ing harness BMW M3 1995 E36 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1995, Model line: M3, Model: BMW M3 1995 E36Pages: 759
Page 370 of 759
540-
4
SUNROOF
3
.
Disconnect
harness
connector
from
motor
and
remove
motor
.
4
.
Installation
is
reverse
of
removal
.
Be
sure
the
motor
is
in
the
"closed"
position
before
installing
it
to
the
sunroof
carrier
.
See
Fig
.
8
.
SLIDE-TILT
SUNROOF
0011813
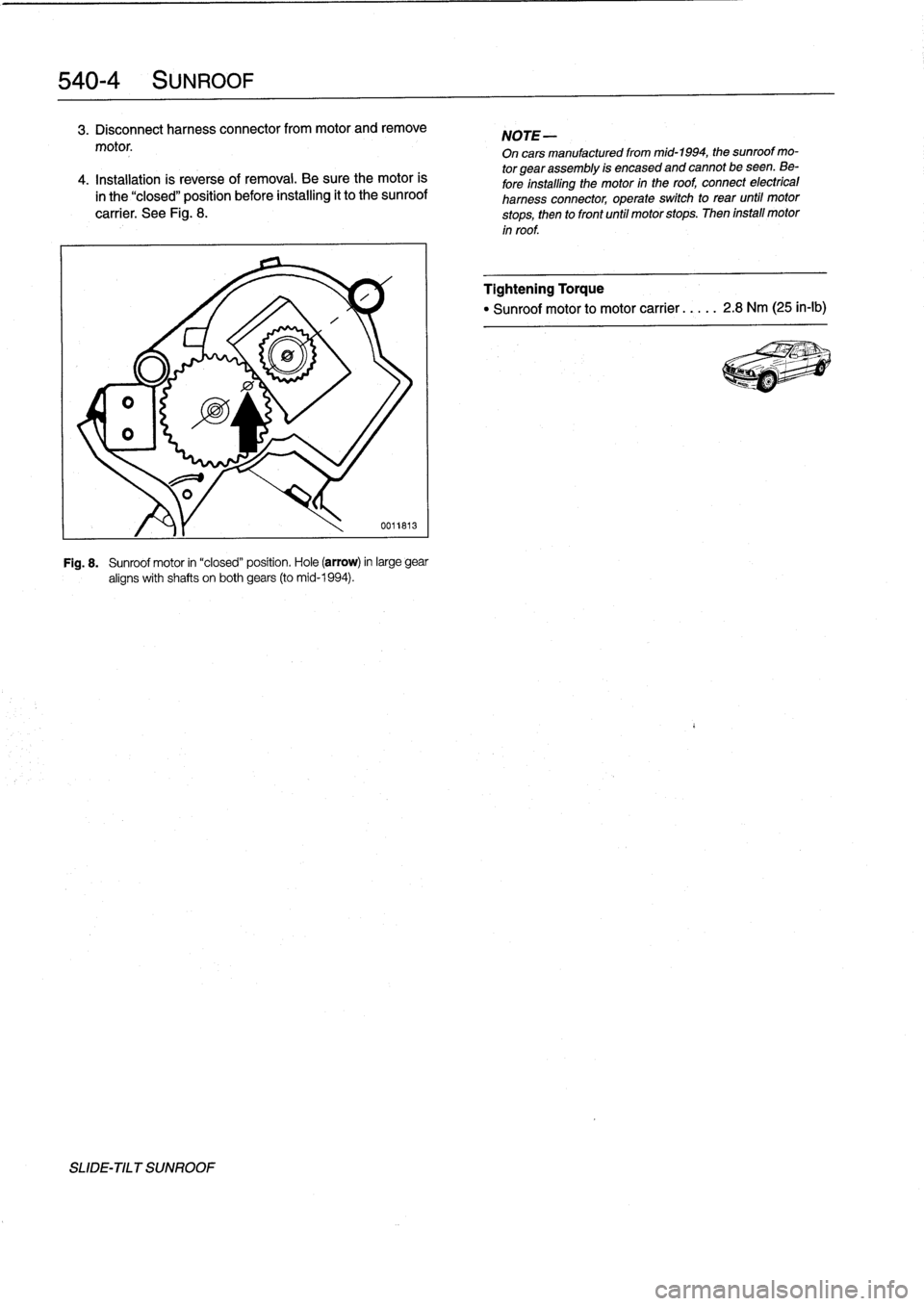
Fig
.
8
.
Sunroof
motor
in
"closed"
position
.
Hole
(arrow)
in
large
gear
aligns
with
shafts
on
both
gears
(to
mid-1994)
.
NOTE-
On
cars
manufacturedfrom
mid-1994,
the
sunroof
mo-
tor
gearassembly
is
encased
and
cannot
be
seen
.
Be-
fore
installing
the
motor
in
the
roof,
connect
electrical
harness
connector,
operate
switch
to
rear
until
motor
stops,
then
to
front
until
motor
stops
.
Then
install
motor
in
roof
.
Tightening
Torque
"
Sunroof
motor
to
motor
carrier
.
.
.
.
.
2
.8
Nm
(25
in-lb)
Page 375 of 759
The
left
latch
in
the
fully
automatic
version
hastwo
mi-
croswitches
(S7
and
S8)which
signal
open,
closed
and
latched
states
.
See
Fig
.
8
.
The
length
of
the
dead
center
point
rod
is
critica¡
lo
correct
opening
and
latching
of
the
convertible
top
.
See
Fig
.
9
.
Dead
Center
Point
Rod
"
Dimension
A
........
205
.5
f
1
mm
(8
.09
t0
.04
in)
Visor
Latch
Motor
The
fully
automatic
convertible
top
is
latched
and
unlatched
by
one
electric
motor
installed
in
the
front
roof
bow
.
To
re-
place,
remove
front
cover
trim
from
the
roof
.
Remove
electri-
cal
harness
connectors
from
motor,
andremove
mounting
screws
.
Slide
the
motor
off
the
output
shafts
to
the
left
and
right
latches
.
During
reinstallation,
theoutput
shafts
must
be
tumed
until
the
S8
microswitch
in
the
left
latch
is
tripped
.
Convertible
top
and
frame,
replacing
1
.
Open
convertible
top
partially
.
Open
convertible
top
lid
.
Fig
.
9
.
Preset
lengthof
dead
centerpoint
rod
.
Open
back
windows
.
2
.
Fully
automatic
power
convertible
top
:
Remove
front
cover
trim
from
top
.
Disconnect
electrical
harness
con-
nectors
from
frontlatch
motor
.
Disconnect
connectors
from
S7
and
S8
microswitches
at
left
latch
.
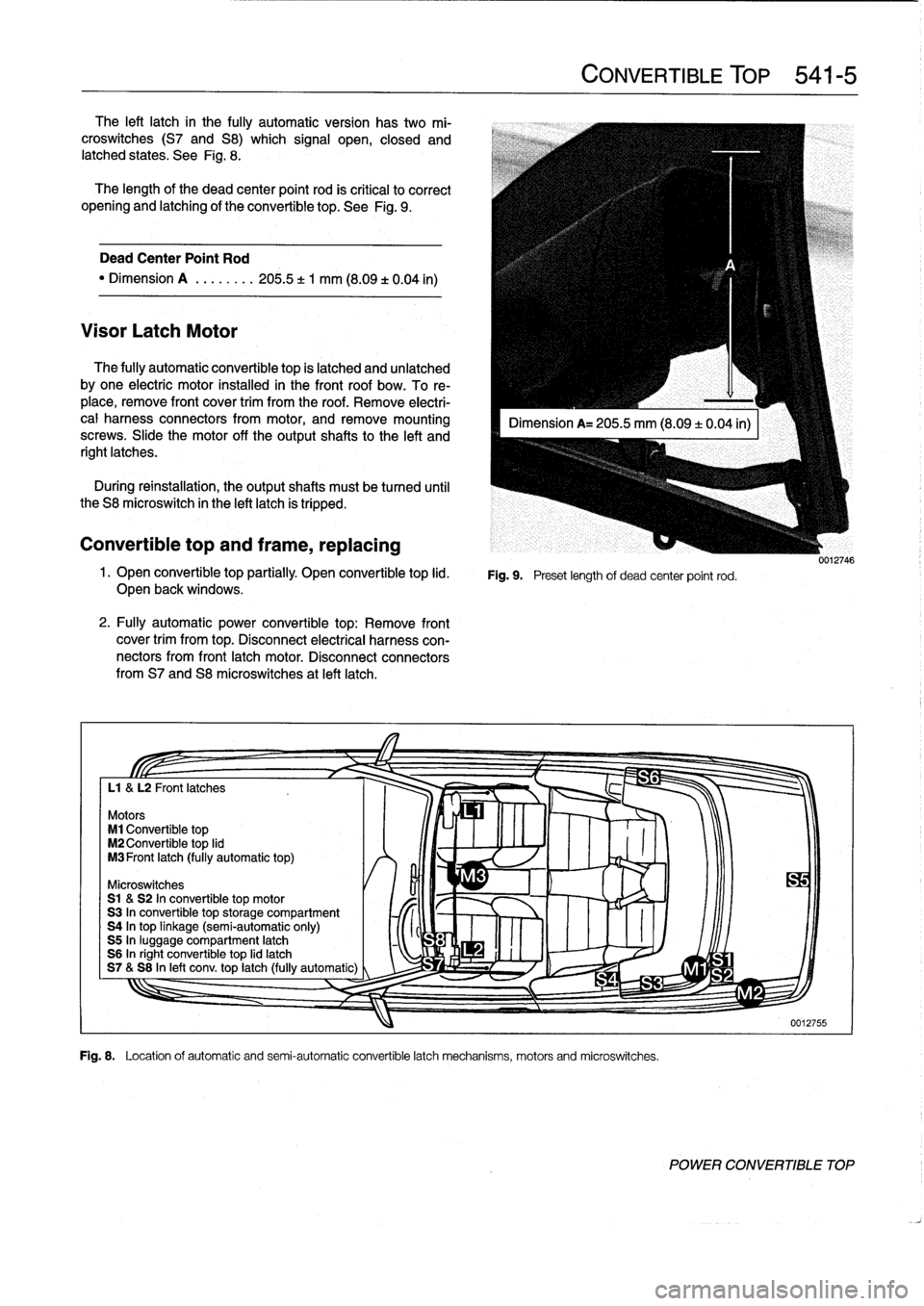
Motors
M1
Convertible
top
M2
Convertible
top
lid
M3Front
latch
(fully
automatic
top)
Microswitches
S1
&S2
In
convertible
top
motor
S3
In
convertible
top
storage
compartment
S4
In
top
linkage
(semi-automatic
only)
S5
In
luggage
compartment
latch
S6
In
right
convertible
top
lid
latch
S7&S8
In
left
conv
.
top
latch
(fully
automatic)
Fig
.
8
.
Locationof
automatic
and
semi-automatic
convertible
latch
mechanisms,
motors
and
microswitches
.
CONVERTIBLE
TOP
541-5
POWER
CONVERTIBLE
TOP
Page 376 of 759
541-
6
CONVERTIBLE
TOP
3
.
Remove
headliner,
starting
from
front
and
working
7
.
Remove
fasteners
in
bottom
of
storage
compartments
backward
.
Note
arrangement
and
lacing
of
tensioning
behind
door
posts
and
lift
out
complete
top
.
Note
num
cable
so
it
can
be
reinstalled
in
its
original
configura-
ber
of
shims
on
horizontal
mounting
bolt
.
See
Fig
.
12
.
tion
.
See
Fig
.
10
.
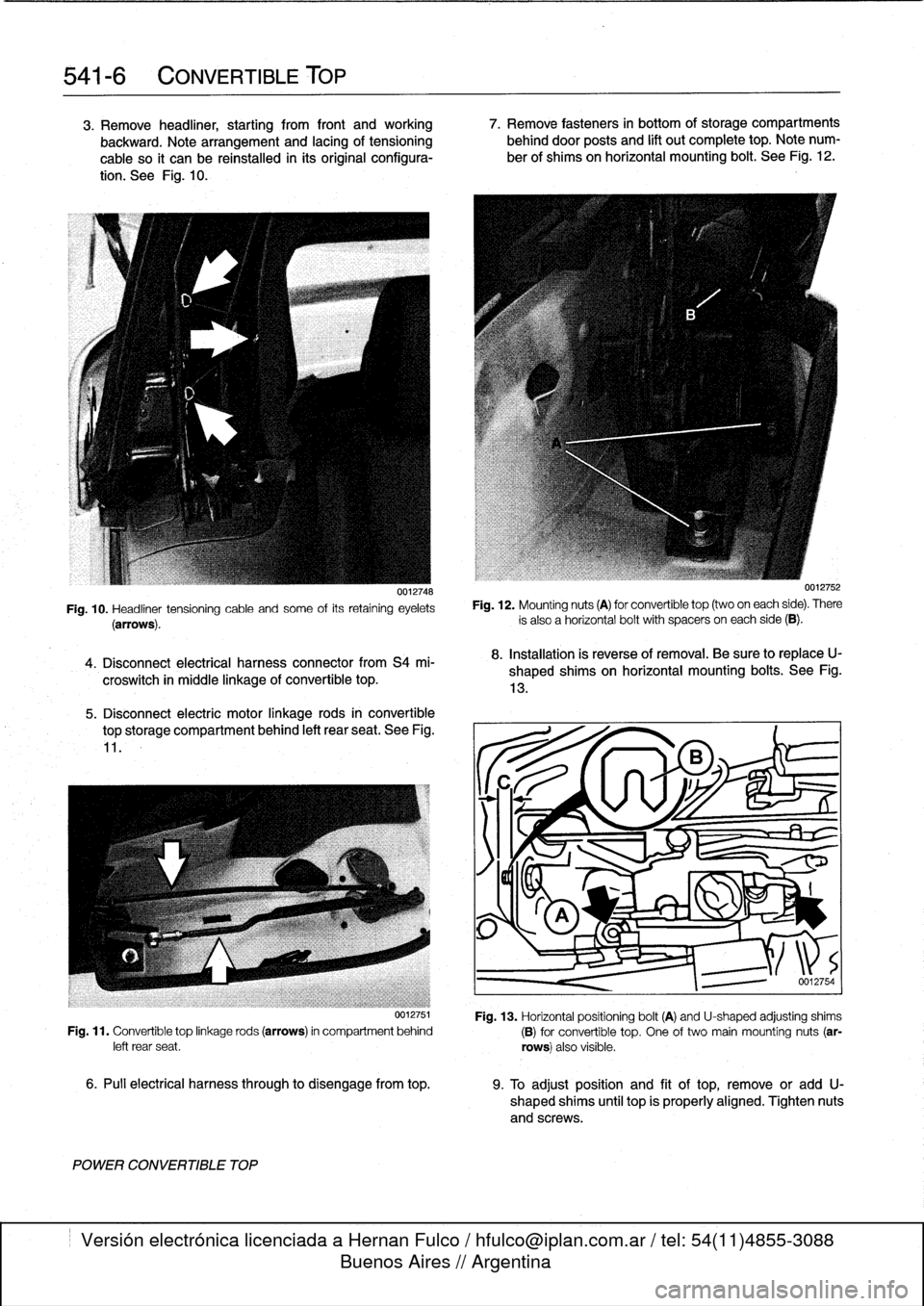
0012748
Fig
.
10
.
Headliner
tensioning
cable
and
some
of
its
retaining
eyelets
(arrows)
.
4
.
Disconnect
electrical
harness
connector
from
S4
mi-
croswitch
in
middle
linkage
of
convertible
top
.
5
.
Disconnect
electric
motor
linkage
rods
in
convertible
top
storage
compartment
behind
left
rearseat
.
See
Fig
.
Vizib1
Fig
.
11
.
Convertible
top
linkage
rods(arrows)
in
compartment
behind
left
rear
seat
.
POWER
CONVERTIBLE
TOP
8
.
Installation
is
reverse
of
removal
.
Be
sure
to
replace
U-
shaped
shims
on
horizontal
mounting
bolts
.
See
Fig
.
13
.
0012754
Fig
.
13
.
Horizontalpositioning
bolt
(A)
and
U-shaped
adjusting
shims
(B)
for
convertible
top
.
One
of
two
main
mounting
nuts
(ar-
rows)
also
visible
.
6
.
Pull
electrical
harness
through
to
disengage
from
top
.
9
.
To
adjust
position
and
fit
oftop,
Rmove
or
add
U-
shaped
shims
until
top
is
properly
aligned
.
Tighten
nuts
and
screws
.
Page 377 of 759

Convertible
top
drive
motor,
replacing
5
.
Working
in
convertible
top
storage
compartment
be-
hind
driver's
seat,
remove
convertible
top
linkage
rods
1
.
Open
convertible
top
partially,
stopping
when
convert-
from
top
of
motor
.
Refer
to
Fig
.
11
.
ible
top
lid
is
fully
upen
.
Remove
lid
.
2
.
Release
luggage
compartment
lock-out
by
pressing
on
microswitch
in
right
convertible
top
lid
latch
.
See
Fig
.
14
.
0012745
Fig
.
14
.
Rightside
convertible
top
lid
latch
.
Arrow
points
to
location
of
luggage
compartment
lock-out
microswitch
.
3
.
Open
luggage
compartment
.
Remove
trim
and
inner
lining
from
left
side
of
compartment
.
4
.
Disconnect
electrical
harness
connectors
at
top
motor
.
Release
emergency
release
cable
from
lever
.
Push
le-
ver
up
to
release
motor
.
See
Fig
.
15
.
uu12759
Fig
.
15
.
Convertible
top
motor
(A)
and
release
lever
(B)
in
luggage
compartment
.
CONVERTIBLE
TOP
541-
7
6
.
Remove
four
fastenersholding
motor
to
body
and
re-
move
motor
through
luggage
compartment
.
See
Fig
.
16
.
0012761
Fig
.
16
.
Convertible
top
motor
mountingscrews
(arrows)
.
Gasket
(A)
mustbe
renewed
when
motor
is
replaced
.
7
.
Installation
is
reverse
of
removal
.
Keep
the
following
in
mind
:
"
Replace
sealing
gasket
between
top
of
motor
and
body
.
"
Securemotormountingscrews
with
Locktite
®
270
or
equivalent
.
Tightening
Torque
"
Convertible
top
motor
to
body
mountingscrews
...
...
.
.
.........
10
Nm
(7
.5
ft-Ib)
Convertible
Top
Emergency
Operation
A
malfunction
in
the
electrical
system
or
another
fault
in
the
convertible
top
mechanism
can
cause
the
automatic
or
semi-
automatic
top
to
be
stuck
in
open,
shut,
or
intermediate
posi-
tion
.
The
following
general
procedures
are
suggested
in
order
to
close
the
top
in
an
emergency
situation
.
Resetting
proce-
dures
for
convertible
top
synchronization
after
emergency
clo-
sure
are
beyond
the
scope
of
this
manual
.
Main
Motor
.
To
release
thetop
linkage
from
the
motor,
lift
the
left
comer
of
the
rearseat
to
access
emergency
release
handle
.
See
Fig
.
17
.
POWER
CONVERTIBLE
TOP
Page 381 of 759

600
Electrical
System-General
GENERAL
.
...........
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
...
.
...
600-1
Voltage
and
Polarity
........
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.....
600-1
Ming,
Fuses
and
Relays
............
.
.
.
.
600-1
Electrical
System
Safety
Precautions
...
.
.
.
.
600-1
Electrical
Test
Equipment
.....
.
.
.
....
.
.
.
.
600-2
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
..
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
........
600-2
Ming
Codes
and
Abbreviations
..
.
...
.
....
600-2
ELECTRICAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
..
.
..
600-3
Voltage
and
Voltage
Drops
..........
.
.
.
.
.
600-4
GENERAL
Electrical
System
Safety
Precautions
A
brief
description
of
the
principal
parts
of
the
electrical
sys-
tem
is
presented
here
.
Also
covered
here
are
basic
electrical
system
troubleshooting
tips
.
Voltage
and
Polarity
The
vehicle
electrical
system
is
a
12-volt
direct
current
(DC)
negative-ground
system
.
A
voltage
regulator
controls
system
voltage
at
approximately
the
12-volt
rating
of
the
battery
.
Al¡
circuits
are
grounded
by
direct
or
indirect
connection
to
the
negative
(-)
terminal
of
the
battery
.
A
number
of
ground
con-
nections
throughout
the
car
connect
the
wiring
harness
to
chassis
ground
.
These
circuits
are
completedby
the
battery
cable
or
ground
strap
between
the
body
and
the
battery
nega-
tive
(-)
terminal
.
Wiring,
Fuses
and
Relays
Nearly
all
parts
of
the
wiring
harnessconnect
to
compo-
nents
of
the
electrical
system
with
keyed,
push-on
connectors
that
lock
into
place
.
Notable
exceptions
arethe
heavy
battery
cables
and
the
starter
wiring
.
The
wiring
is
color-coded
for
cir-
cuitidentification
.
With
theexception
of
the
battery
charging
system,
most
electrical
power
is
routed
from
the
ignition
switch
or
the
bat-
tery
through
the
main
fuse/relay
panel,
located
in
¡he
left
rear
comer
of
the
engine
compartment
.
Fuses
are
color
coded
to
indicate
current
capacities
.
The
relays
and
control
units/modules
are
mounted
in
vari-
ous
places
throughout
the
vehicle
.
See610
Electrical
Com-
ponent
Locations
.
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM-GENERAL
600-1
Voltage,
measuring
.
.
.
................
.
.
600-4
Voltage
drop,
testing
.
.
.....
.
.....
.
......
600-4
Continuity,
checking
..
.
...
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
600-5
Short
Circuits
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.....
.
...
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
600-5
Short
circuit,
testing
with
ohmmete'r
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
600-6
Short
circuit,
testing
with
voitmeter
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
600-6
TABLES
a
.
Terminal
and
Circuit
Numbers
..............
..
.600-3
Please
read
the
following
warnings
and
cautions
before
do-
ing
any
work
on
your
electrical
system
.
WARNING
-
"
The
cars
covered
by
this
manual
are
equipped
with
aSupplemental
Restraint
System
(SRS)
that
automatically
deploys
one
or
more
airbags
.
Each
airbag
unit
houses
an
explosive
powerful
charge
.
Any
work
involving
the
SRS
system
should
only
be
performed
byan
authorized
BMW
dealer
.
Making
repairs
without
the
proper
knowledge
and
special
test
equipment
may
cause
serious
per-
sonal
injury
.
See
721
Airbag
System
(SRS)
.
"
The
ignition
system
of
the
car
operates
at
lethal
voltages
.
People
with
pacemakers
or
weak
hearts
should
not
expose
themselves
to
the
ignition
sys-
tem
.
Extra
caution
mustbe
taken
when
working
on
the
ignition
system
or
when
servicing
theen-
gine
while
it
is
runningor
the
key
is
on
.
See
120
Ignition
System
for
additional
ignition
system
warnings
and
cautions
.
"
Before
operating
the
starter
without
starting
the
engine
(as
when
making
a
compressfon
test),
dis-
able
the
ignition
system
as
described
in
120
Igni-
tion
System
.
"
Keep
hands,
clothing
and
other
objects
clear
of
the
electric
radiator
coollng
fan
when
working
on
a
warm
engine
.
The
fan
may
start
at
any
tíme,
even
when
the
ignition
is
switched
off
.
GENERAL
Page 382 of 759

600-2
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM-GENERAL
CAUTION
-
"
Always
turn
off
the
engine
and
disconnect
the
negative
()
cable
from
the
batterybefore
remov-
ing
any
electrical
components
.
Disconnecting
the
battery
may
erase
fault
code(s)
stored
in
control
module
memory
.
Check
for
fault
codes
using
spe-
cial
BMW
diagnostic
equipment
.
"
Prior
to
disconnecting
the
battery,
read
the
bat-
tery
disconnection
cautions
given
at
the
front
of
this
manual
onpage
viii
.
"
Connect
and
disconnect
ignition
system
wires,
multiple
connectors,
and
ignition
test
equipment
leads
only
while
the
ignition
is
off
.
"
Do
not
disconnect
the
battery
with
engine
run-
ning
.
"
Do
not
quick-charge
the
battery
(for
boost
start-
ing)
for
longer
than
one
minute,
and
do
not
ex-
ceed
16
.5
volts
at
the
battery
with
the
boosting
cables
attached
.
Wait
at
feast
one
minute
before
boosting
the
battery
a
second
time
.
"
Do
not
usea
test
famp
that
has
a
normal
incan-
descent
bulb
to
test
circuits
contafning
electronic
components
.
The
high
electrical
consumptionof
these
test
lamps
may
damage
the
components
.
"
Do
not
use
an
analog
meter
.
Use
onfy
a
digital
multimeter
.
"
Many
of
the
solid-state
modules
are
static
sensi-
tive
.
Static
discharge
will
permanently
damage
them
.
Always
handle
the
modules
using
proper
static
prevention
equipment
and
techniques
.
"
To
avoid
damaging
harness
connectors
or
relay
panel
sockets,
use
jumper
wires
with
flat-blade
connectors
that
are
the
same
size
as
the
connec-
tor
or
relay
terminals
.
"
Always
switch
a
digital
multimeter
to
the
appropri-
ate
function
and
range
before
making
test
con-
nections
.
"
Do
not
tryto
start
the
engine
of
a
carwhich
has
been
heated
above176°F
(80°C),
(for
example,
in
a
paint
dryingbooth)
.
Allow
it
to
cool
to
normal
temperature
.
"
Disconnect
the
battery
before
dolng
any
electric
welding
on
the
car
.
"
Do
not
wash
the
engine
while
it
is
runnfng,
or
any-
time
the
ignition
is
switched
on
.
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
Electrical
Test
Equipment
Many
of
the
electrical
tests
described
in
this
manual
call
for
measuring
voltage,
currentorresistanceusing
a
digital
multi-
meter
(DMM)
.
Digital
meters
are
preferred
for
precise
mea-
surements
and
for
electronics
work
because
they
are
generally
more
accuratethan
analog
meters
.
The
numerical
display
is
alsoless
likely
to
be
misread,
since
there
is
no
nee-
dle
position
to
be
misinterpreted
by
reading
at
an
angle
.
An
LED
test
light
is
a
safe,
inexpensive
tool
that
can
be
used
to
perform
many
simple
electrical
tests
that
would
otherwise
require
a
digital
multimeter
.
The
LED
indicates
when
voltage
is
present
between
anytwo
test-points
in
a
circuit
.
CA
UTION-
"
Choose
test
equipment
carefully
.
Use
a
digital
multimeter
with
at
leadt
10
megaohm
input
im-
pedance,or
an
LED
test
light
.
An
analog
meter
(swing-need1e)
ora
test
light
with
a
normal
incan-
descent
bulb
may
draw
enough
current
to
dam-
age
sensitive
electronic
components
.
"
An
ohmmeter
must
not
beused
to
measure
resis-
tance
on
solidstate
components
suchas
controlunits
or
time
delay
relays
.
"
Always
disconnect
the
battery
before
making
re-
sístance
(ohm)
measurements
on
the
circuit
.
WIRING
DIAGRAMS
The
wiring
diagrams
shown
in
Electrical
Wiring
Diagrams
have
been
specially
designed
to
enable
quick
and
efficientdi-
agnosis
and
troubleshooting
of
electrical
malfunctions
.
Wiring
Codes
and
Abbreviations
A
lot
of
information
is
included
in
each
wiring
diagram
if
you
know
how
to
read
them
.
Wire
colors
in
the
diagrams
are
ab-
breviated
.
Combined
color
codes
indicate
a
multi-colored
wire
.
For
example
the
code
BLU/RED
indicates
a
Blue
wire
with
a
Red
stripe
.
Many
electrical
components,
connectors,
fuses,
and
ground
locations
are
identified
using
a
unique
number
.
Each
of
there
numbers
corresponds
to
a
particular
part
in
the
circuit
commonly
found
in
Electrical
Wiring
Diagrams
.
Page 383 of 759

NOTE
-
Sometimes
the
color
of
en
installed
wire
may
be
differ-
ent
than
the
one
on
the
wiring
diagram
.
Don't
be
con-
cerned
.
Just
be
sure
lo
confirm
that
the
wire
connects
lo
the
proper
terminals
.
Wire
color
codes
"
BLU
.........
.
..
..
...
.
.................
Blue
"
BRN
....:....
.
..
..
...
..
...............
Brown
"
YEL
.........
.
..
..
...................
.Yellow
"
GRN
.........
.
..
..
...
.
................
creen
"
G
RY
.......
.
.
.
..
..
.....................
G
ray
"
ORG
.........
.
..
..
...
.
..............
.Orange
"
RED
......
...
.
.
..
.....................
.Red
"
BLK
.........
.
..
..
...
.
................
Black
"
VIO
..........
.
..
...
..
..
.......
.
.......
Violet
"
WHT
.........
.
.
....
.
...
:..............
White
Table
a
.
Terminal
and
Circuit
Numbers
Number
1
Circuít
description
1
j
Low
voltage
switched
terminal
of
coi¡
4
1
High
voltage
center
termina¡
of
coi¡
+x
Originates
atignition
switch
.
Supplies
powerwhen
the
ignition
switch
is
in
the
PARK,
RUN,
or
START
position
15
Originates
atignition
switch
.
Supplies
powerwhen
ignition
switch
is
in
RUN
or
START
position
30
Battery
positive
(+)
voltage
.
Supplies
power
whenever
battery
is
connected
.
(Not
dependent
on
ignition
switch
position,
unfused)
31
1
Ground,
battery
negative
(-)
terminal
50
Supplies
power
from
battery
to
starter
solenoid
when
ignition
switch
isin
START
position
only
+54
Originates
atignition
switch
.
Supplies
power
when
ignition
switch
isin
the
RUN
position
only
85
1
Ground
side
(-)
ofrelay
coil
86
1
Power-in
side
(+)
ofrelay
coil
87
1
Relay
actuatedcontact
D
Alternator
warning
light
and
field
energizing
circuit
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM-GENERAL
600-
3
Additional
abbreviations
shown
in
the
wiring
diagrams
are
given
below
.
Abbreviations
"
ABS
........
.
...
.
...
.
..........
antilock
brakes
"
A/C
........
.
...
..
..
.
.........
.airconditioning
"
AST/ASC+T
.......
...
.
.
.......
al¡
season
traction
"
CONV
.......
.
.
...
.................
convertible
"
DME
........
.
.
...
.......
digital
motor
electronics
"
ECM
.......
.
...
..
..
.
..
electronic
control
module
"
EWS/EWS
II
......
...
.
.
coded
driveaway
protection
"
SRS
........
.
supplemental
restraint
system-airbag
"
TCM
........
.
..
....
.
transmission
control
module
"
ZKE
(94-98
models)
..
..
.
...
central
body
electronics
"
ZVM
(92-93
models)
...
.
.
..
.
.......
central
locking
ELECTRICAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
Most
terminals
are
identified
by
numbers
on
the
compo-
nents
and
harness
connectors
.
The
terminal
numbers
for
ma-
Four
things
are
required
for
current
toflow
in
any
electrical
jor
electrical
connections
are
shown
in
the
diagrams
.
Though
circuit
:
a
voltagesource,
wires
or
connections
to
transport
the
many
terminal
numbers
appear
only
once,
severa¡other
num-
voltage,
a
load
or
device
that
uses
the
electricity,
and
a
con-
bers
appear
in
numerous
places
throughout
the
electrical
sys-
nection
to
ground
.
Most
problemscanbefound
using
a
digital
tem
and
identify
certain
types
ofcircuits
.
Some
of
the
most
multimeter
(volt/ohm/amp
meter)to
check
for
voltage
supply,
common
circuit
numbers
are
listed
below
in
Table
a
.
for
breaks
in
the
wiring
(infinite
resistance/no
continuity),
orfor
a
path
to
ground
that
completesthe
circuit
.
Electric
current
is
logical
in
its
flow,
always
moving
from
the
voltage
sourcetoward
ground
.
Electricalfaults
can
usually
be
located
through
a
process
of
elimination
.
When
troubleshoot-
ing
a
complex
circuit,
separate
the
circuit
into
smaller
parts
.
The
general
testsoutlined
below
may
be
helpful
in
finding
electrical
problems
.
The
information
is
most
helpful
when
used
with
the
wiring
diagrams
.
Be
sure
to
analyze
the
problem
.
Use
the
wiring
diagrams
to
determine
the
most
likely
cause
.
Getan
understanding
of
how
the
circuit
works
by
following
the
circuit
from
groundback
to
the
power
source
.
When
making
test
connections
at
connectors
andcompo-
nents,
use
care
to
avoidspreading
or
damaging
the
connec-
tors
or
terminals
.
Some
tests
may
require
jumper
wires
to
bypass
components
or
connections
in
the
wiring
harness
.
When
connecting
jumper
wires,
use
bladeconnectors
at
the
wire
ends
that
match
the
size
of
the
terminal
being
tested
.
The
small
interna¡
contacts
are
easily
spread
apart,
and
this
can
cause
intermittent
or
faultyconnections
that
can
leadto
more
problems
.
ELECTRICAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 386 of 759
00-
6
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM-GENERAL
Short
circuit,
testing
with
ohmmeter
Short
circuit,
testing
with
voltmeter
1
.
Remove
blown
fuse
from
circuit
and
disconnect
cables
1
.
Remove
blown
fusefrom
circuit
.
from
battery
.
2
.
Disconnect
harness
connector
from
circuifs
loador
2
.
Disconnect
harness
connector
from
circuit's
loador
consumer
.
consumer
.
3
.
Using
an
ohmmeter,
connect
one
test
lead
to
loadside
of
f
use
terminal
(terminal
leading
to
circuit)
and
the
oth-
ertest
lead
to
ground
.
See
Fig
.
4
.
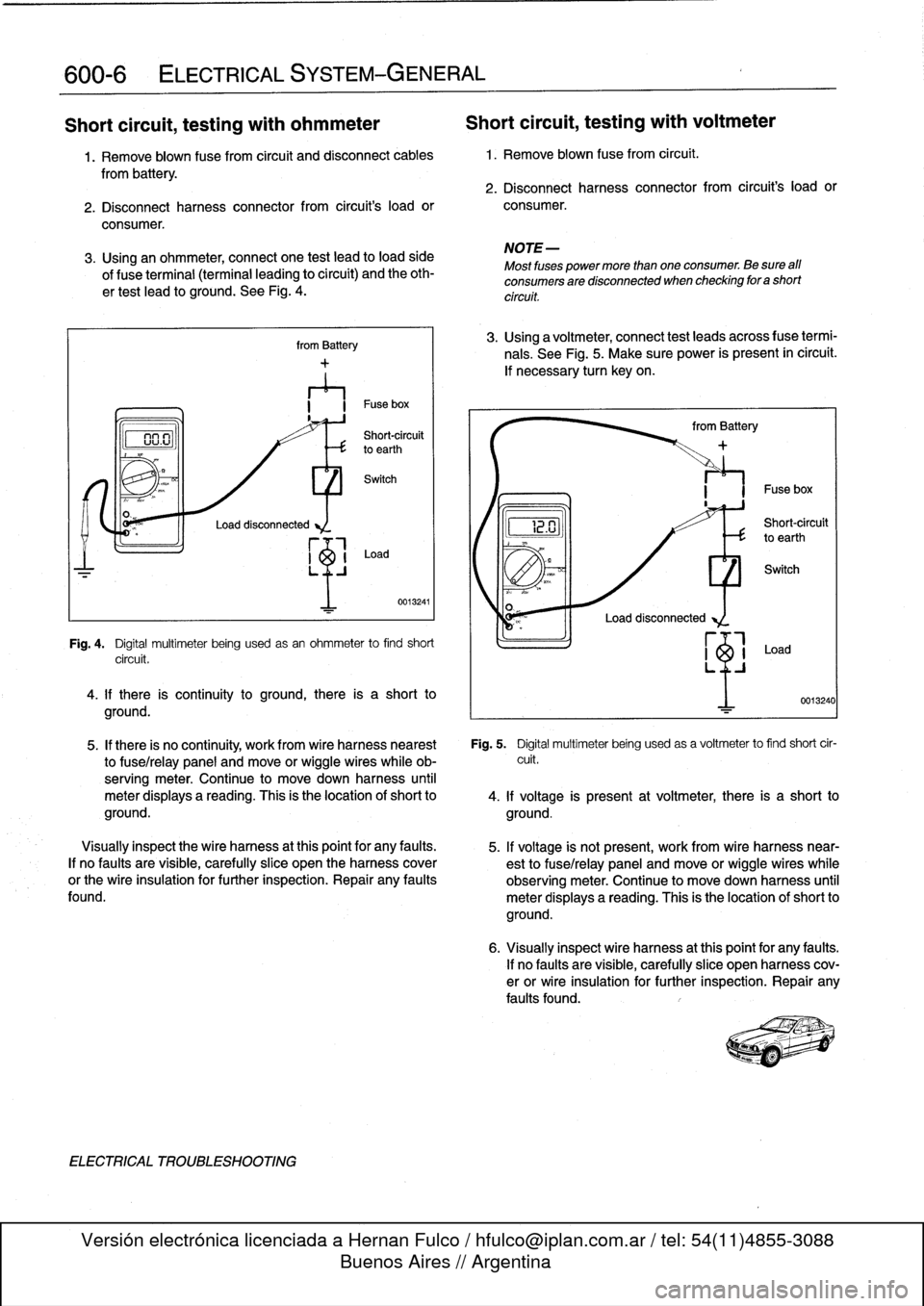
Load
disconnected
from
Battery
LO
n
I
~
Shotrouit
vu
.uto
earthth
Switch
Load
0013241
Fig
.
4
.
Digital
multimeter
being
usedasan
ohmmeter
to
find
short
circuit
.
4
.
lf
there
is
continuity
to
ground,
there
is
a
short
to
ground
.
ELECTRICAL
TROUBLESHOOTING
NOTE-
Most
fuses
power
more
than
one
consumer
.
Be
sure
aff
consumers
are
disconnected
when
checking
for
a
short
circuit
.
3
.
Using
a
voltmeter,
connect
test
leads
across
f
use
termi-
nals
.
See
Fig
.
5
.
Make
sure
power
is
present
ín
circuit
.
lf
necessary
turn
keyon
.
~2
.U
from
Battery
Load
disconnected
Short-circuit
to
earth
I
Fuse
box
0013240
5
.
If
there
is
no
continuity,
work
from
wire
harness
hearest
Fig
.
5
.
Digital
multimeter
being
usedas
a
voltmeter
to
find
short
cir
to
fuse/relay
panel
and
move
or
wiggle
wireswhile
ob-
cuit
.
serving
meter
.
Continue
to
movedown
harness
until
meter
displays
a
reading
.
This
is
the
location
of
short
to
4
.
lf
voltage
is
present
at
voltmeter,
there
is
a
short
to
ground
.
ground
.
Visually
inspect
the
wire
harness
at
this
point
for
any
faults
.
5
.
lf
voltage
is
not
present,
work
from
wire
harness
near-
If
no
faults
are
visible,
carefully
slice
open
the
harnesscover
est
to
fuse/relay
panel
and
move
orwiggle
wireswhile
or
the
wire
insulation
for
further
inspection
.
Repair
any
faults
observing
meter
.
Continue
to
move
down
harness
until
found
.
meter
displays
a
reading
.
This
is
the
location
of
short
to
ground
.
6
.
Visually
inspect
wire
harness
atthis
point
for
any
faults
.
lf
no
faults
are
visible,
carefully
slice
open
harness
cov-
erorwire
insulation
for
further
inspection
.
Repair
any
faults
found
.
Page 390 of 759
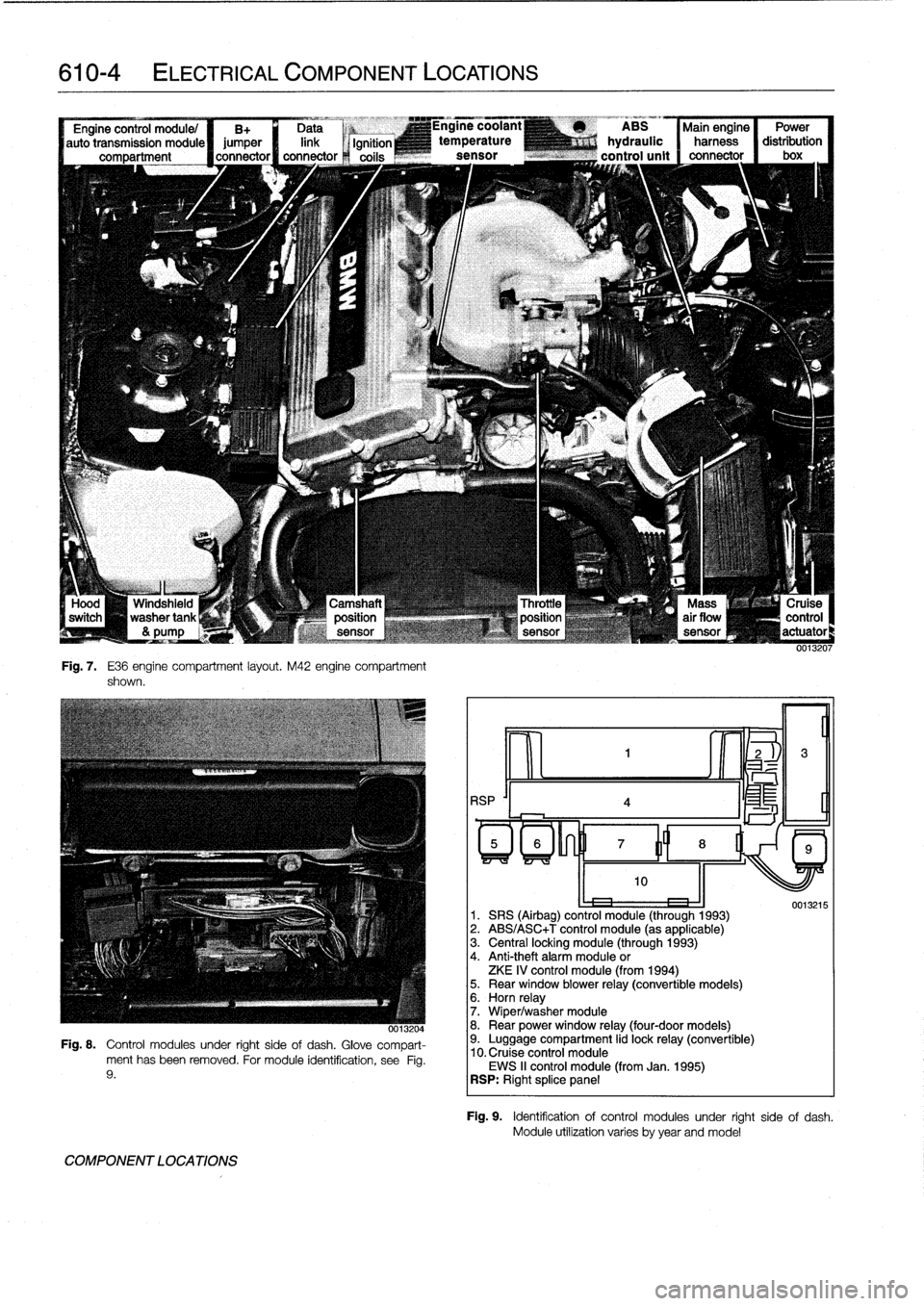
610-4
ELECTRICAL
COMPONENT
LOCATIONS
--J
L
Windshield
washertank
&
pump
Fig
.
7
.
E36
engine
compartment
layout
.
M42
engine
compartment
shown
.
-,x
0013204
Fig
.
8
.
Control
modules
under
right
sideof
dash
.
Glove
compart-
ment
has
been
removed
.
For
module
identification,
see
Fig
.
9
.
COMPONENT
LOCATIONS
RSP
'I
4
ABS
Main
engine
Power
hydraulic
harness
distribution
control
unit
connector
I
box
oe
1
.
SRS
(Airbag)
control
module
(through
1993)
2
.
ABS/ASC+T
control
module
(as
applicable)
3
.
Central
locking
module
(through
1993)
4
.
Anti-theft
alarm
module
or
ZKE
IV
control
module
(from
1994)5
.
Rear
window
blower
relay
(convertible
models)6
.
Horn
relay
7
.
Wiper/washer
module
8
.
Rear
power
window
relay
(four-door
models)9
.
Luggage
compartment
lid
lock
relay
(convertible)
10
.
Cruise
control
module
EWS
II
control
module
(from
Jan
.
1995)
RSP
:
Right
splice
panel
0013215
Fig
.
9
.
Identificationof
control
modules
under
right
side
of
dash
.
Module
utilízation
varies
byyear
andmodel
Page 391 of 759
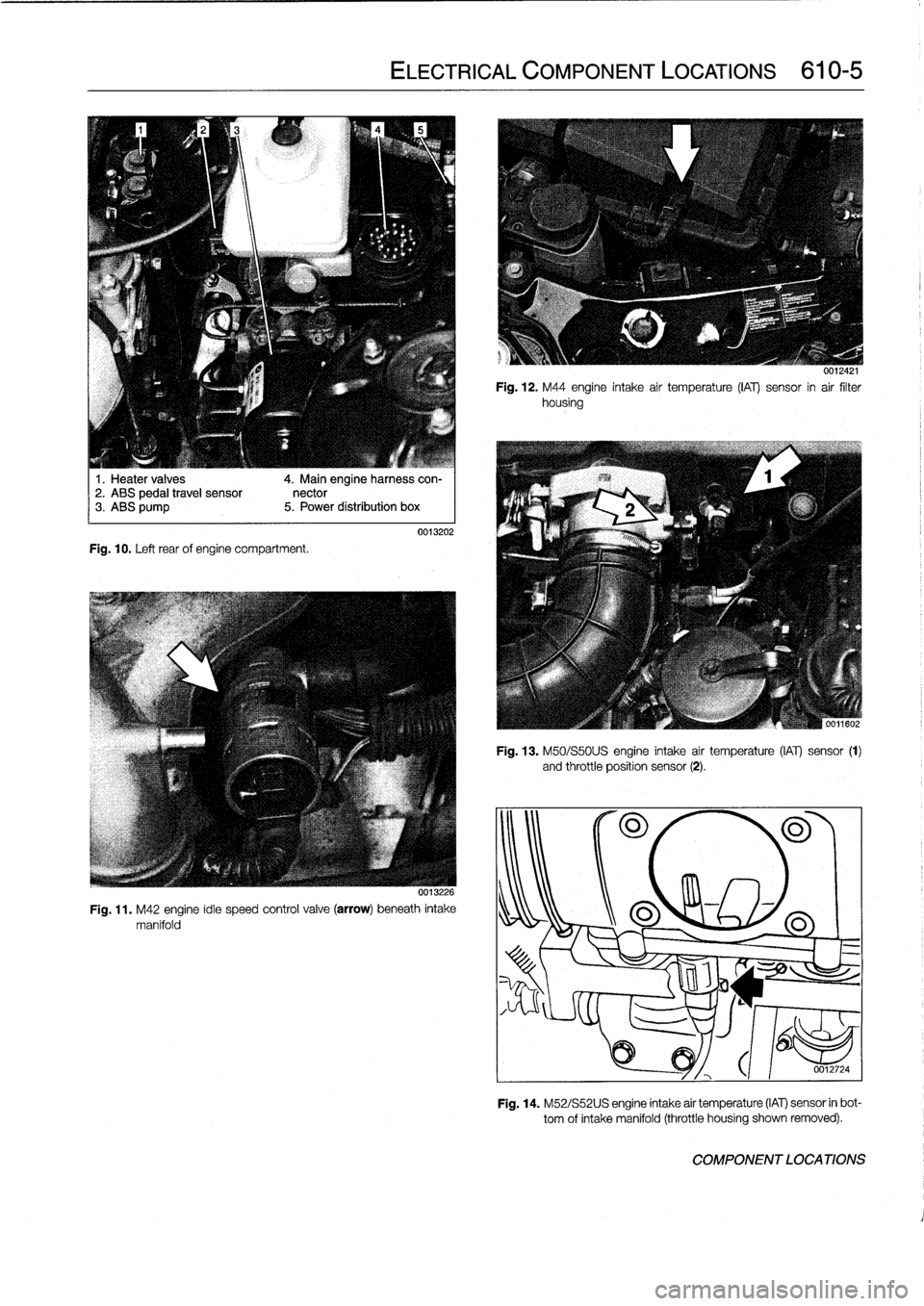
1
.
Heater
valves
2
.
ABS
pedal
travel
sensor3
.
ABS
pump
Fig
.
10
.
Left
rear
of
engine
compartment
.
4
.
Main
engineharness
con-
nector
5
.
Power
distribution
box
ELECTRICAL
COMPONENT
LOCATIONS
610-5
0013202
0013226
Fig
.
11
.
M42
engine
idie
speed
control
valve
(arrow)
beneath
intake
manifold
0012421
Fig
.
12
.
M44
engine
intake
air
temperature
(¡Al)
sensor
in
air
filter
housing
Fig
.
13
.
M50/S50U
S
engine
intake
air
temperature
(IAT)
sensor
(1)
and
throttle
position
sensor
(2)
.
301180
0012724
Fig
.
14
.
M52/S52U
S
engine
intake
air
temperature
(IAT)
sensor
in
bot-
tom
of
intake
manifold
(throttle
housing
shown
removed)
.
COMPONENT
LOCATIONS