Egr CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1874 of 1938

move towards the Cold position. When Pin 13 is High
and Pin 15 is Low the door will move towards the
Heat position. When both Pins are high or when both
Pins are low, the actuator will not move. The Driver
feedback signal is a voltage signal that is supplied by
the actuator to the control. The signal will be about
4.0 volts in the Heat position and 1.0 volt in the Cold
position. As the position of the Driver Actuator
changes, so will the feedback signal. The feedback
signal is necessary for the correct positioning of the
temperature door.
MODE ACTUATOR BACKGROUND
The Mode actuator can move the mode door in two
directions. When the voltage at Pin 18 of the control
module is high, about 11.5 volts, and the voltage at
Pin 12 is low, about 1.5 volts the door will move
towards the Panel position. When Pin 12 is High and
Pin 18 is Low the door will move towards the Defrost
position. When both Pin are high or when both Pins
are low, the actuator will not move. The Mode door
feedback signal is a voltage signal that is supplied by
the actuator to the control. The signal will be about
4.5 volts in the Panel position and 0.5 volts in the
Defrost position. As the position of the Mode actuator
changes, so will the feedback signal. The feedback
signal is necessary for the correct positioning of the
mode door.
FAIL CODES/LEVEL DISPLAY
Fail Codes/Level are displayed using the REAR
WIPER and INTERMITTENT LED's flashing in the
sequence indicated below. The REAR WIPER LED
represents the Level and the INTERMITTENT LED
represents the Value. After Calibration/Diagnostics is
completed, the control will begin flashing Level 1
codes. Depressing the WASH button will cycle to
Level 2, depressing WASH again will cycle to Level 3.
Each time the WASH button is depressed will cycle
to the next level. After Level 5 is reached, you will
cycle back to Level 1. If the Control is a Heater Only
you will only cycle from Levels 1 to 3.
TEMPERATURE AND MODE POTENTIOMETER
DIAGNOSTICS
The Temperature and Mode Potentiometer can be
tested after calibration is complete by pressing the
WASH button and cycling to Levels 2, 3 or 5 as dis-
played by the REAR WIPER LED. On Heater Only
units you can only cycle to Levels 2 and 3. In each
individual test the INTERMITTENT LED flash rate
will change as the Temperature or Mode potentiome-
ter is moved from one end to the other, see Potenti-
ometer vs. Position and Flash Rate table.
EVAPORATOR PROBE TEMPERATURE
DIAGNOSTICS
The evaporator probe can be tested by using the
INTERMITTENT LED to display the actual temper-
ature the sensor is reading. The HVAC control mod-
ule can only display temperatures from 1 to 99
degrees. To read the temperature, perform the follow-
ing:
²Set Blower motor to any speed other than OFF
WIPE BUTTON LED
LEVEL DISPLAY
1 FAIL CODES
2 MODE POTENTIOMETER TEST
3 BLEND/PASS. POTENTIOMETER TEST
4 EVAPORATOR PROBE (A/C AND ZONE
UNITS ONLY)
5 DRIVER POTENTIOMETER (ZONE UNITS
ONLY)
LEVEL 1±FAILURE CODE VALUES
(INTERMITTENT WIPE BUTTON LED)
CODE DEFINITION
0 PASSED ALL TESTS
1 MODE ACTUATOR DID NOT REACH
DEFROST POSITION
2 MODE ACTUATOR DID NOT REACH
PANEL POSITION
3 BLEND/PASS. ACTUATOR DID NOT
REACH COLD STOP
4 BLEND PASS. ACTUATOR DID NOT
REACH HEAT STOP
5 EVAPORATOR PROBE OPEN
6 EVAPORATOR PROBE SHORTED
7 DRIVER ACTUATOR DID NOT REACH
COLD STOP
8 ZONE/DRIVER ACTUATOR DID NOT
REACH HEAT STOP
9 CONTROL HEAD INTERNAL FAILURE
POTENTIOMETER VS. POSITION
AND FLASH RATE
POTENTIOMETERINTERMITTENT
LED FASTER
FLASH RATEINTERMITTENT
LED SLOWER
FLASH RATE
MODE PANEL DEFROST
BLEND/PASS. HOT COLD
DRIVER HOT COLD
24 - 8 HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONINGNS/GS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 1885 of 1938

SYSTEM LEAK CHECKING
WARNING: R-134a SERVICE EQUIPMENT OR VEHI-
CLE A/C SYSTEM SHOULD NOT BE PRESSURE
TESTED OR LEAK TESTED WITH COMPRESSED
AIR. SOME MIXTURES OF AIR/R-134a HAVE BEEN
SHOWN TO BE COMBUSTIBLE AT ELEVATED
PRESSURES. THESE MIXTURES ARE POTENTIALLY
DANGEROUS AND MAY RESULT IN FIRE OR
EXPLOSION CAUSING INJURY OR PROPERTY
DAMAGE.
If the A/C system is not cooling properly, determine
if the refrigerant system is fully charged with
R-134a. This is accomplished by performing a system
Charge Level-Check or Fill. If while performing this
test A/C liquid line pressure is less than 207 kPa (30
psi) proceed to Empty Refrigerant System Leak Test.
If liquid line pressure is greater than 207 kPa (30
psi) proceed to low refrigerant level leak test. If the
refrigerant system is empty or low in refrigerant
charge, a leak at any line fitting or component seal is
likely. A review of the fittings, lines and components
for oily residue is an indication of the leak location.
To detect a leak in the refrigerant system, perform
one of the following procedures as indicated by the
symptoms.
WARNING: AVOID BREATHING A/C REFRIGERANT
AND LUBRICANT VAPOR OR MIST. EXPOSURE MAY
IRRITATE EYES, NOSE AND THROAT. USE ONLY
APPROVED SERVICE EQUIPMENT MEETING SAE
REQUIREMENTS TO DISCHARGE R-134a SYSTEM.
IF ACCIDENTAL SYSTEM DISCHARGE OCCURS,
VENTILATE WORK AREA BEFORE RESUMING SER-
VICE.
EMPTY REFRIGERANT SYSTEM LEAK TEST
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system to the lowest
degree of vacuum possible (about 28 in Hg.). Deter-
mine if the system holds a vacuum for 15 minutes. If
vacuum is held, a leak is probably not present. If sys-
tem will not maintain vacuum level, proceed with
this procedure.
(2) Prepare a .284 Kg. (10 oz.) refrigerant charge
to be injected into the system.
(3) Connect and dispense .284 Kg. (10 oz.) of
refrigerant into the evacuated refrigerant system.
(4) Proceed to step two of Low Refrigerant Level
Leak Test.
LOW REFRIGERANT LEVEL LEAK TEST
(1) Determine if there is any (R-134a) refrigerant
in the system. Use the scan tool (DRB) under the
menu Systems Sensors±A/C Pressure test or pressuregauge liquid line temperature partial charge check.
See system charge level check or fill for procedure.
(2) Position the vehicle in a wind free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(3) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run for five minutes with the system
set to the following:
²Transaxle in Park
²Engine Idling at 700 rpm
²A/C Controls Set in 100 percent outside air
²Full Panel Mode
²Blower motor ON HIGH
²A/C in the ON position
²Front Windows Open.
²Rear Air Off (If Equipped)
CAUTION: A leak detector designed for R-12 refrig-
erant will not detect leaks in a R-134a refrigerant
system.
(4) Shut off the vehicle and wait 2 to 7 minutes.
Then use an Electronic Leak Detector that is
designed to detect R-134a type refrigerant and search
for leaks. Fittings, lines, or components that appear
to be oily usually indicates a refrigerant leak. To
inspect the evaporator core for leaks, insert the leak
detector probe into the recirculating air door opening
or a heat duct.
If a thorough leak check has been completed with-
out indication of a leak, proceed to System Charge
Level-Check or Fill.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
A/C PRESSURE TRANSDUCER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the wire connector at the pressure
transducer.
(2) Using an open end wrench, remove the trans-
ducer from the liquid line (Fig. 11).
INSTALLATION
(1) Replace transducer O-ring.
(2) For installation, reverse the above procedures.
A/C SERVICE PORTS
WARNING: THE REFRIGERATION SYSTEM MUST
BE COMPLETELY EMPTY BEFORE PROCEEDING
WITH THIS OPERATION.
The High Side service port is serviceable, the Low
Side is not serviceable.
NS/GSHEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 19
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 1905 of 1938

EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS
CONTENTS
page page
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROLS........ 13
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR)
SYSTEM.............................. 18ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS.................. 1
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION................... 1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE........... 3
COMPONENT MONITORS................. 10
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES............. 3
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS................... 11LOAD VALUE........................... 12
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL)....... 1
MONITORED SYSTEMS.................... 8
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS............... 11
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE............... 2
TRIP DEFINITION........................ 10
GENERAL INFORMATION
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
many different circuits in the fuel injection, ignition,
emission and engine systems. If the PCM senses a
problem with a monitored circuit often enough to
indicate an actual problem, it stores a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) in the PCM's memory. If the
code applies to a non-emissions related component or
system, and the problem is repaired or ceases to
exist, the PCM cancels the code after 40 warmup
cycles. Diagnostic trouble codes that affect vehicle
emissions illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL). Refer to Malfunction Indicator Lamp in this
section.
Certain criteria must be met before the PCM
stores a DTC in memory. The criteria may be a spe-
cific range of engine RPM, engine temperature,
and/or input voltage to the PCM.
The PCM might not store a DTC for a monitored
circuit even though a malfunction has occurred. This
may happen because one of the DTC criteria for the
circuit has not been met.For example, assume the
diagnostic trouble code criteria requires the PCM to
monitor the circuit only when the engine operates
between 750 and 2000 RPM. Suppose the sensor'soutput circuit shorts to ground when engine operates
above 2400 RPM (resulting in 0 volt input to the
PCM). Because the condition happens at an engine
speed above the maximum threshold (2000 rpm), the
PCM will not store a DTC.
There are several operating conditions for which
the PCM monitors and sets DTC's. Refer to Moni-
tored Systems, Components, and Non-Monitored Cir-
cuits in this section.
NOTE: Various diagnostic procedures may actually
cause a diagnostic monitor to set a DTC. For
instance, pulling a spark plug wire to perform a
spark test may set the misfire code. When a repair
is completed and verified, use the DRB scan tool to
erase all DTC's and extinguish the MIL.
Technicians can display stored DTC's by using the
DRB scan tool. Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in
this section. For DTC information, refer to charts in
this section.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LAMP (MIL)
As a functional test, the Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) illuminates at key-on before engine
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 1
Page 1906 of 1938

cranking. Whenever the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) sets a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) that
affects vehicle emissions, it illuminates the MIL. If a
problem is detected, the PCM sends a message over
the CCD Bus to the instrument cluster to illuminate
the lamp. The PCM illuminates the MIL only for
DTC's that affect vehicle emissions. The MIL stays
on continuously when the PCM has entered a
Limp-In mode or identified a failed emission compo-
nent or system. The MIL remains on until the DTC
is erased. Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Code
charts in this group for emission related codes.
Also, the MIL either flashes or illuminates contin-
uously when the PCM detects active engine misfire.
Refer to Misfire Monitoring in this section.
Additionally, the PCM may reset (turn off) the MIL
when one of the following occur:
²PCM does not detect the malfunction for 3 con-
secutive trips (except misfire and fuel system moni-
tors).
²PCM does not detect a malfunction while per-
forming three successive engine misfire or fuel sys-
tem tests. The PCM performs these tests while the
engine is operating within6375 RPM of and within
10 % of the load of the operating condition at which
the malfunction was first detected.
STATE DISPLAY TEST MODE
The switch inputs to the Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) have two recognized states; HIGH and
LOW. For this reason, the PCM cannot recognize the
difference between a selected switch position versus
an open circuit, a short circuit, or a defective switch.
If the State Display screen shows the change from
HIGH to LOW or LOW to HIGH, assume the entire
switch circuit to the PCM functions properly. From
the state display screen, access either State Display
Inputs and Outputs or State Display Sensors.
STATE DISPLAY INPUTS AND OUTPUTS
Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link connec-
tor and access the State Display screen. Then access
Inputs and Outputs. The following list contains the
PCM system functions accessible through the Inputs
and Outputs screen.
Park/Neutral Switch
Speed Control Resume
Brake Switch
Speed Control On/Off
Speed Control Set
S/C Vent Solenoid
Actual S/C Vent Sol.
S/C Vacuum Solenoid
Actual S/C Vacuum Sol.
S/C Cancel
S/C Last Cutout
S/C Working Status
S/C Denied Status
A/C Clutch Relay
Actual A/C Clutch Relay
EGR Solenoid
Actual EGR Sol.
Automatic Shutdown Relay
Actual Automatic Shutdown Relay
Automatic Shutdown Relay Sense
Radiator Fan Control Module
Actual Radiator Fan Control Module
Duty Cycle EVAP Purge Solenoid
Actual EVAP Purge Sol.
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
Power Steering Switch
Closed Loop State
Current CMP Edge
Current CKP State
Current Sync State
Fuel Pump Relay
Actual Fuel Pump Relay
Ignition Sense (A21)
Malfunction Lamp
Limp-in Reason
STATE DISPLAY SENSORS
Connect the DRB scan tool to the vehicle and
access the State Display screen. Then access Sensor
Display. The following list contains the PCM system
functions accessible through the Sensor Display
screen.
Battery Temperature
Engine Coolant Temperature
Engine Coolant Temp Sensor
Throttle Position Volts
Minimum Throttle
Knock Sensor Volts
Battery Voltage
MAP Sensor Reading
Idle Air Control Motor Position
Fig. 1 Data Link (Diagnostic) Connector
25 - 2 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1907 of 1938

Adaptive Fuel Factor
Barometric Pressure
Engine Speed
Module Spark Advance
Speed Control Target
Intake Air Temp Degrees
Intake Air Temp Volts
Charging System Goal
Theft Alarm Status
Map Sensor Voltage
Vehicle Speed
Throttle Opening (percentage)
TPS Calculated
Cam Timing Position
Target Idle
Time From Start To Run
Run Time At Stall
Injector Pulse-width
Upstream O2S Volts
Downstream O2S Volts
Closed Loop Timer
Short Term Adaptive
Current Adaptive Cell
Adaptive Memory Cell 0
Adaptive Memory Cell 1
Adaptive Memory Cell 2
Adaptive Memory Cell 3
Adaptive Memory Cell 4
Adaptive Memory Cell 5
Adaptive Memory Cell 6
Adaptive Memory Cell 7
Adaptive Memory Cell 8
Adaptive Memory Cell 9
Adaptive Memory Cell 10
Adaptive Memory Cell 11
Adaptive Memory Cell 12
Adaptive Memory Cell 13
Adaptive Memory Cell 14
Adaptive Memory Cell 15
Purge Free Idle Cell
Purge Free Cell 2 (corresponds to memory cell 2)
Purge Free Cell 3 (corresponds to memory cell 5)
Target IAC Steps
Retard Cylinder (1)
Retard Cylinder (2)
Retard Cylinder (3)
Retard Cylinder (4)
Retard Cylinder (5)
Retard Cylinder (6)CIRCUIT ACTUATION TEST MODE
The Circuit Actuation Test Mode checks for proper
operation of output circuits or devices the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) may not internally recognize.
The PCM attempts to activate these outputs and
allow an observer to verify proper operation. Most of
the tests provide an audible or visual indication of
device operation (click of relay contacts, fuel spray,
etc.). Except for intermittent conditions, if a device
functions properly during testing, assume the device,
its associated wiring, and driver circuit work cor-
rectly.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) indicates the
PCM has recognized an abnormal condition in the
system.
The preferred and most accurate method of retriev-
ing a DTC is by using the DRB scan tool. The scan
tool supplies detailed diagnostic information which
can be used to more accurately diagnose causes for a
DTC.
Remember that DTC's are the results of a sys-
tem or circuit failure, but do not directly iden-
tify the failed component or components.
NOTE: For a list of DTC's, refer to the charts in this
section.
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1908 of 1938
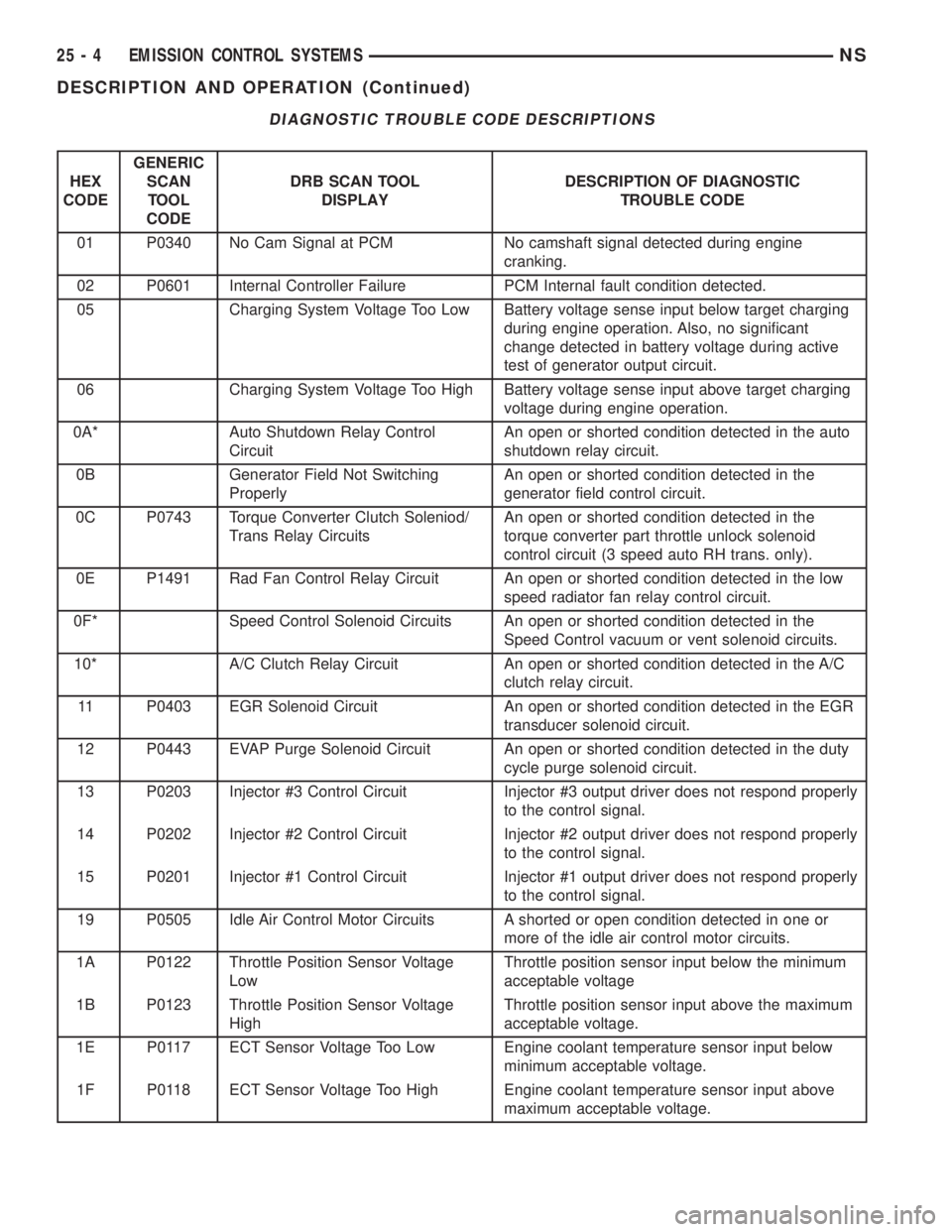
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE DESCRIPTIONS
HEX
CODEGENERIC
SCAN
TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL
DISPLAYDESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODE
01 P0340 No Cam Signal at PCM No camshaft signal detected during engine
cranking.
02 P0601 Internal Controller Failure PCM Internal fault condition detected.
05 Charging System Voltage Too Low Battery voltage sense input below target charging
during engine operation. Also, no significant
change detected in battery voltage during active
test of generator output circuit.
06 Charging System Voltage Too High Battery voltage sense input above target charging
voltage during engine operation.
0A* Auto Shutdown Relay Control
CircuitAn open or shorted condition detected in the auto
shutdown relay circuit.
0B Generator Field Not Switching
ProperlyAn open or shorted condition detected in the
generator field control circuit.
0C P0743 Torque Converter Clutch Soleniod/
Trans Relay CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the
torque converter part throttle unlock solenoid
control circuit (3 speed auto RH trans. only).
0E P1491 Rad Fan Control Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the low
speed radiator fan relay control circuit.
0F* Speed Control Solenoid Circuits An open or shorted condition detected in the
Speed Control vacuum or vent solenoid circuits.
10* A/C Clutch Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the A/C
clutch relay circuit.
11 P0403 EGR Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EGR
transducer solenoid circuit.
12 P0443 EVAP Purge Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the duty
cycle purge solenoid circuit.
13 P0203 Injector #3 Control Circuit Injector #3 output driver does not respond properly
to the control signal.
14 P0202 Injector #2 Control Circuit Injector #2 output driver does not respond properly
to the control signal.
15 P0201 Injector #1 Control Circuit Injector #1 output driver does not respond properly
to the control signal.
19 P0505 Idle Air Control Motor Circuits A shorted or open condition detected in one or
more of the idle air control motor circuits.
1A P0122 Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
LowThrottle position sensor input below the minimum
acceptable voltage
1B P0123 Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
1E P0117 ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below
minimum acceptable voltage.
1F P0118 ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above
maximum acceptable voltage.
25 - 4 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1909 of 1938

HEX
CODEGENERIC
SCAN
TOOL
CODEDRB SCAN TOOL
DISPLAYDESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC
TROUBLE CODE
20 P0134 Right Rear (or just) Upstream O2S
Stays at CenterNeither rich or lean condition detected from the
oxygen sensor.
21* Engine Is Cold Too Long Engine did not reach operating temperature within
acceptable limits.
23 P0500 No Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal No vehicle speed sensor signal detected during
road load conditions.
24 P0107 MAP Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable
voltage.
25 P0108 MAP Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable
voltage.
27 P1297 No Change in MAP From Start to
RunNo difference recognized between the engine MAP
reading and the barometric (atmospheric) pressure
reading from start-up.
28* No Crank Reference Signal at PCM No crank reference signal detected during engine
cranking.
29 P0353 Ignition Coil #3 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with
maximum dwell time.
2A P0352 Ignition Coil #2 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with
maximum dwell time.
2B P0351 Ignition Coil #1 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with
maximum dwell time.
2C* No ASD Relay Output Voltage at
PCMAn Open condition Detected In The ASD Relay
Output Circuit.
2E P0401 EGR System Failure Required change in air/fuel ratio not detected
during diagnostic test.
30* P1697 PCM Failure SRI Miles Not Stored Unsuccessful attempt to update EMR mileage in
the PCM EEPROM.
31 P1698 PCM Failure EEPROM Write
DeniedUnsuccessful attempt to write to an EEPROM
location by the PCM.
39 P0112 Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage
LowIntake air temperature sensor input below the
maximum acceptable voltage.
3A P0113 Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage
HighIntake air temperature sensor input above the
minimum acceptable voltage.
3C P0106 Barometric Pressure Out Of Range MAP sensor has a baro reading below an
acceptable value.
3D P0204 Injector #4 Control Circuit Injector #4 output driver does not respond properly
to the control signal.
3E P0132 Right Rear (or just) Upstream O2S
Shorted to VoltageOxygen sensor input voltage maintained above the
normal operating range.
44 P0600 PCM Failure SPI Communications PCM Internal fault condition detected.
45 P0205 Injector #5 Control Circuit Injector #5 output driver does not respond properly
to the control signal.
46 P0206 Injector #6 Control Circuit Injector #6 output driver does not respond properly
to the control signal.
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1912 of 1938

MONITORED SYSTEMS
There are new electronic circuit monitors that
check fuel, emission, engine and ignition perfor-
mance. These monitors use information from various
sensor circuits to indicate the overall operation of the
fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems and thus
the emissions performance of the vehicle.
The fuel, engine, ignition and emission systems
monitors do not indicate a specific component prob-
lem. They do indicate that there is an implied prob-
lem within one of the systems and that a specific
problem must be diagnosed.
If any of these monitors detect a problem affecting
vehicle emissions, the Malfunction Indicator (Check
Engine) Lamp will be illuminated. These monitors
generate Diagnostic Trouble Codes that can be dis-
played with the check engine lamp or a scan tool.
The following is a list of the system monitors:
²EGR Monitor
²Misfire Monitor
²Fuel System Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Catalyst Monitor
²Evaporative System Leak Detection Monitor
Following is a description of each system monitor,
and its DTC.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnos-
tics Procedures manual for diagnostic proce-
dures.
HEX 66, and 7AÐOXYGEN SENSOR (O2S)
MONITOR
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572É to 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 air fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrous oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The O2S is also the main sensing element for the
EGR, Catalyst and Fuel Monitors.
The O2S may fail in any or all of the following
manners:
²Slow response rate
²Reduced output voltage
²Dynamic shift
²Shorted or open circuitsResponse rate is the time required for the sensor to
switch from lean to rich once it is exposed to a richer
than optimum A/F mixture or vice versa. As the sen-
sor starts malfunctioning, it could take longer to
detect the changes in the oxygen content of the
exhaust gas.
The output voltage of the O2S ranges from 0 to 1
volt. A good sensor can easily generate any output
voltage in this range as it is exposed to different con-
centrations of oxygen. To detect a shift in the A/F
mixture (lean or rich), the output voltage has to
change beyond a threshold value. A malfunctioning
sensor could have difficulty changing beyond the
threshold value.
HEX 67, 69, 7C, and 7DÐOXYGEN SENSOR
HEATER MONITOR
If there is an oxygen sensor (O2S) DTC as well as
a O2S heater DTC, the O2S fault MUST be repaired
first. After the O2S fault is repaired, verify that the
heater circuit is operating correctly.
Effective control of exhaust emissions is achieved
by an oxygen feedback system. The most important
element of the feedback system is the O2S. The O2S
is located in the exhaust path. Once it reaches oper-
ating temperature 300É to 350ÉC (572 Éto 662ÉF), the
sensor generates a voltage that is inversely propor-
tional to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. The
information obtained by the sensor is used to calcu-
late the fuel injector pulse width. This maintains a
14.7 to 1 Air Fuel (A/F) ratio. At this mixture ratio,
the catalyst works best to remove hydrocarbons (HC),
carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) from
the exhaust.
The voltage readings taken from the O2S are very
temperature sensitive. The readings are not accurate
below 300ÉC. Heating of the O2S is done to allow the
engine controller to shift to closed loop control as
soon as possible. The heating element used to heat
the O2S must be tested to ensure that it is heating
the sensor properly.
The O2S circuit is monitored for a drop in voltage.
The sensor output is used to test the heater by iso-
lating the effect of the heater element on the O2S
output voltage from the other effects.
HEX 2EÐEGR MONITOR
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) performs
an on-board diagnostic check of the EGR system.
The EGR system consists of two main components:
a vacuum solenoid and a vacuum operated valve with
a back pressure transducer. The EGR monitor is used
to test whether the EGR system is operating within
specifications. The diagnostic check activates only
during selected engine/driving conditions. When the
25 - 8 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1913 of 1938

conditions are met, the EGR is turned off (solenoid
energized) and the O2S compensation control is mon-
itored. Turning off the EGR shifts the air fuel (A/F)
ratio in the lean direction. The O2S data should indi-
cate an increase in the O2 concentration in the com-
bustion chamber when the exhaust gases are no
longer recirculated. While this test does not directly
measure the operation of the EGR system, it can be
inferred from the shift in the O2S data whether the
EGR system is operating correctly. Because the O2S
is being used, the O2S test must pass its test before
the EGR test.
HEX 6A,6B, 6C, 6D, 6E, AE, and AFÐMISFIRE
MONITOR
Excessive engine misfire results in increased cata-
lyst temperature and causes an increase in HC emis-
sions. Severe misfires could cause catalyst damage.
To prevent catalytic convertor damage, the PCM
monitors engine misfire.
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
for misfire during most engine operating conditions
(positive torque) by looking at changes in the crank-
shaft speed. If a misfire occurs the speed of the
crankshaft will vary more than normal.
HEX 76, 77, 78, and 79ÐFUEL SYSTEM
MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide. The catalyst works best
when the air fuel (A/F) ratio is at or near the opti-
mum of 14.7 to 1.
The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S output. The programmed memory
acts as a self calibration tool that the engine control-
ler uses to compensate for variations in engine spec-
ifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue over
the life span of the engine. By monitoring the actual
air-fuel ratio with the O2S (short term) and multiply-
ing that with the program long-term (adaptive) mem-
ory and comparing that to the limit, it can be
determined whether it will pass an emissions test. If
a malfunction occurs such that the PCM cannot
maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the MIL will
be illuminated.
HEX 70, and B4ÐCATALYST MONITOR
To comply with clean air regulations, vehicles are
equipped with catalytic converters. These converters
reduce the emission of hydrocarbons, oxides of nitro-
gen and carbon monoxide.Normal vehicle miles or engine misfire can cause a
catalyst to decay. A meltdown of the ceramic core can
cause a reduction of the exhaust passage. This can
increase vehicle emissions and deteriorate engine
performance, driveability and fuel economy.
The catalyst monitor uses dual oxygen sensors
(O2S's) to monitor the efficiency of the converter. The
dual O2Ss strategy is based on the fact that as a cat-
alyst deteriorates, its oxygen storage capacity and its
efficiency are both reduced. By monitoring the oxy-
gen storage capacity of a catalyst, its efficiency can
be indirectly calculated. The upstream O2S is used to
detect the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas
before the gas enters the catalytic converter. The
PCM calculates the A/F mixture from the output of
the O2S. A low voltage indicates high oxygen content
(lean mixture). A high voltage indicates a low content
of oxygen (rich mixture).
When the upstream O2S detects a lean condition,
there is an abundance of oxygen in the exhaust gas.
A functioning converter would store this oxygen so it
can use it for the oxidation of HC and CO. As the
converter absorbs the oxygen, there will be a lack of
oxygen downstream of the converter. The output of
the downstraem O2S will indicate limited activity in
this condition.
As the converter loses the ability to store oxygen,
the condition can be detected from the behavior of
the downstream O2S. When the efficiency drops, no
chemical reaction takes place. This means the con-
centration of oxygen will be the same downstream as
upstream. The output voltage of the downstream
O2S copies the voltage of the upstream sensor. The
only difference is a time lag (seen by the PCM)
between the switching of the O2S's.
To monitor the system, the number of lean-to-rich
switches of upstream and downstream O2S's is
counted. The ratio of downstream switches to
upstream switches is used to determine whether the
catalyst is operating properly. An effective catalyst
will have fewer downstream switches than it has
upstream switches i.e., a ratio closer to zero. For a
totally ineffective catalyst, this ratio will be one-to-
one, indicating that no oxidation occurs in the device.
The system must be monitored so that when cata-
lyst efficiency deteriorates and exhaust emissions
increase to over the legal limit, the MIL (check
engine lamp) will be illuminated.
HEX A0, A1, B7, and B8ÐLEAK DETECTION
PUMP MONITOR
The leak detection assembly incorporates two pri-
mary functions: it must detect a leak in the evapora-
tive system and seal the evaporative system so the
leak detection test can be run.
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 9
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1915 of 1938

components now have input (rationality) and output
(functionality) checks. Previously, a component like
the Throttle Position sensor (TPS) was checked by
the PCM for an open or shorted circuit. If one of
these conditions occurred, a DTC was set. Now there
is a check to ensure that the component is working.
This is done by watching for a TPS indication of a
greater or lesser throttle opening than MAP and
engine rpm indicate. In the case of the TPS, if engine
vacuum is high and engine rpm is 1600 or greater
and the TPS indicates a large throttle opening, a
DTC will be set. The same applies to low vacuum
and 1600 rpm.
Any component that has an associated limp in will
set a fault after 1 trip with the malfunction present.
Refer to the Diagnostic Trouble Codes Description
Charts in this section and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Procedure Manual for diagnostic
procedures.
NON-MONITORED CIRCUITS
The PCM does not monitor all circuits, systems
and conditions that could have malfunctions causing
driveability problems. However, problems with these
systems may cause the PCM to store diagnostic trou-
ble codes for other systems or components. For exam-
ple, a fuel pressure problem will not register a fault
directly, but could cause a rich/lean condition or mis-
fire. This could cause the PCM to store an oxygen
sensor or misfire diagnostic trouble code.
The major non-monitored circuits are listed below
along with examples of failures modes that do not
directly cause the PCM to set a DTC, but for a sys-
tem that is monitored.
FUEL PRESSURE
The fuel pressure regulator controls fuel system
pressure. The PCM cannot detect a clogged fuel
pump inlet filter, clogged in-line fuel filter, or a
pinched fuel supply or return line. However, these
could result in a rich or lean condition causing the
PCM to store an oxygen sensor or fuel system diag-
nostic trouble code.
SECONDARY IGNITION CIRCUIT
The PCM cannot detect an inoperative ignition coil,
fouled or worn spark plugs, ignition cross firing, or
open spark plug cables.
CYLINDER COMPRESSION
The PCM cannot detect uneven, low, or high engine
cylinder compression.
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The PCM cannot detect a plugged, restricted or
leaking exhaust system. It may set a EGR or Fuel
system fault or O2S.
FUEL INJECTOR MECHANICAL
MALFUNCTIONS
The PCM cannot determine if a fuel injector is
clogged, the needle is sticking or if the wrong injector
is installed. However, these could result in a rich or
lean condition causing the PCM to store a diagnostic
trouble code for either misfire, an oxygen sensor, or
the fuel system.
EXCESSIVE OIL CONSUMPTION
Although the PCM monitors engine exhaust oxygen
content when the system is in closed loop, it cannot
determine excessive oil consumption.
THROTTLE BODY AIR FLOW
The PCM cannot detect a clogged or restricted air
cleaner inlet or filter element.
VACUUM ASSIST
The PCM cannot detect leaks or restrictions in the
vacuum circuits of vacuum assisted engine control
system devices. However, these could cause the PCM
to store a MAP sensor diagnostic trouble code and
cause a high idle condition.
PCM SYSTEM GROUND
The PCM cannot determine a poor system ground.
However, one or more diagnostic trouble codes may
be generated as a result of this condition. The mod-
ule should be mounted to the body at all times, also
during diagnostic.
PCM CONNECTOR ENGAGEMENT
The PCM may not be able to determine spread or
damaged connector pins. However, it might store
diagnostic trouble codes as a result of spread connec-
tor pins.
HIGH AND LOW LIMITS
The PCM compares input signal voltages from each
input device with established high and low limits for
the device. If the input voltage is not within limits
and other criteria are met, the PCM stores a diagnos-
tic trouble code in memory. Other diagnostic trouble
code criteria might include engine RPM limits or
input voltages from other sensors or switches that
must be present before verifying a diagnostic trouble
code condition.
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)