relay CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1891 of 2438

within a range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. Refer to Group
8A for charging system information.
AUTO SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY AND FUEL PUMP
RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM operates the auto shutdown (ASD) relay
and fuel pump relay through one ground path. The
PCM operates the relays by switching the ground
path on and off. Both relays turn on and off at the
same time. The ASD relay connects battery voltage to the fuel
injector and ignition coil. The fuel pump relay con-
nects battery voltage to the fuel pump and oxygen
sensor heating element. The PCM turns the ground path off when the igni-
tion switch is in the Off position. Both relays are off.
When the ignition switch is in the On or Crank po-
sition, the PCM monitors the crankshaft position
sensor and camshaft position sensor signals to deter-
mine engine speed and ignition timing (coil dwell). If
the PCM does not receive the crankshaft position
sensor and camshaft position sensor signals when the
ignition switch is in the Run position, it de-energizes
both relays. When the relays are de-energized, bat-
tery voltage is not supplied to the fuel injector, igni-
tion coil, fuel pump and oxygen sensor heating
element. The ASD relay and fuel pump relay are located in
the power distribution center (Fig. 14).
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The idle air control motor is mounted on the throt-
tle body. The PCM operates the idle air control motor
(Fig. 13). The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through
the idle air control motor to compensate for engine
load or ambient conditions. The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine at idle (the throttle blade is closed). The idle air control motor pintle protrudes
into the air bypass passage and regulates air flow
through it. The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by moving the
idle air control motor pintle in and out of the bypass
passage. The adjustments are based on inputs the
PCM receives. The inputs are from the throttle posi-
tion sensor, crankshaft position sensor, coolant tem-
perature sensor, and various switch operations
(brake, park/neutral, air conditioning). Deceleration
die out is also prevented by increasing airflow when
the throttle is closed quickly after a driving (speed)
condition.
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT
Vacuum for the Evaporative Canister is controlled
by the Canister Purge Solenoid (Fig. 15). The sole-
noid is controlled by the PCM.
The PCM operates the solenoid by switching the
ground circuit on and off based on engine operating
conditions. When energized, the solenoid prevents
vacuum from reaching the evaporative canister.
When not energized the solenoid allows vacuum to
flow to the canister. The PCM removes the ground to the solenoid when
the engine reaches a specified temperature and the
time delay interval has occurred. When the solenoid
is de-energized, vacuum flows to the canister purge
valve. Vapors are purged from the canister and flow
to the throttle body. The purge solenoid will also be energized during
certain idle conditions, in order to update the fuel de-
livery calibration.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK ENGINE
LAMP)ÐPCM OUTPUT
The malfunction indicator lamp (instrument panel
Check Engine Lamp) comes on each time the ignition
key is turned ON and stays on for 3 seconds as a
bulb test. The malfunction indicator lamp warns the
Fig. 14 Relay Identification
Fig. 15 Canister Purge Solenoid
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 151
Page 1893 of 2438

the PCM determines crankshaft position, it begins
energizing the injectors in sequence.The auto shutdown (ASD) relay supplies battery
voltage to the injectors. The PCM provides the
ground path for the injectors. By switching the
ground path on and off, the PCM adjusts injector
pulse width. Pulse width is the amount of time the
injector is energized. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width based on inputs it receives.
IGNITION COILÐPCM OUTPUT
The coil assembly consists of 3 molded coils to-
gether (Fig. 18). The coil assembly is mounted on the
intake manifold. High tension leads route to each
cylinder from the coil. The coil fires two spark plugs
every power stroke. One plug is the cylinder under
compression, the other cylinder fires on the exhaust
stroke. The PCM determines which of the coils to
charge and fire at the correct time.
The auto shutdown (ASD) relay provides battery
voltage to the ignition coil. The PCM provides a
ground contact (circuit) for energizing the coil. When
the PCM breaks the contact, the energy in the coil
primary transfers to the secondary, causing the
spark. The PCM will de-energize the ASD relay if it
does not receive the crankshaft position sensor and
camshaft position sensor inputs. Refer to Auto Shut-
down (ASD) Relay/Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output
in this section for relay operation.
RADIATOR FAN RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The radiator fan is energized by the PCM through
the radiator fan relay. The radiator fan relay is lo-
cated on the drivers side fender well near the PCM
(Fig. 14). The PCM grounds the radiator fan relay
when engine coolant reaches a predetermined tem-
perature or the A/C system head pressure is high.
SPEED CONTROL SOLENOIDSÐPCM OUTPUT
The speed control vacuum and vent solenoids are
operated by the PCM. When the PCM supplies a ground to the vacuum and vent solenoids, the speed
control system opens the throttle blade. When the PCM
supplies a ground only to the vent solenoid, the throttle
blade holds position. When the PCM removes the
ground from both the vacuum and vent solenoids, the
throttle blade closes. The PCM balances the two sole-
noids to maintain the set speed. Refer to Group 8H for
speed control information.
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies engine RPM to the instrument
panel tachometer through the CCD Bus. The CCD Bus
is a communications port. Various modules use the
CCD Bus to exchange information. Refer to Group 8E
for more information.
MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example, the
PCM must calculate a different injector pulse width
and ignition timing for idle than it does for wide open
throttle (WOT). There are several different modes of
operation that determine how the PCM responds to the
various input signals. There are two different areas of operation, Open
Loop and Closed Loop. During Open Loop modes the PCM receives input
signals and responds according to preset PCM pro-
gramming. Input from the oxygen (O
2) sensor is not
monitored during Open Loop modes. During Closed Loop modes the PCM does monitor
the oxygen (O
2) sensor input. This input indicates to
the PCM whether or not the calculated injector pulse
width results in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7 parts air
to 1 part fuel. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen
content through the O
2sensor, the PCM can fine tune
the injector pulse width. Fine tuning injector pulse
width allows the PCM to achieve optimum fuel
economy combined with low emissions. The 3.3L multi-port fuel injection system has the
following modes of operation:
² Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
² Engine start-up
² Engine warm-up
² Cruise (Idle)
² Acceleration
² Deceleration
² Wide Open Throttle
² Ignition switch OFF
The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up, and
wide open throttle modes are OPEN LOOP modes.
Under most operating conditions, the acceleration,
deceleration, and cruise modes, with the engine at
operating temperature are CLOSED LOOP modes.
Fig. 18 Coil PackÐ3.3L Engine
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 153
Page 1894 of 2438

IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE When the multi-port fuel injection system is acti-
vated by the ignition switch, the following actions oc-
cur:
² The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to determine basic fuel
strategy.
² The PCM monitors the coolant temperature sensor
and throttle position sensor input. The PCM modifies
fuel strategy based on this input. When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the auto shutdown (ASD)
relay and fuel pump relay are not energized. There-
fore battery voltage is not supplied to the fuel pump,
ignition coil, fuel injectors or oxygen sensor heating
element.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following ac-
tions occur when the starter motor is engaged. If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the auto shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay.
These relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump,
fuel injectors, ignition coil, and oxygen sensor heat-
ing element. If the PCM does not receive the cam-
shaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor
signals within approximately one second, it de-ener-
gizes the ASD relay and fuel pump relay. The PCM energizes all six injectors until it deter-
mines crankshaft position from the camshaft position
sensor and crankshaft position sensor signals. The
PCM determines crankshaft position within 1 engine
revolution. After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. The PCM
adjusts injector pulse width and controls injector syn-
chronization by turning the individual ground paths
to the injectors On and Off. When the engine idles within 664 RPM of its tar-
get RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (Zero RPM) mode. If
the PCM does not detect a minimum difference be-
tween the two values, it sets a MAP fault into mem-
ory. Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been en-
ergized, the PCM:
² Determines injector pulse width based on battery
voltage, coolant temperature, engine rpm and the
number of engine revolutions since cranking was ini-
tiated.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE This is a OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature ²
manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² throttle position
² A/C switch
² battery voltage
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off. The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising speed the
following inputs are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² throttle position
² exhaust gas oxygen content
² A/C control positions
² battery voltage
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off. The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas.
ACCELERATION MODE This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in throttle position or MAP
pressure as a demand for increased engine output
and vehicle acceleration. The PCM increases injector
pulse width in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed
² throttle position
² exhaust gas oxygen content
² A/C control positions
² battery voltage
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the throttle position sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. The PCM will reduce injector
pulse width. This helps maintain better control of the
air-fuel mixture (as sensed through the O
2sensor).
During a closed throttle deceleration condition, the
PCM grounds the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
solenoid. When the solenoid is grounded, EGR func-
tion stops.
14 - 154 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1895 of 2438

WIDE OPEN THROTTLE MODE This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
² battery voltage
² engine coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed
² throttle position
When the PCM senses wide open throttle condition
through the throttle position sensor (TPS) it will:
² De-energize the air conditioning relay. This dis-
ables the air conditioning system.
² Provide a ground for the electrical EGR transducer
(EET) solenoid. When the PCM grounds the solenoid,
the EGR system stops operating. The exhaust gas oxygen content input is not ac-
cepted by the PCM during wide open throttle opera-
tion. The PCM will adjust injector pulse width to
supply a predetermined amount of additional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE When the ignition switch is turned to the OFF po-
sition, the following occurs:
² All outputs are turned off.
² No inputs are monitored.
² The PCM shuts down.
THROTTLE BODY
The throttle body assembly is located on the left
side of the intake manifold plenum (Fig. 19). The
throttle body houses the throttle position sensor and
the idle air control motor. Air flow through the throt- tle body is controlled by a cable operated throttle
blade located in the base of the throttle body.
FUEL SUPPLY CIRCUIT
Fuel is pumped to the fuel rail by an electrical
pump in the fuel tank. The pump inlet is fitted with
a strainer to prevent water and other contaminants
from entering the fuel supply circuit. Fuel pressure is controlled to a preset level above
intake manifold pressure by a pressure regulator.
The regulator is mounted on the fuel rail. The regu-
lator uses intake manifold pressure as a reference.
FUEL INJECTORS AND FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
Six fuel injectors are retained in the fuel rail by
lock rings (Fig. 20). The rail and injector assembly is
installed in position with the injectors inserted in re-
cessed holes in the intake manifold.
Fig. 19 Throttle Body
Fig. 20 Fuel Rail Assembly
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 155
Page 1900 of 2438
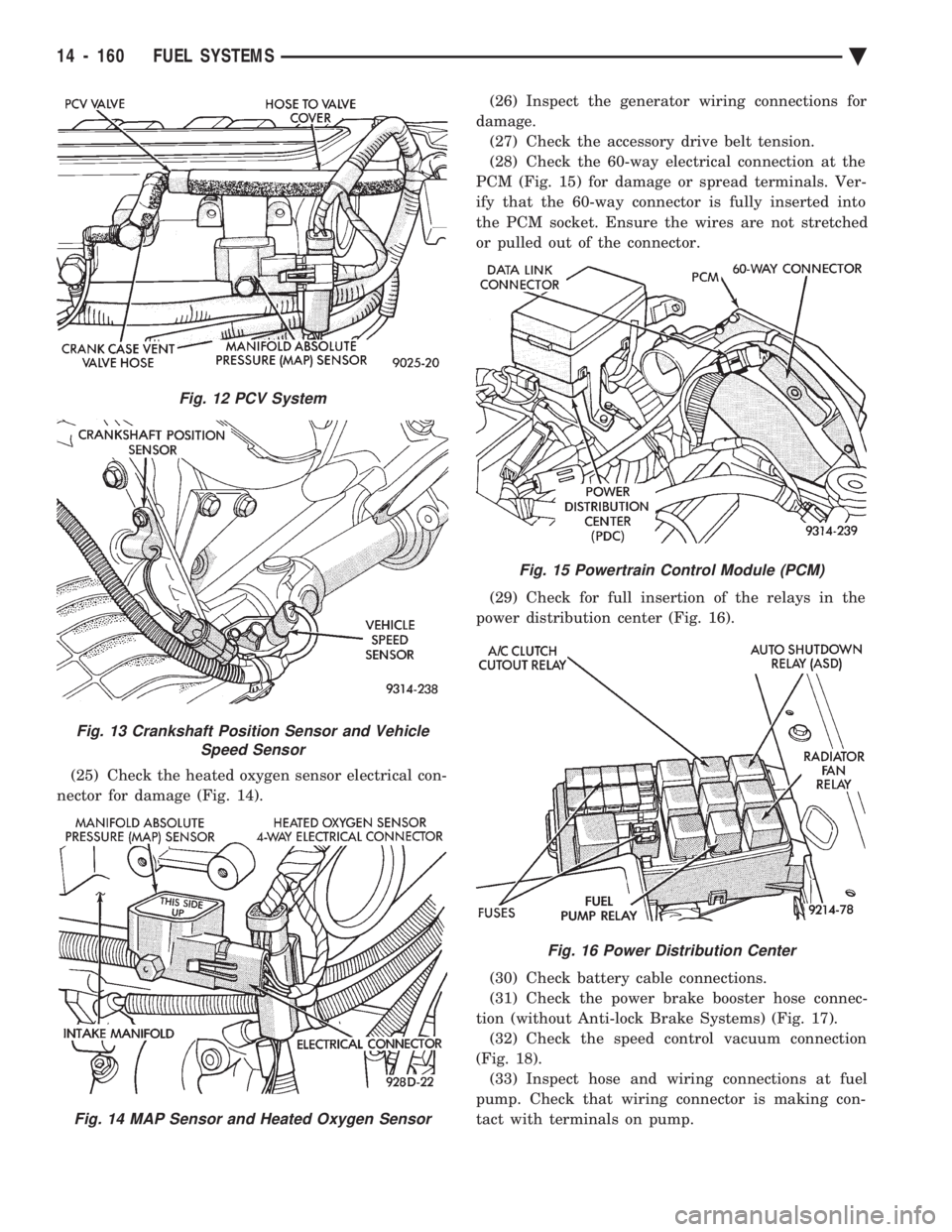
(25) Check the heated oxygen sensor electrical con-
nector for damage (Fig. 14). (26) Inspect the generator wiring connections for
damage. (27) Check the accessory drive belt tension.
(28) Check the 60-way electrical connection at the
PCM (Fig. 15) for damage or spread terminals. Ver-
ify that the 60-way connector is fully inserted into
the PCM socket. Ensure the wires are not stretched
or pulled out of the connector.
(29) Check for full insertion of the relays in the
power distribution center (Fig. 16).
(30) Check battery cable connections.
(31) Check the power brake booster hose connec-
tion (without Anti-lock Brake Systems) (Fig. 17). (32) Check the speed control vacuum connection
(Fig. 18). (33) Inspect hose and wiring connections at fuel
pump. Check that wiring connector is making con-
tact with terminals on pump.
Fig. 12 PCV System
Fig. 13 Crankshaft Position Sensor and Vehicle Speed Sensor
Fig. 14 MAP Sensor and Heated Oxygen Sensor
Fig. 15 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Fig. 16 Power Distribution Center
14 - 160 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1906 of 2438

S/C Vacuum Solenoid
A/C Clutch Relay
EGR Solenoid
Auto Shutdown Relay
Radiator Fan Relay
Purge Solenoid
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Sensor Dis-
play screen. Oxygen Sensor Signal
Engine Coolant Temperature
Engine Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position
Minimum Throttle
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Adaptive Fuel Factor
Barometric Pressure
Min Airflow Idle Spd (speed)
Engine Speed
DIS Sensor Status
Fault #1 Key-On Info
Module Spark Advance
Speed Control Target
Fault #2 Key-on Info
Fault #3 Key-on Info
Speed Control Status
Speed Control Switch Voltage
Charging System Goal
Theft Alarm Status
Map Sensor Voltage
Vehicle Speed
Oxygen Sensor State
MAP Gauge Reading
Throttle Opening (percentage)
Total Spark Advance
CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE
The circuit actuation test mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices which the pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) cannot internally rec-
ognize. The PCM can attempt to activate these
outputs and allow an observer to verify proper oper-
ation. Most of the tests provide an audible or visual
indication of device operation (click of relay contacts,
spray fuel, etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if
a device functions properly during testing, assume
the device, its associated wiring, and driver circuit
working correctly.
OBTAINING CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and ac-
cess the Actuators screen. The following is a list of
the engine control system functions accessible
through Actuators screens. Stop All Tests
Ignition Coil #1
Ignition Coil #2
Ignition Coil #3
Fuel Injector #1
Fuel Injector #2
Fuel Injector #3
Fuel Injector #4
Fuel Injector #5
Fuel Injector #6
Idle Air Control Motor Open/Close
Radiator Fan Relay
A/C Clutch Relay
Auto Shutdown Relay
EVAP Purge Solenoid
S/C Servo Solenoids
Generator Field
EGR Solenoid
All Solenoids/Relays
ASD Fuel System Test
Speed Control Vacuum Solenoid
Speed Control Vent Solenoid
THROTTLE BODY MINIMUM AIR FLOW CHECK
PROCEDURE
(1) Warm engine in Park or Neutral until the cool-
ing fan has cycled on and off at least once. (2) Ensure that all accessories are off.
(3) Shut off engine.
(4) Disconnect the PCV valve hose from the intake
manifold nipple. (5) Attach Air Metering Fitting #6457 (0.125 in.
orifice) to the intake manifold PCV nipple (Fig. 2).
(6) Disconnect the 3/16 inch idle purge line from
the throttle body nipple. Cap the 3/16 inch nipple. (7) Connect DRBII scan tool to vehicle.
(8) Restart the engine. Allow engine to idle for at
least one minute. (9) Using the DRBII scan tool, access Min. Airflow
Idle Spd.
Fig. 2 Air Metering Fitting #6457
14 - 166 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1913 of 2438

(5) Install fuel tube retaining bracket screw.
Tighten screw to 4 N Im (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect electrical connectors to camshaft posi-
tion sensor, coolant temperature sensor and engine
temperature sensors (Fig. 13). (7) Install fuel injector harness wiring clips on the
generator bracket and intake manifold water tube
(Fig. 13). (8) Connect vacuum line to fuel pressure regulator.
(9) Remove covering on lower intake manifold and
clean surface. (10) Place intake manifold gasket on lower mani-
fold. Put upper manifold into place and install bolts
finger tight. (11) Install the generator bracket to intake mani-
fold bolt and the cylinder head to intake manifold
strut bolts. (Do not tighten.) (12) Following the tightening sequence in Figure
11, tighten intake manifold bolts to 28 N Im (250 in.
lbs.) torque. (13) Tighten generator bracket to intake manifold
bolt to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 13).
(14) Tighten the cylinder head to intake manifold
strut bolts to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 8).
(15) Connect ground strap, MAP and heated oxy-
gen sensor electrical connectors. (16) Connect vacuum harness to intake plenum.
Connect PCV system hoses. (17) Using a new gasket, connect the EGR tube to
the intake manifold plenum. Tighten screws to 22
N Im (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(18) Clip wiring harness into the hole in the throt-
tle cable bracket. (19) Connect electrical connectors to the throttle
position sensor (TPS) and idle air control motor. (20) Connect vacuum harness to throttle body.
(21) Install the direct ignition system (DIS) coils.
Tighten fasteners to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(22) Install fuel hose quick connectors fittings to
chassis tubes. Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel Delivery Sec-
tion of this Group. Push the fittings onto the chas-
sis tubes until they click into place. Pull on the
fittings to ensure complete insertion. Fuel supply fit-
ting is 5/16 inch and fuel return fitting is 1/4 inch. (23) Install throttle cable.
(24) Install air cleaner and hose assembly.
(25) Connect negative cable to battery.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position.
(26) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pres-
surize the fuel system. Check for leaks.FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs. Refer to Fuel Pressure
Regulator Procedure in this section. (2) Remove fuel pressure regulator vacuum connec-
tor. (Fig. 15). (3) Remove regulator retainer screw (Fig. 15).
(4) Remove the fuel pressure regulator retainer
(Fig. 15).
Fig. 13 Fuel Injector Wiring Clip
Fig. 14 Fuel Rail Removal
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 173
Page 1914 of 2438
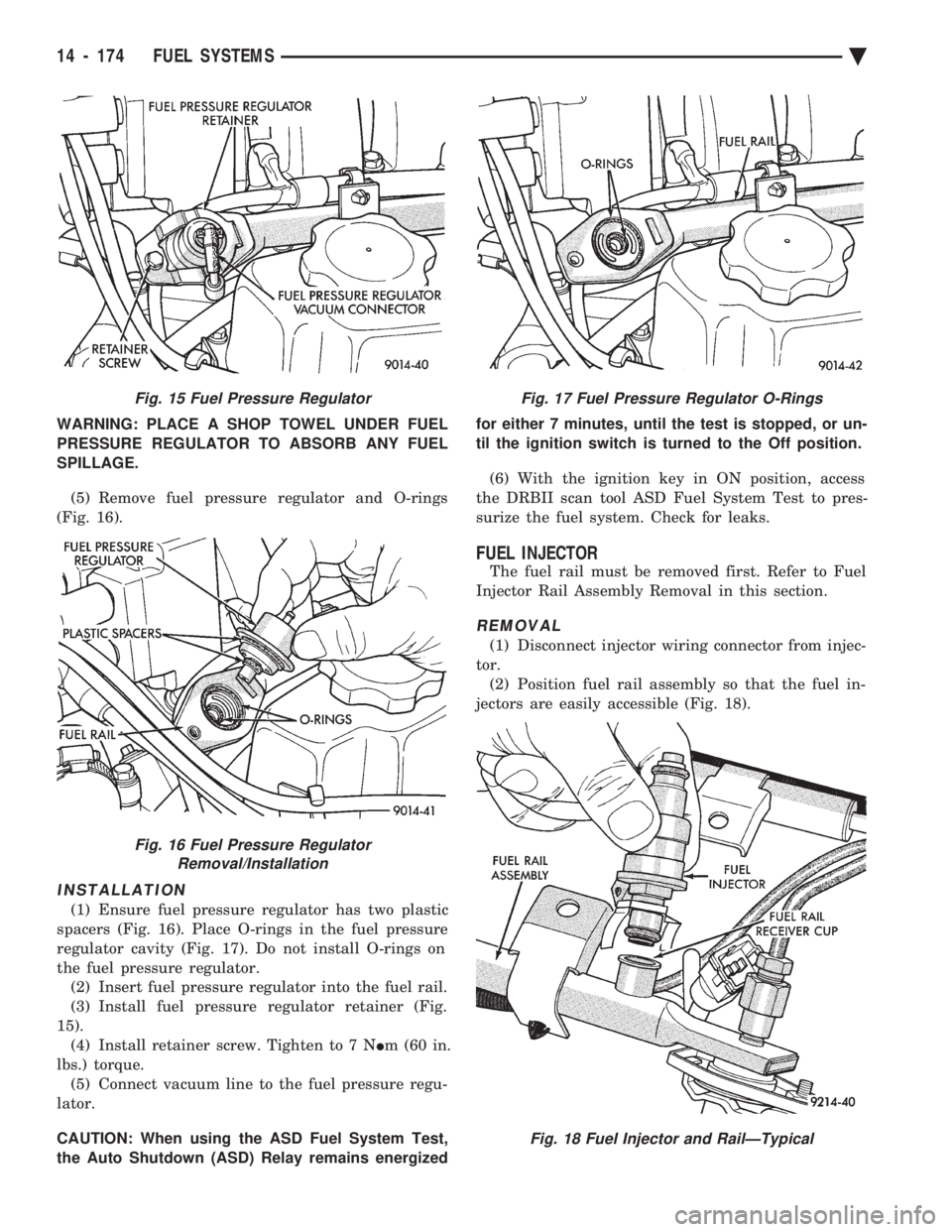
WARNING: PLACE A SHOP TOWEL UNDER FUEL
PRESSURE REGULATOR TO ABSORB ANY FUEL
SPILLAGE.
(5) Remove fuel pressure regulator and O-rings
(Fig. 16).
INSTALLATION
(1) Ensure fuel pressure regulator has two plastic
spacers (Fig. 16). Place O-rings in the fuel pressure
regulator cavity (Fig. 17). Do not install O-rings on
the fuel pressure regulator. (2) Insert fuel pressure regulator into the fuel rail.
(3) Install fuel pressure regulator retainer (Fig.
15). (4) Install retainer screw. Tighten to 7 N Im (60 in.
lbs.) torque. (5) Connect vacuum line to the fuel pressure regu-
lator.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position.
(6) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pres-
surize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL INJECTOR
The fuel rail must be removed first. Refer to Fuel
Injector Rail Assembly Removal in this section.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect injector wiring connector from injec-
tor. (2) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel in-
jectors are easily accessible (Fig. 18).
Fig. 15 Fuel Pressure Regulator
Fig. 16 Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/Installation
Fig. 17 Fuel Pressure Regulator O-Rings
Fig. 18 Fuel Injector and RailÐTypical
14 - 174 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 2169 of 2438

(2) Remove push-in fasteners holding hood latch
cover to radiator closure panel and separate cover
from vehicle. (3) Disconnect hood release cable casing and cable
end from hood latch assembly. Refer to Hood Latch
Removal procedure in this section. (4) Remove hood latch release cable handle attach-
ing bolts from under left lower edge of instrument
panel. (5) Disengage release cable rubber grommet from
engine compartment dash panel behind instrument
panel. (6) Rout cable assembly through engine compart-
ment around battery, under fender lip, under relay
bank, and under wiring harnesses, toward dash
panel. Push cable through access hole in dash panel
under the brake master cylinder, into passenger com-
partment.
HOOD LATCH RELEASE CABLE INSTALLATION
Reverse the preceding operation.
COWL COVER
REMOVAL (FIG. 6)
(1) Raise hood to full up position.
(2) Disconnect windshield washer hoses from wiper
arms. (3) Remove windshield wiper arm assemblies. Re-
fer to Group 8K, Windshield Wiper and Washer Sys-
tems. (4) Remove plastic expanding type fasteners hold-
ing cowl cover to cowl, below windshield. (5) Lift back of cowl cover and slide cover rearward
from under dash panel to hood seal and separate
cover from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
Reverse the preceding operation.
FRONT END SPLASH SHIELDS
FRONT WHEELHOUSE SPLASH SHIELD REMOVAL (FIG. 7)
(1) Hoist vehicle and support on suitable safety
stands. (2) Remove front wheel assembly.
(3) Remove push-in fasteners holding front wheel-
house splash shield to fender opening lip and inner
wheelhouse area. (4) Separate wheelhouse splash shield from vehi-
cle.
FRONT WHEELHOUSE SPLASH SHIELD INSTALLATION
Reverse the preceding operation.
TRANSAXLE SPLASH SHIELD REMOVAL (FIG.7)
(1) Remove one front wheelhouse splash shield
push-in fastener and separate wheelhouse splash
shield from transaxle splash shield. (2) Remove transaxle splash shield attaching bolts
and separate transaxle splash shield from vehicle.
TRANSAXLE SPLASH SHIELD INSTALLATION
Reverse the preceding operation.
ENGINE DRIVE BELT SPLASH SHIELD REMOVAL (FIG. 8)
(1) Hoist vehicle and support on suitable safety
stands. (2) Remove bolts holding engine drive belt splash
shield to right frame rail. (3) Separate drive belt splash shield from vehicle.
ENGINE DRIVE BELT SPLASH SHIELDINSTALLATION
Reverse the preceding operation.
Fig. 5 Hood Latch Release Cable Assembly
Fig. 6 Cowl Cover Assembly
Ä AA-BODY 23 - 13
Page 2195 of 2438

ing hood, align all marks and secure bolts. The hood
should be aligned to 4 mm (0.160 in.) gap to the front
fenders and flush across the top surfaces along fend-
ers.(4) Remove the top hood to hinge bolts and loosen
the bottom bolts until they can be removed by hand. (5) With assistance of a helper at the opposite side
of the vehicle to support the hood, remove the bottom
hood to hinge bolts. Separate the hood from the ve-
hicle.
HOOD INSTALLATION
Reverse the preceding operation.
HOOD HINGE REMOVAL (FIG. 6)
(1) Support hood on the side that requires hinge
replacement. (2) Mark all bolt and hinge attachment locations
with a grease pencil or other suitable device to pro-
vide reference marks for installation. When install-
ing hood hinge, align all marks and secure bolts. The
hood should be aligned to 4 mm (0.160 in.) gap to the
front fenders and flush across the top surfaces along
fenders. Shims can be added or removed under hood
hinge to achieve proper hood height. (3) Remove hood to hinge attaching bolts.
(4) Remove hood hinge to front fender attaching
bolts and separate hinge from vehicle.
HOOD HINGE INSTALLATION
Reverse the preceding operation. If necessary, paint
new hinge before installation.
HOOD LATCH AND RELEASE CABLE
HOOD LATCH REMOVAL (FIG. 7)
(1) Raise hood top the full up position.
(2) Remove hood latch attaching bolts holding
latch to radiator closure panel and separate from ve-
hicle. (3) Pry release cable casing attachment from slot
receiver on latch, disengage cable end from latch arm
hook.
HOOD LATCH INSTALLATION
Reverse the preceding operation.
HOOD LATCH RELEASE CABLE
REMOVAL (FIG. 8)
(1) Raise hood to the full up position.
(2) Remove push-in fasteners holding hood latch
cover to radiator closure panel and separate cover
from vehicle, if equipped. (3) Disconnect hood release cable casing and cable
end from hood latch assembly. Refer to Hood Latch
Removal procedure in this section. (4) Remove hood latch release cable handle attach-
ing bolts from under left lower edge of instrument
panel. (5) Disengage release cable rubber grommet from
engine compartment dash panel behind instrument
panel. (6) Rout cable assembly through engine compart-
ment around battery, under fender lip, under relay
bank, and under wiring harnesses, toward dash
Fig. 5 Hood Remove or InstallÐTypical
Fig. 6 Hood Hinge AssemblyÐTypical
Ä AC-BODY 23 - 39