diagram CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 336 of 2339

STARTING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STARTING
DESCRIPTION.........................31
OPERATION...........................31
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM TEST.......................31
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONTROL
CIRCUIT TEST........................33
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
RESISTANCE TEST....................35
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
TEST...............................36SPECIFICATIONS
Torques.............................36
STARTER ...........................37
STARTER MOTOR
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L......................37
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L...................38
REMOVAL - 2.5L......................38
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L..................39
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L................39
INSTALLATION - 2.5L..................39
STARTING
DESCRIPTION
The starting system consists of:
²Starter relay
²Starter motor (including an integral starter sole-
noid)
Other components to be considered as part of start-
ing system are:
²Battery
²Battery cables
²Ignition switch and key lock cylinder
²Clutch pedal position switch (manual transmis-
sion)
²Park/neutral position switch (automatic trans-
mission)
²Wire harnesses and connections.
The Battery, Starting, and Charging systems oper-
ate in conjunction with one another, and must be
tested as a complete system. For correct operation of
starting/charging systems, all components used in
these 3 systems must perform within specifications.
When attempting to diagnose any of these systems, it
is important that you keep their interdependency in
mind.
The diagnostic procedures used in each of these
groups include the most basic conventional diagnostic
methods, to the more sophisticated On-Board Diag-
nostics (OBD) built into the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM). Use of an induction-type milliampere
ammeter, volt/ohmmeter, battery charger, carbon pile
rheostat (load tester), and 12-volt test lamp may be
required.
OPERATION
These components form two separate circuits. A
high amperage circuit that feeds the starter motor up
to 300+ amps, and a control circuit that operates on
less than 20 amps.
The PCM controls a double start over-ride safety
that does not allow the starter to be engaged if the
engine is already running.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM TEST
For circuit descriptions and diagrams, refer to the
Wiring Diagrams.
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO THE PASSIVE RESTRAINT SYS-
TEMS BEFORE ATTEMPTING STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
INSPECTION
Before removing any unit from the starting system
for repair or diagnosis, perform the following inspec-
tions:
²Battery- Visually inspect the battery for indi-
cations of physical damage and loose or corroded
cable connections. Determine the state-of-charge and
cranking capacity of the battery. Charge or replace
RSSTARTING8F-31
Page 337 of 2339
the battery, if required. Refer to the Battery section
for more information.
²Ignition Switch- Visually inspect the ignition
switch for indications of physical damage and loose
or corroded wire harness connections.
²Transmission Range Sensor or Park/Neu-
tral Switch- Visually inspect the transmission
range sensor for indications of physical damage and
loose or corroded wire harness connections.
²Starter Relay- Visually inspect the starter
relay for indications of physical damage and loose or
corroded wire harness connections.
²Starter Motor- Visually inspect the starter
motor for indications of physical damage and loose or
corroded wire harness connections.²Starter Solenoid- Visually inspect the starter
solenoid for indications of physical damage and loose
or corroded wire harness connections.
²Wiring- Visually inspect the wire harness for
damage. Repair or replace any faulty wiring, as
required. Check for loose or corroded wire harness
connections at main engine ground and remote jump
post.
²Power Distribution Center (PDC)- Visually
inspect the B+ connections at the PDC for physical
damage and loose or corroded harness connections.
STARTING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER FAILS
TO ENGAGE.1. BATTERY
DISCHARGED OR
FAULTY.1. REFER TO THE BATTERY SECTION FOR MORE
INFORMATION. CHARGE OR REPLACE BATTERY, IF
REQUIRED.
2. STARTING CIRCUIT
WIRING FAULTY.2. REFER TO FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST AND FEED
CIRCUIT TEST IN THIS SECTION.
3. STARTER RELAY
FAULTY.3. REFER TO RELAY TEST, IN THIS SECTION. REPLACE
RELAY, IF NECESSARY.
4. IGNITION SWITCH
FAULTY.4. REFER TO IGNITION SWITCH TEST, IN THE STEERING
SECTION OR 8 WIRING DIAGRAMS. REPLACE SWITCH, IF
NECESSARY.
5. PARK/NEUTRAL
POSITION SWITCH
(AUTO TRANS) FAULTY
OR MIS-ADJUSTED.5. REFER PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH TEST, IN THE
TRANSAXLE. SECTION FOR MORE INFORMATION. REPLACE
SWITCH, IF NECESSARY.
6. CLUTCH INTERLOCK
SWITCH (MAN TRANS)
FAULTY.6. REFER TO CLUTCH PEDAL POSITION SWITCH TEST, IN
THE CLUTCH. SECTION. REPLACE SWITCH, IF NECESSARY.
7. STARTER SOLENOID
FAULTY.7. REFER TO SOLENOID TEST, IN THIS SECTION. REPLACE
STARTER ASSEMBLY, IF NECESSARY.
8. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.8. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
9. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR.9. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETH AND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
10. PCM DOUBLE
START OVERRIDE
OUTPUT FAILURE.10. REFER TO PCM DIAGNOSTIC. CHECK FOR CONTINUITY
BETWEEN PCM AND TERMINAL 85. REPAIR OPEN CIRCUIT
AS REQUIRED. IF OK, PCM MAY BE DEFECTIVE.
STARTER
ENGAGES,
FAILS TO TURN
ENGINE.1. BATTERY
DISCHARGED OR
FAULTY.1. REFER TO THE BATTERY SECTION FOR MORE
INFORMATION. CHARGE OR REPLACE BATTERY AS
NECESSARY.
8F - 32 STARTINGRS
STARTING (Continued)
Page 340 of 2339

RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the PDC fuse as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the starter solenoid field coils. There should be
continuity between the cavity for relay terminal 87
and the starter solenoid terminal at all times. If OK,
go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit to the
starter solenoid as required.
(4) The coil battery terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is energized when
the ignition switch is held in the Start position and
the clutch pedal is depressed (manual trans). Check
for battery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 86
with the ignition switch in the Start position and the
clutch pedal is depressed (manual trans), and no
voltage when the ignition switch is released to the
On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, check for
an open or short circuit to the ignition switch and
repair, if required. If the circuit to the ignition switch
is OK, see the Ignition Switch Test procedure in this
group.
(5) The coil ground terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is grounded by the
PCM if the conditions are right to start the car. For
automatic trans. cars the PCM must see Park Neu-
tral switch low and near zero engine speed (rpm).
For manual trans. cars the PCM only needs to see
near zero engine speed (rpm) and low clutch inter-
lock input and see near zero engine speed (rpm). To
diagnose the Park Neutral switch of the trans range
sensor refer to the transaxle section. Check for conti-
nuity to ground while the ignition switch is in the
start position and if equipped the clutch pedal
depressed. If not OK and the vehicle has an auto-
matic trans. verify Park Neutral switch operation. If
that checks OK check for continuity between PCM
and the terminal 86. Repair open circuit as required.
Also check the clutch interlock switch operation if
equipped with a manual transmission. If OK, the
PCM may be defective.
SAFETY SWITCHES
For diagnostics of the Transmission Range Sensor,
refer to the Transaxle section for more information.
If equipped with Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch,
refer to Diagnosis and Testing in the Clutch section.
IGNITION SWITCH
After testing starter solenoid and relay, test igni-
tion switch and wiring. Refer to the Ignition Section
or Wiring Diagrams for more information. Check all
wiring for opens or shorts, and all connectors for
being loose or corroded.
BATTERY
For battery diagnosis and testing, refer to the Bat-
tery section for procedures.
ALL RELATED WIRING AND CONNECTORS
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for more information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
RESISTANCE TEST
Before proceeding with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter,
accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition and Fuel systems must be dis-
abled to prevent engine start while performing the
following tests.
(1) To disable the Ignition and Fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(2) Gain access to battery terminals.
(3) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following:
(a) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative post, and positive lead to the
battery negative cable clamp. Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between cable clamp and post.
(b) Connect positive lead of the voltmeter to the
battery positive post, and negative lead to the bat-
tery positive cable clamp. Rotate and hold the igni-
tion switch key in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between the cable clamp and post.
(c) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to battery
negative terminal, and positive lead to engine
block near the battery cable attaching point.
Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct
poor contact at ground cable attaching point. If
voltage reading is still above 0.2 volt after correct-
ing poor contacts, replace ground cable.
(4) Connect positive voltmeter lead to the starter
motor housing and the negative lead to the battery
negative terminal. Hold the ignition switch key in
RSSTARTING8F-35
STARTING (Continued)
Page 347 of 2339

OPERATION
When the rear window defogger button is
depressed to the On position, current is directed to
the rear defogger grid lines and the heated power
mirrors (if equipped). The heated grid lines heat the
glass to help clear the rear window and side mirror
surfaces of fog or frost.
The electric backlight (EBL) system is controlled
by a momentary switch located in the A/C-heater
control on the instrument panel. A yellow indicator in
the switch will illuminate to indicate when the sys-
tem is turned on. The integrated power module (IPM)
contains the EBL system control circuitry.
NOTE: The rear window defogger turns off automat-
ically after approximately 10 minutes of initial oper-
ation. Each following activation cycle of the
defogger system will last approximately five min-
utes.
The EBL system will be automatically turned off
after a programmed time interval of about ten min-
utes. After the initial time interval has expired, if the
defogger switch is turned on again during the same
ignition cycle, the defogger system will automatically
turn off after about five minutes.
The EBL system will automatically shut off if the
ignition switch is turned to the Off position, or it can
be turned off manually by depressing the defogger
switch a second time.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ELECTRIC BACKLIGHT (EBL) SYSTEM
NOTE: Illumination of the defogger switch indicator
lamp means that there is electrical current available
at the output of the rear window defogger logic cir-
cuitry, but does not confirm that the electrical cur-
rent is reaching the rear glass heating grid lines.
NOTE: For circuit descriptions and diagrams of the
rear window defogger system, refer to 8W - WIRING
DIAGRAM INFORMATION.
Operation of the electrical backlight (EBL) system
can be confirmed by the following:(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position. Set
the defogger switch in the On position. The rear win-
dow defogger operation can be checked by feeling the
rear window glass. A distinct difference in tempera-
ture between the grid lines and the adjacent clear
glass can be detected within three to four minutes of
operation.
(2) If a temperature difference is not detected, use
a 12-volt DC voltmeter and contact the rear glass
heating grid terminal B with the negative lead, and
terminal A with the positive lead (Fig. 2). The volt-
meter should read battery voltage. If the voltmeter
does not read battery voltage, check the following:
²Confirm that the ignition switch is in the On
position.
²Make sure that the rear glass heating grid feed
wire and ground wire are connected to the terminals.
Confirm that the ground wire has continuity to
ground.
²Check that fuse 13 (40 amp) in the integrated
power module (IPM) is OK. The fuse must be tight in
it's receptacle and all electrical connections must be
secure.
(3) When the above steps have been completed and
the rear glass heating grid is still inoperative, one or
more of the following is faulty. It may be necessary to
connect a DRBIIItscan tool to perform further diag-
nostics. Refer to Body Diagnostic Procedures.
²Rear window defogger switch in the A/C-heater
control.
²J1850 bus communication between the A/C-
heater control and the front control module (FCM).
²Rear window defogger (EBL) relay in the IPM.
²Rear window defogger (EBL) relay control circu-
ity in the IPM.
²Check for a loose wire connector or a wire
pushed out of a connector.
²Rear window grid lines (all grid lines would
have to be broken, or the power feed or ground wire
not connected, for the entire heating grid to be inop-
erative).
(4) If the system operation has been verified but
defogger switch LED indicator does not illuminate,
replace the A/C-heater control.
8G - 2 HEATED GLASSRS
HEATED GLASS (Continued)
Page 348 of 2339
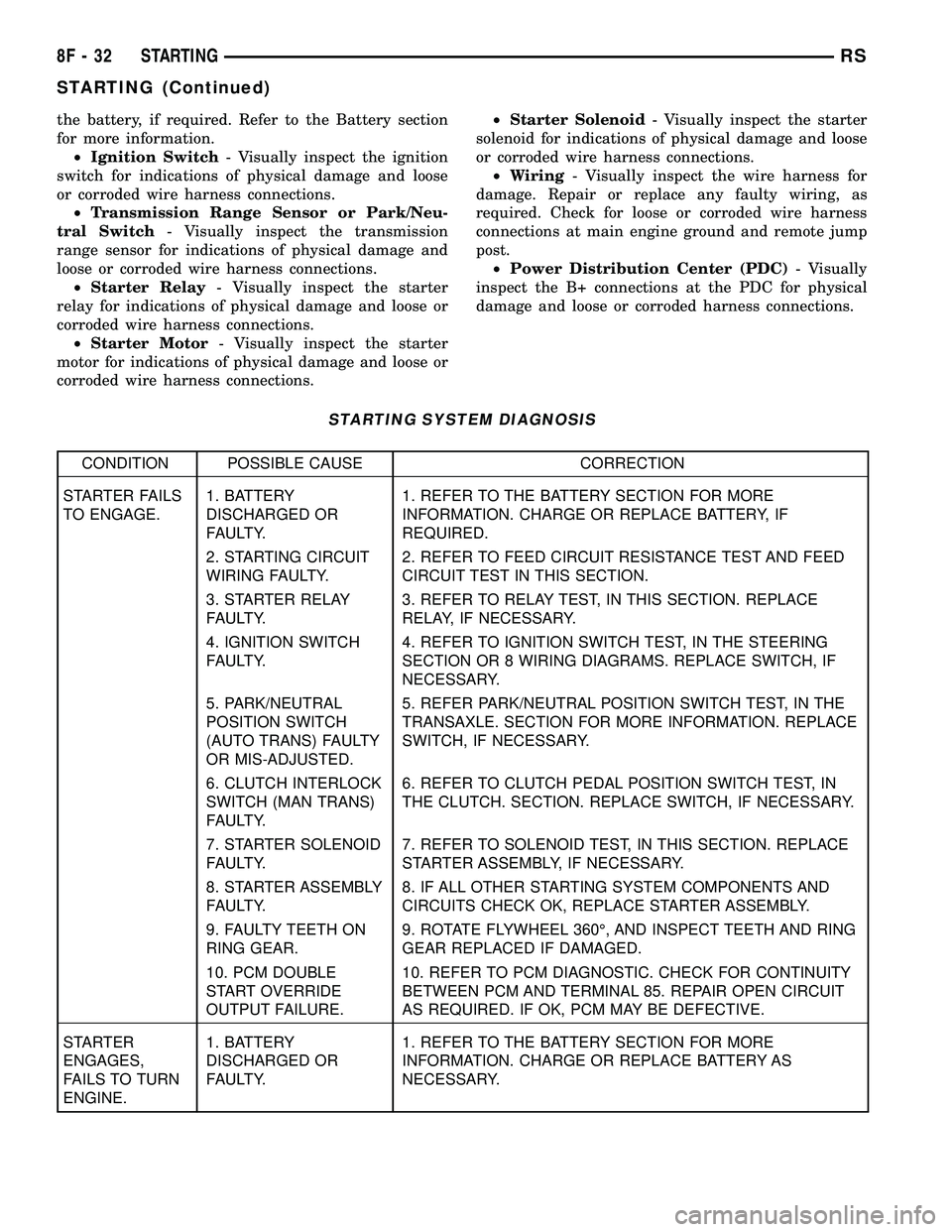
(5) If broken defogger grid lines are suspected, use
a 12-volt DC voltmeter and contact terminal B with
the negative lead and each rear glass heating grid
line at it's mid-point with the positive lead. The volt-
meter should read approximately 6 volts at each grid
line mid-point C. If the voltmeter does not read
approximately 6 volts, repair the open grid line(s)
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/HEATED GLASS/REAR
WINDOW DEFOGGER GRID - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
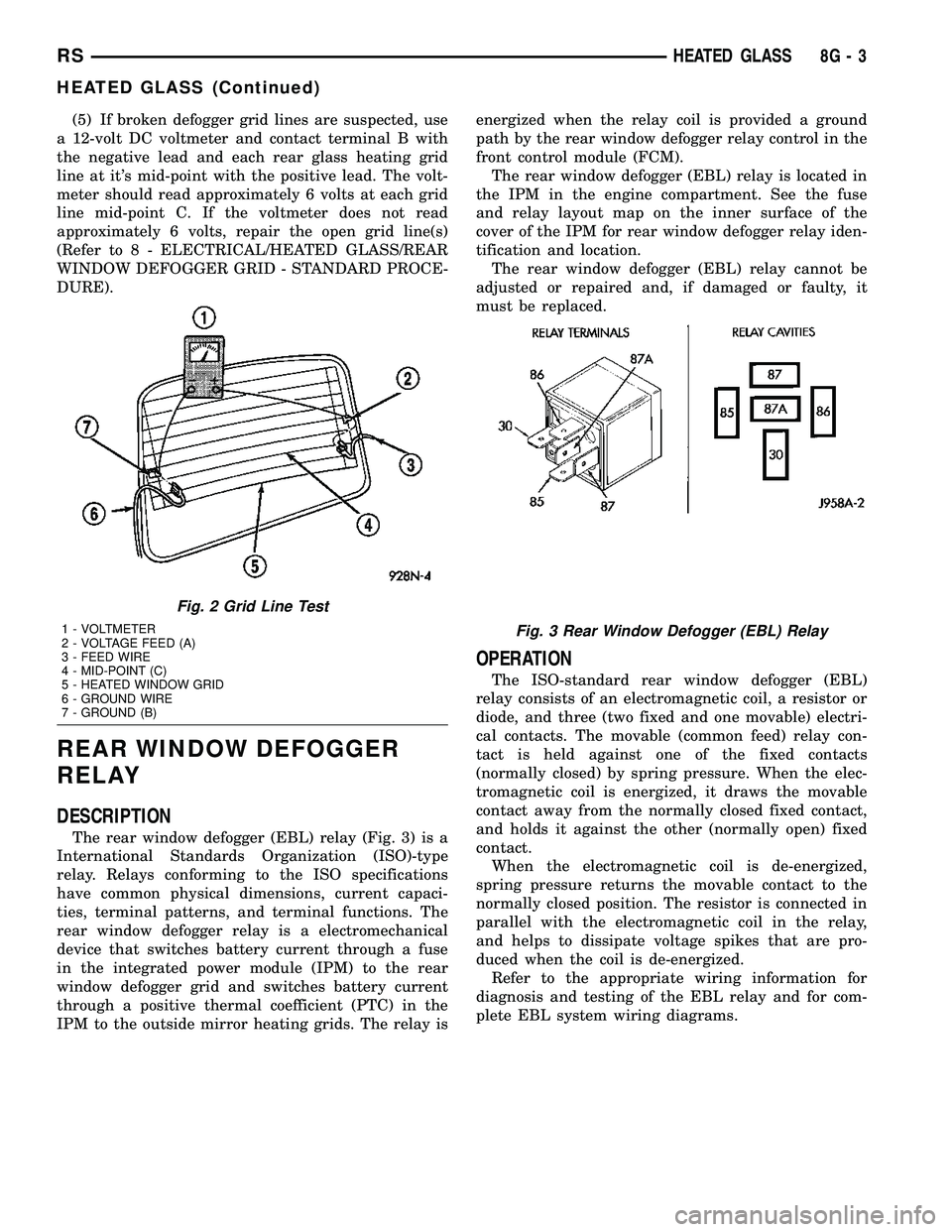
The rear window defogger (EBL) relay (Fig. 3) is a
International Standards Organization (ISO)-type
relay. Relays conforming to the ISO specifications
have common physical dimensions, current capaci-
ties, terminal patterns, and terminal functions. The
rear window defogger relay is a electromechanical
device that switches battery current through a fuse
in the integrated power module (IPM) to the rear
window defogger grid and switches battery current
through a positive thermal coefficient (PTC) in the
IPM to the outside mirror heating grids. The relay isenergized when the relay coil is provided a ground
path by the rear window defogger relay control in the
front control module (FCM).
The rear window defogger (EBL) relay is located in
the IPM in the engine compartment. See the fuse
and relay layout map on the inner surface of the
cover of the IPM for rear window defogger relay iden-
tification and location.
The rear window defogger (EBL) relay cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if damaged or faulty, it
must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO-standard rear window defogger (EBL)
relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a resistor or
diode, and three (two fixed and one movable) electri-
cal contacts. The movable (common feed) relay con-
tact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor is connected in
parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the relay,
and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are pro-
duced when the coil is de-energized.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
diagnosis and testing of the EBL relay and for com-
plete EBL system wiring diagrams.
Fig. 2 Grid Line Test
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - VOLTAGE FEED (A)
3 - FEED WIRE
4 - MID-POINT (C)
5 - HEATED WINDOW GRID
6 - GROUND WIRE
7 - GROUND (B)Fig. 3 Rear Window Defogger (EBL) Relay
RSHEATED GLASS8G-3
HEATED GLASS (Continued)
Page 360 of 2339

HORN
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HORN SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
HORN SYSTEM........................1
HORN
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
HORN...............................3REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................4
HORN SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................4
HORN SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAG, REFER TO ELECTRICAL, RESTRAINTS FOR
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS. DISCONNECT THE NEGA-
TIVE CABLE FROM THE BATTERY BEFORE SER-
VICING COMPONENTS INVOLVING THE AIRBAG
SYSTEM. ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT OF AIRBAG
AND PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
The horn circuit consists of a horn switch, clock-
spring, horn relay, horns and Integrated Power Mod-
ule (IPM). The horn switch is a membrane switch
located in the airbag trim cover. The horns are
located forward of the left front wheel behind the
bumper fascia.
OPERATION
The horn relay plugs into the Integrated Power
Module (IPM) which is located in the engine com-
partment. For circuit information and component
locations, refer to the appropriate wiring information.
The wiring information includes wiring diagrams,
proper wire and connector repair procedures, details
of wire harness routing and retention, connector pin-
out information and location views for the various
wire harness connectors, splices and grounds.
The horns will not function if the switch is
ªCLOSEDº for more than 30 seconds. Once the
switch is ªOPENº, a 20±30 second delay will occur
before the horns are functional again.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
HORN SYSTEM
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO ELECTRICAL, RESTRAINTS
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
Refer to Horn System Test below. If the horn does
not sound, check horn fuse located in the Integrated
Power Module (IPM). If the fuse is blown, replace
with the correct fuse. If the horns fail to sound and
the new fuse blows when depressing the horn switch,
a short circuit in the horn or the horn wiring
between the fuse terminal and the horn is responsi-
ble, or a defective horn switch allowed the horn to
burn out is responsible.
If the fuse is OK, test horn relay.
If the relay is OK, test horn.
CAUTION: Continuous sounding of horn may
cause horn failure.
Should the horn sound continuously, unplug the
horn relay from IPM.
Refer to the appropriate wiring information.
RSHORN8H-1
Page 362 of 2339

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
(6) CLOCKSPRING
INOPERATIVE.(6) REPLACE CLOCKSPRING.
(7) FRONT CONTROL
MODULE INOPERATIVE.(7) REFER TO ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/FRONT CONTROL MODULE.
FUSE BLOWS WHEN HORN SOUNDS (1) SHORT CIRCUIT IN
HORN OR HORN WIRING.(1) REMOVE HORN RELAY, CHECK
FOR SHORTED HORN OR HORN
WIRING. DISCONNECT HORN WIRE
HARNESS TO ISOLATE SHORT AND
REPAIR AS NECESSARY.
(2) CLOCKSPRING
INOPERATIVE.(2) REPLACE CLOCKSPRING.
FUSE BLOWS WITHOUT BLOWING
HORN(1) SHORT CIRCUIT. (1) REMOVE RELAY, INSTALL NEW
FUSE, IF FUSE DOES NOT BLOW
REPLACE HORN RELAY. IF FUSE
BLOWS WITH RELAY REMOVED,
CHECK FOR SHORT TO GROUND
WITH OHMMETER ON CIRCUIT
BETWEEN TERMINALS 30 & 86 AND
THE FUSE TERMINAL. REPAIR AS
NECESSARY.
(2) CLOCKSPRING
INOPERATIVE.(2) REPLACE CLOCKSPRING.
HORN
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
HORN
HORN
(1) Disconnect wire connector at horn.
(2) Using a voltmeter, connect one lead to ground
terminal and the other lead to the positive wire ter-
minal (Fig. 1).
(3) Depress the horn switch, battery voltage
should be present.
(4) If no voltage, refer toHORNS WILL NOT
SOUND. If voltage is OK, go to step Step 5.
(5) Using ohmmeter, test ground wire for continu-
ity to ground.
(6) If no ground repair as necessary.
(7) If wires test OK and horn does not sound,
replace horn.
HORNS SOUND CONTINUOUSLY
CAUTION: Continuous sounding of horns may
cause relay to fail.
The horn switch (membrane) sometimes can be the
cause without the switch being depressed.(1) Remove the horn relay from the intelligent
power module.
(2)
Using a continuity tester, test continuity from the
X3 cavity of the horn relay to ground. Refer to the
appropriate wiring information. The wiring information
includes wiring diagrams, proper wire and connector
repair procedures, details of wire harness routing and
retention, connector pin-out information and location
views for the various wire harness connectors, splices
and grounds.
(a)If continuity is detected, proceed to step Step 3.
(b) If NO continuity, replace the horn relay.
(3) Remove the airbag trim cover from the steering
wheel and disengage horn connector.
(4) Install horn relay into Integrated Power Mod-
ule (IPM).
(a)
If horn does not sound, replace airbag trim
cover.
(b) If horn sounds, repair grounded X3 circuit
from IPM to clockspring in the steering column.
HORNS WILL NOT SOUND
Check horn fuse#8intheIPM. If fuse is blown,
check for a shorted switch in the airbag module. and
refer to FUSE BLOWN section. If fuse is OK, refer to
FUSE OK section.
FUSE BLOWN
(1) Verify condition of battery terminals and volt-
age, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM
RSHORN8H-3
HORN SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 376 of 2339
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUSTER
DIAGNOSIS
CONDITIONS
Refer to the following tables for possible problems,
causes, and corrections.
²INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS
²SPEEDOMETER DIAGNOSIS
²TACHOMETER DIAGNOSIS²FUEL GAUGE DIAGNOSIS
²TEMPERATURE GAUGE DIAGNOSIS
²ODOMETER DIAGNOSIS
²ELECTRONIC GEAR INDICATOR DISPLAY
DIAGNOSIS
NOTE: Always check the functionality of the cluster
by running the self test prior to troubleshooting.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
INOPERATIVE. NO
RESPONSE FROM
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER.NO PCI BUS MESSAGES
FROM THE BCM.USE A DRB IIITSCAN TOOL TO CHECK THE BCM.
IF OK, LOOK FOR ANOTHER POSSIBLE CAUSE
FOR CLUSTER FAILURE. IF NOT OK, REFER TO
THE PROPER BODY DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
MANUAL.
SPREAD TERMINAL(S)
ON WIRING HARNESS
CLUSTER CONNECTOR.REMOVE CLUSTER FROM INSTRUMENT PANEL
AND CHECK WIRING HARNESS CONNECTOR FOR
SPREAD TERMINAL. IF OK, LOOK FOR ANOTHER
POSSIBLE CAUSE FOR THE CLUSTER FAILURE. IF
NOT OK, REPAIR CONNECTOR.
BCM IS NOT RECEIVING
PROPER INPUT FROM
THE IGNITION SWITCH.1. USE A DRB IIITSCAN TOOL TO VERIFY IGNITION
SWITCH STATUS INTO THE BCM. IF NOT OK, GO
TO STEP (2). IF OK, LOOK AT ANOTHER POSSIBLE
CAUSE OF FAILURE.
2. CHECK IGNITION SWITCH FUNCTION AND
WIRING.
INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.REPLACE CLUSTER.
WAKE UP CIRCUIT
FAULTY.VERIFY CONTINUITY OF WAKE UP CIRCUIT FROM
BCM TO MIC. CIRCUIT SHALL BE LOW WHENEVER
BCM IS AWAKE.
POWER OR GROUND
MISSING.IF NO RESPONSE FROM THE MIC, CHECK FOR
POWER AND GROUND AT THE MIC CONNECTOR.
REFER TO WIRING DIAGRAMS FOR CONNECTOR
CALL OUTS.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-3
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 396 of 2339
HEADLAMP
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEADLAMP
When a vehicle experiences problems with the
headlamp system, verify the condition of the battery
connections, fuses, charging system, headlamp bulbs,
wire connectors, relay, high beam switch, dimmer
switch, and headlamp switch. Refer to the appropri-
ate wiring information.
Each vehicle is equipped with various lamp assem-
blies. A good ground is necessary for proper lighting
operation. Grounding is provided by the lamp socketwhen it comes in contact with the metal body, or
through a separate ground wire.
When changing lamp bulbs check the socket for
corrosion. If corrosion is present, clean it with a wire
brush.
When it is necessary to remove components to ser-
vice another, it should not be necessary to apply
excessive force or bend a component to remove it.
Before damaging a trim component, verify hidden
fasteners or captured edges are not holding the com-
ponent in place.
HEADLAMP DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HEADLAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE IDLING
OR IGNITION TURNED
OFF.1. Loose or corroded battery
cables.1. Clean and secure battery cable clamps and
posts.
2. Loose or worn generator drive
belt.2. Adjust or replace generator drive belt.
3. Charging system output too low. 3. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Electrical, Charging
4. Battery has insufficient charge. 4. Test battery state-of-charge, refer to
Electrical, Battery System.
5. Battery is sulfated or shorted. 5. Load test battery, refer to Electrical, Battery
System.
6. Poor lighting circuit Z343/Z344-
ground.6. Test for voltage drop across Z343/Z344-
ground locations, refer to Electrical, Wiring
Diagram Information.
HEADLAMP BULBS
BURN OUT
FREQUENTLY.1. Integrated Power Module (IPM)
not controlling voltage.1. Test and repair Integrated Power Module.
2. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.2. Inspect and repair all connectors and splices.
Refer to Electrical, Wiring Information.
HEADLAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE
RUNNING ABOVE IDLE.1. Charging system output too low. 1. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Electrical, Wiring Information.
2. Poor lighting circuit Z343/Z344-
ground.2. Test for voltage drop across Z343/Z344-
ground locations, refer to Electrical, Wiring
Information.
3. High resistance in headlamp
circuit.3. Test amperage draw of headlamp circuit.
RSLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR8L-11
Page 403 of 2339

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MULTI-FUNCTION
SWITCH
To test turn signal, headlamp beam select and opti-
cal horn portion of the multi-function switch:
(1) Remove the multi-function switch, refer to
Electrical, Lamps/Lighting - Exterior, Multi-Function
Switch, Removal, and Installation.
(2) Using an ohmmeter check the resistance read-
ings between multi-function switch pins. Refer to
Wiring Diagrams for proper pin numbers and the
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH RESISTANCE table.
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH RESISTANCE
SWITCH
POSITIONPIN NUMBER RESISTANCE
LEFT 2 AND 3 2.7V 5%
RIGHT 2 AND 3 1KV 5%
OPTICAL
HORN2 AND 4 1.7KV 5%
HI BEAM 2 AND 4 2.32KV 5%
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate battery negative cable.
(2) Remove upper and lower steering column
shrouds. Refer to Steering, Column, Shroud,
Removal.
(3) Disconnect wire connector from back of multi-
function switch.
(4) Remove screws holding multi-function switch to
steering column adapter collar.
(5) Remove the multi-function switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the switch on to the steering column.
(2) Install the two retaining screws.
(3) Connect the wire harness connector.
(4) Install the upper and lower steering column
shrouds. Refer to Steering, Column, Shroud, Installa-
tion.
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
PARK/TURN SIGNAL LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate battery negative cable.
(2) Remove headlamp retaining screws.
(3) Twist socket counter - clockwise and remove
(Fig. 20).
(4) Pull bulb from socket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Push bulb into socket.
(2) Twist socket into headlamp.
(3) Install headlamp retaining screws.
(4) Reconnect battery negative cable.
TAIL LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the tail lamp unit. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/TAIL
LAMP UNIT - REMOVAL).
(3) Squeeze the tabs on the bulb socket and
remove from tail lamp unit (Fig. 21).
(4) Pull bulb from lamp socket.
Fig. 20 PARK/TURN SIGNAL LAMP
1 - PARK/TURN SIGNAL LAMP
2 - LAMP SOCKET
Fig. 21 TAIL LAMP SOCKET
1 - LAMP SOCKET
2 - TAIL LAMP UNIT
8L - 18 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORRS
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH (Continued)