engine CHEVROLET SUBURBAN 1994 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1994, Model line: SUBURBAN, Model: CHEVROLET SUBURBAN 1994Pages: 385, PDF Size: 19.88 MB
Page 128 of 385
Listed are four situations you may experience with your fuel gage:
0 At the gas station, the fuel pump shuts off before the gage reads full.
0 It takes a little more or less fuel to fill up than the fuel gage indicated.
For example, the gage may have indicated the tank was half full, but it
actually took a little more or less than half the tank’s capacity to fill the
tank.
0 The gage moves a little when you turn a corner or speed up.
0 The gage doesn’t go back to empty when you turn off the ignition.
None of these indicate a problem
with the fuel gage.
For information
on how to fill your fuel tank, see “Fuel - Filling Your
Tank”
in the Index.
For your fuel tank capacity, see “Fuel -Tank Capacity”
in the Index.
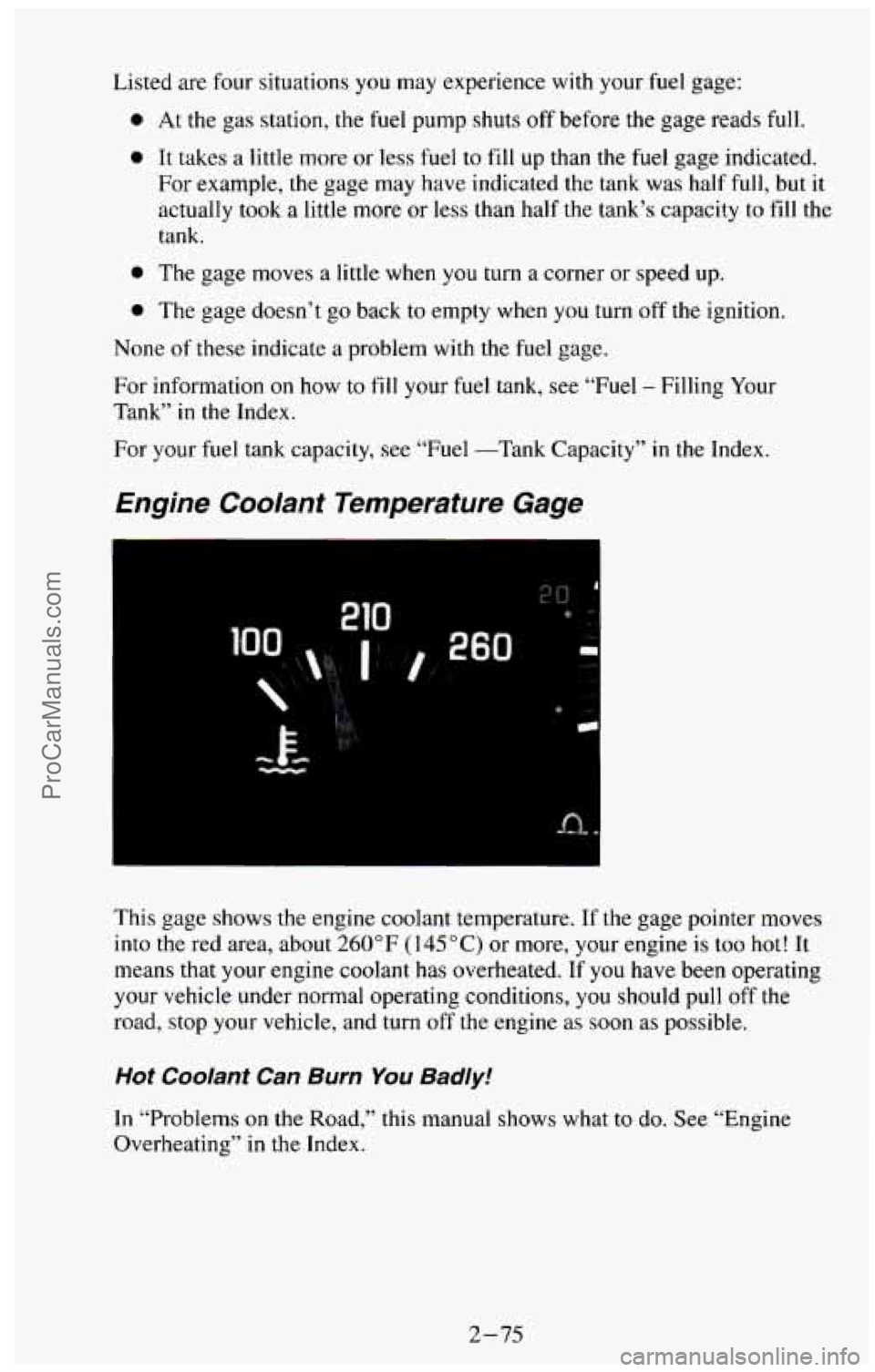
This gage shows the engine coolant temperature. If the gage pointer moves
into the red area, about
260°F (145°C) or more, your engine is too hot! It
means that your engine coolant has overheated.
If you have been operating
your vehicle under normal operating conditions, you should pull
off the
road, stop your vehicle, and turn off the engine as soon as possible.
Hot Coolant Can Burn You Badly!‘
In “Problems on the Road,” this manual shows what to do. See “Engine
Overheating” in the Index.
2-75
ProCarManuals.com
Page 129 of 385
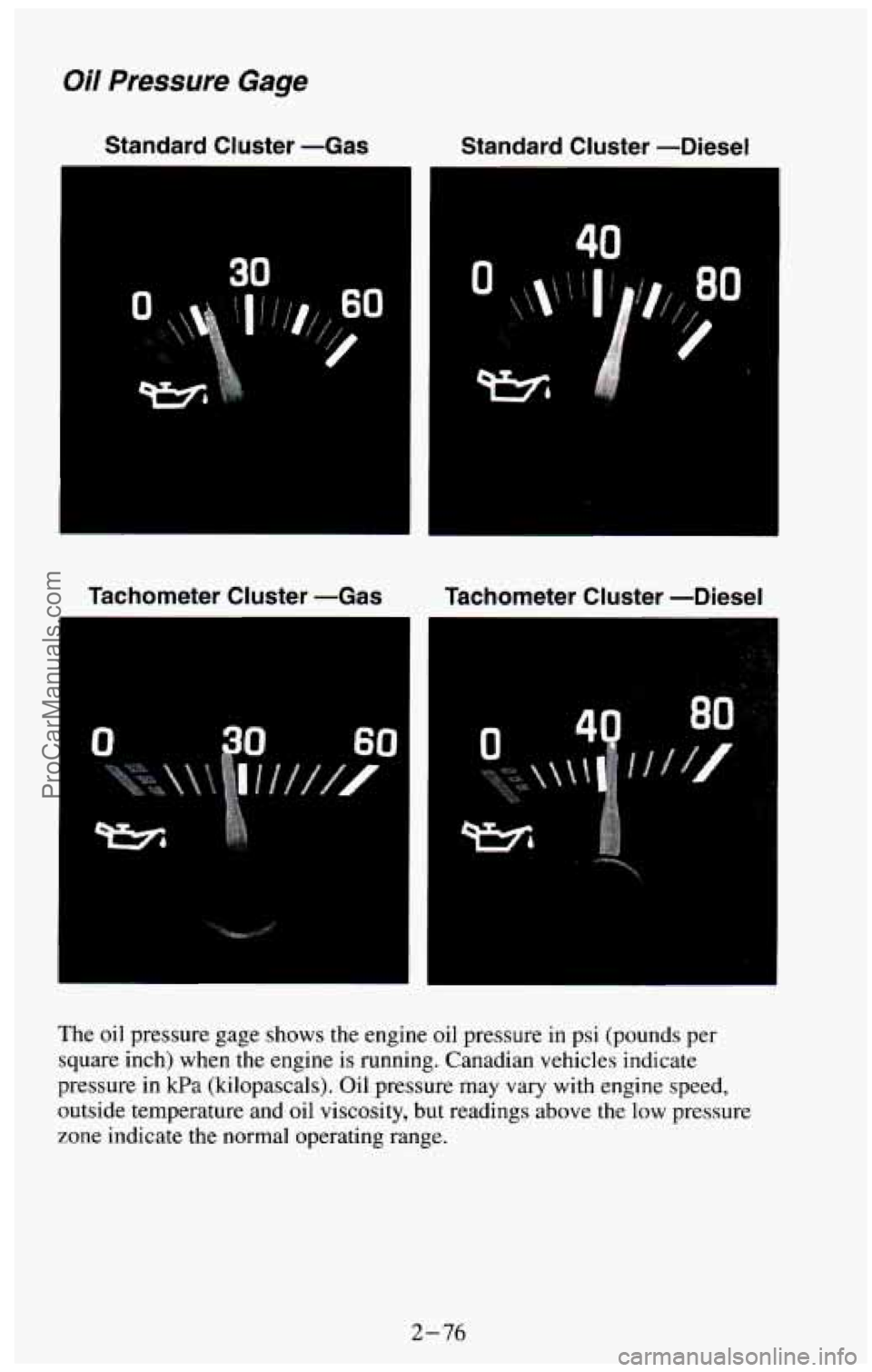
Oil Pressure Gage
Standard Cluster -Gas Standard Cluster -Diesel
40
Tachometer Cluster -Gas Tachometer Cluster -Diesel
The oil pressure gage shows the engine oil pressure in psi (pounds per
square inch) when the engine is running. Canadian vehicles indicate
pressure in
kPa (kilopascals). Oil pressure may vary with engine speed,
outside temperature and oil viscosity,
but readings above the low pressure
zone indicate the normal operating range.
2-76
ProCarManuals.com
Page 132 of 385

A reading in the low pressure zone may be caused by a dangerously low oil
level or other problem causing low oil pressure. Check your oil as soon as
possible.
I NOTICE:
Damage to your engine from neglected oil problems can be
costly and
is not covered by your warranty.
Voltmeter
Standard Cluster Tachometer Cluster
14
When your engine is not running, but the ignition is on (in the RUN
Position), this gage shows your battery’s state of charge in DC volts. When
the engine is running, the gage shows the condition
of the charging system.
Readings between the
low and high warning zones indicate the normal
operating range.
Readings
in either warning zone indicate a possible problem in the electrical
system.
2-77
ProCarManuals.com
Page 141 of 385

Heater Output
Engine Coolant Heater
If your vehicle has a diesel engine, it is equipped with an engine coolant
heater. An engine coolant heater
is optional on gas engine vehicles. You can
use an engine coolant heater during initial start-up
in cold weather (20” F,
-8” C, or lower) to help heat the passenger compartment faster. Because an
engine coolant heater warms the engine coolant, your vehicle’s heating
system can provide some heat as soon as you start the engine.
The use
of an engine coolant heater also reduces the time it takes for the
engine to reach normal operating temperature, and shortens the time it takes
the heater
to reach full output. For more information, See “Engine Coolant
Heater” in the Index.
Diesel Engine
If you idle your diesel engine for a long time when it’s cold outside, your
heater may blow out cool air. This is normal. When you increase the engine
speed, your heater should blow
out warmer air. If it doesn’t, your coolant
level may be low. See “Engine Coolant”
in the Index to find out how to
check your coolant level.
Heating System (Without Air Conditioning)
If your vehicle does not have air conditioning, this is what your heating
system will look like.
3-4
ProCarManuals.com
Page 149 of 385

A udia Systems
Your Delco@ audio system has been designed to operate easily and give
years
of listening pleasure. You will get the most enjoyment out of it if you
acquaint yourself with it first. Find out what your Delco@ system can do
and how to operate all its controls, to be sure you’re getting the most out of
the advanced engineering that went into it.
Be aware that hearing damage from loud noise is almost undetectable until
it is too late. Your hearing can adapt to higher volumes of
sound. Sound that
seems normal can be loud and harmful to your hearing. Take precautions by
adjusting the volume control on your radio to
a safe sound level before your
hearing adapts to it.
To help avoid hearing loss or damage:
0 Adjust the volume control to the lowest setting.
0 Increase volume slowly until you hear comfortably and clearly.
FM Stereo
FM stereo will give you the best sound. But FM signals can only reach
about 10 to
40 miles (16 to 65 km). And, tall buildings or hills can interfere
with FM signals, causing the sound
to come and go.
AM
The range for most AM stations is greater than for FM, especially at night.
The longer range, however, can cause stations to interfere with each other.
AM can pick up noise from things like electrical storms and power lines.
If
the noise interferes with your listening, try reducing the treble to lessen the
noise.
AM Stereo
This means the Delco@ system can receive C-QUAM@ stereo broadcasts.
Many
AM stations around the country use C-QUAM@ to produce stereo,
though some
do not. If your Delco@ system can get C-QUAM@, your
“STEREO” light will come on when you’re receiving it. (C-QUAM@ is a
registered trademark of Motorola, Inc.).
3-12
ProCarManuals.com
Page 150 of 385

NOTICE:
Before you add any sound equipment to your vehicle - like a
tape player,
CB radio, mobile telephone or two-way radio - be
sure you can add what you want.
If you can, it’s very important
to do it properly. Added sound equipment may interfere with the
operation of your vehicle’s engine, Delco@ radio or other
systems, and even damage them. And, your vehicle’s systems
may interfere with the operation
of sound equipment that has
been added improperly.
So, before adding sound equipment, check with your dealer and
be sure to check Federal rules covering mobile radio and
telephone units.
How to Operate Your AM ETR Radio
To Play the Radio
Press the PWR-VOL-TONE knob to switch the radio on and off. This
knob does two other things:
It controls the volume. Rotate the VOL knob clockwise to increases the
volume.
The knob behind the PWR-VOL knob is the TONE knob. Rotate this
knob clockwise
for more treble and counterclockwise for more bass.
3-13
ProCarManuals.com
Page 164 of 385

Sometimes, as when you’re driving on snow or ice, it’s easy to ask more of
those control systems than the tires and road can provide. That means you
can
lose control of your vehicle.
Braking
Brakmg action involves perception time and reaction time.
First, you have to decide to push on the brake pedal. That’s perception. time.
Then you have to bring up your foot and do it. That’s reaction time.
Average reaction time is about 314 of a second. But that’s only an average. It
might be less with one driver and as long as two or three seconds or more
with another. Age, physical condition, alertness, coordination, and eyesight
all play a part.
So do alcohol, drugs and frustration. But even in 3/4 of a
second, a vehicle moving at
60 mph ( 100 kdh) travels 66 feet (20 m). That
could
be a lot of distance in an emergency, so keeping enough space
between your vehicle and others is important.
And, of course, actual stopping distances vary greatly with the surface of the
road (whether it’s pavement or gravel); the condition of the road (wet, dry,
icy); tire tread; and
the condition of your brakes.
Avoid needless heavy braking. Some people drive in spurts
- heavy
acceleration followed by heavy braking
- rather than keeping pace with
traffic. This is a mistake. Your brakes may not have time to
cool between
hard
stops. Your brakes will wear out much faster if you do a lot of heavy
braking.
If you keep pace with the traffic and allow realistic following
distances, you will eliminate a lot
of unnecessary braking. That means better
braking and longer brake life.
If your engine ever stops while you’re driving, brake normally but don’t
pump your brakes. If
you do, the pedal may get harder to push down. If
your engine stops, you will still have some power brake assist. But
you will
use it when you brake. Once the power assist is used
up, it may take longer
to stop and the brake pedal will be harder to push.
4-5
ProCarManuals.com
Page 166 of 385

Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time you need to get your foot up
to the brake pedal. If you get too close to the vehicle in front of you, you
won’t have time
to apply your brakes if that vehicle suddenly slows or
stops. Always
leave enough room up ahead to stop, even though you have
anti-lock brakes.
To Use Four-wheel Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down and let anti-lock
work for you. You may feel the brakes vibrate, or you may notice some
noise, but this is normal.
Braking in Emergencies
Use your anti-lock braking system when you need to. With anti-lock, you
can steer and brake at the same time. In many emergencies, steering can
help you more than even the very best braking.
Power Steering
If you lose power steering assist because the engine stops or the system is
not functioning, you can steer but it will take much more effort.
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control’’ accidents mentioned on the news happen
on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each
of us is subject to the same laws of
physics when driving
on curves. The traction of the tires against the road
surface makes
it possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels. If there’s no traction, inertia will keep the vehicle going in
the same direction. If you’ve ever tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll
understand this.
The traction you can get
in a curve depends on the condition of your tires
and the road surface, the angle at which the curve
is banked, and your
speed. ,- While you’re in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control.
Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve. Then you suddenly
accelerate. Both control systems
- steering and acceleration - have to do
their work where the tires meet the road. Adding
the sudden acceleration
can demand too
much of those places. You can lose control.
4-7 ProCarManuals.com
Page 170 of 385

Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle. Defensive drivers avoid
most skids by taking reasonable care suited to existing conditions, and by
not “overdriving” those conditions. But skids are always possible.
The three types
of skids correspond to your vehicle’s three control systems.
In the braking skid your wheels aren’t rolling. In the steering or cornering
skid, too much speed or steering
in a curve causes tires to slip and lose
cornering force. And
in the acceleration skid too much throttle causes the
driving wheels to spin.
A cornering skid and an acceleration skid are best handled by easing your
foot off
the accelerator pedal.
If your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot off the accelerator pedal and
quickly steer the way you want the vehicle to
go. If you start steering
quickly enough, your vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready for a
second skid if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice, gravel, or other material
is on the road. For safety, you’ll want to slow down and adjust your driving
to
these conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery surfaces because
stopping distance will be longer and vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface
with reduced traction, try your best to avoid
sudden steering, acceleration, or braking (including engine braking by
shifting to a lower gear).
Any sudden changes could cause the tires to slide.
You may not realize the surface is slippery
until your vehicle is skidding.
Learn to recognize warning clues
- such as enough water, ice or packed
snow on the road to make a “mirrored surface”
- and slow down when you
have
any doubt.
Remember: Any anti-lock braking
system (ABS) helps avoid only the
braking skid.
Driving Guidelines
This multipurpose passenger vehicle is defined as a utility vehicle in
Consumer Information Regulations issued by the National Highway Traffic
Safety Administration (NHTSA) of the United States Department of
Transportation. Utility vehicles have higher ground clearance and a narrower
track to make them capable
of performing in a wide variety of off-road
applications. Specific design characteristics give them
a higher center of
gravity than ordinary cars.
An advantage of the higher ground clearance is a
better view of the road allowing you to anticipate problems. They are not
designed for cornering at the same speeds as conventional 2-wheel drive
vehicles any more than low-slung
sports cars are designed to perform
satisfactorily under off-road conditions.
If at all possible, avoid sharp turns or
abrupt maneuvers. As
with other vehicles of this type, failure to operate this
vehicle correctly may result in loss of control or vehicle rollover.
4-11
ProCarManuals.com
Page 172 of 385

You’ll find other important information in this manual. See “Vehicle
Loading,’’ “Luggage Carrier” and “Tires” in the Index.
Traveling to Remote Areas
It makes sense to plan your trip, especially when going to a remote area.
Know the terrain and plan your route.
You are much less likely to get bad
surprises. Get accurate maps
of trails and terrain. Try to learn of any
blocked or closed roads.
It’s also a good idea to travel with at least one other vehicle.
If something
happens to one
of them, the other can help quickly.
Does your vehicle have a winch? If
so, be sure to read the winch
instructions.
In a remote area, a winch can be handy if you get stuck. But
you’ll want
to know how to use it properly.
Getting Familiar with Off-Road Driving
It’s a good idea to practice in an area that’s safe and close to home before
you go into the wilderness. Off-road driving does require some new and
different driving
skills. Here’s what we mean.
Tune your senses to different kinds
of signals. Your eyes, for example, need
to constantly sweep the terrain for unexpected obstacles. Your ears need to
listen for unusual tire or engine sounds. With your arms, hands, feet, and
body you’ll need to respond to vibrations and vehicle bounce.
4-13
ProCarManuals.com