wheel CHEVROLET BLAZER 1994 2.G Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1994, Model line: BLAZER, Model: CHEVROLET BLAZER 1994 2.GPages: 348, PDF Size: 17.88 MB
Page 88 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3. 4 LO: This setting also engages your front axle to give you extra
traction. You may never need
4 LO. It sends the maximum power to all
four wheels.
You might choose 4 LO if you were driving off-road in
sand, mud, deep snow and climbing or descending steep hills.
Indicator lights
in the switch show you which setting you are in. Both
indicator lights will come on briefly when
you turn on the ignition. If both
lights do
not come on, you should take your vehicle in for service. The 4 HI
position has a green indicator light and the 4 LO position has an amber
indicator light. When shifting, an indicator light will flash
until the shift is
completed then remain solidly lit.
Two-wheel drive, (2 WHEEL), does not have a switch position or an
indicator light. Your vehicle will be
in two wheel drive if neither indicator
light is
on.
To shift from two-wheel drive, (2 WHEEL) to 4 HI: Press and release the
4 HI switch. This can be done at any speed, and the front axle will lock
automatically.
To shift from 4 HI to two-wheel drive (2 WHEEL): Press and release the
4 HI switch. This can be done at any speed, and the front axle will unlock
automatically.
To shift from two-wheel drive (2 WHEEL) to 4 LO: The vehicle must be
stopped or moving less than
3 mph (4.8 km/h) with the transmission in “N’
(Neutral) or the clutch pedal depressed. The preferred method for shifting
into
4 LO is to have your vehicle slowly moving one-to-two mph (1.6 to
3.2 kdh). Press and release the 4 LO switch. You must wait for the amber
4 LO indicator light to stop flashing and go solid amber before shifting your
transmission
into gear or releasing the clutch pedal.
If the
4 LO switch is pressed when your vehicle is in gear and/or moving,
the amber
4 LO indicator light will flash for 30 seconds and not complete
the shift unless your vehicle is below
3 mph (4.8 kdh) and the transmission
is in
“N” (Neutral) or the clutch pedal depressed.
On automatic transmission equipped vehicles: If your transfer case does not
shift into
4 LO, your transmission indicator switch may require adjustment.
With your transmission in
“N” (Neutral), press and release the 4 LO
switch. While the amber 4 LO indicator light is flashing, shift your
transmission into
P (Park).
2-34
Page 89 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wait until the 4 LO indicator light goes solid amber before shifting your
transmission into gear. This
will get you into 4 LO, but you should take
your vehicle in for service so normal operation can be restored.
To shift from 4 LO to 4 HI: Your vehicle must be stopped or moving less
than
3 mph (4.8 kdh) with the transmission in “N” (Neutral) and the clutch
pedal depressed. The preferred method for shifting out of
4 LO is to have
your vehicle slowly moving
1 to 2 mph (1.6 to 3.2 kmh). Press and release
the
4 HI switch. You must wait for the 4 HI indicator light to stop flashing
and
go solid amber before shifting your transmission into gear or releasing
the clutch pedal.
If the 4 HI switch is pressed when your vehicle is in gear and/or moving,
the
4 HI indicator light will flash for 30 seconds but not complete the shift
unless the vehicle is below
3 mph (4.8 kdh) and the transmission is in “N”
(Neutral) or the clutch pedal depressed.
On automatic transmission equipped vehicles:
If your transfer case does not
shift into
4 HI, your transmission indicator switch may require adjustment.
With your transmission
in “N” (Neutral), press and release the 4 HI switch.
While the
4 HI indicator light is flashing, shift your transmission into P
(Park). Wait until the 4 HI indicator light goes solid green before shifting
your transmission into gear. This
will get you into 4 HI, but you should
take your vehicle
in for service so normal operation can be restored.
To shift from 4 LO to two-wheel drive (2 WHEEL): You must shift from
4 LO to 4 HI before shifting back into two-wheel drive.
Windows
1
To open your manual
windows,
turn the
hand crank
on each
door to raise or lower
your side door
windows.
Page 91 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Horn
Press the pad in the
center
of the steering
wheel
to sound the
horn.
Tilt Wheel (Option)
A tilt steering wheel
allows
you to adjust
the steering wheel
before
you drive.
You can also raise it to the highest level to give your legs more room when
you enter and exit the vehicle.
To tilt the wheel, hold the steering wheel and pull the lever. Move the
steering wheel to a comfortable level, then release the lever to lock the
wheel
in place.
Do not adjust the steering wheel while driving.
2-37
Page 119 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 13. Light Switches
14. Rear Window Defogger Switch*
15. Fog Light Switch** or Rear Window Defogger Switch with Electronic
16. Remote Outside Mirror Switch
*Without Electronic Transfer Case
“*Without Four-wheel Drive
Transfer
Case
Instrument Cluster
Your instrument cluster is designed to let you know at a glance how your
vehicle is running. You’ll know how
fast you’re going, about how much
fuel you’ve used, and many other things
you’ll need to know to drive safely
and economically.
If you have the digital cluster it looks different but will tell you everything
the standard cluster does. The digital cluster
also includes a tachometer and
will give readings
in either English or Metric. To switch from English to
Metric, just press down on the E/M button.
Speedometer and Odometer
#3
Your speedometer lets
you see your speed
in
both miles per hour
(mph) and kilometers
per hour (kdh).
Y
Your odometer shows how far your vehicle has been driven, in either miles
(used in the
U.S.) or kilometers (used in Canada).
2-65
Page 159 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Your Driving and the Road
Section
Here you'll find information about driving on different kinds of roads and in
varying weather conditions . We've also included many other useful tips on
driving
.
Defensive Driving ..................... ................. 4-2
DrunkenDriving ........................................... 4-2
Braking ................................................ 4-5
Steering Tips ............................................ 4-8
Control
of a Vehicle
Steering
................................................ 4-8
Passing
............................................... 4-10
Loss of Control ......................................... 4-11
Driving Guidelines
......................................... 4-12
Off-Road Driving With Your Four-wheel Vehicle
............... 4-13
DrivingatNight ........................................... 4-24
Driving
in the Rain ........................................ 4-25
Freeway Driving
........................................... 4-8
Hill and Mountain Roads
.................................... 4-30
Winter Driving
............................................ 4-32
CityDriving
.............................................. 4-27
Recreational Vehicle Towing (Four-wheel Drive Only)
........... 4-35
TowingaTrailer
........................................... 4-37
4-1
Page 164 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Avoid needless heavy braking. Some people drive in spurts - heavy
acceleration followed by heavy braking
- rather than keeping pace with
traffic. This is a mistake. Your brakes may not have time to cool between
hard
stops. Your brakes will wear out much faster if you do a lot of heavy
braking. If
you keep pace with the traffic and allow realistic following
distances, you will eliminate a
lot of unnecessary braking. That means better
braking and longer brake life.
If your engine ever stops while you’re driving, brake normally but don’t
pump your brakes. If
you do, the pedal may get harder to push down. If
your engine stops, you will still have some power brake assist. But you will
use it when you brake. Once the power assist is used up, it may take longer
to stop and the brake pedal will be harder to push.
Anti-Lock Brakes (ABS)
Your vehicle has an advanced electronic braking system that can help you
keep it under control. When you start your vehicle and begin to drive away,
you may hear
a momentary motor or clicking noise. This is the ABS system
testing
itself.
Here’s how anti-lock works. Let’s say the road is wet. You’re driving safely.
Suddenly
an animal jumps out in front of you.
You slam
on the brakes. Here’s what happens with ABS.
A computer senses that wheels are slowing down. If one of the wheels is
about to stop rolling, the computer will separately work the brakes at each
front wheel and at the rear wheels. The anti-lock system can change the
brake pressure faster than any driver could. The computer
is programmed to
make the most of available tire and road conditions. You can steer around
the obstacle while braking hard.
4-6
Page 165 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates on wheel speed and
controls braking pressure accordingly.
Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time
you need to get your foot up
to the brake pedal. If you get too close to the vehicle
in front of you, you
won’t have time to apply your brakes
if that vehicle suddenly slows or
stops. Always leave enough room up ahead
to stop, even though you have
anti-lock brakes.
To Use Four-wheel Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down and let anti-lock
work for
you. You may feel the brakes vibrate, or you may notice some
noise, but this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
Use your anti-lock braking system when you need to. With anti-lock, you
can steer and brake at
the same time. In many emergencies, steering can
help you more than even the very best braking.
4-7
Page 166 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine stops or the system is
not functioning, you can steer but it will take much more effort.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot
of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on the news happen
on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each
of us is subject to the same laws of
physics when driving on curves. The traction of the tires against the road
surface makes it possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels. If there’s
no traction, inertia will keep the vehicle going in
the same direction. If you’ve ever tried to steer
a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll
understand this.
The traction you can get in a curve depends on the condition of your tires
and the road surface, the angle at which the curve
is banked, and your
speed. While you’re
in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control.
Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve. Then
you suddenly
accelerate. Both control systems
- steering and acceleration - have to do
their work where the tires meet the road. Adding the sudden acceleration
can demand too much
of those places. You can lose control,
What should you do
if this ever happens? Ease up on the accelerator pedal,
steer
the vehicle the way you want it to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that
you should adjust your speed. Of
course, the posted speeds are based
on good weather and road conditions.
Under less favorable conditions you’ll want
to go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a curve, do it before you
enter the curve, while your front wheels are straight ahead.
Try
to adjust your speed so you can “drive” through the curve. Maintain a
reasonable, steady speed. Wait to accelerate until you are out of the curve,
and then accelerate gently into
the straightaway.
4-8
Page 168 of 348
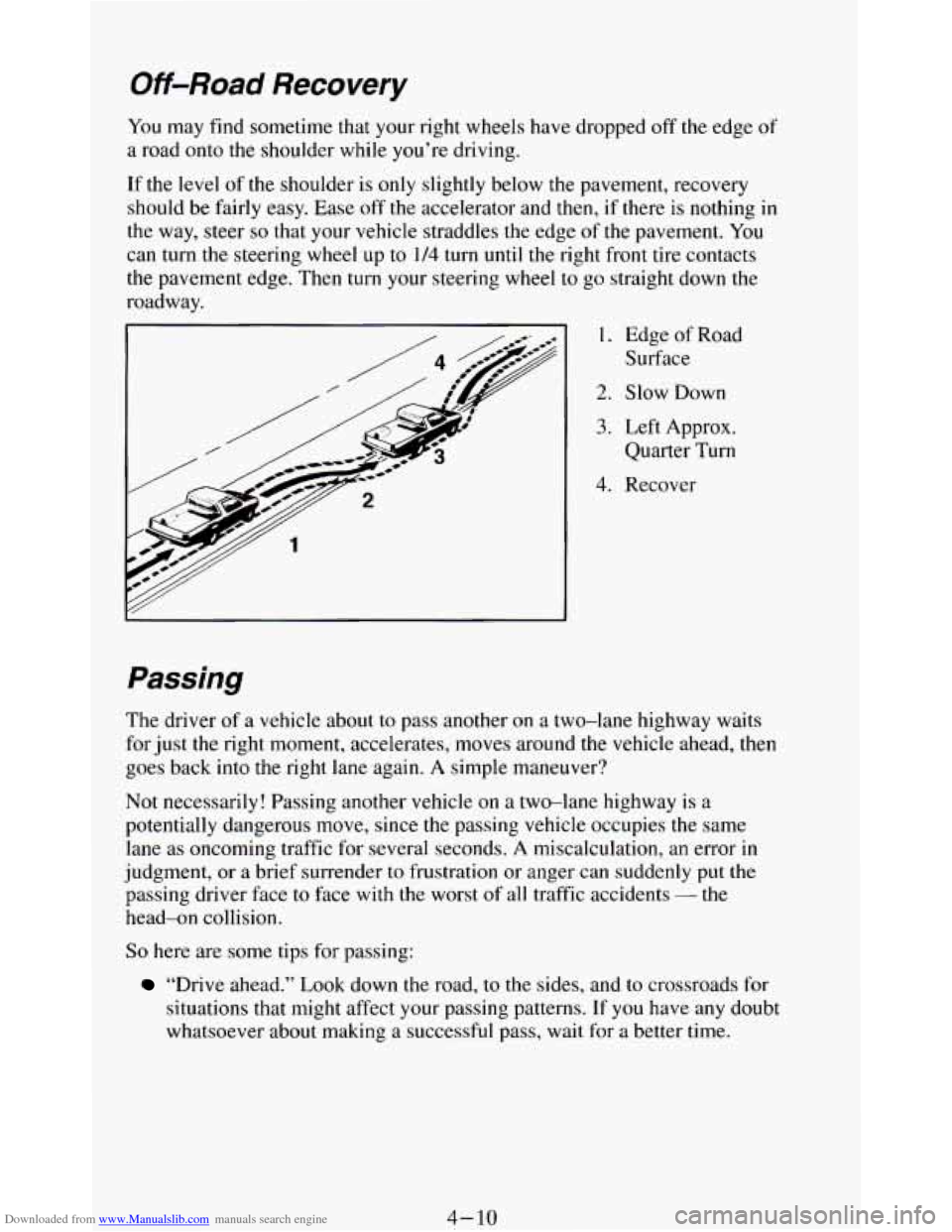
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Off-Road Recovery
You may find sometime that your right wheels have dropped off the edge of
a road onto the shoulder while you’re driving.
If the
level of the shoulder is only slightly below the pavement, recovery
should be fairly easy. Ease
off the accelerator and then, if there is nothing in
the way, steer so that your vehicle straddles the edge of the pavement. You
can turn the steering wheel up to
1/4 turn until the right front tire contacts
the pavement edge. Then turn your steering wheel to go straight down the
roadway.
1. Edge of Road
Surface
2. Slow Down
3. Left Approx.
Quarter Turn
4. Recover
Passing
The driver of a vehicle about to pass another on a two-lane highway waits
for just the right moment, accelerates, moves around
the vehicle ahead, then
goes back into the right lane again. A simple maneuver?
Not necessarily! Passing another vehicle on a two-lane highway is a
potentially dangerous move, since the passing vehicle occupies the same
lane as oncoming traffic for several seconds.
A miscalculation, an error in
judgment, or a brief surrender to frustration or anger can suddenly put the
passing driver face to face with the worst of all traffic accidents - the
head-on collision.
So here are some tips for passing:
“Drive ahead.” Look down the road, to the sides, and to crossroads for
situations that might affect your passing patterns. If
you have any doubt
whatsoever about making a successful pass, wait for a better time.
4- 10
Page 170 of 348

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle. Defensive drivers avoid
most skids by taking reasonable care suited to existing conditions, and
by
not “overdriving” those conditions. But skids are always possible.
The three types of skids correspond
to your Vehicle’s three control systems.
In the braking skid your wheels aren’t rolling.
In the steering or cornering
skid, too much speed or steering
in a curve causes tires to slip and lose
cornering force. And in the acceleration skid too much throttle causes the
driving wheels
to spin.
A cornering skid and an acceleration skid are best handled by easing your
foot off the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot off the accelerator pedal and
quickly steer the way you want
the vehicle to go. If you start steering
quickly enough, your vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready for a
second skid
if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice, gravel, or other material
is on the road. For safety, you’ll want to slow down and adjust your driving to
these conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery surfaces because
stopping distance will be longer and vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface
with reduced traction, try your best to avoid
sudden steering, acceleration, or braking (including engine braking by
shifting to a lower gear). Any sudden changes could cause the tires to slide.
You may not realize the surface is slippery until your vehicle is skidding.
Learn to recognize warning clues
- such as enough water, ice or packed
snow on the road to make a “mirrored surface” - and slow down when you
have any doubt.
Remember: Any anti-lock braking system (ABS) helps avoid only the
braking skid.
Driving Guidelines
This multipurpose passenger vehicle is defined as a utility vehicle in
Consumer Information Regulations issued by the National Highway Traffic
Safety Administration (NHTSA) of the United States Department of
Transportation. Utility vehicles have higher ground clearance and a narrower
track to make them capable of performing
in a wide variety of off-road
applications. Specific design characteristics give them a higher center of
gravity than ordinary cars.
An advantage of the higher ground clearance is a
better view of the road allowing you to anticipate problems. They are not
designed for cornering at the same speeds as conventional 2-wheel drive
vehicles any more than low-slung sports cars are designed to perform
satisfactorily under off-road conditions. If at
all possible, avoid sharp turns or
abrupt maneuvers.
As with other vehicles of this type, failure to operate this
vehicle correctly may result
in loss of control or vehicle rollover.
4-12