lock CHEVROLET EXPRESS CARGO VAN 2006 1.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 2006, Model line: EXPRESS CARGO VAN, Model: CHEVROLET EXPRESS CARGO VAN 2006 1.GPages: 406, PDF Size: 2.51 MB
Page 211 of 406

If your engine ever stops while you are driving, brake
normally but do not pump your brakes. If you do,
the pedal may get harder to push down. If your engine
stops, you will still have some power brake assist.
But you will use it when you brake. Once the power
assist is used up, it may take longer to stop and
the brake pedal will be harder to push.
Adding non-GM accessories can affect your vehicle’s
performance. SeeAccessories and Modi�cations
on page 5-3.
Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS)
Your vehicle has the Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS),
an advanced electronic braking system that will
help prevent a braking skid.
When you start your engine and begin to drive away,
ABS will check itself. You may hear a momentary
motor or clicking noise while this test is going on.
This is normal.
If there is a problem with
the ABS, this warning
light will stay on. See
Anti-Lock Brake System
Warning Light on
page 3-34.Let us say the road is wet and you are driving safely.
Suddenly, an animal jumps out in front of you. You slam
on the brakes and continue braking. Here is what
happens with ABS:
A computer senses that wheels are slowing down.
If one of the wheels is about to stop rolling, the computer
will separately work the brakes at each front wheel
and at both rear wheels.
4-7
Page 212 of 406

ABS can change the brake pressure faster than any
driver could. The computer is programmed to make the
most of available tire and road conditions. This can
help you steer around the obstacle while braking hard.
As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates
on wheel speed and controls braking pressure
accordingly.Remember: ABS does not change the time you need to
get your foot up to the brake pedal or always decrease
stopping distance. If you get too close to the vehicle
in front of you, you will not have time to apply your
brakes if that vehicle suddenly slows or stops. Always
leave enough room up ahead to stop, even though
you have ABS.
Using ABS
Do not pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal
down firmly and let anti-lock work for you. You may feel
the brakes vibrate, or you may notice some noise,
but this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
With ABS, you can steer and brake at the same time.
In many emergencies, steering can help you more than
even the very best braking.
Locking Rear Axle
If your vehicle has this feature, your locking rear axle
can give you additional traction on snow, mud, ice, sand
or gravel. It works like a standard axle most of the
time, but when one of the rear wheels has no traction
and the other does, this feature will allow the wheel with
traction to move the vehicle.
4-8
Page 213 of 406
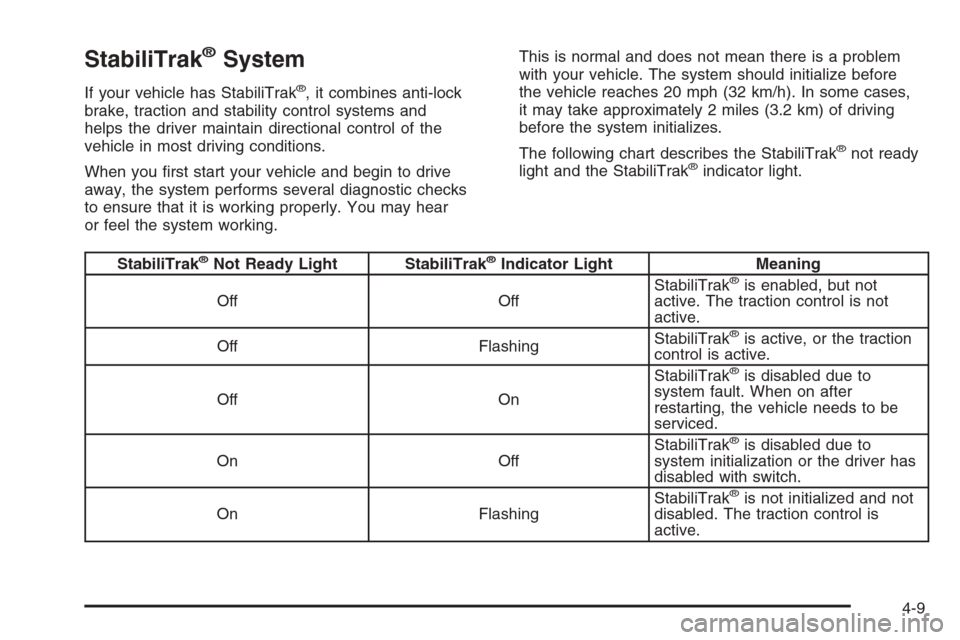
StabiliTrak®System
If your vehicle has StabiliTrak®, it combines anti-lock
brake, traction and stability control systems and
helps the driver maintain directional control of the
vehicle in most driving conditions.
When you first start your vehicle and begin to drive
away, the system performs several diagnostic checks
to ensure that it is working properly. You may hear
or feel the system working.This is normal and does not mean there is a problem
with your vehicle. The system should initialize before
the vehicle reaches 20 mph (32 km/h). In some cases,
it may take approximately 2 miles (3.2 km) of driving
before the system initializes.
The following chart describes the StabiliTrak
®not ready
light and the StabiliTrak®indicator light.
StabiliTrak®Not Ready Light StabiliTrak®Indicator Light Meaning
Off OffStabiliTrak®is enabled, but not
active. The traction control is not
active.
Off FlashingStabiliTrak
®is active, or the traction
control is active.
Off OnStabiliTrak
®is disabled due to
system fault. When on after
restarting, the vehicle needs to be
serviced.
On OffStabiliTrak
®is disabled due to
system initialization or the driver has
disabled with switch.
On FlashingStabiliTrak
®is not initialized and not
disabled. The traction control is
active.
4-9
Page 217 of 406

Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can be more effective
than braking. For example, you come over a hill and find
a truck stopped in your lane, or a car suddenly pulls
out from nowhere, or a child darts out from between
parked cars and stops right in front of you. You can
avoid these problems by braking — if you can stop in
time. But sometimes you cannot; there is not room. That
is the time for evasive action — steering around the
problem.
Your vehicle can perform very well in emergencies like
these. First apply your brakes.
SeeBraking on page 4-6. It is better to remove as much
speed as you can from a possible collision. Then steer
around the problem, to the left or right depending on the
space available.An emergency like this requires close attention and a
quick decision. If you are holding the steering wheel at
the recommended 9 and 3 o’clock positions, you can
turn it a full 180 degrees very quickly without removing
either hand. But you have to act fast, steer quickly,
and just as quickly straighten the wheel once you have
avoided the object.
The fact that such emergency situations are always
possible is a good reason to practice defensive driving
at all times and wear safety belts properly.
4-13
Page 220 of 406

Loss of Control
Let us review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems — brakes,
steering, and acceleration — do not have enough friction
where the tires meet the road to do what the driver
has asked.
In any emergency, do not give up. Keep trying to steer
and constantly seek an escape route or area of less
danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not overdriving
those conditions. But skids are always possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your vehicle’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your
wheels are not rolling. In the steering or cornering
skid, too much speed or steering in a curve causes
tires to slip and lose cornering force. And in the
acceleration skid, too much throttle causes the driving
wheels to spin.
A cornering skid is best handled by easing your foot off
the accelerator pedal.If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want
the vehicle to go. If you start steering quickly enough,
your vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready
for a second skid if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice,
gravel, or other material is on the road. For safety, you
will want to slow down and adjust your driving to these
conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance will be longer and
vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface with reduced traction, try
your best to avoid sudden steering, acceleration,
or braking, including reducing vehicle speed by shifting
to a lower gear. Any sudden changes could cause
the tires to slide. You may not realize the surface is
slippery until your vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize
warning clues — such as enough water, ice, or packed
snow on the road to make a mirrored surface — and
slow down when you have any doubt.
Remember: Any Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) helps
avoid only the braking skid.
4-16
Page 231 of 406

Accelerate gently. Try not to break the fragile traction.
If you accelerate too fast, the drive wheels will spin and
polish the surface under the tires even more.
Your Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) improves your
vehicle’s stability when you make a hard stop on
a slippery road. Even though you have ABS, you will
want to begin stopping sooner than you would on
dry pavement. SeeAnti-Lock Brake System (ABS)
on page 4-7.
•Allow greater following distance on any
slippery road.
•Watch for slippery spots. The road might be fine
until you hit a spot that is covered with ice. On
an otherwise clear road, ice patches may appear
in shaded areas where the sun cannot reach, such
as around clumps of trees, behind buildings, or
under bridges. Sometimes the surface of a curve or
an overpass may remain icy when the surrounding
roads are clear. If you see a patch of ice ahead
of you, brake before you are on it. Try not to brake
while you are actually on the ice, and avoid
sudden steering maneuvers.
If You Are Caught in a Blizzard
If you are stopped by heavy snow, you could be in a
serious situation. You should probably stay with your
vehicle unless you know for sure that you are near
help and you can hike through the snow. Here are some
things to do to summon help and keep yourself and
your passengers safe:
•Turn on your hazard flashers.
•Tie a red cloth to your vehicle to alert police that
you have been stopped by the snow.
•Put on extra clothing or wrap a blanket around you.
If you do not have blankets or extra clothing, make
body insulators from newspapers, burlap bags,
rags, floor mats — anything you can wrap around
yourself or tuck under your clothing to keep warm.
4-27
Page 232 of 406

You can run the engine to keep warm, but be careful.
{CAUTION:
Snow can trap exhaust gases under your
vehicle. This can cause deadly CO (carbon
monoxide) gas to get inside. CO could
overcome you and kill you. You cannot see it
or smell it, so you might not know it is in your
vehicle. Clear away snow from around the
base of your vehicle, especially any that is
blocking the exhaust pipe and/or the fuel
operated heater exhaust system, if equipped.
And check around again from time to time to
be sure snow does not collect there. If your
vehicle has a diesel engine and a fuel operated
heater, see “Fuel Operated Heater (FOH)” in
the diesel engine supplement.
Open a window just a little on the side of the
vehicle that is away from the wind. This will
help keep CO out.
4-28
Page 235 of 406

Tire and Loading Information Label
A vehicle specific Tire and Loading Information label
is attached to the center pillar (B-pillar). With the
driver’s door open, you will find the label attached
below the door lock post (striker). The tire and loading
information label shows the number of occupant
seating positions (A), and the maximum vehicle
capacity weight (B) in kilograms and pounds.The Tire and Loading Information label also shows
the size of the original equipment tires (C) and
the recommended cold tire inflation pressures (D).
For more information on tires and inflation seeTires on
page 5-53andIn�ation - Tire Pressure on page 5-59.
There is also important loading information on the
vehicle Certification/Tire label. It tells you the Gross
Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) and the Gross Axle
Weight Rating (GAWR) for the front and rear axle.
See “Certification/Tire Label” later in this section.
Steps for Determining Correct Load Limit
1. Locate the statement “The combined weight
of occupants and cargo should never exceed
XXX kg or XXX lbs” on your vehicle’s placard.
2. Determine the combined weight of the driver and
passengers that will be riding in your vehicle.
3. Subtract the combined weight of the driver and
passengers from XXX kg or XXX lbs. Label Example
4-31
Page 241 of 406

4. Follow the dolly manufacturer’s instructions to
attach and secure the vehicle being towed to
the dolly and then the loaded dolly to the tow
vehicle. Make sure the wheels are straight
before towing.
Use an adequate clamping device to ensure that
the front wheels are locked into the straight position.
5. Release the parking brake only after the vehicle
being towed is firmly attached to the tow vehicle.
6. Turn the ignition to LOCK.
If the tow vehicle will not be started or driven for
six weeks or more, remove the battery cable
from the negative terminal (post) of the battery to
prevent your battery from draining while towing.
All-Wheel-Drive Vehicles
Your vehicle was not designed to be towed with
two wheels on the ground. To properly tow these
vehicles, they should be placed on a platform trailer
with all four wheels off the ground.
Notice:Towing an all-wheel-drive vehicle with all
four wheels on the ground, or even with only two of
its wheels on the ground, will damage drivetrain
components. Do not tow an all-wheel-drive vehicle if
any of its wheels will be on the ground.
Towing a Trailer
{CAUTION:
If you do not use the correct equipment and
drive properly, you can lose control when you
pull a trailer. For example, if the trailer is too
heavy, the brakes may not work well — or even
at all. You and your passengers could be
seriously injured. Pull a trailer only if you have
followed all the steps in this section. Ask your
dealer for advice and information about towing
a trailer with your vehicle.
Notice:Pulling a trailer improperly can damage
your vehicle and result in costly repairs that would
not be covered by your warranty. Always follow
the instructions in this section and check with your
dealer for more information about towing a trailer
with your vehicle.
To identify the trailering capacity of your vehicle, you
should read the information in “Weight of the Trailer” that
appears later in this section.
4-37
Page 258 of 406

Tires..............................................................5-53
Tire Sidewall Labeling...................................5-54
Tire Terminology and Definitions.....................5-57
Inflation - Tire Pressure.................................5-59
Dual Tire Operation.......................................5-61
Tire Inspection and Rotation...........................5-61
When It Is Time for New Tires.......................5-63
Buying New Tires.........................................5-64
Different Size Tires and Wheels......................5-65
Uniform Tire Quality Grading..........................5-66
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance..................5-67
Wheel Replacement......................................5-67
Tire Chains..................................................5-69
If a Tire Goes Flat........................................5-70
Changing a Flat Tire.....................................5-71
Removing the Spare Tire and Tools................5-72
Removing the Flat Tire and Installing
the Spare Tire..........................................5-75
Secondary Latch System...............................5-80
Storing a Flat or Spare Tire and Tools............5-82
Spare Tire...................................................5-84
Appearance Care............................................5-84
Cleaning the Inside of Your Vehicle.................5-84
Fabric/Carpet...............................................5-86
Instrument Panel, Vinyl, and
Other Plastic Surfaces................................5-87Care of Safety Belts......................................5-87
Weatherstrips...............................................5-87
Washing Your Vehicle...................................5-88
Cleaning Exterior Lamps/Lenses.....................5-88
Finish Care..................................................5-88
Windshield and Wiper Blades.........................5-89
Aluminum Wheels.........................................5-90
Tires...........................................................5-90
Sheet Metal Damage.....................................5-91
Finish Damage.............................................5-91
Underbody Maintenance................................5-91
Chemical Paint Spotting.................................5-91
Vehicle Care/Appearance Materials..................5-92
Vehicle Identi�cation......................................5-93
Vehicle Identification Number (VIN).................5-93
Service Parts Identification Label.....................5-93
Electrical System............................................5-94
Add-On Electrical Equipment..........................5-94
Headlamp Wiring..........................................5-94
Windshield Wiper Fuses................................5-94
Fuses and Circuit Breakers............................5-94
Floor Console Fuse Block..............................5-95
Engine Compartment Fuse Block....................5-96
Capacities and Speci�cations..........................5-99
Section 5 Service and Appearance Care
5-2