wheel bolts CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 147 of 2438

REAR (STUB) AXLE ALIGNMENT ALL MODELS INDEX
page page
General Information ....................... 89 Rear Wheel Alignment..................... 89
GENERAL INFORMATION
Because front wheel drive vehicles are equipped with
rear suspension incorporating stub axles (or wheel
spindles). It is possible to align both the camber and toe
of the rear wheels.
REAR WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Alignment adjustment if required. Is made by adding
0.010 inch shims (from the service package kit) be-
tween the spindle mounting surface and axle mounting
plate. Each shim equals wheel change by .3É as shown
(for all car lines) in (Figs. 3 to 6). If rear wheel alignment is required, place vehicle on
alignment rack and check alignment specifications.
When recording rear toe-in (vehicle backed onto
alignment rack) REMEMBER to reverse sign
convention; a total toe-in on direct reading
charts is actually toe-out while driving. Maintain
rear alignment within Chrysler Motors recommenda-
tions, found in Specifications.
INSTALLATION OF REAR ALIGNMENT SHIMS
(1) Block front tires so vehicle will not move.
(2) Release parking brake.
(3) Hoist vehicle so that rear suspension is in full
rebound and tires are off the ground. See Hoisting in
Lubrication and Maintenance, Group 0. (4) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(5) Pry off grease cap.
(6) Remove cotter pin and castle lock.
(7) Remove adjusting nut.
(8) Remove brake drum (Fig. 1). (9) Loosen four (4) brake assembly and spindle
mounting bolts enough to allow clearance for shim
installation (Fig. 2). Do not remove mounting
bolts.
(10) Install shims as shown in Figs. 3, 4, 5 and 6
for desired wheel change. No more than two shims
on each spindle should be used to bring alignment
within acceptable range. Wheel change by .3É per shim.
(11) Tighten down the 4 brake support plate and
spindle to axle mounting bolts until they are snug.
Then tighten the 4 bolts to the torque values listed
for the vehicle line which is being serviced.
² AA, AG, AJ, AP Bodies 75 N Im (55 ft. lbs.)
Fig. 2 Loosen Mounting Bolts
Fig. 3 Shim Installation for Toe-Out
Fig. 1 Remove Brake Drum
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 89
Page 161 of 2438

BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
INSPECTION OF BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes and
at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses should be
performed whenever the brake system is serviced and
every 7,500 miles or 12 months, whichever comes first
(every engine oil change). Inspect hydraulic brake
hoses for severe surface cracking, scuffing, or worn
spots. Should the fabric casing of the rubber hose be
exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the rubber hose
cover, the hose should be replaced immediately. Even-
tual deterioration of the hose can take place with
possible burst failure. Faulty installation can cause
twisting and wheel, tire or chassis interference. The steel brake tubing should be inspected periodi-
cally for evidence of physical damage or contact with
moving or hot components.
INSTALLATION OF BRAKE HOSE
Always use factory recommended brake hose to en-
sure quality, correct length and superior fatigue life.
Care should be taken to make sure that the tube and
hose mating surfaces are clean and free from nicks and
burrs. Front right and left side hoses are not
interchangeable. Connections should be correct and properly made.
Use new copper seal washers on all connections using
Banjo Bolts and tighten all fittings to their specified
torques. The flexible front hydraulic brake hose should al-
ways be installed on the vehicle by first attaching the
Banjo connector to the caliper assembly. Then bolt the
intermediate hose bracket to the strut assembly allow-
ing the bracket to position the hose to prevent twisting.
Attach the hose to the body bracket and steel brake
tubing. Tighten all fittings to specified torque. The
body bracket and hose end are keyed so that they will
only fit one way. Install rear brake hoses first to the trailing arm
tubes and then to the floor pan tubes. Minimize hose
twisting. Vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes have
brake hoses attached to the caliper on each side. The
brake hose should be first attached by the Banjo bolt to
the caliper and then secured to the hose bracket with
the retaining clip. The attach the steel brake tubing to
the hose fitting.
REPAIR AND INSTALLATION OF BRAKE TUB- ING
Only double wall 4.75mm (3/16 in.) steel tubing
should be used for replacement. Care should be taken
when replacing brake tubing, to be sure the proper
bending and flaring tools and procedures are used, to
avoid kinking. Do not route the tubes against sharp edges, moving components or into hot areas. All
tubes should be properly attached with recommended
retaining clips.
TYPES OF TUBING FLARES
Two different tubing flares (Fig. 13) are used on 93
M.Y. vehicles. On some ABS brake systems the tub-
ing connections made to the hydraulic assembly use
an ISO flare. All other ABS brake system compo-
nent, tubing connections are made using a double in-
verted flare. On non-ABS brake systems all
component tubing connections use only the double in-
verted flare. No ISO flares are used.
CAUTION: ALWAYS USE THE PROPER FLARING
TOOL AND PROCEDURE, FOR THE TYPE OF
BRAKE SYSTEM THAT IS BEING SERVICED TO IN-
SURE THE INTEGRITY OF THE HYDRAULIC SYS-
TEM.
TO REPAIR OR FLARE TUBING
Using Tubing Cutter, Special Tool C-3478-A or
equivalent, cut off damaged seat or tubing (Fig. 14).
Ream out any burrs or rough edges showing on in-
side of tubing (Fig. 15). This will make the ends of
tubing square (Fig. 15) and ensure better seating of
flared end tubing. PLACE TUBE NUT ON TUB-
ING BEFORE FLARING THE TUBING.
DOUBLE INVERTED TUBING FLARES.
To make a double inverted tubing flare (Fig. 13 &
16). Open handles of Flaring Tool, Special Tool
C-4047 or equivalent. Then rotate jaws of tool until
the mating jaws of tubing size are centered between
vertical posts on tool. Slowly close handles with tub-
Fig. 13 Identifying Hydraulic Brake Tubing Flares
Ä BRAKES 5 - 11
Page 173 of 2438

WHEEL CYLINDERS INDEX
page page
General Information ....................... 23
Installing Wheel Cylinders .................. 24 Service Procedures
....................... 23
GENERAL INFORMATION
The piston boots are of the push-on type and pre-
vent moisture from entering the wheel cylinder. To perform service operations or inspections of the
rear wheel brake cylinders. It will be necessary to re-
move the cylinders from the support plate and disas-
semble on the bench.
CAUTION: Wheel cylinders with cup expanders
must have cup expanders after any service proce-
dures (reconditioning or replacement).
SERVICE PROCEDURES
REMOVING WHEEL CYLINDERS FROM BRAKE SUPPORT PLATES
With brake drums removed, inspect the wheel cyl-
inder boots for evidence of a brake fluid leak. Then
block the brake pedal in the stroke position, and vi-
sually check the boots for cuts, tears, or heat cracks.
If any of these conditions exist, the wheel cylinders
should be completely cleaned, inspected and new
parts installed. (A slight amount of fluid on the boot
may not be a leak, but may be preservative fluid
used at assembly.) (1) In case of a leak, remove brake shoes, (replace
if soaked with grease or brake fluid.) (2) Thoroughly clean area of wheel cylinder, where
hydraulic brake line connects to wheel cylinder. Dis-
connect hydraulic brake tube from wheel cylinder
(Fig. 1). (3) Remove the rear wheel cylinder attaching bolts
(Fig. 1). Then pull wheel cylinder assembly off the
brake support plate (Fig. 2). (4) Clean the surface sealant off the support plate
and wheel cylinder surfaces.
DISASSEMBLING WHEEL CYLINDERS
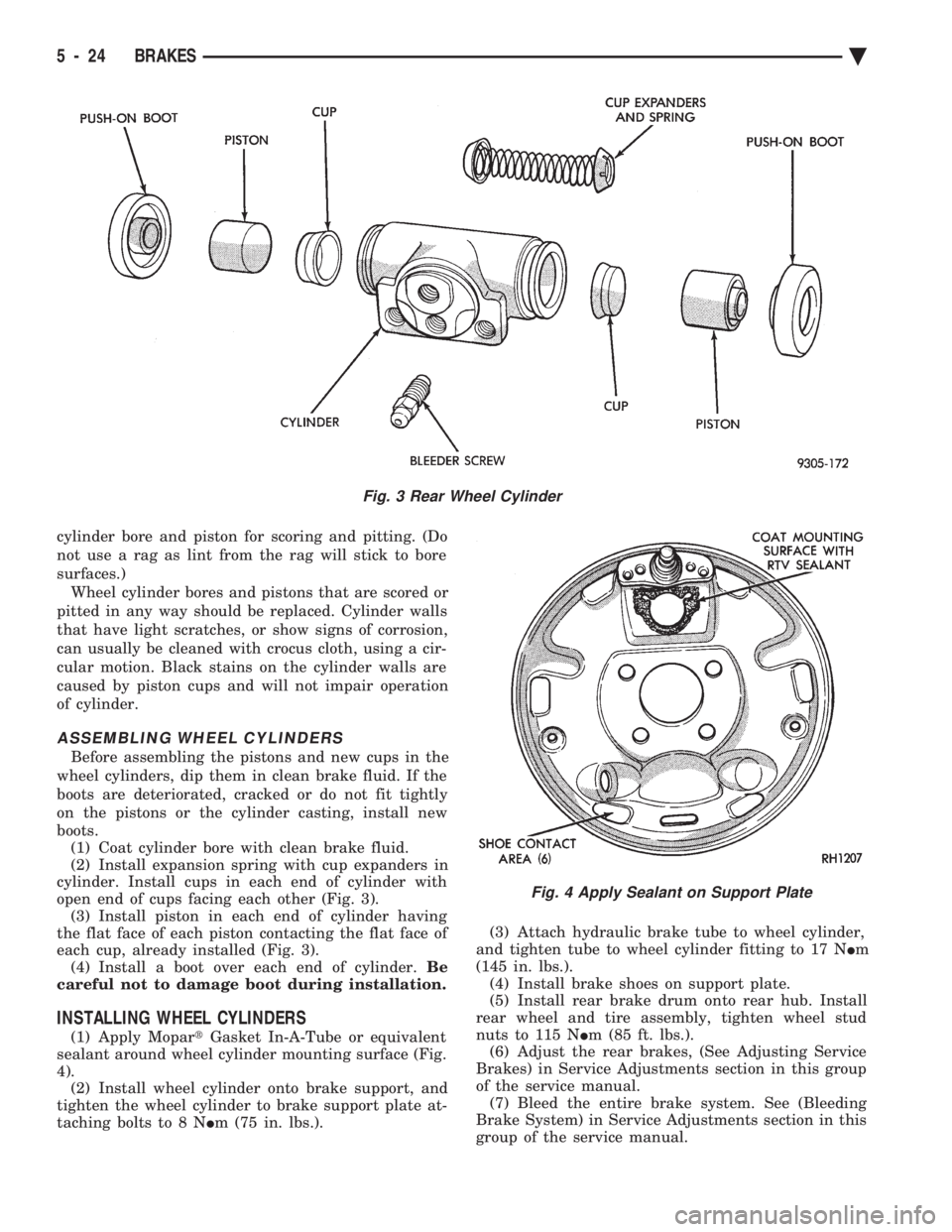
To disassemble the wheel cylinders, (Fig. 3) pro-
ceed as follows: (1) Pry boots away from cylinders and remove.
(2) Press INon one piston to force out opposite pis-
ton, cup and spring (with cup expanders). Then using
a soft tool such as a dowel rod, press out the cup and
piston that remain in the wheel cylinder. (3) Wash wheel cylinder, pistons, and spring in
clean brake fluid or alcohol; (DO NOT USE ANY
PETROLEUM BASE SOLVENTS) clean thor- oughly and blow dry with compressed air. Inspect
Fig. 1 Brake Tube Disconnected
Fig. 2 Remove or Install Wheel Cylinder
Ä
BRAKES 5 - 23
Page 174 of 2438
cylinder bore and piston for scoring and pitting. (Do
not use a rag as lint from the rag will stick to bore
surfaces.) Wheel cylinder bores and pistons that are scored or
pitted in any way should be replaced. Cylinder walls
that have light scratches, or show signs of corrosion,
can usually be cleaned with crocus cloth, using a cir-
cular motion. Black stains on the cylinder walls are
caused by piston cups and will not impair operation
of cylinder.
ASSEMBLING WHEEL CYLINDERS
Before assembling the pistons and new cups in the
wheel cylinders, dip them in clean brake fluid. If the
boots are deteriorated, cracked or do not fit tightly
on the pistons or the cylinder casting, install new
boots. (1) Coat cylinder bore with clean brake fluid.
(2) Install expansion spring with cup expanders in
cylinder. Install cups in each end of cylinder with
open end of cups facing each other (Fig. 3). (3) Install piston in each end of cylinder having
the flat face of each piston contacting the flat face of
each cup, already installed (Fig. 3). (4) Install a boot over each end of cylinder. Be
careful not to damage boot during installation.
INSTALLING WHEEL CYLINDERS
(1) Apply Mopar tGasket In-A-Tube or equivalent
sealant around wheel cylinder mounting surface (Fig.
4). (2) Install wheel cylinder onto brake support, and
tighten the wheel cylinder to brake support plate at-
taching bolts to 8 N Im (75 in. lbs.). (3) Attach hydraulic brake tube to wheel cylinder,
and tighten tube to wheel cylinder fitting to 17 N Im
(145 in. lbs.). (4) Install brake shoes on support plate.
(5) Install rear brake drum onto rear hub. Install
rear wheel and tire assembly, tighten wheel stud
nuts to 115 N Im (85 ft. lbs.).
(6) Adjust the rear brakes, (See Adjusting Service
Brakes) in Service Adjustments section in this group
of the service manual. (7) Bleed the entire brake system. See (Bleeding
Brake System) in Service Adjustments section in this
group of the service manual.
Fig. 3 Rear Wheel Cylinder
Fig. 4 Apply Sealant on Support Plate
5 - 24 BRAKES Ä
Page 175 of 2438

BRAKE SUPPORT ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
Back off parking brake adjusting nut to provide
slack in cable. With wheel and brake drum removed, disconnect
hydraulic tube from wheel cylinder.Disconnect park-
ing brake cable and adjuster lever spring (Fig. 1).
Using a suitable tool such as an aircraft type hose
clamp, install the clamp over the retainer on the end
of the parking brake cable (Fig. 2). Compress cable
housing retainer and start housing out of support
plate (Fig. 2). Remove clamp when retainer is free
from the park brake cable mounting hole in the rear
brake support plate. Alternate method is to slide a
14 mm box wrench over housing end fitting com-
pressing the three fingers. Remove attaching bolts and washers and separate
brake support and spindle from rear support trailing
arm.
INSTALLATION
Insert parking brake cable and housing into sup-
port plate. Install support plate, spindle and gasket between
support plate and spindle on to rear suspension mem-
ber. Tighten support plate attaching bolts to 71 N Im
(53 ft. lbs) torque. Attach cable to parking brake lever.
Connect brake tube to wheel cylinder. Tighten
brake tube to wheel cylinder fitting to 17 N Im (145
in. lbs.). Install brake drum and wheel. Adjust and bleed
service brakes. Adjust parking brake.
Fig. 1 Removing Adjuster Lever Spring
Fig. 2 Removing Park Brake Cable From Support Plate
Ä BRAKES 5 - 25
Page 185 of 2438

KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN FAMILY CALIPER
BRAKE SHOE SERVICE PROCEDURES
BRAKE SHOE REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. See Hoisting Information in the Lubrication
and Maintenance section of this manual. (2) Remove front wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Remove caliper guide pin bolts (Fig. 1).
(4) After removing caliper guide pin bolts. Lift cal-
iper away from braking disc using a pry bar or
screwdriver (Fig. 2). (5) Remove caliper assembly from braking disc and
adapter by sliding the assembly out and away from
the braking disc and adapter (Fig. 3). (6) Support caliper firmly to prevent weight of cal-
iper from damaging the flexible brake hose (Fig. 4). (7) Remove the outboard brake shoe assembly from
the caliper adapter (Fig. 5). (8) Remove the braking disk (rotor) from the hub
by pulling it straight off the wheel mounting studs
(Fig. 6).
Fig. 1 Removing or Installing Caliper Guide Pin Bolts
Fig. 2 Loosening Family Caliper Assembly FromAdapter And Rotor
Fig. 3 Removing or Installing Caliper Assembly
Ä BRAKES 5 - 35
Page 187 of 2438

material, (Fig. 7). Be sure inboard brake shoe assem-
bly is correctly positioned against anti-rattle clip
(Fig. 6). (4) Reinstall the Braking Disk on the hub, by in-
stalling it over the wheel studs until it is seated
against the face of the hub (Fig. 6). (5) Slide the new outboard brake shoe assembly on
the adapter abutment, (Fig. 5). (6) Carefully lower caliper over the braking disk and
brake shoe assemblies (Fig. 3). Make sure that the
caliper guide pin bolt, bushings and sleeves are clear of
the adapter. (7) Install the caliper guide pin bolts and tighten to
34 to 37 N Im (25 to 35 ft. lbs.). Extreme caution
should be taken not to cross the threads of the
caliper guide pin bolts. (8) Install the wheel and tire assembly. Tighten the
wheel mounting stud nuts in proper sequence (Fig. 9)
until all nuts are torqued to half specification. This is
important. Then repeat the tightening sequence to the
full specified torque of 129 N Im (95 ft. lbs.).
(9) Remove jackstands or lower hoist. Before mov-
ing vehicle, pump the brake pedal several times
to insure the vehicle has a firm brake pedal to
adequately stop vehicle. .
(10) Road test the vehicle and make several stops to
wear off any foreign material on the brake linings and
to seat the brake shoe linings.
Fig. 8 Remove Or Replace Anti-Rattle Clip
Fig. 9 Tightening Wheel Nuts
Ä BRAKES 5 - 37
Page 188 of 2438
KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN NON-FAMILY CALIPER INDEX
page page
Assembling Disc Brake Caliper .............. 42
Cleaning and Inspection of Brake Caliper ...... 41 Disc Brake Caliper Disassembly
............. 40
Service Procedures ....................... 38
SERVICE PROCEDURES
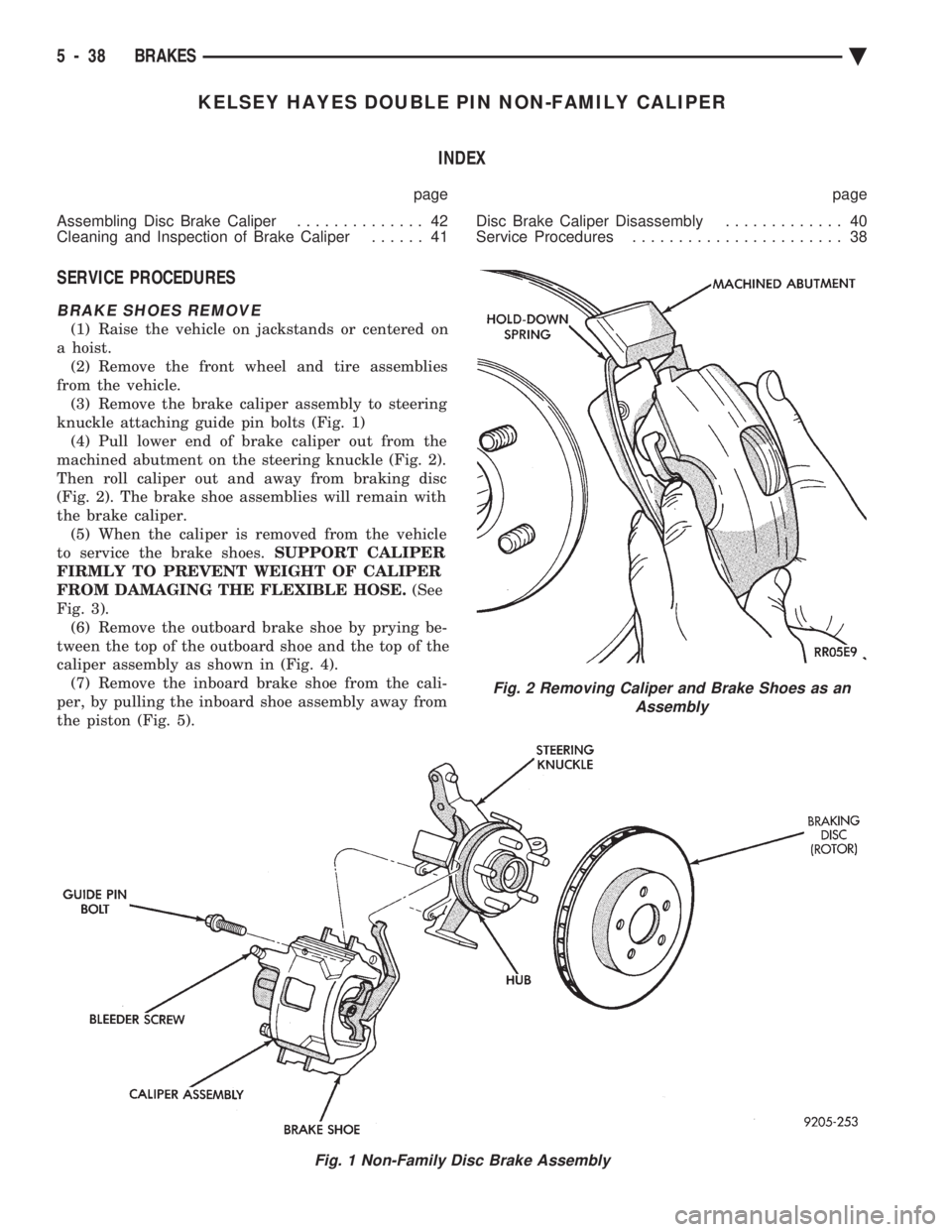
BRAKE SHOES REMOVE
(1) Raise the vehicle on jackstands or centered on
a hoist. (2) Remove the front wheel and tire assemblies
from the vehicle. (3) Remove the brake caliper assembly to steering
knuckle attaching guide pin bolts (Fig. 1) (4) Pull lower end of brake caliper out from the
machined abutment on the steering knuckle (Fig. 2).
Then roll caliper out and away from braking disc
(Fig. 2). The brake shoe assemblies will remain with
the brake caliper. (5) When the caliper is removed from the vehicle
to service the brake shoes. SUPPORT CALIPER
FIRMLY TO PREVENT WEIGHT OF CALIPER
FROM DAMAGING THE FLEXIBLE HOSE. (See
Fig. 3). (6) Remove the outboard brake shoe by prying be-
tween the top of the outboard shoe and the top of the
caliper assembly as shown in (Fig. 4). (7) Remove the inboard brake shoe from the cali-
per, by pulling the inboard shoe assembly away from
the piston (Fig. 5).
Fig. 1 Non-Family Disc Brake Assembly
Fig. 2 Removing Caliper and Brake Shoes as an Assembly
5 - 38 BRAKES Ä
Page 190 of 2438

iper, by installing retaining clip into the bore of the
piston (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Use care when installing the caliper as-
sembly onto the steering knuckle, so the seal on the
sealed for life bushings does not get damaged.
(5) Carefully lower caliper over braking disc and
guide holddown spring under machined abutment on
knuckle assembly (Fig. 8).
(6) Install caliper guide pin bolts and tighten to
24-34 N Im (18-25 ft. lbs.) torque. When installing guide pin bolts, use extreme caution not to cross
thread the guide pin bolts.
(7) Install wheel and tire assembly. Tighten stud
nuts in proper sequence until all nuts are torqued to
half specification. This is important. Then repeat
sequence to full specification. (8) Remove jackstands or lower hoist. Before mov-
ing vehicle be sure it has a firm pedal, pump
pedal several times. (9) Road test vehicle and make several stops to
wear off any foreign material on the brakes and
to seat the linings.
DISC BRAKE CALIPER DISASSEMBLY
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Check for piston fluid seal leaks (brake fluid in and
around boot area and inboard lining) and for any
ruptures of piston dust boot. If boot is damaged, or fluid
leak is visible, disassemble caliper assembly and in-
stall a new seal and boot,(and piston if scored). Refer to
procedures titled Disc Brake Caliper Disassembly. Check the caliper dust boot and caliper pin bushings
to determine if they are in good condition. Replace if
they are damaged, dry, or found to be brittle. Refer to
Cleaning And Inspection Of Brake Caliper. (1) Remove caliper from braking disc (See Brake
Shoe Removal). Hang assembly on a wire hook away
from braking disc, so hydraulic fluid cannot get on
braking disc (See Fig. 3 in Brake Shoe Removal). Place
a small piece of wood between the piston and caliper
fingers. (2) Carefully depress brake pedal to hydraulically
push piston out of bore. (Brake pedal will fall away
when piston has passed bore opening.) Then prop up
the brake pedal to any position below the first inch of
pedal travel, this will prevent loss of brake fluid from
the master cylinder. (3) If both front caliper pistons are to be removed,
disconnect flexible brake line at frame bracket after
removing piston. Plug brake tube and remove piston
from opposite caliper. Using the same process as above
for the first piston removal.
WARNING: UNDER NO CONDITION SHOULD AIR
PRESSURE BE USED TO REMOVE PISTON FROM
CALIPER BORE. PERSONAL INJURY COULD RE-
SULT FROM SUCH A PRACTICE.
(4) Disconnect brake flexible hose from the caliper.
To disassemble, mount caliper assembly in a vise
equipped with protective jaws.
CAUTION: Excessive vise pressure will cause bore
distortion and binding of piston.
Fig. 7 Installing Outboard Shoe Assembly onto Cali- per
Fig. 8 Guiding Holddown Spring Under MachinedAbutment
5 - 40 BRAKES Ä
Page 195 of 2438

REAR DISC BRAKES INDEX
page page
Assembling Rear Disc Brake Caliper .......... 49
Brake Shoe Removal ..................... 46
Cleaning and Inspection ................... 49
Disassembling Rear Caliper Assembly ......... 48 General Information
....................... 45
Lining Wear ............................. 45
Service Precautions ....................... 46
GENERAL INFORMATION
The rear disc brakes are similar to front disc
brakes, however, there are several distinctive fea-
tures that require different service procedures. This
single piston, floating caliper rear disc brake assem-
bly includes a hub assembly, adapter, braking disc
(rotor), caliper, shoes and linings. The parking brake
system on all vehicles equipped with rear disc
brakes. Consists of a small duo-servo drum brake
mounted to the caliper adapter. The drum brake
shoes expand out against a braking surface (hat sec-
tion) on the inside area of the braking disk (rotor). The AC and AY body vehicles are equipped with a
caliper assembly that has a 36 mm (1.42 inch) piston,
and utilizes a 14 inch solid braking disc (rotor). The AA body vehicle are equipped with a caliper
assembly that uses a 34 mm (1.34 inch) piston. The
AA body uses the same 14 inch solid braking disc
(rotor) as on the AC and AY applications. Also avail-
able on the AA body is a caliper assembly with a 36
mm (1.42 inch) piston, with a 15 inch vented braking
disc (rotor). The AG AJ and AP body vehicles are also equipped
with different size caliper pistons depending on the size and type of braking disk used on the vehicle.
The 14 9solid braking disk (rotor) applications use a
34 mm (1.34 inch) piston, and the 15 9vented braking
disk (rotor) applications use a 36 mm (1.42 inch) pis-
ton. The caliper assembly on all applications float on
rubber bushings using internal metal sleeves which
are attached to the adapter using threaded guide pin
bolts. The adapter is mounted to the rear axle of the ve-
hicle and is used to mount the brake shoes and actu-
ating cables for the parking brake system. The
adapter also mounts the rear caliper assembly to the
vehicle. The adapter has two machined abutments
which are used to position and align the caliper and
brake shoes for movement for and aft (Fig. 1)
LINING WEAR
To check the amount of lining wear, remove the
wheel and tire assemblies. If a visual inspection does
not adequately determine the condition of the lining,
Fig. 1 Rear Disc Brake Assembly
Ä BRAKES 5 - 45