traction control CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001Pages: 4284, PDF Size: 83.53 MB
Page 1210 of 4284
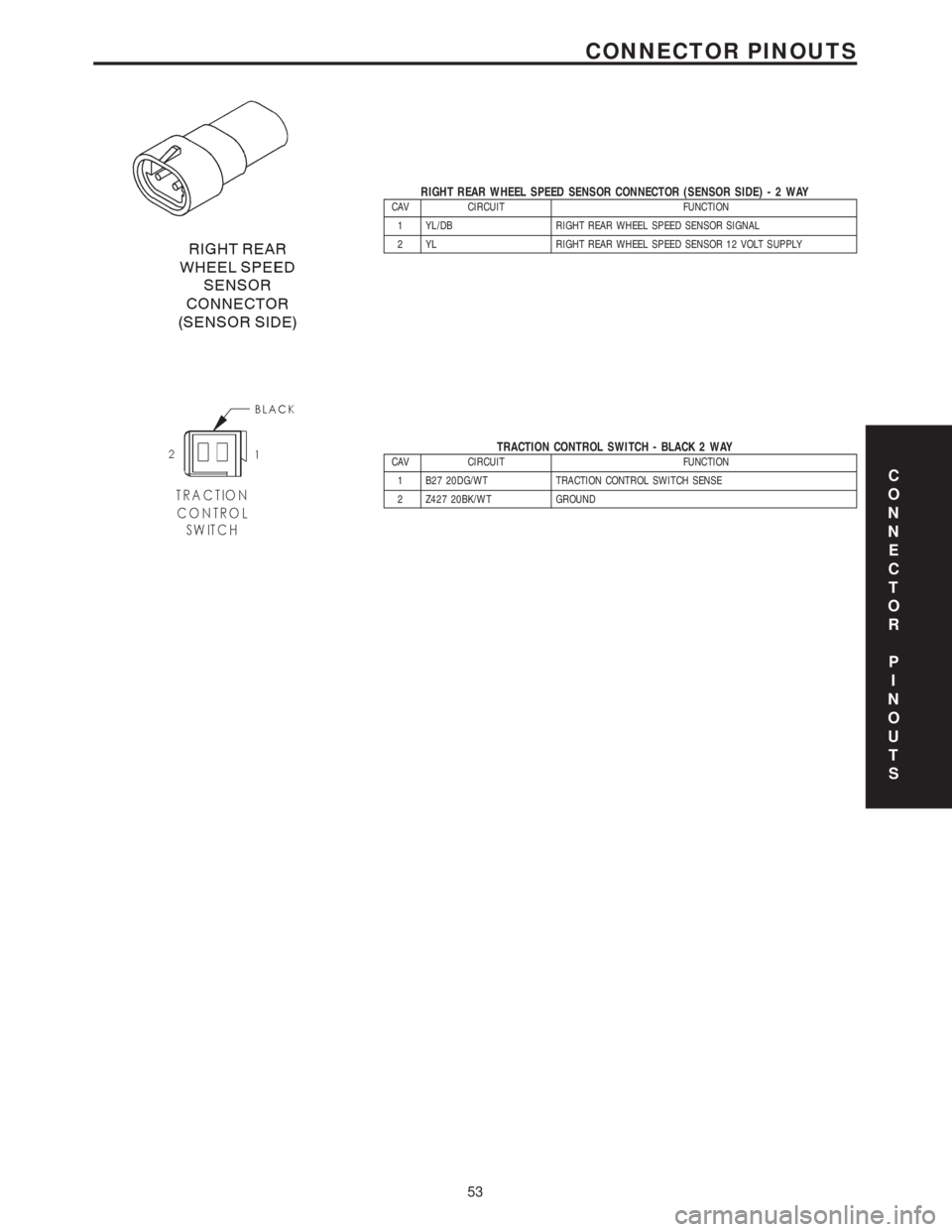
RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR (SENSOR SIDE)-2WAYCAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 YL/DB RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR SIGNAL
2 YL RIGHT REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR 12 VOLT SUPPLY
TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH - BLACK 2 WAYCAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 B27 20DG/WT TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH SENSE
2 Z427 20BK/WT GROUNDC
O
N
N
E
C
T
O
R
P
I
N
O
U
T
S
53
CONNECTOR PINOUTS
Page 1602 of 4284

REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
DESCRIPTION...........................26
OPERATION.............................26
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................27
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE NOISE.........27
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE OPERATION....29
REMOVAL..............................29
DISASSEMBLY...........................30
ASSEMBLY.............................32
INSTALLATION...........................36
SPECIFICATIONS........................37
SPECIAL TOOLS.........................37
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION...........................37
OPERATION.............................38
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION...........................43
OPERATION.............................43FLUID - DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................44
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY FLUID CHANGE . . 44
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................44
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH HOUSING FLUID
CHANGE..............................44
VISCOUS COUPLER
DESCRIPTION...........................45
OPERATION.............................45
TORQUE ARM
REMOVAL..............................47
INSTALLATION...........................47
INPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL..............................47
INSTALLATION...........................47
OUTPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL..............................49
INSTALLATION...........................50
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The rear driveline module assembly (Fig. 1) con-
sists of four main components:
²Bi-Directional Overrunning Clutch (BOC)
²Viscous Coupling
²Differential Assembly
²Torque Arm
The viscous coupling and bi-directional overrun-
ning clutch are contained within an overrunning
clutch housing, which fastens to the differential
assembly. The overrunning clutch housing and differ-
ential assembly have unique fluid sumps, each
requiring their own type and capacity of fluid. The
overrunning clutch housing requires MopartATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602) or equiv-
alent. The differential assembly requires
Driveline module service is limited to the following
components:
²Differential Assembly (serviced only as assem-
bly)
²Viscous Coupling
²Bi-Directional Overrunning Clutch (BOC)
²Overrunning Clutch Housing
²Seals (Input Flange, Output Flange, Overrun-
ning Clutch Housing O-rings)
²Input Flange/Shield²Torque Arm
²Vents
²FastenersOPERATION
The primary benefits of All Wheel Drive are:
²Superior straight line acceleration, and corner-
ing on all surfaces
²Better traction and handling under adverse con-
ditions, resulting in improved hill climbing ability
and safer driving.
The heart of the system is an inter-axle viscous
coupling. The vehicle retains predominantly front-
wheel drive characteristics, but the All Wheel Drive
capability takes effect when the front wheels start to
slip. Under normal level road, straight line driving,
100% of the torque is allocated to the front wheels.
The viscous coupling controls and distributes torque/
power to the rear wheels. The viscous coupling trans-
mits torque to the rear wheels in proportion of the
amount of the slippage at the front wheels. Thais
variable torque distribution is automatic with no
driver inputs required. The coupling is similar to a
multi-plate clutch. It consists of a series of closely
spaced discs, which are alternately connected to the
front and rear drive units. The unit is totally sealed
and partially filled with silicone fluid. There is no
3 - 26 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
Page 1623 of 4284

When a high speed difference (shear) occurs
because of loss of traction (one axle spinning faster
than the other), the silicone fluid expands as it heats
from this shearing. When the silicone expands to fill
the viscous coupler completely, this pressure differ-
ence is high enough to squeeze each pair of plates
together. The resulting hump torque is up to 8 times
higher than the shear torque. When the viscous cou-
pler is in the hump mode, it does not lock the axles
(undifferentiated 4-Wheel Drive). It controls the
amount of slippage while delivering maximum power
to the axle having greatest traction. Once the speed
difference equalizes the fluid and plates cool down
and the viscous coupler goes back to the shear mode.
TORQUE ARM
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove rear driveline module assembly. (Refer
to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR DRIV-
ELINE MODULE - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove six torque arm-to-differential assembly
bolts (Fig. 47). Remove torque arm.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install six torque arm-to-differential assembly
bolts (Fig. 47) and torque to 60 N´m (44 ft. lbs.).
(2) Install rear driveline module assembly. (Refer
to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/REAR DRIV-
ELINE MODULE - INSTALLATION)
(3) Lower vehicle.
INPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(3) Using tool 6958, remove input flange nut and
washer (Fig. 48).
(4) Remove input flange (Fig. 49).
(5) Using suitable screwdriver, remove input
flange seal from overrunning clutch housing (Fig.
50).
INSTALLATION
(1) Using tool 8802, install input flange seal to
overrunning clutch case (Fig. 51).
(2) Install input flange (Fig. 52).
(3) Install flange nut and washer. Using tool 6958,
torque flange nut to 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 53).
(4) Install propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT -
INSTALLATION)
(5) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 47 Torque Arm Fasteners
1 - TORQUE ARM ASSEMBLY
2 - BOLT (SIX)
Fig. 48 Input Flange Nut
1 - INPUT FLANGE
2 - TOOL 6958
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-47
VISCOUS COUPLER (Continued)
Page 1628 of 4284

JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION...........................32
OPERATION.............................32
REMOVAL..............................32
INSTALLATION...........................33
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION...........................33
OPERATION.............................34
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................34
MASTER CYLINDER BLEEDING...........34
REMOVAL..............................34
DISASSEMBLY...........................35
ASSEMBLY.............................36
INSTALLATION...........................36
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
DESCRIPTION...........................37
OPERATION.............................37
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................38
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER...............38
REMOVAL..............................38
INSTALLATION...........................40
PROPORTIONING VALVE
DESCRIPTION...........................41
OPERATION.............................42
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................42
PROPORTIONING VALVE (HEIGHT
SENSING).............................42
REMOVAL..............................43
INSTALLATION...........................43
ROTORS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................44BRAKE ROTOR........................44
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................47
BRAKE ROTOR MACHINING..............47
REMOVAL..............................48
INSTALLATION...........................48
SUPPORT PLATE - DRUM BRAKE
REMOVAL..............................48
INSTALLATION...........................49
WHEEL CYLINDERS
REMOVAL..............................50
INSPECTION............................50
INSTALLATION...........................50
PARKING BRAKE
DESCRIPTION...........................50
OPERATION.............................51
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................51
PARKING BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER
MECHANISM RELEASE..................51
PARKING BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER
RESET...............................51
LEVER - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL..............................52
INSTALLATION...........................53
SHOES - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL..............................53
INSTALLATION...........................58
ADJUSTMENTS..........................59
CABLES - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL..............................61
INSTALLATION...........................65
ADJUSTMENTS..........................66
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION - BASE BRAKES
The base brake system consists of the following
components:
²Brake pedal
²Power brake booster
²Master cylinder
²Brake tubes and hoses
²Proportioning valve (non-ABS vehicles only)
²Disc brakes
²Drum brakes
²Brake lamp switch
²Brake fluid level switch
²Parking brakes
Front disc brakes control the braking of the front
wheels; rear braking is controlled by rear drum
brakes or rear disc brakes depending on options.
The hydraulic brake system is diagonally split on
both the non-antilock braking systems and antilock
braking systems. That means the left front and right
rear brakes are on one hydraulic circuit and the right
front and left rear are on the other.For information on the brake lamp switch, (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERI-
OR/BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - DESCRIPTION)
Vehicles equipped with the optional antilock brake
system (ABS) use a system designated Mark 20e. It
is available with or without traction control. This
system shares most base brake hardware used on
vehicles without ABS. ABS components are described
in detail in ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM.
OPERATION - BASE BRAKES
When a vehicle needs to be stopped, the driver
applies the brake pedal. The brake pedal pushes the
input rod of the power brake booster into the booster.
The booster uses vacuum to ease pedal effort as force
is transferred through the booster to the master cyl-
inder. The booster's output rod pushes in the master
cylinder's primary and secondary pistons applying
hydraulic pressure through the chassis brake tubes
to the brakes at each tire and wheel assembly.
The parking brakes are foot-operated. When
applied, the parking brake lever pulls on cables that
actuate brake shoes at each rear wheel. These shoes
come in contact with a hub mounted drum (drum for
5 - 2 BRAKES - BASERS
Page 1660 of 4284

For information on master cylinder application,
bore and type, view the following table:
BRAKE SYSTEMMASTER CYLINDER
BORE/TYPE
Disc/Drum - ABS23.8 mm Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Drum - Non-ABS23.8 mm Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Disc - ABS25.4 mm (1-1/16 in.)
Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Disc ABS With
Traction Control25.4 mm (1-1/16 in.) Dual
Center Port
CAUTION: When replacing a master cylinder, be
sure to use the correct master cylinder for the type
of brake system the vehicle is equipped with.
The body of the master cylinder is an anodized alu-
minum casting. It has a machined bore to accept the
master cylinder pistons and threaded ports with
seats for the hydraulic brake line connections.
The brake fluid reservoir is mounted on the top of
the master cylinder. It is made of a see-through
polypropylene type plastic for easy fluid level view-
ing. A brake fluid level switch is attached to the
brake fluid reservoir.
The master cylinder is not a repairable component
and must be replaced if diagnosed to be functioning
improperly. The brake fluid reservoir and brake fluid
level switch can be replaced separately.
CAUTION: Do not hone the bore of the cylinder as
this will remove the anodized surface from the bore.
OPERATION
When the brake pedal is depressed, the master cyl-
inder primary and secondary pistons apply brake
pressure through the chassis tubes to the brakes at
each tire and wheel assembly.
The master cylinder primary outlet port supplies
hydraulic pressure to the right front and left rear
brakes. The secondary outlet port supplies hydraulic
pressure to the left front and right rear brakes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER CYLINDER
BLEEDING
CAUTION: When clamping master cylinder in vise,
only clamp master cylinder by its mounting flange,
do not clamp on primary piston, seal or body of
master cylinder.(1) Clamp the master cylinder in a vise using only
the mounting flange.
NOTE: Two different size bleeding tubes need to be
used depending on which type of master cylinder
the vehicle is equipped with. Vehicles equipped
with traction control have different size brake tubes
and nuts at the master cylinder than the non-trac-
tion control equipped vehicles. Be sure the correct
size bleeding tubes are used when bleeding the
master cylinder.
(2) Thread Bleeding Tubes, Special Tool 8358, for a
non-traction control master cylinder or Special Tool
8129 for a traction control master cylinder into mas-
ter cylinder primary and secondary ports. Position
outlet ends of bleeding tubes in reservoir with the
outlets below surface of brake fluid when reservoir is
filled to its proper level.
(3) Fill brake fluid reservoir with Mopartbrake
fluid or equivalent conforming to DOT 3 (DOT 4 and
DOT 4+ are acceptable) specifications.
(4) Using a wooden dowel, depress push rod slowly,
and then allow pistons to return to released position.
Repeat several times until all air bubbles are
expelled from master cylinder.
(5) Remove bleeding tubes from master cylinder
outlet ports, and then plug outlet ports and install
fill cap on reservoir.
(6) Remove master cylinder from vise.
(7) Install the filler cap on master cylinder fluid
reservoir.
(8) Install master cylinder. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES -
BASE/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/MASTER CYL-
INDER - INSTALLATION)
REMOVAL - MASTER CYLINDER
CAUTION: Vacuum in the power brake booster must
be pumped down (removed) before removing mas-
ter cylinder from power brake booster. This is nec-
essary to prevent the power brake booster from
sucking in any contamination as the master cylin-
der is removed. This can be done simply by pump-
ing the brake pedal, with the vehicle's engine not
running, until a firm feeling brake pedal is achieved.
(1) With engine not running, pump brake pedal
until a firm pedal is achieved (4-5 strokes).
(2) Disconnect negative battery terminal.
(3) Disconnect positive battery terminal.
(4) Remove battery shield.
(5) Remove nut and clamp securing battery to tray,
remove battery.
5 - 34 BRAKES - BASERS
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 1693 of 4284

BRAKES - ABS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION...........................67
OPERATION.............................67
CAUTION...............................69
STANDARD PROCEDURE..................70
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM BLEEDING.....70
SPECIFICATIONS........................71
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL..............................71
INSTALLATION...........................71
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - AWD
REMOVAL..............................72
INSTALLATION...........................72
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - FWD
REMOVAL..............................73INSTALLATION...........................74
TONE WHEEL
INSPECTION............................74
TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.................74
TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH............74
ICU (INTEGRATED CONTROL UNIT)
DESCRIPTION...........................75
OPERATION.............................75
REMOVAL..............................76
DISASSEMBLY...........................77
ASSEMBLY.............................77
INSTALLATION...........................77
BRAKES - ABS
DESCRIPTION - ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
This section covers the physical and operational
descriptions and the on-car service procedures for the
Mark 20e Antilock Brake System and the Mark 20e
Antilock Brake System with traction control.
The purpose of the antilock brake system (ABS) is
to prevent wheel lockup under braking conditions on
virtually any type of road surface. Antilock braking is
desirable because a vehicle that is stopped without
locking the wheels retains directional stability and
some steering capability. This allows the driver to
retain greater control of the vehicle during braking.
DESCRIPTION - ELECTRONIC BRAKE
DISTRIBUTION
Vehicles equipped with ABS use electronic brake
distribution (EBD) to balance front-to-rear braking.
The EBD is used in place of a rear proportioning
valve. The EBD system uses the ABS system to con-
trol the slip of the rear wheels in partial braking
range. The braking force of the rear wheels is con-
trolled electronically by using the inlet and outlet
valves located in the integrated control unit (ICU).
DESCRIPTION - TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
Traction control reduces wheel slip and maintains
traction at the driving wheels at speeds below 56
km/h (35 mph) when road surfaces are slippery. The
traction control system reduces wheel slip by braking
the wheel that is losing traction.
HYDRAULIC SHUTTLE VALVES
Two pressure relief hydraulic shuttle valves are
included on vehicles with traction control. These
valves are located inside the HCU and cannot be ser-
viced separately from the HCU.
TRACTION CONTROL LAMP
The traction control function lamp is located in the
transmission range indicator display of the instru-
ment cluster, displaying TRAC, TRAC OFF or nei-
ther depending on system mode.
The TRAC OFF lamp is controlled by a Traction
Control Off switch that is a momentary contact type
switch. The Traction Control Off switch is located on
the steering column upper shroud.
OPERATION - ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
There are a few performance characteristics of the
Mark 20e Antilock Brake System that may at first
seem abnormal, but in fact are normal. These char-
acteristics are described below.
NORMAL BRAKING
Under normal braking conditions, the ABS func-
tions the same as a standard base brake system with
a diagonally split master cylinder and conventional
vacuum assist.
ABS BRAKING
ABS operation is available at all vehicle speeds
above 3±5 mph. If a wheel locking tendency is
detected during a brake application, the brake sys-
RSBRAKES - ABS5-67
Page 1695 of 4284

the rear brake pressure, the outlet valve is switched
off and the inlet valve is pulsed. This increases the
pressure to the rear brakes. This back-and-forth pro-
cess will continue until the required slip difference is
obtained. At the end of EBD braking (brakes
released) the fluid in the LPA drains back to the
master cylinder by switching on the outlet valve and
draining through the inlet valve check valve. At the
same time the inlet valve is switched on in case of
another brake application.
The EBD will remain functional during many ABS
fault modes. If both the red BRAKE, and amber ABS
warning indicators are illuminated, the EBD may not
be functioning.
OPERATION - TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
The traction control module monitors wheel speed.
During acceleration, if the module detects front
(drive) wheel slip and the brakes are not applied, the
module enters traction control mode. Traction control
operation proceeds in the following order:
(1) Close the normally open isolation valves.
(2) Start the pump/motor and supply volume and
pressure to the front (drive) hydraulic circuit. (The
pump/motor runs continuously during traction con-
trol operation.)
(3) Open and close the build and decay valves to
maintain minimum wheel slip and maximum trac-
tion.
The cycling of the build and decay valves during
traction control is similar to that during antilock
braking, except the valves work to control wheel spin
by applying the brakes, whereas the ABS function is
to control wheel skid by releasing the brakes.
If the brakes are applied at anytime during a trac-
tion control cycle, the brake lamp switch triggers the
controller to switch off traction control.
HYDRAULIC SHUTTLE VALVES
Two pressure relief hydraulic shuttle valves allow
pressure and volume to return to the master cylinder
reservoir when not consumed by the build and decay
valves. These valves are necessary because the
pump/motor supplies more volume than the system
requires.
TRACTION CONTROL LAMP
The traction control system is enabled at each igni-
tion cycle. It may be turned off by depressing the
Traction Control Off switch button when the ignition
is in the ON position. The traction control function
lamp (TRAC OFF) illuminates immediately upon
depressing the button.
The traction control function lamp illuminates dur-
ing a traction control cycle, displaying TRAC.If the CAB calculates that the brake temperatures
are high, the traction control system becomes inoper-
ative until a time-out period has elapsed. During this
ªthermo-protection mode,º the traction control func-
tion lamp illuminates TRAC OFF; note that no trou-
ble code is registered.
CAUTION
The ABS uses an electronic control module, the
CAB. This module is designed to withstand normal
current draws associated with vehicle operation.
Care must be taken to avoid overloading the CAB
circuits.
CAUTION: In testing for open or short circuits, do
not ground or apply voltage to any of the circuits
unless instructed to do so for a diagnostic proce-
dure.
CAUTION: These circuits should only be tested
using a high impedance multi-meter or the DRBIIIT
scan tool as described in this section. Power
should never be removed or applied to any control
module with the ignition in the ON position. Before
removing or connecting battery cables, fuses, or
connectors, always turn the ignition to the OFF
position.
CAUTION: The CAB 24-way connector should never
be connected or disconnected with the ignition
switch in the ON position.
CAUTION: Use only factory wiring harnesses. Do
not cut or splice wiring to the brake circuits. The
addition of aftermarket electrical equipment (car
phone, radar detector, citizen band radio, trailer
lighting, trailer brakes, etc.) on a vehicle equipped
with antilock brakes may affect the function of the
antilock brake system.
CAUTION: When performing any service procedure
on a vehicle equipped with ABS, do not apply a
12-volt power source to the ground circuit of the
pump motor in the HCU. Doing this will damage the
pump motor and will require replacement of the
entire HCU.
CAUTION: An attempt to remove or disconnect cer-
tain system components may result in improper
system operation. Only those components with
approved removal and installation procedures in
this manual should be serviced.
RSBRAKES - ABS5-69
BRAKES - ABS (Continued)
Page 1700 of 4284

INSTALLATION - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
(REAR-FWD)
CAUTION: Proper installation of wheel speed sen-
sor cable is critical to continued system operation.
Be sure that cable is installed in routing retainers/
clips. Failure to install cable in retainers may result
in contact with moving parts or over extension of
cable, resulting in an open circuit.
NOTE: Make sure wheel speed sensor stays clean
and dry as it is installed into the hub and bearing
cap.
(1) If metal sensor retaining clip is not in the neu-
tral installed position on hub and bearing cap, install
from the bottom, if necessary, and push clip upward
until it snaps into position.
(2) Install wheel speed sensor head into rear of
hub and bearing aligning index tab with the notch in
the top of the mounting hole. Push the sensor in
until it snaps into place on the metal retaining clip.
(3) Install secondary (yellow) retaining clip over
wheel speed sensor head and engage the tabs on each
side.
(4) Route sensor cable under leaf spring along rear
of axle. Install speed sensor cable into routing clips
on rear brake flex hose (Fig. 4).
(5) Install cable into metal routing clip and attach
it to the rear axle with mounting bolt (Fig. 4).
Tighten mounting bolt to 16 N´m (140 in. lbs.).
(6) Connect wheel speed sensor cable to vehicle
wiring harness (Fig. 3).Be sure speed sensor
cable connector is fully seated and locked into
vehicle wiring harness connector.
(7) Install speed sensor cable grommet into hole in
floor pan making sure grommet is fully seated into
hole.
(8) Lower vehicle.
(9) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation of
the base and ABS braking systems.
TONE WHEEL
INSPECTION - TONE WHEEL
NOTE: Rear tone wheels for front-wheel-drive vehi-
cles are sealed within the hub and bearing assem-
bly and cannot be inspected or replaced.
Replacement of the hub and bearing is necessary.Tone wheels can cause erratic wheel speed sensor
signals. Inspect tone wheels for the following possible
causes.
²missing, chipped, or broken teeth
²contact with the wheel speed sensor
²wheel speed sensor to tone wheel alignment
²wheel speed sensor to tone wheel clearance
²excessive tone wheel runout
²tone wheel loose on its mounting surface
If a front tone wheel is found to need replacement,
the drive shaft must be replaced. No attempt should
be made to replace just the tone wheel. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
If a rear tone wheel is found to need replacement
on an all-wheel-drive model, the drive shaft must be
replaced. No attempt should be made to replace just
the tone wheel. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL &
DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT - REMOVAL)
If wheel speed sensor to tone wheel contact is evi-
dent, determine the cause and correct it before
replacing the wheel speed sensor or tone wheel.
Check the gap between the speed sensor head and
the tone wheel to ensure it is within specifications.
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - ABS/ELECTRICAL - SPEC-
IFICATIONS)
Excessive wheel speed sensor runout can cause
erratic wheel speed sensor signals. Refer to SPECI-
FICATIONS in this section of the service manual for
the maximum allowed tone wheel runout (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - ABS/ELECTRICAL - SPECIFICATIONS).
If tone wheel runout is excessive, determine if it is
caused by a defect in the driveshaft assembly or hub
and bearing. Replace as necessary.
Tone wheels are pressed onto their mounting sur-
faces and should not rotate independently from the
mounting surface. Replacement of the front drive-
shaft, rear driveshaft (AWD only) or rear hub and
bearing is necessary.
TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRACTION
CONTROL SWITCH
(1) Remove lower column shroud.
(2) Disconnect traction control switch harness from
column harness below column.
(3) Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity read-
ing between pins. Refer to test table and (Fig. 6).
5 - 74 BRAKES - ABSRS
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - FWD (Continued)
Page 1701 of 4284

TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH CONTINUITY
SWITCH POSITION CONTINUITY BETWEEN
ACTUATED PINS 1 AND 2
ILLUMINATION PINS 1 AND 3
ICU (INTEGRATED CONTROL
UNIT)
DESCRIPTION
The hydraulic control unit (HCU) and the control-
ler antilock brake (CAB) used with this antilock
brake system are combined (integrated) into one
unit, which is called the integrated control unit (ICU)
(Fig. 7). The ICU is located below the master cylinder
in the engine compartment (Fig. 8).
Two different ICU's (HCU and CAB) are used on
this vehicle depending on whether or not the vehicle
is equipped with traction control. The HCU on a
vehicle equipped with traction control has a valveblock that is approximately one inch longer than a
HCU on a vehicle that is equipped with ABS only.
The ABS-only ICU consists of the following compo-
nents: the CAB, eight (build/decay) solenoid valves
(four inlet valves and four outlet valves), valve block,
fluid accumulators, a pump, and an electric motor.
The ABS-with traction control ICU consists of the
following components: the CAB, eight (build/decay)
solenoid valves (four inlet valves and four outlet
valves), two traction control (ASR) valves, two
hydraulic shuttle valves, valve block, fluid accumula-
tors, a pump, and an electric motor.
The replaceable components of the ICU are the
HCU and the CAB. No attempt should be made to
service any individual components of the HCU or
CAB. For information on the CAB, (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE -
DESCRIPTION).
OPERATION
For information of the ICU, refer to these individ-
ual components of the ICU:
²CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE (CAB)
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/CONTROLLER ANTILOCK
BRAKE - OPERATION)
²HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT (HCU) (Refer to
5 - BRAKES - ABS/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT) - OPERA-
TION)
For information on the ICU's hydraulic circuits,
refer to HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND VALVE
OPERATION. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES - ABS/HY-
DRAULIC/MECHANICAL - OPERATION)
Fig. 6 TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH CONNECTOR
Fig. 7 INTEGRATED CONTROL UNIT (ICU)
1 - PUMP/MOTOR
2 - HCU
3 - PUMP/MOTOR CONNECTOR
4 - CAB
Fig. 8 ICU LOCATION IN VEHICLE
1 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
2 - MASTER CYLINDER
3 - ICU
RSBRAKES - ABS5-75
TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH (Continued)
Page 1827 of 4284

OPERATION
The Body Control Module (BCM) is designed to
control and integrate many of the electronic features
and functions of the vehicle. The microprocessor-
based BCM hardware and software monitors many
hard wired switch and sensor inputs as well as those
resources it shares with other electronic modules in
the vehicle through its communication over the PCI
data bus network. The internal programming and all
of these inputs allow the BCM microprocessor to
determine the tasks it needs to perform and their
priorities, as well as both the standard and optional
features that it should provide. The BCM program-
ming then performs those tasks and provides those
features through both PCI data bus communication
with other electronic modules and through hard
wired low current outputs to a number of relays.
These relays provide the BCM with the ability to
control numerous high current accessory systems in
the vehicle.
The BCM monitors its own internal circuitry as
well as many of its input and output circuits, and
will store a Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. These DTCs
can be retrieved and diagnosed using a DRBIIItscan
tool. Refer to the appropriate diagnostic information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove lower steering column cover and knee
blocker reinforcement.
(3) Disconnect two wire connectors from bottom of
Body Control Module (BCM)
(4) Remove bolts holding the BCM to the dash
panel mounting bracket.
(5) Remove the BCM from the mounting bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the BCM onto the mounting bracket.
(2) Install the bolts holding the BCM to dash
panel mounting bracket.
(3) Connect two wire connectors to the bottom of
the BCM.
(4) Install the lower steering column cover and
knee blocker reinforcement.
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK
BRAKE
DESCRIPTION
The controller antilock brake (CAB) is a micropro-
cessor-based device which monitors the antilock
brake system (ABS) during normal braking and con-trols it when the vehicle is in an ABS stop. The CAB
is mounted to the HCU as part of the integrated con-
trol unit (ICU) (Fig. 1). The CAB uses a 24-way elec-
trical connector on the vehicle wiring harness. The
power source for the CAB is through the ignition
switch in the RUN or ON position. The CAB is on
the PCI bus.
OPERATION
The primary functions of the controller antilock
brake (CAB) are to:
²Monitor the antilock brake system for proper
operation.
²Detect wheel locking or wheel slipping tenden-
cies by monitoring the speed of all four wheels of the
vehicle.
²Control fluid modulation to the wheel brakes
while the system is in an ABS mode.
²Store diagnostic information.
²Provide communication to the DRBIIItscan tool
while in diagnostic mode.
²Illuminate the amber ABS warning indicator
lamp.
²(With traction control only) Illuminate the TRAC
ON lamp in the message center on the instrument
panel when a traction control event occurs.
²(with traction control only) Illuminate the TRAC
OFF lamp when the amber ABS warning indicator
lamp illuminates.
The CAB constantly monitors the antilock brake
system for proper operation. If the CAB detects a
fault, it will turn on the amber ABS warning indica-
tor lamp and disable the antilock braking system.
Fig. 1 INTEGRATED CONTROL UNIT (ICU)
1 - PUMP/MOTOR
2 - HCU
3 - PUMP/MOTOR CONNECTOR
4 - CAB
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-3
BODY CONTROL MODULE (Continued)