drive BMW 528i 1997 E39 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1997, Model line: 528i, Model: BMW 528i 1997 E39Pages: 1002
Page 956 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
721 -8
(Airbag System (SRS)
4 Remove electrical harness connector from crash sensor (A).
Remove sensor retaining screws (6) and remove sensor.
Note direction of sensor before removing.
- Installation is reverse of removal,
NOTE -
Arrow on sensor must point to door sill.
Driver airbag, removing and installing
- Disconnect negative (-) cable from battery and cover nega-
tive terminal with insulating material.
WARNING-
After disconnecting the batter)! wait 5 seconds before begin-
ning work on
airbag components.
CAUTION-
Prior to disconnecting the batter)! read the battery discon-
nection cautionsgiven
in001 General Warnings and Cau-
tions.
4 Multifunction (MFL) steering wheel:
. Working behind steering wheel, completely loosen Torx
screws
(T30) while holding airbag in place.
Support
airbag unit to prevent it from falling out.
Page 957 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
721 -9
Airbaq System ~SRS)~
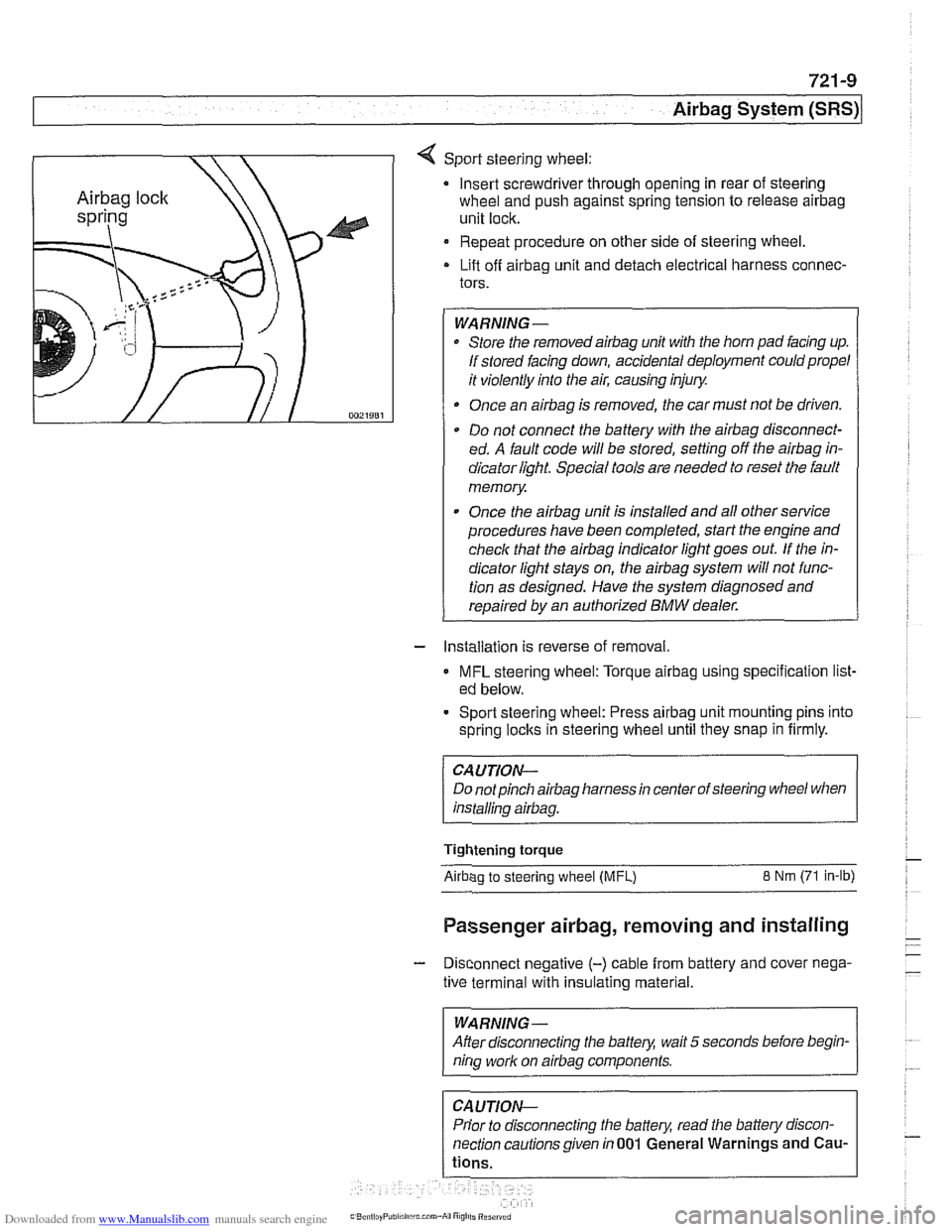
4 Sport steering wheel:
Insert screwdriver through opening in rear of steering
wheel and push against spring tension to release
airbag
unit lock.
Repeat procedure on other side of steering wheel.
Lift off
airbag unit and detach electrical harness connec-
tors.
WARNING-
Store the removedairbag unit with the horn pad facing up.
If stored facing down, accidental deployment could propel
it violently into the air, causing injury.
Once an
airbag is removed, the car must not be driven.
Do not connect the battery with the
airbag disconnect-
ed. A fault code will be stored, setting off the
airbag in-
dicator light Special tools are needed to reset the fault
memory
Once the
airbag unit is installed and all other service
procedures have been completed, start the engine and
check that the
airbag indicator light goes out. If the in-
dicator light stays on, the
airbag system will not func-
tion as designed. Have the system diagnosed and
repaired by an authorized
BMW dealer.
- Installation is reverse of removal.
MFL steering wheel: Torque airbag using specification list-
ed below.
- Sport steering wheel: Press airbag unit mounting pins into
spring
loclts in steering wheel until they snap in firmly.
CAUTION--
Do notpinch airbag harness in center of steering wheel when
installino
airbaa.
Tightening torque
Airbao to steerino wheel IMFL) 8 Nm (71 in-lb)
Passenger airbag, removing and installing
- Disconnect negative (-) cable from battery and cover nega-
tive terminal with insulating material.
--
WARNING -
After disconnecting the batteg wait 5 seconds before begin-
nina work on airbaa components.
Prior to disconnecting the battery, read the battery discon-
nection cautionsgiven in001 General Warnings and
Cau-
Page 961 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD On-Board Diagnostics
I I
General ........................... OBD-1 Diaqnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) . . OBD-9
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD I!) ..... OBD-I
Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL)
........ OBD-2
Scan tools and scan tool display.
........ OBD-3
Diagnostic monitors
.................. OED-4
Drive cycle
......................... OED-6
Readiness codes
.................... OBD-6
Diagnostic trouble codes
(DTCs) ........ OBD-7
-
Automatic transmission diagnostic
trouble codes
....................... OBD-9
Engine diagnostic trouble
codes: M52 engine.
................. OED-13
Engine diagnostic trouble
codes: M54 engine.
................. OBD-17
Engine diagnostic trouble
codes: M62 engine.
................. OBD-24
This chapter outlines the fundamentals and equipment
requirements of On-Board Diagnostics
I1 (OBD 11) standards
as they apply to BMW vehicles. Also covered here is a listing
of BMW and OBD
I1 diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS (QBD !I)
OBD II standards were developed by the SAE (Society of
Automotive Engineers) and CARB (California Air Resources
Board).
OED I1 is the second generation of on-board self-
diagnostic equipment requirements. These standards were
originally mandated for California vehicles. Since
1996 they
have been applied
toall passengervehicles sold in the United
States.
On-board diagnostic capabilities are incorporated into the
hardware and soflwareof the enginecontrol module
(ECM) to
monitor virtually every component that can affect vehicle
emissions. The
OED I1 system works to ensure that
emissions remain as clean as possible over the life of the
vehicle.
Each emission-influencing component is checked by a
diagnostic routine (called a monitor) to verify that it is
functioning properly.
If a problem or malfunction is detected,
the
diagnostic executive built into the OBD I1 system
illuminates a malfunction indicator light (MIL) on the
instrument panel.
The OBD
I1 system also stores diagnostic trouble codes
(DTCs) about the detected malfunction in the ECM so that a
repair technician can accurately find and fix the problem.
Page 962 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OED-2
On-Board Diagnostics
Specialized OED II scan tool equipment is needed to access
the fault memory and
OED I1 data.
The extra hardware needed to operate the OED
I1 system
consists mainly of the following:
* Additional oxygen sensors downstream of the catalytic
converters.
Fuel tank pressure sensor and device to pressurize
fuel
storage system.
Several engine and performance monitoring devices
Standardized 16-pin
OED II connector under the
dashboard.
Upgraded components for the federally required reliability
mandate.
Malfunction indicator light (MIL)
OED II software illuminates the malfunction indicator light
(MIL) when emission levels exceed 1.5 times Federal
standards.
4 For E34 cars covered by this manual, three different MIL
symbols were used, depending on year and model.
MIL illuminates under the following conditions:
Engine management system fault detected for
two
consecutive OED iI drive cycles. See Drive cycle in this
repair group.
- Catalyst damaging fault detected.
Component malfunction causes emissions to exceed 1.5
times OED
II standards.
Manufacturer-defined specifications exceeded. Implausible input signal.
Misfire
faults.
Leak in evaporative system,
Oxygen sensors observe no purge
flow from purge valve 1
evaporative system.
ECM fails to enter closed-loop operation within specified
time.
ECM or automatic transmission control
module (TCM) in
"limp home" mode.
ignition key ON before cranking (bulb
check function).
OED
II fault memory (including the MIL) can only be reset
using a special scan tool. Removing the connector from the
ECM or disconnecting the battery does not erase the fault
memory.
Page 963 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-3
On-Board
~iactnosticsl
Additional MIL information:
A fault code is stored within the ECM upon the first
occurrence of a fault in the system being checlted.
Two complete consecutive drive cycles with the iault
present illuminate the MIL. The exception to the two-fault
requirement is a catalyst-damaging fault, which illuminates
the MIL immediately.
If the second drive cycle was not complete and the fault
was not checked, the ECM counts the third drive cycle as
the next consecutive drive cycle. The MIL illuminates
if the
system is checked and the fault is still present.
Once the MIL is illuminated, it remains illuminated until the
vehicle completes three consecutive drive cycles without
detecting a fault.
0 An existing fault code is cleared from memory
automatically when the vehicle completes
40 consecutive
drive cycles without the fault being detected.
In order to automatically clear a catalyst-damaging fault from
memory, the condition underwhich the fault occurred must be
evaluated for 80 consecutive drive cycles without the fault
reoccurring.
A generic scan tool connected to the BMW data link
connector (DLC) or OBD
I1 plug can display diagnostic trouble
codes (DTCs), along with the conditions associated with the
illumination of the MIL. Using a more advanced or
BMW-
dedicated scan tool, additional proprietary information is
normally available.
Scan tool and scan tool display
The complexity of the OBD I1 system requires that all
diagnostics begin by connecting a scan tool to the vehicle.
Aftermarltet scan tools can be connected to either the 16-pin
OBD
I1 plug or the 20-pin BMW DLC in the engine
compartment
(ii installed). Data from the OBD II plug may be
limited, depending on scan tool and vehicle.
OBD
I1 standards reouire that the 16-oin OBD I1 oluo be
located within three
(3) feet of the driier and not're&ire any
tools to access.
Starting with June 2000 production, the 20-pin BMW DLC,
previously located in the engine compartment, was
discontinued. Diagnostic, coding and programming functions
are incorporated into the OBD
II plug, located under left side
of dashboard.
On cars built up to 06
/ 2000: when accessing emissions
related DTCs through the 16-pin OBD
I1 plug, malte sure the
BMW 20-oin DLC
caD is installed.
Page 964 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
- -
On-Board Diagnostics
Professional diagnostic scan tools available atthe time of this
printing include the BMW factory tools
(DISplus, GTI,
MoDiC) and a small number of aftermarket BMW-specific
tools. See
020 Maintenance.
In addition to the professional line of scan tools, inexpensive
generic OBD
II scan tool software programs and handheld
units are readily available. Though limited, they are
nonetheless powerful diagnostic tools. These tools read live
data streams and freeze frame data as well as a host of other
valuable diagnostic data.
Diagnostic monitors
Diagnostic monitors run tests and checks on specific
emission control systems, components, and functions.
A complete drive cycle is requiredforthe tests to bevalid. See
Drive cycle in this repair group. The diagnostic monitor
signals the
ECM of the loss or impairment of the signal or
component and determines if a signal or sensor is faulty
based on
3 conditions:
* Signal or component shorted to ground
Signal or component shorted to
B+
Signal or component missing (open circuit)
The OBD
II system monitors all emission control systems that
are installed. Emission control systems vary by vehicle model
and year. For example, a vehicle may not be equipped with
secondary air injection, so no secondary air readiness code
would be present.
OBD
II software monitors the following:
Oxygen sensors
Catalysts
Engine misfire
- Fuel tank evaporative control system
Secondary air injection Fuel system
Oxygen sensor monitoring. When driving conditions allow,
response rate and switching time of each oxygen sensor is
monitored. The oxygen sensor heater function is also
monitored. The OBD
II system differentiates between
precataylst and post-catalyst oxygen sensors and reads each
one individually. In order
forthe oxygen sensor to be
effectively monitored, the system must be in closed loop
operation.
Page 966 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-6
On-Board Diagnostics
Fuel system monitoring. This monitor looks at the fuel
delivery needed (long
/short term fuel trim) for proper engine
operation based on programmed data. If too much or not
enough fuel is delivered over a predetermined time, a DTC is
set and the MIL illuminates.
Fuel trim refers to adiustments to base fuel schedule.
Lono- ., term fuel trim refers to gradual adjustments to the fuel
calibration adjustment as compared to short term fuel trim.
Long term fuel trim adjustments compensate for gradual
changes that occur over time.
Fuel system monitoring monitors the calculated injection time
(ti) in relation to enginespeed, load and precatalyticconverter
oxygen
sensor(s) signals.
Using this data, the system optimizes fuel delivery for all
engine operating conditions.
Evaporative system monitoring. This monitor checks the
the fuel storage system and related fuel lines for leaks. It can
detect very small leaks anywhere in the system.
A leak detection unit (LDP or DMTL) is used to pressurize the
evaporative control system on a continuous basis (as the
drive cycle allows) and to
check system integrity.
Drive cycle
The OED II drive cycle is an important concept in
understanding OBD
II requirements. The purpose of the drive
cycle is to run ail of the emission-related on-board diagnostics
over a broad range of driving conditions.
A drive cycle is considered complete when all of the
diagnostic monitors have run their tests without interruption.
~ora drive cycle to be initiated, the vehicle must be started
cold and brought up to
1 60°F and at least 40°F above its
original starting temperature.
Readiness codes
Inspection/maintenance (I/M) readiness codes are mandated
as part of OBD
II. The readiness code is stored aftercomplete
diagnostic monitoring of specified components and systems
is carried out. The readiness code function was designed to
prevent manipulating an
I/M emission test procedure by
clearing faults codes or disconnecting the ECM or battery.
Page 967 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
On-Board Diagnostics
Readiness codes indicate whether the OED Ii system is
actually ready to monitor the various emission control
systems on the vehicle. The vehicle must complete a drive
cycle to set readiness codes. The code is binary:
0 for ready
1 for not ready
f
4 The parameters which are monitored for readiness are:
llM readiness codes
1. Catalyst efficiency
2. Catalyst heating
3. Fuel tank evaporative control
4. Secondary air injection
5.
NC refrigerant
6. Oxygen sensors
7. Oxygen sensor heaters
8. Exhaust gas recirculation
Readiness codes are set to 1 (not ready) in the following
cases:
~9~~.f~[<+t~t~p:,~;:#j~~{]~y~ ,,... , , 8701Dbd001
The battery or ECM is disconnected.
When
all zeros are displayed, the system has established
DTCs are erased after completion of repairs and a drive
cycle is not completed.
readiness. Readiness codes
can be displayed using BMW
and aftermarket scan tools.
An
OED II scan tool can be used to determine IIM readiness.
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
SAE standard J2012 mandates a 5-digit diagnostic trouble
code (DTC) standard. Each digit represents a specific value.
Emission related DTCs
start with the letter P for power train.
When the engine service
light (MIL) is illuminated it indicates
that a DTC has been stored.
DTCs are stored as soon as they occur, whether or not the
engine service light illuminates.
DTCs store and display a time stamp.
DTCs record the current fault status: Present, not currently
present, or intermittent.
Page 991 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
INDEX 'tl
WARNING
Your common sense, good
judgemenl, and general alertness are
crucial to sale and successiul service
worlr. Belore attempting any work on
your
BMM be sure lo read 001
General Warnings and Cautions
and the
copyriglll page at the front 01
the manual. Review these warnings
and
caulions each lime you prepare
lo work on your BMW. Please also
read any warnings and cautions that
accompany
tile procedures in the
manual.
312-way valve (running losses)
see Fuel tank
Abbreviations, commonly used 600-14
ABS (antilock brake system)
see
Bral(es
A/C air distribution motors
see stepper motors (below)
blower final stage (resistor pack),
replacing
640-16
blower, removinglinslalling
640-1 5
compressor, replacing
640-24 condenser, replacing 64045
control panellmodule, removing1
installing
640-1 1
evaporakr, removinglinstalling 640-29
evaporator temperature sensor
640-12 expansion valve, removinglinstailing
640-27
IHKA/ IHKR system description 640-5
receiveridrier, replacing 640-26
stepper motors 640-1 3 ventilation microiilter, replacing
020-22. 640-17
see also Heating
Accelerator
iinlcage
see Maintenance
Activated carbon canister
see Fuel tank
ADS (auxiliary throttle valve)
130-57
Air compressor
330-44
Air conditioning
see
AIC
Air distribution (flap) motors
seeNC, stepper motors
Air filter see Maintenance
Air spring
300-6, 330-12
Airbag system (SRS)
2-stage
airbag 721-4
control module, replacing 721-7 driver airbag, removinglinstalling
721-8
iiead protection airbag 721-12 components 721-1 1
indicator
lighl721-4
passenger airbag, removinglinstalling
721-9 side-impact airbags crash sensor,
replacing
721-7
Airflow sensor see 130 under appropriate
fuel
injection system
Air pump
see 130 under appropriate fuel
injection system, secondary air
injection system
Air suspension
see Electronic height control
(EHC)
Alarm
see Anti-theft alarm
Alignment see
Wheei alignment
Aluminum suspension components
300-2
Antenna 650-6
Alternator see Battery, starter, alte rnator
Amplifier
650-4
Anti-theft alarm (DWA)
515-24 emergency disarming 515-31
Antifreeze (engine coolant)
see Maintenance
see also Cooling system
Antilock brake system (ABS) see Brakes
ASC see Brakes
ATF (automatic transmission fluid)
see Automatic transmission
see also Cooling systern
Automatic headlight adjustmenl
(LWR) see Lights
Automatic seat belt tensioner
720-4
Automatic shiftloclc
see
Gearshift
Automatic transmission
applications
200-3, 240-4
ATF 020-10, 200-4
capacity 240-8 checking 240-6
drainingifilling 240-7
heat exchanger 170-5
fluid pan and strainer 240-9 gearshift
see Gearshift
ID tag
200-3 range switch 610-6
removaliinstallation 240-10
steptronic see Gearshift
Auxiliary cooling fan
see
Coollng system, electric Ian
Auxiliary throttle valve (ADS)
130-57
Axle joint
see Drive axle
Back-up light switch
automatic transmission see Automatic transmission. range switch
- .~.~~~
manual transmission 230-8 -
- I
Page 992 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
2 INDEX
Battery, starter, alternator
alternator (generator)
121-10
6-cylinder engine, removingi
installing 121-15
M62 engine 121-16
M62 TU engine (water cooled)
121-18
battery
121-5 charging 121-9
safety terminal 121-3
testing 121-5 charging system, troubleshooting
121-12
starter
121-1 9
6-cylinder engine, removingi instaliinq 121-20 . V-8 engine, rernovinglinsialiing
121-21
solenoid, removinglinstalling
121-23 troubleshooting 121-19
see also Maintenance
Bearing, wheel
see Front suspension
see also Rear suspension
Belts see Maintenance, drive belts
Blade, wiper
see Wipers and Washers
Blower motor see
A/C
BMW emblem
see Exterior trim
BMW special tools 010-18 see also special tools section at
beginning
of each repair group
Body dimensions 400-2
interior features
400-9 salety and security 400-7
Body side molding
see Exterior trim
Bonnet see Engine hood
Boot see Trunk
Brake fluid
020-24, 340-8
Brake fluid pressure sensor
340-30
Brakes
ABS, ASC or DSC system
300-12
component replacement 340-26
ASCIDSC switch
see Switches
bleeding
bralces 340-8
brake booster 340-1 9 bralce Dads. caiioers and rotors ,., 340-1 1
descriotion 300-10
e~ectrdnic brake & stability 300-11
light switch
see Switches
master cylinder
340-16 pariking brake 340-22
troubleshooting 340-5
Bulbs see Lights
Bumper
lront 510-6 height, adjusting 510-12
rear 510-9
Bus system
600-4
Camber
320-33
Camshaft
removingiinslaiiing
M52 engine 116-12
M52 TU
/ M54 engine 116-1 9 M62 engine 11 6-39
wear
116-6
Camshaft position sensors
see ignition system
Camshaft timing chain
adjusting M52 engine
117-22
M52 TU I M54 engine 117-43
M62 engine 117-79 removinglinstalling
M52 engine 117-26
M52TU 1 M54 engine 113-46.116-
28
M62 engine 117-66
Capacities, fluid
020.10
Car rnemorvlicev memorv . . 600-10
see also Centrai
lociking
Carbon canister, activated
see Fuel
tank
Caster
320-33
Catalytic converter and oxygen sensor 020-19
see also Exhaust system: exhaust
manilolds
Cautions
001-3
CD changer
650-4
Center bearing, driveshaft
see Driveshait
Center brake light
sedan
630-13
Center console
513-3
Centrai body electronics (ZKE 111)
600-6
Central locking
car memoryiey memory 515.12 general module iunctions 515-2
remote entry (FZV) 515-8
remote lkey initialization 515-10 single lociddouble ioclk 515-6
switch 515-4
Chain
see Camshaft liming chain
Characteristic map (electrically heated) thermostat
see Electrically heated thermostat
Charging system
see Battery, starter, alternator
Cluster see instruments
Clutch fluid see Maintenance
hydraulics
210-4
mechanical 210-9
switch
see Switches, pedal ciuster
variations
210.10
Codes, fault OED-1
Coil
see Ignition system
Coil spring
see Front suspension
see also Rear
suspe nsion