width CADILLAC ESCALADE ESV 2011 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CADILLAC, Model Year: 2011, Model line: ESCALADE ESV, Model: CADILLAC ESCALADE ESV 2011Pages: 548, PDF Size: 8.45 MB
Page 83 of 548
Black plate (27,1)Cadillac Escalade/Escalade ESV Owner Manual - 2011
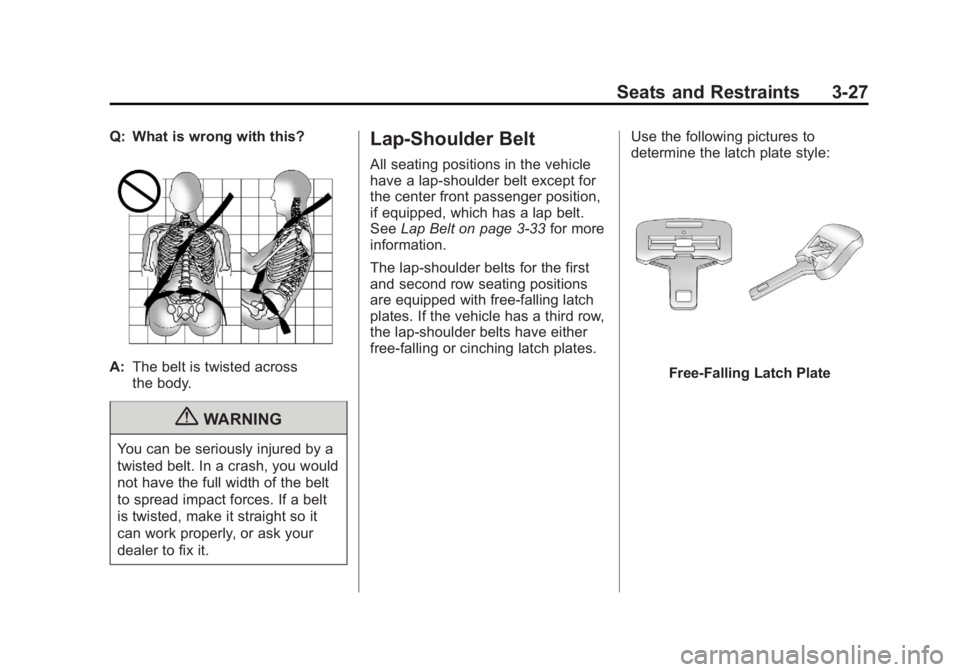
Seats and Restraints 3-27Q: What is wrong with this?
A: The belt is twisted across
the body.
{ WARNING
You can be seriously injured by a
twisted belt. In a crash, you would
not have the full width of the belt
to spread impact forces. If a belt
is twisted, make it straight so it
can work properly, or ask your
dealer to fix it. Lap-Shoulder Belt All seating positions in the vehicle
have a lap-shoulder belt except for
the center front passenger position,
if equipped, which has a lap belt.
See Lap Belt on page 3 ‑ 33 for more
information.
The lap ‐ shoulder belts for the first
and second row seating positions
are equipped with free ‐ falling latch
plates. If the vehicle has a third row,
the lap ‐ shoulder belts have either
free ‐ falling or cinching latch plates. Use the following pictures to
determine the latch plate style:
Free-Falling Latch Plate
Page 336 of 548

Black plate (16,1)Cadillac Escalade/Escalade ESV Owner Manual - 2011
9-16 Driving and Operating But when driving across an
incline, the narrower track
width — the distance between
the left and right wheels — might
not prevent the vehicle from
tilting and rolling over. Driving
across an incline puts more
weight on the downhill wheels
which could cause a downhill
slide or a rollover. .
Surface conditions can be a
problem. Loose gravel, muddy
spots, or even wet grass can
cause the tires to slip sideways,
downhill. If the vehicle slips
sideways, it can hit something
that will trip it — a rock, a rut,
etc. — and roll over..
Hidden obstacles can make the
steepness of the incline even
worse. If you drive across a rock
with the uphill wheels, or if the
downhill wheels drop into a rut
or depression, the vehicle can tilt
even more. For these reasons, carefully
consider whether to try to drive
across an incline. Just because the
trail goes across the incline does
not mean you have to drive it. The
last vehicle to try it might have
rolled over.
If you feel the vehicle starting to
slide sideways, turn downhill.
This should help straighten out
the vehicle and prevent the side
slipping. The best way to prevent
this is to “ walk the course ” first, so
you know what the surface is like
before driving it. Stalling on an Incline
{ WARNINGGetting out on the downhill (low)
side of a vehicle stopped across
an incline is dangerous. If the
vehicle rolls over, you could be
crushed or killed. Always get out
on the uphill (high) side of the
vehicle and stay well clear of the
rollover path.
If the vehicle stalls when crossing
an incline, be sure you, and any
passengers, get out on the uphill
side, even if the door there is
harder to open. If you get out on
the downhill side and the vehicle
starts to roll over, you will be right in
its path.
If you have to walk down the slope,
stay out of the path the vehicle will
take if it does roll over.
Page 437 of 548

Black plate (35,1)Cadillac Escalade/Escalade ESV Owner Manual - 2011
Vehicle Care 10-353. Record the distance from the
ground to the center of the
projector lens of the low ‐ beam
headlamp.
4. At a wall, measure from the
ground upward (A) to the
recorded distance from
Step 3 and mark it.
5. Draw or tape a horizontal line (B)
on the wall the width of the
vehicle at the height of the mark
in Step 4.
Notice: Do not cover a headlamp
to improve beam cut-off when
aiming. Covering a headlamp may
cause excessive heat build-up
which may cause damage to the
headlamp. 6. Turn on the low-beam
headlamps and place a piece
of cardboard or equivalent in
front of the headlamp not being
adjusted. This allows only the
beam of light from the headlamp
being adjusted to be seen on the
flat surface.
7. Locate the vertical headlamp
aiming screws, which are under
the hood near each headlamp
assembly. 8. Turn the vertical aiming screw
until the headlamp beam is
aimed to the horizontal tape
line. Turn it clockwise or
counterclockwise to raise or
lower the angle of the beam.
9. Make sure that the light from
the headlamp is positioned
at the bottom edge of the
horizontal tape line. The lamp
on the left (A) shows the correct
headlamp aim. The lamp on the
right (B) shows the incorrect
headlamp aim.
10. Repeat Steps 7 through 9 for
the opposite headlamp.
Page 450 of 548

Black plate (48,1)Cadillac Escalade/Escalade ESV Owner Manual - 2011
10-48 Vehicle Care
Tire Sidewall Labeling Useful information about a tire is
molded into the sidewall. The
following illustration is an
example of a typical P ‐ Metric
tire sidewall.
Passenger (P ‐ Metric) Tire
(A) Tire Size :
The tire size
code is a combination of letters
and numbers used to define a
particular tire's width, height,
aspect ratio, construction type, and service description. See the
“ Tire Size ” illustration later in this
section for more detail.
(B) TPC Spec (Tire
Performance Criteria
Specification) :
Original
equipment tires designed to
GM's specific tire performance
criteria have a TPC specification
code molded onto the sidewall.
GM's TPC specifications meet
or exceed all federal safety
guidelines.
(C) DOT (Department of
Transportation) :
The
Department of Transportation
(DOT) code indicates that
the tire is in compliance with
the U.S. Department of
Transportation Motor Vehicle
Safety Standards. (D) Tire Identification Number
(TIN) :
The letters and numbers
following DOT code are the Tire
Identification Number (TIN). The
TIN shows the manufacturer
and plant code, tire size, and
date the tire was manufactured.
The TIN is molded onto both
sides of the tire, although only
one side may have the date of
manufacture.
(E) Tire Ply Material :
The type
of cord and number of plies in
the sidewall and under the tread.
(F) Uniform Tire Quality
Grading (UTQG) :
Tire
manufacturers are required
to grade tires based on
three performance factors:
treadwear, traction, and
temperature resistance. For
more information, see Uniform
Tire Quality Grading on
page 10 ‑ 63 .
Page 451 of 548

Black plate (49,1)Cadillac Escalade/Escalade ESV Owner Manual - 2011
Vehicle Care 10-49(G) Maximum Cold Inflation
Load Limit :
Maximum load
that can be carried and the
maximum pressure needed
to support that load. For
information on recommended
tire pressure see Tire Pressure
on page 10 ‑ 52 and Vehicle Load
Limits on page 9 ‑ 24 .
Tire Designations Tire Size
The following examples show
the different parts of a tire size.
Passenger (P ‐ Metric) Tire
(A) Passenger (P ‐ Metric) Tire :
The United States version of a
metric tire sizing system. The
letter P as the first character in the tire size means a passenger
vehicle tire engineered to
standards set by the U.S. Tire
and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width :
The three ‐ digit
number indicates the tire section
width in millimeters from
sidewall to sidewall.
(C) Aspect Ratio :
A two ‐ digit
number that indicates the tire
height ‐ to ‐ width measurements.
For example, if the tire size
aspect ratio is 75, as shown
in item C of the light truck
(LT ‐ Metric) tire illustration, it
would mean that the tire's
sidewall is 75% as high as it
is wide.
(D) Construction Code :
A
letter code is used to indicate
the type of ply construction in
the tire. The letter R means
radial ply construction; the
letter D means diagonal or bias ply construction; and the
letter B means belted ‐ bias ply
construction.
(E) Rim Diameter :
Diameter of
the wheel in inches.
(F) Service Description :
These
characters represent the load
index and speed rating of the
tire. The load index represents
the load carrying capacity a tire
is certified to carry. The speed
rating is the maximum speed a
tire is certified to carry a load.
Tire Terminology and
Definitions Air Pressure :
The amount
of air inside the tire pressing
outward on each square inch
of the tire. Air pressure is
expressed in kPa (kilopascal)
or psi (pounds per square inch).
Page 452 of 548

Black plate (50,1)Cadillac Escalade/Escalade ESV Owner Manual - 2011
10-50 Vehicle Care Accessory Weight :
The
combined weight of optional
accessories. Some examples
of optional accessories are
automatic transmission, power
steering, power brakes, power
windows, power seats, and air
conditioning.
Aspect Ratio :
The relationship
of a tire's height to its width.
Belt :
A rubber coated layer of
cords that is located between
the plies and the tread. Cords
may be made from steel or other
reinforcing materials.
Bead :
The tire bead contains
steel wires wrapped by steel
cords that hold the tire onto
the rim.
Bias Ply Tire :
A pneumatic tire
in which the plies are laid at
alternate angles less than
90 degrees to the centerline of
the tread. Cold Tire Pressure :
The
amount of air pressure in a tire,
measured in kPa (kilopascal)
or psi (pounds per square inch)
before a tire has built up heat
from driving. See Tire Pressure
on page 10 ‑ 52 .
Curb Weight :
The weight of a
motor vehicle with standard and
optional equipment including
the maximum capacity of fuel,
oil, and coolant, but without
passengers and cargo.
DOT Markings :
A code
molded into the sidewall of
a tire signifying that the tire
is in compliance with the U.S.
Department of Transportation
(DOT) Motor Vehicle Safety
Standards. The DOT code
includes the Tire Identification
Number (TIN), an alphanumeric
designator which can also identify the tire manufacturer,
production plant, brand, and
date of production.
GVWR :
Gross Vehicle Weight
Rating. See Vehicle Load Limits
on page 9 ‑ 24 .
GAWR FRT :
Gross Axle Weight
Rating for the front axle. See
Vehicle Load Limits on
page 9 ‑ 24 .
GAWR RR :
Gross Axle Weight
Rating for the rear axle. See
Vehicle Load Limits on
page 9 ‑ 24 .
Intended Outboard Sidewall :
The side of an asymmetrical tire,
that must always face outward
when mounted on a vehicle.
Kilopascal (kPa) :
The metric
unit for air pressure.
Light Truck (LT ‐ Metric) Tire :
A
tire used on light duty trucks and
some multipurpose passenger
vehicles.
Page 465 of 548

Black plate (63,1)Cadillac Escalade/Escalade ESV Owner Manual - 2011
Vehicle Care 10-63
{ WARNINGIf different sized wheels are used,
there may not be an acceptable
level of performance and safety
if tires not recommended for
those wheels are selected. This
increases the chance of a crash
and serious injury. Only use GM
specific wheel and tire systems
developed for the vehicle, and
have them properly installed by a
GM certified technician.
See Buying New Tires on
page 10 ‑ 61 and Accessories and
Modifications on page 10 ‑ 3 for
additional information. Uniform Tire Quality
Grading Quality grades can be found
where applicable on the tire
sidewall between tread shoulder
and maximum section width. For
example:
Treadwear 200 Traction AA
Temperature A
The following information relates
to the system developed by the
United States National Highway
Traffic Safety Administration
(NHTSA), which grades tires
by treadwear, traction, and
temperature performance. This
applies only to vehicles sold in
the United States. The grades
are molded on the sidewalls
of most passenger car tires. The
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
(UTQG) system does not apply to deep tread, winter-type snow
tires, space-saver, or temporary
use spare tires, tires with
nominal rim diameters of
10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm),
or to some limited-production
tires.
While the tires available on
General Motors passenger cars
and light trucks may vary with
respect to these grades, they
must also conform to federal
safety requirements and
additional General Motors Tire
Performance Criteria (TPC)
standards.
All Passenger Car Tires Must
Conform to Federal Safety
Requirements In Addition To
These Grades.
Page 467 of 548

Black plate (65,1)Cadillac Escalade/Escalade ESV Owner Manual - 2011
Vehicle Care 10-65
Wheel Alignment and Tire
Balance The tires and wheels were aligned
and balanced at the factory to
provide the longest tire life and best
overall performance. Adjustments to
wheel alignment and tire balancing
will not be necessary on a regular
basis. However, check the
alignment if there is unusual tire
wear or if the vehicle is pulling to
one side or the other. If the vehicle
vibrates when driving on a smooth
road, the tires and wheels might
need to be rebalanced. See your
dealer for proper diagnosis.
Wheel Replacement Replace any wheel that is bent,
cracked, or badly rusted or
corroded. If wheel nuts keep
coming loose, the wheel, wheel
bolts, and wheel nuts should be
replaced. If the wheel leaks air,
replace it. Some aluminum wheels
can be repaired. See your dealer if
any of these conditions exist. Your dealer will know the kind of
wheel that is needed.
Each new wheel should have the
same load-carrying capacity,
diameter, width, offset, and be
mounted the same way as the
one it replaces.
Replace wheels, wheel bolts, wheel
nuts, or Tire Pressure Monitor
System (TPMS) sensors with new
GM original equipment parts.
{ WARNINGUsing the wrong replacement
wheels, wheel bolts, or wheel
nuts can be dangerous. It could
affect the braking and handling of
the vehicle. Tires can lose air,
and cause loss of control, causing
a crash. Always use the correct
wheel, wheel bolts, and wheel
nuts for replacement. Notice: The wrong wheel can
also cause problems with
bearing life, brake cooling,
speedometer or odometer
calibration, headlamp aim,
bumper height, vehicle ground
clearance, and tire or tire chain
clearance to the body and
chassis.
See If a Tire Goes Flat on
page 10 ‑ 66 for more information.
Used Replacement Wheels
{ WARNINGReplacing a wheel with a used
one is dangerous. How it has
been used or how far it has been
driven may be unknown. It could
fail suddenly and cause a crash.
When replacing wheels, use a
new GM original equipment
wheel.