transmission CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2003 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2003, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2003Pages: 2177, PDF Size: 59.81 MB
Page 35 of 2177
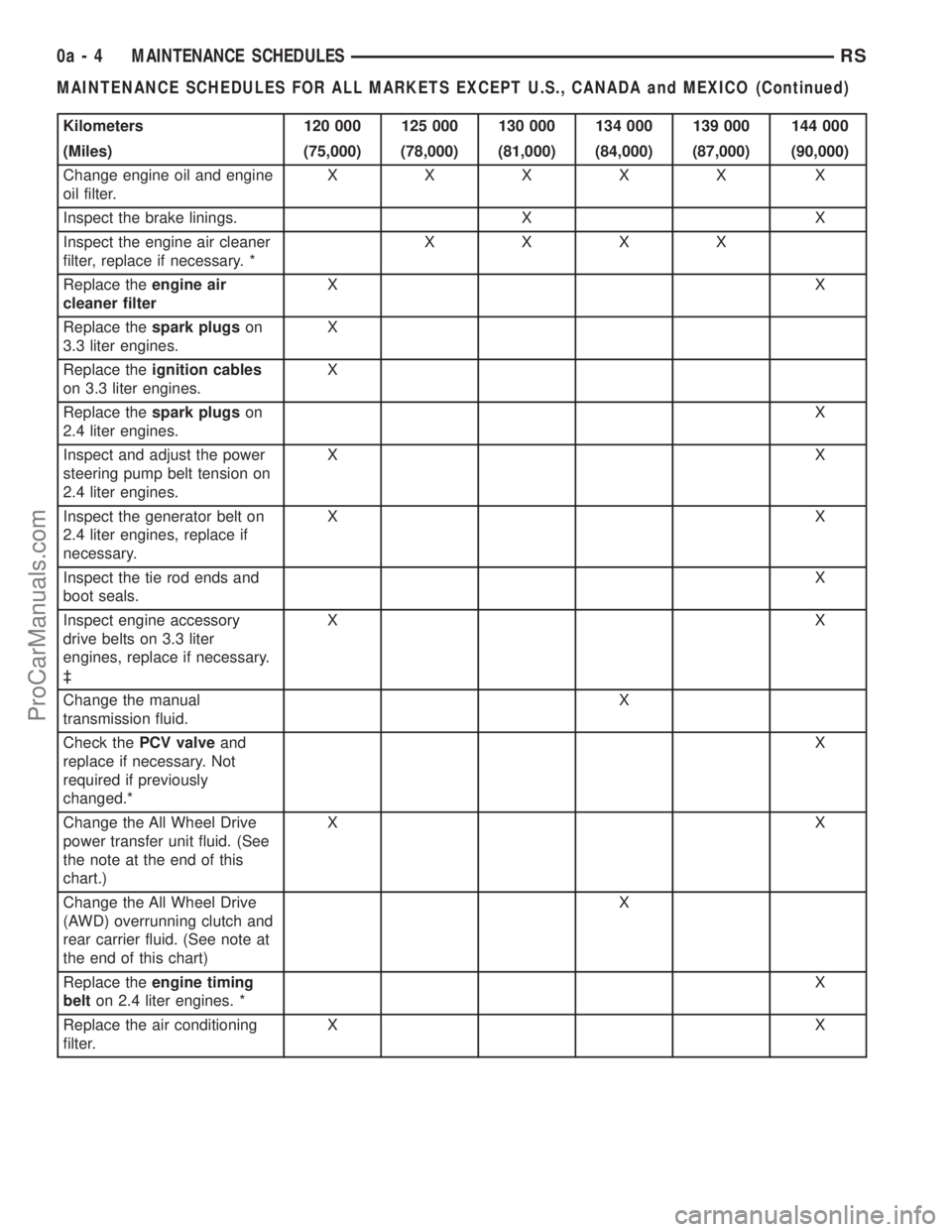
Kilometers 120 000 125 000 130 000 134 000 139 000 144 000
(Miles) (75,000) (78,000) (81,000) (84,000) (87,000) (90,000)
Change engine oil and engine
oil filter.XXXXX X
Inspect the brake linings. X X
Inspect the engine air cleaner
filter, replace if necessary. *XXXX
Replace theengine air
cleaner filterXX
Replace thespark plugson
3.3 liter engines.X
Replace theignition cables
on 3.3 liter engines.X
Replace thespark plugson
2.4 liter engines.X
Inspect and adjust the power
steering pump belt tension on
2.4 liter engines.XX
Inspect the generator belt on
2.4 liter engines, replace if
necessary.XX
Inspect the tie rod ends and
boot seals.X
Inspect engine accessory
drive belts on 3.3 liter
engines, replace if necessary.
³XX
Change the manual
transmission fluid.X
Check thePCV valveand
replace if necessary. Not
required if previously
changed.*X
Change the All Wheel Drive
power transfer unit fluid. (See
the note at the end of this
chart.)XX
Change the All Wheel Drive
(AWD) overrunning clutch and
rear carrier fluid. (See note at
the end of this chart)X
Replace theengine timing
belton 2.4 liter engines. *X
Replace the air conditioning
filter.XX
0a - 4 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULESRS
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES FOR ALL MARKETS EXCEPT U.S., CANADA and MEXICO (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 36 of 2177
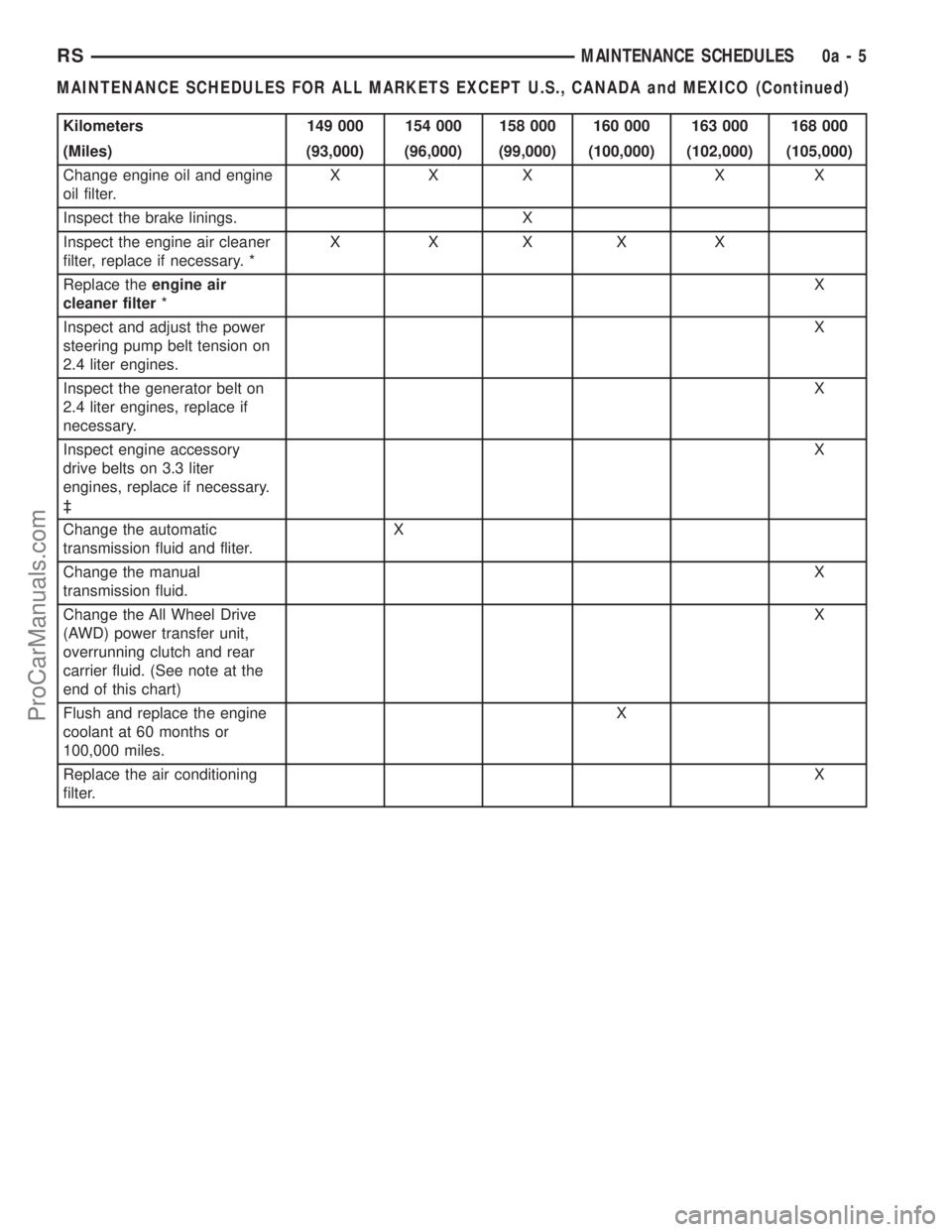
Kilometers 149 000 154 000 158 000 160 000 163 000 168 000
(Miles) (93,000) (96,000) (99,000) (100,000) (102,000) (105,000)
Change engine oil and engine
oil filter.XXX X X
Inspect the brake linings. X
Inspect the engine air cleaner
filter, replace if necessary. *X XXX X
Replace theengine air
cleaner filter*X
Inspect and adjust the power
steering pump belt tension on
2.4 liter engines.X
Inspect the generator belt on
2.4 liter engines, replace if
necessary.X
Inspect engine accessory
drive belts on 3.3 liter
engines, replace if necessary.
³X
Change the automatic
transmission fluid and fliter.X
Change the manual
transmission fluid.X
Change the All Wheel Drive
(AWD) power transfer unit,
overrunning clutch and rear
carrier fluid. (See note at the
end of this chart)X
Flush and replace the engine
coolant at 60 months or
100,000 miles.X
Replace the air conditioning
filter.X
RSMAINTENANCE SCHEDULES0a-5
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES FOR ALL MARKETS EXCEPT U.S., CANADA and MEXICO (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 40 of 2177

DESCRIPTION Ð DIESEL ENGINES
Maintenance Schedule Information not included in
this section, is located in the appropriate Owner's
Manual.
There are two maintenance schedules that show
therequiredservice for your vehicle.
First is ScheduleªBº. It is for vehicles that are
operated under the conditions that are listed below
and at the beginning of the schedule.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).
²Trailer towing.
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
NOTE: Most vehicles are operated under the condi-
tions listed for Schedule(B(.
Second is ScheduleªAº. It is for vehicles that are
not operated under any of the conditions listed under
Schedule9B9.
Use the schedule that best describes your driving
conditions. Where time and mileage are listed, follow
the interval that occurs first.
CAUTION: Failure to perform the required mainte-
nance items may result in damage to the vehicle.
At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check the engine oil level about 5 minutes after
a fully warmed engine is shut off. Checking the oil
level while the vehicle is on level ground will
improve the accuracy of the oil level reading. Add oil
only when the level is at or below the ADD or MIN
mark.
²Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
²Check the tire pressure and look for unusual
wear or damage.
²Inspect the battery and clean and tighten the
terminals as required.
²Check the fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering and transmission
and add as needed.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
At Each Oil Change
²Change the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the exhaust system.
²Inspect the brake hoses.
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents.
²Check the manual transmission fluid level.
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
²Inspect engine accessory drive belts. Replace as
necessary.
²Inspect for the presence of water in the fuel fil-
ter/water separator unit.
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval (20
000 km).
SCHEDULE ªBº
Follow schedule ªBº if you usually operate your
vehicle under one or more of the following conditions.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).
²Trailer towing.
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
RSMAINTENANCE SCHEDULES0a-9
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES FOR ALL MARKETS EXCEPT U.S., CANADA and MEXICO (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 104 of 2177

CAUTION: The steering knuckle to strut assembly
attaching bolts are serrated and must not be turned
during installation. Install nuts while holding bolts
stationary in the steering knuckle.
CAUTION: If the vehicle being serviced is equipped
with eccentric strut assembly attaching bolts, the
eccentric bolt must be installed in the bottom (slot-
ted) hole on the strut clevis bracket (Fig. 10).
(7) Install steering knuckle in clevis bracket of
strut damper assembly. Install the strut damper to
steering knuckle attaching bolts. Tighten both bolts
to a torque of 81 N´m (60 ft. lbs.) plus an additional
1/4 turn.
(8) Install braking disc on hub and bearing assem-
bly.
(9) Install disc brake caliper assembly on steering
knuckle. Caliper is installed by first sliding bottom of
caliper assembly under abutment on steering
knuckle, and then rotating top of caliper against top
abutment.
(10) Install disc brake caliper adapter to steering
knuckle attaching bolts (Fig. 4). Tighten the discbrake caliper adapter attaching bolts to a torque of
169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.).
(11) Clean all foreign matter from the threads of
the outer CV joint. Install the washer and half shaft
to hub/bearing assembly nut on half shaft and
securely tighten nut.
(12) Install front wheel and tire assembly. Install
and tighten the wheel mounting stud nuts in proper
sequence until all nuts are torqued to half the
required specification. Then repeat the tightening
sequence to the full specified torque of 135 N´m (100
ft. lbs.).
(13) Lower vehicle.
(14) With the vehicle's brakes applied to keep hub
from turning, tighten the hub nut to a torque of 244
N´m (180 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 11).
(15) Install the spring wave washer on the end of
the half shaft.
(16) Install the hub nut lock, and anewcotter pin
(Fig. 2). Wrap cotter pin prongs tightly around the
hub nut lock as shown in (Fig. 2).
(17) Check for correct fluid level in transaxle
assembly. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
Fig. 10 Correctly Installed Eccentric Attaching Bolt
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - FLANGED BOLT IN TOP HOLE
3 - CAM BOLT IN BOTTOM HOLE
4 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
Fig. 11 Torquing Front Half Shaft To Hub Nut
1 - TORQUE WRENCH
RSHALF SHAFT - FRONT3-5
HALF SHAFT - FRONT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 122 of 2177

REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................23
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR
DRIVELINE MODULE NOISE.............24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR
DRIVELINE MODULE OPERATION........26
REMOVAL.............................26
DISASSEMBLY.........................27
ASSEMBLY............................29
INSTALLATION.........................33
SPECIFICATIONS - REAR DRIVELINE
MODULE............................34
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................34
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION.........................34
OPERATION...........................36
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION.........................39OPERATION...........................39
FLUID - DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIFFERENTIAL
ASSEMBLY FLUID CHANGE.............40
FLUID - OVERRUNNING CLUTCH HOUSING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH HOUSING FLUID CHANGE.......41
VISCOUS COUPLER
DESCRIPTION.........................41
OPERATION...........................42
TORQUE ARM
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................44
INPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL.............................44
INSTALLATION.........................45
OUTPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL.............................45
INSTALLATION.........................46
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The rear driveline module assembly (Fig. 1) con-
sists of four main components:
²Bi-Directional Overrunning Clutch (BOC)
²Viscous Coupling
²Differential Assembly
²Torque Arm
The viscous coupling and bi-directional overrun-
ning clutch are contained within an overrunning
clutch housing, which fastens to the differential
assembly. The overrunning clutch housing and differ-
ential assembly have unique fluid sumps, each
requiring their own type and capacity of fluid. The
overrunning clutch housing requires MopartATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602) or equiv-
alent. The differential assembly requires Mopart
80W-90 Gear and Axle Lubricant.
Driveline module service is limited to the following
components:
²Differential Assembly (serviced only as assem-
bly)
²Viscous Coupling
²Bi-Directional Overrunning Clutch (BOC)
²Overrunning Clutch Housing²Seals (Input Flange, Output Flange, Overrun-
ning Clutch Housing O-rings)
²Input Flange/Shield
²Torque Arm
²Vents
²Fasteners
OPERATION
The primary benefits of All Wheel Drive are:
²Superior straight line acceleration, and corner-
ing on all surfaces
²Better traction and handling under adverse con-
ditions, resulting in improved hill climbing ability
and safer driving.
The heart of the system is an inter-axle viscous
coupling. The vehicle retains predominantly front-
wheel drive characteristics, but the All Wheel Drive
capability takes effect when the front wheels start to
slip. Under normal level road, straight line driving,
100% of the torque is allocated to the front wheels.
The viscous coupling controls and distributes torque/
power to the rear wheels. The viscous coupling trans-
mits torque to the rear wheels in proportion of the
amount of the slippage at the front wheels. Thais
variable torque distribution is automatic with no
driver inputs required. The coupling is similar to a
multi-plate clutch. It consists of a series of closely
spaced discs, which are alternately connected to the
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-23
ProCarManuals.com
Page 123 of 2177

front and rear drive units. The unit is totally sealed
and partially filled with silicone fluid. There is no
adjustment, maintenance or fluid checks required
during the life of the unit.
The overrunning clutch allows the rear wheels to
overrun the front wheels during a rapid front wheel
lock braking maneuver. The overrunning action pre-
vents any feed-back of front wheel braking torque to
the rear wheels. It also allows the braking system to
control the braking behavior as a two wheel drive
(2WD) vehicle.
The overrunning clutch housing has a separate oil
sump and is filled independently from the differen-
tial. The fill plug is located on the side of the over-
running clutch case. When filling the overrunning
clutch with lubricant use MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission FluidÐType 9602) or equivalent.
The differential assembly contains a conventional
open differential with hypoid ring gear and pinion
gear set. The hypoid gears are lubricated by SAE
80W-90 gear lubricant.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR DRIVELINE
MODULE NOISE
Different sources can be the cause of noise that the
rear driveline module assembly is suspected of mak-
ing. Refer to the following causes for noise diagnosis.
DRIVELINE MODULE ASSEMBLY NOISE
The most important part of driveline module ser-
vice is properly identifying the cause of failures and
noise complaints. The cause of most driveline module
failures is relatively easy to identify. The cause of
driveline module noise is more difficult to identify.
If vehicle noise becomes intolerable, an effort
should be made to isolate the noise. Many noises that
are reported as coming from the driveline module
may actually originate at other sources. For example:
²Tires
²Road surfaces
²Wheel bearings
Fig. 1 AWD Driveline Module Assembly
1 - TORQUE ARM 8 - WASHER 15 - PLUG-OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
HOUSING DRAIN
2 - INPUT FLANGE 9 - BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH (BOC)16 - SNAP RING
3 - FLANGE NUT 10 - VISCOUS COUPLER 17 - BEARING
4 - WASHER 11 - SHIM (SELECT) 18 - OVERRUNING CLUTCH HOUSING
5 - SHIELD 12 - O-RING 19 - SEAL-INPUT FLANGE
6 - VENT 13 - DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
7 - O-RING 14 - PLUG-DIFFERENTIAL FILL
3 - 24 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 124 of 2177

²Engine
²Transmission
²Exhaust
²Propeller shaft (vibration)
²Vehicle body (drumming)
Driveline module noises are normally divided into
two categories: gear noise or bearing noise. A thor-
ough and careful inspection should be completed to
determine the actual source of the noise before
replacing the driveline module.
The rubber mounting bushings help to dampen-out
driveline module noise when properly installed.
Inspect to confirm that no metal contact exists
between the driveline module case and the body. The
complete isolation of noise to one area requires
expertise and experience. Identifying certain types of
vehicle noise baffles even the most capable techni-
cians. Often such practices as:
²Increase tire inflation pressure to eliminate tire
noise.
²Listen for noise at varying speeds with different
driveline load conditions
²Swerving the vehicle from left to right to detect
wheel bearing noise.
All driveline module assemblies produce noise to a
certain extent. Slight carrier noise that is noticeable
only at certain speeds or isolated situations should be
considered normal. Carrier noise tends to peak at a
variety of vehicle speeds. Noise isNOT ALWAYSan
indication of a problem within the carrier.
TIRE NOISE
Tire noise is often mistaken for driveline module
noise. Tires that are unbalanced, worn unevenly or
are worn in a saw-tooth manner are usually noisy.
They often produce a noise that appears to originate
in the driveline module.
Tire noise changes with different road surfaces, but
driveline module noise does not. Inflate all four tires
with approximately 20 psi (138 kPa) more than the
recommended inflation pressure (for test purposes
only). This will alter noise caused by tires, but will
not affect noise caused by the differential. Rear axle
noise usually ceases when coasting at speeds less
than 30 mph (48 km/h); however, tire noise contin-
ues, but at a lower frequency, as the speed is
reduced.
After test has been completed lower tire pressure
back to recommended pressure.
GEAR NOISE (DRIVE PINION AND RING GEAR)
Abnormal gear noise is rare and is usually caused
by scoring on the ring gear and drive pinion. Scoring
is the result of insufficient or incorrect lubricant in
the carrier housing.Abnormal gear noise can be easily recognized. It
produces a cycling tone that will be very pronounced
within a given speed range. The noise can occur dur-
ing one or more of the following drive conditions:
²Drive
²Road load
²Float
²Coast
Abnormal gear noise usually tends to peak within
a narrow vehicle speed range or ranges. It is usually
more pronounced between 30 to 40 mph (48 to 64
km/h) and 50 to 60 mph (80 to 96 km/h). When objec-
tionable gear noise occurs, note the driving condi-
tions and the speed range.
BEARING NOISE (DRIVE PINION AND
DIFFERENTIAL)
Defective bearings produce a rough growl that is
constant in pitch and varies with the speed of vehi-
cle. Being aware of this will enable a technician to
separate bearing noise from gear noise.
Drive pinion bearing noise that results from defec-
tive or damaged bearings can usually be identified by
its constant, rough sound. Drive pinion front bearing
is usually more pronounced during a coast condition.
Drive pinion rear bearing noise is more pronounced
during a drive condition. The drive pinion bearings
are rotating at a higher rate of speed than either the
differential side bearings or the axle shaft bearing.
Differential side bearing noise will usually produce
a constant, rough sound. The sound is much lower in
frequency than the noise caused by drive pinion bear-
ings.
Bearing noise can best be detected by road testing
the vehicle on a smooth road (black top). However, it
is easy to mistake tire noise for bearing noise. If a
doubt exists, the tire treads should be examined for
irregularities that often causes a noise that resem-
bles bearing noise.
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSION NOISE
Sometimes noise that appears to be in the driv-
eline module assembly is actually caused by the
engine or the transmission. To identify the true
source of the noise, note the approximate vehicle
speed and/or RPM when the noise is most noticeable.
Stop the vehicle next to a flat brick or cement wall
(this will help reflect the sound). Place the transaxle
inNEUTRAL. Accelerate the engine slowly up
through the engine speed that matches the vehicle
speed noted when the noise occurred. If the same
noise is produced, it usually indicates that the noise
is being caused by the engine or transaxle.
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-25
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 125 of 2177

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR DRIVELINE
MODULE OPERATION
Driveline module operation requires relatively
straight-forward diagnosis. Refer to the following
chart:
DRIVELINE MODULE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Rear wheels not
overrunning1) Bi-directional overrunning clutch
failure1) Replace overrunning clutch
components as required
No AWD in forward or
reverse directions, propeller
shaft turning1) Bi-directional overrunning clutch
failure1) Replace overrunning clutch
components as required
2) Viscous coupling failure 2) Replace viscous coupling
3) Rear differential failure 3) Replace the rear differential
assembly
No AWD in forward or
reverse directions, propeller
shaft not turning1) Power transfer unit failure. 1) Replace power transfer unit
components as necessary
Vibration at all speeds,
continuous torque transfer1) Mis-matched tires, worn tires on
front axle.1) Replace worn or incorrect
(mis-matched) tires with same
make and size
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Drain fluid from overrunning clutch housing
and/or differential assembly if necessary.
(3) Remove propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(4) Disconnect left and right rear halfshafts from
output flanges (Fig. 2).
(5) Remove torque arm mount to body bolts.(6) Position transmission jack to driveline module
assembly and secure assembly to jack.
(7) Remove two driveline module-to-body bolts
(Fig. 3).
(8) Lower driveline module from vehicle and
remove from jack.
Fig. 2 Half Shaft Mounting Bolts
1 - SHAFT
2 - FLANGE
Fig. 3 Rear Drive Line Module Assembly Mounting
Bolts
1 - DRIVELINE MODULE RETAINING BOLT (2)
2 - RUBBER ISOLATOR
3 - WASHER
3 - 26 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 132 of 2177

(14) Install torque arm assembly into position.
Install and torque torque arm-to-differential assem-
bly bolts (Fig. 25) to 60 N´m (44 ft. lbs.).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install rear driveline module assembly to
transmission jack and secure.
(2) Raise rear driveline module into position and
install and torque mounting bolts (Fig. 26) to 54 N´m
(40 ft. lbs.).(3) Remove transmission jack.
(4) Install and torque torque arm mount-to-body
bolts to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install halfshafts to differential output flanges
and torque bolts (Fig. 27) to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(6) Install propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT -
INSTALLATION)
(7) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 25 Torque Arm Fasteners
1 - TORQUE ARM ASSEMBLY
2 - BOLT (SIX)
Fig. 26 Rear Drive Line Module Assembly Rear
Mounting Bolts
1 - DRIVELINE MODULE RETAINING BOLT (2)
2 - RUBBER ISOLATOR
3 - WASHER
Fig. 27 Half Shaft Mounting Bolts
1 - SHAFT
2 - FLANGE
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-33
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 133 of 2177

SPECIFICATIONS - REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Bolt, Driveline Module-to-Body 54 40 Ð
Bolt, Halfshaft-to-Ouput Flange 61 45 Ð
Bolt, Overrunning Clutch Housing-to-Differential 60 44 Ð
Bolt, Torque Arm-to-Differential Assembly 60 44 Ð
Bolt, Torque Arm Mount-to-Body 54 40 Ð
Nut, Input Flange 135 100 Ð
Plug, Differential Drain/Fill 35 26 Ð
Plug, Overrunning Clutch Housing Drain/Fill 30 22 Ð
Vent, Differential/Overrunning Clutch Housing 12 Ð 110
SPECIAL TOOLSBI-DIRECTIONAL
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The bi-directional overrunning clutch (BOC) (Fig.
28) works as a mechanical disconnect between the
front and rear axles, preventing torque from being
transferred from the rear axle to the front. The BOC
is a simply an overrunning clutch which works in
both clockwise and counter-clockwise rotations. This
means that when the output (the rear axle) is rotat-
ing faster in one direction than the input (front axle),
there is no torque transmission. But when the input
speed is equal to the output speed, the unit becomes
locked. The BOC provides significant benefits regard-
ing braking stability, handling, and driveline durabil-
ity. Disconnecting the front and the rear driveline
during braking helps to maintain the braking stabil-
ity of an AWD vehicle. In an ABS/braking event, the
locking of the rear wheels must be avoided for stabil-
ity reasons. Therefore brake systems are designed to
lock the front wheels first. Any torque transfer from
the rear axle to the front axle disturbs the ABS/brak-
ing system and causes potential instabilities on a
slippery surface. The BOC de-couples the rear driv-
eline as soon the rear wheels begin to spin faster
than the front wheels (front wheels locked) in order
to provide increased braking stability. Furthermore
the BOC also reduces the likelihood of throttle off
over-steer during cornering. In a throttle off maneu-
ver, the BOC once again de-couples the rear driveline
forcing all the engine brake torque to the front
wheels. This eliminates the chance of lateral slip on
the rear axle and increases it on the front. The vehi-
cle will therefore tend to understeer, a situation
which is considered easier to manage in most circum-
stances. During this maneuver, and during the ABS
braking event, the BOC does not transmit torque
Tool 6958
Tool 8493
Tool 8802
3 - 34 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com