height CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 149 of 2438
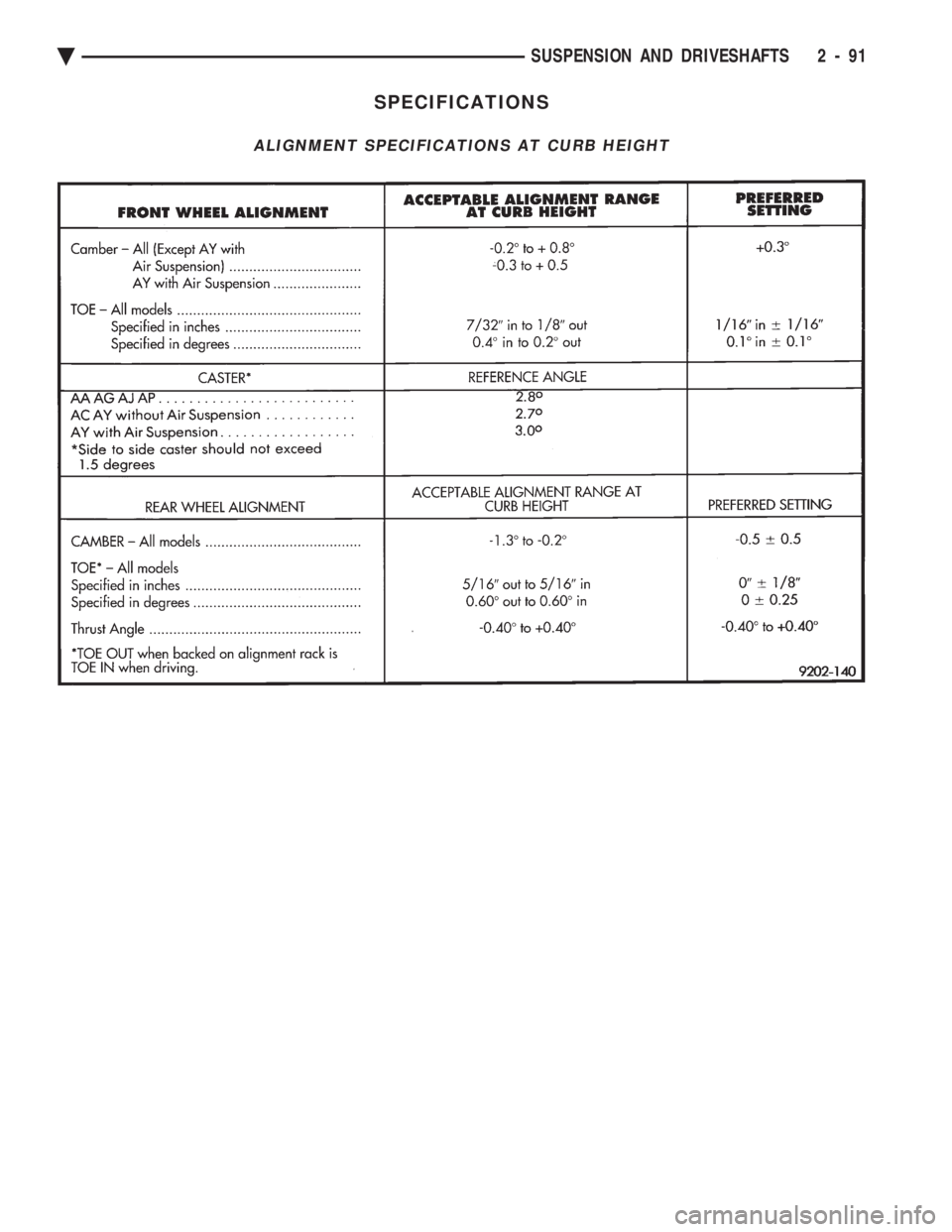
SPECIFICATIONS
ALIGNMENT SPECIFICATIONS AT CURB HEIGHT
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 91
Page 228 of 2438
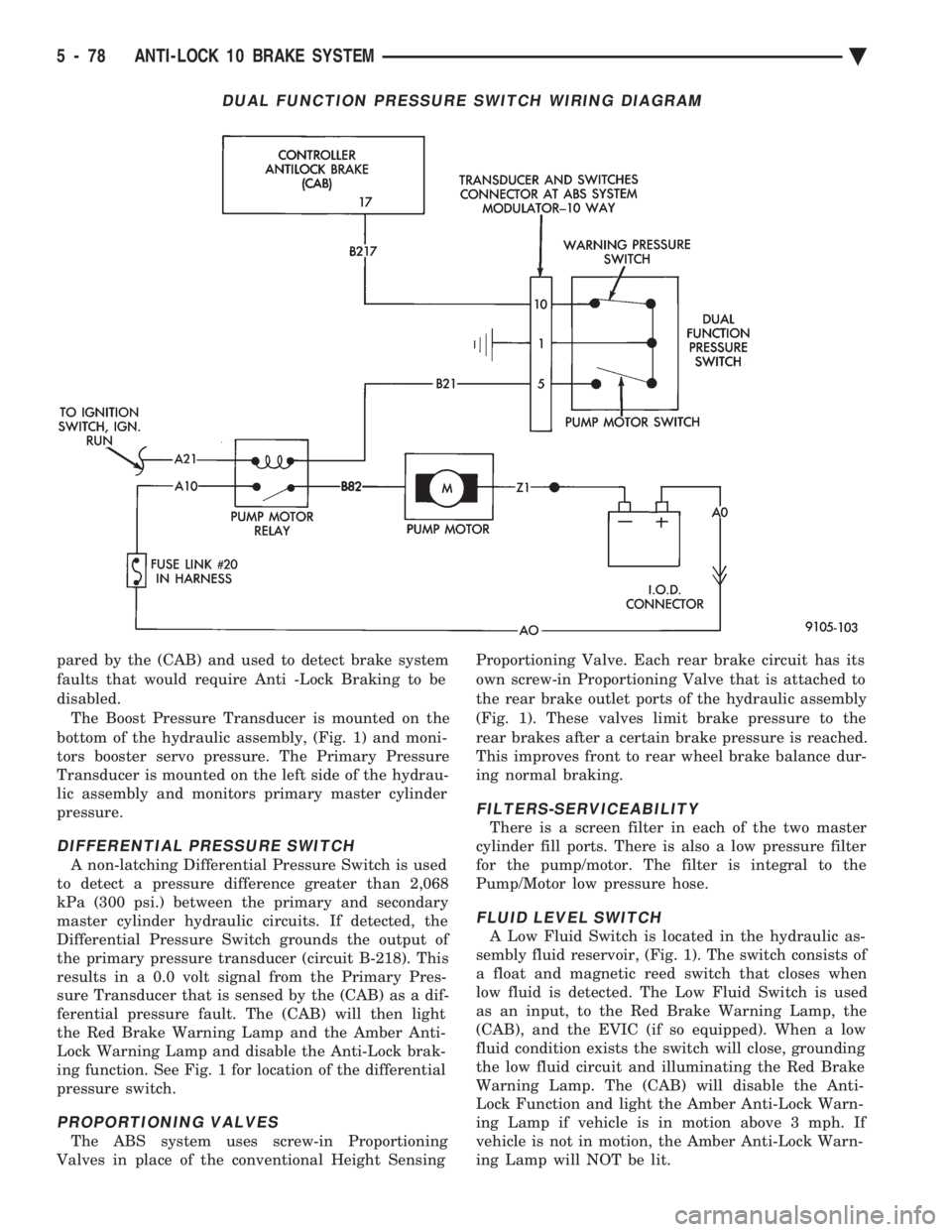
pared by the (CAB) and used to detect brake system
faults that would require Anti -Lock Braking to be
disabled.The Boost Pressure Transducer is mounted on the
bottom of the hydraulic assembly, (Fig. 1) and moni-
tors booster servo pressure. The Primary Pressure
Transducer is mounted on the left side of the hydrau-
lic assembly and monitors primary master cylinder
pressure.
DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SWITCH
A non-latching Differential Pressure Switch is used
to detect a pressure difference greater than 2,068
kPa (300 psi.) between the primary and secondary
master cylinder hydraulic circuits. If detected, the
Differential Pressure Switch grounds the output of
the primary pressure transducer (circuit B-218). This
results in a 0.0 volt signal from the Primary Pres-
sure Transducer that is sensed by the (CAB) as a dif-
ferential pressure fault. The (CAB) will then light
the Red Brake Warning Lamp and the Amber Anti-
Lock Warning Lamp and disable the Anti-Lock brak-
ing function. See Fig. 1 for location of the differential
pressure switch.
PROPORTIONING VALVES
The ABS system uses screw-in Proportioning
Valves in place of the conventional Height Sensing Proportioning Valve. Each rear brake circuit has its
own screw-in Proportioning Valve that is attached to
the rear brake outlet ports of the hydraulic assembly
(Fig. 1). These valves limit brake pressure to the
rear brakes after a certain brake pressure is reached.
This improves front to rear wheel brake balance dur-
ing normal braking.
FILTERS-SERVICEABILITY
There is a screen filter in each of the two master
cylinder fill ports. There is also a low pressure filter
for the pump/motor. The filter is integral to the
Pump/Motor low pressure hose.
FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
A Low Fluid Switch is located in the hydraulic as-
sembly fluid reservoir, (Fig. 1). The switch consists of
a float and magnetic reed switch that closes when
low fluid is detected. The Low Fluid Switch is used
as an input, to the Red Brake Warning Lamp, the
(CAB), and the EVIC (if so equipped). When a low
fluid condition exists the switch will close, grounding
the low fluid circuit and illuminating the Red Brake
Warning Lamp. The (CAB) will disable the Anti-
Lock Function and light the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp if vehicle is in motion above 3 mph. If
vehicle is not in motion, the Amber Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp will NOT be lit.
DUAL FUNCTION PRESSURE SWITCH WIRING DIAGRAM
5 - 78 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 1063 of 2438

WIRING DIAGRAMS AC-AY BODY INDEX
Wiring Diagram
Name Sheet Number
ABS Data Link Connector ........................49
Airbag System ........................... .57, 58
Clockspring ...............................57
Diagnostic Module ..........................57
Interface Grommet ..........................58
Sensor-Left ...............................58
Sensor-Right ..............................58
Squib (Airbag Igniter) ........................57
Air Conditioning and Heater System (2.5L) .............53
A/C Switch ...............................53
Blower Motor ..............................53
Compressor ...............................53
Defrost Switch .............................53
Diode ...................................53
Illumination Lamps ..........................53
Low Pressure Switch .........................53
Resistor .................................53
Switch-Blower .............................53
Air Conditioning Variable Output Compressor ..........113
Air Exhaust Solenoid-Automatic Air Load Leveling ........40
Air Suspension System .................41, 42, 43, 44
Air Exhaust Solenoid .........................42
Air Suspension Relay .........................42
Air Suspension System Control Module .......41, 43, 176
Compressor Assembly ........................42
Compressor Motor ..........................42
Height Sensors ............................44
Shock Absorber ............................43
Solenoids ............................ .41, 44
Air Suspension System Control Module .........41, 43, 176
Antennas ............................. .118, 126
Anti-Lock Brake System ............45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50
ABS System Relay ..........................47
Controller .................. .45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50
Data Link Connector .........................49
Left Front Wheel Sensor .......................50
Left Rear Wheel Sensor .......................50
Modulator ............................ .45, 48
Pump Motor ..............................46
Pump and Motor Relay .......................46
Right Front Wheel Sensor ......................50
Right Rear Wheel Sensor ......................50
Yellow Lamp Relay ..........................49
Anti-Lock Brake System Controller .....45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50
Anti-Lock Brake System Modulator Connectors .........172
Anti-Lock Brake System Controller Connector ..........175
Anti-Lock Brake System Modulator ...............45, 48
ATC In-line Connector ........................ .117
Automatic Air Load Leveling System ..............39, 40
Air Exhaust Solenoid .........................40
Compressor Assembly ........................40
Compressor Motor ..........................40Wiring Diagram
Name Sheet Number
Load Leveling Relay .........................40
Shock Absorber ............................40
Automatic Day/Night Mirror .................... .124
Automatic Temperature Control .............115, 116, 117
A/C Blower Motor ......................... .115
Ambient Sensor .......................... .117
ATC Control Switch ........................ .116
ATC In Line Connector ...................... .117
ATC Power Module ........................ .115
In Car Senso r............................ .115
In Car Sensor Motor ....................... .115
Sun Sensor ............................. .115
Water Sensor ............................ .117
Automatic Temperature Control (Radiator and
Compressor 3.3L & 3.8L) .................. .113, 114
A/C Ambient Temperature Switch ................114
A/C Compressor Clutch Relay ...................113
A/C Fan Cutout Switch ...................... .114
A/C High Pressure Cutout Switch ................114
A/C Low Pressure Switch .................... .114
A/C Variable Output Compressor .................113
Diode ................................. .113
Radiator Fan Motor ........................ .113
Radiator Fan Relay ........................ .114
Automatic Shutdown Relay .......................29
Automatic Temperature Control In-line Connector ........206
Automatic Temperature Control Module Connector .......200
Back-Up Lamp Relay ..........................33
Battery ...............................2,5,7,9
Body Computer 2 (Electronic Cluster) .........101, 102, 194
25-Pin Connector ...................... .101, 102
Body Computer 1 (Electronic Cluster) .........103, 104, 195
25-Pin Connector ...................... .103, 104
Data Link Connector ....................... .103
Halo Lamp .............................. .104
Relay ................................. .103
Body Computer (Mechanical Cluster w/Visual Message Ctr) ......................... .196, 197
Body Computer (Mechanical Cluster w/o Visual Message Ctr) ......................... .198, 199
Body Computer 1 (Mechanical Cluster w/o Visual Message Ctr) ..................... .108, 109, 110
25-Pin Connector ................... .108, 109, 110
Data Link Connector ....................... .110
Halo Lamp .............................. .108
Key-In Switch ............................ .109
Relay Bank ............................. .108
Body Computer 2 (Mechanical Cluster with Visual Message Ctr) ..................... .105, 106, 107
25-Pin Connector ................... .105, 106, 107
Data Link Connector ....................... .106
Halo Lamp .............................. .106
Key-In Switch ............................ .107
Ä WIRING DIAGRAMS AC-AY BODY 8W - 313
Page 1069 of 2438

Wiring Diagram
Name Sheet Number
Left Side Marker Lamp ...................... .163
Right Back-Up Lamp ....................... .164
Right Center High Mounted Stop Lamps ............164
Right Inboard Tail, Stop & Turn Signal Lamp .........164
Right License Lamp ........................ .164
Right Outboard Tail, Stop & Turn Signal Lamp ........164
Right Side Marker Lamp ..................... .164
Recliner Position Sense Resistor ..................154
Relay Bank ............................... .171
Relay Module ............................. .171
Relays ABS System Relay ..........................47
A/C Compressor Clutch .................54, 56, 113
Air Suspension .............................42
Automatic Shut Down .................. .15, 23, 29
Automatic Load Leveling .......................40
Back-Up Lamp .............................33
Door Lock/Unlock ......................... .140
Engine Starter .......................... .12, 13
Fan Control ............................. .114
Fuel Pump ...............................36
Horn ...................................63
Headlamp ................................68
Headlamp Door ............................68
Park Lamp .............................. .125
Power Antenna/Name Brand Speaker Relay ..........118
Pump and Motor Relay .......................46
Radiator Fan Control Relay A/C ................54, 56
Radiator Fan Relay ATC ..................... .114
Radiator Fan Relay-Heater ......................52
Safety Shut Down ...........................35
Yellow Lamp Relay ..........................49
Remote Keyless Entry ..................... .141, 142
Program Module .......................... .141
Remote Keyless Entry Module ...............141, 142
Right Body to Instrument Panel Wiring ...........192, 193
Right Front Wheel Sensor .......................50
Right Rear Wheel Sensor ........................50
RS Amplifier ........................... .122, 123
Safety Shut Down Relay ........................35
Seat Belt Warning System .......................67
Seat Belt Switch .............................67
Seat Track Position Sense Resistor .................154
Security Alarm Module Connector (Elec Cluster) ........202
Security Alarm Module Connector (Mech Cluster) ........203
Security Alarm System (Electronic Cluster) ........135, 136,
137, 138
Deck Lid Key Cylinder ...................... .135
Data Link Connector ....................... .136
Left Door Key Cylinder ...................... .135
Relay Bank ............................. .138
Relay Module ............................ .137
Right Door Key Cylinder ..................... .135
Security Alarm Hood Switch ...................136
Security Alarm Module .............135, 136, 137, 138
Security Lamp ........................... .136Wiring Diagram
Name Sheet Number
Security Alarm System (Mech Cluster w/VMC) ......127, 128,
129, 130
Deck Lid Key Cylinder ...................... .127
Data Link Connector ....................... .130
Left Door Key Cylinder ...................... .127
Relay Bank ............................. .130
Relay Module ............................ .129
Right Door Key Cylinder ..................... .127
Security Alarm Hood Switch ...................128
Security Alarm Module .............127, 128, 129, 130
Security Lamp ........................... .128
Security Alarm System (Mech Cluster w/o VMC) . . . .131, 132,
133, 134
Deck Lid Key Cylinder ...................... .131
Data Link Connector ....................... .134
Left Door Key Cylinder ...................... .131
Relay Bank ............................. .134
Relay Module ............................ .133
Right Door Key Cylinder ..................... .131
Security Alarm Hood Switch ...................132
Security Alarm Module .............131, 132, 133, 134
Security Lamp ........................... .132
Sensors Airbag Sensor .............................58
Ambient Sensor .......................... .117
Brake Fluid Level Sensor ......................98
Camshaft Position Sensor ......................28
Coolant Level Sensor .........................98
Crankshaft Position Sensor .....................28
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensors ..........17, 19, 25
Engine Oil Level Sensor .................... .31, 32
Heated Oxygen Sensors ................. .14, 19, 25
Height Sensors ............................44
In Car Senso r............................ .115
Left Front Wheel Sensor .......................50
Left Rear Wheel Sensor .......................50
MAP Sensors ........................ .18, 21, 26
Right Front Wheel Sensor ......................50
Right Rear Wheel Sensor ......................50
Sun Sensor ............................. .115
Throttle Position (Sensors) ................18, 21, 26
Transmission Output Speed Sensor ................34
Turbine Speed Sensor ........................34
Vehicle Speed Sensor .................. .17, 19, 25
Water Sensor ............................ .117
Windshield Washer Low Fluid Level Sensor ...........61
Solenoids Air Exhaust-Automatic Load Leveling Solenoid .........42
Air Suspension Solenoid ................... .41, 44
Deck Lid Release Solenoid ................... .159
EVAP/Purge Solenoids .................. .15, 20, 27
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Solenoids ..........14, 21, 26
Transmission Solenoid .................... .12, 35
Transmission TCC LU Solenoid ..................12
Splices Splice A1 ...........................4,6,8,10
Splice A3 .........................2,37,59,66
Splice A3-1 .....................2,6,8,10,69,71
Ä WIRING DIAGRAMS AC-AY BODY 8W - 319
Page 1594 of 2438

springs using Tool C-3422-B. (2) Remove valve retaining locks, valve spring re-
tainers, valve stem seals and valve springs. (3) Before removing valves, remove any burrs
from valve stem lock grooves to prevent damage
to the valve guides. Identify valves to insure instal-
lation in original location.
VALVE INSPECTION (1) Clean valves thoroughly and discard burned,
warped and cracked valves. (2) Measure valve stems for wear.
(3) If valve stems are worn more than 0.05 mm (.002
inch.) replace valve.
VALVE GUIDES
(1) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from inside
of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner. (2) Checking Valve Guide Wear:
² Insert valve with valve head positioned 10 mm (.400
inch) above cylinder head gasket surface.
²
Move valve to and from the indicator (Fig. 17). The
total dial indicator reading should not exceed the amount
specified in (Fig. 18). Readings should be taken for length-
wise and crosswise (with respect to cylinder head) move-
ment for each valve. Ream the guides for valves with
oversize stems if dial indicator reading is excessive or if
the stems are scuffed or scored.
(3) Service valves with oversize stems and oversize
seals are available in 0.15mm, (.005 inch) 0.40mm,
(.015 inch) and 0.80mm(.031 inch) oversize. Oversize seals must be used with oversize
valves. Reamers sizes to accommodate the oversize valve
stem are shown in (Fig. 18)
(4) Slowly turn reamer by hand and clean guide thor-
oughly before installing new valve. Do not attempt to
ream the valve guides from standard directly to
0.80mm (.030 inch). Use step procedure of 0.15mm
(.005 inch), 0.40mm (.015 inch) and 0.80mm (.030 inch) so the valve guides may be reamed true in
relation to the valve seat. After reaming guides, the
seat runout should be measured and resurfaced if
necessary. Refer to Refacing Valves and Valve Seats.
Replace cylinder head if guide does not clean
up with 0.80 mm (.030 inch) oversize reamer, or if
guide is loose in cylinder head.
TESTING VALVE SPRINGS
(1) Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should be
tested. As an example, the compression length of the
spring to be tested is 33.34mm (1-5/16 inches). Turn table
of Tool C-647 until surface is in line with the 33.34mm
(1-5/16 inch) mark on the threaded stud and the zero
mark on the front. Place spring over stud on the table and
lift compressing lever to set tone device (Fig. 20). Pull on
torque wrench until ping is heard. Take reading on torque
wrench at this instant. Multiply this reading by two. This
will give the spring load at test length. Fractional mea-
surements are indicated on the table for finer adjust-
ments. Refer to specifications to obtain specified height
and allowable tensions. Discard the springs that do not
meet specifications.
Fig. 18 Checking Wear on Valve GuideÐTypical
Fig. 19 Valve Guide Specification
Fig. 20 Testing Valve Spring with Tool C-647
9 - 28 2.2/2.5L ENGINE Ä
Page 1596 of 2438

(8) Check the valve spring installed height after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 26).
CAUTION: If more than .5mm (.020 inch) must be
ground from the valve tip, check the clearance be-
tween the rocker arm and the valve spring retainer
if below 1.25mm (.050 inch), grind the rocker arm
ears according to the procedure described in Refac-
ing Valves and Valve Seats.
CLEANING
Clean all valve guides, valves and valve spring as-
semblies thoroughly with suitable cleaning solution
before reassembling.
VALVE GEAR REASSEMBLY AFTER VALVE SERVICE (1) Coat valve stems with lubrication oil and insert
in cylinder head. CAUTION: Flexible Fuel Vehicles use unique valve
stem oil seals they are green in color. Standard
valve stem oil seals are NOT to be interchanged with
Flexible Fuel Vehicles engines.
(2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves. The
valve stem seals should be pushed firmly and
squarely over valve guide. The lower edge of the seal
should be resting on the valve guide boss.
CAUTION: When oversize valves are used, the cor-
responding oversize valve seal must also be used.
Excessive guide wear may result if oversize seals
are not used with oversize valves.
(3) Install valve spring seats and springs and re-
tainers. Compress valve springs only enough to in-
stall locks, taking care not to misalign the direction
of compression. Nicked valve stems may result from
misalignment of the valve spring compressor.
CAUTION: When depressing the valve spring retain-
ers with Tool C-3422-B the locks can become dislo-
cated. Check to make sure both locks are in their
correct location after removing tool .
(4) Check installed height of springs. Measurement
is to be taken from the spring seat to the bottom of
the spring retainer. Correct height is 41.2mm to
42.7mm (1.62 to 1.68 inches). If seats have been re-
ground an additional spring seat may be required to
maintain correct installed spring height. (5) Install adjusters, rocker arms in order, and
camshaft as previously described, see Camshaft-In-
stall. Check for clearance between the projecting ears
(either side of valve tip) of the rocker arms and the
valve spring retainers. At least 1.25 mm (.050 inch)
clearance must be present, if necessary, the rocker
arm ears may be ground to obtain this clearance
(Fig. 26). (6) Checking dry lash. Dry lash is the amount of
clearance that exists between the base circle of an in-
stalled cam and the rocker arm roller when the ad-
juster is drained of oil and completely collapsed.
Specified dry lash is 0.62 to 1.52 mm (.024 to .060
inch). To completely collapse adjuster for dry lash
measurement, pry off retainer cap, disassemble,
drain the adjuster of oil, reassemble, and install. Af-
ter performing dry lash check, refill adjuster with oil
(do not reuse retainer cap/s) and allow 10 minutes for
adjuster/s to bleed down before rotating cam.
Fig. 25 Valve Tip to Spring Seat Dimensions
Fig. 26 Checking Spring Installed Height and Spring Retainer Clearance
9 - 30 2.2/2.5L ENGINE Ä
Page 1605 of 2438
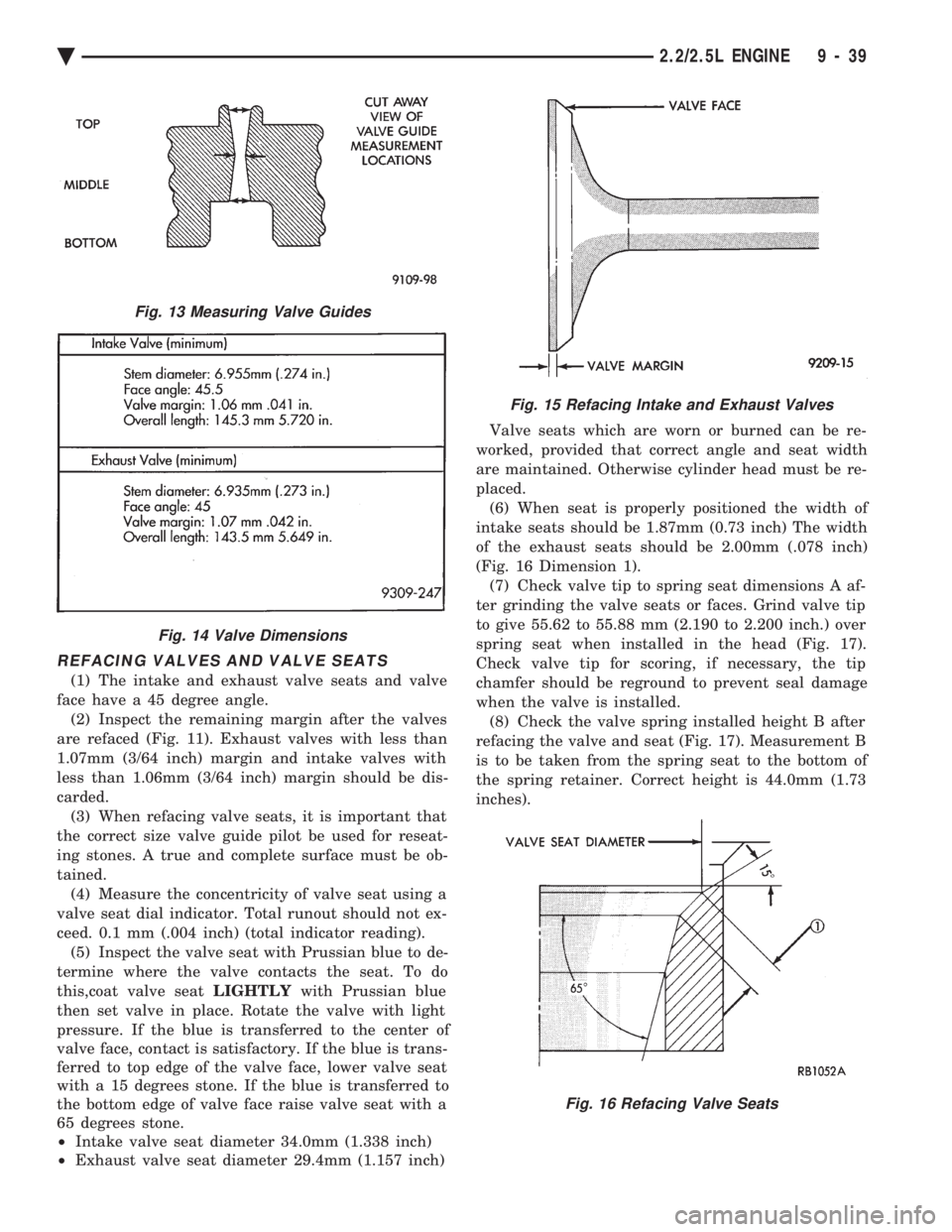
REFACING VALVES AND VALVE SEATS
(1) The intake and exhaust valve seats and valve
face have a 45 degree angle. (2) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced (Fig. 11). Exhaust valves with less than
1.07mm (3/64 inch) margin and intake valves with
less than 1.06mm (3/64 inch) margin should be dis-
carded. (3) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be ob-
tained. (4) Measure the concentricity of valve seat using a
valve seat dial indicator. Total runout should not ex-
ceed. 0.1 mm (.004 inch) (total indicator reading). (5) Inspect the valve seat with Prussian blue to de-
termine where the valve contacts the seat. To do
this,coat valve seat LIGHTLYwith Prussian blue
then set valve in place. Rotate the valve with light
pressure. If the blue is transferred to the center of
valve face, contact is satisfactory. If the blue is trans-
ferred to top edge of the valve face, lower valve seat
with a 15 degrees stone. If the blue is transferred to
the bottom edge of valve face raise valve seat with a
65 degrees stone.
² Intake valve seat diameter 34.0mm (1.338 inch)
² Exhaust valve seat diameter 29.4mm (1.157 inch) Valve seats which are worn or burned can be re-
worked, provided that correct angle and seat width
are maintained. Otherwise cylinder head must be re-
placed. (6) When seat is properly positioned the width of
intake seats should be 1.87mm (0.73 inch) The width
of the exhaust seats should be 2.00mm (.078 inch)
(Fig. 16 Dimension 1). (7) Check valve tip to spring seat dimensions A af-
ter grinding the valve seats or faces. Grind valve tip
to give 55.62 to 55.88 mm (2.190 to 2.200 inch.) over
spring seat when installed in the head (Fig. 17).
Check valve tip for scoring, if necessary, the tip
chamfer should be reground to prevent seal damage
when the valve is installed. (8) Check the valve spring installed height B after
refacing the valve and seat (Fig. 17). Measurement B
is to be taken from the spring seat to the bottom of
the spring retainer. Correct height is 44.0mm (1.73
inches).
Fig. 13 Measuring Valve Guides
Fig. 14 Valve Dimensions
Fig. 15 Refacing Intake and Exhaust Valves
Fig. 16 Refacing Valve Seats
Ä 2.2/2.5L ENGINE 9 - 39
Page 1606 of 2438

VALVE GEAR REASSEMBLY AFTER VALVE SERVICE
(1) Coat valve stems with lubrication oil and insert
in cylinder head. (2) Install new valve stem seals on all valves. The
valve stem seals should be pushed firmly and
squarely over valve guide. The lower edge of the seal
should be resting on the valve guide boss. (3) Install valve spring seats and springs and re-
tainers. Compress valve springs only enough to in-
stall locks, taking care not to misalign the direction
of compression. Nicked valve stems may result from
misalignment of the valve spring compressor.
CAUTION: When depressing the valve spring retain-
ers with Valve Spring Compressor Tool C-3422-B
with adopters 6537 and 6526 (Fig. 11) the locks can
become dislocated. Check to make sure both locks
are in their correct location after removing tool.
(4) Check installed height of springs. Measurement
B is to be taken from the spring seat to the bottom of
the spring retainer. Correct height is 44.0mm (1.73
inches). If seats have been ground an additional
spring seat may be required to maintain correct in-
stalled spring height (Fig. 17). (5) Install camshaft and rocker arms as previously
described, see Camshaft-Install.
Fig. 17 Checking Valve Tip Height and Spring Installed Height
9 - 40 2.2/2.5L ENGINE Ä
Page 1633 of 2438

PISTONS: Are aluminum alloy with a steel strut,
short height, and thin wall so as to be autothermic
and light weight. The piston head with valve re-
cesses, in combination with the cylinder head, forms
a compact spherical head with clearance for total
valve lift with pistons at top dead center. The piston
skirt, top and second ring lands are finished to a ta-
pered roughness for oil retention and high resistance
to scuffing. Piston pins, press-fitted into place, join
the pistons to the connecting rods. CYLINDER HEAD: The alloy cylinder heads fea- ture cross-flow type intake and exhaust ports. Valve
guides and inserts are hardened cast iron. Valves of
heat resistance steel are arranged i
n a V with each
camshaft on center. To improve combustion speed the
chambers are a compact spherical design with a
squish area of approximately 30 percent of the piston
top area. The cylinder heads are common to either
cylinder bank by reversing the direction of installa-
tion. CAMSHAFTS: Two overhead camshafts provide
valve actuation, one front (radiator side of cylinder
bank) and one rear. The front camshaft is provided
with a distributor drive and is longer. Both cam-
shafts are supported by four bearing journals, thrust
for the front camshaft is taken at journal two and
the rear at journal three. Front and rear camshaft
driving sprockets are interchangeable. The sprockets
and the engine water pump are driven by a single
notched timing belt. ROCKER ARM SHAFTS: The shafts are retained
by the camshaft bearing journal caps. Four shafts are
used, one for each intake and exhaust rocker arm as-
sembly on each cylinder head. The hollow shafts pro-
vide a duct for lubricating oil flow from the cylinder
head to the valve mechanisms. ROCKER ARMS: Are of light weight die-cast
with roller type follower operating against the cam
shaft. The valve actuating end of the rocker arms are
machined to retain hydraulic lash adjusters, elimi-
nating valve lash adjustment. VALVES: Are made of heat resistant steel and are
further treated to resist heat. VALVE SPRINGS: Are especially designed to be
short. The valve spring wire cross-section is oval
SPECIFICATIONS
Fig. 1 Engine Identification
Ä 3.0L ENGINE 9 - 67
Page 1642 of 2438
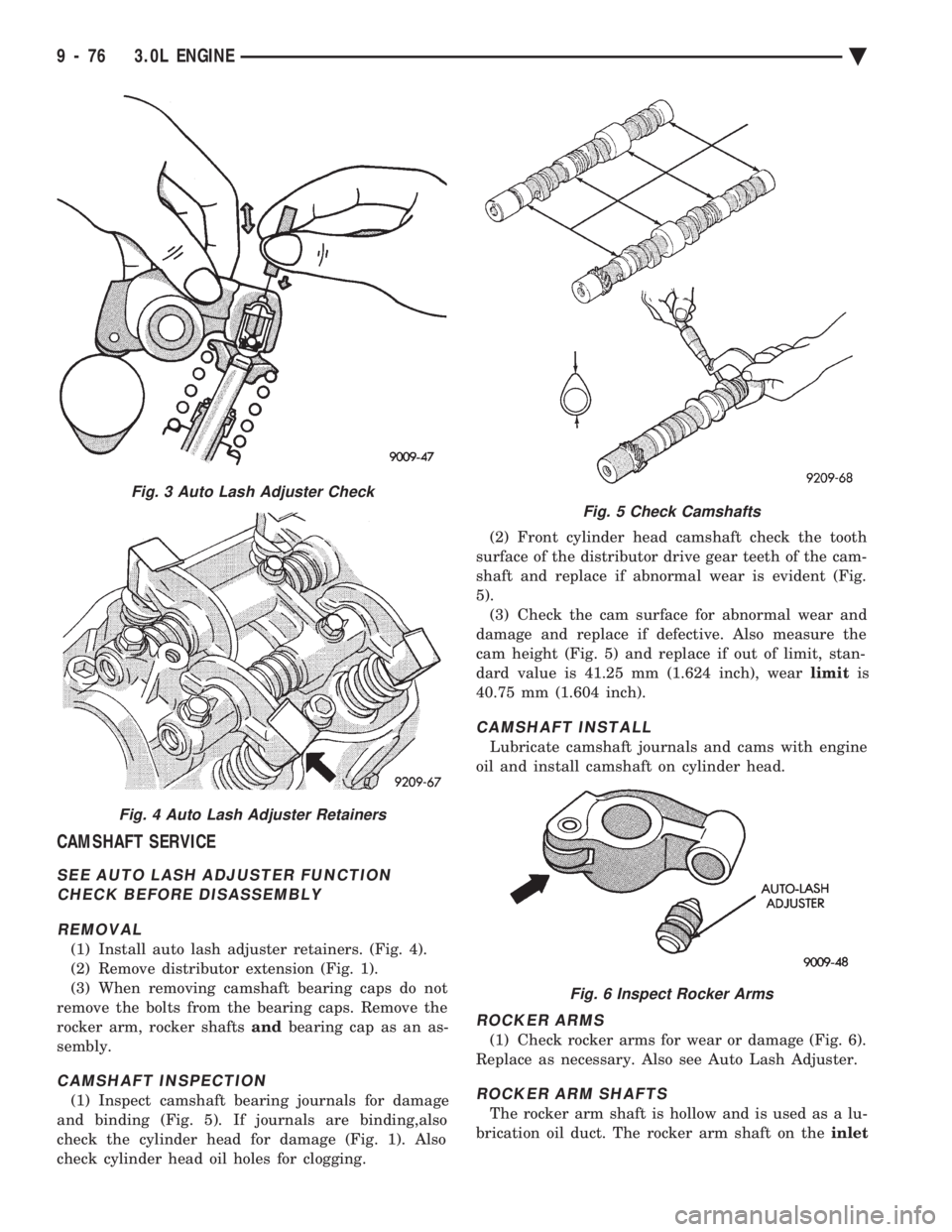
CAMSHAFT SERVICE
SEE AUTO LASH ADJUSTER FUNCTION CHECK BEFORE DISASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Install auto lash adjuster retainers. (Fig. 4).
(2) Remove distributor extension (Fig. 1).
(3) When removing camshaft bearing caps do not
remove the bolts from the bearing caps. Remove the
rocker arm, rocker shafts andbearing cap as an as-
sembly.
CAMSHAFT INSPECTION
(1) Inspect camshaft bearing journals for damage
and binding (Fig. 5). If journals are binding,also
check the cylinder head for damage (Fig. 1). Also
check cylinder head oil holes for clogging. (2) Front cylinder head camshaft check the tooth
surface of the distributor drive gear teeth of the cam-
shaft and replace if abnormal wear is evident (Fig.
5). (3) Check the cam surface for abnormal wear and
damage and replace if defective. Also measure the
cam height (Fig. 5) and replace if out of limit, stan-
dard value is 41.25 mm (1.624 inch), wear limitis
40.75 mm (1.604 inch).
CAMSHAFT INSTALL
Lubricate camshaft journals and cams with engine
oil and install camshaft on cylinder head.
ROCKER ARMS
(1) Check rocker arms for wear or damage (Fig. 6).
Replace as necessary. Also see Auto Lash Adjuster.
ROCKER ARM SHAFTS
The rocker arm shaft is hollow and is used as a lu-
brication oil duct. The rocker arm shaft on the inlet
Fig. 3 Auto Lash Adjuster Check
Fig. 4 Auto Lash Adjuster Retainers
Fig. 5 Check Camshafts
Fig. 6 Inspect Rocker Arms
9 - 76 3.0L ENGINE Ä