tow CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001Pages: 4284, PDF Size: 83.53 MB
Page 2717 of 4284

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Unsnap 2 clips.
(2) Lift cover and pull toward the engine and
remove cover tabs from air box.
(3) Lift cover and remove the element (Fig. 13).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the air filter element into air box (Fig.
11).
(2) Move cover so that the tabs insert into the air
box.
(3) Push cover down and snap the 2 clips.
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect the inlet air temperature sensor
(Fig. 14).
(3) Remove the inlet hose to throttle body.
(4) Remove the bolt for air box at upper radiator
cross member.(5) Pull air box up and off over the single locating
pin.
(6) Remove air box from vehicle
INSTALLATION
(1) Install air box into vehicle and onto the locat-
ing pin.
(2) Install bolt to hold air box to the upper radia-
tor cross member.
(3) Install the inlet hose to the throttle body.
(4) Connect the inlet air temperature sensor (Fig.
14).
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
Cooling System Tester 7700
Combustion Leak Tester C-3685-A
Compression Test Adapter 8116
Fig. 13 AIR BOX COVER
Fig. 14 Inlet Air Temperature Sensor
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-93
SPECIAL TOOLS (Continued)
Page 2729 of 4284

DISASSEMBLY - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
CAUTION: Do not attempt to drive the bolt from the
rocker shaft. This can damage the retainer and bolt
assembly.
(1) Remove the rocker arm retainer and bolt by
performing the following procedure:
(a) Using adjustable pliers, grip the edges of the
retainer (Fig. 39).
(b) Apply an upward force with a slight rocking
motion until the retainer disengages from shaft
(Fig. 39).
(2) Remove rocker arms (Fig. 40). Identify the
component locations for reassembly in original loca-
tions.
ASSEMBLY - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
(1) Install rocker arms on the shaft (Fig. 40).
Install in the orginal positions if re-used.Ensurethe
rocker shaft, all the retainers and washers are prop-
erly positioned and installed in the correct locations
(Fig. 40).(2) Install rocker arms and shaft to the cylinder
head. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/
ROCKER ARMS - INSTALLATION)
INSTALLATION - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
CAUTION: Ensure the longer shaft retaining bolt is
installed in the proper location on the rocker shaft.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER
ARMS - ASSEMBLY)
(1) Position the rocker arm and shaft assemblies
on the pedestal mounts.
CAUTION: Ensure all pushrods are properly located
on the lifter and the rocker arm socket.
(2) Align each rocker arm socket with each push-
rod end.
CAUTION: The rocker arm shaft should be tight-
ened down slowly, starting with the center bolts.
Allow 20 minutes lifter bleed down time after instal-
lation of the rocker shafts before engine operation.
Fig. 40 ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT
1 - BOLT (ROCKER SHAFT OIL FEED - LONGER LENGTH) 5 - ROCKER ARM - EXHAUST
2 - SHAFT RETAINER/SPACER - 21.5 mm (0.84 in.) 6 - WASHER
3 -SHAFT RETAINER/SPACER - 37.5 mm (1.47 in.) 7 - ROCKER ARM - INTAKE (LARGER OFFSET)
4 - SHAFT RETAINER/SPACER - 40.9 mm (1.61 in.) 8 - ROCKER ARMS LUBRICATION FEED HOLE (POSITION
UPWARD & TOWARD VALVE SPRING_
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 105
ROCKER ARMS (Continued)
Page 2743 of 4284

OIL LEVEL TOO HIGH
If oil level is above the MAX mark on dipstick, it is
possible for the connecting rods to dip into the oil
while engine is running and create foaming. Foam in
oil pan would be fed to the hydraulic lifters by the oil
pump causing them to become soft and allow valves
to seat noisily.
OIL LEVEL TOO LOW
Low oil level may allow pump to take in air which
when fed to the lifters it causes them to become soft
and allows valves to seat noisily. Any leaks on intake
side of pump, through which air can be drawn, will
create the same lifter noise. Check the lubrication
system from the intake strainer to the oil pump
cover, including the relief valve retainer cap. When
lifter noise is due to aeration, it may be intermittent
or constant, and usually more than one lifter will be
noisy. When oil level and leaks have been corrected,
the engine should be operated at fast idle to allow all
of the air inside of the lifters to be bled out.
VALVE TRAIN NOISE
To determine source of valve train noise, operate
engine at idle with cylinder head covers removed and
listen for source of the noise.
NOTE: Worn valve guides or cocked springs are
sometimes mistaken for noisy lifters. If such is the
case, noise may be dampened by applying side
thrust on the valve spring. If noise is not apprecia-
bly reduced, it can be assumed the noise is in the
tappet. Inspect the rocker arm push rod sockets
and push rod ends for wear.
Valve lifter noise ranges from light noise to a
heavy click. A light noise is usually caused by exces-
sive leak-down around the unit plunger which will
necessitate replacing the lifter, or by the plunger par-
tially sticking in the lifter body cylinder. A heavy
click is caused either by a lifter check valve not seat-
ing, or by foreign particles becoming wedged between
the plunger and the lifter body causing the plunger
to stick in the down position. This heavy click will be
accompanied by excessive clearance between the
valve stem and rocker arm as valve closes. In either
case, lifter assembly should be removed for inspec-
tion.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cylinder head(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove the yoke retainer and aligning yokes
(Fig. 71).
(3) Remove the hydraulic lifters. If necessary use
Special Tool C-4129, or equivalent to remove liftersfrom bores. If lifters are to be reused, identify each
lifter to ensure installation in original location.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate the lifters with engine oil.
NOTE: Position the lifter in bore with the lubrication
hole facing upward (Fig. 70).
(2) Install the hydraulic lifters with the lubrication
hole facing upward towards middle of block (Fig. 70).
Install lifters in original positions, if reused.
(3) Install lifter aligning yokes (Fig. 71).
(4) Install yoke retainer and torque screws to 12
N´m (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 71).
(5) Install the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION)
(6) Start and operate engine. Warm up to normal
operating temperature.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to valve mechanism,
engine must not be run above fast idle until all
hydraulic lifters have filled with oil and have
become quiet.
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are made of cast aluminum alloy and
are a strutless, short skirt design. The piston rings
consist of two compression rings and a three piece oil
ring. Piston pins connect the piston to the forged
steel connecting rods. The piston pins are a press fit
into the connecting rod.
Fig. 70 LIFTER LUBRICATION HOLE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 119
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 2756 of 4284
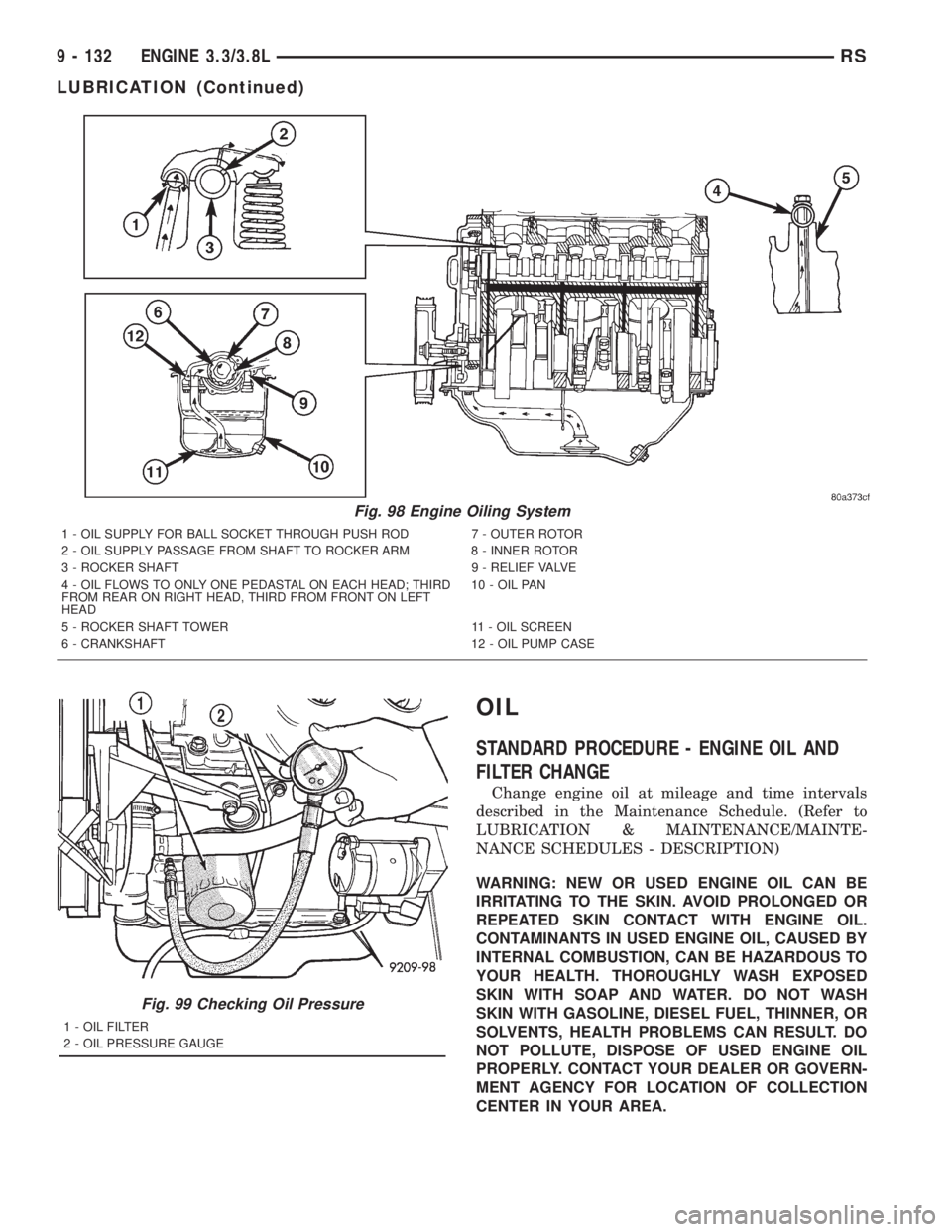
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL AND
FILTER CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTE-
NANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
Fig. 98 Engine Oiling System
1 - OIL SUPPLY FOR BALL SOCKET THROUGH PUSH ROD 7 - OUTER ROTOR
2 - OIL SUPPLY PASSAGE FROM SHAFT TO ROCKER ARM 8 - INNER ROTOR
3 - ROCKER SHAFT 9 - RELIEF VALVE
4 - OIL FLOWS TO ONLY ONE PEDASTAL ON EACH HEAD; THIRD
FROM REAR ON RIGHT HEAD, THIRD FROM FRONT ON LEFT
HEAD10 - OIL PAN
5 - ROCKER SHAFT TOWER 11 - OIL SCREEN
6 - CRANKSHAFT 12 - OIL PUMP CASE
Fig. 99 Checking Oil Pressure
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - OIL PRESSURE GAUGE
9 - 132 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 2820 of 4284

cylinder bore. Check gap with feeler gauge (Fig. 49).
Top compression ring gap .30 to .45mm (.0118 to
.0177 in.). Second compression ring gap .30 to .45mm
(.0118 to .0177 in.). Oil control ring gap .25 to .50mm
(.0098 to .0196 in.).
(2) If ring gaps exceed dimension given, new rings
or cylinder liners must be fitted. Keep piston rings in
piston sets.
(3) Check piston ring to groove clearance (Fig. 50).
Top compression ring gap .080 to .130mm (.0031 to
.0051 in.). Second compression ring gap .070 to
.110mm (.0027 to .0043 in.). Oil control ring gap .040
to .080mm (.0015 to .0031 in.).REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove cylinder head (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD - REMOVAL).
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(4) Remove oil pan (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(5) Remove oil pump pickup tube.(Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - REMOVAL)
(6) Remove balance shaft assembly (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/BALANCE SHAFT -
REMOVAL).
(7) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a ridge
reamer before removing pistons from cylinder block.
Be sure to keep top of pistons covered during
this operation.
(8) Piston and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. Rotate crankshaft so that
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
NOTE: Be careful not to nick or scratch crankshaft
journals
(9) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat-
ing rod and mark pistons with matching cylinder
number when removed from engine block.
PISTON PIN - REMOVAL
(1) Secure connecting rods in a soft jawed vice.
(2) Remove 2 snap rings securing piston pin (Fig.
51).
(3) Push piston pin out of piston and connecting
rod (Fig. 51).
PISTON RING - REMOVAL
(1) ID mark on face of top and second piston rings
must point toward piston crown.
(2) Using a suitable ring expander, remove top and
second piston rings (Fig. 52).
(3) Remove upper oil ring side rail, lower oil ring
side rail and then the oil expander from piston.
(4) Carefully clean carbon from piston crowns,
skirts and ring grooves ensuring the 4 oil holes in
the oil control ring groove are clear.
INSPECTION
PISTONS
(1) Piston Diameter: Size: 91.912-91.928mm
(3.6185-3.6192 in.) Maximum wear limit .05mm
(.0019 in.).
(2) Check piston pin bores in piston for roundness.
Make 3 checks at 120É intervals. Maximum out of
roundness .05mm (.0019in.).
(3) The piston diameter should be measured
approximately 15 mm (.590 in.) up from the base.
Fig. 49 RING END GAP MEASUREMENT
1 - FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 50 PISTON RING TO GROOVE CLEARANCE
9a - 38 ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESELRG
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 2822 of 4284

PISTON PINS
(1) Measure the diameter of piston pin in the cen-
ter and both ends.
(2) Piston pin diameter is 29.992 to 29.996mm
(1.1807 to 1.1809 in.).
INSTALLATION
PISTON PIN INSTALLATION
(1) Secure connecting rod in soft jawed vice.
(2) Lubricate piston pin and piston with clean
engine oil.
(3) Position piston on connecting rod (Fig. 53).
CAUTION: Ensure arrow on piston crown and the
bearing cap numbers on the connecting rod are on
the opposite side.
(4) Install piston pin (Fig. 53).
(5) Install clips in piston to retain piston pin (Fig.
53).
(6) Remove connecting rod from vice.
PISTON RINGS - INSTALLATION
(1) Install rings on the pistons using a suitable
ring expander (Fig. 54).
(2) Top compression ring is tapered and chromium
plated. The second ring is of the scraper type and
must be installed with scraping edge facing bottom of
the piston. The third is an oil control ring. Ring gaps
must be positioned, before inserting piston into the
liners, as follows.
(3) Top ring gap must be positioned at the #3 posi-
tion (looking at the piston crown from above) (Fig.
55).
(4) Second piston ring gap should be positioned at
the #1 position (Fig. 55).
(5) Oil control ring gap should be positioned at the
#2 position (Fig. 55).
(6) When assembling pistons check that compo-
nents are installed in the same position as before dis-
assembly, determined by the numbers stamped on
the crown of individual pistons. Engine cylinders are
numbered starting from gear train end of the engine.
Face arrow on top of piston toward front of
engine. Therefore, the numbers stamped on connect-
ing rod big end should face toward the injection
pump side of engine. To insert piston into cylinder
use a ring compressor as shown in (Fig. 56).
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing pistons, and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, be sure that compression
ring gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with
oil ring rail gap (Fig. 55).
Fig. 53 PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
1 - PISTON PIN
2 - PISTON
3 - SNAP RING
4 - CONNECTING ROD ALIGNMENT NUMBERS
5 - CONNECTING ROD BOLT
6 - CONNECTING ROD BEARING
7 - CONNECTING ROD
8 - SNAP RING
9a - 40 ENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESELRG
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 2823 of 4284

(2) Before installing the ring compressor, make
sure the oil ring expander ends are butted together.
(3) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil, slide the ring compressor, over the piston
and tighten (Fig. 56).Ensure position of rings
does not change during this operation.
(4) Face arrow on piston towards front of engine.
NOTE: Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(5) Rotate crankshaft so that the connecting rod
journal is on the center of the cylinder bore. Insert
rod and piston into cylinder bore and guide rod over
the crankshaft journal.
(6) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on connecting rod journal.
(7) Install connecting rod caps (Fig. 57). Install rod
bolts and tighten to 30N´m (22 ft.lb.) plus 60É. Then
torque to 88N´m (65 ft.lb).
Fig. 54 PISTON RINGS-INSTALLATION
Fig. 55 PISTON RING GAP LOCATION
3 - TOP COMPRESSION RING GAP POSITION
1 - SECOND COMPRESSION RING GAP POSITION
2 - OIL CONTROL RING GAP POSITION
Fig. 56 PISTON INSTALLATION USING VM.1065
1 - PISTON
2 - VM.1065
3 - ENGINE BLOCK
Fig. 57PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD INSTALLATION
1 - PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
2 - FOUR DIGIT NUMBER
3 - CONNECTING ROD BOLT
4 - FOUR DIGIT NUMBER
RGENGINE 2.5L TURBO DIESEL9a-41
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 2874 of 4284

The fuel filter is replaceable, it is mounted on the
outside and on top of the fuel tank. Refer to the
Maintenance Schedules in the Introduction section of
this manual for recommended fuel filter replacement
intervals.
FFV REPLACEMENT PARTS
Many components in a Flexible Fuel Vehicle (FFV)
are designed to be compatible with ethanol. Always
be sure that the vehicle is serviced with correct etha-
nol compatible parts.
CAUTION: Replacing fuel system components with
non-ethanol compatible components can damage
your vehicle and may void the warranty.
OPERATION
The fuel system is provided fuel pressure by an in-
tank pump module. The PCM controls the operation
of the fuel system by providing battery voltage to the
fuel pump through the fuel pump relay. The PCM
requires only three inputs and a good ground to oper-
ate the fuel pump relay. The three inputs are:
²Ignition voltage
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL DELIVERY
SYSTEM
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnositic Information)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
(1) Remove Fuel Pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.(2) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(3) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(4) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
(5) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(6) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(7) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRB IIItscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING FUEL
TANK
(1) Release fuel system pressure, refer to the Fuel
System Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Insert a 1/4 inch siphon (max. O. D. 5/16) hose
from a portable fuel siphoning tank through the fuel
filler neck opening into the fuel tank. Hose most
have a 30 degree angle cut on the end to bypass the
check valve in the end of the filler neck. Refer to the
siphoning tank's Manufacturing Instructions.
(3) Drain fuel from fuel tank into siphoning tank.
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
400 kpa634 kpa (58 psi65 psi)
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fuel Rail 2.4L 22 200
Fuel Rail 3.3/3.8L 11.8 105
Fuel Tank Strap 54 40
Fuel Tank T Strap 28.2 250
Fuel Filter Bolt 4.5 40
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 2881 of 4284

FUEL RAIL
REMOVAL - 2.4L
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before servicing or starting repairs.Refer to
Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure in this sec-
tion.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Disconnect the wiring connectors for fuel injec-
tors harness (Fig. 13).
(4) Remove wiring harness from brackets.
(5) Disconnect the connectors from the fuel injec-
tors.
(6) Remove harness from vehicle.
(7) Remove fuel hose quick connect fitting from the
chassis tube.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.Place a
shop towel under the connections to absorb any fuel
spilled from the fitting.
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(8) Remove fuel rail attaching bolts.
(9) Remove fuel rail. Be careful not to damage the
injector O-rings upon removal from their ports.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before servicing or starting repairs.Refer to
Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure in this sec-
tion.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Remove upper intake manifold, refer to the
Engine/Manifolds/Upper Intake for more informa-
tion..
(4) Cover intake manifold with suitable cover
when servicing.(5) Remove the fuel hose quick connect fitting from
the chassis tube.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps
and Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(6) Remove the fuel rail attaching bolts (Fig. 14).
(7) Remove fuel rail. Be careful not to damage the
injector O-rings upon removal from their ports.
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged.
(2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation.
(3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports.
(4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect the connectors to the fuel injectors.
(6) Install wiring harness to brackets.
(7) Connect the wiring connectors to fuel injectors
harness (Fig. 13).
(8) Connect negative battery cable.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged.
(2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation.
Fig. 13 FUEL RAIL AND INJECTORS 2.4L
1 - Fuel Injectors
2 - Fuel Rail
Fig. 14 FUEL INJECTORS 3.3/3.8L
1 - FUEL INJECTORS
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-9
Page 2887 of 4284

PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting can be identified by the use of a
full-round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 25) usually black
in color.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers, retainers) of this type of quick-connect fitting
are not serviced separately. Do not attempt to repair
damaged fittings or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is nec-
essary, replace the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To release fuel system component from quick-
connect fitting, firmly push fitting towards compo-
nent being serviced while firmly pushing plastic
retainer ring into fitting (Fig. 25). With plastic ring
depressed, pull fitting from component.The plastic
retainer ring must be pressed squarely into fit-
ting body. If this retainer is cocked during
removal, it may be difficult to disconnect fit-
ting. Use an open-end wrench on shoulder of
plastic retainer ring to aid in disconnection.
(5) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(6) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage. Replace
as necessary.
(7) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(8) Insert quick-connect fitting into component
being serviced until a click is felt.
(9) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery or
auxiliary jumper terminal.
(11) Use the DRB IIItscan tool ASD Fuel System
Test to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
ROLLOVER VALVE
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles have rollover valve(s) on top of the fuel
tank.
OPERATION
The valves prevent fuel flow through the fuel tank
vent valve hoses should the vehicle rollover.
The rollover valves on the fuel tank are not ser-
viceable.
Fig. 25 Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting
1 - FUEL TUBE
2 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
3 - PUSH
4 - PLASTIC RETAINER
5 - PUSH
6 - PUSH
7 - PUSH
8 - PUSH
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-15
QUICK CONNECT FITTING (Continued)