oil type CHERY TIGGO 2009 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHERY, Model Year: 2009, Model line: TIGGO, Model: CHERY TIGGO 2009Pages: 1903, PDF Size: 33.38 MB
Page 32 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
The 1.6L & 1.8L in-line four cylinder engines have the following features:
•Dual overhead camshafts
• Four valves per cylinder
• Aluminum cylinder head
• Cast iron cylinder block (1.8L Engine)
• Aluminum cylinder block (1.6L Engine)
Operation
The 1.6L & 1.8L engines utilize 4 valve-per-cylinder and a dual overhead camshaft design. The engines use an indi-
vidual coil ignition system. The 1.6L engine uses an aluminum cylinder block, and the 1.8L engine is made of cast
iron. The bearing caps are integrated into the lower cylinder block assembly. An aluminum oil pan bolts to the bottom
of the lower cylinder block. The camshafts are mounted in the cylinder head and act against valve tappets to open
and close the valves. The camshafts are driven off the front of the cylinder head by one timing belt. The belt is driven
by a sprocket that is located on the crankshaft. The piston assembly is an aluminum piston with a cast iron con-
necting rod.
The aluminum cylinder head contains dual overhead camshafts with 4 valve-per-cylinder construction. The valves are
arranged in two in-line banks. The cylinder head incorporates powdered metal valve guides and seats. The cylinder
head is sealed to the block using a multi-layer steel head gasket and retaining bolts.
Specifications
1.6L Engine Specifications
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Type In-Line OHV, DOHC
Number of Cylinders 4
Compression Ratio 10.5:1
Compression Pressure 10 - 15 bar
Max. Compression Pressure Variation Between
Cylinders 25%
Stroke 77.5 mm
Bore 81 mm
Displacement 1597 cc
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
1.8L Engine Specifications
DESCRIPTIONSPECIFICATION
Type In-Line OHV, DOHC
Number of Cylinders 4
Compression Ratio 10.5:1
Compression Pressure 10 - 15 bar
Max. Compression Pressure Variation Between
Cylinders 25%
Stroke 89.5 mm
Bore 81 mm
Displacement 1845 cc
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
02
02–3Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 39 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Flywheel FixtureCH-20043
Engine Hoist
Oil Filter Remover CH-10003
Lubrication System
The engine lubrication system operates as follows:
•Oil is drawn into the oil pump through the oil pump strainer tube in the sump of the oil pan.
• Oil is pumped through the oil filter on the cylinder block.
• Oil enters the main oil gallery where it is distributed to the crankshaft main journals and to the cylinder head.
• From the main journals, the oil is routed through cross-drilled passages in the crankshaft to lubricate the con-
necting rod bearings. Controlled leakage through the crankshaft main bearings and connecting rod bearings is
slung radially outward to cool and lubricate the cylinder walls as well as the entire connecting rod, piston and
piston ring assembly.
• The engine lubrication system is a full-flow filtration, pressure feed type. The oil pump body is mounted to the
engine block. The pump inner rotor is driven by the crankshaft.
Engine Oil Pressure Specifications
Lower Idle Speed (800 ± 50 RPM) 1.2 - 1.5 bar
High Idle Speed (2000 RPM) 3.2 - 3.5 bar
High Speed (4000 RPM) 3.7 ± 0.5 bar
GENERAL INFORMATION
02–10Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 106 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
The 2.0L in-line four cylinder engine has the following features:
•Dual overhead camshafts
• Four valves per cylinder
• Aluminum cylinder head
• Aluminum cylinder block
Operation
The 2.0L engine utilizes 4 valve-per-cylinders and a dual overhead camshaft design. The engine uses an individual
coil ignition system. The cylinder block is made of aluminum and the bearing caps are integrated into the lower cyl-
inder block assembly. An aluminum oil pan bolts to the bottom of the lower cylinder block. The camshafts are
mounted in the cylinder head and act against valve tappets to open and close the valves. The camshafts are driven
off the front of the cylinder head by one timing belt. The belt is driven by a sprocket that is located on the crankshaft.
The piston assembly is an aluminum piston with a cast iron connecting rod.
The aluminum cylinder head contains dual overhead camshafts with 4 valve-per-cylinder construction. The valves are
arranged in two in-line banks. The cylinder head incorporates powdered metal valve guides and seats. The cylinder
head is sealed to the block using a multi-layer steel head gasket and retaining bolts.
Specifications
2.0L Engine Specifications
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Type In-Line OHV, DOHC
Number of Cylinders 4
Compression Ratio 10:1
Compression Pressure 10 - 15 bar
Max. Compression Pressure Variation Between
Cylinders 25%
Stroke 90 mm
Bore 83.5 mm
Displacement 1971 cc
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
Mechanical Specifications
DESCRIPTIONITEMSTANDARD LIMIT
Engine Oil Pressure Lower Idle Speed (800 ±
50 RPM) 1.2 - 1.5 bar
-
High Idle Speed (2000 RPM) 3.2 - 3.5 bar
-
High Speed (4000 RPM) 3.7 ± 0.5 bar -
Engine Block Clearance Surface Distortion
-0.15 mm
Inner Diameter 83.500 - 83.510 mm -
Out-Of-Round -< 0.008 mm
Taper -< 0.01 mm
Piston Ring Groove
Clearance First Ring
0.04 - 0.08 mm -
Second Ring 0.0251 - 0.01 mm -
02
02–77Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 113 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Hoist
Flywheel FixtureCH-20043
Oil Filter Remover CH-10003
Lubrication System
The engine lubrication system operates as follows:
•Oil is drawn into the oil pump through the oil pump strainer tube in the sump of the oil pan.
• Oil is pumped through the oil filter on the cylinder block.
• Oil enters the main oil gallery where it is distributed to the crankshaft main journals and to the cylinder head.
• From the main journals, the oil is routed through cross-drilled passages in the crankshaft to lubricate the con-
necting rod bearings. Controlled leakage through the crankshaft main bearings and connecting rod bearings is
slung radially outward to cool and lubricate the cylinder walls as well as the entire connecting rod, piston and
piston ring assembly.
• The engine lubrication system is a full-flow filtration, pressure feed type. The oil pump body is mounted to the
engine block. The pump inner rotor is driven by the crankshaft.
Engine Oil Pressure Specifications
Lower Idle Speed (800 ± 50 RPM) 1.2 - 1.5 bar
High Idle Speed (2000 RPM) 3.2 - 3.5 bar
High Speed (4000 RPM) 3.7 ± 0.5 bar
GENERAL INFORMATION
02–84Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 180 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
The 2.4L in-line four cylinder engine has the following features:
•Single overhead camshaft
• Four valves per chamber cylinder head design
• Aluminum cylinder head
• Cast iron cylinder block
Operation
The 2.4L engine utilizes 4 valves-per-cylinder and a single-overhead-camshaft design. The engine uses an individual
coil ignition system and multi-point sequential injection. The cylinder block is made of cast iron and the bearing caps
are integrated into the lower cylinder block assembly. A cast iron oil pan is located at the bottom of the lower cylinder
block. The camshaft is mounted in the cylinder head and acts against the valve tappets to open and close the valves.
The camshaft is driven off the front of the cylinder head by the timing belt. The belt is driven by a sprocket that is
located on the crankshaft. The piston assembly is an aluminum piston with a cast iron connecting rod.
The aluminum cylinder head contains a single overhead camshaft with 4 valves-per-cylinder construction. The valves
are arranged in two in-line banks. The cylinder head incorporates powdered metal valve guides and seats. The cyl-
inder head is sealed to the block using a multi-layer steel head gasket and retaining bolts.
Specifications
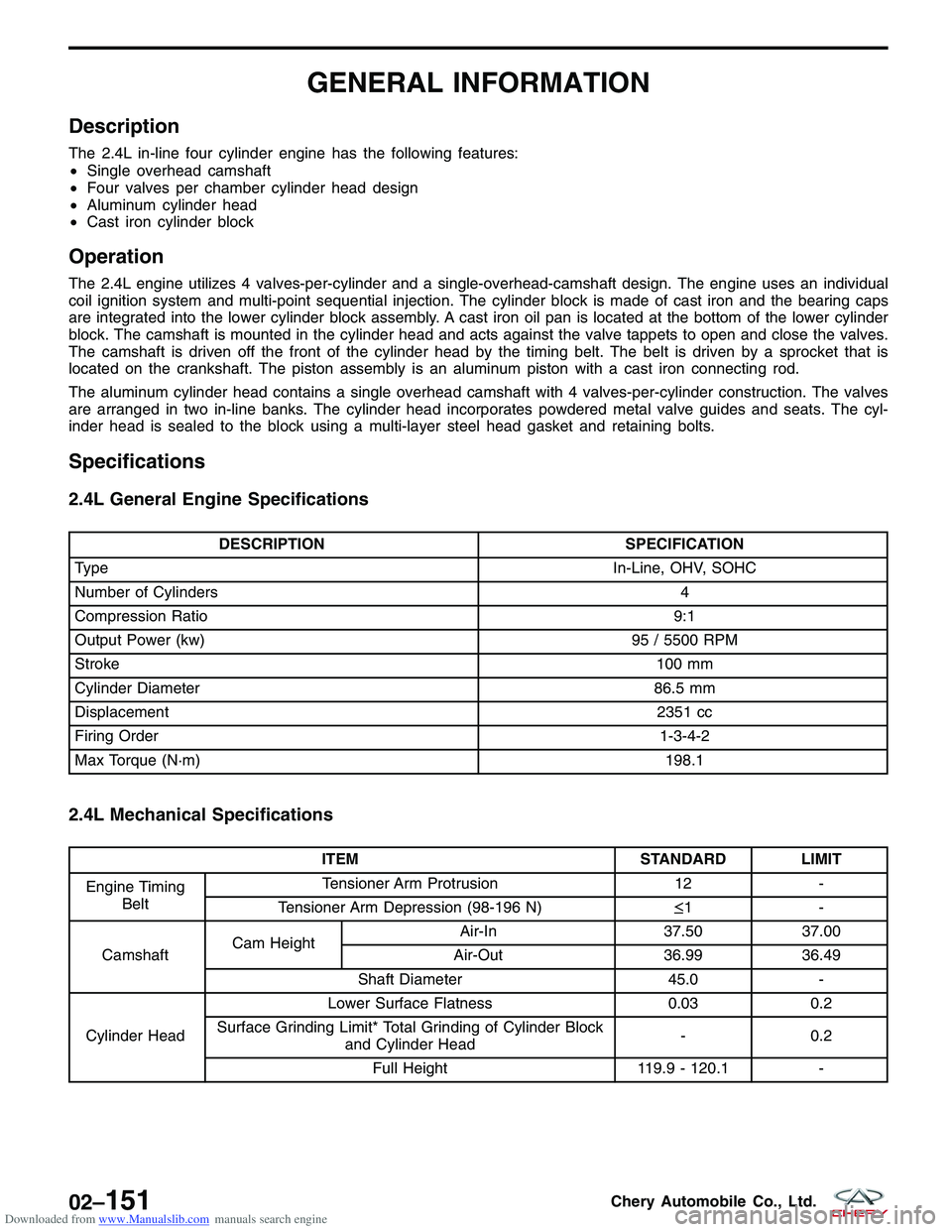
2.4L General Engine Specifications
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Type In-Line, OHV, SOHC
Number of Cylinders 4
Compression Ratio 9:1
Output Power (kw) 95 / 5500 RPM
Stroke 100 mm
Cylinder Diameter 86.5 mm
Displacement 2351 cc
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
Max Torque (N·m) 198.1
2.4L Mechanical Specifications
ITEMSTANDARD LIMIT
Engine Timing Belt Tensioner Arm Protrusion
12-
Tensioner Arm Depression (98-196 N) ≤1-
Camshaft Cam Height Air-In
37.5037.00
Air-Out 36.9936.49
Shaft Diameter 45.0-
Cylinder Head Lower Surface Flatness
0.030.2
Surface Grinding Limit* Total Grinding of Cylinder Block and Cylinder Head -
0.2
Full Height 119.9 - 120.1-
02–151Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 189 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Oil Filter WrenchMB-991828
Oil Filter WrenchMB-991396
Lubrication System
The engine lubrication system operates as follows:
• Oil is drawn into the oil pump through the oil pump strainer tube in the sump of the oil pan.
• Oil is pumped through the oil filter to the cylinder block.
• Oil enters the main oil gallery where it is distributed to the crankshaft main journals and to the cylinder head.
• From the main journals, the oil is routed through cross-drilled passages in the crankshaft to lubricate the con-
necting rod bearings. Controlled leakage through the crankshaft main bearings and connecting rod bearings is
slung radially outward to cool and lubricate the cylinder walls as well as the entire connecting rod, piston and
piston ring assembly.
• The lubrication system is a fully force-fed, full-flow filtration type. The oil pump is a gear type which is driven by
the crankshaft via the timing belt.
GENERAL INFORMATION
02
02–160Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 287 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) consists of a microcomputer and electrical connectors containing circuits for signal
input, output, power supply and ground. The ECM controls the engine functions.
The following are the input and output components monitored by the ECM. The monitored functions include compo-
nents from the engine, ignition, transaxle, air conditioning, or any other ECM supported subsystem.
ECM Inputs
•Brake Switch Sensor
• Refrigerant Pressure Sensor
• Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
• Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
• Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor (1.6L)
• Air Flow Sensor (1.8L)
• Throttle Position Sensor (Integral with Electronic Throttle Control Actuator)
• Power Steering Switch
• Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
• Knock Sensor
• Oxygen Sensor (Upstream & Downstream)
• Vehicle Speed Sensor
• Clutch Pedal Switch (Manual transaxle only)
ECM Outputs
• Canister Control Valve
• Fuel Injectors
• Fuel Pump Relay
• Electronic Throttle Control Actuator
• Ignition Coil
• A/C Compressor
• Cooling Fan
• Oxygen Sensor Heater (Upstream & Downstream)
Operation
The ECM monitors components and circuits, and tests them in various ways depending on the hardware, function,
and type of signal. For example, analog inputs, such as throttle position or engine coolant temperature are typically
checked for opens, shorts and out-of-range values. This type of monitoring is carried out continuously. Some digital
inputs like vehicle speed or crankshaft position rely on rationality checks - checking to see if the input value makes
sense at the current engine operating conditions. These types of tests may require monitoring several components
and can only be carried out under appropriate test conditions.
The ECM is a pre-programmed, microprocessor-based digital computer. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain transmission features, speed control, air conditioning compressor
clutch engagement and idle speed. The ECM can adapt its programming to meet changing operating conditions.
03
03–3Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 513 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) utilizes integrated circuitry and information carried on the Controller Area Network
(CAN) data bus along with many hard wired inputs to monitor many sensors and switches inputs throughout the
vehicle. In response to those inputs, the internal circuitry and programming of the ECM allow it to control and inte-
grate many electronic functions and features of the vehicle through both hard wired outputs and the transmission of
electronic message outputs to other electronic modules in the vehicle over the CAN data bus.
The following are the input and output components monitored by the ECM. The monitored functions include compo-
nents from the engine, ignition, transaxle, air conditioning, or any other ECM supported subsystem.
ECM Inputs
•Brake Switch Sensor
• A/C Pressure Switch
• Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
• Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
• Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
• Air Flow Sensor
• Throttle Position Sensor (integral with Electronic Throttle Control Actuator)
• Power Steering Switch
• Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
• Knock Sensor
• Oxygen Sensor (Upstream & Downstream)
• Clutch Pedal Switch (manual transaxle only)
ECM Outputs
• Canister Control Valve
• Fuel Injectors
• Fuel Pump Relay
• Electronic Throttle Control Actuator
• Ignition Coil
• A/C Compressor
• Cooling Fan
• Oxygen Sensor heating coil (Upstream & Downstream)
Operation
The ECM monitors components and circuits and tests them in various ways depending on the hardware, function,
and type of signal. For example, analog inputs such as throttle position or engine coolant temperature are typically
checked for opens, shorts and out-of-range values. This type of monitoring is carried out continuously. Some digital
inputs like vehicle speed or crankshaft position rely on rationality checks - checking to see if the input value makes
sense at the current engine operating conditions. These types of tests may require monitoring several components
and can only be carried out under appropriate test conditions.
The ECM is a pre-programmed, microprocessor-based digital computer. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain transmission features, speed control, air conditioning compressor
clutch engagement and idle speed. The ECM can adapt its programming to meet changing operating conditions.
03
03–229Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 726 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) consists of a microcomputer and connectors for signal input and output and for
power supply. The ECM controls the engine.
The following are the input and output components monitored by the ECM. The monitored functions include compo-
nents from the engine, ignition, transaxle, air conditioning, or any other ECM supported subsystem.
ECM Inputs
•Brake Switch Sensor
• Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
• Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
• Air Flow Sensor
• Coolant Temperature Sensor (For Instrument Cluster)
• Throttle Position Sensor (Integral with Electronic Throttle Control Actuator)
• Power Steering Switch
• Knock Sensor
• Oxygen Sensor (Upstream & Downstream)
• Clutch Pedal Switch (Manual transmission only)
ECM Outputs
• Canister Control Valve
• Fuel Injectors
• Fuel Pump Relay
• Electronic Throttle Control Actuator
• Ignition Coil
• A/C Compressor
• Cooling Fan
• Oxygen Sensor heating coil (Upstream & Downstream)
Operation
The ECM monitors components and circuits and tests them in various ways depending on the hardware, function,
and type of signal. For example, analog inputs such as throttle position or engine coolant temperature are typically
checked for opens, shorts and out-of-range values. This type of monitoring is carried out continuously. Some digital
inputs like vehicle speed or crankshaft position rely on rationality checks - checking to see if the input value makes
sense at the current engine operating conditions. These types of tests may require monitoring several components
and can only be carried out under appropriate test conditions.
The ECM is a pre-programmed, microprocessor-based digital computer. It regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, charging system, certain transmission features, speed control, air conditioning compressor
clutch engagement and idle speed. The ECM can adapt its programming to meet changing operating conditions.
03–442Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 909 of 1903
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine GENERAL INFORMATION
Description
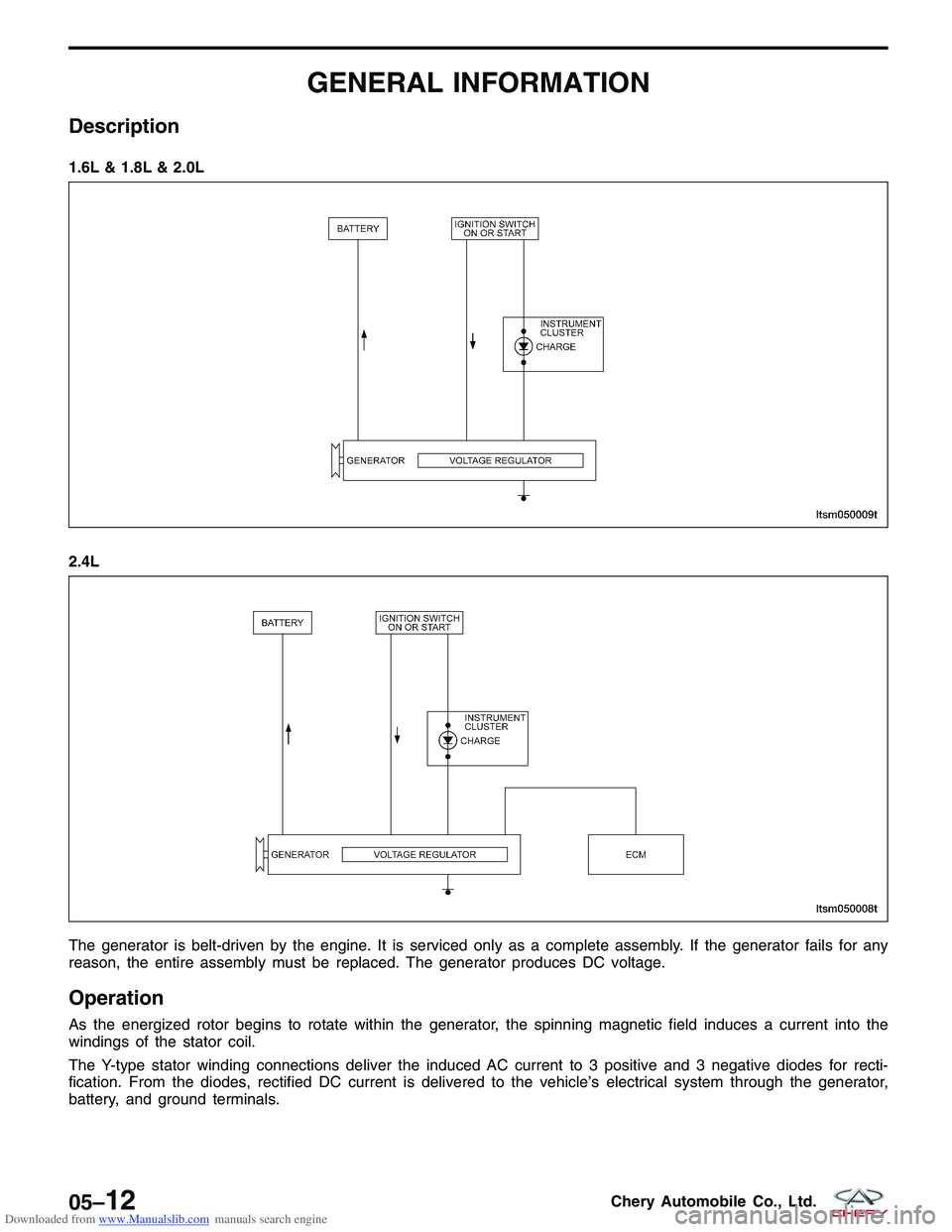
The generator is belt-driven by the engine. It is serviced only as a complete assembly. If the generator fails for any
reason, the entire assembly must be replaced. The generator produces DC voltage.
Operation
As the energized rotor begins to rotate within the generator, the spinning magnetic field induces a current into the
windings of the stator coil.
The Y-type stator winding connections deliver the induced AC current to 3 positive and 3 negative diodes for recti-
fication. From the diodes, rectified DC current is delivered to the vehicle’s electrical system through the generator,
battery, and ground terminals. 1.6L & 1.8L & 2.0L
2.4L
LTSM050009T
LTSM050008T
05–12Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.