headlamp CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 6 of 2339
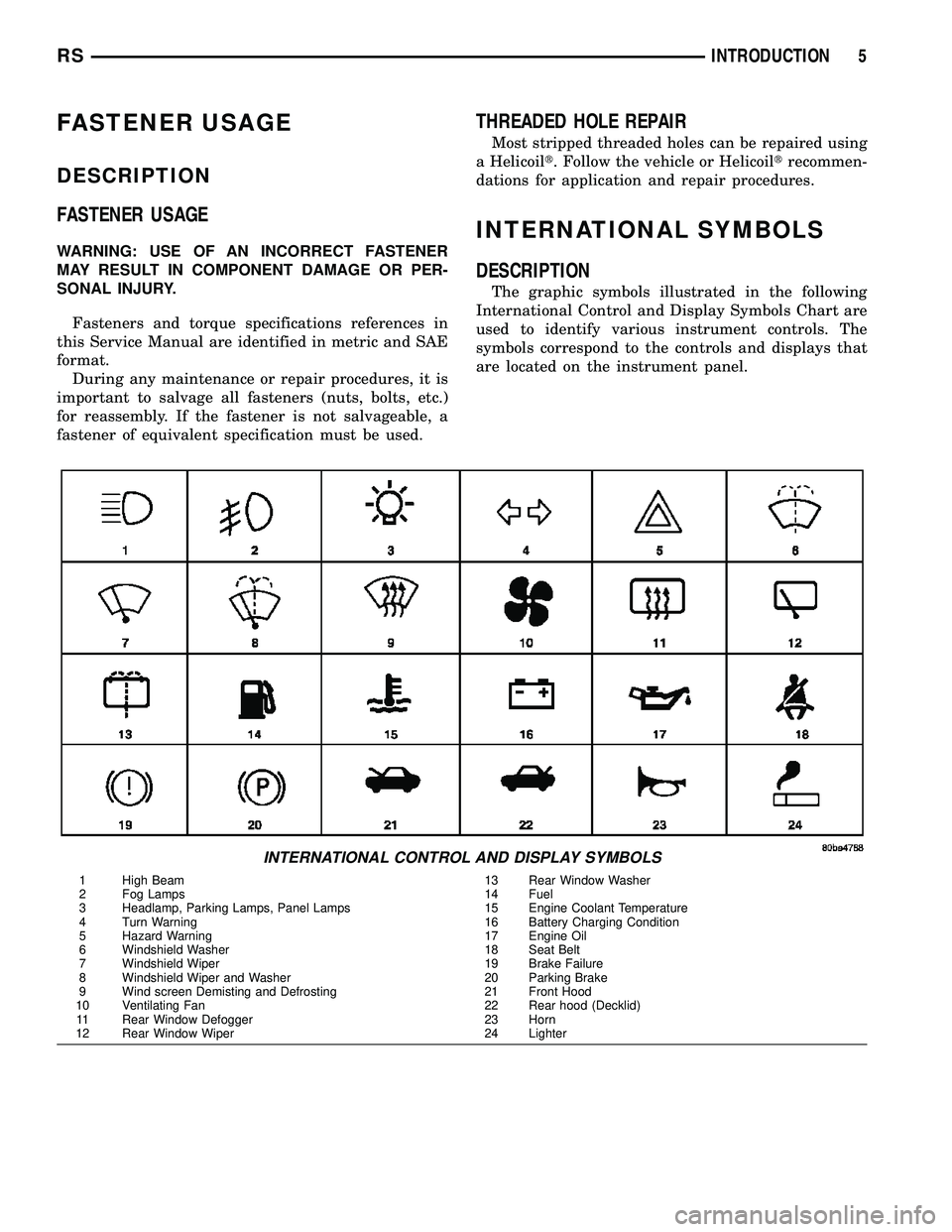
FASTENER USAGE
DESCRIPTION
FASTENER USAGE
WARNING: USE OF AN INCORRECT FASTENER
MAY RESULT IN COMPONENT DAMAGE OR PER-
SONAL INJURY.
Fasteners and torque specifications references in
this Service Manual are identified in metric and SAE
format.
During any maintenance or repair procedures, it is
important to salvage all fasteners (nuts, bolts, etc.)
for reassembly. If the fastener is not salvageable, a
fastener of equivalent specification must be used.
THREADED HOLE REPAIR
Most stripped threaded holes can be repaired using
a Helicoilt. Follow the vehicle or Helicoiltrecommen-
dations for application and repair procedures.
INTERNATIONAL SYMBOLS
DESCRIPTION
The graphic symbols illustrated in the following
International Control and Display Symbols Chart are
used to identify various instrument controls. The
symbols correspond to the controls and displays that
are located on the instrument panel.
INTERNATIONAL CONTROL AND DISPLAY SYMBOLS
1 High Beam 13 Rear Window Washer
2 Fog Lamps 14 Fuel
3 Headlamp, Parking Lamps, Panel Lamps 15 Engine Coolant Temperature
4 Turn Warning 16 Battery Charging Condition
5 Hazard Warning 17 Engine Oil
6 Windshield Washer 18 Seat Belt
7 Windshield Wiper 19 Brake Failure
8 Windshield Wiper and Washer 20 Parking Brake
9 Wind screen Demisting and Defrosting 21 Front Hood
10 Ventilating Fan 22 Rear hood (Decklid)
11 Rear Window Defogger 23 Horn
12 Rear Window Wiper 24 Lighter
RSINTRODUCTION5
Page 282 of 2339

NO FASTEN SEAT BELT LAMP WHEN IGNITION
SWITCH IS TURNED ON.
(1) Check for burned out lamp.
(2) Using a voltmeter check for voltage at the clus-
ter connector:
(a) Pin 2 of the mechanical instrument cluster
for battery feed.
(b) Pin 11 of the mechanical instrument cluster
for ignition voltage.
(3) Repair as necessary.
FASTEN SEAT BELT LAMP OR TONE CONTINUES
FOR MORE THAN 10 SECONDS AFTER SEAT
BELTS ARE FASTENED AND DRIVER'S DOOR IS
CLOSED.
Refer to the proper Body Diagnostic Procedures
manual.
NO TONE WHEN PARK OR HEADLAMPS ARE ON
AND DRIVER'S DOOR IS OPEN.
Make sure ignition is in lock position with the key
removed.
(1) Check the BCM DTC's and BCM sensors to
verify the door is open. Repair as necessary.
(2) Actuate Chime (BCM actuates).
(3) Inspect BCM connectors and wires for proper
connection.
(4) Measure with a voltmeter the voltage (12v) on
BCM connector (PX2) pin 34 with harness connected.
(5) Check BCM sensors to verify headlamp switch
position.
PARK ASSIST DISPLAY
DESCRIPTION
The Park Assist Display is located in the rear of
vehicle, over the rear window in the headliner (Fig.
1). It is a molded plastic unit housing Light Emitting
Diodes (LED's) and a chime module. Located in the
rear of the vehicle for easy visual reference when the
driver is backing up.
The display is used to alert the driver of any obsta-
cles detected in the rear of the vehicle. The chime or
audible signal also comes from the display unit.
OPERATION
When the ignition is put in the RUN position, all
the Light Emitting Diodes (LED's) will illuminate for
approximately one second. This will be interrupted if
the system senses an obstacle.
The ready status will be sensed by the outermost
two yellow LED's being illuminated at 50% intensity.
As the obstacle is sensed, the yellow LED's will start
illuminating inward until the object in approximately
one foot away and then the inner red LED will light.
The display is sensitive to which side of the rear of
the vehicle that the object is detected. If on the left
rear, the left segments will light and the same for the
right side of the vehicle.
Fig. 1 PARK ASSIST DISPLAY
RSCHIME/BUZZER8B-3
CHIME/BUZZER (Continued)
Page 288 of 2339

The BCM utilizes integrated circuitry and informa-
tion carried on the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus network along with many
hard wired inputs to monitor many sensor and
switch inputs throughout the vehicle. In response to
those inputs, the internal circuitry and programming
of the BCM allow it to control and integrate many
electronic functions and features of the vehicle
through both hard wired outputs and the transmis-
sion of electronic message outputs to other electronic
modules in the vehicle over the PCI data bus.
OPERATION
The Body Control Module (BCM) supplies vehicle
occupants with visual and audible information and
controls various vehicle functions. To provide and
receive information, the BCM is interfaced to the
vehicle's serial bus communications network, referred
to as the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) bus.
This network consists of the;
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Transmission Control Module (TCM)
²Mechanical Instrument Cluster (MIC)
²Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC)
²Compass/Mini-Trip Computer (CMTC)
²Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC)
²Controller Antilock Brake (CAB)
²HVAC Control Module
²Sliding Door Control Modules (driver and pas-
senger side doors)
²Power Liftgate Module (PLG)
²Audio system equipped with RAZ, RBU, RBK,
and RBB radios.
²Sentry Key Remote Entry Module (SKREEM).
²Side Impact Airbag Control Module (SIACM)²Memory Seat Module (MSM)
²Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM)
The BCM is operational when battery power is
supplied to the module.
The BCM provides the following features:
²Power Door Locks
²Automatic Door Locks
²Battery Protection - The BCM will automatically
turn off all exterior lamps after 3 minutes, and all
interior lamps after 15 minutes after the ignition is
turned off, if they are not turned off by the driver.
²Chime Control
²Compass/Mini-Trip support.
²Interior Lighting (Courtesy/Reading Lamps)
²BCM Diagnostic Reporting
²Electronic Liftgate Release (with Power Door
Locks)
²Exterior Lighting
²Headlamp Time Delay (with/without Automatic
Headlamps)
²Illuminated Entry
²Fade to Off Interior Lamps - This feature dims
the interior lighting (courtesy lamps) gradually if the
BCM does not receive any new inputs that would
cause the interior lamps to remain on.
²Pulse Width Modulated Instrument Panel Dim-
ming
²Door Lock Inhibit - This feature disables the
door lock functions if the key is in the ignition and
either front door is ajar. Pressing the Remote Keyless
Entry (RKE) lock/unlock button under these condi-
tions result in normal lock/unlock activation.
The BCM has the ability to LEARN additional fea-
tures in the vehicle, provided the appropriate switch
input and PCI data bus messages are received. Refer
to the LEARNED FEATURES table.
LEARNED FEATURES
FEATURE LEARNING KEY
REAR WIPER CONTROL ON HVAC CONTROL ON
INSTRUMENT PANELPCI BUS MESSAGE RECEIVED FROM HVAC
CONTROL
AUTOMATIC HEADLAMPS PCI MESSAGE FROM OVERHEAD OR HEADLAMP
SWITCH POSITION (AUTO)
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY SKREEM MESSAGE RECEIVED FROM MODULE
FRONT FOG LAMPS HEADLAMP SWITCH POSITION (PARK W/FRONT
FOG LAMPS)
POWER SLIDING DOOR PCI IFR RECEIVED FROM MODULE
THE BCM HAS FOUR SWITCH INPUTS FOR THE POWER SLIDING DOOR FEATURE; LOCATED IN THE
OVERHEAD CONSOLE ARE THE LEFT AND RIGHT SIDE SLIDING DOOR SWITCHES TO ACTIVATE EITHER
OR BOTH SLIDING DOORS UNDER THE PROPER CONDITIONS. ALSO ARE B-PILLAR SWITCHES LOCATED
ON THE LEFT AND RIGHT B-PILLAR POSTS.
POWER LIFTGATE PCI IFR RECEIVED FROM MODULE
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-3
BODY CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 292 of 2339

FRONT CONTROL MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Front Control Module (FCM) is a micro con-
troller based module located in the engine compart-
ment. The FCM mates to the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) to form the Integrated Power Module
(IPM). The IPM connects directly to the battery and
provides the primary means of circuit protection and
power distribution for all vehicle electrical systems.
The FCM controls power to some of these vehicle sys-
tems electrical and electromechanical loads based on
inputs received from hard wired switch inputs and
data received on the Programmable Communications
Interface (PCI) data bus.
For information on the IPM, (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/POWER DISTRIBUTION/INTEGRATED
POWER MODULE - DESCRIPTION)
OPERATION
As messages are sent over the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus, the Front Con-
trol Module (FCM) reads these messages and controls
power to some of the vehicles electrical systems by
completing the circuit to ground (low side driver) or
completing the circuit to 12 volt power (high side
driver).
The following functions arecontrolledby the
Front Control Module:
²Accessory Relay Actuation
²Brake Transmission Shift Interlock Functions
(BTSI - gas engine only)
²Diesel Cabin Heater (Diesel Engine Vehicles)
²Electronic Back Light (EBL) Rear Defogger
²Front and Rear Blower Motor Relay Actuation
²Front Fog Lamp Relay Actuation
²Washer Motor (front and rear)
²Front Windshield Wiper ªHIº & ªLOº Relay
Actuation
²Front Windshield Wiper ªONº Relay Actuation
²Headlamp Power with Voltage Regulation
²Horn Relay Actuation
²Headlamp Washer Relay Actuation (IF
EQUIPPED - EXPORT ONLY)
²Name Brand Speaker (NBS) Relay Actuation
²Park Lamp Relay Actuation
The following inputs areReceived/Monitoredby
the Front Control Module:
²Ambient Temperature Sensing
²Back-Up switch
²Brake Fluid Level
²B+ Connection Detection
²Engine Crank Signal (Diesel Engine Vehicles)
²Horn Input
²Ignition Switch Start Only
²Ignition Switch Run and Start Only²Stop Lamp Sense
²Washer Fluid Level
²Windshield Wiper Park
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FRONT CONTROL MODULE
The Front Control Module (FCM) is a printed cir-
cuit board based module with a on-board micro-pro-
cessor. The FCM interfaces with other electronic
modules in the vehicle via the Programmable Com-
munications Interface (PCI) data bus. In order to
obtain conclusive testing the PCI data bus and all of
the electronic modules that provide inputs to, or
receive outputs from the FCM must be checked. All
PCI communication faults must be resolved prior to
further diagnosing any front control module related
issues.
The FCM was designed to be diagnosed with an
appropriate diagnostic scan tool, such as the DRB
IIIt. The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means
to diagnose the front control module requires the use
of a DRB IIItscan tool and the proper Body Diag-
nostic Procedures manual.
Before any testing of the FCM is attempted, the
battery should be fully charged and all wire harness
and ground connections inspected around the affected
areas on the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative and posi-
tive battery cables from the battery.
(2) Remove the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - REMOVAL).
(3) Using a long flat-bladed screwdriver, gently
twist the Integrated Power Module (IPM) retaining
clip outboard to free the IPM from its mounting
bracket (Fig. 5). Rotate IPM upward to access the
Front Control Module (FCM) retaining screws.
(4) Remove the front control module retaining
screws.
(5) Pull the FCM straight from the IPM assembly
to disconnect the electrical connector (Fig. 6) and
remove the FCM from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: Front Control Module must be programmed
to the correct radio EQ curve using the DRB IIIT.
This will ensure that the audio system is operating
correctly.
(1) Install the Front Control Module (FCM) in the
Integrated Power Module (IPM) assembly by pushing
the 49-way electrical connector straight in.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-7
Page 293 of 2339

(2) Install the FCM retaining screws. Torque the
screws to 1 N´m (7 in. lbs).
(3) Rotate the IPM assembly downward to secure
in mounting bracket.
(4) Install the battery in the vehicle. Refer to the
procedure in Battery Systems.
(5) Connect the positive and negative battery
cables.(6) Using the DRB IIIt, under ªFRONT CON-
TROL MODULEº then ªMISCº program the EQ
curve of the radio into the Front Control Module.
Refer to the appropriate diagnostic manual.
NOTE: If the vehicle is not equipped with Name
Brand Speakers (Infinity, etc.) or Headlamp Washers
the DRB IIITmust be used to Disable the appropri-
ate relays in the Integrated Power Module Assem-
bly.
HEATED SEAT MODULE
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with heated seats utilize two
heated seat modules. The heated seat modules are
located under the front seats, where they are secured
to the seat cushion pans. Each heated seat module
has three connector receptacles that allow the mod-
ules to be connected to all of the required inputs and
outputs through the seat wire harness.
The heated seat modules are an electronic micro-
processor controlled device designed and programmed
to use inputs from the ignition switch, heated seat
switch and the heated seat sensor to operate and
control the heated seat elements in the front seat.
OPERATION
The heated seat module operates on fused battery
current received from the Integrated Power Module
(IPM). The module is grounded at all times through
the seat wire harness. Inputs to the module include a
resistor multiplexed heated seat switch request cir-
cuit for the heated seat switch and the heated seat
sensor inputs from the seat cushions of each front
seat. In response to those inputs the heated seat
module controls battery current feeds to the heated
seat elements.
When a heated seat switch request signal is
received by the heated seat module and the enable
input is high, the heated seat module energizes the
selected heated seat sensor circuit and the sensor
provides the module with an input indicating the
surface temperature of the selected seat cushion.
The Low heat set point is approximately 35É C (95É
F), and the High heat set point is approximately 40É
C (104É F). If the seat cushion surface temperature
input is below the temperature set point for the
selected temperature setting, the heated seat module
energizes an N-channel Field Effect Transistor
(N-FET) within the module which energizes the
heated seat elements in the selected seat cushion and
back. When the sensor input to the module indicates
the correct temperature set point has been achieved,
the module de-energizes the N-FET which de-ener-
Fig. 5 REMOVING INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
Fig. 6 FRONT CONTROL MODULE
1 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
8E - 8 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
FRONT CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 301 of 2339
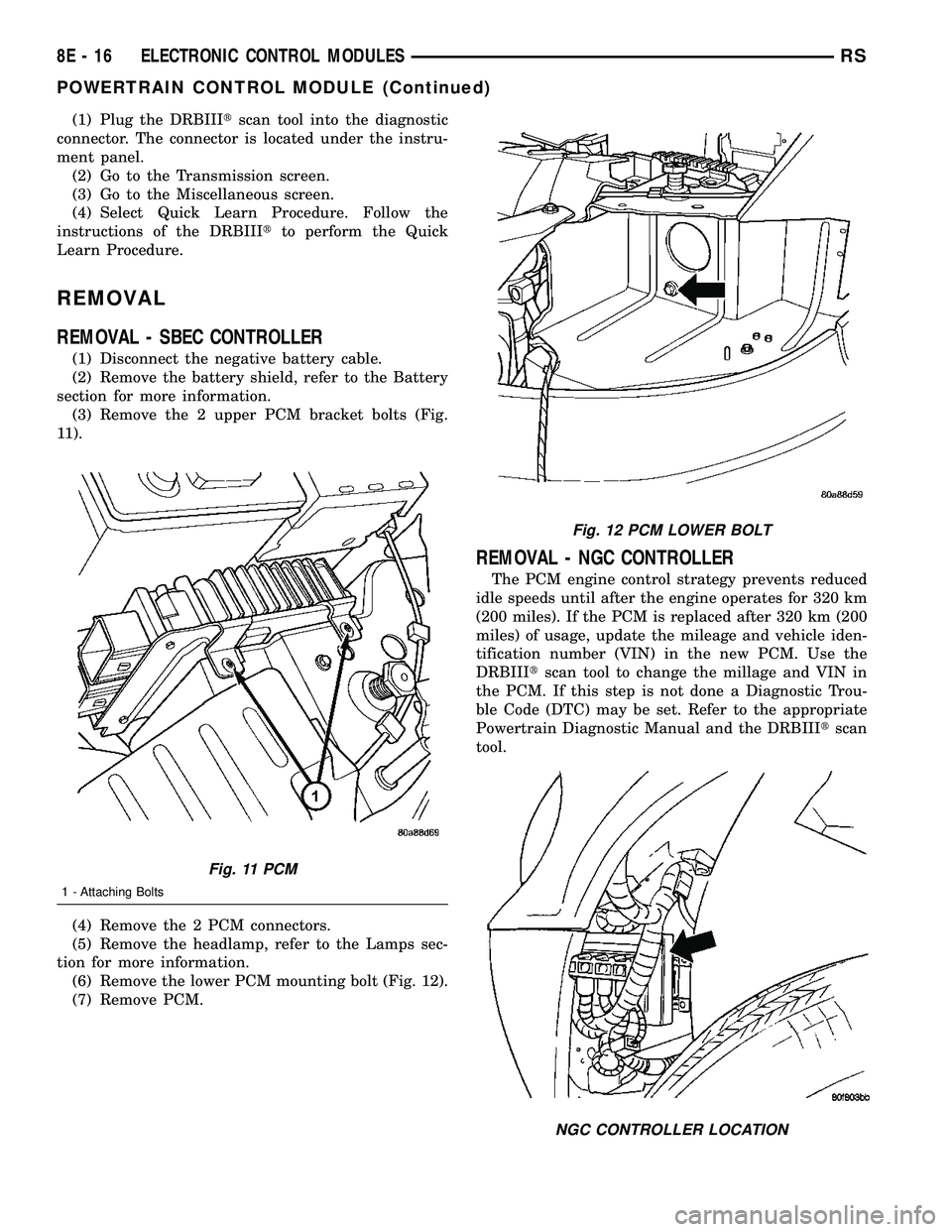
(1) Plug the DRBIIItscan tool into the diagnostic
connector. The connector is located under the instru-
ment panel.
(2) Go to the Transmission screen.
(3) Go to the Miscellaneous screen.
(4) Select Quick Learn Procedure. Follow the
instructions of the DRBIIItto perform the Quick
Learn Procedure.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - SBEC CONTROLLER
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the battery shield, refer to the Battery
section for more information.
(3) Remove the 2 upper PCM bracket bolts (Fig.
11).
(4) Remove the 2 PCM connectors.
(5) Remove the headlamp, refer to the Lamps sec-
tion for more information.
(6) Remove the lower PCM mounting bolt (Fig. 12).
(7) Remove PCM.
REMOVAL - NGC CONTROLLER
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage and vehicle iden-
tification number (VIN) in the new PCM. Use the
DRBIIItscan tool to change the millage and VIN in
the PCM. If this step is not done a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC) may be set. Refer to the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostic Manual and the DRBIIItscan
tool.
Fig. 11 PCM
1 - Attaching Bolts
Fig. 12 PCM LOWER BOLT
NGC CONTROLLER LOCATION
8E - 16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 302 of 2339

(1) Turn wheels to the left.
(2) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(3) Raise vehicle and support.
(4) Remove the left front wheel well splash shield
(Fig. 13).
(5) Unlock and disconnect the electrical connectors
(Fig. 14).
(6) Remove 3 screws from PCM to mounting
bracket.
(7) Remove the PCM.INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - SBEC CONTROLLER
(1) Install the PCM.
(2) Install the lower PCM mounting bolt. Tighten
bolt.
(3) Install the 2 upper PCM bracket bolts. Tighten
bolt.
(4) Install the headlamp, refer to the Lamps sec-
tion for more information.
(5) Install the 2 PCM connectors.
(6) Install the battery shield, refer to the Battery
section for more information.
(7) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage and vehicle iden-
tification number (VIN) in the new PCM. Use the
DRBIIItscan tool to change the millage and VIN in
the PCM. If this step is not done a diagnostic trouble
code (DTC) may be set and SKIM must be done or
car will not start if it is a SKIM equipped car. If a
SKIM car you must do a secret key transfer also.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Man-
ual and the DRBIIItscan tool.
(1) Install PCM module to the mounting bracket.
(2) Install electrical connectors and lock.
(3) Install the splash shield.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
(6) Using DRBIIItscan tool, program mileage and
vehicle identification number (VIN) into PCM. Refer
to the DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Manual.
Fig. 13 SPLASH SHIELD
Fig. 14 NGC CONTROLLER
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-17
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 318 of 2339
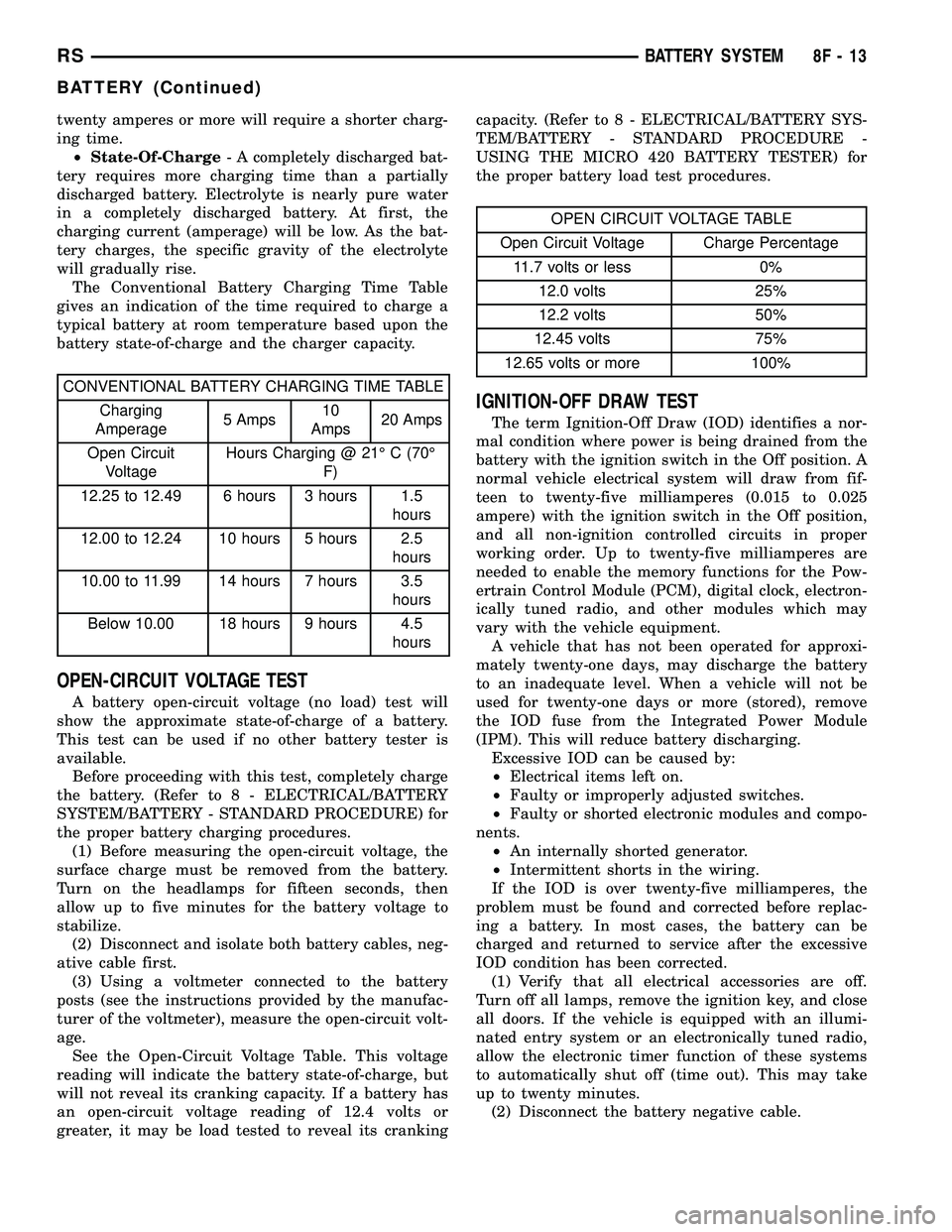
twenty amperes or more will require a shorter charg-
ing time.
²State-Of-Charge- A completely discharged bat-
tery requires more charging time than a partially
discharged battery. Electrolyte is nearly pure water
in a completely discharged battery. At first, the
charging current (amperage) will be low. As the bat-
tery charges, the specific gravity of the electrolyte
will gradually rise.
The Conventional Battery Charging Time Table
gives an indication of the time required to charge a
typical battery at room temperature based upon the
battery state-of-charge and the charger capacity.
CONVENTIONAL BATTERY CHARGING TIME TABLE
Charging
Amperage5 Amps10
Amps20 Amps
Open Circuit
VoltageHours Charging @ 21É C (70É
F)
12.25 to 12.49 6 hours 3 hours 1.5
hours
12.00 to 12.24 10 hours 5 hours 2.5
hours
10.00 to 11.99 14 hours 7 hours 3.5
hours
Below 10.00 18 hours 9 hours 4.5
hours
OPEN-CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
A battery open-circuit voltage (no load) test will
show the approximate state-of-charge of a battery.
This test can be used if no other battery tester is
available.
Before proceeding with this test, completely charge
the battery. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM/BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE) for
the proper battery charging procedures.
(1) Before measuring the open-circuit voltage, the
surface charge must be removed from the battery.
Turn on the headlamps for fifteen seconds, then
allow up to five minutes for the battery voltage to
stabilize.
(2) Disconnect and isolate both battery cables, neg-
ative cable first.
(3) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts (see the instructions provided by the manufac-
turer of the voltmeter), measure the open-circuit volt-
age.
See the Open-Circuit Voltage Table. This voltage
reading will indicate the battery state-of-charge, but
will not reveal its cranking capacity. If a battery has
an open-circuit voltage reading of 12.4 volts or
greater, it may be load tested to reveal its crankingcapacity. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYS-
TEM/BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE -
USING THE MICRO 420 BATTERY TESTER) for
the proper battery load test procedures.
OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TABLE
Open Circuit Voltage Charge Percentage
11.7 volts or less 0%
12.0 volts 25%
12.2 volts 50%
12.45 volts 75%
12.65 volts or more 100%
IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST
The term Ignition-Off Draw (IOD) identifies a nor-
mal condition where power is being drained from the
battery with the ignition switch in the Off position. A
normal vehicle electrical system will draw from fif-
teen to twenty-five milliamperes (0.015 to 0.025
ampere) with the ignition switch in the Off position,
and all non-ignition controlled circuits in proper
working order. Up to twenty-five milliamperes are
needed to enable the memory functions for the Pow-
ertrain Control Module (PCM), digital clock, electron-
ically tuned radio, and other modules which may
vary with the vehicle equipment.
A vehicle that has not been operated for approxi-
mately twenty-one days, may discharge the battery
to an inadequate level. When a vehicle will not be
used for twenty-one days or more (stored), remove
the IOD fuse from the Integrated Power Module
(IPM). This will reduce battery discharging.
Excessive IOD can be caused by:
²Electrical items left on.
²Faulty or improperly adjusted switches.
²Faulty or shorted electronic modules and compo-
nents.
²An internally shorted generator.
²Intermittent shorts in the wiring.
If the IOD is over twenty-five milliamperes, the
problem must be found and corrected before replac-
ing a battery. In most cases, the battery can be
charged and returned to service after the excessive
IOD condition has been corrected.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are off.
Turn off all lamps, remove the ignition key, and close
all doors. If the vehicle is equipped with an illumi-
nated entry system or an electronically tuned radio,
allow the electronic timer function of these systems
to automatically shut off (time out). This may take
up to twenty minutes.
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
RSBATTERY SYSTEM8F-13
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 386 of 2339

LAMPS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR............... 1LAMPS/LIGHTING - INTERIOR............... 20
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
DESCRIPTION..........................2
OPERATION............................2
WARNING.............................3
SPECIFICATIONS
EXTERIOR LAMPS.....................3
BRAKE LAMP SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................4
OPERATION............................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE LAMP
SWITCH.............................4
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
FRONT FOG LAMP
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FRONT FOG
LAMP...............................7
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
FRONT FOG LAMP UNIT
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FRONT FOG
LAMP UNIT ALIGNMENT.................9
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FRONT FOG
LAMP UNIT ALIGNMENT - EXPORT........9
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
HEADLAMP
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEADLAMP.....11
REMOVAL.............................12INSTALLATION.........................13
HEADLAMP SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEADLAMP
SWITCH............................13
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
HEADLAMP UNIT
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEADLAMP UNIT
ALIGNMENT.........................14
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
HEADLAMP UNIT - EXPORT
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEADLAMP UNIT
ALIGNMENT - EXPORT.................15
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
LICENSE LAMP
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
MULTI-FUNCTION SWITCH
DESCRIPTION - TURN SIGNAL SYSTEM.....17
OPERATION - TURN SIGNAL SYSTEM.......17
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MULTI-
FUNCTION SWITCH...................18
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18
PARK/TURN SIGNAL LAMP
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18
TAIL LAMP
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................19
TAIL LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
RSLAMPS8L-1
Page 387 of 2339

LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
DESCRIPTION
LAMP SYSTEMS
Lighting circuits are protected by fuses. Lighting
circuits require an overload protected power and high
side drivers source, ON/OFF device, lamps and body
grounds to operate properly. Plastic lamps require a
wire in the harness to supply body ground to the
lamp socket. Replace sockets and bulbs that are cor-
roded.
Some of the interior and exterior lighting functions
are governed by the Body Control Module (BCM).
The headlamp, dome, and the door ajar switches pro-
vide signals to the BCM. The BCM in turn sends a
Programmable Communication Interface (PCI) bus
message to the Front Control Module (FCM) to
enable the necessary drivers to set the required illu-
mination configuration.
Wire connectors can make intermittent contact or
become corroded. Before coupling wire connectors,
inspect the terminals inside the connector. Male ter-
minals should not be bent or disengaged from the
insulator. Female terminals should not be sprung
open or disengaged from the insulator. Bent and
sprung terminals can be repaired using needle nose
pliers and pick tool. Corroded terminals appear
chalky or green. Corroded terminals should be
replaced to avoid recurrence of the problem symp-
toms.
Begin electrical system failure diagnosis by testing
related fuses in the fuse block and intelligent power
module. Verify that bulbs are in good condition and
test continuity of the circuit ground. Refer to the
appropriate wiring information.
AUTOMATIC HEADLAMP SYSTEM
The Automatic Headlamp system turns the instru-
mentation and exterior illumination lamps ON when
the ambient light levels are Night and the engine
RPM is 450 or above, and OFF when light levels are
Day.
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMPS
Operating the high-beam headlamps at reduced
power provides daytime running lamps, which are
required on all new Canadian vehicles. Daytime run-
ning lamps are functional when 450 rpm's are
reached.
HEADLAMPS ON WITH WINDSHIELD WIPERS
For vehicles equipped with the Automatic Head-
lamp System, the instrumentation and exterior illu-
mination lamps will be turned ON when the
headlamp switch is in the AUTO position, RPM >450 and the windshield wipers have been in the
intermittent, low or high mode of operation for more
than ten seconds. When the windshield wipers are
turned OFF the Body Control Module will determine
if the instrumentation and exterior illumination
lamps should remain ON base upon the current
ambient light level.
HEADLAMP SYSTEM
The configuration of the headlamp system of head-
lamps, park lamps and fog lamps is determined by
the BCM. The BCM determines the lighting configu-
ration as a result of the inputs from the ignition
switch, headlamp switch and multi-function switch. A
PCI bus is transmitted from the BCM to the FCM to
enable the necessary drivers to set the illumination
configuration. Four wires are connected between the
headlamp switch and the BCM. The first wire con-
tains information regarding the position of the head-
lamp switch (Off, Automatic Headlamps, Automatic
Headlamp switch fog, Park with Fog, Head, or Head
with Fog Lamps). The second wire contains informa-
tion regarding the position of the dimmer switch
(Dome Lamp, Daytime Brightness, Dimming Level or
Off). The third wire is a dedicated signal return
(ground) wire. The fourth wire provides power to the
front fog lamp indicator.
HEADLAMP TIME DELAY SYSTEM
The headlamp time delay system is controlled by
the Body Control Module (BCM) via a PCI bus mes-
sage transmitted by the BCM to the FCM to turn off
the headlamps.
OPERATION
AUTOMATIC HEADLAMP SYSTEM
Automatic headlamps are controlled by the Body
Control Module (BCM). With the headlamp switch in
the AUTO position, the BCM will control the head-
lamp, parking, side marker, tail and instrumentation
lamps based on ambient light levels. Ambient light
levels are monitored by the BCM using the Day/
Night signal and Electrochromatic Mirror (ECM)
present from the Compass Mini Trip (CMTC) located
on the front windshield in front of the rear view mir-
ror ECM. Ambient light readings are averaged to
limit cycling the lamps ON and OFF when passing
through areas with varying light levels. The auto-
matic headlamps will only function when the engine
is running with RPM > 450. When the headlamp
switch is in the AUTO position (Automatic mode), the
Headlamp Time Delay system will function when the
ignition switch is placed in any position other than
run/start.
8L - 2 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORRS