Rear ac CADILLAC DEVILLE 2001 8.G User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CADILLAC, Model Year: 2001, Model line: DEVILLE, Model: CADILLAC DEVILLE 2001 8.GPages: 397, PDF Size: 3.02 MB
Page 40 of 397

1-28
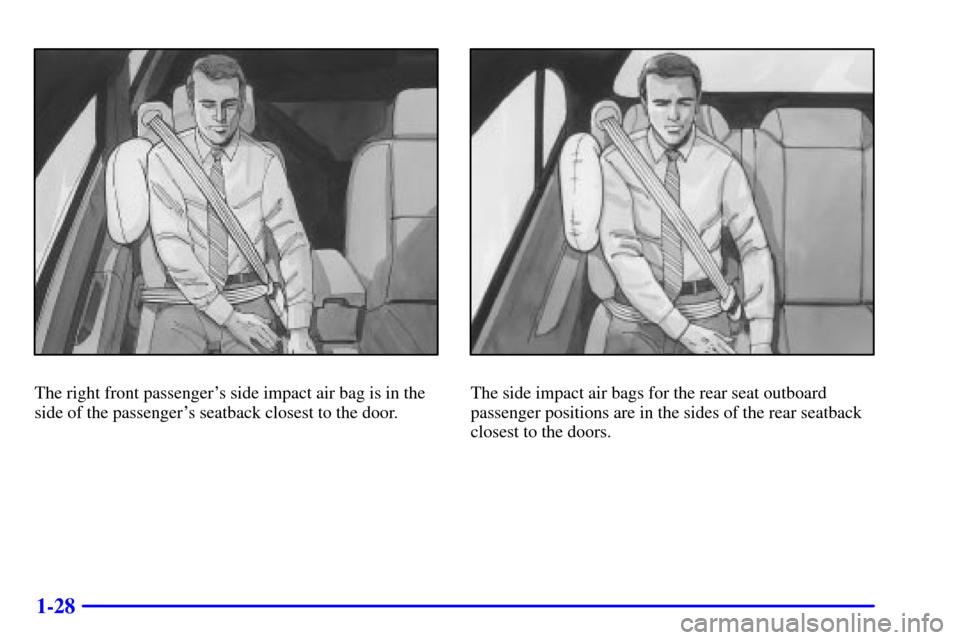
The right front passenger's side impact air bag is in the
side of the passenger's seatback closest to the door.The side impact air bags for the rear seat outboard
passenger positions are in the sides of the rear seatback
closest to the doors.
Page 41 of 397

1-29
CAUTION:
If something is between an occupant and an
air bag, the bag might not inflate properly or it
might force the object into that person. The path
of an inflating air bag must be kept clear. Don't
put anything between an occupant and an air
bag, and don't attach or put anything on the
steering wheel hub or on or near any other air
bag covering and don't let seat covers block
the inflation path of a side impact air bag.
When should an air bag inflate?
The driver's and right front passenger's frontal air bags
are designed to inflate in moderate to severe frontal or
near
-frontal crashes. But they are designed to inflate
only if the impact speed is above the system's designed
ªthreshold level.º
In addition, your vehicle has ªdual stageº frontal air
bags, which tailor the amount of restraint according to
crash severity. For moderate frontal impacts, these air
bags inflate at a level less than full deployment. For more severe frontal impacts, full deployment occurs.
If the front of your vehicle goes straight into a wall
that doesn't move or deform, the threshold level
for the reduced deployment is about 10 to 16 mph
(16 to 26 km/h), and the threshold level for a full
deployment is about 18 to 24 mph (29 to 38.5 km/h).
The threshold level can vary, however, with specific
vehicle design, so that it can be somewhat above or
below this range.
If your vehicle strikes something that will move or
deform, such as a parked car, the threshold level will be
higher. The driver's and right front passenger's frontal
air bags are not designed to inflate in rollovers, side
impacts, or rear impacts, because inflation would not
help the occupant.
The side impact air bags are designed to inflate in
moderate to severe side crashes. A side impact air bag
will inflate if the crash severity is above the system's
designed ªthreshold level.º The threshold level can vary
with specific vehicle design. Side impact air bags are not
designed to inflate in frontal or near
-frontal impacts,
rollovers or rear impacts, because inflation would not
help the occupant. A side impact air bag will only
deploy on the side of the vehicle that is struck.
Page 42 of 397

1-30
In any particular crash, no one can say whether an air
bag should have inflated simply because of the damage
to a vehicle or because of what the repair costs were. For
frontal air bags, inflation is determined by the angle of
the impact and how quickly the vehicle slows down in
frontal and near
-frontal impacts. For side impact air
bags, inflation is determined by the location and severity
of the impact.
What makes an air bag inflate?
In an impact of sufficient severity, the air bag sensing
system detects that the vehicle is in a crash. For both
frontal and side impact air bags, the sensing system
triggers a release of gas from the inflator, which inflates
the air bag. The inflator, air bag and related hardware are
all part of the air bag modules inside the steering wheel,
instrument panel and the side of the front seatbacks and
behind the rear seatbacks closest to the door.
How does an air bag restrain?
In moderate to severe frontal or near frontal collisions,
even belted occupants can contact the steering wheel or
the instrument panel. In moderate to severe side
collisions, even belted occupants can contact the inside
of the vehicle. The air bag supplements the protection
provided by safety belts. Air bags distribute the force of
the impact more evenly over the occupant's upper body,
stopping the occupant more gradually. But the frontal air bags would not help you in many
types of collisions, including rollovers, rear impacts, and
side impacts, primarily because an occupant's motion is
not toward the air bag. Side impact air bags would not
help you in many types of collisions, including frontal
or near frontal collisions, rollovers, and rear impacts,
primarily because an occupant's motion is not toward
those air bags. Air bags should never be regarded as
anything more than a supplement to safety belts, and
then only in moderate to severe frontal or near
-frontal
collisions for the driver's and right front passenger's
frontal air bags, and only in moderate to severe side
collisions for the side impact air bags.
What will you see after an air bag inflates?
After an air bag inflates, it quickly deflates, so quickly that
some people may not even realize the air bag inflated.
Some components of the air bag module
-- the steering
wheel hub for the driver's air bag, the instrument panel for
the right front passenger's bag, the side of the seatback
closest to the door for the side impact air bags
-- will be
hot for a short time. The parts of the bag that come into
contact with you may be warm, but not too hot to touch.
There will be some smoke and dust coming from the vents
in the deflated air bags. Air bag inflation doesn't prevent
the driver from seeing or being able to steer the vehicle,
nor does it stop people from leaving the vehicle.
Page 44 of 397

1-32
NOTICE:
If you damage the covering for the driver's or
the right front passenger's air bag, or the air bag
covering on the driver's, right front passenger's
or rear seatback, the bag may not work properly.
You may have to replace the air bag module
in the steering wheel, both the air bag module
and the instrument panel for the right front
passenger's air bag, or both the air bag module
and seatback for the side impact air bag. Do not
open or break the air bag coverings.
Servicing Your Air Bag-Equipped Vehicle
Air bags affect how your vehicle should be serviced.
There are parts of the air bag systems in several places
around your vehicle. Your dealer and the service manual
have information about servicing your vehicle and
the air bag systems. To purchase a service manual,
see ªService and Owner Publicationsº in the Index.
CAUTION:
For up to 10 seconds after the ignition key is
turned off and the battery is disconnected, an air
bag can still inflate during improper service. You
can be injured if you are close to an air bag when
it inflates. Avoid yellow connectors. They are
probably part of the air bag systems. Be sure to
follow proper service procedures, and make sure
the person performing work for you is qualified
to do so.
The air bag systems do not need regular maintenance.
Page 46 of 397
1-34
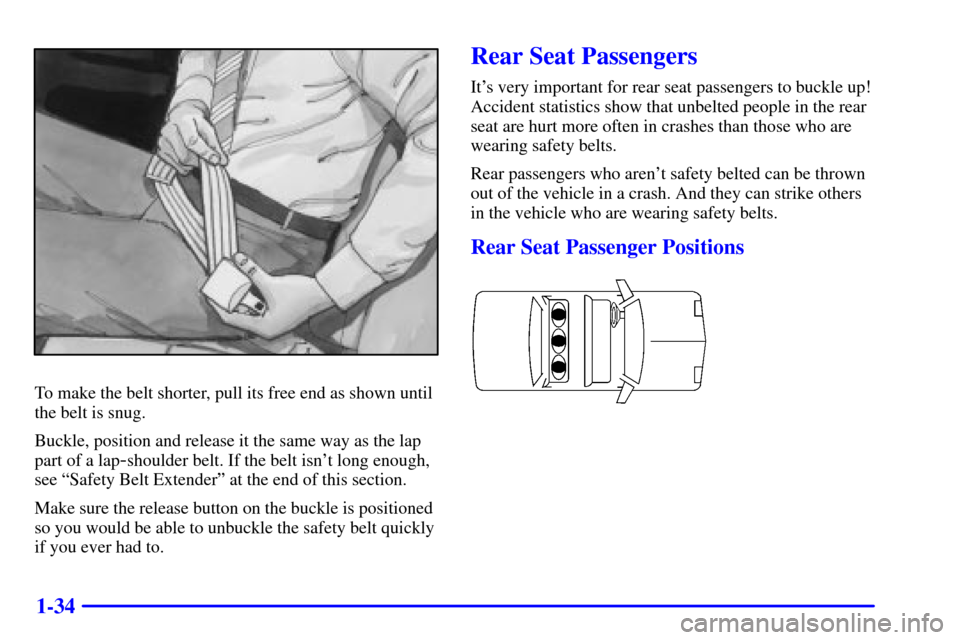
To make the belt shorter, pull its free end as shown until
the belt is snug.
Buckle, position and release it the same way as the lap
part of a lap
-shoulder belt. If the belt isn't long enough,
see ªSafety Belt Extenderº at the end of this section.
Make sure the release button on the buckle is positioned
so you would be able to unbuckle the safety belt quickly
if you ever had to.
Rear Seat Passengers
It's very important for rear seat passengers to buckle up!
Accident statistics show that unbelted people in the rear
seat are hurt more often in crashes than those who are
wearing safety belts.
Rear passengers who aren't safety belted can be thrown
out of the vehicle in a crash. And they can strike others
in the vehicle who are wearing safety belts.
Rear Seat Passenger Positions
Page 47 of 397
1-35
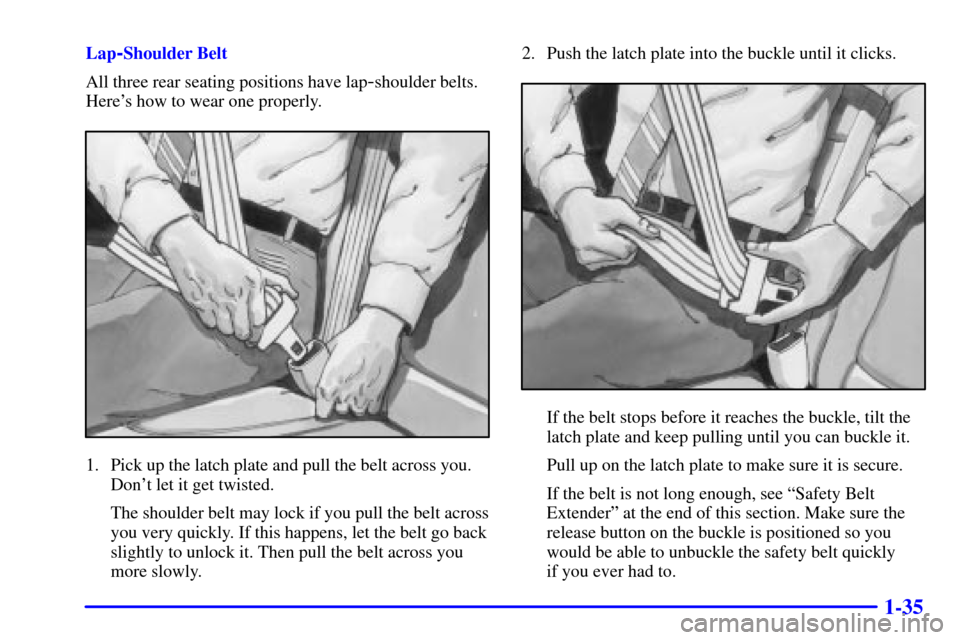
Lap-Shoulder Belt
All three rear seating positions have lap
-shoulder belts.
Here's how to wear one properly.
1. Pick up the latch plate and pull the belt across you.
Don't let it get twisted.
The shoulder belt may lock if you pull the belt across
you very quickly. If this happens, let the belt go back
slightly to unlock it. Then pull the belt across you
more slowly.2. Push the latch plate into the buckle until it clicks.
If the belt stops before it reaches the buckle, tilt the
latch plate and keep pulling until you can buckle it.
Pull up on the latch plate to make sure it is secure.
If the belt is not long enough, see ªSafety Belt
Extenderº at the end of this section. Make sure the
release button on the buckle is positioned so you
would be able to unbuckle the safety belt quickly
if you ever had to.
Page 50 of 397
1-38
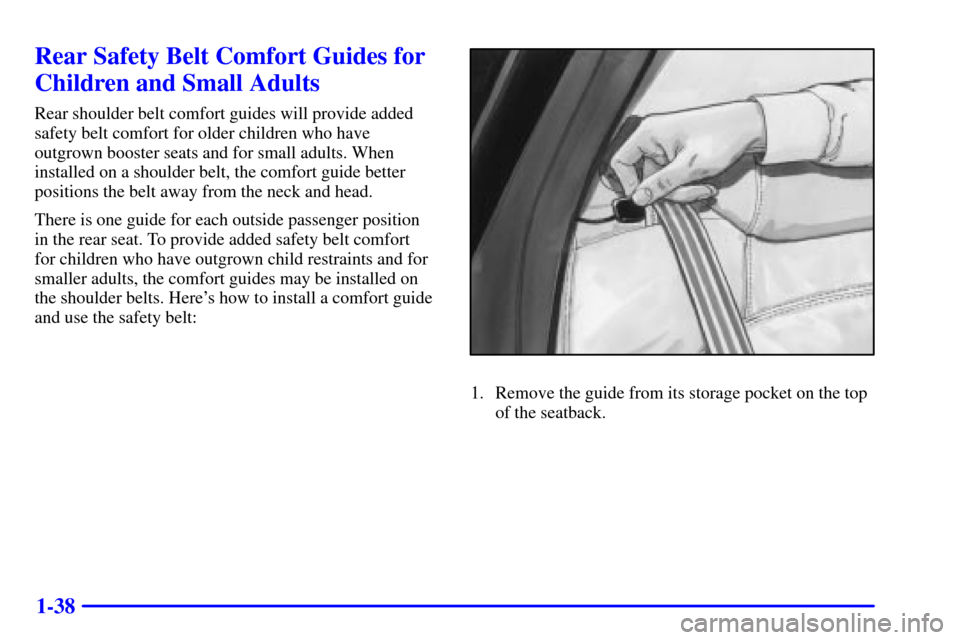
Rear Safety Belt Comfort Guides for
Children and Small Adults
Rear shoulder belt comfort guides will provide added
safety belt comfort for older children who have
outgrown booster seats and for small adults. When
installed on a shoulder belt, the comfort guide better
positions the belt away from the neck and head.
There is one guide for each outside passenger position
in the rear seat. To provide added safety belt comfort
for children who have outgrown child restraints and for
smaller adults, the comfort guides may be installed on
the shoulder belts. Here's how to install a comfort guide
and use the safety belt:
1. Remove the guide from its storage pocket on the top
of the seatback.
Page 52 of 397

1-40
4. Buckle, position and release the safety belt as
described in ªRear Seat Passenger Positionsº earlier
in this section. Make sure that the shoulder belt
crosses the shoulder.
To remove and store the comfort guides, squeeze the
belt edges together so that you can take them out from
the guides. Slide the guide into its storage pocket on the
top of the seatback.
Children
Everyone in a vehicle needs protection! This includes
infants and all other children. Neither the distance
traveled nor the age and size of the traveler changes
the need, for everyone, to use safety restraints. In fact,
the law in every state in the United States and in every
Canadian province says children up to some age must
be restrained while in a vehicle.
Infants and Young Children
Every time infants and young children ride in vehicles,
they should have the protection provided by the
appropriate restraint. Young children should not use
the vehicle's safety belts, unless there is no other choice.
Page 55 of 397

1-43
CAUTION:
Newborn infants need complete support,
including support for the head and neck. This
is necessary because a newborn infant's neck is
weak and its head weighs so much compared
with the rest of its body. In a crash, an infant in
a rear
-facing seat settles into the restraint, so
the crash forces can be distributed across the
strongest part of an infant's body, the back and
shoulders. Infants always should be secured in
appropriate infant restraints.
CAUTION:
The body structure of a young child is quite
unlike that of an adult or older child, for whom
the safety belts are designed. A young child's hip
bones are still so small that vehicle's regular
safety belt may not remain low on the hip bones,
as it should. Instead, it may settle up around the
child's abdomen. In a crash, the belt would apply
force on a body area that's unprotected by any
bony structure. This alone could cause serious
or fatal injuries. Young children always should
be secured in appropriate child restraints.
Page 56 of 397
1-44
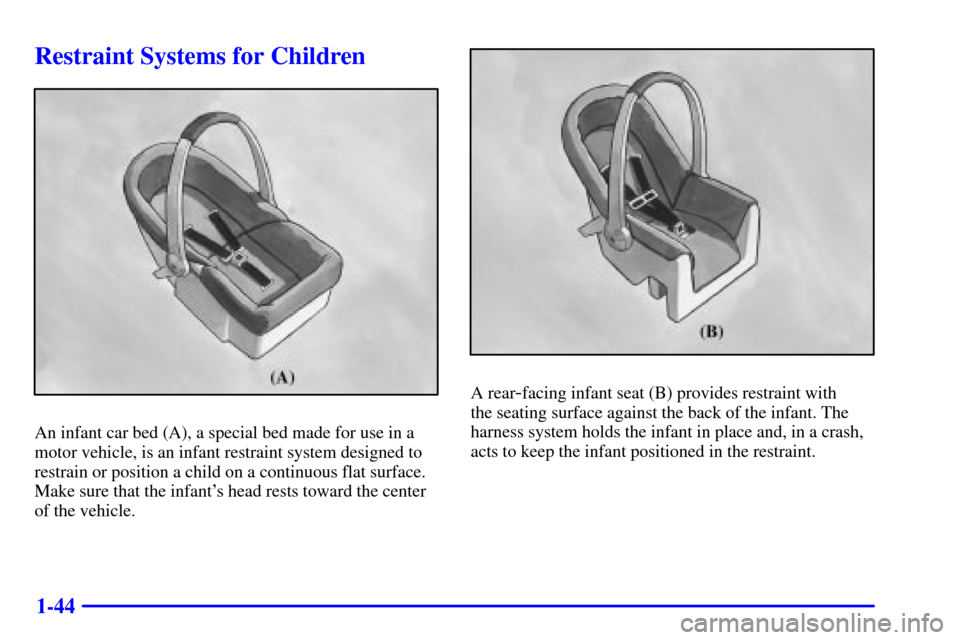
Restraint Systems for Children
An infant car bed (A), a special bed made for use in a
motor vehicle, is an infant restraint system designed to
restrain or position a child on a continuous flat surface.
Make sure that the infant's head rests toward the center
of the vehicle.
A rear-facing infant seat (B) provides restraint with
the seating surface against the back of the infant. The
harness system holds the infant in place and, in a crash,
acts to keep the infant positioned in the restraint.