battery CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982 Repair Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1982, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982Pages: 875, PDF Size: 88.64 MB
Page 136 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 136
accidental grounding. It is al
so advisable to include a standard automotive fuse
in any jumper wire. This is commonly referred to as a "fused jumper". By
inserting an in-line fuse holder between a set of test leads, a fused jumper wire
can be used for bypassing open circuits. Use a 5 amp fuse to provide protection
against voltage spikes.
Jumper wires are used primarily to locate open electrical circuits, on either the
ground (—) side of the circuit or on the power (+) side. If an electrical
component fails to operate, connect t he jumper wire between the component
and a good ground. If the component operates only with the jumper installed,
the ground circuit is open. If the ground circuit is good, but the component does
not operate, the circuit between the power feed and component may be open.
By moving the jumper wire successively back from the component toward the
power source, you can isolate the area of the circuit where the open is located.
When the component stops func tioning, or the power is cut off, the open is in
the segment of wire between the jumper and the point previously tested.
You can sometimes connect the jumper wir e directly from the battery to the
"hot" terminal of the component, but firs t make sure the component uses 12
volts in operation. Some electrical components, such as fuel injectors or
sensors, are designed to operate on about 4 to 5 volts, and running 12 volts
directly to these components will cause damage.
TEST LIGHTS
Fig. 1: A 12 volt test light is used to detect the presence of voltage in a circuit
The test light is used to check circuits and components while electrical current is
flowing through them. It is used for volt age and ground tests. To use a 12 volt
test light, connect the ground clip to a good ground and probe wherever
necessary with the pick. The test light will illuminate when voltage is detected.
This does not necessarily mean that 12 volts (or any particular amount of
Page 137 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 137
voltage) is present; it only means that so
me voltage is present. It is advisable
before using the test light to touch its ground clip and probe across the battery
posts or terminals to make sure the light is operating properly.
WARNING - Do not use a test light to probe electronic ignition, spark plug or
coil wires. Never use a pick-type test light to probe wiring on computer
controlled systems unless spec ifically instructed to do so. Any wire insulation
that is pierced by the test light pr obe should be taped and sealed with silicone
after testing
Like the jumper wire, the 12 volt test li ght is used to isolate opens in circuits.
But, whereas the jumper wire is used to bypass the open to operate the load,
the 12 volt test light is us ed to locate the presence of voltage in a circuit. If the
test light illuminates, there is power up to t hat point in the circuit; if the test light
does not illuminate, there is an open circui t (no power). Move the test light in
successive steps back toward the power source until the light in the handle
illuminates. The open is between the pr obe and a point which was previously
probed.
The self-powered test light is similar in design to the 12 volt test light, but
contains a 1.5 volt penlight battery in the handle. It is most often used in place
of a multimeter to check for open or shor t circuits when power is isolated from
the circuit (continuity test).
The battery in a self-powered test light does not provide much current. A weak
battery may not provide enough power to illuminate the test light even when a
complete circuit is made (especially if there is high resistance in the circuit).
Always make sure that the test battery is strong. To check the battery, briefly
touch the ground clip to the pr obe; if the light glows brightly, the battery is strong
enough for testing.
A self-powered test light should not be used on any co mputer controlled system
or component. The small amount of electr icity transmitted by the test light is
enough to damage many electr onic automotive components.
MULTIMETERS
Multimeters are an extremely useful tool for troubleshooting electrical problems.
They can be purchased in either analog or digital form and have a price range
to suit any budget. A multimeter is a voltmeter, ammeter and ohmmeter (along
with other features) combined into one instrument. It is often used when testing
solid state circuits because of its hi gh input impedance (usually 10 megaohms
or more). A brief description of the mult imeter main test functions follows:
• Voltmeter - the voltmeter is used to measure voltage at any point in a
circuit, or to measure the voltage drop across any part of a circuit.
Voltmeters usually have various scales and a selector switch to allow the
reading of different volt age ranges. The voltmeter has a positive and a
negative lead. To avoid damage to the meter, always connect the
negative lead to the negative (—) side of the circ uit (to ground or nearest
Page 138 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 138
the ground side of the circuit) and
connect the positive lead to the
positive (+) side of the circuit (to t he power source or the nearest power
source). Note that the negative voltme ter lead will always be black and
that the positive voltmeter will alwa ys be some color other than black
(usually red).
• Ohmmeter - the ohmmeter is designed to read resistance (measured in
ohms) in a circuit or component. Mo st ohmmeters will have a selector
switch which permits the measurement of different ranges of resistance
(usually the selector swit ch allows the multiplication of the meter reading
by 10, 100, 1,000 and 10,000). Some ohmmeters are "auto-ranging"
which means the meter itself will dete rmine which scale to use. Since the
meters are powered by an internal battery, the ohmmeter can be used
like a self-powered test light. When the ohmmeter is connected, current
from the ohmmeter flows through the ci rcuit or component being tested.
Since the ohmmeter's internal resi stance and voltage are known values,
the amount of current flow throug h the meter depends on the resistance
of the circuit or component being test ed. The ohmmeter can also be used
to perform a continuity test for suspected open circuits. In using the
meter for making continuity checks, do not be concerned with the actual
resistance readings. Zero resistance, or any ohm reading, indicates
continuity in the circui t. Infinite resistance indi cates an opening in the
circuit. A high resistance reading w here there should be none indicates a
problem in the circuit. Checks for s hort circuits are made in the same
manner as checks for open circuits, ex cept that the circuit must be
isolated from both power and normal gr ound. Infinite resistance indicates
no continuity, while zero resi stance indicates a dead short.
WARNING - Never use an ohmmeter to check the resistance of a component or
wire while there is volt age applied to the circuit
• Ammeter - an ammeter measures the am ount of current flowing through
a circuit in units called amperes or amps. At normal operating voltage,
most circuits have a characteristic amount of amperes, called "current
draw" which can be measured usi ng an ammeter. By referring to a
specified current draw rating, then measuring the amperes and
comparing the two values, one can det ermine what is happening within
the circuit to aid in diagnosis. An open circuit, for example, will not allow
any current to flow, so the amme ter reading will be zero. A damaged
component or circuit will have an incr eased current draw, so the reading
will be high. The ammeter is always connected in series with the circuit\
being tested. All of the current that normally flows through the circuit
must also flow through the ammeter; if there is any other path for the
current to follow, the ammeter readi ng will not be accurate. The ammeter
itself has very little resistance to curr ent flow and, therefore, will not affect
the circuit, but it will measure current draw only when the circuit is closed
and electricity is flowing. Excessive current draw can blow fuses and
drain the battery, while a reduced current draw can cause motors to run \
slowly, lights to dim and other components to not operate properly.
Page 141 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 141
4. To isolate the short, probe a test point
at either end of the isolated circuit
(the light should be on or the mete r should indicate continuity).
5. Leave the test light probe engaged and sequentiall y open connectors or
switches, remove parts, etc. until t he light goes out or continuity is
broken.
6. When the light goes out, the shor t is between the last two circuit
components which were opened.
VOLTAGE
This test determines voltage available fr om the battery and should be the first
step in any electrical troubleshooting pr ocedure after visual inspection. Many
electrical problems, especially on co mputer controlled systems, can be caused
by a low state of charge in the battery. Excessive corrosion at the battery cable
terminals can cause poor contact that will prevent proper charging and f\
ull
battery current flow.
1. Set the voltmeter selector switch to the 20V position.
2. Connect the multimeter negative lead to the battery's negative (-) post or
terminal and the positive lead to t he battery's positive (+) post or
terminal.
3. Turn the ignition switch ON to provide a load.
4. A well charged battery should register over 12 volts. If the meter reads
below 11.5 volts, the battery power may be insufficient to operate the
electrical system properly.
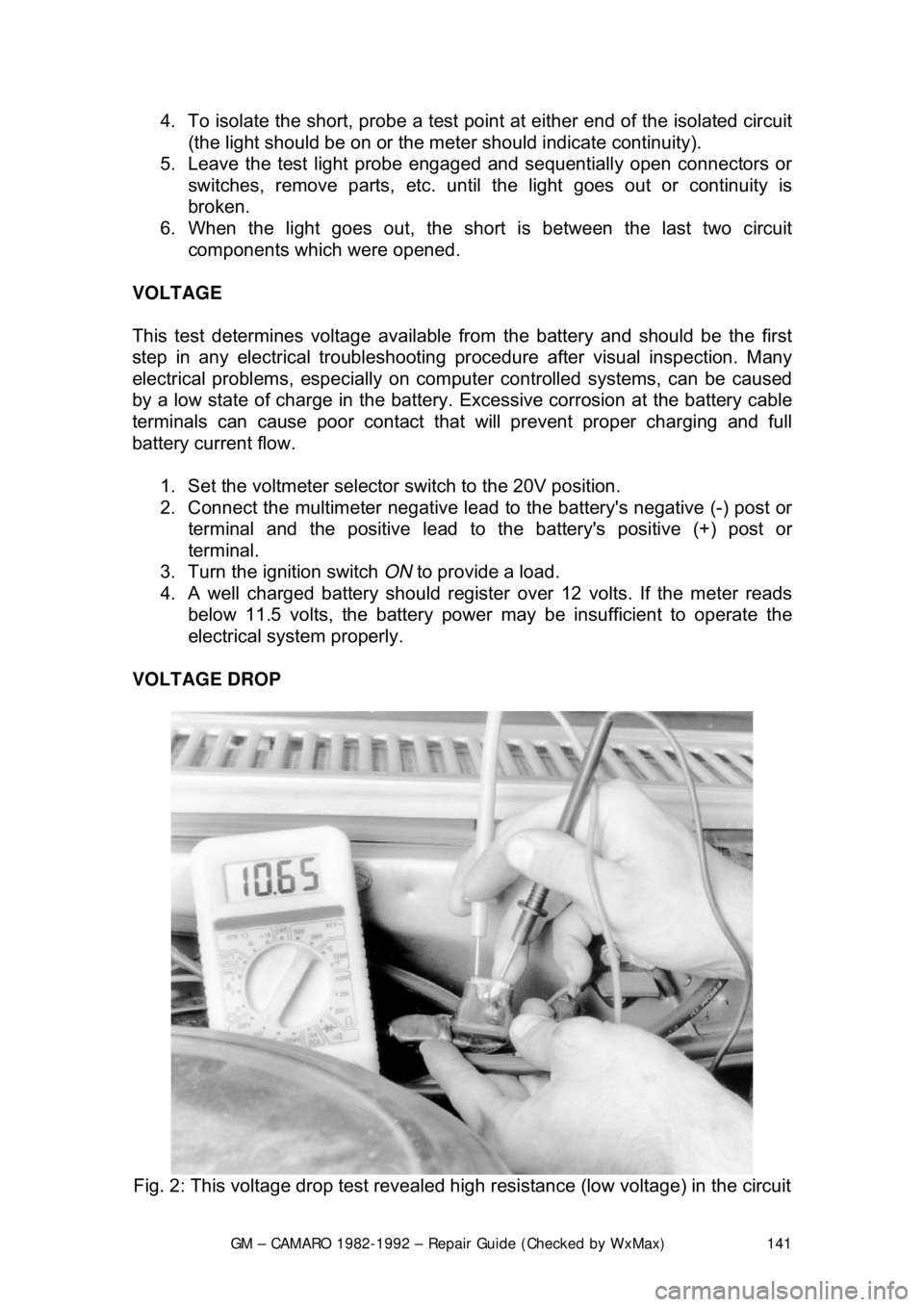
VOLTAGE DROP
Fig. 2: This voltage drop test revealed high resistance (low voltage) in the circuit
Page 144 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 144
1. Isolate the circuit from
the vehicle's power source.
2. Ensure that the ignition key is OFF when disconnecting any components
or the battery.
3. Where necessary, also isolate at least one side of the circuit to be
checked, in order to avoid reading parallel resistances. Parallel circuit
resistances will always give a lower reading than the actual resistance of
either of the branches.
4. Connect the meter leads to both sides of the circuit (wire or component)
and read the actual measured ohms on the meter scale. Make sure the
selector switch is set to the proper ohm scale for the circuit being tested,
to avoid misreading the oh mmeter test value.
WIRE AND CONNECTOR REPAIR
Almost anyone can replace damaged wires, as long as the proper tools and
parts are available. Wire and terminals ar e available to fit almost any need.
Even the specialized weatherproof, mol ded and hard shell connectors are now
available from aftermarket suppliers.
Be sure the ends of all the wires are fitted with t he proper terminal hardware
and connectors. Wrapping a wire around a stud is never a permanent solution
and will only cause trouble later. Repl ace wires one at a time to avoid
confusion. Always route wires exac tly the same as the factory.
If connector repair is necessary, only atte mpt it if you have the proper tools.
Weatherproof and hard shell con nectors require special tools to release the pins
inside the connector. Attempting to r epair these connectors with conventional
hand tools will damage them.
BATTERY CABLES
DISCONNECTING THE CABLES
When working on any electrical component on the vehicle, it is always a good
idea to disconnect the negative (-) battery cable. This will prevent potential
damage to many sensitive electrical co mponents such as the Engine Control
Module (ECM), radio, alternator, etc.
Any time you disengage the battery cables, it is recommended that you
disconnect the negative (&mdash) battery cable first. This will prevent your
accidentally grounding the positive (+) term inal to the body of the vehicle when
disconnecting it, thereby prevent ing damage to the above mentioned
components.
Before you disconnect the cable(s), first turn the ignition to the OFF position.
This will prevent a draw on the battery which could cause arcing (electricity
trying to ground itself to the body of a vehi cle, just like a spark plug jumping the
gap) and, of course, damaging some com ponents such as the alternator diodes.
Page 145 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 145
When the battery cable(s) are reconnecte
d (negative cable last), be sure to
check that your lights, windshield wipers and other electrically operated safety
components are all working correctly. If your vehicle contains an Electronically
Tuned Radio (ETR), don't forget to also reset your radio stations. Ditto for the
clock.
Page 147 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 147
SYSTEM OPERATION
The main portions of the SIR system
are the deployment loops and the
Diagnostic Energy Reserve Module (D ERM). The main function of the
deployment loops is to supply current through the inflator module(s), which will
cause deployment of the air bag(s) in t he event of a frontal crash of sufficient
force. The arming sensor, SIR coil assembly (driver side only), passen\
ger
inflator module jumper (passenger side only), inflator module(s), passenger
compartment discriminating sensor and fo rward discriminating sensor make up
the deployment loops.
The DERM has two functions. One to supply the deployment loops with a 36
volt reserve to ensure sufficient energy is available to deploy the airbag(s) if the
battery voltage feed to the arming sensor is lost during a frontal crash. Another
function is SIR electrical system diagnostics.
The arming sensor switches power to th e inflator module(s) on the high side
(power side) of the deployment loops. Ei ther of the discriminating sensors can
supply ground to the inflator module(s) on the low side (ground side) of the loop.
The inflator module(s) ar e only supplied sufficient cu rrent to deploy when the
arming sensor and at least one of the two discriminating sensors are closed
simultaneously.
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
DIAGNOSTIC ENERGY RESERVE MODULE
The DERM is designed to perform the following functions in the SIR system:
• Energy Reserve - Maintains 36 volt energy reserve(s) to provide
deployment energy when the vehicle volt age is low or lost in a frontal
impact
• Malfunction Detection - Performs diagnostic monitoring of the SIR
system electrical components
• Malfunction Recording - Provides diagnostic trouble code information
• Frontal Crash Recording - Record s the SIR system status during a
frontal crash
WARNING LAMP
The "INFL REST" or "AIR BAG" warning lamp is used to do the following:
• Verify lamp and DERM oper ation by flashing seven to nine times when
the ignition key is first turned ON
• Warn the driver of SIR electrical system faults which could potentially
affect the operation of the SIR system
• Provide diagnostic information by fl ashing the fault codes when the
diagnostic mode is enabled
Page 148 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 148
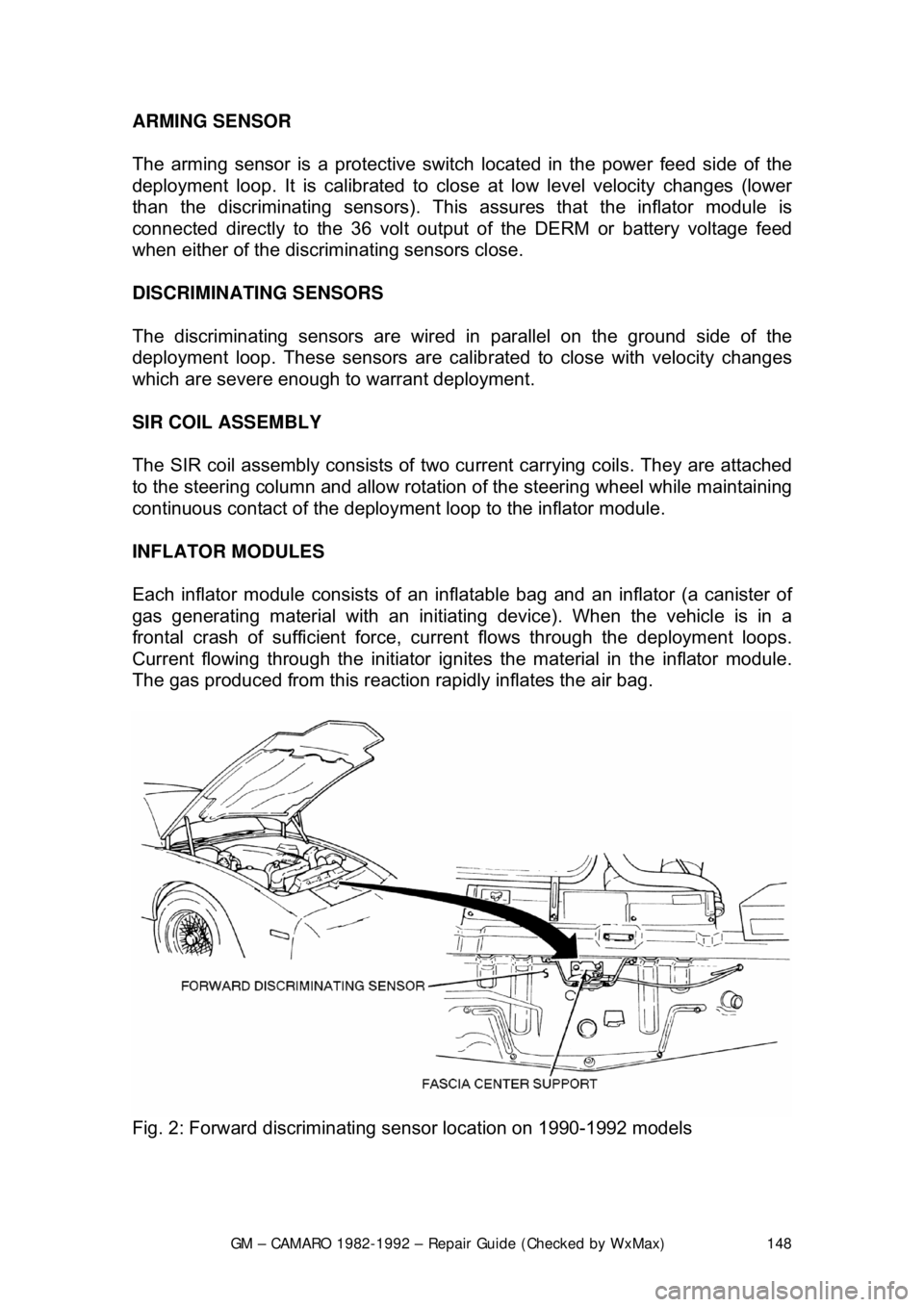
ARMING SENSOR
The arming sensor is a protective switch
located in the power feed side of the
deployment loop. It is calibrated to clos e at low level velocity changes (lower
than the discriminating sens ors). This assures that the inflator module is
connected directly to the 36 volt output of the DERM or battery voltage feed
when either of the discrim inating sensors close.
DISCRIMINATING SENSORS
The discriminating sensors are wired in parallel on the ground side of the
deployment loop. These sensors are calib rated to close with velocity changes
which are severe enough to warrant deployment.
SIR COIL ASSEMBLY
The SIR coil assembly consists of two cu rrent carrying coils. They are attached
to the steering column and allow rotation of the steering wheel while maintaining
continuous contact of the deployment loop to the inflator module.
INFLATOR MODULES
Each inflator module consists of an inflat able bag and an inflator (a canister of
gas generating material with an initiati ng device). When the vehicle is in a
frontal crash of sufficient force, current flows through the deployment loops.
Current flowing through the initiator ignite s the material in the inflator module.
The gas produced from this reaction rapidly inflates the air bag.
Fig. 2: Forward discriminating se nsor location on 1990-1992 models
Page 149 of 875
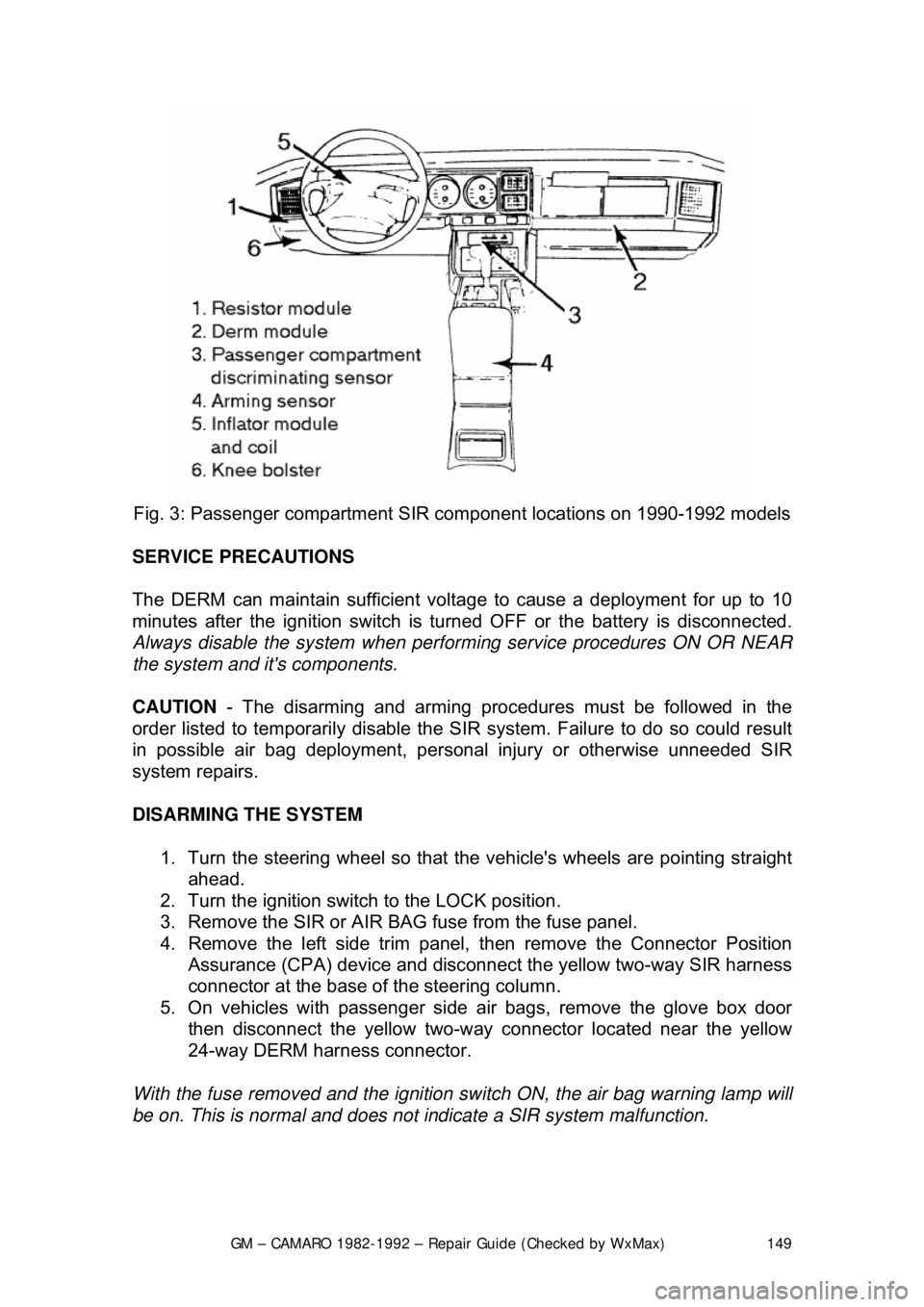
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 149
Fig. 3: Passenger com partment SIR component lo cations on 1990-1992 models
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
The DERM can maintain sufficient volt age to cause a deployment for up to 10
minutes after the ignition switch is tur ned OFF or the battery is disconnected.
Always disable the system when perfo rming service procedures ON OR NEAR
the system and it's components.
CAUTION - The disarming and arming procedures must be followed in the
order listed to temporarily disable the SI R system. Failure to do so could result
in possible air bag deployment, pers onal injury or otherwise unneeded SIR
system repairs.
DISARMING THE SYSTEM
1. Turn the steering wheel so that t he vehicle's wheels are pointing straight
ahead.
2. Turn the ignition switch to the LOCK position.
3. Remove the SIR or AIR BAG fuse from the fuse panel.
4. Remove the left side trim panel, t hen remove the Connector Position
Assurance (CPA) device and disconnec t the yellow two-way SIR harness
connector at the base of the steering column.
5. On vehicles with passenger side air bags, remove the glove box door
then disconnect the yellow two-way c onnector located near the yellow
24-way DERM harness connector.
With the fuse removed and the ignition sw itch ON, the air bag warning lamp will
be on. This is normal and does not indicate a SIR system malfunction.
Page 151 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 151
ARMING THE SYSTEM
1. Turn the ignition key to the LO CK position and remove the key.
2. On vehicles with a passenger side ai r bag, reconnect the yellow two-way
connector assembly located near the yellow 24-way DERM harness
connector. Install the glov e box door assembly.
3. Connect the yellow two-way connector assembly at the base of the
steering column.
Always be sure to reinstall the Connec tor Position Assurance (CPA) device.
4. Install the left side trim panel and rein stall the fuse in the fuse block.
5. Turn the ignition key to the RUN posit ion and verify that the warning lamp
flashes seven to nine times and then turn s OFF. If it does not operate as
described, have the system repair ed by a qualified technician.
HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING
BLOWER MOTOR
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable. If necessary, remove the diagonal
fender brace at the right rear corner of the engine compartment to gain
access to the blower motor.
2. Disconnect the electrical wiring fr om the blower motor. If equipped with
air conditioning, remove the blower relay and bracket as an assembly
and swing them aside.
3. Remove the blower motor cooling tube.
4. Remove the blower mo tor retaining screws.
5. Remove the blower motor and fan as an assembly from the case.
To install: 6. Position the blower motor into pl ace and install the retaining screws.
7. Install the blower motor cooling tube.
8. Connect all the electrical connections.
9. Connect the negative battery cable.