coolant temperature CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1401 of 1938

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SYSTEM DIAGNOSISÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to System diagnosis for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULEÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Powertrain Control Module for 2.4/3.0/
3.3/3.8L engines under Description and Operation in
the Fuel Injection System section of group 14 for
more information.
AIR CONDITIONING PRESSURE TRANSDUCERÐ
PCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Air Conditioning Pressure Transducer
for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and
Operation in the Fuel Injection System section of
group 14 for more information.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSEÐPCM
INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Air Conditioning Switch Sense for 2.4/
3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and Operation
in the Fuel Injection System section of group 14 for
more information.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD) SENSEÐPCM
INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Automatic Shutdown (ASD) Sense for
2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and Oper-
ation in the Fuel Injection System section of group 14
for more information.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Battery Voltage for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUTÐ
2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Camshaft Position Sensor for 2.4L
engine under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM
INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Crankshaft Position Sensor for 2.4L
engine under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
The coolant temperature sensor threads into the
rear of the cylinder head, next to the camshaft posi-
tion sensor (Fig. 3). New sensors have sealant
applied to the threads.
Refer to the Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
for the 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Description and
Operation in the Fuel Injection System section of
group 14 for more information.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSORÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L
ENGINE
Refer to the Heated Oxygen Sensor for 2.4/3.0/3.3/
3.8L engines under Description and Operation in the
Fuel Injection System section of group 14 for more
information.
Fig. 1 Camshaft Position SensorÐ2.0L Engine
Fig. 2 Crankshaft Posistion SensorÐ2.0L engine
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 33
Page 1402 of 1938

KNOCK SENSORÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Knock Sensor for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP
SENSOR)ÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Manifold Absolute Pressure and
Intake Air Temperature sensors for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM INPUTÐ2.0L ENGINE
Refer to the Speed Control for 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L
engines under Description and Operation in the Fuel
Injection System section of group 14 for more infor-
mation.
Fig. 3 Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐ2.0L
engine
Fig. 4 Upstream Heated Oxygen SensorÐ2.0L
Engine
Fig. 5 Downstream Heated Oxygen SensorÐ2.0L
Engine
Fig. 6 Knock SensorÐ2.0L engine
Fig. 7 MAP/IAT sensorÐ2.0L engine
14 - 34 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1405 of 1938
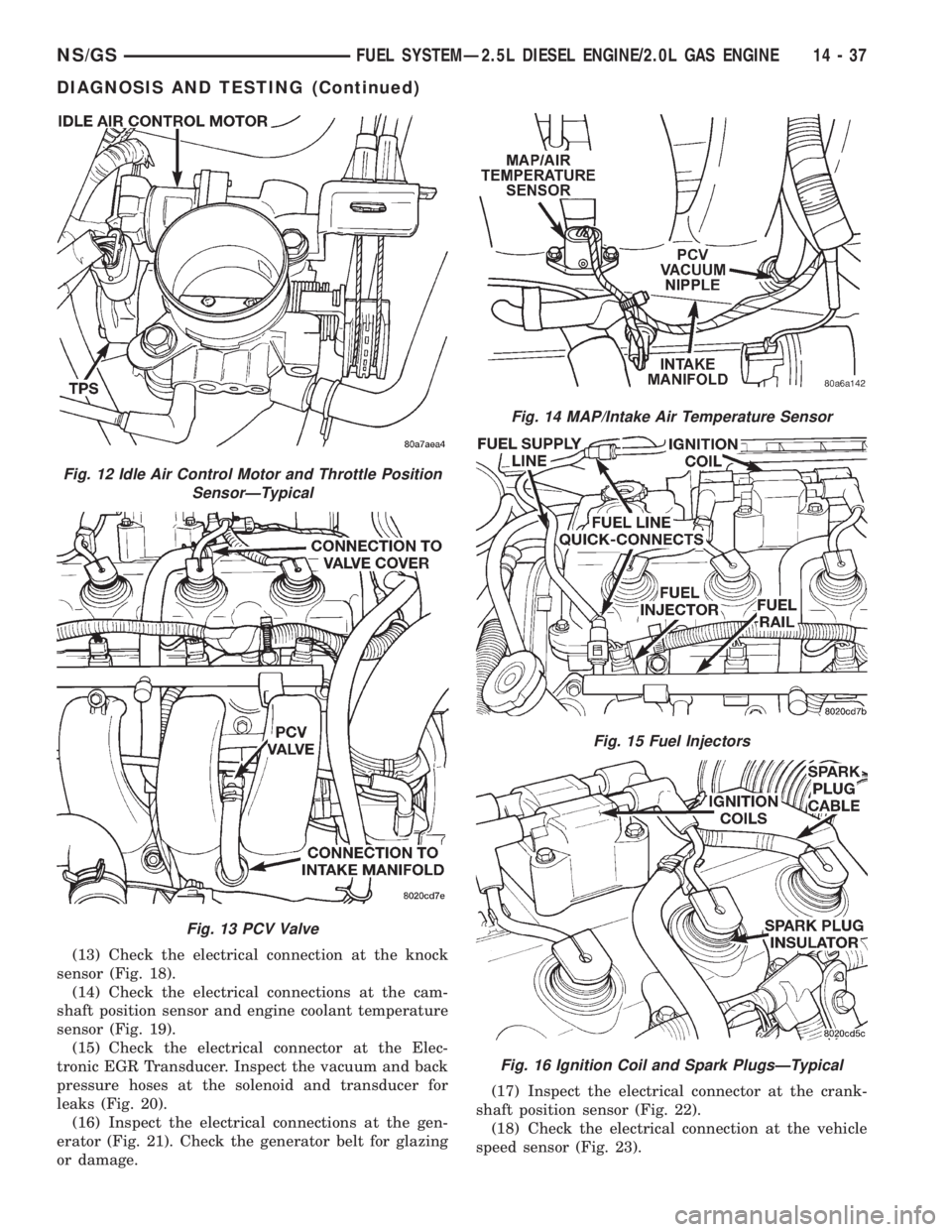
(13) Check the electrical connection at the knock
sensor (Fig. 18).
(14) Check the electrical connections at the cam-
shaft position sensor and engine coolant temperature
sensor (Fig. 19).
(15) Check the electrical connector at the Elec-
tronic EGR Transducer. Inspect the vacuum and back
pressure hoses at the solenoid and transducer for
leaks (Fig. 20).
(16) Inspect the electrical connections at the gen-
erator (Fig. 21). Check the generator belt for glazing
or damage.(17) Inspect the electrical connector at the crank-
shaft position sensor (Fig. 22).
(18) Check the electrical connection at the vehicle
speed sensor (Fig. 23).
Fig. 12 Idle Air Control Motor and Throttle Position
SensorÐTypical
Fig. 13 PCV Valve
Fig. 14 MAP/Intake Air Temperature Sensor
Fig. 15 Fuel Injectors
Fig. 16 Ignition Coil and Spark PlugsÐTypical
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 37
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1406 of 1938

(19) Check the electrical connection at the power
steering pressure switch on the power steering gear
housing (Fig. 24).
Fig. 17 Starter Motor and Ground Strap
Fig. 18 Knock Sensor
Fig. 19 Camshaft Position Sensor and Engine
Coolant Temperature Sensor
Fig. 20 Electronic EGR Transducer
Fig. 21 Generator
Fig. 22 Crankshaft Position Sensor
14 - 38 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1408 of 1938

CAUTION: When testing the MAP sensor, be sure
that the harness wires are not damaged by the test
meter probes.
(1) Test the MAP sensor output voltage at the
MAP sensor connector between terminals 1 and 4
(Fig. 29). With the ignition switch ON and the engine
not running, output voltage should be 4 to 5 volts.
The voltage should drop to 1.5 to 2.1 volts with a hot,
neutral idle speed condition. If OK, go to next step. If
not OK, go to step 3.
(2) Test PCM terminal 36 for the same voltage
described in the previous step to verify wire harness
condition. Repair as required.(3) Test the MAP sensor ground circuit at sensor
connector terminal 1 and PCM terminal 43. If OK, go
to next step. If not OK, repair as required.
(4) Test MAP sensor supply voltage between sen-
sor connector terminals 3 and 1 with the key ON.
The voltage should be approximately 5 volts (6.5V).
Five volts (6.5V) should also be at terminal 61 of the
PCM. If OK, replace MAP sensor. If not OK, repair or
replace the wire harness as required.
KNOCK SENSORÐ2.0L ENGINE
The knock sensor output voltage to the PCM can
be read with the DRB III scan tool. Sensor output
should be between 80 mV and 4 volts with the engine
running between 576 and 2208 rpm. If the output
falls outside of this range a DTC will be set.
CAMSHAFT AND CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Refer to Group 8D, Ignition for Diagnosis and Test-
ing of Camshaft and Crankshaft Sensors.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Refer to the Engine Coolant Temperature sensor
for the 2.4/3.0/3.3/3.8L engines under Diagnosis and
Testing in the Fuel Injection System section of group
14 for more information.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
To perform a complete test of the this sensor and
its circuitry, the DRB III scan tool is the best
method. To test the throttle position sensor only,
refer to the following:
The Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) can be tested
with a digital voltmeter (DVM). The center terminal
of the sensor is the output terminal. One of the other
terminals is a 5 volt supply and the remaining ter-
minal is ground.
Fig. 28 ASD and Fuel Pump Relay Terminals
Fig. 29 MAP Sensor Connector
Fig. 30 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
LocationÐSOHC
14 - 40 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1410 of 1938

(a) Remove the throttle body from engine.
(b) While holding the throttle open, spray the
entire throttle body bore and the manifold side of
the throttle plate with Mopar Parts Cleaner.Only
use Mopar Parts Cleaner to clean the throttle
body.
(c) Using a soft scuff pad, clean the top and bot-
tom of throttle body bore and the edges and mani-
fold side of the throttle blade.The edges of the
throttle blade and portions of the throttle
bore that are closest to the throttle blade
when closed, must be free of deposits.
(d) Use compressed air to dry the throttle body.
(e) Inspect throttle body for foreign material.
(f) Install throttle body on manifold.
(g) Repeat steps 1 through 14. If the minimum
air flow is still not within specifications, the prob-
lem is not caused by the throttle body.
(12) Shut off engine.
(13) Remove Air Metering Orifice 6457. Install
purge hose.
(14) Remove cap from PCV valve. Connect hose to
PCV valve.
(15) Remove DRB scan tool.SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION TORQUE
Air Cleaner Wingnut.........1.5N´m(15in.lbs.)
Air Cleaner Mount. Stud-To-Thrott. Body . . 10 N´m
(90 in. lbs.)
Crankshaft Position Sensor Mounting Bolts . . 8 N´m
(70 in. lbs.)
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor......18N´m
(165 in. lbs.)
IAC Motor-To-Throttle Body Bolts.........7N´m
(60 in. lbs.)
MAP/IAT Sensor.............2N´m(20in.lbs.)
MAP/IAT Sensor.............3N´m(30in.lbs.)
Oxygen Sensor..............28N´m(20ft.lbs.)
Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) Mounting Screws.....4N´m(35in.lbs.)
Throttle Cable Cover........4.5N´m(40in.lbs.).
Throttle Body Mounting Bolts...........23N´m
(200 in. lbs.)
Throttle Position Sensor Mounting Screws . . . 2 N´m
(20 in. lbs.)
Vehicle Speed Sensor Mounting Bolt......2.2N´m
(20 in. lbs.)
14 - 42 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1411 of 1938

FUEL INJECTION SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION....................... 43
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
AIR CONDITIONING (A/C) CONTROLSÐ
PCM INPUTS........................ 47
AIR CONDITIONING RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT . . 48
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT.......... 45
BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR............. 45
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT............. 47
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐ
PCM INPUT AND OUTPUT.............. 47
DIESEL PCM RELAYÐPCM INPUT......... 48
ENGINE COOLANT GAUGEÐPCM OUTPUT . . 48
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐ
PCM INPUT......................... 46
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE GAUGEÐ
PCM OUTPUT........................ 48
ENGINE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT..... 46
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT............. 50
FIVE VOLT POWERÐPCM OUTPUT........ 48
FUEL INJECTOR SENSORÐGROUND...... 46
FUEL TIMING SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT.... 48
GLOW PLUG LAMPÐPCM OUTPUT........ 48
GLOW PLUG RELAYÐPCM OUTPUT....... 49
GLOW PLUGS......................... 49
IGNITION CIRCUIT SENSEÐPCM INPUT.... 45
NEEDLE MOVEMENT OR INSTRUMENTED
FIRST INJECTORÐPCM INPUT.......... 45
POWER GROUND...................... 45
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM) . . . 44
SENSOR RETURNÐPCM INPUT (ANALOG
GROUND)........................... 45SIGNAL GROUNDÐPCM INPUT........... 45
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM INPUTS.......... 48
SPEED CONTROLÐPCM OUTPUTS........ 48
START SIGNALÐPCM INPUT............. 45
TACHOMETERÐPCM OUTPUT............ 49
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT.... 47
VEHICLE THEFT ALARM................. 45
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR............. 53
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES........... 53
DIESEL DIAGNOSTICS.................. 50
DIESEL PCM RELAY TEST............... 50
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR TEST....................... 50
ENGINE SPEED SENSOR TEST........... 50
GLOW PLUG RELAY TEST............... 51
GLOW PLUG TEST..................... 51
RELAYSÐOPERATION/TESTING........... 52
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR TEST........... 53
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
A/C CLUTCH RELAY.................... 53
DIESEL PCM RELAY.................... 53
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR............................ 54
ENGINE SPEED SENSOR................ 53
GLOW PLUG RELAY.................... 55
GLOW PLUGS......................... 54
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM) . . . 55
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR............... 55
SPECIFICATIONS
GLOW PLUG CURRENT DRAW............ 56
TORQUE CHARTÐ2.5L DIESEL............ 57
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
This section will cover components either regulated
or controlled by the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The fuel heater relay, fuel heater and fuel
gauge are not operated by the PCM. These compo-
nents are controlled by the ignition (key) switch. All
other fuel system electrical components necessary to
operate the engine are controlled or regulated by the
PCM. Refer to the following PCM description for
more information.
Certain fuel system component failures may cause
a no start, or prevent the engine from running. It is
important to know that the PCM has a featurewhere, if possible, it will ignore the failed sensor, set
a code related to the sensor, and operate the engine
in a ªLimp Homeº mode. When the PCM is operating
in a ªLimp Homeº mode, the Diesel Glow Plug lamp
on the instrument panel will be constantly illumi-
nated, and the engine will most likely have a notice-
able loss of performance. An example of this would be
an Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor failure, and in
that situation, the engine would run at a constant
1100 RPM, regardless of the actual position of the
pedal. This is the most extreme of the three ªLimp
Homeº modes.
In addition to indicating that the glow plugs are
hot enough to start combustion, the Glow Plug Lamp
is also used in the diagnosis of the PCM, and when
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 43
Page 1412 of 1938

illuminated constantly, it usually indicates a problem
has been detected somewhere within the fuel system.
The DRBIII scan tool is the best method for commu-
nicating with the PCM to diagnose faults within the
system.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (PCM)
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is mounted
in the center consule to a bracket located in front of
the Air Bag Module (Fig. 1).
The PCM is a pre±programmed, dual micro±proces-
sor digital computer. It will either directly operate or
partially regulate the:
²Speed Control
²Speed Control LED lamp
²Fuel Timing Solenoid
²Glow Plug Relay
²Glow Plugs
²EGR Solenoid
²Glow Plug Lamp
²Diesel PCM Relay
²Air Conditioning Operation
²Tachometer
²Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet
changing operating conditions.
The PCM receives input signals from various
switches and sensors. Based on these inputs, the
PCM regulates various engine and vehicle operationsthrough different system components. These compo-
nents are referred to asPCM Outputs.The sensors
and switches that provide inputs to the PCM are con-
sideredPCM Inputs.
PCM Inputs are:
²Air Conditioning Selection
²Theft Alarm
²Clutch Switch
²Diesel PCM Relay
²ISO-Protocol
²Control Sleeve
²Fuel Temperature
²Boost Pressure Sensor
²Accelerator Pedal Sensor
²EGR
²A/C Pressure
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Low Idle Position Switch
²5 Volt Supply
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Sensor Return
²Glow Plug
²Engine Speed Sensor (rpm)
²Fuel Injector #1 Sensor
²Starter Signal
²Brake Switch
²Speed Control Switch Position
²Power Ground
²Signal Ground
²Ignition (key) Switch Sense
²Battery Voltage
²SCI Receive (DRB scan tool connection)
PCM Outputs:
After inputs are received by the PCM, certain sen-
sors, switches and components are controlled or reg-
ulated by the PCM. These are consideredPCM
Outputs.These outputs are for:
²A/C Clutch Relay (for A/C clutch operation)
²Speed Control LED
²Data Link Connectors (for DRB scan tool)
²Diesel PCM Relay
²Diesel PCM Sense
²Accelarator Pedal
²5 Volts Supply
²Glow Plug Relay
²Fan Relay
²Fuel Quantity
²Fuel Timing Solenoid
²Fuel Shut-Off Solenoid
²Engine Speed Sensor
²Glow Plug Lamp (malfunction indicator lamp)
²Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid
²Glow Plug Relay
²Tachometer
²SCI transmit (DRB scan tool connection)
Fig. 1 PCM Location
14 - 44 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1414 of 1938

The first injector sensor is used only on the fuel
injector for the number±1 cylinder (Fig. 3). It is not
used on the injectors for cylinders number 2, 3, or 4.
FUEL INJECTOR SENSORÐGROUND
Provides a low noise ground for the fuel injector
sensor only.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
The 0±5 volt input from this sensor tells the PCM
the temperature of the engine coolant. Based on the
voltage received at the PCM, it will then determine
operation of the fuel timing solenoid, glow plug relay,
electrical vacuum modulator (emission component)
and generator (charging system).
The sensor is located on the side of the #3 cylinder
head near the rear of fuel injection pump (Fig. 4).
ENGINE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The engine speed sensor is mounted to the trans-
mission bellhousing at the left/rear side of the engine
block (Fig. 5).
The engine speed sensor produces its own output
signal. If this signal is not received the engine will
not start by the PCM.
The engine speed sensor input is used in conjunc-
tion with the first injector sensor to establish fuel
injection pump timing.
The flywheel has four notches at its outer edge
(Fig. 6). Each notch is spaced equally every 90É. The
notches cause a pulse to be generated when they
pass under the speed sensor (Fig. 6). These pulses
are the input to the PCM. The input from this sensor
determines crankshaft position (in degrees) by moni-
toring the notches.The sensor also generates an rpm signal to the
PCM. This signal is used as an input for the Diesel
relay for control of the generator field, vehicle speed
control, and instrument panel mounted tachometer.
If the engine speed sensor should fail, the system
is unable to compensate for the problem and the car
will stop.
Fig. 3 Fuel Injector Sensor
Fig. 4 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Location
Fig. 5 Engine Speed Sensor Location
14 - 46 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1415 of 1938

AIR CONDITIONING (A/C) CONTROLSÐPCM
INPUTS
The A/C control system information applies to fac-
tory installed air conditioning units.
A/C REQUEST SIGNAL:When either the A/C or
Defrost mode has been selected and the A/C low and
high±pressure switches are closed, an input signal is
sent to the powertrain control module (PCM). The
PCM uses this input to cycle the A/C compressor
through the A/C relay.
If the A/C low or high±pressure switch opens, the
PCM will not receive an A/C request signal. The
PCM will then remove the ground from the A/C relay.
This will deactivate the A/C compressor clutch. Also,
if the engine coolant reaches a temperature outside
normal of its normal range, or it overheats, the PCM
will deactivate the A/C clutch.
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake light switch is activated, the PCM
receives an input indicating that the brakes are
being applied. After receiving this input, the PCM is
used to control the speed control system. There is a
Primary and a Secondary brake switch. The Second-
ary brake switch is closed until the brake pedal is
pressed.
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐPCM INPUT AND
OUTPUT
The 16±way data link connector (diagnostic scan
tool connector) links the Diagnostic Readout Box(DRB) scan tool with the PCM. The data link connec-
tor is located under the instrument panel near the
bottom of steering column (Fig. 7).
VEHICLE SPEED SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The vehicle speed sensor (Fig. 8) is located in the
extension housing of the transmission. The sensor
input is used by the PCM to determine vehicle speed
and distance traveled.
Fig. 6 Speed Sensor Operation
Fig. 7 Data Link Connector Location
Fig. 8 Vehicle Speed SensorÐTypical
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 47
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)