check engine light CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.G Chassis User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1967, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1967 1.GPages: 659, PDF Size: 114.24 MB
Page 302 of 659

ENGINE 6-37
Fig.
27V—Removing Camshaft
4.
Set dial indicator on zero, then rotate the damper
slowly, or attach an auxiliary starter switch and
"bump" the engine over, until the push rod is in the
fully raised position.
CAUTION: The primary distributor lead must
be disconnected from the negative post on the
coil and the ignition switch must be in the on
position. Failure to do this will result in a dam-
aged grounding circuit in the ignition switch.
5.
Compare the total lift recorded from the dial indica-
tor with specifications.
6. Continue to rotate the crankshaft until the indicator
reads zero. This will be a check on the accuracy of
the original indicator reading.
7.
If camshaft readings for all lobes are within specifi-
cations, remove dial indicator assembly.
8. Install and adjust valve mechanism as outlined.
Removal
1.
Remove valve lifters as outlined.
2.
Remove crankshaft front cover as outlined.
3.
Remove grille as outlined in Section 13.
4.
Remove fuel pump push rod as outlined * in Sec-
tion 6M.
5.
Complete camshaft removal as follows:
CAUTION: All camshaft journals are the same
diameter and care must be used in removing
camshaft to avoid damage to bearings.
Remove camshaft sprocket to camshaft bolts then
remove sprocket and timing chain together. Sprocket
is a light fit on camshaft. If sprocket does not come
off easily a light blow on the lower edge of the
sprocket (with a plastic mallet) should dislodge the
sprocket.
Install two 5/16" - 18 x 4" bolts in camshaft bolt
holes then remove camshaft (fig. 27V).
Installation
NOTE: Whenever a new camshaft is installed
CONVERTER
BOLT AREA -
DEPRESSED
SYNCHROMESH
RING
GEAR
TRANS.,
AUTOMATIC
Fig.
28V - Flywheel Installation (Typical)
coat camshaft lobes with Molykote or its
equivalent.
1.
Lubricate camshaft journals with engine oil and in-
stall camshaft.
2.
Install timing chain on camshaft sprocket. Hold the
sprocket vertical with the chain hanging down, and
orient to align marks on camshaft and crankshaft
sprockets. Refer to Figure 20V.
3.
Align dowel in camshaft with dowel in hole in cam-
shaft sprocket then install sprocket on camshaft.
Refer to Figure 25V.
4.
Draw the camshaft sprocket onto camshaft using the
mounting bolts. Torque to specifications.
5.
Lubricate timing chain with engine oil.
6. Install fuel pump push rod as outlined in Section 6M.
7.
Install grille as outlined in Section 13.
8. Install crankcase front cover as outlined.
9. Install valve lifters as outlined.
FLYWHEEL
Removal
With transmission and/or clutch housing and clutch
removed from engine, remove the flywheel.
Installation
1.
Clean the mating surfaces of flywheel and crankshaft
to make certain there are no burrs.
2.
Install flywheel on crankshaft and position to align
dowel hole of crankshaft flange and flywheel (fig.
28V).
NOTE: On Automatic Transmission equipped
engines, the flywheel must be installed with the
flange collar to transmission side (fig. 33V).
ENGINE MOUNTS
Engine mounts (fig. 34V) are the nonr adjustable type
and seldom require service. Broken or deteriorated
mounts should be replaced immediately, because of the
added strain placed on other mounts and drive line
components.
Front Mount Replacement
1.
Remove nut, washer and engine mount through-bolt.
2.
Raise engine to release weight from mount.
3.
Remove mount from engine.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 309 of 659

SECTION 6M
ENGINE FUEL
CONTENTS OF THIS SECTION
Page
Carburetors 6M-1 Fuel Pumps .
Air Cleaners 6M-7 Special Tools
Page
6M-10
6M-12
CARBURETORS
INDEX
Page
General Description 6M-1
Service Procedures 6M-1
Preliminary Checks 6M-1
Idle Speed and Mixture Adjustment ........... 6M-1
Fast Idle Adjustment .................. 6M-3
Choke Adjustment 6M-3
Float Adjustment 6M-4
Page
Additional Adjustments 6M-4
Removal 6M-4
Test Before Installation 6M-5
Installation 6M-5
Fuel Filter Maintenance 6M-5
Choke Coil Replacement 6M-5
Throttle Linkage Adjustment . . 6M-6
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Various carburetors (fig. lc) are used with Chevrolet,
Chevelle, Chevy II, Camaro and Corvette passenger
vehicles. These carburetors are designed to meet the
particular requirements of engines, transmissions and
vehicles, therefore carburetors that look alike are not
always interchangeable. (Refer to carburetor part num-
ber and/or specifications.)
Because many service procedures for the various
carburetors are similar, typical illustrations and pro-
cedures are used except where specific illustrations or
procedures are necessary to clarify the operation.
This section covers removal, installation and adjust-
ments (on engine) of carburetors. Also covered in this
section are maintenance procedures for choke coils,
throttle linkage and fuel filters. For carburetor .over-
haul procedures and additional adjustments (bench), re-
fer to Section 6M of the Overhaul Manual under the
carburetor being serviced.
Specifications for carburetors are located in the back
of this manual.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
Preliminary Checks
1.
Thoroughly warm-up engine. If the engine is cold,
allow to run for at least 15 minutes.
2.
Inspect torque of carburetor to intake manifold bolts
and intake manifold to cylinder head bolts to exclude
the possibility of air leaks.
3.
Inspect manifold heat control valve (if used) for free-
dom of action and correct spring tension.
Idle Speed and Mixture Adjustment (Except Air Injection
Reactor System)
NOTE:
This adjustment should be performed
with engine at operating temperature and park-
ing brake applied.
1.
Remove Air Cleaner.
2.
Connect tachometer and vacuum gauge to engine, then
set hand brake and shift transmission into neutral.
3.
As a preliminary adjustment, turn idle mixture
screws lightly to seat and back out 1-1/2 turns.
CAUTION: Do not turn idle mixture screw
tightly against seat or damage may result.
4.
With engine running (choke wide open) adjust idle
speed screw to specified idle speed, (automatic
transmission in drive, synchronized transmission in
neutral).
5. Adjust idle mixture screw to obtain highest steady
vacuum at specified idle speed.
NOTE:
On air conditioned vehicles, turn air
conditioning to the "on" position and hold the
hot idle compensator valve closed while adjust-
ing idle speed and idle mixture screws.
NOTE:
On Rochester BV carburetors the idle
mixture screw should be turned out 1/4 turn
from the "lean roll" position. The definition
of "lean roll" point is a 20 to 30 rpm drop
in engine speed obtained by leaning the idle
mixture.
6. Repeat Steps 4 and5 as needed for final adjustment.
NOTE:
If necessary, final adjustment of the \
carburetor may be made with the air cleaner
installed.
7. Turn engine off, remove gauges and install air
clearer.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 311 of 659

ENGINE FUEL 6M-3
Idle Speed and Mixture Adjustment (With Air Injection
Reactor System)
The following is the recommended procedure for Air
Injection Reactor System equipped engines.
NOTE: This adjustment should be performed
with engine at operating temperature and parking
brake applied.
1.
Remove air cleaner.
2.
Connect tachometer to engine, then set hand brake
and shift transmission into neutral.
3.
As a preliminary adjustment, turn idle mixture
screws lightly to seat and back out 3 turns.
CAUTION: Do not turn idle mixture screw
tightly against seat or damage may result."
4.
With engine running (choke wide open) adjust idle
speed screw to specified idle speed. (Automatic
transmission in dirve, synchronized transmission in
neutral).
5.
Adjust idle mixture screw (turn in) to "lean roll"
position; then turn screw out 1/4 turn (1/4 turn
rich from "lean roll"). The definition of "lean
roll" point is a 20 to 30 rpm drop in engine speed,
obtained by leaning the idle mixture.
NOTE: On air conditioned vehicles, turn air
conditioning "OFF" on in-line, 283, 327, and'
350 cu. in. engines, and turned "ON" and hot
idle compensator held closed on 396 and 427 cu.
in. engines.
6. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 as needed for final adjustment.
NOTE: If necessary, final adjustment of the
carburetor may be made with air cleaner
installed.
7.
Shut down the engine, remove gauges and install air
cleaner. *
Fast Idle Adjustment
Rochester
4MV and Holley
With fast idle lever on high step of cam and choke valve
open (engine warm) set fast idle to give specified engine
rpm. Adjust sejrew on Rochester 4MV and bend fast
idle lever *pn Holley. .
Choke Adjustment
With Remote Choke (Fig. 2c)
1.
Remove air cleaner and check to see that choke
valve and rod move freely.
2.
Disconnect choke rod at choke lever.
3.
Check choke adjustment as follows:
On all except 275 and 300 h.p. 327 cu. in. engines,
hold choke valve closed and pull.rod up against stop.
The top of choke rod end should be 1/2-1 rod diame-
ter above top of hole in choke valve lever.
On 275 and 300 h.p. 327 cu. in. engines, hold choke
valve closed and push rod down against stop on ther-
mostat bracket. The top of the choke rod should be
1/2-1 rod diameter below the top of the hole in the
choke lever.
4.
If necessary, adjust rod length by bending rod at
offset bend. (Bend must be such that rod enters
choke lever hole freely and squarely).
5.
Connect rod at choke lever and install air cleaner.
With Manual Choke (Carter YF)
1.
Remove air cleaner.
CHOKE VALVE
COMPLETELY
CLOSED
PULL UPWARD ON
ROD TO END OF
TRAVEL
BEND ROD
TO ADJUST
ROD IN BOTTOM
OF SLOT
BOTTOM OF
ROD SHOULD
BE EVEN WITH
TOP OF
HOLE
CHOKE VALVE
CLOSED
BOTTOM OF
ROD SHOULD
BE EVEN WITH
TOP OF HOLE
TOP OF ROD
SHOULD BE EVEN
WITH BOTTOM
OF HOLE (CHOKE
CLOSED)
BEND ROD TO
ADJUST
PULL DOWNWARD'
ON ROD TO CON-
TACT STOP
L6 (TYPICAL)
[
V8 327-275 HP
V8 350-295 HP
BEND ROD
TO ADJUST
PULL UPWARD ON
ROD TO CONTACT
STOP ON BRACKET
ALL V8 (EXCEPT 327-275 HP
AND 350-295 HP)
Fig.
2C—Remote Choke Adjustment
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 312 of 659

ENGINE FUEL 6M-4
Fig.
3C-Fuel Level Sight Plug
2.
Push hand choke knob in to within 1/8" of instru-
ment panel.
3.
Loosen choke cable clamp at carburetor bracket and
adjust cable through the clip until the choke valve
is wide open.
4.
Tighten cable clamp at carburetor bracket and check
operation of choke valve to ensure full closed and
wide open positions.
5. Install air cleaner.
Float Adjustment
Ho/fey (Model 4150
Center
Inlet & Model 2300)
1.
Remove air cleaner then remove the fuel level sight
plugs (Fig. 3c)
2.
With parking brake on, and transmission in neutral,
start the engine and allow it to idle.
3.
With the car on a level surface, the fuel level should
be on a level with the threads at the bottom of the
sight plug port (plus or minus 1/32 inch).
NOTE:
No float drop adjustment is required
on this carburetor.
4.
If necessary to adjust (either or both bowls), loosen
inlet needle lock screw and turn the adjusting nut
clockwise to lower or counter-clockwise to raise
fuel level, then tighten lock screw.
NOTE:
1/6 turn of adjusting nut equals ap-
proximately 1/16" fuel level change.
5. Allow a minute for fuel level to stabilize then re-
check the level at sight plug.
6. Readjust, if necessary, until proper level is obtained,
then install sight plug and air cleaner.
NOTE:
To assure proper secondary float level
setting it is advisable to accelerate primary
throttles slightly and hand operate secondary
throttle. This assures a stabilized secondary
fuel level.
Additional Adjustments
The following adjustments may be made without re-
moving the carburetor from the engine. For procedure
refer to Section 6M of the Overhaul Manual under the
carburetor being serviced.
Rochester BV
• Float
• Idle Vent
• Choke Rod (Fast Idle)
• Choke Vacuum Break
• Choke Unloader
Rochester 2GV
• Float
• Accelerator Pump
• Idle Vent
• Choke Rod (Fast Idle)
• Choke Vacuum Break
• Choke Unloader
• Secondary Throttle Opening
• Secondary Throttle Lockout
Rochester 4MV
• Float
• Accelerator Pumj)
• Idle Vent
• Air Valve
• Choke Rod
• Choke Vacuum Break
• Choke Unloader
• Air Valve Lockout
• Secondary Opening
• Secondary Lockout
Carter YF
• Float
• Idle Vent
• Choke Rod (Fast Idle)
• Choke Vacuum Break
• Choke Unloader
Holley 4160 and 4150
(Except End
Inlet)
• Float
• Air Vent Valve
• Accelerator Pump
• Choke Vacuum Break
• Choke Unloader
Holley 2300 and 4150
(End
Inlet)
• Air Vent Valve (except 2300)
• Accelerator Pump
• Choke Vacuum Break
• Choke Unloader
Removal
Flooding, stumble on acceleration and other perform-
mance complaints are, in many instances, caused by the
presence of dirt, water, or other foreign matter in the
carburetor. To aid in diagnosing the cause of the com-
plaint, the carburetor should be carefully removed from
the engine without draining the fuel from the bowl.
The contents of the fuel bowl may then be examined for
contamination as the carburetor is disassembled.
1.
Remove air cleaner and gasket.
2.
Disconnect fuel and vacuum lines from carburetor.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 316 of 659

ENGINE FUEL 6M-8
^T^l^^/'-vN
COVER
BOTTOM
Fig. 1A—Polyurethane Element Air Cleaner
OIL RESISTANCE
SEAL
BOTTOM
BONDED PAPER
ELEMENT
COVER
Fig. 2A—Paper Element Air Cleaner
SERVICE
PROCEDURES
POLYURETHANE ELEMENT
Maintenance
1.
Remove cover wing nut, cover and filter element.
2.
Visibly check the element for tears or rips and re-
place if necessary.
3.
Clean all accumulated dirt and grime from air
cleaner bottom and cover. Discard air horn to air
cleaner gasket.
4.
/Remove support screen from element and wash
element in kerosene or mineral spirits; then squeeze
out excess solvent (fig. 3A).
NOTE: Never use a hot degreaser or any sol-
vent containing acetone or similar solvent*
5.
Dip element into light engine oil and squeeze out
excess oil.
NOTE: Never shake, swing or wring the ele-
me.nt to remove excess oil or solvent as this
may tear the polyurethane material. Instead,
"squeeze" the excess from the element.
6. Install element'on screen support (fig. 4A).
7.
Using a new gasket, replace air cleaner body over
carburetor air horn.
8. Replace the element in the air cleaner. Care must
be taken that the lower lip of the element is properly
placed in the assembly and that the filter material
is not folded or creased in any manner that would
cause an imperfect seal. Take the same precautions
when replacing the cover that the upper lip of the
element is in proper position.
9.<•
Replace cover and wing nut.
OIL BATH
Maintenance
L Remove air cleaner assembly.
2.
Remove cover and filter element assembly.
Empty oil out of
accumulated dirt.
cleaner and clean out all oil and
Fig. 3A—Cleaning Polyurethane Element
Fig.
4A—Polyurethane Support
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 317 of 659

ENGINE FUEL 6M-9
4.
Wash body with cleaning solvent and wip dry.
5. Wash filter element by sloshing up and down in
cleaning solvent.
6. Dry filter unit with an air hose or let stand until
dry.
7. Fill body of cleaner to full mark with SAE 50 engine
oil. If expected temperatures are to be consistently
below freezing, use SAE 20 engine oil.
8. Assemble filter and cover assembly to body of
cleaner.
9. Install cleaner, making sure it fits tight and is set
down securely. \
OIL
WETTED
PAPER
ELEMENT
Replacement
1.
Remove wing nut, washer and cover.
2.
Remove paper element and discard.
3.
Remove bottom section of air cleaner and gasket
on air horn of carburetor. Discard air horn gasket.
4.
Clean bottom section of air cleaner and cover pieces
thoroughly, to remove dust and grime.
NOTE:
Check bottom section of air cleaner
seal for tears or cracks.
5. Install a new gasket on carburetor air horn and set
bottom section of air cleaner on carburetor.
6. Install new paper element on bottom section of air
cleaner with either end up.
NOTE:
Plastisol seal is the same material on
both ends.
7. Install cover, washer and wing nut.
Testing (Fig. 5A)
Tool J-7825, is designed to check paper element air
cleaners to determine whether the element has ma-
terially decreased in efficiency arid should be replaced
or has only slightly increased air restriction and is
suitable for further service. In combination with a
tachometer, this instrument will quickly and accurately
determine the air cleaner element condition.
VENT HOLE
TOWARD DASH
NOTE:
t Before testing, inspect for holes or
breaks in the element, as these defects re-
quire immediate replacement. If no holes or
breaks exist, proceed as follows:
1.
Remove all hoses and plug all openings except air
cleaner inlet.
2.
Install air cleaner, using Tool J-7825 in place of the
wing nut. Screw Tool J-7825 onto the stud until it
seals tightly against the air cleaner cover. Rotate
the entire tool so that the scale can be read from
the left side of the car. Be sure the vent hole is
toward the dash.
3.
Connect a tachometer and place it so that it may be
read simultaneously with Tool J-7825.
4.
Zero oil level in the inner tube by pulling inner tube
upward until the rubber seal is above the vent hole,
then raise or lower as' required until the inner tube
oil level is exactly to the "0" mark.
5. Start engine. If engine is cold, allow to run for 2 to
3 minutes. The automatic choke must be fully open.
6. Accelerate the engine slowly until the inner tube oil
level of Tool J-7825 just reaches the 1/4 mark.
Allow engine speed to stabilize and note tachometer
(rpm) reading. Decelerate engine.
7. If the tachometer reading is at or below the follow-
ing, the oil wetted paper air cleaner element is re-
stricted beyond the allowable limit and should be
replaced. If testing indicates that the element
restriction is satisfactory at 12,000 miles, the ele-
ment need not be replaced but should be retested
every 6,000 miles thereafter until replaced.
Engine
Displacement
283 cu.
in.
327 cu.
in.
350 cu. in.
396 cu.
in.
427 cu.
in.
Horsepower
195
210
275
300
325
350
295
325
350
385
390
425
Minimum
Allowable
RPM
2300
2100
210Q
2600
2600
1550
1950
1850
1850
2140
Fig.
5A—Testing Air Cleaner
8. Remove tachometer and Tool J-7825 from vehicle
and push down inner tube until seal is below vent
hole to prevent oil loss.
Tool J-7825
FiHing
Tool
Tool J-7825 is shipped dry and must be filled with the
red gauge oil (specific gravity .826) provided.
Pull the knurled inner tube completely out of the gauge
and add oil to the reservoir until the oil level is between
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE /MANUAL
Page 328 of 659

ENGINE-EIECTRICAI 6Y-3
PERIODIC SERVICING
Since the Battery is a perishable item which requires
periodic servicing, a good maintenance program will
insure the longest possible Battery life.
COMMON CAUSES OF FAILURE
If the Battery tests good but fails to perform satis-
factorily in service for no apparent reason, the following
are some of the more important factors that may point to
the cause of the trouble.
1.
Vehicle accessories inadvertently left on overnight to
cause a discharged condition.
2.
Slow speed driving of short duration, to cause an
3.
undercharged condition.
A vehicle
capacity.
electrical load exceeding the generator
4.
Defect in the charging system such as high resist-
ance, slipping fan belt, faulty generator or voltage
regulator.
5. Battery abuse, including failure to keep the Battery
top clean, cable clamps and posts clean and tight,
and improper addition of water to the cells.
LEVEL INDICATOR
The Battery features an electrolyte level indicator,
which is a specially designed vent plug with a transparent
rod extending through the center (fig. 5b). When the elec-
trolyte is at the proper level, the lower tip of the rod is
immersed, and the exposed top of the rod will appear
very dark; when the level falls below the tip of the rod,
the top will glow. ,
The Indicator reveals at a glance if water is needed,
without the necessity of removing the vent plugs (fig. 6b).
The Level Indicator is used in only one cell (second
cell cap from positive Battery post) because when the
electrolyte level is low in one cell, it is normally low in
all cells. Thus when the Indicator shows water is needed,
check the level in all six cells.
An alternate method of checking the electrolyte level is
to remove the vent plug and visually observe the electro-
lyte level in the vent well. The bottom of the vent well
features a split vent which will cause the surface of the
electrolyte to appear distorted when it makes contact.
The electrolyte level is. correct when the distortion first
appears at the bottom of the split vent (fig. 4b).
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
The electrolyte level in the Battery should be checked
regularly. In hot weather, particularly during trip driv-
ing, checking should be more frequent because of more
rapid loss of water. If the electrolyte level is found to be
low, then colorless, odorless, drinking water should be
added to each cell until the liquid level rises to the split
vent located in the bottom of the vent well. DO NOT
OVERFILL because this will cause loss of electrolyte
resulting in poor performance, short life, and excessive
corrosion.
CAUTION: During service only water should be
added to the Battery, not electrolyte.
The liquid level in the cells should never be allowed to
drop below the top of the plates, as the portion of the
INDICATOR
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
CORRECT
Fig.
5b—Cut-Away View Showing Electrolyte at Proper Level
with Indicator Having Dark Appearance
plates exposed to air may be permanently damaged with a
resulting loss in performance.
WATER USAGE
Excessive usage of water indicates the Battery is being
overcharged. The most common causes of overcharge
are high Battery operating temperatures, too high a volt-
age regulator setting, poor regulator ground wire con-
nection. Normal Battery water usage is approximately
one to two ounces per month per battery.
INDICATOR
Fig.
6b—Cut-Away View Showing Electrolyte at Low Level
with Indicator Having Light Appearance
CHASSIS SBtVKZ MANUAL
Page 329 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL
6Y-4
CLEANING
The external condition of the Battery should be checked
periodically for damage or for the presence of dirt and
corrosion. The top of the Battery should be kept clean.
An accumulation of acid film and dirt may permit current
to flow between the terminals, which will slowly dis-
charge the Battery. For best results when cleaning the
top of Batteries, wash first with a diluted ammonia or a
soda solution to neutralize any acid present; then flush
with clean water. Care must be taken to keep vent plugs
tight, so that the neutralizing solution does not enter the
cells.
CABLES
To insure good electrical contact, the cables should be
clean and tight on the Energizer posts. If the posts or
cable terminals are corroded, the cables should be dis-
connected and the terminals and clamps cleaned sepa-
rately with a soda solution and a wire brush. After
cleaning and installing clamps, apply a thin coating of
petroleum jelly on the cable clamps to retard corrosion.
CARRIER
AND
HOLD-DOWN
The Battery carrier and hold-down should be clean and
free from corrosion before installing the Battery. The
carrier should be in a sound mechanical condition so that
it will support the Battery securely and keep it level.
To prevent the Battery from shaking in its carrier,
the hold-down bolts should be tight (60-80 in. lbs.). How-
ever, the bolts should not be tightened to the point where
the Battery case or cover will be placed under a severe
strain.
BATTERY SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
When Batteries are being charged, an explosive gas
mixture forms in each cell. Part of this gas escapes
through the holes in the vent plugs and may form an
explosive atmosphere around the Battery itself if ventila-
tion is poor. This explosive gas may remain in or around
the Battery for several hours after it has been charged.
Sparks or flames can ignite this gas causing an internal
explosion which may shatter the Battery.
The following precautions should be observed to pre-
vent an explosion:
1.
Do not smoke near Batteries being charged or which
have been very recently charged.
2.
Do not break live circuits at the terminals- of Batr
teries because a spark usually occurs at the point
where a live circuit is broken. Care must always be
taken when connecting or disconnecting booster leads
or cable clamps on fast chargers. Poor connections
are a common cause of electrical arcs which cause
BATTERY CHARGING PROCEDURES
There are three methods of recharging Batteries.
They differ basically in the length of time the Battery is
charged and the rate at which charging current is sup-
plied. One is the Slow Charge method, the second is the
Fast Charge method, and the third is the Emergency
Boost Charge method.
Before recharging a Battery by any method, the elec-
trolyte level must be checked and adjusted if necessary.
SLOW CHARGING
The Slow Charge method supplies the Battery with a
relatively low current flow for a relatively long period of
time. This is the only method that will bring the Battery
to a full state of charge.
The Slow Charge method consists of charging at
approximately a 4 ampere rate for 24 hours or more if
necessary to bring the Battery to full charge. A fully
charged condition is reached when the cells are gassing
freely and three corrected specific gravity readings
taken at hourly intervals show no increase.
FAST CHARGING
The Fast Charge method supplies current to the Bat-
tery at a 40 to 50 ampere rate for a 1 1/2 hour period of
time. If the electrolyte temperature reaches 125°F before
the 1 1/2 hour period is completed, the Battery must be
taken off charge temporarily, or the charging rate
reduced to avoid damage to the Battery.
Although a Battery cannot be brought to a fully charged
condition during Fast Charge, it can be substantially
recharged or "boosted". In order to bring the Battery to
a fully charged condition, the charging cycle must be
finished by the Slow Charge method.
EMERGENCY BOOST CHARGING
In cases where the Battery is not sufficiently charged
to crank the engine, an emergency boost charge may be
applied as a temporary expedient in order to crank the
engine. The Emergency Boost Charge method consists of
charging at a 40 to 50 ampere rate for a period of one-
half hour.
It should be particularly noted that the Emergency
Boost Charge will not necessarily restore the Battery to
a useful state of. charge for continued service. After an
emergency boost charge, failure to charge the Battery
further, either by a long uninterrupted driving period or
by the Fast Charge or Slow Charge method, may result
in failure to crank the engine the next time cranking is
attempted. A Battery should never be condemned on the
basis of failure to crank the engine after an emergency
boost charge. Although an emergency boost charge may
put enough energy into the Battery to crank the engine
once, further charging usually is necessary in order to
create a sufficient reserve to crank a second and third
time.
12
VOLT BATTERY SUGGESTED
CHARGING RATES
(100 Amp/hr or Less Capacity)
TYPE OF
CHARGE
Boost Charge for
Light Load Test
Slow Charge
Fast Charge
Quick Boost .
Dry Charge
Warm-up Boost
LENGTH
OF TIME
20 Minutes
24 Hours
1-1/2 Hours
30 Minutes
10 Minutes
CHARGING
RATE
50 Amps
4 Amps
40-50 Amps
40-50 Amps
15 Amps
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 332 of 659
ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-7
CHARGING SYSTEM
INDEX
Page
General Description . 6Y-7
Maintenance and Adjustments 6Y-9
Static Checks . 6Y-10
System Condition Check and Voltage
•Regular Adjustment. 6Y-10
General Output 6Y-11
Generator Diode and Field Test 6Y-12
Indicator Lamp-Initial Field Excitation
Circuit Tests . 6Y-12
Page
Field Circuit Resistance Wire Tests 6Y-13
Field Relay Test and Adjustment 6Y-14
Other Harness Checks 6Y-14
Service Operations 6Y-14
Generator 6Y-14
Removal and Installation 6Y-14
Pulley Replacement. 6Y-14
Brush Replacement (6" Delcotron). 6Y-15
Double Contact Regulator . . . . . . 6Y-16
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The charging system includes the battery, generator,
regulator, telltale light, and necessary wiring to connect
these components. The Delcotron is offered as standard
equipment, although there are various capacities avail-
able on all models.
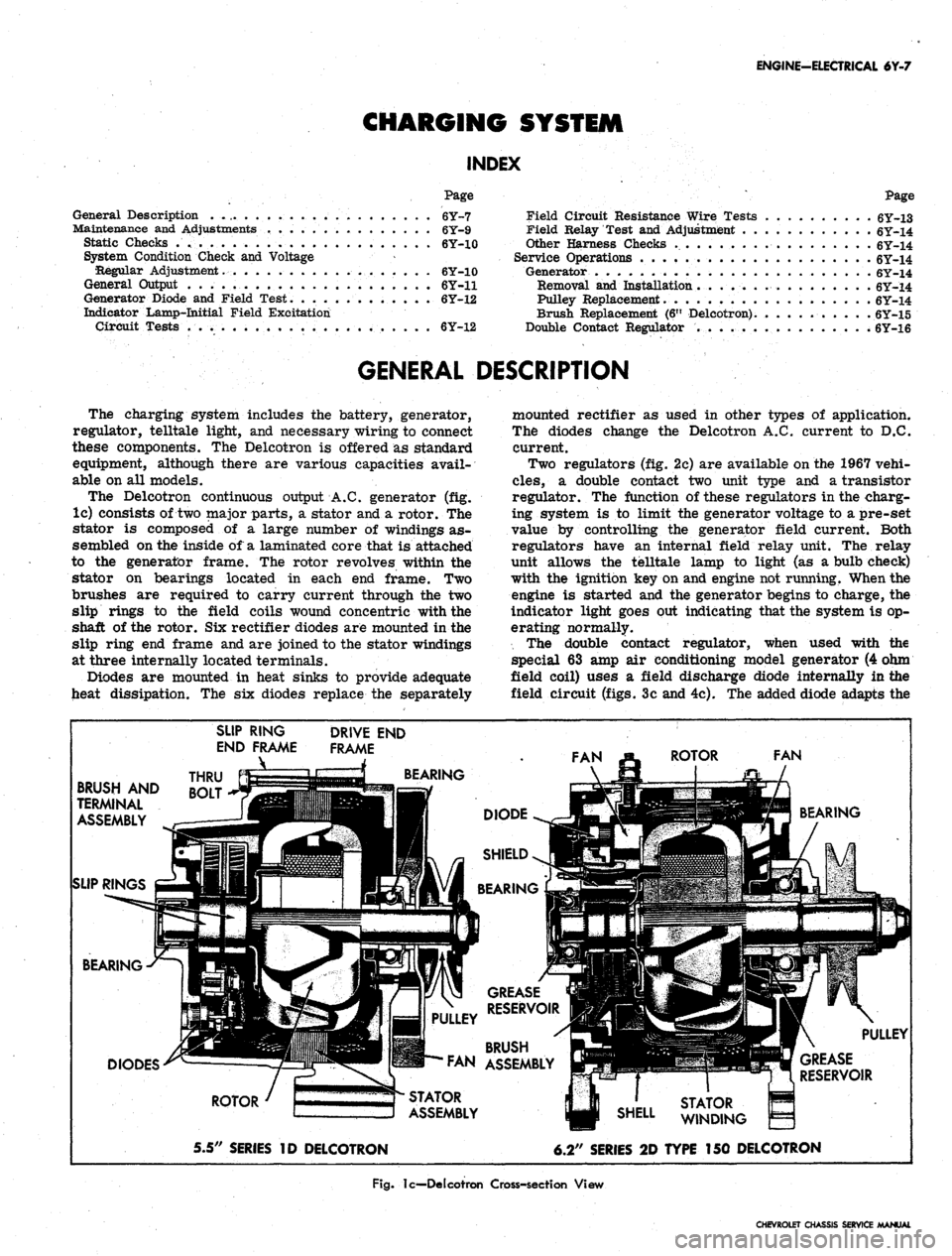
The Delcotron continuous output A.C. generator (fig.
lc) consists of two major parts, a stator and a rotor. The
stator is composed of a large number of windings as-
sembled on the inside of a laminated core that is attached
to the generator frame. The rotor revolves within the
stator on bearings located in each end frame. Two
brushes are required to carry current through the two
slip rings to the field coils wound concentric with the
shaft of the rotor. Six rectifier diodes are mounted in the
slip ring end frame and are joined to the stator windings
at three internally located terminals.
Diodes are mounted in heat sinks to provide adequate
heat dissipation. The six diodes replace the separately
mounted rectifier as used in other types of application.
The diodes change the Delcotron A.C. current to D.C.
current.
Two regulators (fig. 2c) are available on the 1967 vehi-
cles,
a double contact two unit type and a transistor
regulator. The function of these regulators in the charg-
ing system is to limit the generator voltage to a pre-set
value by controlling the generator field current. Both
regulators have an internal field relay unit. The relay
unit allows the telltale lamp to light (as a bulb check)
with the ignition key on and engine not running. When the
engine is started and the generator begins to charge, the
indicator light goes out indicating that the system is op-
erating normally.
The double contact regulator, when used with the
special 63 amp air conditioning model generator (4 ohm
field coil) uses a field discharge diode internally in the
field circuit (figs. 3c and 4c). The added diode adapts the
BRUSH AND
TERMINAL
ASSEMBLY
SLIP RINGS
SLIP RING
END FRAME
_\
THRU
BOLT
DRIVE END
FRAME
BEARING
BEARING
DIODES
ROTOR
5.5" SERIES ID DELCOTRON
STATOR
ASSEMBLY
GREASE
RESERVOIR
BRUSH
FAN ASSEMBLY
6.2" SERIES 2D TYPE 150 DELCOTRON
Fig.
lc—Delcotron Cross-section View
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 334 of 659
ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-9
63 AMP 1
MODELS ONLY'
BATTERY FUSIBLE
LINK
HORN
FUSIBLE LINK'
TRANSISTOR
FUSIBLE LINK'
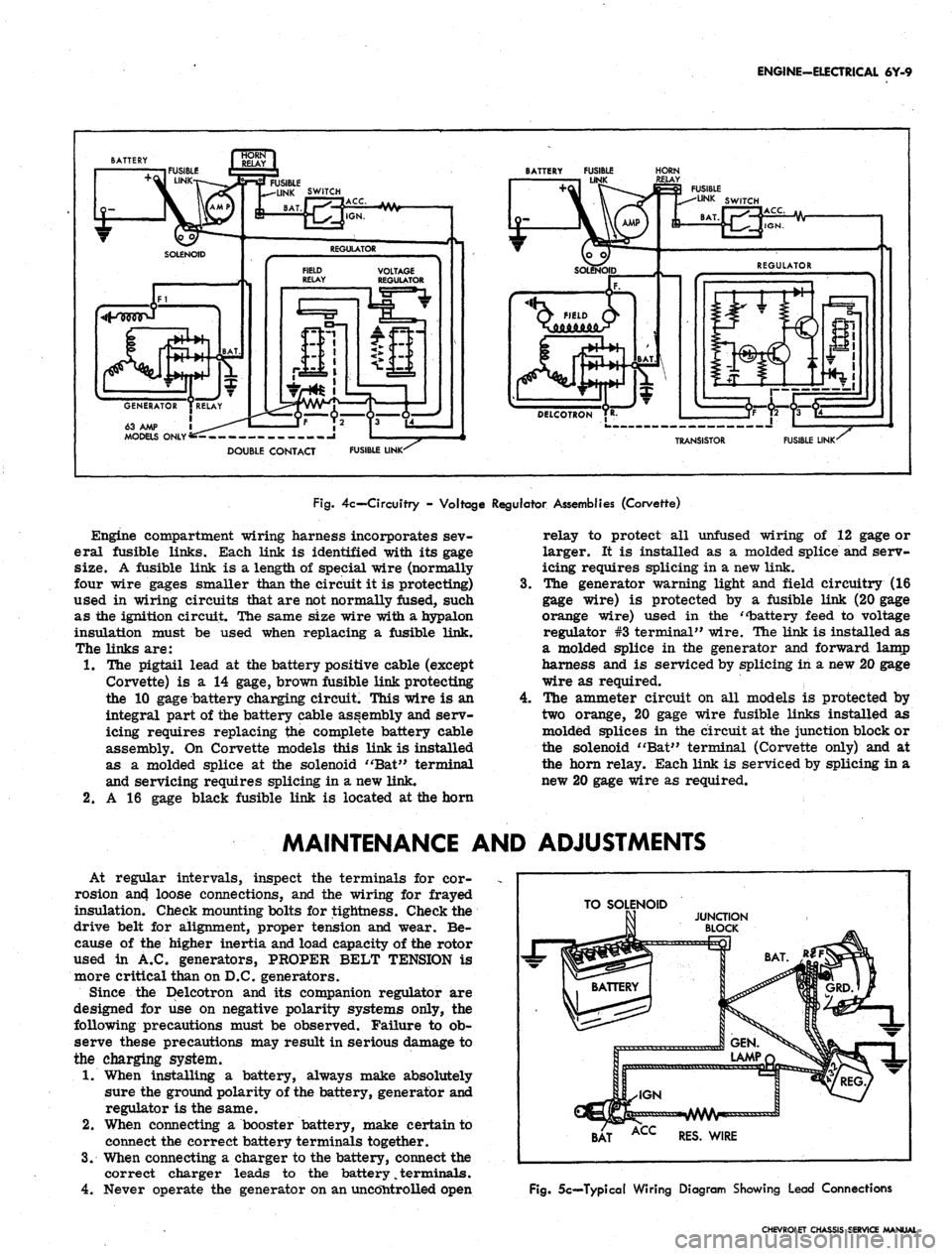
Fig.
4c— Circuitry - Voltage Regulator Assemblies (Corvette)
Engine compartment wiring harness incorporates sev-
eral fusible links. Each link is identified with its gage
size. A fusible link is a length of special wire (normally
four wire gages smaller than the circuit it is protecting)
used in wiring circuits that are not normally fused, such
as the ignition circuit. The same size wire with a hypalon
insulation must be used when replacing a fusible link.
The links are:
1.
The pigtail lead at the battery positive cable (except
Corvette) is a 14 gage, brown fusible link protecting
the 10 gage battery charging circuit. This wire is an
integral part of the battery cable assembly and serv-
icing requires replacing the complete battery cable
assembly. On Corvette models this link is installed
as a molded splice at the solenoid "Bat" terminal
and servicing requires splicing in a new link.
2.
A 16 gage black fusible link is located at the horn
4.
relay to protect all unfused wiring of 12 gage or
larger. It is installed as a molded splice and serv-
icing requires splicing in a new link.
The generator warning light and field circuitry (16
gage wire) is protected by a fusible link (20 gage
orange wire) used in the "battery feed to voltage
regulator #3 terminal" wire. The link is installed as
a molded splice in the generator and forward lamp
harness and is serviced by splicing in a new 20 gage
wire as required.
The ammeter circuit on all models is protected by
two orange, 20 gage wire fusible links installed as
molded splices in the circuit at the junction block or
the solenoid "Bat" terminal (Corvette only) and at
the horn relay. Each link is serviced by splicing in a
new 20 gage wire as required.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
At regular intervals, inspect the terminals for cor-
rosion an4 loose connections, and the wiring for frayed
insulation. Check mounting bolts for tightness. Check the
drive belt for alignment, proper tension and wear. Be-
cause of the higher inertia and load capacity of the rotor
used in A.C. generators, PROPER BELT TENSION is
more critical than on D.C. generators.
Since the Delcotron and its companion regulator are
designed for use on negative polarity systems only, the
following precautions must be observed. Failure to ob-
serve these precautions may result in serious damage to
the charging system.
1.
When installing a battery, always make absolutely
sure the ground polarity of the battery, generator and
regulator is the same.
2.
When connecting a booster battery, make certain to
connect the correct battery terminals together.
3.
When connecting a charger to the battery, connect the
correct charger leads to the battery
%
terminals.
4.
Never operate the generator on an uncontrolled open
TO SOLENOID
BAT ACC RES. WIRE
Fig.
5c—Typical Wiring Diagram Showing Lead Connections
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL