check engine CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2000 Diagnostic Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2000, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2000Pages: 364, PDF Size: 2.17 MB
Page 3 of 364

TABLE OF CONTENTS - Continued
P-0443 EVAP PURGE SOLENOID CIRCUIT................................143
P-0460 FUEL LEVEL UNIT NO CHANGE OVER MILES.......................148
P-0462 FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT VOLTS TOO LOW......................149
P-0463 FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT VOLTS TOO HIGH......................151
P-0500 NO VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL.............................153
P-0505 IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR CIRCUITS.............................159
P-0505B IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR CIRCUIT.............................164
P-0505C IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR CIRCUIT.............................165
P-0505D IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR CIRCUIT.............................166
P-0505E IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR CIRCUIT.............................167
P-0600 PCM FAILURE SPI COMMUNICATIONS.............................168
P-0601 INTERNAL CONTROLLER FAILURE................................169
P-0645 A/C CLUTCH RELAY CIRCUIT.....................................170
P-0703 BRAKE SWITCH STUCK PRESSED OR RELEASED..................172
P-1195 SLOW 1/1 O2S DURING CATALYST MONITOR.......................175
P-1281 ENGINE IS COLD TOO LONG.....................................177
P1282 FUEL PUMP RELAY CONTROL CIRCUIT.............................178
P-1294 TARGET IDLE NOT REACHED....................................180
P-1297 NO CHANGE IN MAP FROM START TO RUN........................183
P-1388 AUTO SHUTDOWN RELAY CONTROL CIRCUIT......................186
P-1389 NO ASD RELAY OUTPUT VOLTAGE AT PCM........................188
P-1391 INTERMITTENT LOSS OF CMP OR CKP............................191
P-1398 MISFIRE ADAPTIVE NUMERATOR AT LIMIT.........................198
P-1486 EVAP LEAK MONITOR PINCHED HOSE FOUND.....................200
P-1491 RADIATOR FAN CONTROL RELAY CIRCUIT.........................203
P-1494 LEAK DETECTION PUMP PRESSURE SWITCH......................206
P-1495 LEAK DETECTION PUMP SOLENOID CIRCUIT.......................209
P-1496 5 VOLT SUPPLY OUTPUT TOO LOW...............................212
P-1598 A/C PRESSURE SENSOR VOLTS TOO HIGH........................214
P-1599 A/C PRESSURE SENSOR VOLTS TOO LOW.........................217
P-1695 NO CCD MESSAGE FROM BODY CONTROLLER....................220
P-1696 PCM FAILURE EEPROM WRITE DENIED...........................222
P-1697 PCM FAILURE SRI MILE NOT STORED.............................222
P-1698 NO CCD MESSAGES FROM TCM..................................224
CHECKING 5 VOLT SUPPLY CIRCUIT.....................................226
* CHECKING EGR SYSTEM.............................................228
* CHECKING ENGINE VACUUM..........................................231
* CHECKING EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM...........................232
* CHECKING FOR OXYGEN SENSOR SWITCHING..........................234
* CHECKING FUEL DELIVERY...........................................237
* CHECKING IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR.................................242
* CHECKING INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR.........................244
* CHECKING MAP SENSOR CALIBRATION................................245
* CHECKING MINIMUM IDLE AIR FLOW...................................246
* CHECKING OXYGEN SENSOR HEATER.................................247
* CHECKING PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION SWITCH..........................249
* CHECKING PCM POWER AND GROUND CIRCUITS.......................251
* CHECKING SECONDARY IGNITION.....................................252
* CHECKING THE ENGINE MECHANICAL SYSTEMS........................253
* CHECKING THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR CALIBRATION.................254
* CHECKING THE A/C PRESSURE SENSOR SIGNAL........................255
iii
ProCarManuals.com
Page 4 of 364

TABLE OF CONTENTS - Continued
SPEED CONTROL
P-1595 SPEED CONTROL SOLENOID CIRCUITS...........................256
P-1683 SPEED CONTROL POWER RELAY OR S/C 12V DRIVER..............256
SPEED CONTROL BRAKE SWITCH OUTPUT..............................261
SPEED CONTROL DENIED MESSAGE....................................263
SPEED CONTROL ON/OFF SWITCH......................................264
* CHECKING SPEED CONTROL OPERATION..............................266
STARTING
*9NO RESPONSE9CONDITION..........................................272
* CHECKING THE CAM AND CRANK SENSORS............................276
* CHECKING THE ENGINE MECHANICAL SYSTEMS........................277
* CHECKING THE FUEL SYSTEM........................................278
* CHECKING THE IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR.............................287
* CHECKING THE SECONDARY IGNITION SYSTEM.........................288
* NO CRANK CONDITION...............................................296
* START AND STALL CONDITION.........................................301
TRANSMISSION
P-0740 TORQUE CONV CLUTCH, NO RPM DROP AT LOCKUP...............302
P-0743 TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID CIRCUIT................304
P-1899 PARK/NEUTRAL SWITCH STUCK IN PARK OR IN GEAR..............307
ANTENNA FAILURE....................................................310
COP FAILURE.........................................................310
EEPROM FAILURE.....................................................310
INTERNAL FAULTS.....................................................310
RAM FAILURE.........................................................310
SERIAL LINK INTERNAL................................................310
STACK OVERFLOW FAILURE............................................310
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER SYSTEM
PCM STATUS FAILURE.................................................311
ROLLING CODE FAILURE...............................................311
SERIAL LINK EXTERNAL FAULT..........................................311
TRANSPONDER COMMUNICATION FAILURE..............................313
TRANSPONDER ID MISMATCH..........................................313
TRANSPONDER RESPONSE MISMATCH..................................313
VIN MISMATCH........................................................315
VERIFICATION TESTS
VERIFICATION TESTS..................................................317
8.0 COMPONENT LOCATIONS..............................................323
8.1CONTROL MODULES AND PDC.....................................323
8.2CONTROLS & SOLENOIDS.........................................323
8.3DATA LINK CONNECTOR..........................................327
8.4SENSORS.......................................................327
8.5FUEL SYSTEM...................................................330
8.6SWITCHES......................................................331
8.7SPECIFICATIONS.................................................332
iv
ProCarManuals.com
Page 9 of 364
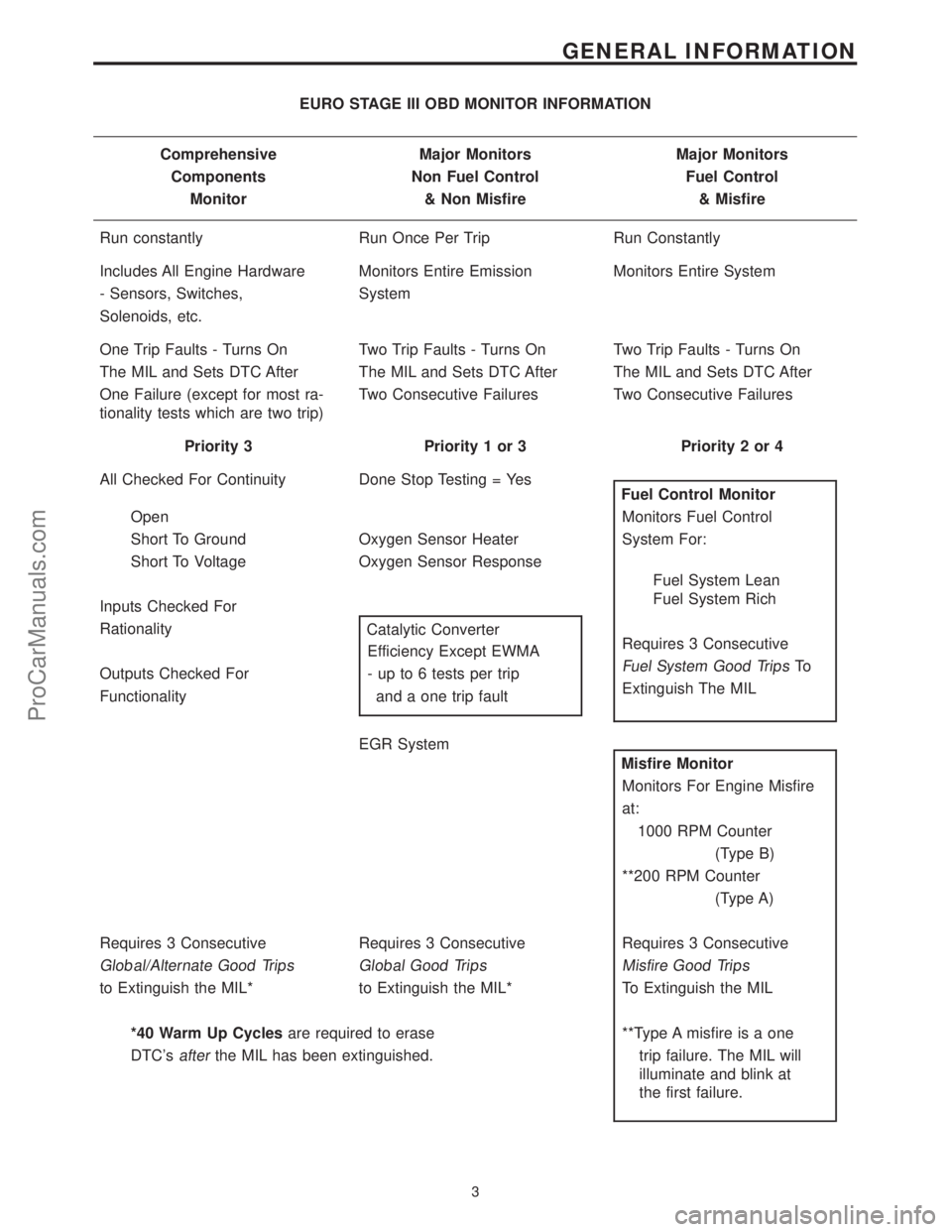
EURO STAGE III OBD MONITOR INFORMATION
Comprehensive Major Monitors Major Monitors
Components Non Fuel Control Fuel Control
Monitor & Non Misfire & Misfire
Run constantly Run Once Per Trip Run Constantly
Includes All Engine Hardware Monitors Entire Emission Monitors Entire System
- Sensors, Switches, System
Solenoids, etc.
One Trip Faults - Turns On Two Trip Faults - Turns On Two Trip Faults - Turns On
The MIL and Sets DTC After The MIL and Sets DTC After The MIL and Sets DTC After
One Failure (except for most ra-
tionality tests which are two trip)Two Consecutive Failures Two Consecutive Failures
Priority 3 Priority 1 or 3 Priority 2 or 4
All Checked For Continuity Done Stop Testing = Yes
Fuel Control Monitor
Open Monitors Fuel Control
Short To Ground Oxygen Sensor Heater System For:
Short To Voltage Oxygen Sensor Response
Fuel System Lean
Fuel System Rich
Inputs Checked For
Requires 3 Consecutive Rationality
Catalytic Converter
Fuel System Good TripsTo Efficiency Except EWMA
Extinguish The MIL Outputs Checked For - up to 6 tests per trip
Functionality and a one trip fault
EGR System
Misfire Monitor
Monitors For Engine Misfire
at:
1000 RPM Counter
(Type B)
**200 RPM Counter
(Type A)
Requires 3 Consecutive Requires 3 Consecutive Requires 3 Consecutive
Global/Alternate Good Trips Global Good Trips Misfire Good Trips
to Extinguish the MIL* to Extinguish the MIL* To Extinguish the MIL
*40 Warm Up Cyclesare required to erase **Type A misfire is a one
DTC's
afterthe MIL has been extinguished. trip failure. The MIL will
illuminate and blink at
the first failure.
3
GENERAL INFORMATION
ProCarManuals.com
Page 12 of 364

Certain criteria must be met for a diagnostic
trouble code to be entered into the SKIM memeory.
The criteria may be a range of; Input voltage, CCD
Bus message, or coded messages to the SKIM. If all
of the criteria for monitoring a circuit or function
are met and a fault is sensed, a diagnostic trouble
code will be stored in the SKIM memory.
3.2.8 SKIS OPERATION
When ignition power is supplied to the SKIM, the
SKIM performs an internal self-test. After the self-
test is completed, the SKIM neergizes the antenna
(this activates the transponder chop responds to the
challenge by generating an encrypted response
message using the following:
Secret Key -This is an electronically stored
value (identification number) that is unique to each
SKIS. The secret key is stored in the SKIM, PCM
and all ignition key tranponders.
Challenge -This is a random numbr that is
generated by the SKIM at each ignition key cycle.
The secret key and challenge are plugged into an
algorithm that produces the encrypted response
message. The transponder uses the crypto algo-
rithm to receive, decode and respond to the message
sent by the SKIM. After responding to the coded
message, the transponder sends a transponder ID
message to the SKIM. The SKIM compares the
transponder ID to the available valid key codes in
the SKIM memory (8 key maximum). After validat-
ing the key the SKIM sends a CCD Bus message
called a ``Seed Request'' to the engine controller
then waits for a PCM response. If the PCM does not
respond, the SKIM will send the seed request agian.
After three failed attempts the SKIM will stop
sending the seed request and store a trouble code. If
the PCM sends a seed response, the SKIM sends a
valid/invalid key message to the PCM. This is an
encrypted message that is generated using the
following:
VIN -Vehicle Identification Number
Seed -This is a random number that is generated
by the PCM at each ignition key cycle.
The VIN and seed are plugged into a rolling code
algorithm that encrypts the ``valid/invalid key'' mes-
sage. The PCM uses the rolling code algorithm to
receive, decode and respond to the valid/invalid key
message sent by the SKIM. After sending the valid/
invalid key massage the SKIM waits 3.5 seconds for
a PCM status message from the PCM. If the PCM
does not respond with a valid key message to the
SKIM, a fault is detected and a trouble code is
stored.
The SKIS incorporates a warning lamp (``ALARM
SET'') located in the message center. The lamp
receives switched ignition voltage and is hardwired
to the body control module. The lamp is actuated
when the SKIM sends a CCD Bus message to thebody controller requesting the lamp on. The body
controller then provides the ground for the lamp.
The SKIM will request lamp operation for the
following:
- bulb checks at ignition on
- to alert the vehicle operator to a SKIS malfunc-
tion
For all faults except transponder faults and VIN
mismatch, the lamp remains on steady. In the event
of a tranponder fault the light flashes at a rate of 1
Hz (once per second). If a fault is pesent the lamp
will emain on or flashing for the complete ignition
cycle. If a fault is stored in SKIM memory which
prevents the system form operating properly, the
PCM will allow the engine to start and run (for 2
seconds) up to six times. After the sixth attempt, the
PCM disables the starter relay until the fault is
corrected.
3.2.9 PROGRAMMING THE POWERTRAIN
CONTROL MODULE
Important Note:Before replacing the PCM for a
failed driver, control circuit or ground circuit, be
sure to check the related component/circuit integ-
rity for failures not detected due to a double fault in
the circuit. Most PCM driver/control circuit failures
are caused by internal failure to components (i.e.
12-volt pull-ups, drivers and ground sensors). These
failures are difficult to detect when a double fault
has occurred and only one DTC has set.
NOTE:IF THE PCM AND THE SKIM ARE
REPLACED AT THE SAME TIME, PROGRAM
THE VIN INTO THE PCM FIRST. ALL VEHICLE
KEYS WILL THEN NEED TO BE REPLACED
AND PROGRAMMED TO THE NEW SKIM.
The SKIS ``Secret Key'' is an ID code that is
unique to each SKIS. This code is programmed and
stored in the SKIM, engine controller and transpon-
der ship (ignition key). When replacing the PCM it
is necessary to program the secret key into the
PCM.
1. Turn the ignition on (transmission in park/
neutral).
2. Use the DRB and select ``THEFT ALARM'',
SKIM then MISCELLANEOUS''.
3. Select ``PCM REPLACED''.
4. Enter secured access mode by entering the vehi-
cle four-digit PIN.
6
GENERAL INFORMATION
ProCarManuals.com
Page 14 of 364

to non-emission codes, they will seem like an intermit-
tent. These codes require a set of parameters to be
performed (The DRBIIItpre-test screens will help
with this for MONITOR codes), this is called a ªTRIPº.
All EURO STAGE III OBD DTCs will be set after one
or in some cases two trip failures, and the MIL will be
turned on. These codes require three successful (no
failures) TRIPS to extinguish the MIL, followed by 40
warm-up cycles to erase the code.
3.3.2 INTERMITTENT CODE
A diagnostic trouble code that is not there every
time the PCM checks the circuit is an ªintermittentº
code. Most intermittent codes are caused by wiring
or connector problems. Defects that come and go
like this are the most difficult to diagnose; they
must be looked for under specific conditions that
cause them. The following checks may assist you in
identifying a possible intermittent problem:
²Visually inspect related wire harness connectors.
Look for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded
terminals.
²Visually inspect the related harnesses. Look for
chafed, pierced, or partially broken wire.
²Refer to any Hotline Newsletters or technical
service bulletins that may apply.
²Use the DRBIIItdata recorder or co-pilot.
²Use the DRBIIItPEP module lab scope.
3.3.3 RESET COUNTER
The reset counter counts the number of times the
vehicle has been started since codes were last set,
erased, or the battery was disconnected. The reset
counter will count up to 255 start counts.
The number of starts helps determine when the
trouble code actually happened. This is recorded by
the PCM and can be viewed on the DRBIIItas
STARTS since set.
When there are no trouble codes stored in mem-
ory, the DRBIIItwill display ªNO DTC'S Detectedº
and the reset counter will show ªSTARTS since
clear = XXX.º
3.3.4 HANDLING NO TROUBLE CODE
PROBLEMS
Symptom checks cannot be used properly unless
the driveability problem characteristic actually
happens while the vehicle is being tested.
Select the symptom that most accurately de-
scribes the vehicle's driveability problem and then
perform the test routine that pertains to this symp-
tom. Perform each routine test in sequence until the
problem is found. For definitions, see Section 6.0
Glossary of Terms.SYMPTOM DIAGNOSTIC TEST
HARD START CHECKING THE 5-VOLT
SUPPLY CIRCUIT
CHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHECKING ENGINE VAC-
UUM
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING COOLANT SEN-
SOR CALIBRATION
CHECKING THROTTLE PO-
SITION SENSOR CALIBRA-
TION
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CALIBRATION
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
CHECKING IDLE AIR CON-
TROL MOTOR OPERATION
CHECKING ENGINE ME-
CHANICAL SYSTEMS
CHECKING EVAP EMISSION
SYSTEM
CHECKING EGR SYSTEM
CHECKING IAT SENSOR
START AND
STALLCHECKING THE 5-VOLT
SUPPLY CIRCUIT
CHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHECKING PCM POWER
AND GND CKT
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING COOLANT SEN-
SOR CALIBRATION
CHECKING THROTTLE PO-
SITION SENSOR CALIBRA-
TION
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CALIBRATION
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
8
GENERAL INFORMATION
ProCarManuals.com
Page 15 of 364

CHECKING IDLE AIR CON-
TROL MOTOR OPERATION
HESITATION/
SAG/
STUMBLECHECKING THE 5-VOLT
SUPPLY CIRCUIT
CHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHECKING PCM POWER
AND GND CKT
CHECKING ENGINE VAC-
UUM
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING COOLANT SEN-
SOR CALIBRATION
CHECKING THROTTLE PO-
SITION SENSOR CALIBRA-
TION
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CALIBRATION
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
CHECKING FOR OXYGEN
SENSOR SWITCHING
CHECKING O2S HEATER
CHECKING IDLE AIR CON-
TROL MOTOR OPERATION
CHECKING ENGINE ME-
CHANICAL SYSTEMS
CHECKING EVAP EMISSION
SYSTEM
CHECKING EGR SYSTEM
CHECKING IAT SENSOR
CHECKING PNP SWITCH
SURGE CHECKING THE 5-VOLT
SUPPLY CIRCUIT
CHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHECKING PCM POWER
AND GND CKT
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING COOLANT SEN-
SOR CALIBRATIONCHECKING THROTTLE PO-
SITION SENSOR CALIBRA-
TION
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CALIBRATION
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
CHECKING FOR OXYGEN
SENSOR SWITCHING
CHECKING IDLE AIR CON-
TROL MOTOR OPERATION
CHECKING EVAP EMISSION
SYSTEM
LACK OF
POWER/
SLUGGISHCHECKING THE 5-VOLT
SUPPLY CIRCUIT
CHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHECKING PCM POWER
AND GND CKT
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING COOLANT SEN-
SOR CALIBRATION
CHECKING THROTTLE PO-
SITION SENSOR CALIBRA-
TION
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CALIBRATION
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
CHECKING FOR OXYGEN
SENSOR SWITCHING
CHECKING IDLE AIR CON-
TROL MOTOR OPERATION
CHECKING EGR SYSTEM
SPARK
KNOCK/
DETONATIONCHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHECKING PCM POWER
AND GND CKT
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING COOLANT SEN-
SOR CALIBRATION
9
GENERAL INFORMATION
ProCarManuals.com
Page 16 of 364

CHECKING THROTTLE PO-
SITION SENSOR CALIBRA-
TION
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CALIBRATION
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
CHECKING FOR OXYGEN
SENSOR SWITCHING
CHECKING IDLE AIR CON-
TROL MOTOR OPERATION
CHECKING EVAP EMISSION
SYSTEM
CUTS OUT/
MISSESCHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHECKING PCM POWER
AND GND CKT
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
CHECKING FOR OXYGEN
SENSOR SWITCHING
CHECKING IDLE AIR CON-
TROL MOTOR OPERATION
CHECKING EGR SYSTEM
BACKFIRE/
POPBACKCHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHECKING PCM POWER
AND GND CKT
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CALIBRATION
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
CHECKING FOR OXYGEN
SENSOR SWITCHING
CHECKING EGR SYSTEM
RUNS
ROUGH/
UNSTABLE/
ERRATIC
IDLECHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEMCHECKING PCM POWER
AND GND CKT
CHECKING ENGINE VAC-
UUM
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING COOLANT SEN-
SOR CALIBRATION
CHECKING THROTTLE PO-
SITION SENSOR CALIBRA-
TION
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CALIBRATION
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
CHECKING FOR OXYGEN
SENSOR SWITCHING
CHECKING O2S HEATER
CHECKING IDLE AIR CON-
TROL MOTOR OPERATION
CHECKING ENGINE ME-
CHANICAL SYSTEMS
CHECKING EVAP EMISSION
SYSTEM
CHECKING EGR SYSTEM
CHECKING IAT SENSOR
CHECKING PNP SWITCH
POOR FUEL
ECONOMYCHECKING SECONDARY
IGNITION SYSTEM
CHECKING PCM POWER
AND GND CKT
CHECKING ENGING VAC-
UUM
CHECKING THE FUEL
PRESSURE
CHECKING COOLANT SEN-
SOR CALIBRATION
CHECKING THROTTLE PO-
SITION SENSOR CALIBRA-
TION
CHECKING MAP SENSOR
CALIBRATION
CHECKING THE MINIMUM
IDLE AIR FLOW
10
GENERAL INFORMATION
ProCarManuals.com
Page 17 of 364

CHECKING FOR OXYGEN
SENSOR SWITCHING
CHECKING O2S HEATER
CHECKING IDLE AIR CON-
TROL MOTOR OPERATION
CHECKING ENGINE ME-
CHANICAL SYSTEMS
CHECKING EVAP EMISSION
SYSTEM
CHECKING EGR SYSTEM
CHECKING IAT SENSOR
CHECKING PNP SWITCH
3.4 USING THE DRBIIIT
Refer to the DRBIIItuser 's guide for instructions
and assistance with reading trouble codes, erasing
trouble codes, and other DRBIIItfunctions.
3.5 DRB ERROR MESSAGES AND BLANK
SCREEN
Under normal operation, the DRBIIItwill dis-
play one of only two error messages:
± User-Requested WARM Boot or User-
Requested COLD Boot.
This is a sample of such an error message display:
ver: 2.14
date: 26 Jul93
file: key_itf.cc
date: Jul 26 1993
line: 548
err: 0x1
User-Requested COLD Boot
Press MORE to switch between this display
and the application screen.
Press F4 when done noting information.
3.5.1 DRB IIITDOES NOT POWER UP
If the LED's do not light or no sound is emitted at
start up, check for loose cable connections or a bad
cable. Check the vehicle battery voltage (data link
connector cavity 16). A minimum of 11 volts is
required to adequately power the DRBIIIt.
If all connections are proper between the
DRBIIItand vehicle or other devices, and the
vehicle battery is fully charged, an inoperative
DRBIIItmay be the result of a faulty cable or
vehicle wiring. For a blank screen, refer to the
appropriate body diagnostics manual.
3.5.2 DISPLAY IS NOT VISIBLE
Low temperatures will affect the visibility of the
display. Adjust the contrast to compensate for this
condition.
4.0 DISCLAIMERS, SAFETY,
WARNINGS
4.1 DISCLAIMERS
All information, illustrations, and specifications
contained in this manual are based on the latest
information available at the time of publication.
The right is reserved to make changes at any time
without notice.
4.2 SAFETY
4.2.1 TECHNICIAN SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: ENGINES PRODUCE CARBON
MONOXIDE THAT IS ODORLESS, CAUSES
SLOWER REACTION TIME, AND CAN LEAD
TO SERIOUS INJURY. WHEN THE ENGINE IS
OPERATING, KEEP SERVICE AREAS WELL
VENTILATED OR ATTACH THE VEHICLE
EXHAUST SYSTEM TO THE SHOP EXHAUST
REMOVAL SYSTEM.
Set the parking brake and block the wheels before
testing or repairing the vehicle. It is especially impor-
tant to block the wheels on front-wheel drive vehicles;
the parking brake does not hold the drive wheels.
When servicing a vehicle, always wear eye pro-
tection, and remove any metal jewelry such as
watchbands or bracelets that might make an inad-
vertent electrical contact.
When diagnosing a powertrain system problem,
it is important to follow approved procedures where
11
GENERAL INFORMATION
ProCarManuals.com
Page 25 of 364

Symptom:
P-1594 CHARGING SYSTEM VOLTAGE TOO HIGH
POSSIBLE CAUSES
GENERATOR FIELD DRIVER CIRCUIT SHORT TO GROUND
GENERATOR SHORTED
PCM DEFECTIVE (CHARGING SYSTEM)
PCM BATT TEMP NOT W/I þ12 DEGREES C (10 DEGREES F) UNDER HOOD TEMP
PCM VOLT & TARGET CHARGING VOLT DIFFER BY > 1.0 V
TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
1 Ignition on, engine not running.
Note: Battery must be fully charged.
Note: Generator Belt tension and condition must be checked before con-
tinuing.
With the DRB, actuate the Generator Field Driver.
Using a voltmeter, backprobe the Generator Field Driver Circuit voltage in back of
Generator.
Does the DRB show voltage shift low to high?All
Ye s®Go To 2
No®Go To 6
2 Ignition On, Engine Not Running
With the DRB, stop the Generator Field Driver actuation.
Read the target charging voltage.
Is the target charging voltage between 13.0 to 14.9 volts?All
Ye s®Test Complete.
No®Go To 3
3 Engine running.
Manually set the engine speed to 1600 RPM.
With the DRB, read both the voltage and the target charging voltage.
Compare the9target9to the9volt9reading.
Watch for up to 5 minutes, if necessary, for a 1.0 volt difference or more.
Was there more than a 1.0 volt difference?All
Ye s®Replace PCM.
Perform Powertrain Verification Test VER-3A.
No®Go To 4
4 Ignition On, Engine Not Running
Using the DRB Temperature Probe, measure the under hood temperature near PCM.
With the DRB, read the BTS temperature.
Is the Battery Temperature within þ12 degrees C (10 degrees F) of the under hood
temperature?All
Ye s®Go To 5
No®Replace PCM.
Perform Powertrain Verification Test VER-3A.
19
CHARGING
ProCarManuals.com
Page 26 of 364

TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
5 Turn ignition on, engine not running.
Erase trouble codes.All
Refer to symptom * CHARGING SYSTEM NO CODE TEST in the
CHARGING category.
6 Ignition Off
Disconnect the Field Harness Connector at back of Generator.
Note: Check connectors - Clean/repair as necessary.
Using an ohmmeter, measure resistance of one of the Generator Field Terminals at
the Generator to Ground.
Is the resistance below 5.0 ohms?All
Ye s®Repair or replace the shorted Generator as necessary.
Perform Powertrain Verification Test VER-3A.
No®Go To 7
7 Ignition Off
Disconnect the PCM Connector.
Disconnect the Field Harness Connector at back of Generator.
Note: Check connectors - Clean/repair as necessary.
Using an ohmmeter, measure the Generator Field Driver Circuit from PCM Connec-
tor to ground.
Is the resistance below 5.0 ohms?All
Ye s®Repair the Generator Field Driver Circuit short to ground.
Perform Powertrain Verification Test VER-3A.
No®Go To 8
8 Ignition off.
If there are no potential causes remaining, the PCM is assumed to be defective.
View repair optionsAll
Repair
Replace the Powertrain Control Module.
Perform Powertrain Verification Test VER-3A.
20
CHARGING
P-1594 CHARGING SYSTEM VOLTAGE TOO HIGH ÐContinued
ProCarManuals.com