sensor CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 451 of 2339

AUTOMATIC DAY / NIGHT
MIRROR
DESCRIPTION
An automatic dimming inside day/night rear view
mirror and an automatic dimming driver side outside
rear view mirror are available factory-installed
options on this model. Following is a general descrip-
tion of this optional equipment.
The automatic day/night mirror is able to automat-
ically change its reflectance. A thin layer of electro-
chromic material between two pieces of conductive
glass make up the face of the mirror. Two photocell
sensors are used to monitor light levels and adjust
the reflectance of the mirror to reduce the glare of
headlamps approaching the vehicle from the rear.
For removal procedures, (Refer to 23 - BODY/IN-
TERIOR/REAR VIEW MIRROR - REMOVAL).
OPERATION
The ambient photocell sensor faces forward, to
detect the outside light levels. A second sensor faces
rearward to detect the light level received through
the vehicles back window. When the difference
between the two light levels becomes too great (the
light level received at the rear of the mirror is much
higher than that at the front of the mirror), the mir-
ror begins to darken.
The mirror switch allows the driver a manual con-
trol of whether the automatic dimming feature is
operational. When AUTO is selected a small Light-
Emitting Diode (LED), to the right of the mirror
switch, is illuminated. The automatic dimming fea-
ture will only operate when the ignition switch is in
the On position. The mirror also senses the backup
lamp circuit, and will automatically disable its self-
dimming feature whenever the transmission gear
selector is in the Reverse position.
NOTE: The mirror always defaults to an ON state
upon ignition.
The driver side automatic dimming mirror is stan-
dard with the automatic dimming inside mirror. The
signal to control the dimming of that mirror is gen-
erated by the automatic day/night inside rear view
mirror circuitry. That signal is then delivered to the
driver side outside rear view mirror on a hard wired
circuit.
The automatic day/night mirror cannot be
repaired. If faulty or damaged, the entire inside rear
view mirror assembly must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AUTOMATIC DAY / NIGHT MIRROR
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring informa-
tion includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and con-
nector repair procedures, details of wire harness
routing and retention, connector pin-out information
and location views for the various wire harness con-
nectors, splices and grounds.
(1) Check the fuse in the intelligent power module.
If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the shorted cir-
cuit or component as required and replace the faulty
fuse.
(2) Turn the ignition switch to the On position.
Check for battery voltage at the fuse in the intelli-
gent power module. If OK, go to Step 3. If not OK,
repair the open circuit to the ignition switch as
required.
(3) Unplug the wire harness connector from the
automatic day/night mirror. Check for battery voltage
at the fused ignition switch output circuit cavity of
the automatic day/night mirror wire harness connec-
tor. If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the junction block as required.
(4) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position.
Check for continuity between the ground circuit cav-
ity of the automatic day/night mirror wire harness
connector and a good ground. There should be conti-
nuity. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, repair the cir-
cuit to ground as required.
(5) Turn the ignition switch to the On position. Set
the parking brake. Place the transmission gear selec-
tor lever in the Reverse position. Check for battery
voltage at the backup lamp switch output circuit cav-
ity of the automatic day/night mirror wire harness
connector. If voltage is present, reinstall the auto-
matic day/night mirror wire harness connector and
go to Step 6. If not OK, repair the open circuit as
required.
(6) Place the transmission gear selector lever in
the Neutral position. Place the automatic day/night
mirror switch in the On (LED in the switch is
lighted) position. Cover the forward facing ambient
photocell sensor to keep out any ambient light.
NOTE: The ambient photocell sensor must be cov-
ered completely, so that no light reaches the sen-
sor. Use a finger pressed tightly against the sensor,
or cover the sensor completely with electrical tape.
(7) Shine a light into the rearward facing head-
lamp photocell sensor. The automatic day/night mir-
ror should darken. The automatic day/night mirror
should darken within 2 minutes if testing for the
first time. For immediate response, turn the vehicle
8N - 28 POWER MIRRORSRS
Page 452 of 2339

OFF and back ON with the forward-facing light sen-
sor still covered. This defeats the day-detect logic. If
OK, go to Step 8. If not OK, replace the faulty mirror
unit.
(8) With the mirror darkened, place the transmis-
sion gear selector lever in the Reverse position. The
automatic day/night mirror should return to its nor-
mal reflectance. If not OK, replace the faulty mirror
unit.
Bench testing both mirrors can be done, of care is
exercised. For an inside mirror, the pin closest to he
mount is 12V (+), the next is 12V (-). The third is
reverse override. The fourth is outside mirror (+), and
the fifth is outside mirror (-).Do not apply 12 volts to
the fourth and fifth pins.With 12 volts on pins 1 and
2, the mirror can be tested by blocking the rear sensor
and shining a light into the forward sensor. For an out-
side mirror, there is a 2±pin connector. Applying 1.2
volts will cause the mirror to dim. If the mirror does not
dim, the entire glass assembly can be replaced just as it
is when the glass is broken.
WARNING: Do not apply 12 volts to the outside mir-
ror. Damage to the mirror will result.
POWER FOLDAWAY MIRROR
SWITCH - EXPORT
DESCRIPTION
These vehicles may be equipped with Power Fold-
away Mirrors. This feature allows both the driver
and passenger side view mirrors to fold inward
(retract) on demand. The vehicle has an additional
switch located on the steering column that controls
the folding function of the mirror assembly (Fig. 2).
The fold-away side view mirror is attached to the
vehicle's door in the same manner as mirrors without
the fold-away option. The fold-away mirrors unique
option is the internal motor which allows the mirrors to
fold inward on demand. The fold-away mirror motor is
not serviceable separately and if a motor is found to be
faulty the entire side view mirror must be replaced.
OPERATION
When the mirror retract switch is depressed, both
of the side view mirrors will fold inward, Thus mak-
ing the overall width of the vehicle the smallest pos-
sible. This can be helpful were parking space is a
absolute minimum.
When the driver's door is opened, only the driver's
door mirror will unfold. If the passenger door is
opened, both mirrors will unfold.
The power fold away mirror system consists of the fol-
lowing components: mirror switch, side view mirror,relay, wires and fuse. Refer to the appropriate wiring
information. The wiring information includes wiring
diagrams, proper wire and connector repair procedures,
details of wire harness routing and retention, connector
pin-out information and location views for the various
wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
REMOVAL
(1)Disconnect and isolate the battery negative cable.
(2) Remove the upper and lower steering column
shroud (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/LOWER
SHROUD - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect electrical harness connector.
(4) Remove switch from steering column shroud
(Fig. 3).
Fig. 2 POWER FOLDAWAY MIRROR SWITCH
1 - POWER FOLDAWAY MIRROR SWITCH
2 - STEERING COLUMN
Fig. 3 POWER FOLDING MIRROR SWITCH
1 - STEERING COLUMN SHROUD
2 - POWER FOLDAWAY SWITCH
RSPOWER MIRRORS8N-29
AUTOMATIC DAY / NIGHT MIRROR (Continued)
Page 464 of 2339
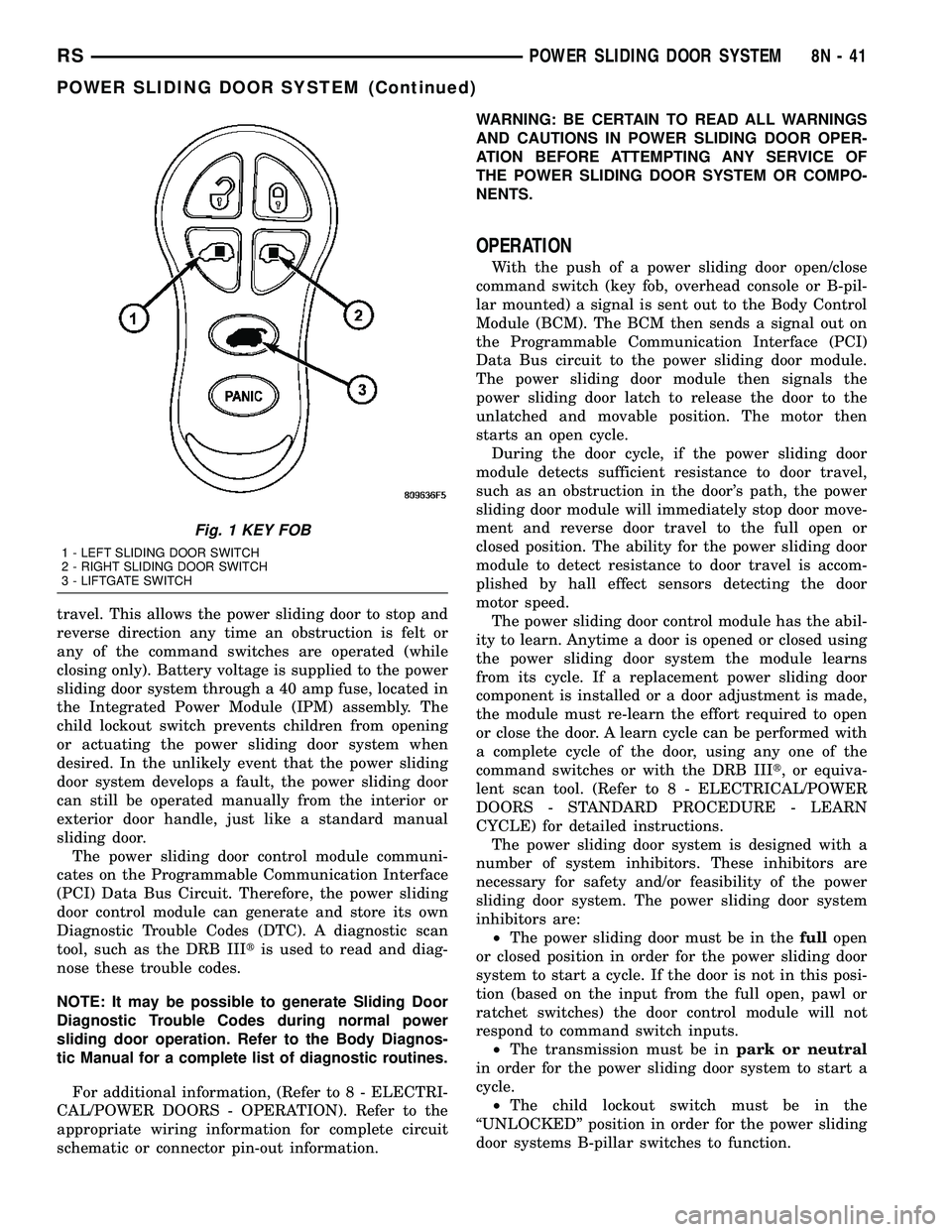
travel. This allows the power sliding door to stop and
reverse direction any time an obstruction is felt or
any of the command switches are operated (while
closing only). Battery voltage is supplied to the power
sliding door system through a 40 amp fuse, located in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM) assembly. The
child lockout switch prevents children from opening
or actuating the power sliding door system when
desired. In the unlikely event that the power sliding
door system develops a fault, the power sliding door
can still be operated manually from the interior or
exterior door handle, just like a standard manual
sliding door.
The power sliding door control module communi-
cates on the Programmable Communication Interface
(PCI) Data Bus Circuit. Therefore, the power sliding
door control module can generate and store its own
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC). A diagnostic scan
tool, such as the DRB IIItis used to read and diag-
nose these trouble codes.
NOTE: It may be possible to generate Sliding Door
Diagnostic Trouble Codes during normal power
sliding door operation. Refer to the Body Diagnos-
tic Manual for a complete list of diagnostic routines.
For additional information, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/POWER DOORS - OPERATION). Refer to the
appropriate wiring information for complete circuit
schematic or connector pin-out information.WARNING: BE CERTAIN TO READ ALL WARNINGS
AND CAUTIONS IN POWER SLIDING DOOR OPER-
ATION BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY SERVICE OF
THE POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM OR COMPO-
NENTS.
OPERATION
With the push of a power sliding door open/close
command switch (key fob, overhead console or B-pil-
lar mounted) a signal is sent out to the Body Control
Module (BCM). The BCM then sends a signal out on
the Programmable Communication Interface (PCI)
Data Bus circuit to the power sliding door module.
The power sliding door module then signals the
power sliding door latch to release the door to the
unlatched and movable position. The motor then
starts an open cycle.
During the door cycle, if the power sliding door
module detects sufficient resistance to door travel,
such as an obstruction in the door's path, the power
sliding door module will immediately stop door move-
ment and reverse door travel to the full open or
closed position. The ability for the power sliding door
module to detect resistance to door travel is accom-
plished by hall effect sensors detecting the door
motor speed.
The power sliding door control module has the abil-
ity to learn. Anytime a door is opened or closed using
the power sliding door system the module learns
from its cycle. If a replacement power sliding door
component is installed or a door adjustment is made,
the module must re-learn the effort required to open
or close the door. A learn cycle can be performed with
a complete cycle of the door, using any one of the
command switches or with the DRB IIIt, or equiva-
lent scan tool. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
DOORS - STANDARD PROCEDURE - LEARN
CYCLE) for detailed instructions.
The power sliding door system is designed with a
number of system inhibitors. These inhibitors are
necessary for safety and/or feasibility of the power
sliding door system. The power sliding door system
inhibitors are:
²The power sliding door must be in thefullopen
or closed position in order for the power sliding door
system to start a cycle. If the door is not in this posi-
tion (based on the input from the full open, pawl or
ratchet switches) the door control module will not
respond to command switch inputs.
²The transmission must be inpark or neutral
in order for the power sliding door system to start a
cycle.
²The child lockout switch must be in the
ªUNLOCKEDº position in order for the power sliding
door systems B-pillar switches to function.
Fig. 1 KEY FOB
1 - LEFT SLIDING DOOR SWITCH
2 - RIGHT SLIDING DOOR SWITCH
3 - LIFTGATE SWITCH
RSPOWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM8N-41
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 488 of 2339

RESTRAINTS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
RESTRAINTS
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................4
WARNING
WARNINGS...........................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM . 6
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HANDLING
AIRBAGS.............................6
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SERVICE
AFTER AN AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT.........7
BELT TENSION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION..........................8
OPERATION............................9
CHILD RESTRAINT ANCHOR
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION...........................10
CLOCKSPRING
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................11
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CLOCKSPRING
CENTERING.........................11
REMOVAL.............................12
INSTALLATION.........................12
CURTAIN AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................13
REMOVAL.............................14
INSTALLATION.........................16
DRIVER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................16
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................18
IMPACT SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................18
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................21
KNEE BLOCKER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION.........................22
OPERATION...........................22
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................23
OCCUPANT CLASSIFICATION MODULE
DESCRIPTION.........................25
OPERATION...........................25
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................26OCCUPANT RESTRAINT CONTROLLER
DESCRIPTION.........................27
OPERATION...........................28
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
PASSENGER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................30
REMOVAL.............................30
INSTALLATION.........................32
PASSENGER AIRBAG DISABLED INDICATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................33
OPERATION...........................33
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
SEAT BELT BUCKLE - FRONT INBOARD
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
SEAT BELT BUCKLE - FIRST ROW INBOARD -
QUAD BUCKET
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................36
SEAT BELT BUCKLE - FIRST ROW - BENCH
REMOVAL.............................36
INSTALLATION.........................37
SEAT BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW
INBOARD - 50/50 BENCH
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................38
SEAT BELT HEIGHT ADJUSTER-BOR
C-PILLAR
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................38
SEAT BELT HEIGHT ADJUSTER KNOB
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................38
SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR - OUTBOARD -
FRONT
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................39
SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR - FIRST ROW -
OUTBOARD
REMOVAL.............................39
INSTALLATION.........................40
SEAT BELT BUCKLE - SECOND ROW - THREE
PASSENGER BENCH
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
RSRESTRAINTS8O-1
Page 489 of 2339

SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR - SECOND ROW -
RIGHT OUTBOARD
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR - SECOND ROW -
RIGHT OUTBOARD WITH REAR HVAC - LWB
REMOVAL.............................41
INSTALLATION.........................41
SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR - SECOND ROW -
LEFT OUTBOARD
REMOVAL.............................42INSTALLATION.........................42
SEAT BELT TENSIONER
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................43
SEAT WEIGHT BLADDER & PRESSURE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................43
OPERATION...........................44
RESTRAINTS
DESCRIPTION
This vehicle is equipped with a Frontal Impact Air-
bag System, which utilizes the driver/passenger air-
bags, two front impact sensors, and seat belt
tensioners located in the front seat belt buckles. This
system is designed to protect occupants in the event
of a front impact collision. These airbags are all ser-
viceable parts. The tensioners are integral to the
front seat belt buckles. If these pyrotechnics are
deployed or defective, they must be replaced.
Vehicles equipped with the Side Impact Airbag
System utilize a curtain airbag, three side impact
sensors, and the Occupant Restraint Controller
(ORC) to determine if the airbag should be deployed.
Following a side impact event where the side airbag
was deployed, the headliner as well as the curtain
airbag must be replaced.
The occupant restraints include both active and
passive types. Active restraints are those which
require the vehicle occupants to take some action to
employ, such as fastening a seat belt; while passive
restraints require no action by the vehicle occupants
to be employed.
ACTIVE RESTRAINTS
The active restraints include:
²Front Seat Belts- Both front seating positions
are equipped with three-point seat belt systems
employing a lower B-pillar mounted inertia latch-
type retractor, height-adjustable upper B-pillar
mounted turning loops, a fixed lower seat belt anchor
secured to the lower B-pillar, and a traveling end-re-
lease buckle secured to the inboard side of the seat
cushion frame. The driver side front seat belt buckle
includes an integral Hall-effect seat belt switch that
detects whether the driver side front seat belt has
been fastened.²Rear Seat Belts- Both outboard rear second
and third seating positions are equipped with three-
point seat belt systems. The outboard seating posi-
tion belts employ a lower C or D-pillar mounted
inertia latch-type retractor, a fixed position upper C
or D-pillar mounted turning loop, and a fixed lower
seat belt anchor secured to the inboard side of the
seat cushion frame.
²Child Restraint Anchors- Also equipped in
this vehicle are two, fixed-position, child seat upper
tether anchors located on the lower seat cushion, in
the rear of the lower seat cushion. There is one
anchor integral to the back of the third row seat back
panel, one on each seat back panel. Two lower second
row anchors are also provided for each rear outboard
seating position. The lower anchors are integral to
the seat cushion frame and are accessed from the
front of the second row seat where the seat back
meets the seat cushion.
PASSIVE RESTRAINTS
The passive restraints available for this model
include the following:
²Dual Front Airbags- Multistage driver. front
passenger, and driver knee blocker airbags are avail-
able for this model. This airbag system is a passive,
inflatable, Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) and
vehicles with this equipment can be readily identified
by the ªSRS - AIRBAGº logo molded into the driver
airbag trim cover in the center of the steering wheel
and also into the passenger airbag door on the
instrument panel above the glove box. Vehicles with
the airbag system can also be identified by the airbag
indicator, which will illuminate in the instrument
cluster for about seven seconds as a bulb test each
time the ignition switch is turned to the ON position.
A pyrotechnic-type seat belt tensioner is integral to
the driver and passenger front seat belt buckle of all
models equipped with dual front airbags.
8O - 2 RESTRAINTSRS
Page 490 of 2339
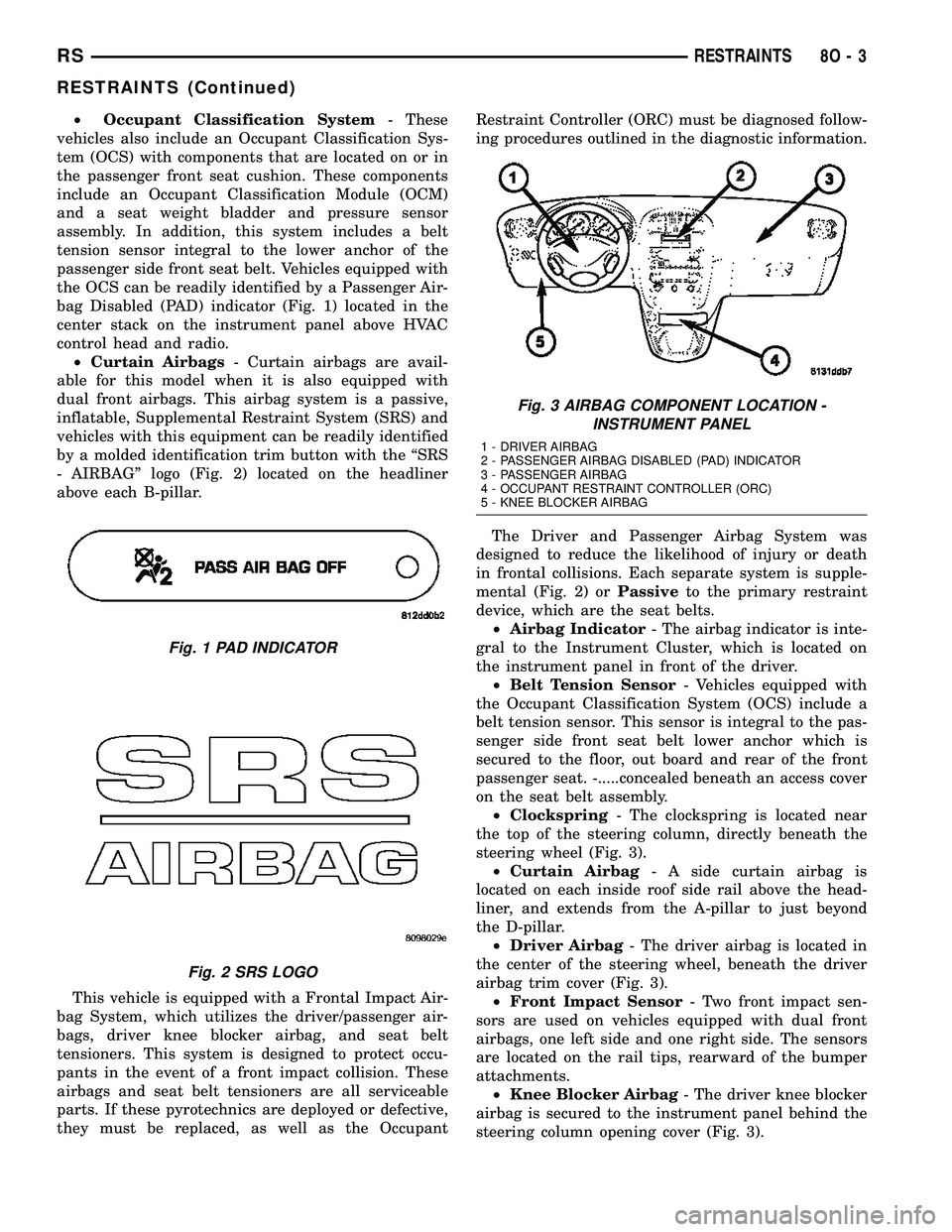
²Occupant Classification System- These
vehicles also include an Occupant Classification Sys-
tem (OCS) with components that are located on or in
the passenger front seat cushion. These components
include an Occupant Classification Module (OCM)
and a seat weight bladder and pressure sensor
assembly. In addition, this system includes a belt
tension sensor integral to the lower anchor of the
passenger side front seat belt. Vehicles equipped with
the OCS can be readily identified by a Passenger Air-
bag Disabled (PAD) indicator (Fig. 1) located in the
center stack on the instrument panel above HVAC
control head and radio.
²Curtain Airbags- Curtain airbags are avail-
able for this model when it is also equipped with
dual front airbags. This airbag system is a passive,
inflatable, Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) and
vehicles with this equipment can be readily identified
by a molded identification trim button with the ªSRS
- AIRBAGº logo (Fig. 2) located on the headliner
above each B-pillar.
This vehicle is equipped with a Frontal Impact Air-
bag System, which utilizes the driver/passenger air-
bags, driver knee blocker airbag, and seat belt
tensioners. This system is designed to protect occu-
pants in the event of a front impact collision. These
airbags and seat belt tensioners are all serviceable
parts. If these pyrotechnics are deployed or defective,
they must be replaced, as well as the OccupantRestraint Controller (ORC) must be diagnosed follow-
ing procedures outlined in the diagnostic information.
The Driver and Passenger Airbag System was
designed to reduce the likelihood of injury or death
in frontal collisions. Each separate system is supple-
mental (Fig. 2) orPassiveto the primary restraint
device, which are the seat belts.
²Airbag Indicator- The airbag indicator is inte-
gral to the Instrument Cluster, which is located on
the instrument panel in front of the driver.
²Belt Tension Sensor- Vehicles equipped with
the Occupant Classification System (OCS) include a
belt tension sensor. This sensor is integral to the pas-
senger side front seat belt lower anchor which is
secured to the floor, out board and rear of the front
passenger seat. -.....concealed beneath an access cover
on the seat belt assembly.
²Clockspring- The clockspring is located near
the top of the steering column, directly beneath the
steering wheel (Fig. 3).
²Curtain Airbag- A side curtain airbag is
located on each inside roof side rail above the head-
liner, and extends from the A-pillar to just beyond
the D-pillar.
²Driver Airbag- The driver airbag is located in
the center of the steering wheel, beneath the driver
airbag trim cover (Fig. 3).
²Front Impact Sensor- Two front impact sen-
sors are used on vehicles equipped with dual front
airbags, one left side and one right side. The sensors
are located on the rail tips, rearward of the bumper
attachments.
²Knee Blocker Airbag- The driver knee blocker
airbag is secured to the instrument panel behind the
steering column opening cover (Fig. 3).
Fig. 1 PAD INDICATOR
Fig. 2 SRS LOGO
Fig. 3 AIRBAG COMPONENT LOCATION -
INSTRUMENT PANEL
1 - DRIVER AIRBAG
2 - PASSENGER AIRBAG DISABLED (PAD) INDICATOR
3 - PASSENGER AIRBAG
4 - OCCUPANT RESTRAINT CONTROLLER (ORC)
5 - KNEE BLOCKER AIRBAG
RSRESTRAINTS8O-3
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 491 of 2339

²Occupant Classification Module- Vehicles
equipped with the Occupant Classification System
(OCS) include an Occupant Classification Module
(OCM) which is secured to a stamped steel mounting
bracket on the underside of the passenger side front
seat cushion frame.
²Occupant Restraint Controller- The Occu-
pant Restraint Controller (ORC) is also sometimes
referred to as the Airbag Control Module (ACM). The
ORC is located on a mount on the floor transmission
tunnel just underneath the instrument panel center
stack (Fig. 3).
²Passenger Airbag- The passenger airbag is
located on the instrument panel, beneath the instru-
ment panel top pad and above the glove box on the
passenger side of the vehicle (Fig. 3).
²Passenger Airbag Disabled (PAD) Indicator
- Vehicles equipped with the Occupant Classification
System (OCS) include a passenger airbag disabled
(PAD) indicator which is located in the instrument
panel center stack (Fig. 3).
²Passenger Knee Blocker- The passenger knee
blocker is a structural reinforcement that is integral
to and concealed within the glove box door (Fig. 3).
²Seat Belt Tensioner- A seat belt tensioner is
integral to both front seat belt buckles. The seat belt
buckles are secured to the inner seat frame sides,
beneath a cushion trim panel.
²Seat Weight Bladder and Pressure Sensor
Assembly- Vehicles equipped with the Occupant
Classification System (OCS) include a seat weight
bladder that is sandwiched between an insulator pad
on the top of the passenger side front seat pan and
the seat cushion foam padding. A short hose connects
the bladder to a pressure sensor which is secured to
the Occupant Classification Module (OCM) mounting
bracket on the underside of the passenger side front
seat cushion frame.
²Side Impact Sensors- Six side impact sensors
are used on vehicles equipped with the curtain air-
bags, three left side and three right side. The first
row side impact sensor is located in the B-pillar, just
above the front seat belt retractor. The second row
side impact sensor is located in the sliding side door
track opening, just in front of the C-pillar. The third
row side impact sensor is located behind the quarter
trim panel, above the rear tire wheel well, between
the C and D-pillars.
The ORC, the OCM, and the cluster each contain a
microprocessor and programming that allow them to
communicate with each other using the Programma-
ble Communications Interface (PCI) data bus net-
work. This method of communication is used by the
ORC for control of the airbag indicators.OPERATION
ACTIVE RESTRAINTS
The primary passenger restraints in this or any
other vehicle are the seat belts and child restraint
anchors. Seat belts and child restraint anchors are
referred to as an active restraint because the vehicle
occupants are required to physically fasten and prop-
erly adjust these restraints in order to benefit from
them. See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove
box for more information on the features, use and
operation of all of the active restraints.
PASSIVE RESTRAINTS
The passive restraints are referred to as a supple-
mental restraint system because they were designed
and are intended to enhance the protection for the
occupants of the vehicleONLYwhen used in con-
junction with the seat belts. They are referred to as
passive restraints because the vehicle occupants are
not required to do anything to make them operate;
however, the vehicle occupants must be wearing their
seat belts in order to obtain the maximum safety
benefit from the supplemental restraint system.
The supplemental restraint system electrical cir-
cuits are continuously monitored and controlled by a
microprocessor and software contained within the
Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC). An airbag indi-
cator in the ElectroMechanical Instrument Cluster
(EMIC) illuminates for about seven seconds as a bulb
test each time the ignition switch is turned to the
ON or START positions. Following the bulb test, the
airbag indicator is turned ON or OFF by the ORC to
indicate the status of the supplemental restraint sys-
tem. If the airbag indicator comes ON at any time
other than during the bulb test, it indicates that
there is a problem in the supplemental restraint sys-
tem electrical circuits. Such a problem may cause air-
bags not to deploy when required, or to deploy when
not required.
Deployment of the supplemental restraints
depends upon the angle and severity of an impact.
Deployment is not based upon vehicle speed; rather,
deployment is based upon the rate of deceleration as
measured by the forces of gravity (G force) upon the
impact sensors. When an impact is severe enough,
the microprocessor in the ORC signals the inflator of
the appropriate airbag units to deploy their airbag
cushions. The front seat belt tensioners are provided
with a deployment signal by the ORC in conjunction
with the front airbags. During a frontal vehicle
impact, the knee blockers work in concert with prop-
erly fastened and adjusted seat belts to restrain both
the driver and the front seat passenger in the proper
position for an airbag deployment. The knee blockers
also absorb and distribute the crash energy from the
8O - 4 RESTRAINTSRS
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 492 of 2339

driver and the front seat passenger to the structure
of the instrument panel (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS/KNEE BLOCKER AIRBAG -
DESCRIPTION). The seat belt tensioners remove the
slack from the front seat belts to provide further
assurance that the driver and front seat passenger
are properly positioned and restrained for an airbag
deployment.
When the ORC monitors a problem in any of the
dual front airbag system circuits or components,
including the seat belt tensioners, it stores a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) in its memory and sends
an electronic message to the EMIC to turn on the
airbag indicator. Proper testing of the supplemental
restraint system components, the Programmable
Communications Interface (PCI) data bus, the elec-
tronic message inputs to and outputs from the EMIC
or the ORC, as well as the retrieval or erasure of a
DTC from the ORC or the EMIC requires the use of
a scan tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic infor-
mation.
OCCUPANT CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
The Occupant Classification System (OCS) auto-
matically suppresses or enables passenger airbag and
seat belt tensioner operation based upon whether or
not the passenger side front seat is occupied and, if
the seat is occupied, classifies the size of the occu-
pant and whether the seat is occupied by a child
seat.
The OCS has an Occupant Classification Module
(OCM) that monitors inputs from the seat weight
bladder pressure sensor under the passenger side
front seat cushion and from the belt tension sensor
on the passenger side front seat belt lower anchor.
Based upon those inputs the microprocessor within
the OCM classifies the occupant of the passenger
side front seat. The OCM then sends electronic occu-
pant classification messages to the ORC. The micro-
processor and programming of the ORC uses these
occupant classification messages to determine
whether to enable or disable the deployment circuits
for the passenger airbag and seat belt tensioner.
The OCS electrical circuits and components are
continuously monitored by the OCM, and the OCM is
continuously monitored by the ORC. A passenger air-
bag ON/OFF indicator is located in the instrument
panel center stack area. This indicator receives bat-
tery current whenever the ignition switch is in the
ON or START positions, and illuminates only when
the ORC pulls the indicator control circuit to ground.
The indicator illuminates for about seven seconds as
a bulb test each time the ignition switch is turned to
the ON or START positions. Following the bulb test,
the indicator is turned ON or OFF by the ORC based
upon the electronic occupant classification messagesreceived from the OCM. This indicator is illuminated
whenever the passenger airbag and seat belt ten-
sioner operation has been suppressed, and is turned
OFF whenever they are enabled or when the passen-
ger seat is classified as empty.
When the OCM monitors a problem in any of the
OCS circuits or components, it stores a fault code or
DTC in its memory circuit and sends an electronic
message to the ORC. The ORC then sends an elec-
tronic message to the EMIC to turn ON the airbag
indicator. If for any reason the OCM is unable to
classify the occupant it sends an electronic message
to the ORC, and the ORC suppresses passenger air-
bag and seat belt tensioner operation. Proper testing
of the OCS components, the Programmable Commu-
nications Interface (PCI) data bus, the electronic
message inputs to and outputs from the OCM, the
EMIC or the ORC, as well as the retrieval or erasure
of a DTC's, requires the use of a scan tool. Refer to
the appropriate diagnostic information.
WARNING
WARNINGS
Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable before beginning any airbag system com-
ponent diagnosis, testing, removal, or installa-
tion procedures. Allow system capacitor to
discharge for two minutes before beginning any
component testing or service. This will disable
the airbag system. Failure to disconnect the
battery negative cable may result in accidental
airbag deployment, personal injury, or death.
Do not place an intact undeployed airbag
face down on a solid surface. The airbag will
propel into the air if accidentally deployed and
may result in personal injury or death.
When carrying or handling an undeployed
airbag, the trim side (face) of the airbag should
be pointing towards the body to minimize pos-
sibility of injury if accidental deployment
occurs. Failure to do this may result in per-
sonal injury or death.
Replace airbag system components with
Mopartreplacement parts. Substitute parts
may appear interchangeable, but internal dif-
ferences may result in inferior occupant protec-
tion. Failure to do so may result in occupant
personal injury or death.
Wear safety glasses, rubber gloves, and long
sleeved clothing when cleaning powder residue
from vehicle after airbag deployment. Sodium
hydroxide powder residue emitted from a
deployed airbag can cause skin irritation.
Flush affected area with cool water if irritation
is experienced. If nasal or throat irritation is
RSRESTRAINTS8O-5
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 494 of 2339

UNDEPLOYED AIRBAG
WARNING: The airbags must be stored in its origi-
nal special container until used for service. At no
time should a source of electricity be permitted
near the inflator on the back of an airbag. When
carrying or handling an undeployed airbag, the trim
side of the airbag should be pointing toward the
body to minimize the possibility of personal injury
or death if accidental deployment occurs. Do not
place undeployed airbag face down on a solid sur-
face, the airbag will propel into the air if accidental
deployment occurs.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SERVICE AFTER AN
AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
DRIVER AIRBAG
After a Driver Airbag has been deployed due to a
collision, the followingMUSTbe replaced:
²Driver Airbag
²Clockspring Assembly
²Steering Wheel
²Complete Steering Column Assembly w/Lower
Steering Column Coupler
All other airbag and vehicle components should be
closely inspected following any airbag deployment,
and should be replaced when visible damage is
incurred.
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
PASSENGER AIRBAG
After a Passenger Airbag has been deployed due to
a collision. the followingMUSTbe replaced:
²Passenger Airbag
²Instrument Panel and Pad Assembly
All other airbag and vehicle components should be
closely inspected following any airbag deployment,
and should be replaced when visible damage is
incurred.
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
KNEE BLOCKER AIRBAG
After a Knee Blocker Airbag has been deployed due
to a collision. the followingMUSTbe replaced:
²Knee Blocker Airbag
²Instrument Panel and Pad Assembly
All other airbag and vehicle components should be
closely inspected following any airbag deployment,
and should be replaced when visible damage is
incurred.
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
CURTAIN AIRBAG
After a Curtain Airbag has been deployed due to a
collision. the followingMUSTbe replaced:
²Curtain Airbag Assembly
²Headliner
²A, B, and C-Pillar Trim on deployed side.
All other airbag and vehicle components should be
closely inspected following any airbag deployment,
and should be replaced when visible damage is
incurred.
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
OCCUPANT CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM (OCS)
After an impact event, either front, rear, or side,
the OCS system components need to be inspected
and replaced if found to be damaged.
This includes:
²Belt Tension Sensor
²Occupant Classification Module (OCM)
²Passenger Airbag ON/Off Indicator
²Seat Weight Bladder and Sensor
RSRESTRAINTS8O-7
RESTRAINTS (Continued)
Page 495 of 2339

WARNING: Never replace both the Occupant Restraint
Controller (ORC) and the Occupant Classification Mod-
ule (OCM) at the same time. If both require replace-
ment, replace one, then perform the Airbag System
test (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM) before replac-
ing the other. Both the ORC and the OCM store
Occupant Classification System (OCS) calibration
data, which they transfer to one another when one of
them is replaced. If both are replaced at the same
time, an irreversible fault will be set in both modules
and the OCS may malfunction and result in personal
injury or death.
Whether replaced or not, the OCS must be re-ze-
roed to make sure that the system in within proper
parameters to sense the occupants weight correctly.
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
WARNING: Following successful completion of the
Airbag System test procedure, the Occupant Classi-
fication System Verification Test must be done
using a scan tool and the appropriate diagnostic
information. Personal injury or death may result if
the system test is not performed.
SEAT BELTS AND TENSIONERS
After a frontal impact where an airbag has been
deployed due to a collision. the followingMUSTbe
replaced:
²Front Seat Belt Buckle (driver and passenger)
with integral Tensioners.
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
All other seat belts should be closely inspected for
cuts, tears, fraying, or damage in any way following
any frontal impact or airbag deployment. The other
seat belts are to be replaced when visible damage is
incurred. Inspect the Lower Anchors and Tether for
CHildren (LATCH) child restraint anchors for dam-
age after an impact event and replace as needed.
CLEAN UP PROCEDURE
Roll or fold the airbag towards its mounting point
(i.e. instrument panel, steering wheel, knee blocker,curtain, or seat back). Then tape the ripped cover
over the deployed airbag if applicable.
Use a vacuum cleaner to remove any residual pow-
der from the vehicle interior. Work from the outside
in to avoid kneeling or sitting in a contaminated
area. Vacuum the heater and A/C outlets as well (Fig.
4). If the heater or air conditioner was in RECIRC
mode at time of airbag deployment, operate blower
motor on low speed and vacuum powder residue
expelled from the heater and A/C outlets. Multiple
vacuum cleaning may be necessary to decontaminate
the interior of the vehicle.
BELT TENSION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the Occupant Classification
System (OCS) include a belt tension sensor (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4 VACUUM HEATER AND A/C OUTLETS - TYPICAL
Fig. 5 BELT TENSION SENSOR
1 - SEAT BELT WEBBING
2 - B-PILLAR
3 - SEAT BELT LOWER ANCHOR BOLT
4 - BELT TENSION SENSOR
8O - 8 RESTRAINTSRS
RESTRAINTS (Continued)