transaxle CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM 1993 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM, Model: CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 89 of 2438
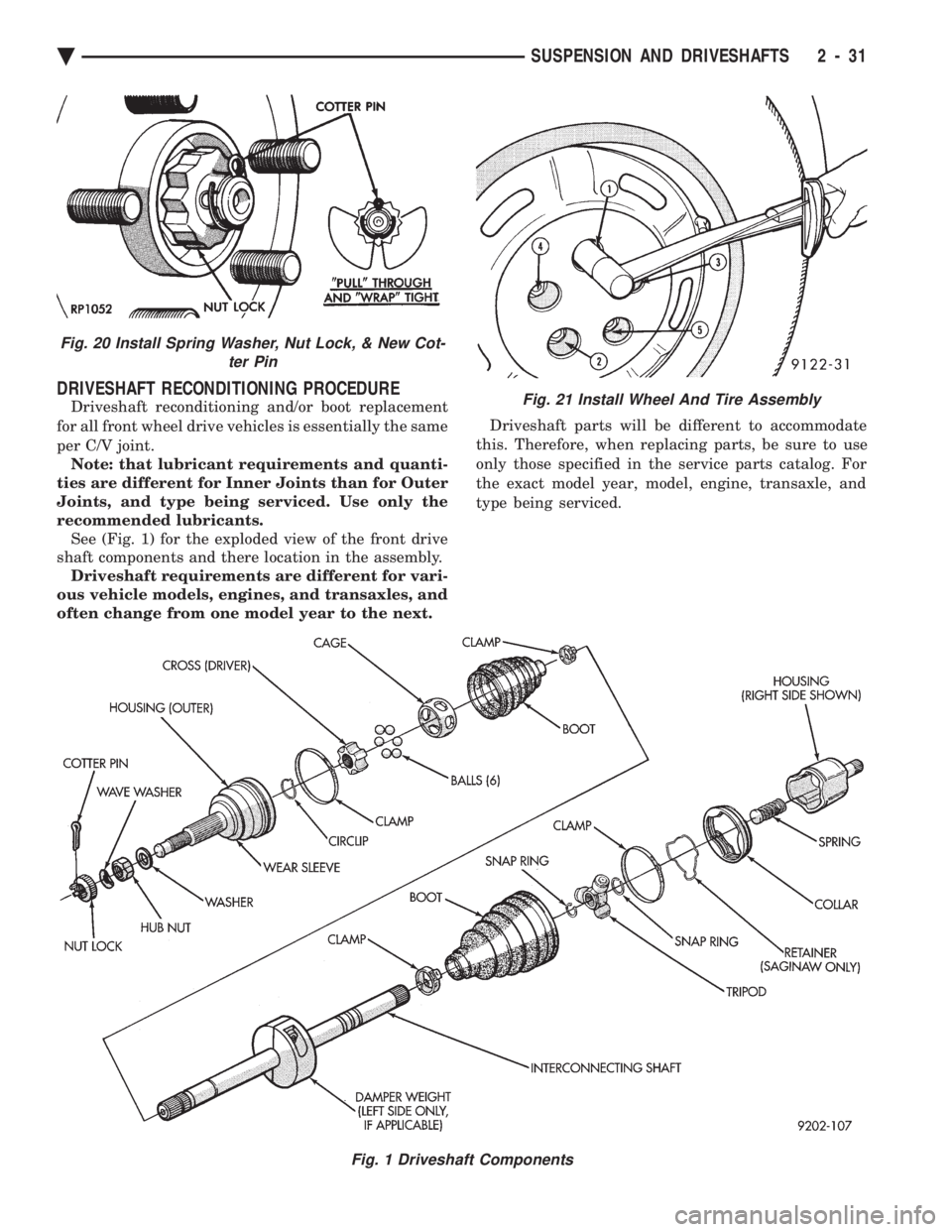
DRIVESHAFT RECONDITIONING PROCEDURE
Driveshaft reconditioning and/or boot replacement
for all front wheel drive vehicles is essentially the same
per C/V joint. Note: that lubricant requirements and quanti-
ties are different for Inner Joints than for Outer
Joints, and type being serviced. Use only the
recommended lubricants. See (Fig. 1) for the exploded view of the front drive
shaft components and there location in the assembly. Driveshaft requirements are different for vari-
ous vehicle models, engines, and transaxles, and
often change from one model year to the next. Driveshaft parts will be different to accommodate
this. Therefore, when replacing parts, be sure to use
only those specified in the service parts catalog. For
the exact model year, model, engine, transaxle, and
type being serviced.
Fig. 1 Driveshaft Components
Fig. 21 Install Wheel And Tire Assembly
Fig. 20 Install Spring Washer, Nut Lock, & New Cot- ter Pin
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 31
Page 99 of 2438
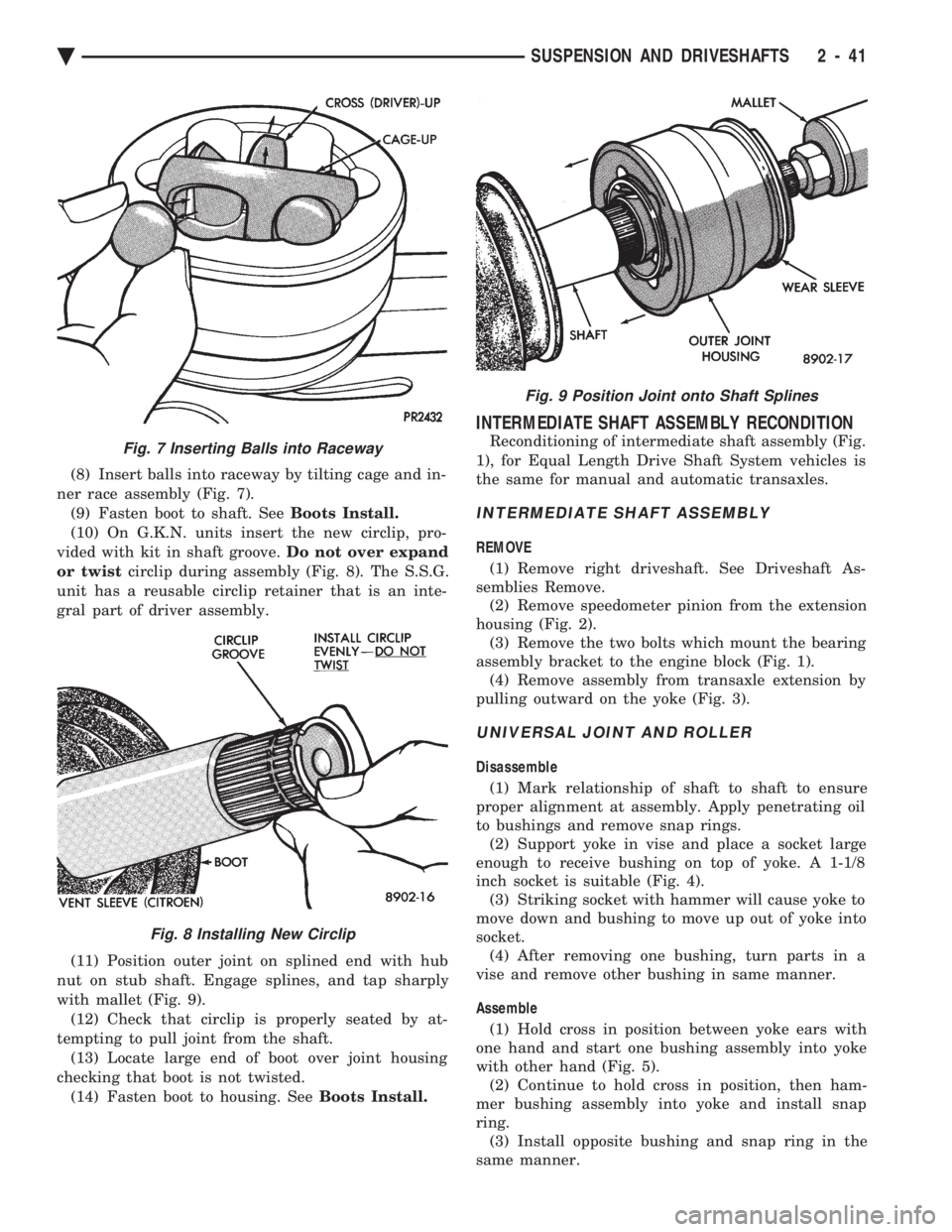
(8) Insert balls into raceway by tilting cage and in-
ner race assembly (Fig. 7). (9) Fasten boot to shaft. See Boots Install.
(10) On G.K.N. units insert the new circlip, pro-
vided with kit in shaft groove. Do not over expand
or twist circlip during assembly (Fig. 8). The S.S.G.
unit has a reusable circlip retainer that is an inte-
gral part of driver assembly.
(11) Position outer joint on splined end with hub
nut on stub shaft. Engage splines, and tap sharply
with mallet (Fig. 9). (12) Check that circlip is properly seated by at-
tempting to pull joint from the shaft. (13) Locate large end of boot over joint housing
checking that boot is not twisted. (14) Fasten boot to housing. See Boots Install.
INTERMEDIATE SHAFT ASSEMBLY RECONDITION
Reconditioning of intermediate shaft assembly (Fig.
1), for Equal Length Drive Shaft System vehicles is
the same for manual and automatic transaxles.
INTERMEDIATE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
REMOVE
(1) Remove right driveshaft. See Driveshaft As-
semblies Remove. (2) Remove speedometer pinion from the extension
housing (Fig. 2). (3) Remove the two bolts which mount the bearing
assembly bracket to the engine block (Fig. 1). (4) Remove assembly from transaxle extension by
pulling outward on the yoke (Fig. 3).
UNIVERSAL JOINT AND ROLLER
Disassemble
(1) Mark relationship of shaft to shaft to ensure
proper alignment at assembly. Apply penetrating oil
to bushings and remove snap rings. (2) Support yoke in vise and place a socket large
enough to receive bushing on top of yoke. A 1-1/8
inch socket is suitable (Fig. 4). (3) Striking socket with hammer will cause yoke to
move down and bushing to move up out of yoke into
socket. (4) After removing one bushing, turn parts in a
vise and remove other bushing in same manner.
Assemble (1) Hold cross in position between yoke ears with
one hand and start one bushing assembly into yoke
with other hand (Fig. 5). (2) Continue to hold cross in position, then ham-
mer bushing assembly into yoke and install snap
ring. (3) Install opposite bushing and snap ring in the
same manner.
Fig. 7 Inserting Balls into Raceway
Fig. 8 Installing New Circlip
Fig. 9 Position Joint onto Shaft Splines
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 41
Page 101 of 2438
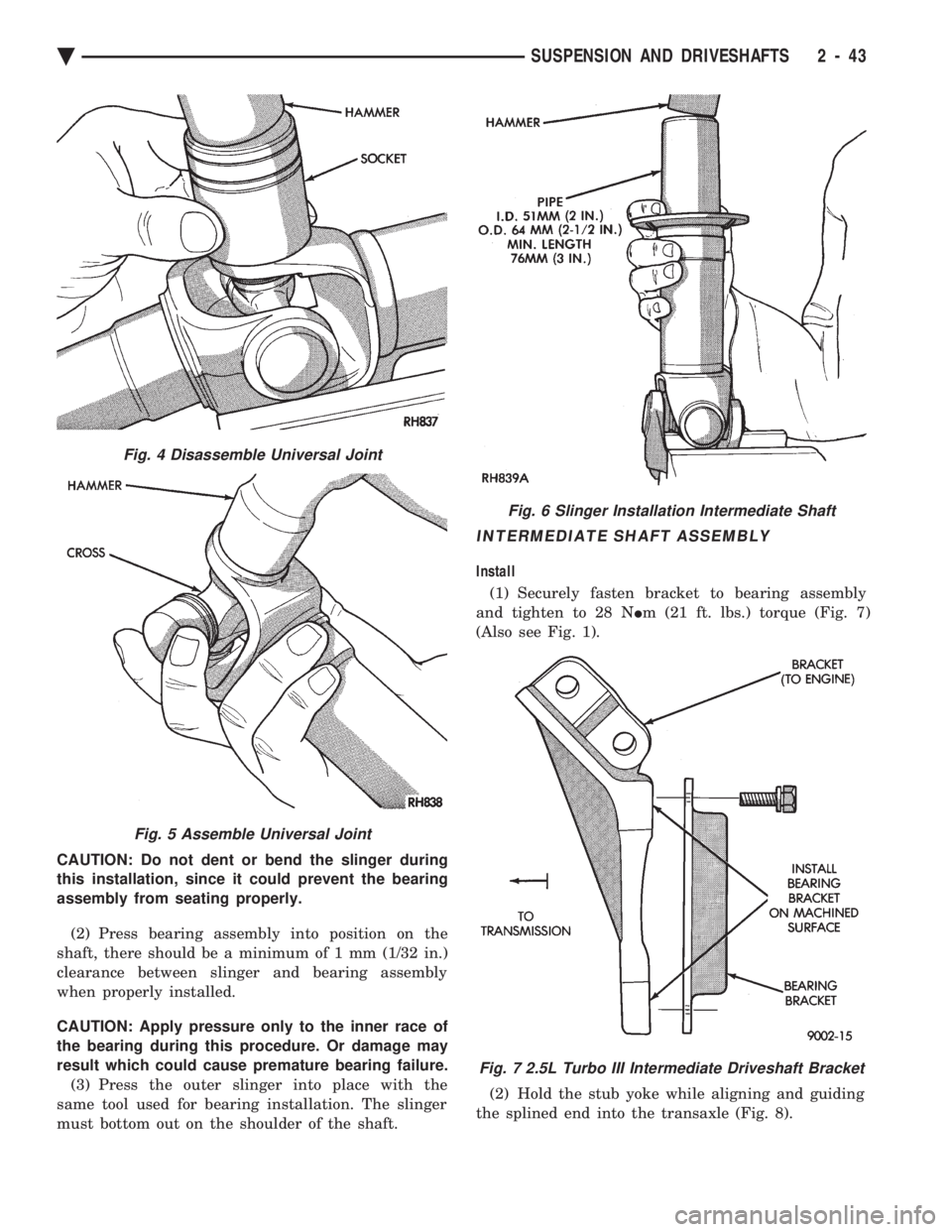
CAUTION: Do not dent or bend the slinger during
this installation, since it could prevent the bearing
assembly from seating properly. (2) Press bearing assembly into position on the
shaft, there should be a minimum of 1 mm (1/32 in.)
clearance between slinger and bearing assembly
when properly installed.
CAUTION: Apply pressure only to the inner race of
the bearing during this procedure. Or damage may
result which could cause premature bearing failure. (3) Press the outer slinger into place with the
same tool used for bearing installation. The slinger
must bottom out on the shoulder of the shaft.
INTERMEDIATE SHAFT ASSEMBLY
Install
(1) Securely fasten bracket to bearing assembly
and tighten to 28 N Im (21 ft. lbs.) torque (Fig. 7)
(Also see Fig. 1).
(2) Hold the stub yoke while aligning and guiding
the splined end into the transaxle (Fig. 8).
Fig. 4 Disassemble Universal Joint
Fig. 5 Assemble Universal Joint
Fig. 6 Slinger Installation Intermediate Shaft
Fig. 7 2.5L Turbo III Intermediate Driveshaft Bracket
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 43
Page 102 of 2438

(3) Swing the bracket into position on the engine and
loosely install the screws through the slotted holes. (4) Push the intermediate shaft assembly into the
transaxle as far as it can travel. Hold the assembly in
this position and tighten the screws (bracket to engine
block) to 54 N Im (40 ft. lbs.) torque. This will ensure
full seal engagement between the journal on the
intermediate shaft and the seal in the transaxle
extension. (5) Distribute a liberal amount of grease in side
spline and pilot bore on bearing end of intermediate
shaft. Use MOPAR Multi-Purpose Lubricant, or
equivalent. (6) Install speedometer pinion (Fig. 9).
(7) Install right driveshaft. See Driveshaft Assem-
blies Install.
C/V JOINT BOOTS Handling and Cleaning
It is vitally important during anyservice procedures
requiring boot handling. That care be taken not to
puncture or tear the boot by over tightening clamps,
misuse of tool(s) or pinching the boot. Pinching can
occur by rotating the C/V joints (especially the tripod)
beyond normal working angles.
The driveshaft boots are not compatible with oil, gaso-
line, or cleaning solvents. Care must be taken that boots
never come in contact with any of these liquids. The only
acceptable cleaning agent for driveshaft boots is
soap and water. After washing, boot must be thor-
oughly rinsed and dried before reusing.
BOOTS INSPECT
Noticeable amounts of grease on areas adjacent to or
on the exterior of the C/V joint boot. Is the first
indication that a boot is punctured, torn or that a
clamp has loosened. When a C/V joint is removed for
servicing of the joint. The boot should be properly
cleaned and inspected for cracks, tears and scuffed
areas on interior surfaces. If any of these conditions
exist, boot replacement is recommended.
BOOTS INSTALL
THE HARD PLASTIC BOOTS REQUIRE APPROXI-
MATELY 100TIMES THE CLAMPING FORCE OF THE
RUBBER BOOT. THE CLAMPS USED ON THE RUB-
BER BOOTS DO NOT HAVE THE TYPE OF LOAD
CAPACITY REQUIRED. TO SEAL THE HARD PLASTIC
BOOTS AND SHOULD NOT BE USED FOR THIS PUR-
POSE.
Rubber boots appear only on the inner joints of
certain driveshafts.
Fig. 9 Install Speedometer PinionFig. 1 C/V Joint Boot Positioning G.K.N.
Fig. 8 Installing Intermediate Shaft Assembly
2 - 44 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä
Page 107 of 2438

mount have been loosened for any reason, or if vehicle
has experienced front structural damage, driveshaft
lengths must be checked and corrected, if required. A
shorter than required driveshaft length can result in ob-
jectionable noise. A longer than required driveshaft
length may result in potential damage.
Use of the following procedure will ensure satisfac-
tory driveshaft engagement under all normal vehicle
operating conditions. (1) The vehicle must be completely assembled.
Front wheels must be properly aligned and in the
straight ahead position. The vehicle must be in a po-
sition so that the full weight of the body is distrib-
uted to all four tires. A platform hoist, or front end
alignment rack, is recommended.
(2) Using a tape measure or other suitable measuring
device. Measure the direct distance from the inner edge of the outboard boot to the inner edge of the inboard
boot on both driveshafts. This measurement must be
taken at the bottom (six o'clock position) of the drive-
shafts (Fig. 1).
Note that the required dimension varies with car-line,
engine, transaxle, and driveshaft manufacturer (Fig. 2).
(3) If the lengths of both shafts are within the
range specified, no further action is required. If either left or right driveshaft length is not
within the specified range. Refer to Group 09, Engine
Removal and Installation to properly position engine
according to specified driveshaft lengths.
(4) If proper driveshaft lengths cannot be achieved
within the travel limits available in the slotted engine
mounts. Check for any condition that could effect the
side to side position of the measurement locations (e.g.,
engine support brackets, siderail alignment, etc.).
(5) After ensuring proper driveshaft lengths the
transmission shift linkage must be adjusted to en-
sure proper operation. Refer to Transaxle, Group 21.
Fig. 2 Driveshaft Identification and Dimensions
Fig. 19 Left Driveshaft with Damper Weight
Fig. 1 Driveshaft Positioning
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 49
Page 333 of 2438

MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH
CONTENTS
page page
CLEANING PRECAUTIONS ................. 6
CLUTCH CABLE MECHANISM .............. 1
CLUTCH CABLE REPLACEMENT ............ 2
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS ........... 1
CLUTCH DISC REPLACEMENT ............. 5
CLUTCH PEDAL NOISE/POP ............... 2 CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
......... 4
EXCESSIVE CLUTCH SPIN TIME/CLASH INTO REVERSE COMPLAINTS ............ 1
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1
RELEASE BEARING AND FORK ............. 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual. The clutch used in all models are a single, dry disc
type with no adjustment for wear being provided in
the clutch itself. The clutch pedal is connected to the release shaft
through a cable and lever. The upper end of the clutch pedal pivots in the
pedal bracket on two nylon bushings. These bushings
do not require periodic lubrication.
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS
For all clutch chatter complaints, do the following:
(1) Check for loose, misaligned, or broken engine
and transmission mounts. If present, they should be
corrected at this time. Test vehicle for chatter. If
chatter is gone, there is no need to go any further. If
chatter persists: (2) Check to see if clutch cable routing is correct
and operates smoothly. (3) Check for loose connections in drive train. Cor-
rect any problems and determine if clutch chatter
complaints has been satisfied. If not, (4) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle, for procedure. (5) Check to see if the release bearing is sticky or
binding. Replace bearing, if needed. (6) Check linkage for excessive wear on bushings.
Replace all worn parts. A small amount of bearing
grease between the release shaft bushings and the
shaft is beneficial, but not required. (7) Check flywheel and clutch pressure plate for
contamination (dirt, oil) or scored. Replace flywheel
and/or pressure plate, if required. (8) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged. Replace with new disc. (9) Check input shaft splines for damage. Replace
if necessary. (10) Check for uneven wear on clutch fingers.
EXCESSIVE CLUTCH SPIN TIME/CLASH INTO
REVERSE COMPLAINTS
For all excessive clutch spin time/clash into reverse
complaints, do the following: (1) Depress clutch pedal to floor and hold. After
three seconds, shift to reverse. If clash is present,
clutch has excessive spin time. (2) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle, for procedure. (3) Check the input shaft spline, clutch disc splines
and release bearing for dry rust. If present, clean
rust off and apply a light coat of bearing grease to
the input shaft splines. Apply grease on the input
shaft splines only where the clutch disc slides. (4) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged, replace with new disc if required. (5) Check the input shaft for damaged splines. Re-
place as necessary. (6) Check for excessive clutch disc runout or
warpage. (7) Install clutch assembly and transaxle.
CLUTCH CABLE MECHANISM
The manual transaxle clutch release system has a
unique self-adjusting mechanism to compensate for
clutch disc wear. This adjuster mechanism is located
within the clutch pedal. The preload spring main-
tains tension on the cable. This tension keeps the
clutch release bearing continuously loaded against
the fingers of the clutch cover assembly. When the pedal is depressed, teeth on the adjuster
and the positioner engage and pull the release cable.
A spring located behind the adjuster ensures proper
tooth engagement. When the pedal is released, the adjuster contacts
the bumper. This separates the adjuster and posi-
tioner teeth, allowing the preload spring to function.
Ä MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH 6 - 1
Page 334 of 2438

CLUTCH PEDAL NOISE/POP
The mechanism which automatically adjusts the
clutch cable to compensate for clutch wear may emit
a loud clicking or pop noise under certain circum-
stances. The cause of this noise in most cases is the clutch
cable auto-adjust spring being below design load
specifications. The condition can be corrected by ei-
ther bending the auto-adjust spring to bring it back
to specifications or replacing the spring (Fig. 1). The auto-adjust spring is located on the back of the
clutch pedal.
CLUTCH CABLE REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove retainer from clutch release lever at
transaxle by pulling on the tail of the ball stud (Fig.
2). (2) Pry out ball end of cable from positioner ad-
juster and remove cable, passing it through the hoop
in the shock tower mounting bracket. (3) Inspect cable for wear and contamination. The
inner cable strand should move smoothly inside the
cable housing. If cable is worn or damaged, replace
the cable. Do not lubricate.
(4) Inspect the clutch pedal and adjuster mecha- nism for wear. Apply a multipurpose lubricant on
parts indicated (Fig. 2). (5) To install, reverse procedure of steps (3)
through (1). (6) After installation, push and lift the clutch
pedal 2 or 3 times to allow adjuster mechanism to
function. (7) Check clutch pedal position switch operation.
Fig. 1 Clutch Cable Auto-Adjust Spring
6 - 2 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH Ä
Page 335 of 2438
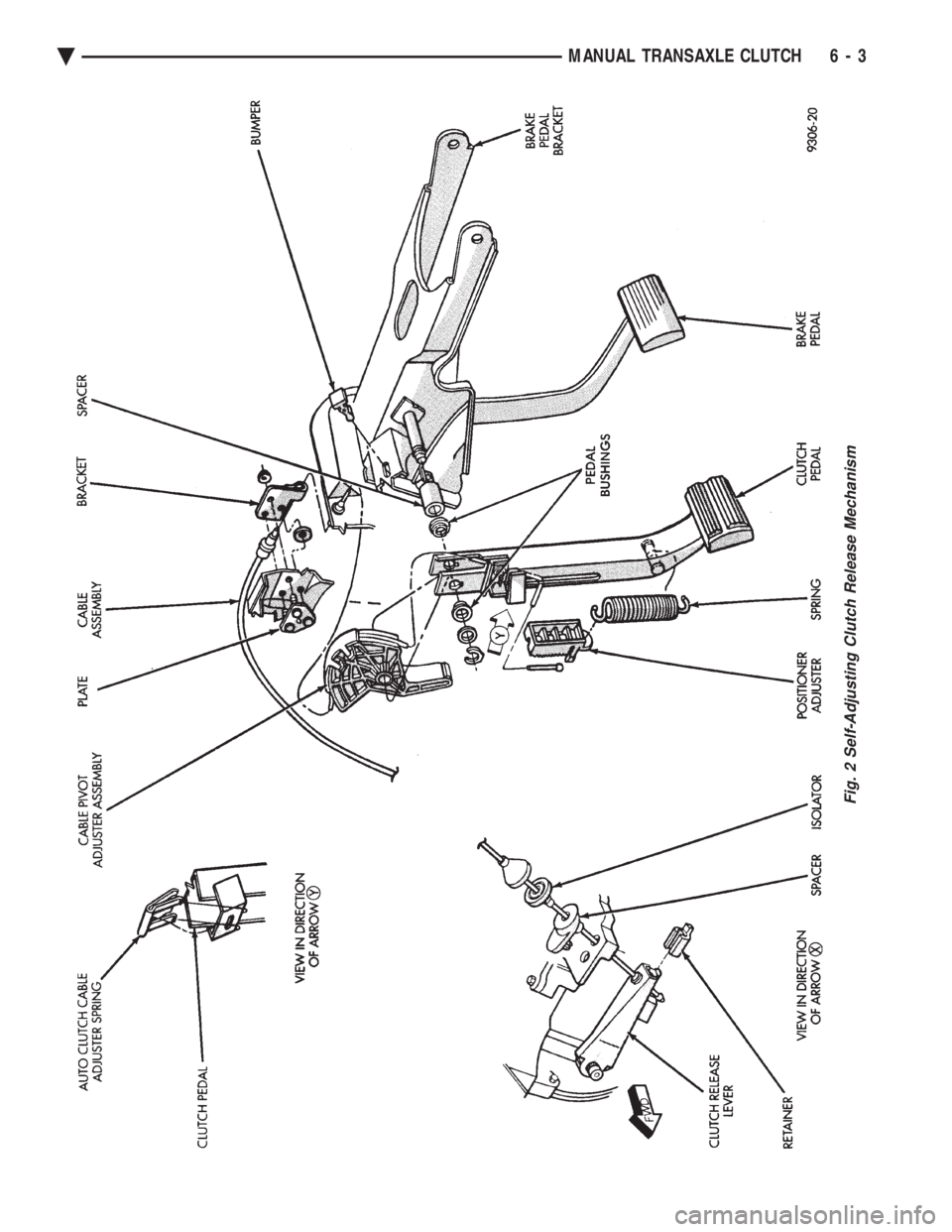
Fig. 2 Self-Adjusting Clutch Release Mechanism
Ä MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH 6 - 3
Page 336 of 2438

CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH
The clutch pedal position switch functions as a
safety interlock device. It prevents possible engine
cranking with the clutch engaged. The clutch pedal position switch is wired in series
between the starter relay coil and the ignition
switch. The clutch pedal position switch is mounted to a
bracket located next to the clutch pedal. The switch
is held in place by four plastic wing tabs. The clutch pedal position switch has an adjustable
striker plate. The striker plate is located on the left
side of the clutch pedal (Fig. 3).
DIAGNOSIS
Disconnect clutch pedal position switch harness
from instrument panel wiring harness. Using a ohm
meter, check for continuity between the two termi-
nals in the connector on the switch harness. There
should be no continuity between the terminals when
the switch is in its neutral (fully extended) position.
When the switch is depressed more than 1.25 mm
(0.050) the ohm meter should show continuity. If all ohm meter readings are correct and the
switch does not operate correctly, adjustment is re-
quired. Refer to Switch Adjustment Procedure to ad-
just switch.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical harness to switch connec-
tor. (2) Depress wing tabs on switch and push switch out
of mounting bracket. Then slide wires through slot in
bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Slide switch wires through slot in switch bracket.
(2) Line up switch tab with slot in switch bracket
and push switch into position. Do not pull on the switch
wires to seat switch into bracket, switch damage may
occur. (3) After installation, the switch must be adjusted
and checked for proper operation. Refer to Switch
Adjustment Procedure.
ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
When performing switch adjustment, the floor mat
should be removed before beginning adjustment proce-
dures. (1) Set the park brake.
(2) Disconnect clutch cable at the transaxle end of
the cable. (3) Depress clutch pedal, loosen adjusting nut and
slide the striker plate forward to fully compress the
clutch pedal position switch plunger. (4) Tighten adjusting nut to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.).
(5) Reconnect clutch cable.
The clutch pedal position switch is now ad-
justed. A final check is required to insure that the
switch is ``made'' below the clutch release point. (1) With the park brake set and the vehicle IN
NEUTRAL turn the key to the start position. The
vehicle should not crank. If the vehicle cranks do
not continue with this test. Recheck the switch and
switch adjustment to determine the cause. If the ve-
hicle does not crank proceed to step 2. (2) With the park brake set and the vehicle IN
GEAR turn the key to the start position.
WARNING: BEFORE PERFORMING STEP THREE BE
SURE THAT THE AREA IN FRONT OF THE VEHICLE
IS CLEAR OF OBSTRUCTIONS AND PEOPLE. VE-
HICLE MAY MOVE WHEN PERFORMING THIS TEST.
(3) Slowly depress the clutch pedal and feel for any
vehicle motion when the starter is energized. If there is
no motion the switch is properly adjusted. If motion is
felt, repeat the adjustment procedure.
Fig. 3 Clutch Pedal Position Switch and Components
6 - 4 MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH Ä
Page 337 of 2438
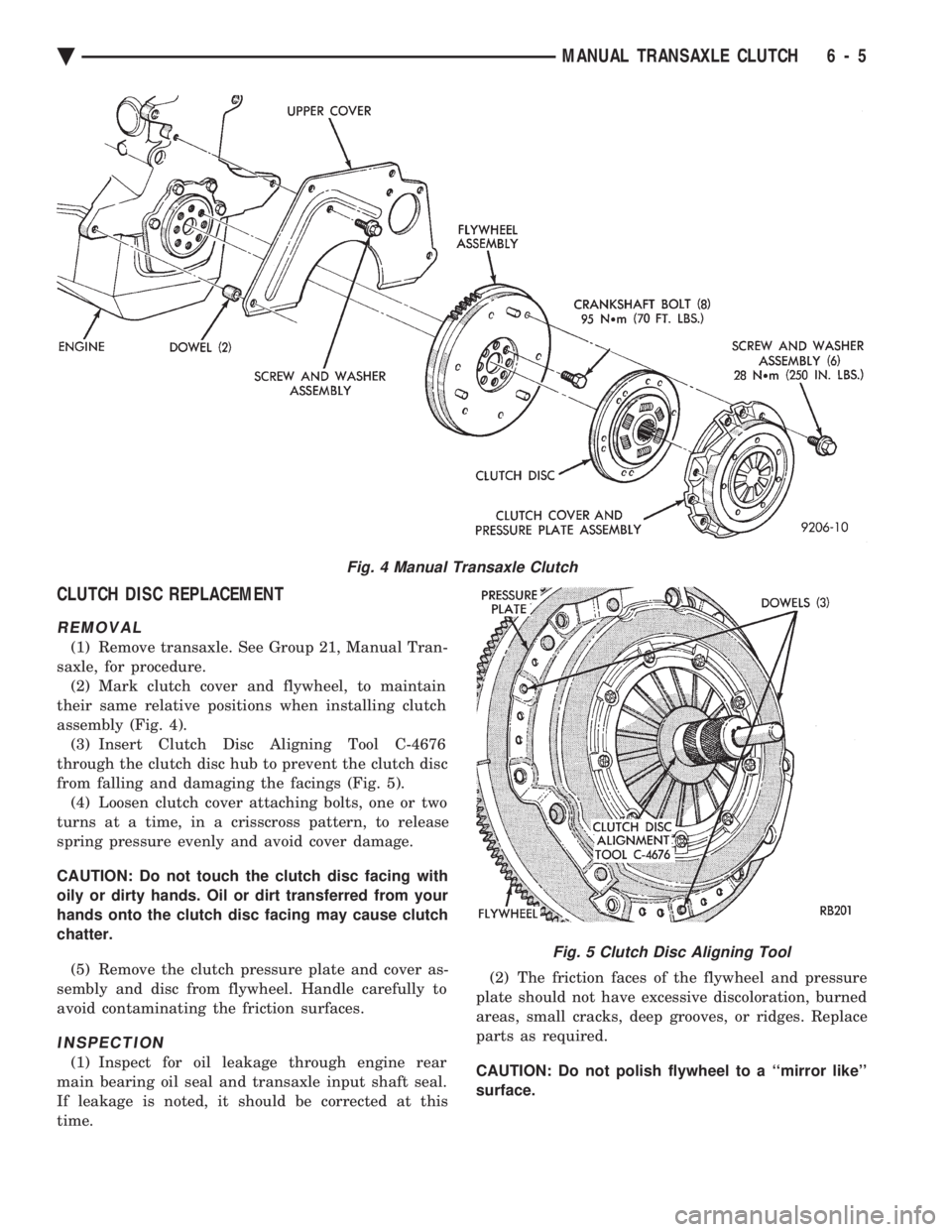
CLUTCH DISC REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle, for procedure. (2) Mark clutch cover and flywheel, to maintain
their same relative positions when installing clutch
assembly (Fig. 4). (3) Insert Clutch Disc Aligning Tool C-4676
through the clutch disc hub to prevent the clutch disc
from falling and damaging the facings (Fig. 5). (4) Loosen clutch cover attaching bolts, one or two
turns at a time, in a crisscross pattern, to release
spring pressure evenly and avoid cover damage.
CAUTION: Do not touch the clutch disc facing with
oily or dirty hands. Oil or dirt transferred from your
hands onto the clutch disc facing may cause clutch
chatter.
(5) Remove the clutch pressure plate and cover as-
sembly and disc from flywheel. Handle carefully to
avoid contaminating the friction surfaces.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect for oil leakage through engine rear
main bearing oil seal and transaxle input shaft seal.
If leakage is noted, it should be corrected at this
time. (2) The friction faces of the flywheel and pressure
plate should not have excessive discoloration, burned
areas, small cracks, deep grooves, or ridges. Replace
parts as required.
CAUTION: Do not polish flywheel to a ``mirror like''
surface.
Fig. 4 Manual Transaxle Clutch
Fig. 5 Clutch Disc Aligning Tool
Ä MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH 6 - 5