CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM 1993 Service Manual
Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM, Model: CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1911 of 2438

(4) Remove throttle cable (Fig. 6). Remove wiring
harness from throttle cable bracket and intake man-
ifold water tube.
(5) Disconnect idle air control motor and throttle
position sensor (TPS) electrical connectors (Fig. 7).
Refer to Idle Air Control Motor and Throttle Position
Sensor in this section. (6) Remove vacuum hose harness from throttle
body (Fig. 7). (7) Remove PCV and brake booster vacuum hoses
from air intake plenum. (8) Remove EGR tube to intake manifold flange
bolts (Fig. 8). (9) Remove vacuum harness connectors from in-
take plenum (Fig. 8). (10) Remove cylinder head to intake plenum strut
(Fig. 8). (11) Disconnect electrical connectors from the MAP
sensor and heated oxygen sensor electrical connec-
tion. Remove the engine mounted ground strap (Fig.
9).
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND
HOSES TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
Fig. 5 Servicing Idle Air Control Motor
Fig. 6 Throttle Cable Attachment
Fig. 7 Electrical and Vacuum Connection to Throttle Body
Fig. 8 EGR Tube
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 171
Page 1912 of 2438

(12) Remove the fuel hose quick connect fittings
from the chassis tubes. Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps
and Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel Delivery
Section of this Group. Place a shop towel under the
connections to absorb any fuel spilled. fittings. (13) Remove direct ignition system (DIS) coils and
generator bracket to intake manifold bolt (Fig. 10).
(14) Remove intake mounting manifold bolts and
rotate manifold back over rear valve cover (Fig. 11). (15) Cover intake manifold with suitable cover when
servicing (Fig. 12). (16) Remove vacuum harness connector from Fuel
Pressure Regulator. (17) Remove fuel tube retainer bracket screw and
fuel rail attaching bolts (Fig. 12). Spread the retainer
bracket to allow fuel tube removal clearance.
(18) Remove fuel rail injector wiring clip from the
generator bracket (Fig. 13). (19) Disconnect camshaft position sensor, coolant
temperature sensor, and engine temperature sensors
(Fig. 13). (20) Remove fuel rail. Be careful not to damage
the injector O-rings upon removal from their ports
(Fig. 14).
INSTALLATION
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged. (2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation. (3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports (Fig. 14). (4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N Im (200 in. lbs.) torque (Fig. 12).
Fig. 11 Intake Manifold Bolts
Fig. 12 Fuel Rail Attaching Bolts
Fig. 9 MAP Sensor Electrical Connector
Fig. 10 Ignition Coils
14 - 172 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1913 of 2438

(5) Install fuel tube retaining bracket screw.
Tighten screw to 4 N Im (35 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect electrical connectors to camshaft posi-
tion sensor, coolant temperature sensor and engine
temperature sensors (Fig. 13). (7) Install fuel injector harness wiring clips on the
generator bracket and intake manifold water tube
(Fig. 13). (8) Connect vacuum line to fuel pressure regulator.
(9) Remove covering on lower intake manifold and
clean surface. (10) Place intake manifold gasket on lower mani-
fold. Put upper manifold into place and install bolts
finger tight. (11) Install the generator bracket to intake mani-
fold bolt and the cylinder head to intake manifold
strut bolts. (Do not tighten.) (12) Following the tightening sequence in Figure
11, tighten intake manifold bolts to 28 N Im (250 in.
lbs.) torque. (13) Tighten generator bracket to intake manifold
bolt to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 13).
(14) Tighten the cylinder head to intake manifold
strut bolts to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 8).
(15) Connect ground strap, MAP and heated oxy-
gen sensor electrical connectors. (16) Connect vacuum harness to intake plenum.
Connect PCV system hoses. (17) Using a new gasket, connect the EGR tube to
the intake manifold plenum. Tighten screws to 22
N Im (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(18) Clip wiring harness into the hole in the throt-
tle cable bracket. (19) Connect electrical connectors to the throttle
position sensor (TPS) and idle air control motor. (20) Connect vacuum harness to throttle body.
(21) Install the direct ignition system (DIS) coils.
Tighten fasteners to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(22) Install fuel hose quick connectors fittings to
chassis tubes. Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel Delivery Sec-
tion of this Group. Push the fittings onto the chas-
sis tubes until they click into place. Pull on the
fittings to ensure complete insertion. Fuel supply fit-
ting is 5/16 inch and fuel return fitting is 1/4 inch. (23) Install throttle cable.
(24) Install air cleaner and hose assembly.
(25) Connect negative cable to battery.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position.
(26) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pres-
surize the fuel system. Check for leaks.FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before attempting any repairs. Refer to Fuel Pressure
Regulator Procedure in this section. (2) Remove fuel pressure regulator vacuum connec-
tor. (Fig. 15). (3) Remove regulator retainer screw (Fig. 15).
(4) Remove the fuel pressure regulator retainer
(Fig. 15).
Fig. 13 Fuel Injector Wiring Clip
Fig. 14 Fuel Rail Removal
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 173
Page 1914 of 2438
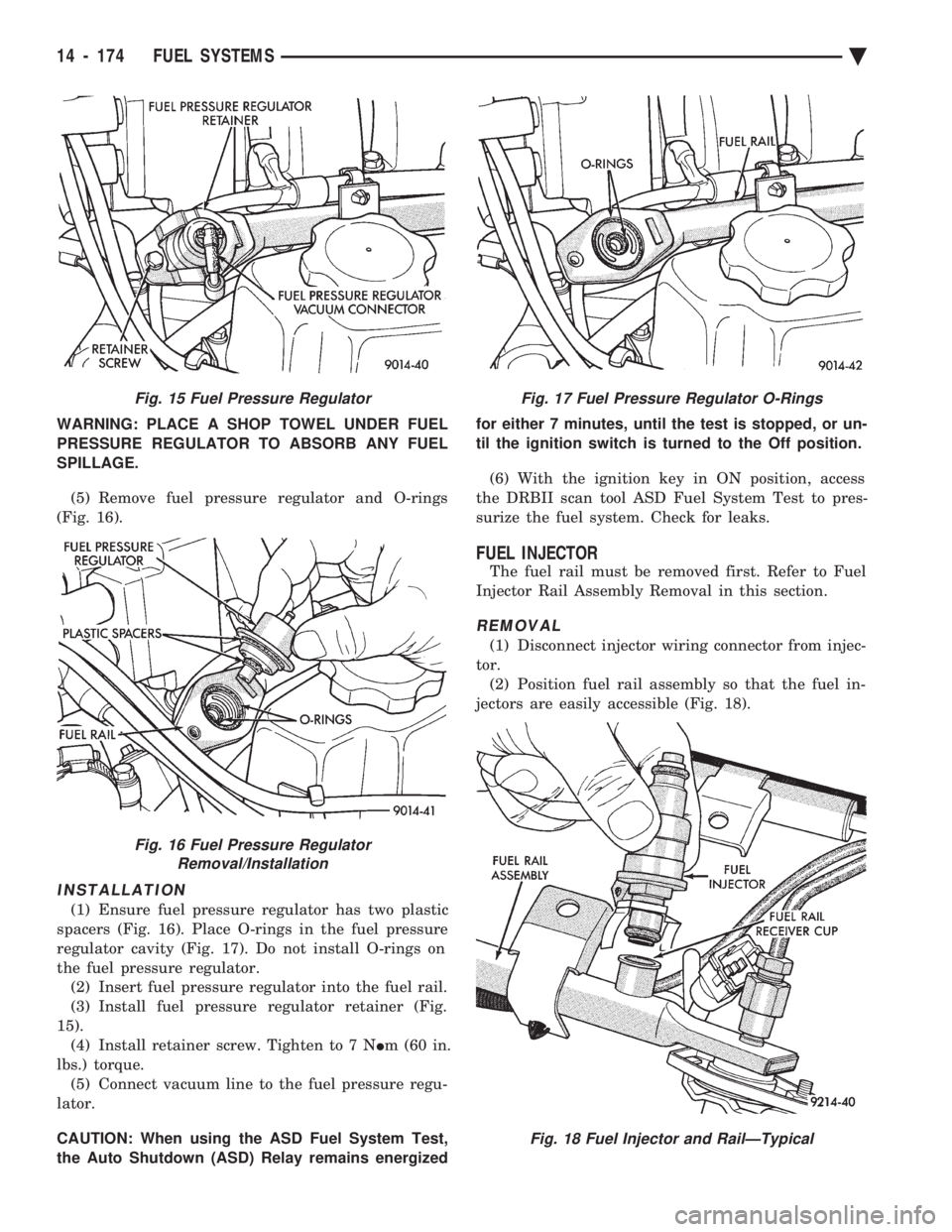
WARNING: PLACE A SHOP TOWEL UNDER FUEL
PRESSURE REGULATOR TO ABSORB ANY FUEL
SPILLAGE.
(5) Remove fuel pressure regulator and O-rings
(Fig. 16).
INSTALLATION
(1) Ensure fuel pressure regulator has two plastic
spacers (Fig. 16). Place O-rings in the fuel pressure
regulator cavity (Fig. 17). Do not install O-rings on
the fuel pressure regulator. (2) Insert fuel pressure regulator into the fuel rail.
(3) Install fuel pressure regulator retainer (Fig.
15). (4) Install retainer screw. Tighten to 7 N Im (60 in.
lbs.) torque. (5) Connect vacuum line to the fuel pressure regu-
lator.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position.
(6) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pres-
surize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL INJECTOR
The fuel rail must be removed first. Refer to Fuel
Injector Rail Assembly Removal in this section.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect injector wiring connector from injec-
tor. (2) Position fuel rail assembly so that the fuel in-
jectors are easily accessible (Fig. 18).
Fig. 15 Fuel Pressure Regulator
Fig. 16 Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal/Installation
Fig. 17 Fuel Pressure Regulator O-Rings
Fig. 18 Fuel Injector and RailÐTypical
14 - 174 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1915 of 2438
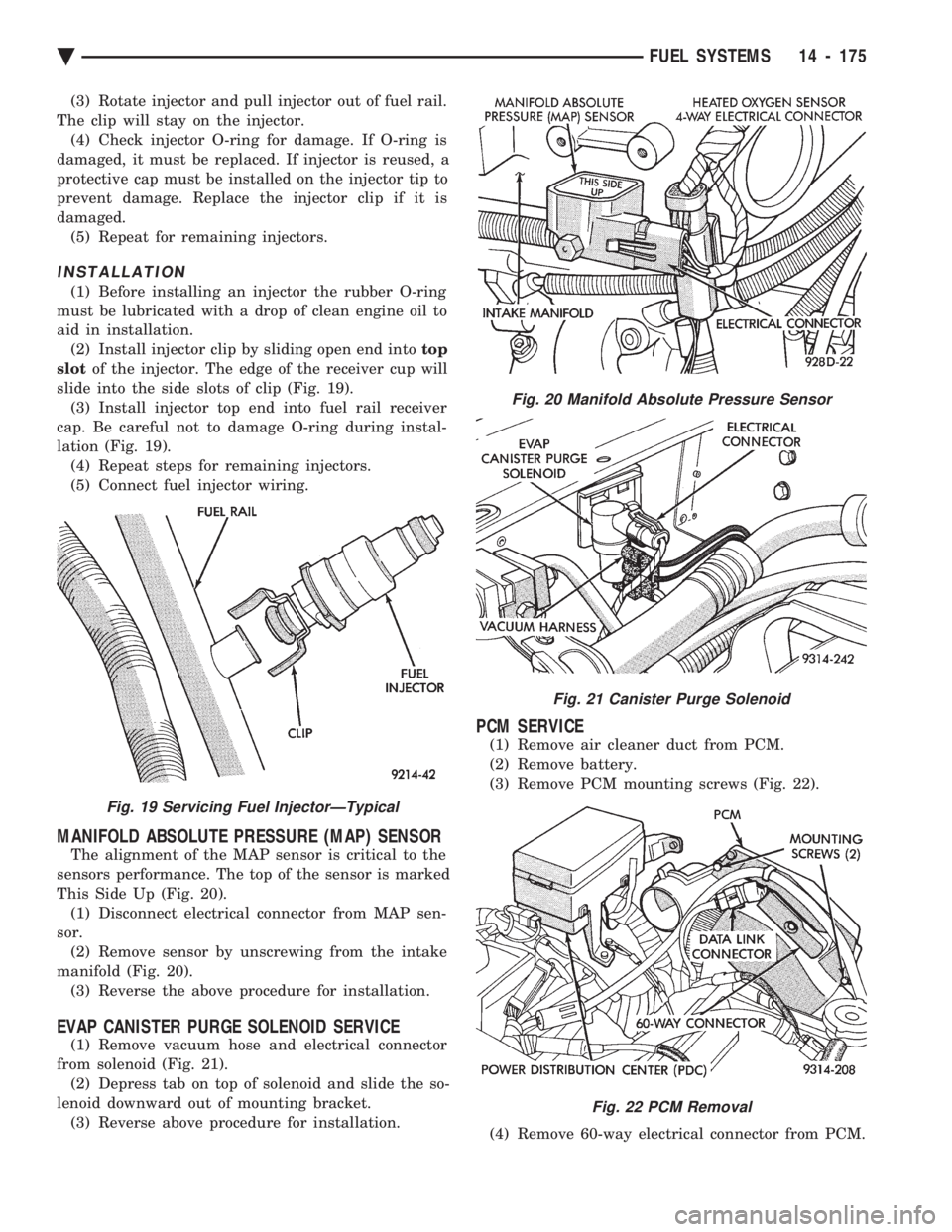
(3) Rotate injector and pull injector out of fuel rail.
The clip will stay on the injector. (4) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is reused, a
protective cap must be installed on the injector tip to
prevent damage. Replace the injector clip if it is
damaged. (5) Repeat for remaining injectors.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing an injector the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation. (2) Install injector clip by sliding open end into top
slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup will
slide into the side slots of clip (Fig. 19). (3) Install injector top end into fuel rail receiver
cap. Be careful not to damage O-ring during instal-
lation (Fig. 19). (4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Connect fuel injector wiring.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
The alignment of the MAP sensor is critical to the
sensors performance. The top of the sensor is marked
This Side Up (Fig. 20). (1) Disconnect electrical connector from MAP sen-
sor. (2) Remove sensor by unscrewing from the intake
manifold (Fig. 20). (3) Reverse the above procedure for installation.
EVAP CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID SERVICE
(1) Remove vacuum hose and electrical connector
from solenoid (Fig. 21). (2) Depress tab on top of solenoid and slide the so-
lenoid downward out of mounting bracket. (3) Reverse above procedure for installation.
PCM SERVICE
(1) Remove air cleaner duct from PCM.
(2) Remove battery.
(3) Remove PCM mounting screws (Fig. 22).
(4) Remove 60-way electrical connector from PCM.
Fig. 19 Servicing Fuel InjectorÐTypical
Fig. 20 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Fig. 21 Canister Purge Solenoid
Fig. 22 PCM Removal
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 175
Page 1916 of 2438

(5) Reverse the above procedure for installation.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor electrical
connector from the wiring harness connector (Fig. 23).
(2) Remove crankshaft position sensor retaining
bolt. (3) Pull sensor straight up out of the transaxle
housing.
INSTALLATION
If installing the original sensor, clean off the
old spacer on the sensor face. A NEW SPACER
must be attached to the sensor face before instal-
lation. If the sensor is being replaced, confirm
that the paper spacer is attached to the face of
the new sensor (Fig. 24).
(1) Install sensor in transaxle and push sensor down
until contact is made with the drive plate. While
holding the sensor in this position, and install and
tighten the retaining bolt to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.)
torque. (2) Connect crankshaft position sensor electrical
connector to the wiring harness connector.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR SERVICE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect camshaft position sensor electrical
connector from the wiring harness connector (Fig. 25).
(2) Loosen camshaft position sensor retaining bolt
enough to allow slot in sensor to slide past the bolt. (3) Pull sensor up out of the chain case cover. Do not
pull on the sensor lead. There is an O-ring on the
sensor case. The O-ring may make removal difficult. A
light tap to top of sensor prior to removal may reduce
force needed for removal.
INSTALLATION
If installing the original sensor, clean off the
old spacer on the sensor face. A NEW SPACER
must be attached to the face before installation.
Inspect O-ring for damage, replace if necessary.
If the sensor is being replaced, confirm that the
paper spacer is attached to the face and O-ring is
positioned in groove of the new sensor (Fig. 26).
(1) Apply a couple drops of clean engine oil to the
O-ring prior to installation. Install sensor in the chain
case cover and push sensor down until contact
Fig. 23 Crankshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 24 Crankshaft Position Sensor and Spacer
Fig. 25 Camshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 26 Camshaft Position Sensor
14 - 176 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1917 of 2438

is made with the camshaft gear. While holding the
sensor in this position, install and tighten the retain-
ing bolt 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect camshaft position sensor electrical con-
nector to harness connector. Position connector away
from the accessory belt.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (O2SENSOR) SERVICE
The oxygen sensor is installed in the exhaust mani-
fold (Fig. 27).
CAUTION: Do not pull on the oxygen sensor wire
when disconnecting the electrical connector.
WARNING: THE EXHAUST MANIFOLD MAY BE EX-
TREMELY HOT. USE CARE WHEN SERVICING THE
OXYGEN SENSOR.
(1) Disconnect oxygen sensor electrical connector
(Fig. 28). (2) Remove sensor using Tool C-4907 (Fig. 29).
Slightly tightening the sensor can ease removal. When the sensor is removed, the exhaust manifold
threads must be cleaned with an 18 mm X 1.5 + 6E tap.
If using original sensor, coat the threads with Loctite
771-64 anti-seize compound or equivalent. New sen-
sors are packaged with compound on the threads and
do not require additional compound. The sensor must
be tightened to 27 N Im (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 27 Oxygen SensorÐ3.3L Engine
Fig. 28 Oxygen Sensor Connector
Fig. 29 Oxygen Sensor Socket
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 177
Page 1918 of 2438

SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
14 - 178 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1919 of 2438

STEERING
CONTENTS
page page
ACUSTAR STANDARD AND TILT STEERING COLUMN ............................ 28
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SHIFTER/IGNITION INTERLOCK .......................... 36
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1 POWER STEERING GEAR
................ 25
POWER STEERING PUMPS ................ 1
SPECIFICATIONS AND TIGHTENING REFERENCE .......................... 42
GENERAL INFORMATION
Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on any steering gear or pump. Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual. The power steering system consists of these four
major components. Power Steering Pump, Power
Steering Gear, Pressure Hose, and Return Line.
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into lin-
ear travel through the meshing of the helical pinion teeth with the rack teeth. Power assist steering is
provided by an open center, rotary type control valve.
It is used to direct oil from the power steering pump
to either side of the integral steering rack piston. Road feel is controlled by the diameter of a torsion
bar which initially steers the vehicle. As steering ef-
fort increases as in a turn, the torsion bar twists,
causing relative rotary motion between the rotary
valve body and valve spool. This movement directs
oil behind the integral rack piston, which in turn,
builds up hydraulic pressure and assists in the turn-
ing effort.
POWER STEERING PUMPS
INDEX
page page
Checking Power Steering Fluid Level .......... 9
Flow Control Valve Fitting O-Ring Seal ........ 23
General Information ........................ 1
Power Steering Hoses ..................... 11
Power Steering Pressure Switch ............. 10
Power Steering Pump Fluid Reservoirs ........ 22 Power Steering Pump Pressure Test
........... 9
Power Steering Pump Pulley Service .......... 20
Power Steering Pump Removal .............. 12
Power Steering Pump Service ................ 2
Power Steering PumpÐInitial Operation ....... 24
Steering Components Service Diagnosis ........ 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
Hydraulic pressure for operation of the power
steering gear is provided by a belt driven power
steering pump. The power steering pump is a con-
stant flow rate and displacement, vane type pump.
Different styles of Saginaw power steering pumps are
used depending on the engine application of the ve-
hicle. On all four cylinder and 3.0-liter V-6 applications
the Saginaw Ham Can power steering pump is used
(Fig. 1). On the 3.3 & 3.8-liter V-6 and Turbo III applica-
tions, different versions of the Saginaw T/C style
power steering pump is used (Fig. 2). The 3.3 & 3.8 liter V-6 engine application uses the T/C style power
steering pump with a remote mounted reservoir for
the power steering fluid. On the Turbo III application
of the T/C style power steering pump, the power
steering fluid reservoir is integral to the power steer-
ing pump. On the integral reservoir type pump (Fig. 1) the
pump housing and internal components are combined
with the reservoir to form a one-piece mechanism. The Saginaw T/C style power steering pump (Fig.
2), consists of the power steering pump internal com-
ponents and pump housing. The Saginaw T/C style
power steering pump though has no internal reser-
voir for the power steering fluid. Depending on vehi-
Ä STEERING 19 - 1
Page 1920 of 2438

cle and or engine application the Saginaw T/C style
power steering pump is used on, it will be equipped
with a plastic integral or remote mounted power
steering fluid reservoir. Drive tangs on the power steering gear pinion, mate
loosely with the stub shaft of the steering gear. This
will allow manual steering control to be maintained, if
the drive belt on the power steering pump should
break. However, under these conditions, steering effort
will significantly increase.
STEERING COMPONENTS SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
POWER STEERING PUMP SERVICE
The service procedures for the Saginaw power steer-
ing pump are limited to the areas and components
listed below. No repair procedures are to be done
on internal components of the Saginaw power
steering pumps.
² Repair of power steering fluid leaks from areas of
the power steering pump sealed by O-rings is allowed
(See Pump Leak Diagnosis). However power steering
pump shaft seal leakage will require replacement of
the pump.
² Power steering fluid reservoirs, related components
and attaching hardware.
² Power steering fluid reservoir filler cap/dipstick as-
semblies. Because of unique shaft bearings, flow control levels
or pump displacements, power steering pumps may be
used only on specific vehicle applications. Be sure that
all power steering pumps are only replaced with a
pump that is the correct replacement for that specific
application. Hydraulic pressure is provided for operation of the
power steering gear by the belt driven power steering
pumps (Fig . 1 & 2). It is a constant displacement, vane
type pump. The power steering pump is connected to
the steering gear by a power steering fluid pressure
hose and return hose.
Rectangular pumping vanes in the shaft driven rotor,
move power steering fluid from the intake to the cam ring
pressure cavities of the power steering pump. As the rotor
begins to turn, centrifugal force throws the vanes against
the inside surface of the cam ring to pickup residual oil.
This oil is then forced into the high pressure area. As more
oil is picked up by the vanes. That additional oil is forced
into the cavities of the thrust plate through two crossover
holes in the cam ring and pressure plate. The crossover
holes empty into the high pressure area between the
pressure plate and the housing end cover.
As the high pressure area is filled, oil flows under
the vanes in the rotor slots, forcing the vanes to follow
the inside surface of the cam ring. As the vanes
reach the restricted area of the cam ring, oil is
forced out from between the vanes. When excess oil
flow is generated during high-speed operation, a regu-
lated amount of oil returns to the pump intake side
through a flow control valve. The flow control valve
reduces the power required to drive the pump
and holds down temperature build-up.
Fig. 1 Saginaw Ham Can Power Steering Pump
Fig. 2 Saginaw T/C Style Power Steering Pump
19 - 2 STEERING Ä