battery is fully charged, as
the control unit and sensors depend on an
accurate supply voltage in order to properly
meter the fuel.
3Check the air filter element - a dirty or
partially-blocked filter will severely impede
performance and economy (see Chapter 1).
4If a blown fuse is found, renew it and see if
it blows again. If it does, search for an earthed
wire in the harness related to the system.
5Check the air intake duct from the airflow
meter to the intake manifold for leaks. Intake
air leaks can cause a variety of problems. Also
check the condition of the vacuum hoses
connected to the intake manifold.
6Remove the air intake duct from the throttle
body, and check for dirt, carbon and other
residue build-up. If it’s dirty, clean it with
carburettor cleaner and a toothbrush.
7With the engine running, place a
screwdriver or a stethoscope against each
injector, one at a time, and listen for a clicking
sound, indicating operation (see illustration).
4•14 Fuel and exhaust systems
15.7 Use a stethoscope or screwdriver to
determine if the injectors are working
properly - they should make a steady
clicking sound that rises and falls with
engine speed changes
Page 103 of 228
8Check the fuel system pressure (see
Section 3).
9If these checks do not locate the problem,
take the vehicle to a BMW dealer, who will be
able to read the fault codes stored in the ECU,
using special equipment.
16 Airflow meter- check,
removal and refitting
2
Check (L-Jetronic systems)
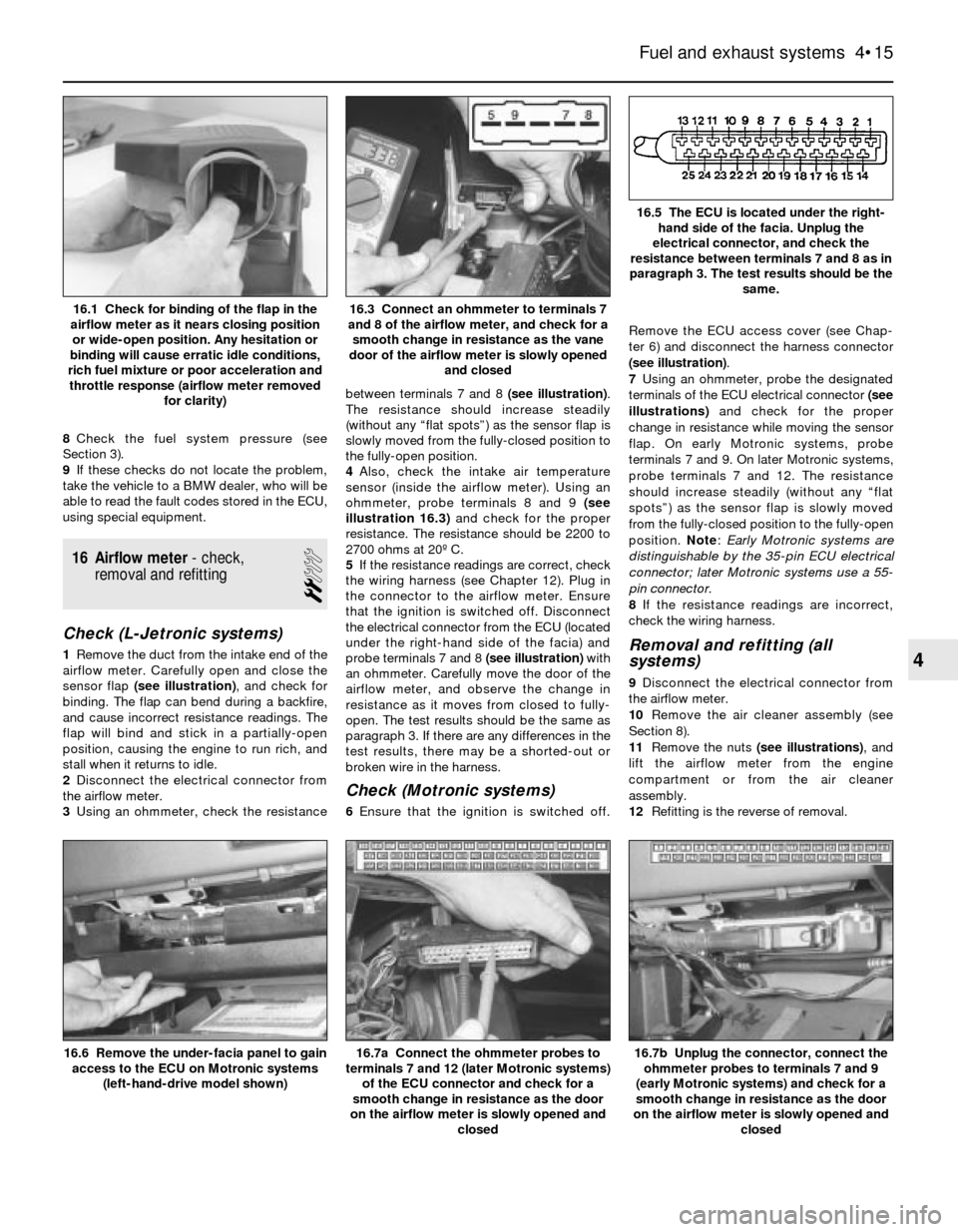
1Remove the duct from the intake end of the
airflow meter. Carefully open and close the
sensor flap (see illustration), and check for
binding. The flap can bend during a backfire,
and cause incorrect resistance readings. The
flap will bind and stick in a partially-open
position, causing the engine to run rich, and
stall when it returns to idle.
2Disconnect the electrical connector from
the airflow meter.
3Using an ohmmeter, check the resistancebetween terminals 7 and 8 (see illustration).
The resistance should increase steadily
(without any “flat spots”) as the sensor flap is
slowly moved from the fully-closed position to
the fully-open position.
4Also, check the intake air temperature
sensor (inside the airflow meter). Using an
ohmmeter, probe terminals 8 and 9 (see
illustration 16.3)and check for the proper
resistance. The resistance should be 2200 to
2700 ohms at 20º C.
5If the resistance readings are correct, check
the wiring harness (see Chapter 12). Plug in
the connector to the airflow meter. Ensure
that the ignition is switched off. Disconnect
the electrical connector from the ECU (located
under the right-hand side of the facia) and
probe terminals 7 and 8 (see illustration)with
an ohmmeter. Carefully move the door of the
airflow meter, and observe the change in
resistance as it moves from closed to fully-
open. The test results should be the same as
paragraph 3. If there are any differences in the
test results, there may be a shorted-out or
broken wire in the harness.
Check (Motronic systems)
6Ensure that the ignition is switched off.Remove the ECU access cover (see Chap-
ter 6) and disconnect the harness connector
(see illustration).
7Using an ohmmeter, probe the designated
terminals of the ECU electrical connector (see
illustrations)and check for the proper
change in resistance while moving the sensor
flap. On early Motronic systems, probe
terminals 7 and 9. On later Motronic systems,
probe terminals 7 and 12. The resistance
should increase steadily (without any “flat
spots”) as the sensor flap is slowly moved
from the fully-closed position to the fully-open
position. Note: Early Motronic systems are
distinguishable by the 35-pin ECU electrical
connector; later Motronic systems use a 55-
pin connector.
8If the resistance readings are incorrect,
check the wiring harness.
Removal and refitting (all
systems)
9Disconnect the electrical connector from
the airflow meter.
10Remove the air cleaner assembly (see
Section 8).
11Remove the nuts (see illustrations), and
lift the airflow meter from the engine
compartment or from the air cleaner
assembly.
12Refitting is the reverse of removal.
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•15
16.5 The ECU is located under the right-
hand side of the facia. Unplug the
electrical connector, and check the
resistance between terminals 7 and 8 as in
paragraph 3. The test results should be the
same.
16.3 Connect an ohmmeter to terminals 7
and 8 of the airflow meter, and check for a
smooth change in resistance as the vane
door of the airflow meter is slowly opened
and closed16.1 Check for binding of the flap in the
airflow meter as it nears closing position
or wide-open position. Any hesitation or
binding will cause erratic idle conditions,
rich fuel mixture or poor acceleration and
throttle response (airflow meter removed
for clarity)
16.7b Unplug the connector, connect the
ohmmeter probes to terminals 7 and 9
(early Motronic systems) and check for a
smooth change in resistance as the door
on the airflow meter is slowly opened and
closed16.7a Connect the ohmmeter probes to
terminals 7 and 12 (later Motronic systems)
of the ECU connector and check for a
smooth change in resistance as the door
on the airflow meter is slowly opened and
closed16.6 Remove the under-facia panel to gain
access to the ECU on Motronic systems
(left-hand-drive model shown)
4
Page 104 of 228
17 Throttle body- check,
removal and refitting
2
Check
1Detach the air intake duct from the throttle
body (see Section 8) and move the duct out of
the way.
2Have an assistant depress the throttle
pedal while you watch the throttle valve.
Check that the throttle valve moves smoothly
when the throttle is moved from closed (idle
position) to fully-open (wide-open throttle).
3If the throttle valve is not working properly,
renew the throttle body unit.
Warning: Wait until the engine is
completely cool before beginning
this procedure.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Removal and refitting
4Detach the battery negative cable.
5Detach the air intake duct from the throttle
body, and place to one side.
6Detach the accelerator cable from the
throttle body (see Section 9).
7Detach the cruise control cable, if applicable.
8Clearly label all electrical connectors
(throttle position sensor, cold start injector,
idle air stabiliser, etc), then unplug them.
9Clearly label all vacuum hoses, then detach
them.
10Unscrew the radiator or expansion tank
cap to relieve any residual pressure in the
cooling system, then refit it. Clamp shut the
coolant hoses, then loosen the hose clamps
and detach the hoses. Be prepared for some
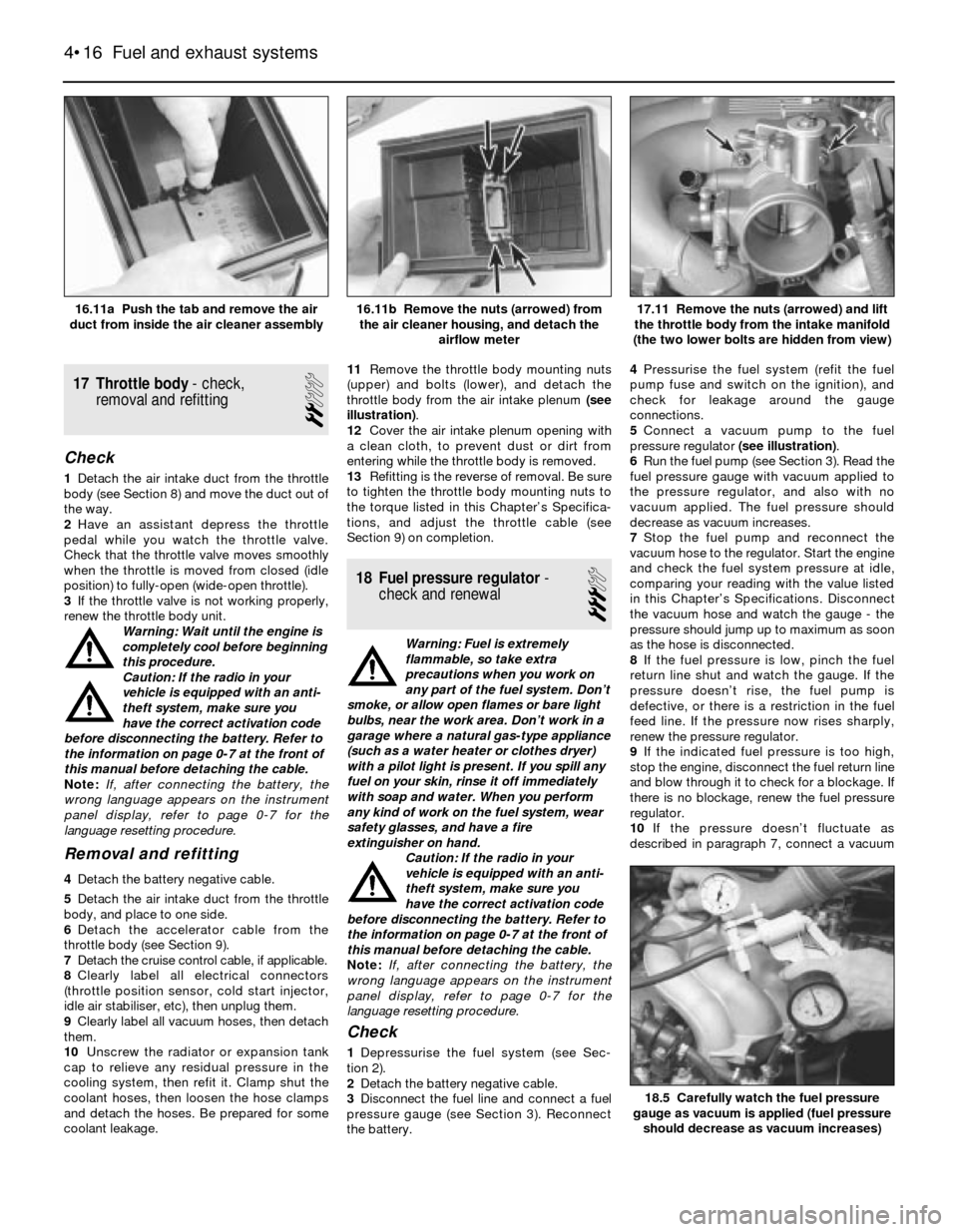
coolant leakage.11Remove the throttle body mounting nuts
(upper) and bolts (lower), and detach the
throttle body from the air intake plenum (see
illustration).
12Cover the air intake plenum opening with
a clean cloth, to prevent dust or dirt from
entering while the throttle body is removed.
13Refitting is the reverse of removal. Be sure
to tighten the throttle body mounting nuts to
the torque listed in this Chapter’s Specifica-
tions, and adjust the throttle cable (see
Section 9) on completion.
18 Fuel pressure regulator-
check and renewal
3
Warning: Fuel is extremely
flammable, so take extra
precautions when you work on
any part of the fuel system. Don’t
smoke, or allow open flames or bare light
bulbs, near the work area. Don’t work in a
garage where a natural gas-type appliance
(such as a water heater or clothes dryer)
with a pilot light is present. If you spill any
fuel on your skin, rinse it off immediately
with soap and water. When you perform
any kind of work on the fuel system, wear
safety glasses, and have a fire
extinguisher on hand.
Caution: If the radio in your
vehicle is equipped with an anti-
theft system, make sure you
have the correct activation code
before disconnecting the battery. Refer to
the information on page 0-7 at the front of
this manual before detaching the cable.
Note: If, after connecting the battery, the
wrong language appears on the instrument
panel display, refer to page 0-7 for the
language resetting procedure.
Check
1Depressurise the fuel system (see Sec-
tion 2).
2Detach the battery negative cable.
3Disconnect the fuel line and connect a fuel
pressure gauge (see Section 3). Reconnect
the battery.4Pressurise the fuel system (refit the fuel
pump fuse and switch on the ignition), and
check for leakage around the gauge
connections.
5Connect a vacuum pump to the fuel
pressure regulator (see illustration).
6Run the fuel pump (see Section 3). Read the
fuel pressure gauge with vacuum applied to
the pressure regulator, and also with no
vacuum applied. The fuel pressure should
decrease as vacuum increases.
7Stop the fuel pump and reconnect the
vacuum hose to the regulator. Start the engine
and check the fuel system pressure at idle,
comparing your reading with the value listed
in this Chapter’s Specifications. Disconnect
the vacuum hose and watch the gauge - the
pressure should jump up to maximum as soon
as the hose is disconnected.
8If the fuel pressure is low, pinch the fuel
return line shut and watch the gauge. If the
pressure doesn’t rise, the fuel pump is
defective, or there is a restriction in the fuel
feed line. If the pressure now rises sharply,
renew the pressure regulator.
9If the indicated fuel pressure is too high,
stop the engine, disconnect the fuel return line
and blow through it to check for a blockage. If
there is no blockage, renew the fuel pressure
regulator.
10If the pressure doesn’t fluctuate as
described in paragraph 7, connect a vacuum
4•16 Fuel and exhaust systems
18.5 Carefully watch the fuel pressure
gauge as vacuum is applied (fuel pressure
should decrease as vacuum increases)
17.11 Remove the nuts (arrowed) and lift
the throttle body from the intake manifold
(the two lower bolts are hidden from view)16.11b Remove the nuts (arrowed) from
the air cleaner housing, and detach the
airflow meter16.11a Push the tab and remove the air
duct from inside the air cleaner assembly
Page 109 of 228

Fuel injection system - fault finding
L-Jetronic fuel injection system
Engine difficult to start, or fails to start (when cold)
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector or thermotime switch faulty Test cold start injector and thermotime switch. Renew faulty components (see Section 19)
Fuel pump inoperative Check fuel pump fuse and fuel pump relay (see Sections 3 and 4)
Airflow meter flap (door) binding or stuck
in open position Inspect the airflow meter for damage (see Section 16)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test system pressure (see Section 3). Test fuel pressure regulator (Section 18)
Intake air leaks Inspect all vacuum lines, air ducts, and oil filler and dipstick seals
Fuel injectors clogged or not operating Check fuel injectors (see Section 20) and wiring harness
Coolant temperature sensor faulty or
wiring problem Test coolant temperature sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Throttle position sensor (TPS) incorrectly adjusted Check TPS adjustment (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Incorrect ignition timing Check ignition timing (see Chapter 5). Check vacuum advance system
Dirt or other contaminants in fuel Check the fuel and drain the tank if necessary
Faulty ECU Have the ECU tested at a dealer service department or other specialist
Engine difficult to start, or fails to start (when warm)
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector leaking or operating continuously Test cold start injector and thermotime switch (see Section 19)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test fuel pump(s). Renew if necessary (see Section 3)
Insufficient residual fuel pressure Test residual fuel pressure. Renew fuel pump or fuel accumulator as necessary
(see Section 18)
Fuel leak(s) Inspect fuel lines and fuel injectors for leaks. Correct leaks as required (see Chapter 4)
Coolant temperature sensor faulty or
wiring problem Test coolant temperature sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Vapour lock (warm weather) Check fuel pressure (see Section 3)
EVAP system faulty (where applicable) Check EVAP system (see Chapter 6, Section 6)
Incorrect ignition timing Check ignition timing (see Chapter 5). Check vacuum advance system
Faulty ECU Have the ECU tested at a dealer service department or other specialist
Idle speed control system faulty Test the idle air stabiliser valve (see Section 21)
Engine misses and hesitates under load
Probable cause Corrective action
Fuel injector clogged or faulty Test fuel injectors. Check for clogged injector lines. Renew faulty injectors (see Section 20)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test fuel system pressure (see Section 3). Test fuel pressure regulator (see Section 18)
Fuel leak(s) Inspect fuel lines and fuel injectors for leaks (see Chapter 4)
Engine maintenance Tune-up engine (see Chapter 1). Check the distributor cap, rotor, HT leads and spark
plugs, and renew any faulty components
Airflow meter flap (door) binding, or
stuck in open position Inspect the airflow meter for damage (see Section 16)
Intake air leaks Inspect all vacuum lines, air ducts and oil filler and dipstick seals
Engine has erratic idle speed
Probable cause Corrective action
Idle air stabiliser valve faulty Check the idle air stabiliser valve (see Section 21)
No power to the idle air stabiliser valve Check the idle air stabiliser relay and wiring circuit (see Chapter 12)
Vacuum advance system faulty Check vacuum advance system and electronic vacuum advance relay
Idle speed control unit faulty Have the idle speed control unit checked by a dealer
Motronic fuel injection system
Note:With this system, when faults occur, the ECU stores a fault code in its memory. These codes can only be read by a BMW dealer, as
specialised equipment is required. It may save time to have at least the initial fault diagnosis carried out by a dealer.
Lack of power
Probable cause Corrective action
Coolant temperature sensor faulty, Test coolant temperature sensor and wiring. Repair wiring or renew sensor if
or wire to sensor broken faulty (see Chapter 6)
Fuel pressure incorrect Check fuel pressure from main pump and transfer pump, as applicable (see Section 3)
Throttle plate not opening fully Check accelerator cable adjustment to make sure throttle is opening fully. Adjust cable if
necessary (see Section 9)
Fuel and exhaust systems 4•21
4
Page 110 of 228

Engine difficult to start, or fails to start (when cold)
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector or thermotime switch
faulty (early Motronic system only) Test cold start injector and thermotime switch. Renew faulty components (see Section 19)
Fuel pump not running Check fuel pump fuse and fuel pump relay (see Sections 2 and 3)
Airflow meter flap (door) binding, or
stuck in open position Inspect the airflow meter for damage (see Section 16)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test system pressure (see Section 3)
Intake air leaks Inspect all vacuum lines, air ducts and oil filler and dipstick seals
Fuel injectors clogged or not operating Check fuel injectors (see Section 20) and wiring harness
Coolant temperature sensor faulty or Test coolant temperature sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
wiring problem
TPS (throttle position sensor) incorrectly adjusted Check TPS adjustment (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Dirt or other contaminants in fuel Check the fuel and drain the tank if necessary
Faulty ECU Have the ECU tested at a dealer service department or other specialist
Crankshaft position signal missing Faulty position sensor or flywheel, or reference pin missing (see Chapter 5)
Engine difficult to start, or fails to start (when warm)
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector leaking or operating
continuously (early Motronic system only) Test cold start injector and thermotime switch (see Section 19)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test fuel pressure (see Section 3)
Insufficient residual fuel pressure Test fuel system hold pressure (see Section 3)
Fuel leak(s) Inspect fuel lines and fuel injectors for leaks. Correct leaks as necessary
Coolant temperature sensor faulty
or wiring problem Test coolant temperature sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Vapour lock (in warm weather) Check fuel pressure (see Section 3)
EVAP system faulty Check EVAP system (see Chapter 6, Section 6)
Faulty ECU Have the ECU tested at a dealer service department or other specialist
Idle speed control system faulty Test the idle air stabiliser valve (see Section 21)
Oxygen sensor faulty (where applicable) Check the oxygen sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4)
Engine misses and hesitates under load
Probable cause Corrective action
Fuel injector clogged Test fuel injectors. Check for clogged injector lines. Renew faulty injectors (see Section 20)
Fuel pressure incorrect Test fuel system pressure (see Section 3). Test fuel pressure regulator (see Section 18)
Fuel leak(s) Inspect fuel lines and fuel injectors for leaks (see Chapter 4)
Engine maintenance Tune-up engine (see Chapter 1). Check the distributor cap, rotor, HT leads and spark
plugs, and renew any faulty components
Airflow meter flap (door) binding, or Inspect the airflow meter for damage (see Section 16)
stuck in open position
Intake air leaks Inspect all vacuum lines, air ducts, and oil filler and dipstick seals
Throttle position sensor (TPS) incorrectly adjusted Check TPS adjustment (see Chapter 6)
Engine idles too fast
Probable cause Corrective action
Accelerator pedal, cable or throttle valve binding Check for worn or broken components, kinked cable, or other damage. Renew faulty
components
Air leaking past throttle valve Inspect throttle valve, and adjust or renew as required
Engine has erratic idle speed
Probable cause Corrective action
Idle air stabiliser valve faulty Check the idle air stabiliser valve (see Section 21)
No power to the idle air stabiliser valve Check the idle air stabiliser relay and wiring circuit (see Chapter 12)
Idle speed control unit faulty Have the idle speed control unit checked by a dealer
Poor fuel economy
Probable cause Corrective action
Cold start injector leaking
(early Motronic system only) Test and, if necessary, renew cold start injector (see Section 19)
Oxygen sensor faulty (where applicable) Test the oxygen sensor (see Chapter 6, Section 4))
Sticking handbrake/binding brakes Check the handbrake/braking system (see Chapter 9)
Tyre pressures low Check tyre pressures (Chapter 1)
4•22 Fuel and exhaust systems
Page 126 of 228
slightly by hand. Release the throttle slowly
until it reaches 0.2 to 0.6 mm from the throttle
stop. There should be continuity.
29Check the resistance between terminals 3
and 18 as the throttle is opened. There should
be continuity when the throttle switch is within
8 to 12 degrees of fully-open. If the readings
are incorrect, adjust the TPS.
30If all the resistance readings are correct
and the TPS is properly adjusted, check for
power (5 volts) at the sensor, and if necessary
trace any wiring circuit problems between the
sensor and ECU (see Chapter 12).
Adjustment
31If the adjustment is not as specified
(paragraphs 28 to 30), loosen the screws on
the TPS, and rotate the sensor into the correct
adjustment. Follow the procedure for
checking the TPS given above, and tighten
the screws when the setting is correct.
32Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
harness connector.
Early 535i models with automatic
transmission
Check
33First test the continuity of the TPS. Follow
paragraphs 28 to 30 and check for continuity.
34Next, test the idle position switch (see
illustration). Unplug the electrical connector
in the idle position switch harness, andconnect an ohmmeter to terminals 1 and 2.
There should be continuity. Open the throttle
slightly, and measure the resistance. There
should now be no continuity.
35Check for the correct voltage signals from
the TPS, with the throttle closed and the
ignition on. Probe the back of the TPS
connector with a voltmeter, and check for
voltage at terminal 3 (black wire) and earth.
There should be 5 volts present. Also, probe
terminal 3 (black wire) and terminal 1 (brown
wire). There should be 5 volts present here
also.
36Check for voltage at terminal 2 (yellow
wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire), and slowly
open the throttle. The voltage should increase
steadily from 0.7 volts (throttle closed) to
4.8 volts (throttle fully-open).
Adjustment
37First measure the stabilised voltage. With
the ignition on and the throttle closed,
measure the voltage between terminal 3
(black wire) and terminal 1 (brown wire). It
should be about 5 volts.
38Next, loosen the sensor mounting screws,
and connect the voltmeter to terminal 2
(yellow wire) and terminal 3 (black wire). With
the throttle fully open, rotate the switch until
there is 0.20 to 0.24 volts less than the
stabilised voltage. Note: You will need a
digital voltmeter to measure these small
changes in voltage.
39Recheck the TPS once more; if the
readings are correct, reconnect the TPS
electrical connector. It is a good idea to lock
the TPS screws with paint or thread-locking
compound.
Airflow meter
General description
40The airflow meter is located on the air
intake duct. The airflow meter measures the
amount of air entering the engine. The ECU
uses this information to control fuel delivery. A
large volume of air indicates acceleration,
while a small volume of air indicates
deceleration or idle. Refer to Chapter 4 for all
the diagnostic checks and renewal
procedures for the airflow meter.
Ignition timing sensors
41Ignition timing is electronically-controlled
on Motronic systems, and is not adjustable.
During starting, a crankshaft position sensor
relays the crankshaft position to the ECU, and
an initial baseline ignition point is determined.
Once the engine is running, the ignition point
is continually changing based on the various
input signals to the ECU. Engine speed is
signalled by a speed sensor. Early Motronic
systems have the reference sensor and the
speed sensor mounted on the bellhousing
over the flywheel. Later Motronic systems
have a single sensor (pulse sensor) mounted
over the crankshaft pulley. This sensor
functions as a speed sensor as well as a
position sensor. Refer to Chapter 5 for more
information. Note: Some models are
equipped with a TDC sensor mounted on the
front of the engine. This sensor is strictly for
the BMW service test unit, and it is not part of
the Motronic ignition system.
5 Positive crankcase
ventilation (PCV) system
1The Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV)
system (see illustration)reduces
hydrocarbon emissions by scavenging
crankcase vapours. It does this by circulating
blow-by gases and then re-routing them to
the intake manifold by way of the air cleaner.
2This PCV system is a sealed system. The
crankcase blow-by vapours are routed
directly to the air cleaner or air collector with
crankcase pressure behind them. The vapour
is not purged with fresh air on most models or
6•4 Engine management and emission control systems
5.2 PCV hose being removed from the
valve cover5.1 Diagram of the PCV system on the
M20 engine (others similar)4.34 Idle position switch and TPS on early
535i models with automatic transmission
4.28c . . . then check for continuity
between terminals 3 and 18 as the throttle
is opened
Page 127 of 228
filtered with a flame trap like most
conventional systems. There are no
conventional PCV valves fitted on these
systems - just a hose (see illustration).
3The main components of the PCV system
are the hoses that connect the valve cover to
the throttle body or air cleaner. If abnormal
operating conditions (such as piston ring
problems) arise, the system is designed to
allow excessive amounts of blow-by gases to
flow back through the crankcase vent tube
into the intake system, to be consumed by
normal combustion. Note: Since these
models don’t use a filtering element, it’s a
good idea to check the PCV system
passageways for clogging from sludge and
combustion residue(see illustration).
6 Evaporative emissions
control (EVAP) system
2
General description
Note:This system is normally only fitted to
those vehicles equipped with a catalytic
converter.
1When the engine isn’t running, the fuel in the
fuel tank evaporates to some extent, creating
fuel vapour. The evaporative emissions control
system (see illustration)stores these fuel
vapours in a charcoal canister. When the
engine is cruising, the purge control valve is
opened slightly, and a small amount of fuel
vapour is drawn into the intake manifold and
burned. When the engine is starting cold or
idling, the purge valve prevents any vapours
from entering the intake manifold and causing
excessively-rich fuel mixture.
2Two types of purge valve are used;
electrically-operated or vacuum-operated. To
find out which type is on your vehicle, follow
the hose from the charcoal canister until you
locate the purge valve. Some are located on
the intake manifold, and others near the
charcoal canister. Look for either an electrical
connector, or vacuum lines, to the purge
valve.3A faulty EVAP system will only affect engine
driveability when the engine is warm. The
EVAP system is not usually the cause of
difficult cold starting or any other cold-running
problems.
Check
Vacuum-operated purge valve
4Remove the vacuum lines from the purge
valve, and blow into the larger valve port. It
should be closed, and not pass any air. Note:
Some models have a thermo-vacuum valve
that delays canister purging until the coolant
temperature reaches approximately 46º C.
Check this valve to make sure that vacuum is
controlled at the proper temperatures. The
valve is usually located in the intake manifold,
near the thermo-time switch and the coolant
temperature sensor.
5Disconnect the small vacuum hose from the
purge valve, and apply vacuum with a hand-
held vacuum pump. The purge valve should
be open, and air should be able to pass
through.6If the test results are unsatisfactory, renew
the purge valve.
Electrically-operated purge valve
7Disconnect any lines from the purge valve,
and (without disconnecting the electrical
connector) place it in a convenient spot for
testing.
8Check that the valve makes a “click” sound
as the ignition is switched on (see
illustration).
9If the valve does not “click”, disconnect the
valve connector, and check for power to the
valve using a test light or a voltmeter (see
illustration).
10If battery voltage is present, but the valve
does not work, renew it. If there is no voltage
present, check the Motronic control unit and
the wiring.
Canister
11Mark all the hoses for position, then
detach them from the canister.
12Slide the canister out of its mounting clip.
Engine management and emission control systems 6•5
6.1 Diagram of the EVAP system on the M10 engine (others similar)
6.9 Check for battery voltage at the
electrical connector to the purge valve6.8 When the ignition is switched on, there
should be a distinct “click” from the purge
valve
6
5.3 It’s a good idea to check for excess
residue from the crankcase vapours
circulating in the hoses and ports - this
can eventually clog the system, and cause
a pressure increase in the engine block