dead battery CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982 Repair Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1982, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982Pages: 875, PDF Size: 88.64 MB
Page 138 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 138
the ground side of the circuit) and
connect the positive lead to the
positive (+) side of the circuit (to t he power source or the nearest power
source). Note that the negative voltme ter lead will always be black and
that the positive voltmeter will alwa ys be some color other than black
(usually red).
• Ohmmeter - the ohmmeter is designed to read resistance (measured in
ohms) in a circuit or component. Mo st ohmmeters will have a selector
switch which permits the measurement of different ranges of resistance
(usually the selector swit ch allows the multiplication of the meter reading
by 10, 100, 1,000 and 10,000). Some ohmmeters are "auto-ranging"
which means the meter itself will dete rmine which scale to use. Since the
meters are powered by an internal battery, the ohmmeter can be used
like a self-powered test light. When the ohmmeter is connected, current
from the ohmmeter flows through the ci rcuit or component being tested.
Since the ohmmeter's internal resi stance and voltage are known values,
the amount of current flow throug h the meter depends on the resistance
of the circuit or component being test ed. The ohmmeter can also be used
to perform a continuity test for suspected open circuits. In using the
meter for making continuity checks, do not be concerned with the actual
resistance readings. Zero resistance, or any ohm reading, indicates
continuity in the circui t. Infinite resistance indi cates an opening in the
circuit. A high resistance reading w here there should be none indicates a
problem in the circuit. Checks for s hort circuits are made in the same
manner as checks for open circuits, ex cept that the circuit must be
isolated from both power and normal gr ound. Infinite resistance indicates
no continuity, while zero resi stance indicates a dead short.
WARNING - Never use an ohmmeter to check the resistance of a component or
wire while there is volt age applied to the circuit
• Ammeter - an ammeter measures the am ount of current flowing through
a circuit in units called amperes or amps. At normal operating voltage,
most circuits have a characteristic amount of amperes, called "current
draw" which can be measured usi ng an ammeter. By referring to a
specified current draw rating, then measuring the amperes and
comparing the two values, one can det ermine what is happening within
the circuit to aid in diagnosis. An open circuit, for example, will not allow
any current to flow, so the amme ter reading will be zero. A damaged
component or circuit will have an incr eased current draw, so the reading
will be high. The ammeter is always connected in series with the circuit\
being tested. All of the current that normally flows through the circuit
must also flow through the ammeter; if there is any other path for the
current to follow, the ammeter readi ng will not be accurate. The ammeter
itself has very little resistance to curr ent flow and, therefore, will not affect
the circuit, but it will measure current draw only when the circuit is closed
and electricity is flowing. Excessive current draw can blow fuses and
drain the battery, while a reduced current draw can cause motors to run \
slowly, lights to dim and other components to not operate properly.
Page 351 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 351
alternating current developed
within the stator windings to a direct (DC) current
at the output (BAT) terminal. Three of these diodes are negative and are
mounted flush with the end frame while t he other three are positive and are
mounted into a strip called a heat sink. The positive diodes are easily identified
as the ones within small cavities or depressions.
The alternator charging system is a negative (-) ground system which consists
of an alternator, a regulat or, a charge indicator, a storage battery and wiring
connecting the components, and fuse link wire.
The alternator is belt-driven from t he engine. Energy is supplied from the
alternator/regulator system to the rotati ng field through two brushes to two slip-
rings. The slip-rings are mounted on the rotor shaft and are connected t\
o the
field coil. This energy supplied to the ro tating field from the battery is called
excitation current and is used to init ially energize the field to begin the
generation of electricity. Once the alter nator starts to generate electricity, the
excitation current comes from its ow n output rather than the battery.
The alternator produces power in the form of alternating current. The alternating
current is rectified by 6 diodes into dire ct current. The direct current is used to
charge the battery and power the rest of the electrical system.
When the ignition key is turned ON, current flows from the battery, through the
charging system indicator light on the in strument panel, to the voltage regulator,
and to the alternator. Since the alternat or is not producing any current, the
alternator warning light comes on. When the engine is started, the alternator
begins to produce current and turns the alte rnator light off. As the alternator
turns and produces current, the current is divided in two ways: part to the
battery(to charge the battery and power the electrical components of the
vehicle), and part is returned to the alte rnator (to enable it to increase its
output). In this situation, the alternator is receiving current from the battery and
from itself. A voltage regulat or is wired into the current supply to the alternator
to prevent it from receiving too much cu rrent which would cause it to put out too
much current. Conversely, if the voltage regulator does not allow the alternator
to receive enough current, the battery will not be fully charged and will
eventually go dead.
The battery is connected to the alternator at all times, whether the ignition key is
turned ON or not. If the battery were shorted to ground, the alternator would
also be shorted. This woul d damage the alternator. To prevent this, a fuse link
is installed in the wiring between the battery and the alternator. If the battery is
shorted, the fuse link melts, protecting the alternator.
An alternator is better that a convent ional, DC shunt generator because it is
lighter and more compact, because it is designed to supply the battery and
accessory circuits through a wide range of engine speeds, and because it
eliminates the necessary maintenance of replacing brushes and servicing
commutators.
PRECAUTIONS
Page 352 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 352
To prevent serious damage to the alte
rnator and the rest of the charging
system, the following precauti ons must be observed:
• Never reverse the battery connections.
• Booster batteries for starting must be connected properly: positive-to-
positive and negative-to-ground.
• Disconnect the battery cables before using a fast charger; the charger
has a tendency to force current through the diodes in the opposite
direction for which they were designed. This burns out the diodes.
• Never use a fast charger as a booster for starting the vehicle.
• Never disconnect the voltage regulator while the engine is running.
• Avoid long soldering times when replacing diodes or transistors.
Prolonged heat is damaging to AC alternators.
• Do not use test lamps of more t han 12 volts (V) for checking diode
continuity.
• Do not short across or ground any of the terminals on the AC alternator.
• The polarity of the battery, alter nator, and regulator must be matched
and considered before making any elec trical connections within the
system.
• Never operate the alternator on an open circuit. make sure that all
connections within the circ uit are clean and tight.
• Disconnect the battery terminals when performing any service on the
electrical system. This wil l eliminate the possibility of accidental reversal
of polarity.
• Disconnect the battery ground cable if arc welding is to be done on any
part of the car.
CHARGING SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOTING
There are many possible ways in whic h the charging system can malfunction.
Often the source of a problem is diffi cult to diagnose, requiring special
equipment and a good deal of experience. However, when the charging system
fails completely and causes the dash boar d warning light to come on or the
battery to become dead the following items may be checked:
1. The battery is known to be good and fully charged.
2. The alternator belt is in good condition and adjusted to the proper
tension.
3. All connections in t he system are clean and tight.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
Page 653 of 875
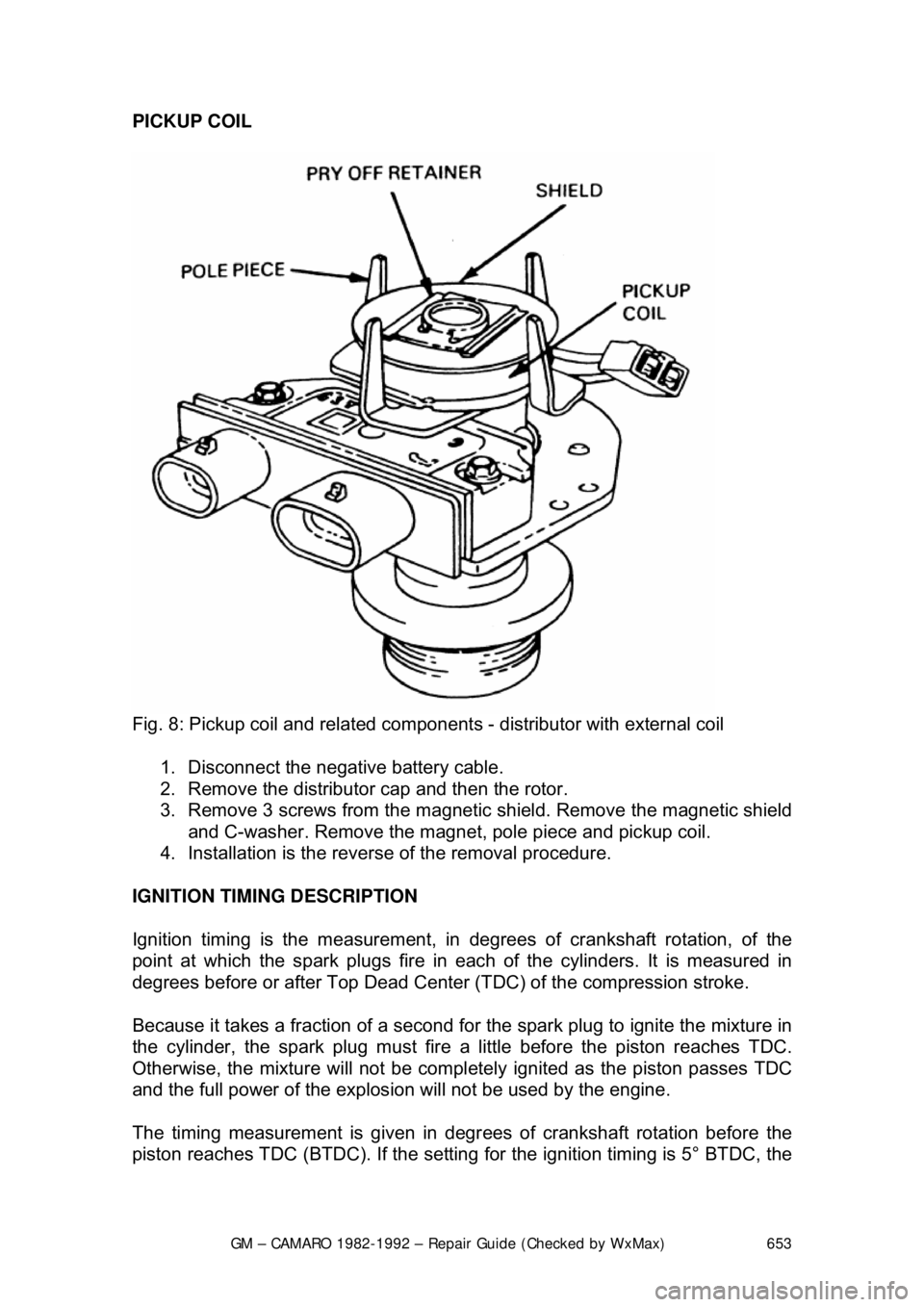
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 653
PICKUP COIL
Fig. 8: Pickup coil and related component s - distributor with external coil
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the distributor cap and then the rotor.
3. Remove 3 screws from the magnetic shield. Remove the magnetic shield
and C-washer. Remove the magnet, pole piece and pickup coil.
4. Installation is the revers e of the removal procedure.
IGNITION TIMING DESCRIPTION
Ignition timing is the measurement, in de grees of crankshaft rotation, of the
point at which the spark plugs fire in eac h of the cylinders. It is measured in
degrees before or after Top Dead Center (TDC) of the compression stroke.
Because it takes a fraction of a second for the spark plug to ignite the mixture in
the cylinder, the spark plug must fire a little before the piston reaches TDC.
Otherwise, the mixture will not be complete ly ignited as the piston passes TDC
and the full power of the explosion will not be used by the engine.
The timing measurement is given in degr ees of crankshaft rotation before the
piston reaches TDC (BTDC). If the setting fo r the ignition timing is 5° BTDC, the
Page 810 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 810
Fig. 14: After the bearings are adjusted, install the dust cap by gently tapping on
the flange - DO NOT damage the c ap by hammering on the center
JUMP STARTING A DEAD BATTERY
Whenever a vehicle is jump started, pr ecautions must be followed in order to
prevent the possibility of personal inju ry. Remember that batteries contain a
small amount of explosive hydrogen gas which is a by-product of battery
charging. Sparks should always be av oided when working around batteries,
especially when attaching jumper cabl es. To minimize the possibility of
accidental sparks, follow the procedure carefully.
Fig. 1: Connect the jumper cables to the batteries and engine in the order
shown
Page 811 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 811
CAUTION
- NEVER hook the batteries up in a series circuit or the entire
electrical system will go up in smoke, including the starter!
Vehicles equipped with a diesel engine may utilize two 12 volt batteries. If so,
the batteries are connected in a parallel circuit (positive terminal to positive
terminal, negative terminal to negative te rminal). Hooking the batteries up in
parallel circuit increases battery cranki ng power without increasing total battery
voltage output. Output remains at 12 vo lts. On the other hand, hooking two 12
volt batteries up in a series circuit (positive terminal to negative terminal,
positive terminal to negative terminal) incr eases total battery output to 24 volts
(12 volts plus 12 volts).
JUMP STARTING PRECAUTIONS
• Be sure that both batteries are of t he same voltage. Vehicles covered by
this information and most vehicles on the road today utilize a 12 volt
charging system.
• Be sure that both batteries are of the same polarity (have the same
terminal, in most cases NEGATIVE grounded).
• Be sure that the vehicles are not touching or a short could occur.
• On serviceable batteries, be sure the v ent cap holes are not obstructed.
• Do not smoke or allow sparks anywhere near the batteries.
• In cold weather, make sure the battery electrolyte is not frozen. This can
occur more readily in a battery that has been in a state of discharge.
• Do not allow electrolyte to c ontact your skin or clothing.
JUMP STARTING PROCEDURE 1. Make sure that the voltages of the 2 batteries are the same. Most
batteries and charging systems are of the 12 volt variety.
2. Pull the jumping vehicle (with t he good battery) into a position so the
jumper cables can reach the dead battery and that vehicle's engine.
Make sure that the ve hicles do NOT touch.
3. Place the transmissions of both vehicles in Neutral (MT) or P (AT), as
applicable, then firmly set their parking brakes.
If necessary for safety reasons, the hazard lights on both vehicles may be
operated throughout the entir e procedure without significantly increasing the
difficulty of jumping the dead battery.
4. Turn all lights and accessories OFF on both vehicles. Make sure the ignition switches on both vehicles are turned to the OFF position.
5. Cover the battery cell caps with a rag, but do not cover the terminals.
6. Make sure the terminals on both batte ries are clean and free of corrosion
or proper electrical connection wil l be impeded. If necessary, clean the
battery terminals before proceeding.
7. Identify the positive (+) and negat ive (-) terminals on both batteries.
8. Connect the first jumper cable to the positive (+) terminal of the dead
battery, then connect the other end of that cable to the positive (+)
terminal of the booster (good) battery.
Page 812 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 812
9. Connect one end of the other jumper
cable to the negative (-) terminal on
the booster battery and the final cable clamp to an engine bolt head,
alternator bracket or ot her solid, metallic point on the engine with the
dead battery. Try to pick a ground on the engine that is positioned away
from the battery in order to minimi ze the possibility of the 2 clamps
touching should one l oosen during the procedure. DO NOT connect this
clamp to the negative (-) term inal of the bad battery.
CAUTION - Be very careful to keep the jum per cables away from moving parts
(cooling fan, belts, etc.) on both engines.
10. Check to make sure that the c ables are routed away from any moving
parts, then start the d onor vehicle's engine. Run the engine at moderate
speed for several minutes to allow the dead battery a chance to receive
some initial charge.
11. With the donor vehicle's engine still r unning slightly above idle, try to start
the vehicle with the dead battery. Crank the engine for no more than 10 \
seconds at a time and let the starter cool for at least 20 seconds between
tries. If the vehicl e does not start in 3 tries, it is likely that something else
is also wrong or that the battery needs additional time to charge.
12. Once the vehicle is star ted, allow it to run at idle for a few seconds to
make sure that it is operating properly.
13. Turn ON the headlight s, heater blower and, if equipped, the rear
defroster of both vehicles in order to reduce the severity of voltage spikes
and subsequent risk of dam age to the vehicles' electrical systems when
the cables are disconnected. This st ep is especially important to any
vehicle equipped with computer control modules.
14. Carefully disconnect the cables in the reverse order of connection. Star\
t with the negative cable that is attached to the engine ground, then the
negative cable on the donor battery. Di sconnect the positive cable from
the donor battery and finally, disconnect the positive cable from the
formerly dead battery. Be careful when disconnecting the cables from the
positive terminals not to allow the alli gator clips to touch any metal on
either vehicle or a short and sparks will occur.
JACKING
Your vehicle was supplied with a jack for emergency road repairs. This jack is
fine for changing a flat tire or other s hort term procedures not requiring you to
go beneath the vehicle. If it is used in an emergency situation, carefully follow
the instructions provided eit her with the jack or in your owner's manual. Do not
attempt to use the jack on any portions of the vehicle other than specified by the
vehicle manufacturer. Always block the diagonally opposite wheel when using a
jack.
A more convenient way of jacking is the use of a garage or floor jack. You may
use the floor jack to raise the vehicle in the areas shown in the illustration .