spare tire CHEVROLET EQUINOX 2010 2.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 2010, Model line: EQUINOX, Model: CHEVROLET EQUINOX 2010 2.GPages: 394, PDF Size: 5.7 MB
Page 212 of 394

8-8 Driving and Operating
Off-Road Driving
Vehicles with all‐wheel drive can be
used for off‐road driving. Vehicles
without all‐wheel drive should not be
driven off-road except on a level,
solid surface.
Many of the vehicle design features
that help make the vehicle more
responsive on paved roads during
poor weather conditions also help
make it better suited for off‐road use
than conventional passenger
vehicles. The vehicle does not have
features usually thought to be
necessary for extended or severe
off‐road use such as special
underbody shielding and transfer
case low gear range.
The airbag system is designed to
work properly under a wide range of
conditions, including off‐road usage.
Always wear your safety belt and
observe safe driving speeds,
especially on rough terrain.
Drinking and driving can be very
dangerous on any road and this is
certainly true for off-road driving.At the very time you need special
alertness and driving skills, your
reflexes, perceptions, and judgment
can be affected by even a small
amount of alcohol. You could have a
serious
—or even fatal —accident
if you drink and drive or ride with a
driver who has been drinking.
Off-roading can be great fun but has
some definite hazards. The greatest
of these is the terrain itself. When
off-road driving, traffic lanes are not
marked, curves are not banked, and
there are no road signs. Surfaces
can be slippery, rough, uphill,
or downhill.
Avoid sharp turns and abrupt
maneuvers. Failure to operate the
vehicle correctly off‐road could
result in loss of vehicle control or
vehicle rollover.
Off-roading involves some new
skills. That is why it is very
important that you read these
driving tips and suggestions to help
make off-road driving safer and
more enjoyable.
Before You Go Off-Roading
.Have all necessary maintenance
and service work done.
.Make sure there is enough fuel,
that fluid levels are where they
should be, and that the spare
tire is fully inflated.
.Be sure to read all the
information about all-wheel-drive
vehicles in this manual.
.Make sure all underbody
shields, if the vehicle has them,
are properly attached.
.Know the local laws that apply to
off-roading where you will be
driving or check with law
enforcement people in the area.
.Be sure to get the necessary
permission if you will be on
private land.
Page 242 of 394
8-38 Driving and Operating
For vehicles with a Driver
Information Center (DIC) an
“ECO Mode On”message displays.
See Fuel System Messages
on
page 4‑30for more information.
When Fuel Economy Mode is on:
.The transmission will upshift
sooner and downshift later.
.The torque converter clutch will
apply sooner and stay on longer.
.The gas pedal will be less
sensitive.
.The vehicle's computer will more
aggressively shut off fuel to the
engine under deceleration.
.The engine idle speed will be
lower.
.Driving performance is more
conservative.
Drive Systems
All-Wheel Drive
With this feature, engine power is
always sent to all four wheels. It is
fully automatic, and adjusts itself as
needed for road conditions.
When using a compact spare tire on
an AWD vehicle, the system
automatically detects the compact
spare and disables AWD. To restore
AWD operation and prevent
excessive wear on system, replace
the compact spare with a full-size
tire as soon as possible. See
Compact Spare Tire
on page 9‑68for more information.
Brakes
Antilock Brake
System (ABS)
This vehicle has the Antilock Brake
System (ABS), an advanced
electronic braking system that helps
prevent a braking skid.
When the engine is started and the
vehicle begins to drive away, ABS
checks itself. A momentary motor or
clicking noise might be heard while
this test is going on, and it might
even be noticed that the brake
pedal moves a little. This is normal.
Page 270 of 394

9-2 Vehicle Care
Wheels and Tires
Tires . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-40
Tire Sidewall Labeling . . . . . . . 9-40
Tire Designations . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-42
Tire Terminology andDefinitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-43
Tire Pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-46
Tire Pressure Monitor System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-47
Tire Pressure Monitor Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-49
Tire Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-52
Tire Rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-52
When It Is Time for New Tires . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-53 Buying New Tires . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-54
Different Size Tires and
Wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-55
Uniform Tire Quality Grading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-56
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-57
Wheel Replacement . . . . . . . . . 9-57
Tire Chains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-58
If a Tire Goes Flat . . . . . . . . . . . 9-59
Tire Changing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-61
Compact Spare Tire . . . . . . . . . 9-68
Jump Starting
Jump Starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-69
Towing
Towing the Vehicle . . . . . . . . . . . 9-72
Recreational Vehicle Towing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-72
Appearance Care
Exterior Care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-75
Interior Care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-79
Page 308 of 394

9-40 Vehicle Care
Wheels and Tires
Tires
Your new vehicle comes with
high-quality tires made by a
leading tire manufacturer. If you
ever have questions about your
tire warranty and where to
obtain service, see your vehicle
Warranty booklet for details. For
additional information refer to
the tire manufacturer.
{WARNING
Poorly maintained and improperly
used tires are dangerous.
.Overloading your tires can
cause overheating as a result
of too much flexing. You
could have an air-out and a
serious accident. SeeVehicle
Load Limits on page 8‑24.
(Continued)
WARNING (Continued)
.Underinflated tires pose the
same danger as overloaded
tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury.
Check all tires frequently to
maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure
should be checked when your
tires are cold. See Tire
Pressure on page 9‑46.
.Overinflated tires are more
likely to be cut, punctured
or broken by a sudden
impact —such as when you
hit a pothole. Keep tires at
the recommended pressure.
.Worn, old tires can cause
accidents. If your tread is
badly worn, or if your tires
have been damaged,
replace them.
Tire Sidewall Labeling
Useful information about a tire is
molded into its sidewall. The
examples below show a typical
passenger vehicle tire and a
compact spare tire sidewall.
Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire Example
(A) Tire Size:The tire size is a
combination of letters and
numbers used to define a
particular tire's width, height,
aspect ratio, construction type,
Page 309 of 394

Vehicle Care 9-41
and service description. See the
“Tire Size”illustration later in this
section for more detail.
(B) TPC Spec (Tire
Performance Criteria
Specification)
:Original
equipment tires designed to
GM's specific tire performance
criteria have a TPC specification
code molded onto the sidewall.
GM's TPC specifications meet or
exceed all federal safety
guidelines.
(C) DOT (Department of
Transportation)
:The
Department of Transportation
(DOT) code indicates that the
tire is in compliance with the
U.S. Department of
Transportation Motor Vehicle
Safety Standards.
(D) Tire Identification Number
(TIN)
:The letters and numbers
following the DOT (Department
of Transportation) code is the Tire Identification Number (TIN).
The TIN shows the
manufacturer and plant code,
tire size, and date the tire was
manufactured. The TIN is
molded onto both sides of the
tire, although only one side may
have the date of manufacture.
(E) Tire Ply Material
:The type
of cord and number of plies in
the sidewall and under the tread.
(F) Uniform Tire Quality
Grading (UTQG)
:Tire
manufacturers are required to
grade tires based on three
performance factors: treadwear,
traction, and temperature
resistance. For more information
see Uniform Tire Quality
Grading
on page 9‑56.
(G) Maximum Cold Inflation
Load Limit
:Maximum load that
can be carried and the
maximum pressure needed to
support that load.
Compact Spare Tire Example
(A) Tire Ply Material:The type
of cord and number of plies in
the sidewall and under the tread.
(B) Temporary Use Only
:The
compact spare tire or temporary
use tire has a tread life of
approximately 5 000 km
(3,000 miles) and should not be
driven at speeds over 105 km/h
(65 mph). The compact spare
tire is for emergency use when a
regular road tire has lost air and
gone flat. If your vehicle has a
Page 310 of 394

9-42 Vehicle Care
compact spare tire, see
Compact Spare Tire
on
page 9‑68
and If a Tire Goes Flat
on page 9‑59.
(C) Tire Identification Number
(TIN)
:The letters and numbers
following the DOT (Department
of Transportation) code is the
Tire Identification Number (TIN).
The TIN shows the
manufacturer and plant code,
tire size, and date the tire was
manufactured. The TIN is
molded onto both sides of the
tire, although only one side may
have the date of manufacture.
(D) Maximum Cold Inflation
Load Limit
:Maximum load that
can be carried and the
maximum pressure needed to
support that load. (E) Tire Inflation
:The
temporary use tire or compact
spare tire should be inflated to
420 kPa (60 psi). For more
information on tire pressure and
inflation see Tire Pressure
on
page 9‑46
.
(F) Tire Size
:A combination of
letters and numbers define a
tire's width, height, aspect ratio,
construction type, and service
description. The letter T as the
first character in the tire size
means the tire is for temporary
use only.
(G) TPC Spec (Tire
Performance Criteria
Specification)
:Original
equipment tires designed to
GM's specific tire performance
criteria have a TPC specification
code molded onto the sidewall.
GM's TPC specifications meet or
exceed all federal safety
guidelines.
Tire Designations
Tire Size
The following illustration shows
an example of a typical
passenger vehicle tire size.
(A) Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire:
The United States version of a
metric tire sizing system. The
letter P as the first character in
the tire size means a passenger
vehicle tire engineered to
standards set by the U.S. Tire
and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width
:The three‐digit
number indicates the tire section
width in millimeters from
sidewall to sidewall.
Page 315 of 394

Vehicle Care 9-47
For additional information
regarding how much weight your
vehicle can carry, and an
example of the Tire and Loading
Information label, seeVehicle
Load Limits
on page 8‑24. How
you load your vehicle affects
vehicle handling and ride
comfort. Never load your vehicle
with more weight than it was
designed to carry.
When to Check
Check your tires once a month
or more. Do not forget to check
the compact spare tire, if the
vehicle has one. The compact
spare should be at 60 psi
(420 kPa). For additional
information regarding the
compact spare tire, see
Compact Spare Tire
on
page 9‑68
. How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type
gauge to check tire pressure.
You cannot tell if your tires are
properly inflated simply by
looking at them. Radial tires may
look properly inflated even when
they are under‐inflated. Check
the tire's inflation pressure when
the tires are cold. Cold means
your vehicle has been sitting for
at least three hours or driven no
more than 1.6 km (1 mile).
Remove the valve cap from the
tire valve stem. Press the tire
gauge firmly onto the valve to
get a pressure measurement.
If the cold tire inflation pressure
matches the recommended
pressure on the Tire and
Loading Information label, no
further adjustment is necessary.
If the inflation pressure is low,
add air until you reach the
recommended amount. If you overfill the tire, release air
by pushing on the metal stem in
the center of the tire valve.
Re‐check the tire pressure with
the tire gauge.
Be sure to put the valve caps
back on the valve stems. They
help prevent leaks by keeping
out dirt and moisture.
Tire Pressure Monitor
System
The Tire Pressure Monitor System
(TPMS) uses radio and sensor
technology to check tire pressure
levels. The TPMS sensors monitor
the air pressure in your vehicle's
tires and transmit tire pressure
readings to a receiver located in the
vehicle.
Each tire, including the spare (if
provided), should be checked
monthly when cold and inflated to
the inflation pressure recommended
by the vehicle manufacturer on the
vehicle placard or tire inflation
Page 317 of 394

Vehicle Care 9-49
Tire Pressure Monitor
Operation
This vehicle may have a Tire
Pressure Monitor System (TPMS).
The TPMS is designed to warn the
driver when a low tire pressure
condition exists. TPMS sensors are
mounted onto each tire and wheel
assembly, excluding the spare tire
and wheel assembly. The TPMS
sensors monitor the air pressure in
the vehicle's tires and transmits the
tire pressure readings to a receiver
located in the vehicle.
When a low tire pressure condition
is detected, the TPMS illuminates
the low tire pressure warning light
located on the instrument panel
cluster. If the warning light comes
on, stop as soon as possible andinflate the tires to the recommended
pressure shown on the tire loading
information label. See
Vehicle Load
Limits on page 8‑24.
At the same time a message to
check the pressure in a specific tire
appears on the Driver Information
Center (DIC) display. The low tire
pressure warning light and the DIC
warning message come on at each
ignition cycle until the tires are
inflated to the correct inflation
pressure. Using the DIC, tire
pressure levels can be viewed by
the driver. For additional information
and details about the DIC operation
and displays see Driver Information
Center (DIC) on page 4‑24.
The low tire pressure warning light
may come on in cool weather when
the vehicle is first started, and then
turn off as you start to drive. This
could be an early indicator that the
air pressure in the tire(s) are getting
low and need to be inflated to the
proper pressure. A Tire and Loading Information
label, attached to your vehicle,
shows the size of your vehicle's
original equipment tires and the
correct inflation pressure for your
vehicle's tires when they are cold.
See
Vehicle Load Limits
on
page 8‑24, for an example of the
Tire and Loading Information label
and its location on your vehicle.
Also see Tire Pressure
on
page 9‑46.
Your vehicle's TPMS can warn you
about a low tire pressure condition
but it does not replace normal tire
maintenance. See Tire Inspection
on page 9‑52,Tire Rotationon
page 9‑52and Tires on page 9‑40.
Notice: Liquid tire sealants could
damage the Tire Pressure Monitor
System (TPMS) sensors. Sensor
damage caused by using a tire
sealant is not covered by your
warranty. Do not use liquid tire
sealants.
Page 318 of 394

9-50 Vehicle Care
TPMS Malfunction Light and
Message
The TPMS will not function properly
if one or more of the TPMS sensors
are missing or inoperable. When the
system detects a malfunction, the
low tire warning light flashes for
about one minute and then stays on
for the remainder of the ignition
cycle. A DIC warning message is
also displayed. The low tire warning
light and DIC warning message
come on at each ignition cycle until
the problem is corrected. Some of
the conditions that can cause the
malfunction light and DIC message
to come on are:
.One of the road tires has been
replaced with the spare tire. The
spare tire does not have a
TPMS sensor. The TPMS
malfunction light and DIC
message should go off once you
re‐install the road tire containing
the TPMS sensor.
.The TPMS sensor matching
process was started but not
completed or not completed
successfully after rotating the
vehicle's tires. The DIC message
and TPMS malfunction light
should go off once the TPMS
sensor matching process is
performed successfully. See
“TPMS Sensor Matching
Process”later in this section.
.One or more TPMS sensors are
missing or damaged. The DIC
message and the TPMS
malfunction light should go off
when the TPMS sensors are
installed and the sensor
matching process is performed
successfully. See your dealer for
service.
.Replacement tires or wheels do
not match your vehicle's original
equipment tires or wheels. Tires
and wheels other than those
recommended for your vehicle
could prevent the TPMS from
functioning properly. See Buying
New Tires on page 9‑54.
.Operating electronic devices or
being near facilities using radio
wave frequencies similar to the
TPMS could cause the TPMS
sensors to malfunction.
If the TPMS is not functioning it
cannot detect or signal a low tire
condition. See your dealer for
service if the TPMS malfunction
light and DIC message comes on
and stays on.
TPMS Sensor Matching
Process
Each TPMS sensor has a unique
identification code. Any time you
rotate your vehicle's tires or replace
one or more of the TPMS sensors,
the identification codes will need to
be matched to the new tire/wheel
position. The sensors are matched
to the tire/wheel positions in the
following order: driver side front tire,
passenger side front tire, passenger
side rear tire, and driver side rear
tire using a TPMS diagnostic tool.
See your dealer for service.
Page 320 of 394
9-52 Vehicle Care
10. Proceed to the driver side reartire, and repeat the procedure
in Step 7. The horn sounds two
times to indicate the sensor
identification code has been
matched to the driver side rear
tire, and the TPMS sensor
matching process is no longer
active. The Tire Learning
Active message on the DIC
display screen goes off.
11. Turn the ignition to LOCK/OFF.
12. Set all four tires to the recommended air pressure
level as indicated on the Tire
and Loading Information label.
13. Put the valve caps back on the valve stems.
Tire Inspection
We recommend that you
regularly inspect your vehicle's
tires, including the spare tire,
if the vehicle has one, for signs of wear or damage. See
When
It Is Time for New Tires
on
page 9‑53
for more information.
Tire Rotation
Tires should be rotated every
8 000 to 13 000 km (5,000 to
8,000 miles). See Scheduled
Maintenance
on page 10‑2.
The purpose of a regular tire
rotation is to achieve a uniform
wear for all tires on the vehicle.
This will ensure that the vehicle
continues to perform most like it
did when the tires were new.
Any time you notice unusual
wear, rotate the tires as soon as
possible and check wheel
alignment. Also check for
damaged tires or wheels. See
When It Is Time for New Tires
on page 9‑53and Wheel
Replacement
on page 9‑57.
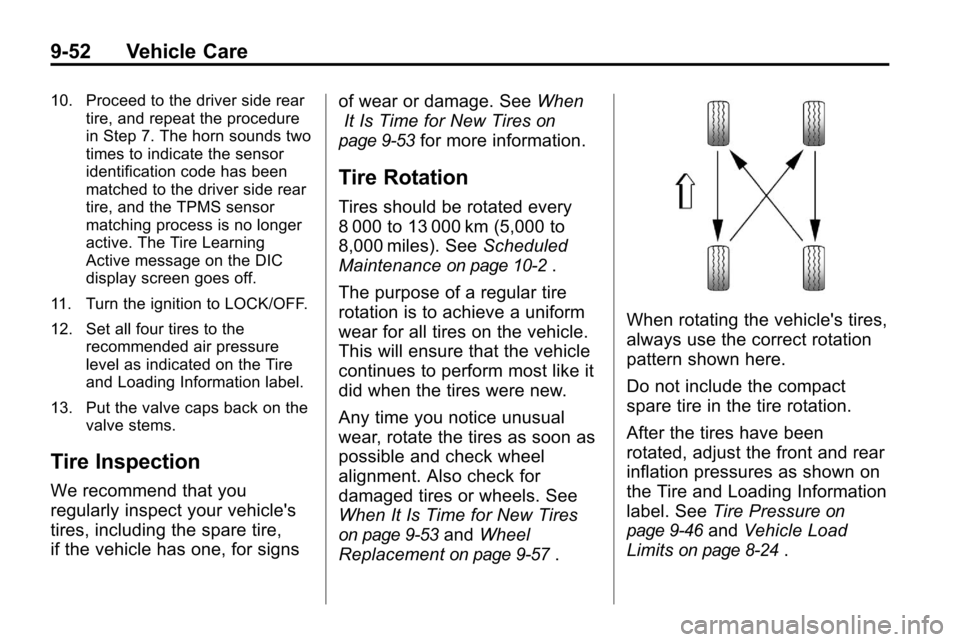
When rotating the vehicle's tires,
always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
Do not include the compact
spare tire in the tire rotation.
After the tires have been
rotated, adjust the front and rear
inflation pressures as shown on
the Tire and Loading Information
label. See Tire Pressure
on
page 9‑46
and Vehicle Load
Limits
on page 8‑24.