check engine light CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982 Repair Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1982, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982Pages: 875, PDF Size: 88.64 MB
Page 491 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 491
The first step for any assembly job is
to have a clean area in which to work.
Next, thoroughly clean all of the parts and components that are to be
assembled. Finally, place all of the co mponents onto a suitable work space and,
if necessary, arrange the parts to their respective positions.
1. Lightly lubricate the valve stems and insert all of the valves into the
cylinder head. If possible, maintain their original locations.
2. If equipped, install any valve spring shims which were removed.
3. If equipped, install the new valve seal s, keeping the following in mind:
• If the valve seal presses over the guide, lightly lubricate the outer
guide surfaces.
• If the seal is an O-ring type, it is installed just after compressing
the spring but before the valve locks.
4. Place the valve spring and retainer over the stem.
5. Position the spring compressor tool and compress the spring.
6. Assemble the valv e locks to the stem.
7. Relieve the spring pressure slowly and insure that neither valve lock
becomes dislodged by the retainer.
8. Remove the spring compressor tool.
9. Repeat Steps 2 through 8 until all of the springs have been installed.
ENGINE BLOCK
GENERAL INFORMATION
A thorough overhaul or rebuild of an engine block would include replacing the
pistons, rings, bearings, timing belt/chai n assembly and oil pump. For OHV
engines also include a new camshaft and lifters. The block would then have the
cylinders bored and honed oversize (or if using removable cylinder sleeves,
new sleeves installed) and the cranksha ft would be cut undersize to provide
new wearing surfaces and per fect clearances. However, your particular engine
may not have everything worn out. What if only the piston rings have worn out
and the clearances on everything else are still within factory specifications?
Well, you could just replace the rings and put it back together, but this would be
a very rare example. Chances are, if one component in your engine is worn,
other components are sure to follow, and soon. At the very least, you should
always replace the rings, bearings and oil pump. This is what is commonly
called a "freshen up".
CYLINDER RIDGE REMOVAL
Because the top piston ring does not travel to the very top of the cylinder, a
ridge is built up between the end of the trav el and the top of the cylinder bore.
Pushing the piston and connecting rod assembly past the ridge can be difficult,
and damage to the piston ring lands could occur. If the ridge is not removed
before installing a new piston or not re moved at all, piston ring breakage and
piston damage may occur.
Page 495 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 495
Again, rotate the engine, this time
to position the number one cylinder bore
(head surface) up. Turn the crankshaft until the number one piston is at the
bottom of its travel, this should allow t he maximum access to its connecting rod.
Remove the number one co nnecting rods fasteners and cap and place two
lengths of rubber hose over the rod bolts/studs to protect the crankshaft from
damage. Using a sturdy wooden dowel and a hammer, push the connecting rod
up about 1 in. (25mm) from the cranks haft and remove the upper bearing insert.
Continue pushing or tapping the connecti ng rod up until the piston rings are out
of the cylinder bore. Remove the piston and rod by hand, put the upper half of
the bearing insert back into the rod, in stall the cap with its bearing insert
installed, and hand-tighten the cap fasteners. If the parts are kept in order in this
manner, they will not get lost and you wil l be able to tell which bearings came
form what cylinder if any problems are discovered and diagnosis is necessary.
Remove all the other piston assemblie s in the same manner. On V-style
engines, remove all of the pistons from one bank, then reposition the engine
with the other cylinder bank head surface up, and remo ve that banks piston
assemblies.
The only remaining component in the engine block should now be the
crankshaft. Loosen the main bearing ca ps evenly until the fasteners can be
turned by hand, then remove them and the caps. Remove the crankshaft fro\
m
the engine block. Thoroughly clea n all of the components.
INSPECTION
Now that the engine block and all of its components ar e clean, it's time to
inspect them for wear and/or damage. To accurately inspect them, you will need
some specialized tools:
• Two or three separate micromet ers to measure the pistons and
crankshaft journals
• A dial indicator
• Telescoping gauges for the cylinder bores
• A rod alignment fixture to check for bent connecting rods
If you do not have access to the proper tools, you may want to bring the
components to a shop that does.
Generally, you shouldn't expect cracks in the engine block or its components
unless it was known to leak, consume or mix engine fluids, it was severely
overheated, or there was ev idence of bad bearings and/or crankshaft damage.
A visual inspection should be performed on all of the components, but just
because you don't see a crack does not mean it is not there. Some more
reliable methods for inspecting for cracks include Magnaflux, a magnetic
process or Zyglo, a dye penetrant. M agnaflux is used only on ferrous metal
(cast iron). Zyglo uses a spray on fluoresce nt mixture along with a black light to
reveal the cracks. It is strongly recommended to have your engine block
checked professionally for cracks, especia lly if the engine was known to have
overheated and/or leaked or consumed coolant. Contact a local shop for
availability and pricing of these services.
Page 496 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 496
ENGINE BLOCK
ENGINE BLOCK BEARING ALIGNMENT
Remove the main bearing caps and, if sti
ll installed, the main bearing inserts.
Inspect all of the main bearing saddles and caps for damage, burrs or high
spots. If damage is found, and it is caused from a spun main bearing, the block
will need to be align-bored or, if severe enough, replacement. Any burrs or high
spots should be carefully removed with a metal file.
Place a straightedge on the bearing saddles, in the engine block, along the
centerline of the crankshaft. If any cl earance exists between the straightedge
and the saddles, the block must be align-bored.
Align-boring consists of machining th e main bearing saddles and caps by
means of a flycutter that runs through the bearing saddles.
DECK FLATNESS
The top of the engine blo ck where the cylinder head m ounts is called the deck.
Insure that the deck surface is clean of dirt, carbon deposits and old gasket
material. Place a straightedge across the surface of the deck along its
centerline and, using feeler gauges, check the clearance along several points.
Repeat the checking procedure with th e straightedge placed along both
diagonals of the deck surface. If the reading exceeds 0.003 in. (0.076mm)
within a 6.0 in. (15.2cm) span, or 0.006 in . (0.152mm) over the total length of
the deck, it must be machined.
CYLINDER BORES
The cylinder bores house the pistons and are slightly larger than the pistons
themselves. A common piston-to-bor e clearance is 0.0015-0.0025 in.
(0.0381mm-0.0635mm). Inspect and measur e the cylinder bores. The bore
should be checked for out-of-roundness, t aper and size. The results of this
inspection will determine w hether the cylinder can be us ed in its existing size
and condition, or a rebore to the next oversize is required (or in the case of
removable sleeves, have replacements installed).
Page 498 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 498
3. Measure the gauge with the microm
eter and record the reading.
4. Again, hold the gauge square in t he bore, this time parallel to the
crankshaft centerline, and ge ntly tighten the lock. Again, you will tilt the
gauge back to remove it from the bore.
5. Measure the gaug e with the micrometer and record this reading. The
difference between these two readings is the out-of-round measurement
of the cylinder.
6. Repeat steps 1 through 5, each time going to the next lower position,
until you reach the bottom of the cyli nder. Then go to the next cylinder,
and continue until all of the cylinders have been measured.
The difference between these measurements will tell you all about the wear in
your cylinders. The measurements whic h were taken 90 degrees from the
crankshaft centerline will always reflect t he most wear. That is because at this
position is where the engine power presses the piston against the cylinder bore
the hardest. This is known as thrust wear. Take your top, 90 degree
measurement and compare it to your bottom, 90 degree measurement. The
difference between them is the taper. W hen you measure your pistons, you will
compare these readings to your pist on sizes and determine piston-to-wall
clearance.
CRANKSHAFT
Inspect the crankshaft for visible signs of wear or damage. All of the journals
should be perfectly round and smooth. Slight scores are normal for a used
crankshaft, but you should hardly feel them with your fingernail. When
measuring the crankshaft wit h a micrometer, you will take readings at the front
and rear of each journal, then turn t he micrometer 90 degrees and take two
more readings, front and rear. The differ ence between the front-to-rear readings
is the journal taper and the first-to -90 degree reading is the out-of-round
measurement. Generally, there should be no taper or out-of-roundness found,
however, up to 0.0005 in. (0.0127mm) fo r either can be overlooked. Also, the
readings should fall within the factory s pecifications for journal diameters.
If the crankshaft journals fall within specif ications, it is recommended that it be
polished before being returned to service. Polishing the crankshaft insures that
any minor burrs or high spots are smoot hed, thereby reducing the chance of
scoring the new bearings.
PISTONS AND CONNECTING RODS
PISTONS
The piston should be visually inspect ed for any signs of cracking or burning
(caused by hot spots or detonation), and scuffing or excessive wear on the
skirts. The wristpin attaches the piston to the connecting rod. The piston should
move freely on the wrist pin, both sliding and pivoting. Grasp the connecting rod
securely, or mount it in a vise, and tr y to rock the piston back and forth along
the centerline of t he wristpin. There should not be any excessive play evident
between the piston and the pin. If there are C-clips retaining the pin in the piston
Page 500 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 500
within specifications, install new bear
ings in the rod and take another
measurement. If the clearance is still out of specifications, and the crankshaft is
not, the rod will need to be reconditioned by a machine shop.
You can also use Plastigage to check the bearing clearances. The assembling
section has complete instructions on its use.
CAMSHAFT
Inspect the camshaft and lifters/followers as described earlier in this section.
BEARINGS
All of the engine bearings should be visua lly inspected for wear and/or damage.
The bearing should look evenly worn a ll around with no deep scores or pits. If
the bearing is severely worn, scored, pi tted or heat blued, then the bearing, and
the components that use it, should be brought to a machine shop for inspection.
Full-circle bearings (used on most camshafts, auxiliary shafts, balance shafts,
etc.) require specialized tools for re moval and installation, and should be
brought to a machine shop for service.
OIL PUMP
The oil pump is responsible for provid ing constant lubrication to the whole
engine and so it is re commended that a new oil pump be installed when
rebuilding the engine.
Completely disassemble the oil pump and thoroughly clean all of the
components. Inspect the oil pump gears and housing for wear and/or damage.
Insure that the pressure relief valve oper ates properly and there is no binding or
sticking due to varnish or debris. If all of the parts are in proper working
condition, lubricate the gears and relie f valve, and assemble the pump.
REFINISHING
Almost all engine block refinishing must be performed by a machine shop. If the
cylinders are not to be rebored, then t he cylinder glaze can be removed with a
ball hone. When removing cylinder glaz e with a ball hone, use a light or
penetrating type oil to lubricate the hone. Do not allow the hone to run dry as
this may cause excessive scoring of t he cylinder bores and wear on the hone. If
new pistons are required, t hey will need to be installed to the connecting rods.
This should be performed by a machine shop as the pistons must be installed in
the correct relationship to the rod or engine damage can occur.
Page 505 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 505
b. Install cap and tighten bolts to spec
ifications. Do not turn crankshaft
while Plastigage® is in place.
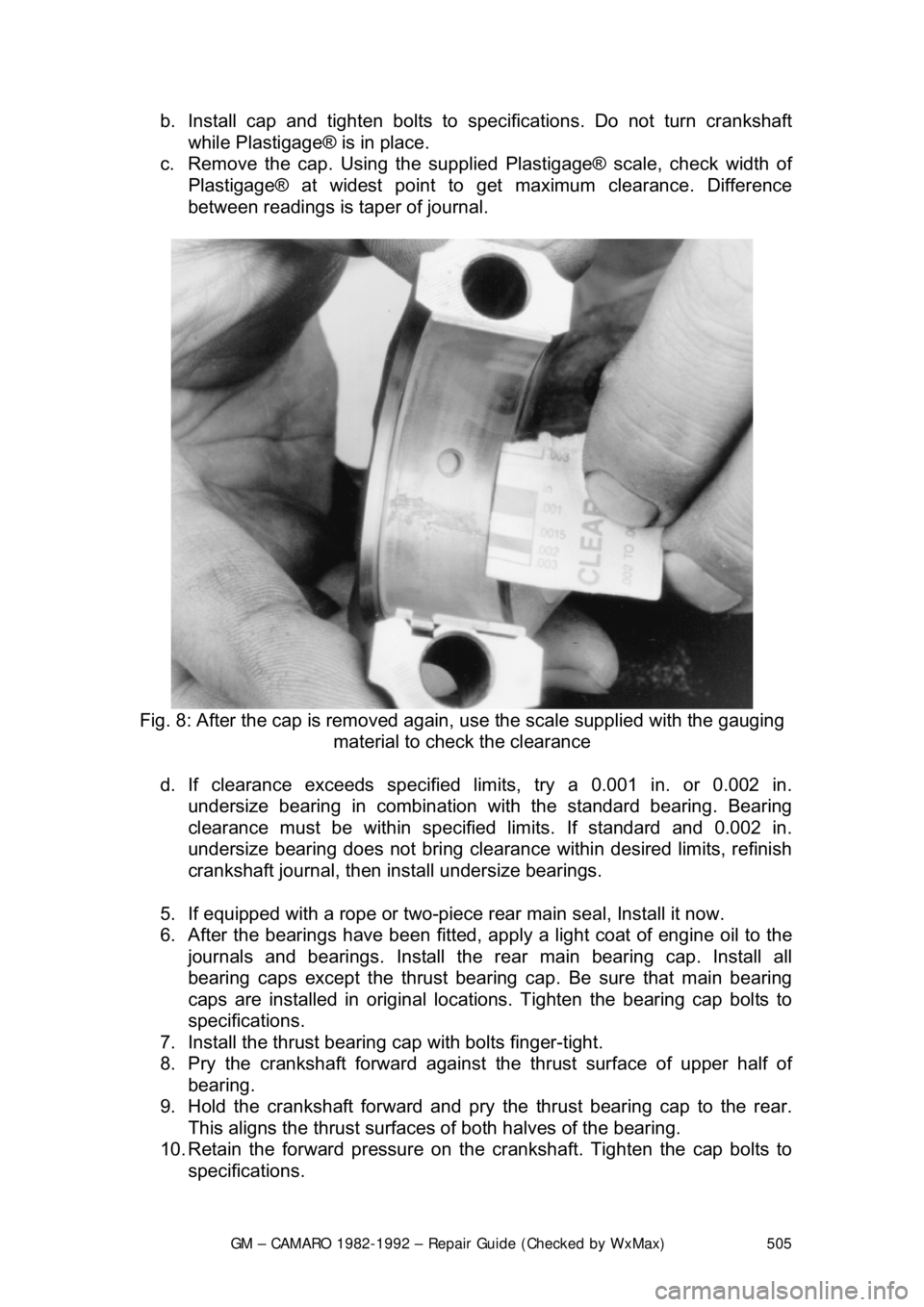
c. Remove the cap. Using the supplie d Plastigage® scale, check width of
Plastigage® at widest point to get maximum clearance. Difference
between readings is ta per of journal.
Fig. 8: After the cap is removed again, use the sca le supplied with the gauging
material to check the clearance
d. If clearance exceeds specified lim its, try a 0.001 in. or 0.002 in.
undersize bearing in combination with the standard bearing. Bearing
clearance must be within specified limits. If standard and 0.002 in.
undersize bearing does not bring clearance within desired limits, refinish
crankshaft journal, then inst all undersize bearings.
5. If equipped with a rope or two-piece r ear main seal, Install it now.
6. After the bearings have been fitted, apply a light coat of engine oil to the
journals and bearings. Install the rear main bearing cap. Install all
bearing caps except the thrust bearing cap. Be sure that main bearing
caps are installed in original locati ons. Tighten the bearing cap bolts to
specifications.
7. Install the thrust bearing cap with bolts finger-tight.
8. Pry the crankshaft forward against the thrust surface of upper half of
bearing.
9. Hold the crankshaft forward and pry the thrust bearing cap to the rear.
This aligns the thrust surfaces of both halves of the bearing.
10. Retain the forward pressure on t he crankshaft. Tighten the cap bolts to
specifications.
Page 509 of 875
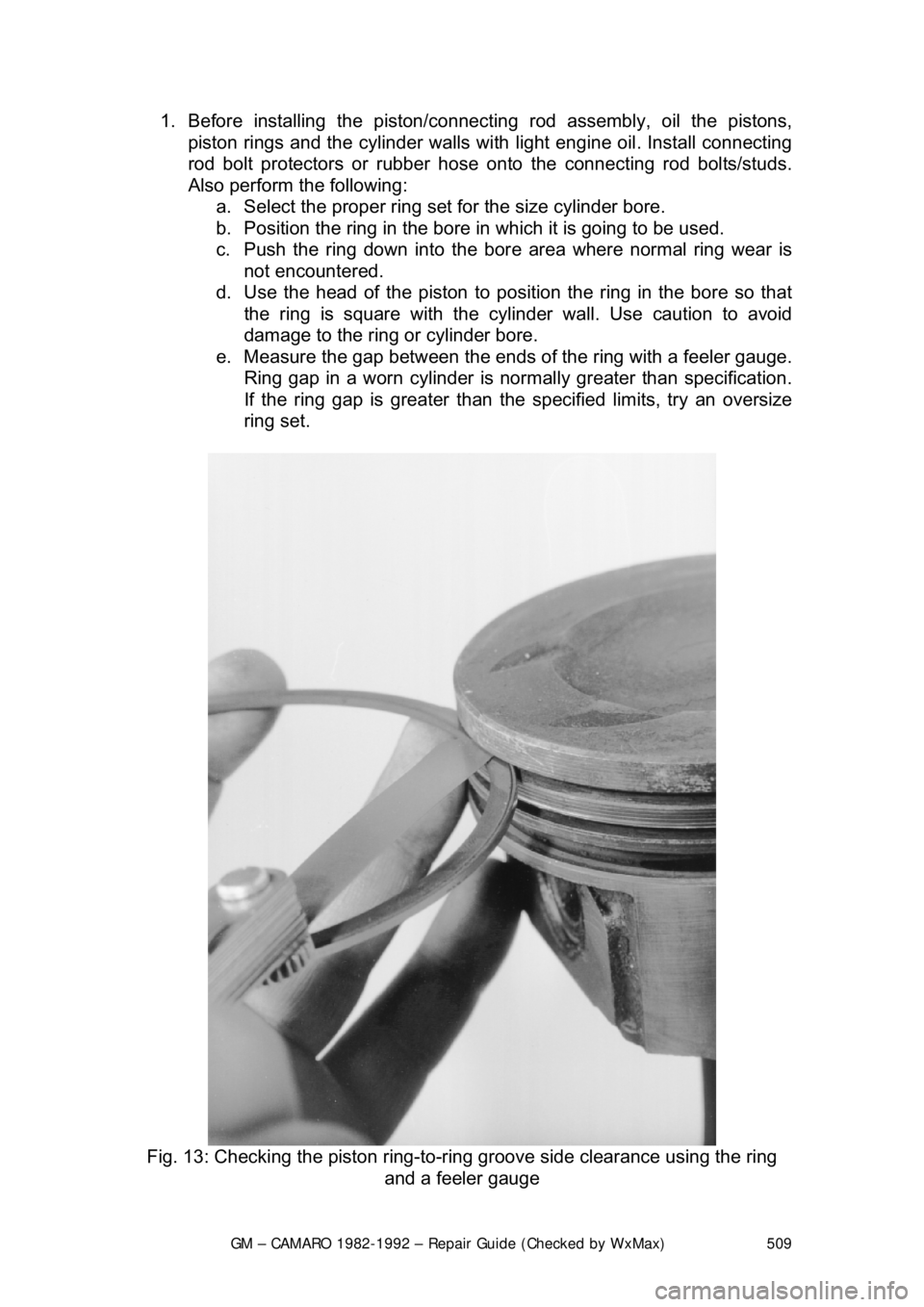

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 509
1. Before installing the
piston/connecting rod assembly, oil the pistons,
piston rings and the cylinder walls with light engine oil. Install connecting
rod bolt protectors or rubber hose onto the connecting rod bolts/studs.
Also perform the following: a. Select the proper ring set for the size cylinder bore.
b. Position the ring in the bore in which it is going to be used.
c. Push the ring down into the bor e area where normal ring wear is
not encountered.
d. Use the head of the piston to posi tion the ring in the bore so that
the ring is square with the cyli nder wall. Use caution to avoid
damage to the ring or cylinder bore.
e. Measure the gap betw een the ends of the ring with a feeler gauge.
Ring gap in a worn cylinder is normally greater than specification.
If the ring gap is greater than the specified limits, try an oversize
ring set.
Fig. 13: Checking the piston ring-to-ri ng groove side clearance using the ring
and a feeler gauge
Page 512 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 512
5. Make sure the ring gaps are pr
operly spaced around the circumference
of the piston. Fit a piston ring co mpressor around the piston and slide the
piston and connecting rod assembly do wn into the cylinder bore, pushing
it in with the wooden hammer handle. Pu sh the piston down until it is only
slightly below the top of the cylinder bore. Guide the connecting rod onto
the crankshaft bearing journal carefully, to avoid damaging the
crankshaft.
6. Check the bearing clearance of all the rod bearings, fitting them to the
crankshaft bearing journals. Follow the procedure in the crankshaft
installation above.
7. After the bearings have been fitted, apply a light coating of assembly oil
to the journals and bearings.
8. Turn the crankshaft until the appropria te bearing journal is at the bottom
of its stroke, then push the piston a ssembly all the way down until the
connecting rod bearing seat s on the crankshaft journal. Be careful not to
allow the bearing cap screws to stri ke the crankshaft bearing journals
and damage them.
9. After the piston and connecting rod assemblies have been installed, check the connecting rod side clearance on each crankshaft journal.
10. Prime and install t he oil pump and the oil pump intake tube.
CAMSHAFT, LIFTERS AND TIMING ASSEMBLY 1. Install the camshaft.
2. Install the lifters/followers into their bores.
3. Install the timing gears/chain assembly.
CYLINDER HEAD(S) 1. Install the cylinder head(s) using new gaskets.
2. Assemble the rest of the valve tr ain (pushrods and rocker arms and/or
shafts).
ENGINE COVERS AND COMPONENTS
Install the timing cover(s) and oil pan. Re fer to your notes and drawings made
prior to disassembly and install all of the components that were removed. Install
the engine into the vehicle.
ENGINE START-UP AND BREAK-IN
STARTING THE ENGINE
Now that the engine is inst alled and every wire and hose is properly connected,
go back and double check that all cool ant and vacuum hoses are connected.
Check that you oil drain plug is instal led and properly tightened. If not already
done, install a new oil filt er onto the engine. Fill the crankcase with the proper
amount and grade of engine oil. Fill the cooling system with a 50/50 mixture of
coolant/water.
Page 570 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 570
Switch (TVS). The electrical type, cons
ists of a ceramic grid located under the
base of the carburetor.
A check of the operation should be made at regular maintenance intervals.
TESTING
VACUUM SERVO TYPE 1. With the engine cold, observe the posit ion of the actuator arm. Start the
engine. The arm should move toward the diaphragm (closing the valve).
2. If the arm does not move, remove the hose and check for vacuum. If still
no vacuum, remove the top hose from the TVS switch and check for
vacuum.
3. If vacuum is present in the top hose, replace the TVS switch.
4. If vacuum is present at the actuator and it does not move, try to free the
valve. If the valve cannot be freed, it must be replaced.
ELECTRICAL TYPE 1. Turn the ignition ON with the engine co ld and probe both terminals of the
heater switch connector with a test light.
• If 1 wire has power, replace the heater switch.
• If neither wire has power, repai r the ignition circuit.
• If both wires have power, probe the pink wire at the heater
connector (if no power, repair the c onnector of the heater switch).
2. If power exists at the pink wire , disconnect the heater connector and
connect a tester across the harness terminal. If no power, repair the
ground wire; if power exists, check the resistance of the heater.
3. If heater is over 3 ohm s, replace the heater. If under 3 ohms, replace the
connector, start the engine (operate to normal temperature) and probe
the pink wire. If no power, the system is OK; if power exists, replace the
heater switch.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
VACUUM SERVO TYPE 1. Disconnect the vacuum hose at the EFE.
2. Remove exhaust pipe to manifold nuts.
3. Remove the crossover pipe. Complete removal is not always necessary.
4. Remove the EFE valve.
To install: 5. Position the EFE valve into place.
6. Install the crossover pipe.
7. Install the exhaust pi pe to manifold nuts.
8. Connect the vacuum hose at the EFE.
Page 582 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 582
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
On some models it may be necessary
to remove the air inlet assembly.
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable. Disconnect the IAC valve
electrical wiring.
2. Remove the IAC valve by performing the following: a. On thread-mounted units, use a 1
1/4 inch (32mm) wrench.
b. On flange-mounted units, remove the mounting screw assemblies.
3. Remove the IAC valve ga sket or O-ring and discard.
To install: 4. Clean the mounting surfaces by performing the following:
a. If servicing a thread-mounted valve, remove the old gasket material from the surf ace of the throttle body to ensure proper
sealing of the new gasket.
b. If servicing a flange-mounted valve, clean the IAC valve surfaces on the throttle body to assure pr oper seal of the new O-ring and
contact of the IAC valve flange.
5. If installing a new IAC valve, meas ure the distance between the tip of the
IAC valve pintle and the mounting flange. If the distance is greater than
1.102 inch (28mm), use finger pressure to slowly retract the pintle. The
force required to retract the pintle of a new valve will not cause damage
to the valve. If reinstalling the origin al IAC valve, do not attempt to adjust
the pintle in this manner.
6. Install the IAC valve into the thro ttle body by performing the following:
a. With thread-mounted valves, in stall with a new gasket. Using a
1
1/4 inch (32mm) wrench, tighten to 13 ft. lbs. (18 Nm).
b. With flange-mounted valves, lubricate a new O-ring with
transmission fluid and install on the IAC valve. Install the IAC
valve to the throttle body. Inst all the mounting screws using a
suitable thread locking compound. Tight en to 28 inch lbs. (3 Nm).
7. Connect the IAC valve electrical wiring.
8. Connect the negative battery cable.
9. No physical adjustment of the IAC valve assembly is required after installation. Reset the IAC valve pintle position by performing the
following:
a. Depress the accelerator pedal slightly.
b. Start the engine and run for 5 seconds.
c. Turn the ignition switch to the OFF position for 10 seconds.
d. Restart the engine and check for proper idle operation.