spark plugs CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001Pages: 4284, PDF Size: 83.53 MB
Page 2703 of 4284

the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE RADIATOR CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the radiator cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum, with 552 kPa (80 psi) rec-
ommended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the radiator coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage per cylinder.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING PLASTIGAGE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedure for the use of
Plastigage:(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 3). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.
(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage with the metric
scale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Compare clearance measurements to specs found in
engine specifications (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECI-
FICATIONS).Plastigage generally is accompa-
nied by two scales. One scale is in inches, the
other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
(4) Install the proper crankshaft bearings to
achieve the specified bearing clearances. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE) (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD
BEARINGS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
Fig. 3 Plastigage Placed in Lower ShellÐTypical
1 - PLASTIC GAUGE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-79
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 2705 of 4284

CAUTION: Excessive pressure or high RPM (beyond
the recommended speed), can damage the sealing
surfaces. The mild (white, 120 grit) bristle disc is
recommended. If necessary, the medium (yellow, 80
grit) bristle disc may be used on cast iron surfaces
with care.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting
rods, pistons, valves, etc.)(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from re-occurring.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately one teaspoon of oil
into the cylinders, rotate engine to lubricate the cyl-
inder walls to prevent damage on restart.
(8) Install new spark plugs.
(9) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(10) Install a new oil filter.
(11) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil.
(12) Connect negative battery cable.
(13) Start engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (excluding spark plug
and camshaft bearing cap attaching threads) can be
repaired. Essentially, this repair consists of drilling
out worn or damaged threads, tapping the hole with
a special Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing
an insert into the tapped hole. This brings the hole
back to its original thread size.
CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
Fig. 4 PROPER TOOL USAGE FOR SURFACE
PREPARATION
1 - ABRASIVE PAD
2 - 3M ROLOCYBRISTLE DISC
3 - PLASTIC/WOOD SCRAPER
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-81
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 2719 of 4284

CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Drain the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Remove upper and lower intake manifolds.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - REMOVAL)
WARNING: INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET IS MADE
OF VERY THIN METAL AND MAY CAUSE PER-
SONAL INJURY, HANDLE WITH CARE.(4) Remove the cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(5) Remove the spark plugs from cylinder head.
(6) Remove the dipstick and tube (Fig. 16).
(7) Remove exhaust manifold(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(8) Remove rocker arm and shaft assemblies.(Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
REMOVAL) Remove push rods andmark positions
to ensure installation in original locations.
(9) Remove the eight head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads (Fig. 20).
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.
NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCE-
Fig. 16 DIPSTICK & TUBE
1 - DIPSTICK
2 - BOLT
3 - TUBE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-95
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 2721 of 4284

(9) Install the cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(10) Install the exhaust manifolds. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
(11) Install new O-ring on dipstick tube. Install
dipstick tube assembly (Fig. 16).
(12) Install the spark plugs.
(13) Install upper and lower intake manifolds.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - INSTALLATION)
(14) Fill the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(15) Connect negative cable to battery.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head covers are made of stamped
steel. The covers are sealed with steel reinforced sil-
icon rubber gaskets. The cylinder head cover uses
rubber isolators at each fastener location (Fig. 21).
NOTE: Due to the tight packaging near the cylinder
head covers, which makes spill clean-up difficult, a
spill during an engine oil change may be misinter-
preted as an oil leak. When investigating an oil leak
in the location of the cylinder head covers and
intake manifold, follow the procedure found in Oil
Leak Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for determining the source of a leak.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER -
RIGHT
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove the wiper module. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE -
REMOVAL)
(3) Disconnect spark plug wires from plugs.(4) Disconnect power steering pump supply hose
support clip from cylinder head cover (Fig. 22).
(5) Disconnect PCV hose from cylinder head cover
(Fig. 23).
(6) Remove cylinder head cover bolts.
(7) Remove cylinder head cover and gasket (Fig.
21).
Fig. 20 CYLINDER HEAD TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
Fig. 21 Cylinder Head Cover
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - BOLT
Fig. 22 P/S Supply Hose
1 - POWER STEERING RESERVOIR
2 - CLAMP
3 - SUPPLY HOSE
4 - CLIP
5 - POWER STEERING PUMP
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-97
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 2722 of 4284

INSTALLATION
(1) Clean cylinder head and cover mating surfaces.
Inspect cylinder head cover surface for flatness.
Replace gasket as necessary.
(2) Inspect seal on the cover bolt for wear or dam-
age (Fig. 24). Replace bolt assembly as necessary.
NOTE: The cylinder head cover bolts contain a
torque limiter sleeve and a seal (Fig. 24). The seal
and torque sleeve is replaced with the bolt.
(3) Assemble gasket to cylinder cover by inserting
the bolt assemblies through each bolt hole on the
cover and gasket (Fig. 24).
(4) Install cylinder head cover and bolts (Fig. 25).
(5) Tighten cylinder head cover bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 25).
(6) Connect PCV hose to cylinder head cover.
(7) Connect power steering pump supply hose sup-
port clip to cylinder head cover (Fig. 22).
(8) Connect spark plug wires to spark plugs.
(9) Install wiper module. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/WIPER MODULE -
INSTALLATION)
(10) Connect negative cable to battery.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER -
LEFT
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect spark plug wires from spark plugs.
(2) Disconnect crankcase vent hose from cylinder
head cover.
(3) Remove cylinder head cover bolts.
(4) Remove cylinder head cover and gasket.
Fig. 23 PCV Hose
1 - HOSE - PCV
2 - P C V VA LV E
Fig. 24 CYLINDER HEAD COVER GASKET
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - BOLT
3 - SEAL (SERVICED WITH BOLT)
4 - GASKET
Fig. 25 Cylinder Head Cover
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - BOLT
9 - 98 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
CYLINDER HEAD COVER - RIGHT (Continued)
Page 2723 of 4284

INSTALLATION
(1) Clean cylinder head and cover mating surfaces.
Inspect cylinder head cover surface for flatness.
Replace gasket as necessary.
(2) Assemble gasket to cylinder cover by inserting
the fasteners through each bolt hole on cover and
gasket (Fig. 24).
(3) Install the cylinder head cover and bolts (Fig.
25).
(4) Tighten cylinder head cover bolts to 12 N´m
(105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 25).
(5) Connect crankcase vent hose.
(6) Connect spark plug wires to spark plugs.
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES &
SEATS
DESCRIPTION
The valves have chrome plated valve stems with
four-bead lock grooves. The valve stem seals are
made of Viton rubber.
OPERATION
The two valves per cylinder are opened using
hydraulic lifters, push rods, and rocker arms.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFACING VALVES
AND VALVE SEATS
The intake and exhaust valves and seats are
machined to specific angles (Fig. 26).
VALVES
(1) Inspect the remaining margin after the valves
are refaced (Fig. 27). (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPEC-
IFICATIONS)
VALVE SEATS
CAUTION: Remove metal from valve seat only. Do
not remove material from cylinder head (Fig. 28).
(1) When refacing valve seats, it is important that
the correct size valve guide pilot be used for reseat-
ing stones. A true and complete surface must be
obtained.
Fig. 26 Valve Face and Seat
1 - SEAT WIDTH
2 - FACE ANGLE
3 - SEAT ANGLE
4 - SEAT CONTACT AREA
Fig. 27 Valve Margin
1 - VALVE FACE
2 - VALVE MARGIN
Fig. 28 Refacing Valve Seats
1 - REFACING STONE MUST NOT CUT INTO CYLINDER HEAD
2-STONE
3 - PILOT
4 - SEAT
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-99
CYLINDER HEAD COVER - LEFT (Continued)
Page 2726 of 4284
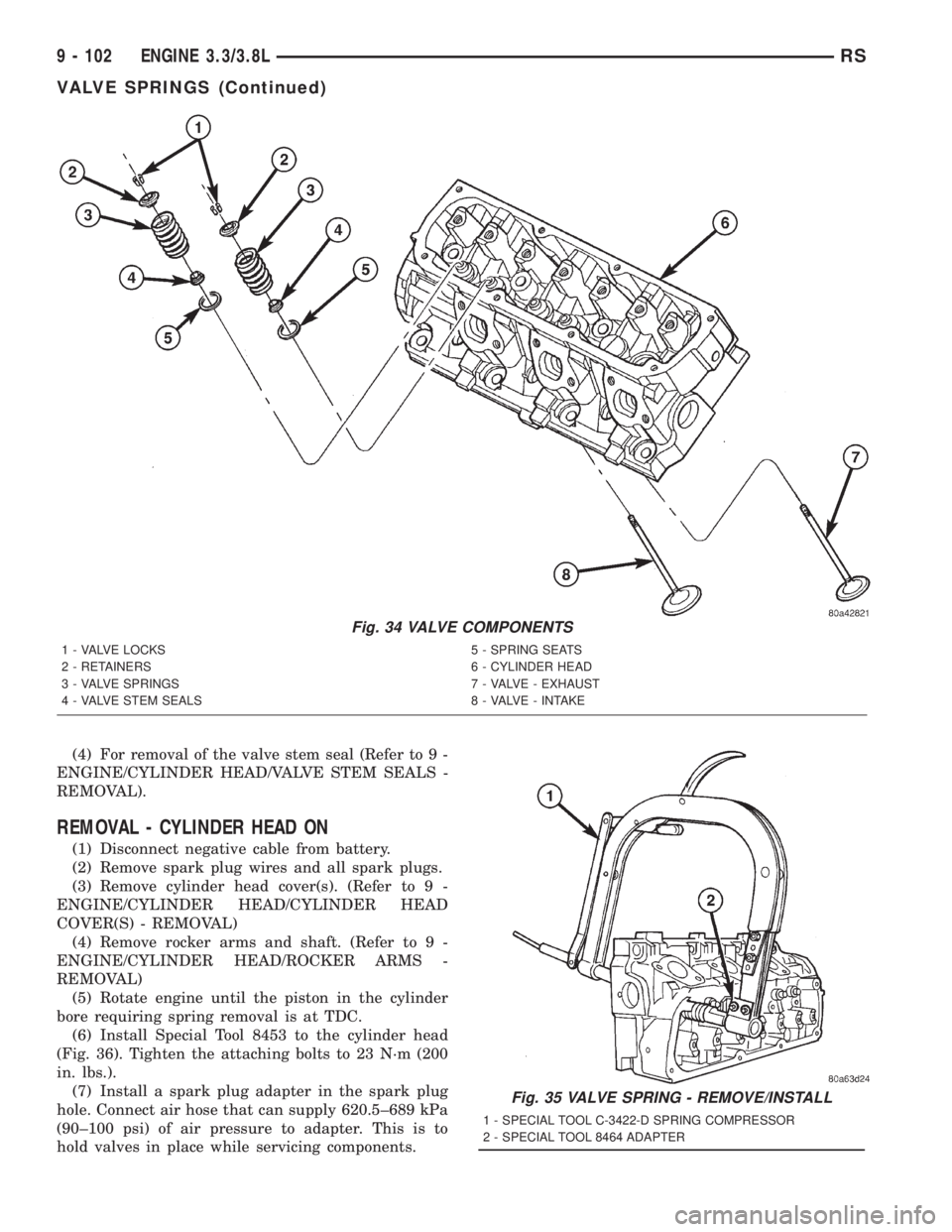
(4) For removal of the valve stem seal (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE STEM SEALS -
REMOVAL).
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove spark plug wires and all spark plugs.
(3) Remove cylinder head cover(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(4) Remove rocker arms and shaft. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
REMOVAL)
(5) Rotate engine until the piston in the cylinder
bore requiring spring removal is at TDC.
(6) Install Special Tool 8453 to the cylinder head
(Fig. 36). Tighten the attaching bolts to 23 N´m (200
in. lbs.).
(7) Install a spark plug adapter in the spark plug
hole. Connect air hose that can supply 620.5±689 kPa
(90±100 psi) of air pressure to adapter. This is to
hold valves in place while servicing components.
Fig. 34 VALVE COMPONENTS
1 - VALVE LOCKS 5 - SPRING SEATS
2 - RETAINERS 6 - CYLINDER HEAD
3 - VALVE SPRINGS 7 - VALVE - EXHAUST
4 - VALVE STEM SEALS 8 - VALVE - INTAKE
Fig. 35 VALVE SPRING - REMOVE/INSTALL
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-3422-D SPRING COMPRESSOR
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 8464 ADAPTER
9 - 102 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 2727 of 4284

(8) Locate the forcing screw and spring retainer
adapter assembly over the spring requiring removal
(Fig. 36).
(9) Slowly turn the forcing screw clockwise (com-
pressing the valve spring) until the valve keepers can
be removed.
(10) Turn forcing screw counterclockwise to relieve
spring tension. Remove retainer and valve spring.
(11) Repeat procedure for each cylinder requiring
valve spring removal.
INSPECTION
Whenever valves have been removed for inspection,
reconditioning or replacement, valve springs should
be tested (Fig. 37).As an example;the compression
length of a spring to be tested is 38.00 mm (1.496
in.). Turn the table of Tool C-647 until surface is in
line with the 38.00 mm (1.496 in.) mark on the
threaded stud and the zero mark on the front. Place
spring over stud on the table and lift compressing
lever to set tone device. Pull on torque wrench until
ping is heard. Take reading on torque wrench at this
instant. Multiply this reading by two. This will give
the spring load at test length. Fractional measure-
ments are indicated on the table for finer adjust-
ments. Refer to Engine Specifications to obtain
specified height and allowable tensions (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). Replace any springs
that do not meet specifications.
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) If removed, install a new valve stem seal.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE
STEM SEALS - INSTALLATION)
(2) Position valve spring and retainer on spring
seat.(3) Using Special Tool C-3422-C with 8464 Adapter
(Fig. 35), compress the spring only enough to install
the valve retainer locks.
(4) Slowly release the spring tension. Ensure the
retainer locks are seated properly.
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON
(1)The intake valve stem seals should be pushed
firmly and squarely over the valve guide using the
valve stem as guide.Do Not Force
seal against top of
guide. When installing the valve retainer locks, com-
press the springonly enoughto install the locks.
CAUTION: Do not pinch seal between retainer and
top of valve guide.
(2) Follow the same procedure on the remaining 5
cylinders using the firing sequence 1-2-3-4-5-6.Make
sure piston in cylinder is at TDC on the valve
spring that is being covered.
(3) Remove spark plug adapter tool.
(4) Install rocker arms and shaft assembly. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
INSTALLATION)
(5) Install cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(6) Install spark plugs and connect wires.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
ROCKER ARMS
DESCRIPTION - ROCKER ARMS
The rocker arms are installed on the rocker arm
shaft. The rocker arms and shaft assembly is attached
to the cylinder head with seven bolts and retainers.
The rocker arms are made of stamped steel.
Fig. 36 VALVE SPRING - REMOVE/INSTALL (HEAD ON)
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8453
2 - BOLTS - SPECIAL TOOL ATTACHING
3 - AIR SUPPLY HOSE ADAPTER
Fig. 37 TESTING VALVE SPRING
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-647
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 103
VALVE SPRINGS (Continued)
Page 2777 of 4284

INSPECTION
Inspect exhaust manifolds for damage or cracks
and check distortion of the cylinder head mounting
surface and exhaust crossover mounting surface with
a straightedge and thickness gauge (Fig. 148).
Manifold surface flatness limits should not exceed
1.0 mm (0.039 in.).
INSTALLATION
(1) Position exhaust manifold on cylinder head
(Fig. 147). Install bolts to center runner (cylinder #4)
and initial tighten to 2.8 N´m (25 in. lbs.).
(2) Using a new gasket, attach crossover pipe to
exhaust manifold and tighten bolts to 41 N´m (30 ft.
lbs.) (Fig. 146).
NOTE: Inspect crossover pipe fasteners for damage
from heat and corrosion. The cross-over bolts are
made of a special stainless steel alloy. If replace-
ment is required, OEM bolts are highly recom-
mended.
(3) Position heat shield on manifold (Fig. 147).
(4) Install the remaining manifold attaching bolts.
Tighten all bolts to 23 N´m (200 in. lbs.).
(5) Install and tighten heat shield attaching nut to
12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) (Fig. 147).
(6) Connect battery negative cable.
VALVE TIMING
VALVE TIMING VERIFICATION
(1) Remove front cylinder head cover and all 6
spark plugs.(2) Rotate engine until the #2 piston is at TDC of
the compression stroke.
(3) Install a degree wheel on the crankshaft pulley.
(4) With proper adaptor, install a dial indicator
into #2 spark plug hole. Using the indicator find TDC
on the compression stroke.
(5) Position the degree wheel to zero.
(6) Remove dial indicator from spark plug hole.
(7) Place a 5.08 mm (0.200 in.) spacer between the
valve stem tip of #2 intake valve and rocker arm pad.
Allow tappet to bleed down to give a solid tappet
effect.
(8) Install a dial indicator so plunger contacts the
#2 intake valve spring retainer as nearly perpendic-
ular as possible. Zero the indicator.
(9) Rotate the engine clockwise until the intake
valve has lifted .254 mm (0.010 in.).
CAUTION: Do not turn crankshaft any further clock-
wise as intake valve might bottom and result in
serious damage.
(10) Degree wheel should read 6 degrees BTDC to
6 degrees ATDC.
TIMING CHAIN COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Drain cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(3) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(4) Drain engine oil.
(5) Remove right wheel and inner splash shield.
(6) Remove oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL)
(7) Remove oil pick-up tube (Fig. 149).
(8) Remove accessory drive belt. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
REMOVAL)
(9) Remove A/C compressor and set aside.
(10) Remove crankshaft vibration damper. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION
DAMPER - REMOVAL)
(11) Remove radiator lower hose.
(12) Remove heater hose from timing chain cover
housing (Fig. 150) or water pump inlet tube (if
engine oil cooler equipped) (Fig. 151).
(13) Remove the right side engine mount. (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT
- REMOVAL)
(14) Remove idler pulley from engine bracket (Fig.
152).
(15) Remove the engine mount bracket (Fig. 152).
(16) Remove cam sensor from timing chain cover
(Fig. 152).
Fig. 148 Check Exhaust Manifold Mounting
1 - STRAIGHT EDGE
2 - CROSSOVER PIPE MOUNTING SURFACE
3 - FEELER GAUGE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 153
EXHAUST MANIFOLD - LEFT (Continued)
Page 2850 of 4284

CATALYTIC CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION
The toe board three-way catalytic converter is con-
nected to the exhaust manifold by the use of flex
joint and a gasket. The outlet connects to the muffler
inlet pipe and is secured with a band type clamp
(Fig. 1).
The exhaust flex-joint coupling (Fig. 3) is used to
secure the catalytic converter to the exhaust mani-
fold. The flex-joint has four bolts, four flag nuts and
a gasket that are separate parts from the exhaust
flex-joint. The flex-joint is welded to the catalytic
converter.
CAUTION: When servicing, care must be exercised
not to dent or bend the bellows or bellows cover of
the flex-joint. Should this occur, the flex-joint will
eventually fail and require the catalytic converter be
replaced.
OPERATION
The three-way catalytic converter simultaneously
converts three exhaust emissions into harmless
gases. Specifically, HC and CO emissions are con-
verted into water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) are converted into elemen-
tal Nitrogen (N) and water. The three-way catalyst is
most efficient in converting HC, CO and NOx at the
stoichiometric air fuel ratio of 14.7:1.
The oxygen content in a catalyst is important for
efficient conversion of exhaust gases. When a high
oxygen content (lean) air/fuel ratio is present for an
extended period, oxygen content in a catalyst canreach a maximum. When a rich air/fuel ratio is
present for an extended period, the oxygen content in
the catalyst can become totally depleted. When this
occurs, the catalyst fails to convert the gases. This is
known as catalyst9punch through.9
Catalyst operation is dependent on its ability to
store and release the oxygen needed to complete the
emissions-reducing chemical reactions. As a catalyst
deteriorates, its ability to store oxygen is reduced.
Since the catalyst's ability to store oxygen is some-
what related to proper operation, oxygen storage can
be used as an indicator of catalyst performance.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Pro-
cedure for diagnosis of a catalyst related Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
The combustion reaction caused by the catalyst
releases additional heat in the exhaust system, caus-
ing temperature increases in the area of the reactor
under severe operating conditions. Such conditions
can exist when the engine misfires or otherwise does
not operate at peak efficiency.Do notremove spark
plug wires from plugs or by any other means short
out cylinders, if exhaust system is equipped with a
catalytic converter. Failure of the catalytic converter
can occur due to temperature increases caused by
unburned fuel passing through the converter. This
deterioration of the catalyst core can result in exces-
sively high emission levels, noise complaints, and
exhaust restrictions.
The use of catalysts also involves some non-auto-
motive problems. Unleaded gasoline must be used to
avoid poisoning the catalyst core. Do not allow engine
to operate above 1200 RPM in neutral for extended
periods over 5 minutes. This condition may result in
excessive exhaust system/floor pan temperatures
because of no air movement under the vehicle.
The flex joint allows flexing as the engine moves,
preventing breakage that could occur from the back-
and-forth motion of a transverse mounted engine.
CAUTION: Due to exterior physical similarities of
some catalytic converters with pipe assemblies,
extreme care should be taken with replacement
parts. There are internal converter differences
required in some parts of the country (particularly
vehicles built for States with strict emission
requirements) and between model years.
REMOVAL
(1) Loosen clamp and disconnect the muffler/reso-
nator assembly from catalytic converter pipe.
(2) Disconnect downstream oxygen sensor electri-
cal connector (Fig. 4). For removal of downstream
oxygen sensor, (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL
INJECTION/O2 SENSOR - REMOVAL).
Fig. 3 Flex-joint
1 - FLANGE
2 - END CAPS
3 - CATALYTIC CONVERTER
4 - FLEXIBLE BELLOWS
11 - 4 EXHAUST SYSTEMRS