brake CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1887 of 2438

² transaxle gear selection (park/neutral switch)
The PCM also adjusts engine idle speed through
the idle air control motor based on the following in-
puts.
² brake switch
² engine coolant temperature
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² throttle position
² transaxle gear selection (park/neutral switch)
² vehicle speed
The auto shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays are
mounted externally, but turned on and off by the
PCM through the same circuit. The camshaft position sensor and crankshaft posi-
tion sensor signals are sent to the PCM. If the PCM
does not receive both signals within approximately
one second of engine cranking, it deactivates the
ASD and fuel pump relays. When these relays are
deactivated, power is shut off to the fuel injector, ig-
nition coil, oxygen sensor heating element and fuel
pump. The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the camshaft position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the coolant
temperature sensor, manifold absolute pressure sen-
sor and throttle position sensor.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSEÐPCM INPUT
When the air conditioning or defrost switch is put
in the ON position and the low pressure, high pres-
sure and ambient temperature switches are closed,
the PCM receives an input for air conditioning. After
receiving this input, the PCM activates the A/C com-
pressor clutch by grounding the A/C clutch relay.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT
The PCM monitors the battery voltage input to de-
termine fuel injector pulse width and generator field
control. If battery voltage is low the PCM will in-
crease injector pulse width.
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake switch is activated, the PCM re-
ceives an input indicating that the brakes are being
applied. the brake signal cancels speed control and
unlocks the torque convertor. The brake switch is
mounted on the brake pedal support bracket.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The camshaft position sensor provides cylinder
identification to the powertrain control module
(PCM) (Fig. 3). The sensor generates pulses as
groups of notches on the camshaft sprocket pass un-
derneath it (Fig. 4). The PCM keeps track of crank-
shaft rotation and identifies each cylinder by the pulses generated by the notches on the camshaft
sprocket. Four crankshaft pulses follow each group of
camshaft pulses.
When the PCM receives two camshaft pulses fol-
lowed by the long flat spot on the camshaft sprocket,
it knows that the crankshaft timing marks for cylin-
der one are next (on driveplate). When the PCM re-
ceives one camshaft pulse after the long flat spot on
the sprocket, cylinder number two crankshaft timing
marks are next. After 3 camshaft pulses, the PCM
knows cylinder four crankshaft timing marks follow.
One camshaft pulse after the three pulses indicates
cylinder five. The two camshaft pulses after cylinder
5 signals cylinder six (Fig. 4). The PCM can synchro-
nize on cylinders 1 or 4.
When metal aligns with the sensor, voltage goes
low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns with
the sensor, voltage spikes high (5.0 volts). As a group
of notches pass under the sensor, the voltage
switches from low (metal) to high (notch) then back
Fig. 3 Camshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 4 Camshaft Sprocket
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 147
Page 1891 of 2438

within a range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. Refer to Group
8A for charging system information.
AUTO SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY AND FUEL PUMP
RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM operates the auto shutdown (ASD) relay
and fuel pump relay through one ground path. The
PCM operates the relays by switching the ground
path on and off. Both relays turn on and off at the
same time. The ASD relay connects battery voltage to the fuel
injector and ignition coil. The fuel pump relay con-
nects battery voltage to the fuel pump and oxygen
sensor heating element. The PCM turns the ground path off when the igni-
tion switch is in the Off position. Both relays are off.
When the ignition switch is in the On or Crank po-
sition, the PCM monitors the crankshaft position
sensor and camshaft position sensor signals to deter-
mine engine speed and ignition timing (coil dwell). If
the PCM does not receive the crankshaft position
sensor and camshaft position sensor signals when the
ignition switch is in the Run position, it de-energizes
both relays. When the relays are de-energized, bat-
tery voltage is not supplied to the fuel injector, igni-
tion coil, fuel pump and oxygen sensor heating
element. The ASD relay and fuel pump relay are located in
the power distribution center (Fig. 14).
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The idle air control motor is mounted on the throt-
tle body. The PCM operates the idle air control motor
(Fig. 13). The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through
the idle air control motor to compensate for engine
load or ambient conditions. The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine at idle (the throttle blade is closed). The idle air control motor pintle protrudes
into the air bypass passage and regulates air flow
through it. The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by moving the
idle air control motor pintle in and out of the bypass
passage. The adjustments are based on inputs the
PCM receives. The inputs are from the throttle posi-
tion sensor, crankshaft position sensor, coolant tem-
perature sensor, and various switch operations
(brake, park/neutral, air conditioning). Deceleration
die out is also prevented by increasing airflow when
the throttle is closed quickly after a driving (speed)
condition.
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT
Vacuum for the Evaporative Canister is controlled
by the Canister Purge Solenoid (Fig. 15). The sole-
noid is controlled by the PCM.
The PCM operates the solenoid by switching the
ground circuit on and off based on engine operating
conditions. When energized, the solenoid prevents
vacuum from reaching the evaporative canister.
When not energized the solenoid allows vacuum to
flow to the canister. The PCM removes the ground to the solenoid when
the engine reaches a specified temperature and the
time delay interval has occurred. When the solenoid
is de-energized, vacuum flows to the canister purge
valve. Vapors are purged from the canister and flow
to the throttle body. The purge solenoid will also be energized during
certain idle conditions, in order to update the fuel de-
livery calibration.
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (CHECK ENGINE
LAMP)ÐPCM OUTPUT
The malfunction indicator lamp (instrument panel
Check Engine Lamp) comes on each time the ignition
key is turned ON and stays on for 3 seconds as a
bulb test. The malfunction indicator lamp warns the
Fig. 14 Relay Identification
Fig. 15 Canister Purge Solenoid
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 151
Page 1892 of 2438

operator that the PCM has entered a Limp-in mode.
During Limp-in Mode, the PCM attempts to keep the
system operational. The malfunction indicator signals
the need for immediate service. In limp-in mode, the
PCM compensates for the failure of certain components
that send incorrect signals. The PCM substitutes for
the incorrect signals with inputs from other sensors. Signals that can trigger the Malfunction Indi-
cator lamp (Check Engine Lamp).
² Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Battery Voltage Input
² An Emission Related System (California vehicles)
² Charging system
The malfunction indicator (Check Engine Lamp) can
also display diagnostic trouble codes. Cycle the ignition
switch on, off, on, off, on, within five seconds and any
diagnostic trouble codes stored in the PCM will be
displayed. Refer to the 3.3L and 3.8L Multi-Port Fuel
InjectionÐOn-Board Diagnostics section of this Group
for Diagnostic Trouble Code Descriptions.
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The data link connector provides the technician with
the means to connect the DRBII scan tool to diagnosis
the vehicle.
TRANSAXLE CONTROL MODULEÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies the following information to the
electronic automatic transaxle control module through
the CCD Bus:
² battery temperature
² brake switch input
² engine coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² speed control information
ELECTRIC EGR TRANSDUCER (EET)
SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT
The electronic EGR transducer (EET) contains an
electrically operated solenoid and a back-pressure
transducer (Fig. 16). The PCM operates the solenoid.
The PCM determines when to energize the solenoid.
Exhaust system back-pressure controls the transducer. When the PCM energizes the solenoid, vacuum does
not reach the EGR valve. Vacuum flows to the EGR
valve when the PCM de-energizes the solenoid. When exhaust system back-pressure becomes high
enough, it fully closes a bleed valve in the transducer.
When the PCM de-energizes the solenoid and back-
pressure closes the transducer bleed valve, vacuum
flows through the transducer to operate the EGR valve. De-energizing the solenoid, but not fully closing the
transducer bleed hole (because of by low back- pressure), varies the strength of vacuum applied to
the EGR valve. Varying the strength of the vacuum
changes the amount of EGR supplied to the engine.
This provides the correct amount of exhaust gas re-
circulation for different operating conditions.
FUEL INJECTORSÐPCM OUTPUT
The fuel injectors are electrical solenoids (Fig. 17).
The injector contains a pintle that closes off an ori-
fice at the nozzle end. When electric current is sup-
plied to the injector, the armature and needle move a
short distance against a spring, allowing fuel to flow
out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high pres-
sure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a hol-
low cone. The spraying action atomizes the fuel,
adding it to the air entering the combustion cham-
ber. The injectors are positioned in the intake mani-
fold.
The fuel injectors are operated by the PCM. They
are energized in a sequential order during all engine
operating conditions except start up. The PCM ini-
tially energizes all injectors at the same time. Once
Fig. 16 Electric EGR Transducer (EET) Assembly
Fig. 17 Fuel InjectorÐ3.3L Engine
14 - 152 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1900 of 2438
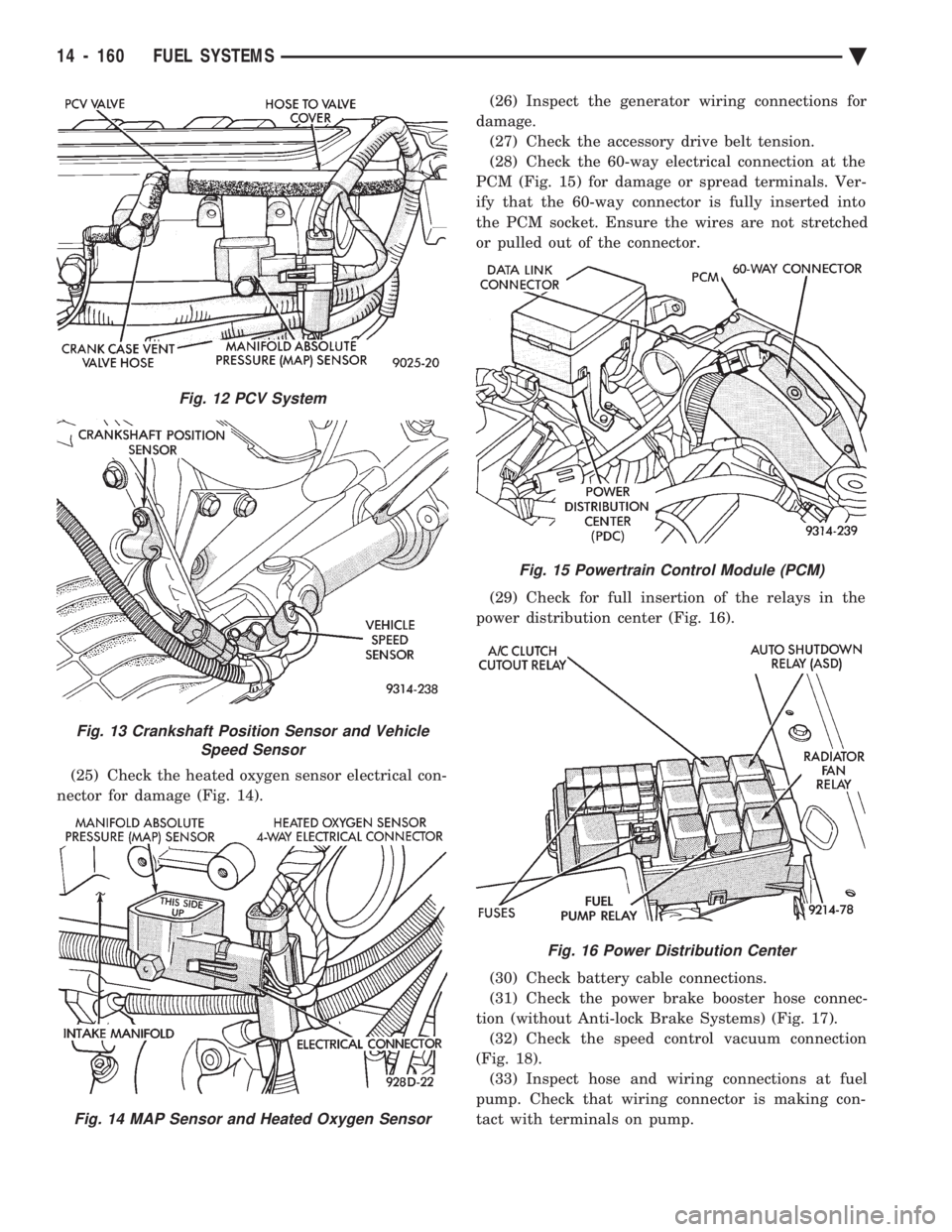
(25) Check the heated oxygen sensor electrical con-
nector for damage (Fig. 14). (26) Inspect the generator wiring connections for
damage. (27) Check the accessory drive belt tension.
(28) Check the 60-way electrical connection at the
PCM (Fig. 15) for damage or spread terminals. Ver-
ify that the 60-way connector is fully inserted into
the PCM socket. Ensure the wires are not stretched
or pulled out of the connector.
(29) Check for full insertion of the relays in the
power distribution center (Fig. 16).
(30) Check battery cable connections.
(31) Check the power brake booster hose connec-
tion (without Anti-lock Brake Systems) (Fig. 17). (32) Check the speed control vacuum connection
(Fig. 18). (33) Inspect hose and wiring connections at fuel
pump. Check that wiring connector is making con-
tact with terminals on pump.
Fig. 12 PCV System
Fig. 13 Crankshaft Position Sensor and Vehicle Speed Sensor
Fig. 14 MAP Sensor and Heated Oxygen Sensor
Fig. 15 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
Fig. 16 Power Distribution Center
14 - 160 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1901 of 2438

Fig. 17 Power Brake Booster Hose
Fig. 18 Speed Control Vacuum
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 161
Page 1903 of 2438

line. However, these could result in a rich or lean
condition causing an oxygen sensor fault to be stored in
the PCM. Secondary Ignition Circuit - The PCM cannot
detect an inoperative ignition coil, fouled or worn spark
plugs, ignition cross firing, or open spark plug cables. Engine Timing - The PCM cannot detect an incor-
rectly indexed timing chain, camshaft sprocket and
crankshaft sprocket. However, these could result in a
rich or lean condition causing an oxygen sensor fault to
be stored in the PCM. Cylinder Compression - The PCM cannot detect
uneven, low, or high engine cylinder compression. Exhaust System - The PCM cannot detect a
plugged, restricted or leaking exhaust system. Fuel Injector Malfunctions - The PCM cannot
determine if a fuel injector is clogged, the needle is
sticking or the wrong injector is installed. However,
these could result in a rich or lean condition causing an
oxygen sensor fault to be stored in the PCM. Excessive Oil Consumption - Although the PCM
monitors exhaust stream oxygen content when the
system is in closed loop, it cannot determine excessive
oil consumption. Throttle Body Air Flow - The PCM cannot detect a
clogged or restricted air cleaner inlet or filter element. Evaporative System - The PCM will not detect a
restricted, plugged or loaded evaporative purge canis-
ter. Vacuum Assist - Leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices are not monitored by the PCM. How-
ever, these could result in a MAP sensor fault being
stored in the PCM. PCM System Ground - The PCM cannot determine
a poor system ground. However, a diagnostic trouble
code may be generated as a result of this condition. PCM Connector Engagement - The PCM cannot
determine spread or damaged connector pins. How-
ever, a diagnostic trouble code may be generated as a
result of this condition.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The powertrain control module (PCM) compares in-
put signal voltages from each input device with estab-
lished high and low limits for the device. If the input
voltage is not within limits and other diagnostic
trouble code criteria are met, a diagnostic trouble code
will be stored in memory. Other diagnostic trouble code
criteria might include engine RPM limits or input
voltages from other sensors or switches that must be
present before a fault condition can be verified.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTION
A diagnostic trouble code indicates that the power-
train control module (PCM) has recognized an abnor- mal condition in the system. Diagnostic trouble codes
can be obtained from the malfunction indicator lamp
(Check Engine lamp on the instrument panel) or from
the DRBII scan tool. Diagnostic trouble codes indicate
the results of a failure but do not identify the failed
component directly.
SYSTEM TESTS
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR BLOCK
WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST ON AN
OPERATING ENGINE.
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
(1) Connect the DRBII scan tool to the data link
connector located in the engine compartment near the
driver side strut tower (Fig. 1). (2) Start the engine if possible, cycle the transaxle
selector and the A/Cswitch if applicable. Shut off the
engine. (3) Turn the ignition switch on, access Read Fault
Screen. Record all the fault messages shown on the
DRBII scan tool. Observe the malfunction indicator
lamp (check engine lamp on the instrument panel). The
lamp should light for 2 seconds then go out (bulb
check). Diagnostic trouble code erasure; access erase
diagnostic trouble code data
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs used by the powertrain control
module (PCM) have only two recognized states, HIGH
and LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize
the difference between a selected switch position ver-
sus an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective
switch. If the change is displayed, it can be assumed
that the entire switch circuit to the PCM is functional.
From the state display screen access either State
Display Inputs and Outputs or State Display Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRBII scan tool to the vehicle and access
the State Display screen. Then access Inputs and
Outputs. The following is a list of the engine control
system functions accessible through the Inputs and
Outputs screen. Park/Neutral Switch
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
A/C Switch Sense
S/C Vent Solenoid
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 163
Page 1911 of 2438

(4) Remove throttle cable (Fig. 6). Remove wiring
harness from throttle cable bracket and intake man-
ifold water tube.
(5) Disconnect idle air control motor and throttle
position sensor (TPS) electrical connectors (Fig. 7).
Refer to Idle Air Control Motor and Throttle Position
Sensor in this section. (6) Remove vacuum hose harness from throttle
body (Fig. 7). (7) Remove PCV and brake booster vacuum hoses
from air intake plenum. (8) Remove EGR tube to intake manifold flange
bolts (Fig. 8). (9) Remove vacuum harness connectors from in-
take plenum (Fig. 8). (10) Remove cylinder head to intake plenum strut
(Fig. 8). (11) Disconnect electrical connectors from the MAP
sensor and heated oxygen sensor electrical connec-
tion. Remove the engine mounted ground strap (Fig.
9).
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND
HOSES TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
Fig. 5 Servicing Idle Air Control Motor
Fig. 6 Throttle Cable Attachment
Fig. 7 Electrical and Vacuum Connection to Throttle Body
Fig. 8 EGR Tube
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 171
Page 1951 of 2438

(3) Position the steering column assembly in the
vehicle. Align the steering column assembly mounting
bracket slots on the brake pedal bracket attaching
studs (Fig. 13). Install, but loose assemblethe two
upper column bracket, washers and nuts.
(4) Make sure the front wheels are in the straight-
ahead position. Align and assemble the upper steering
coupler to lower steering coupler. Install the upper to
lower steering coupler retaining bolt and nut. Torque
the retaining bolt nut to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.). Be sure
to install the upper to lower steering coupler
retaining bolt retention pin (Fig. 6). (5) Install the buttons which retain the multi func-
tion switch wiring harness to the steering column.
Connect the multi-function switch wiring harness con-
nector to the multi-function switch. Torque the connec-
tor retaining bolt to 2 N Im (17 in. lbs) usin ga7mm
socket (Fig. 8). (6) Install the upper fixed shroud onto the steering
column assembly. (7) Be sure both breakaway capsules are fully seated
in the slots of the steering column upper support
bracket. Torque the 2 upper steering column assembly
to support bracket nuts to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.). Torque
the 2 lower steering column assembly to mounting
bracket nuts to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.).
(8) Complete the wiring harness connections to the
remaining steering column switches (Fig. 9). Install
the lower fixed shroud onto the steering column.
(9) Route the PRNDL actuator assembly under left
steering column wing and along left side of steering
column. Insert the flange of the PRNDL actuator steering
column insert into the steering column jacket (Fig. 7).
Squeeze the legs of the steering column insert together
and install tabs under steering column jacket. Engage
lock bar to secure the actuator assembly into the steering
column jacket (Fig. 7). (10) Hook the PRNDL actuator cable eyelet to the
steering column actuator arm (Fig. 7). Move the shift
lever to neutral, check pointer location, should indicate neutral. If pointer does not indicate neutral adjust actua-
tor with tool (Fig. 14) to center pointer on N (Neutral) and
then check pointer location in other gears.
(11) Install the lock housing shrouds. The shroud
fasteners are Torx-headscrews. Install the tilt lever
(if equipped). (12) Install the lower dash panel cover.
(13) For steering wheel installation with speed con-
trol refer to Group 8 Electrical. For non-speed control,
place the steering wheel on the steering column shaft
with the master splines aligned. Install the steering
wheel to column shaft retaining nut. Tighten retaining
nut to 61 N Im (45 ft. lbs.) torque. Do not force the
steering wheel onto the column shaft by driving
it on with a heavy object. Pull steering wheel
down onto column shaft using ONLY the steering
wheel retaining nut.
(14) For vehicles equipped with a column shift. Pass
the transmission shift cable through its mounting bracket
on the steering column assembly. Connect the transmis-
sion shift cable to the shift lever on the steering column
assembly. Install the shift cable to mounting bracket
retaining clip (Fig. 2). The grommet must be installed
in the shift lever (Fig. 11) before the cable is in-
serted into the grommet. Use MopartMultipurpose
Lubricant, or an equivalent product, to aid installation of
shift link rod into grommet.
(15) Re-adjust the transmission shift linkage.
Whenever the steering column is loosened or
removed, the shift linkage MUST be adjusted and
tested. Refer to Group 21 Transmission for the shift
linkage adjustment procedure.
Fig. 13 Steering Column Mounting
Fig. 14 PRNDL Actuator Cable Adjustment
Ä STEERING 19 - 33
Page 2000 of 2438

FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION
The transmission and differential sump have a
common oil sump with a communicating opening
between the two. Before removing the dipstick, wipe all dirt off of the
protective disc and the dipstick handle. The torque converter will fill in both the PPark or N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in PPark to
check fluid level. Inspect fluid level on dipstick every six months.
Allow the engine to idle for at least one minute
with vehicle on level ground. This will assure
complete oil level stabilization between differen-
tial and transmission. A properly filled transaxle
will read near the addmark when fluid temperature is
21 degrees Celsius (70 degrees Fahrenheit). When the
transaxle reaches operating temperature the fluid
should be in the HOTregion.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with the
fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles make the
fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be low and build
up slowly. Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the gears
churn up foam and cause the same conditions which
occur with a low fluid level. In either case, the air bubbles can cause overheating,
fluid oxidation, and varnishing, which can interfere
with normal valve, clutch, and servo operation. Foam-
ing can also result in fluid escaping from the transaxle
vent (dipstick handle) where it may be mistaken for a
leak. Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle overhaul is needed. Be
sure to examine the fluid on the dipstick closely. If
there is any doubt about its condition, drain out a
sample for a double check. After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
SELECTION OF LUBRICANT
It is important that the proper lubricant be used in
these transmissions. MOPAR tATF PLUS (Automatic
Transmission Fluid-Type 7176) should be used to aid in
assuring optimum transmission performance. Fluids of
the type labeled DEXRON II Automatic Transmission
Fluid should be used only if the recommended fluid is
not available. It is important that the transmission
fluid be maintained at the prescribed level using the
recommended fluids.
SPECIAL ADDITIVES
Chrysler Corporation does not recommend the addi-
tion of any fluids to the transmission, other than the
automatic transmission fluid listed above. An ex- ception to this policy is the use of special dyes to aid in
detecting fluid leaks. The use of transmission sealers
should be avoided, since they may adversely affect
seals.
FLUID AND FILTER CHANGE
When the factory fill fluid is changed, only
fluids of the type labeled MOPAR tATF PLUS
(Automatic Transmission fluid) Type 7176 should
be used. A band adjustment and filter change
should be made at the time of the oil change. The
magnet (on the inside of the oil pan) should also
be cleaned with a clean, dry cloth. If the transaxle is disassembled for any reason,
the fluid and filter should be changed, and the
band(s) adjusted.
FLUID DRAIN AND REFILL
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist (See Lubrication, Group
0). Place a drain container with a large opening, under
transaxle oil pan. (2) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner to
break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove the
oil pan. (3) Install a new filter and gasket on bottom of the
valve body and tighten retaining screws to 5 N Im (40
in. lbs.). (4) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new MOPAR tAdhesive sealant. Tighten oil pan
bolts to 19 N Im (165 in. lbs.).
(5) Pour four quarts of MOPAR tATF PLUS (Auto-
matic Transmission Fluid) Type 7176 through the
dipstick opening. (6) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes ap-
plied, move selector lever momentarily to each posi-
tion, ending in the park or neutral position. (7) Add sufficient fluid to bring level to 1/8 inch
below the ADD mark. Recheck fluid level after transaxle is at normal
operating temperature. The level should be in the HOT
region (Fig. 1). To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make cer-
tain that dipstick is full seated into the dipstick open-
ing.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID WIRING
CONNECTOR
If wiring connector is unplugged, the torque con-
verter clutch will not operate (Fig. 2).
ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, be certain that the
fluid level and condition, and control cable adjustments
have been checked and approved. During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting.
21 - 40 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2006 of 2438

so that pump housing and case front may be covered
with soapy solution or water. Leaks are sometimes
caused by porosity in the case or pump housing.If a leak source is located, that part and all associ-
ated seals, O-rings, and gaskets should be replaced
with new parts.
GEARSHIFT LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
Normal operation of the Park/Neutral Position
Switch provides a quick check to confirm proper
manual linkage adjustment. Move the selector level slowly upward until it
clicks into the ``P'' Park notch in the selector gate. If
the starter will operate the ``P'' position is correct. After checking ``P'' position, move selector slowly
toward ``N'' Neutral position until lever drops in the
``N'' stop. If the starter will also operate at this point
the gearshift linkage is properly adjusted. If the
starter fails to operate in either position, linkage ad-
justment is required.
CAUTION: When it is necessary to disassemble
linkage cable from levers, which use plastic grom-
mets as retainers, the grommets should be replaced
with new grommets. Use a prying tool to force rod
from grommet in lever, then cut away old grommet.
Use pliers to snap new grommet into lever and rod
into grommet.
(1) Set parking brake.
(2) Place gearshift lever in P(PARK) position.
(3) Loosen clamp bolt on gearshift cable bracket.
(4) Column shift: Insure that preload adjustment
spring engages fork on transaxle bracket. (5) Pull the shift lever by hand to the front detent
position (PARK) and tighten lock. Tighten screw to
11 N Im (100 in. lbs.). Gearshift linkage should now
be properly adjusted. (6) Check adjustment as follows:(a) Detent position for neutral and drive should
be within limits of hand lever gate stops. (b) Key start must occur only when shift lever is
in park or neutral positions.
THROTTLE PRESSURE LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
The throttle pressure cable adjustment is very im-
portant to proper transaxle operation. This adjust-
ment positions a valve which controls shift speed,
shift quality, and part throttle downshift sensitivity.
If the setting is too long, early shifts and slippage be-
tween shifts may occur. If the setting is too short,
shifts may be delayed and part throttle downshifts
may be very sensitive.
CABLE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE (4-CYL.)
(1) Perform transaxle throttle pressure cable ad-
justment while engine is at normal operating tem-
perature. (2) Loosen cable mounting bracket lock screw.
(3) Bracket should be positioned with both bracket
alignment tabs touching the transaxle cast surface.
Tighten lock screw to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.) see Fig-
ure 8.
(4) Release cross-lock on the cable assembly (pull
cross-lock upward) see Figure 7. (5) To insure proper adjustment, the cable must be
free to slide all the way toward the engine, against
its stop, after the cross-lock is released. (6) Move transaxle throttle control lever fully
clockwise, against its internal stop, and press cross-
lock downward into locked position (Fig. 7). (7) The adjustment is complete and transaxle
throttle cable backlash was automatically removed. (8) Test cable freedom of operation by moving the
transaxle throttle lever forward (counterclockwise).
Then slowly release it to confirm it will return fully
rearward (clockwise). (9) No lubrication is required for any component of
the throttle cable system.
ROD ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE (6-CYL.)
(1) Perform transaxle throttle pressure cable ad-
justment while engine is at normal operating tem-
perature. (2) Loosen adjustment swivel lock screw.
(3) To insure proper adjustment, swivel must be
free to slide along flat end of throttle rod so that pre-
load spring action is not restricted. Disassemble and
clean or repair parts to assure free action, if neces-
sary. (4) Hold transaxle throttle lever firmly toward en-
gine, against its internal stop and tighten swivel lock
screw to 11 N Im (100 in. lbs.)
(5) The adjustment is finished and linkage back
lash was automatically removed by the preload
spring. (6) If lubrication is required see Lubrication,
Group 0.
Fig. 8 Throttle Pressure CableÐTypical
21 - 46 TRANSAXLE Ä