engine CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001Pages: 4284, PDF Size: 83.53 MB
Page 1565 of 4284

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SUSPENSION AND STEERING
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Front End Whine On Turns 1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Incorrect wheel alignment 2. Check and reset wheel alignment
3. Worn tires 3. Replace tires
Front End Growl Or
Grinding On Turns1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Engine mount grounding 2. Check for motor mount hitting frame
rail and reposition engine as required
3. Worn or broken C/V joint 3. Replace C/V joint
4. Loose wheel lug nuts 4. Verify wheel lug nut torque
5. Incorrect wheel alignment 5. Check and reset wheel alignment
6. Worn tires 6. Replace tires
7. Front strut pin in upper strut mount 7. Replace the front strut upper mount
and bearing
Front End Clunk Or Snap
On Turns1. Loose lug nuts 1. Verify wheel lug nut torque
2. Worn or broken C/V joint 2. Replace C/V joint
3. Worn or loose tie rod 3. Tighten or replace tie rod end
4. Worn or loose ball joint 4. Tighten or replace ball joint
5. Worn/loose control arm bushing 5. Replace control arm bushing
6. Loose stabilizer bar. 6. Tighten stabilizer bar to specified
torque
Fig. 6 Thrust Angle
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-49
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 1566 of 4284
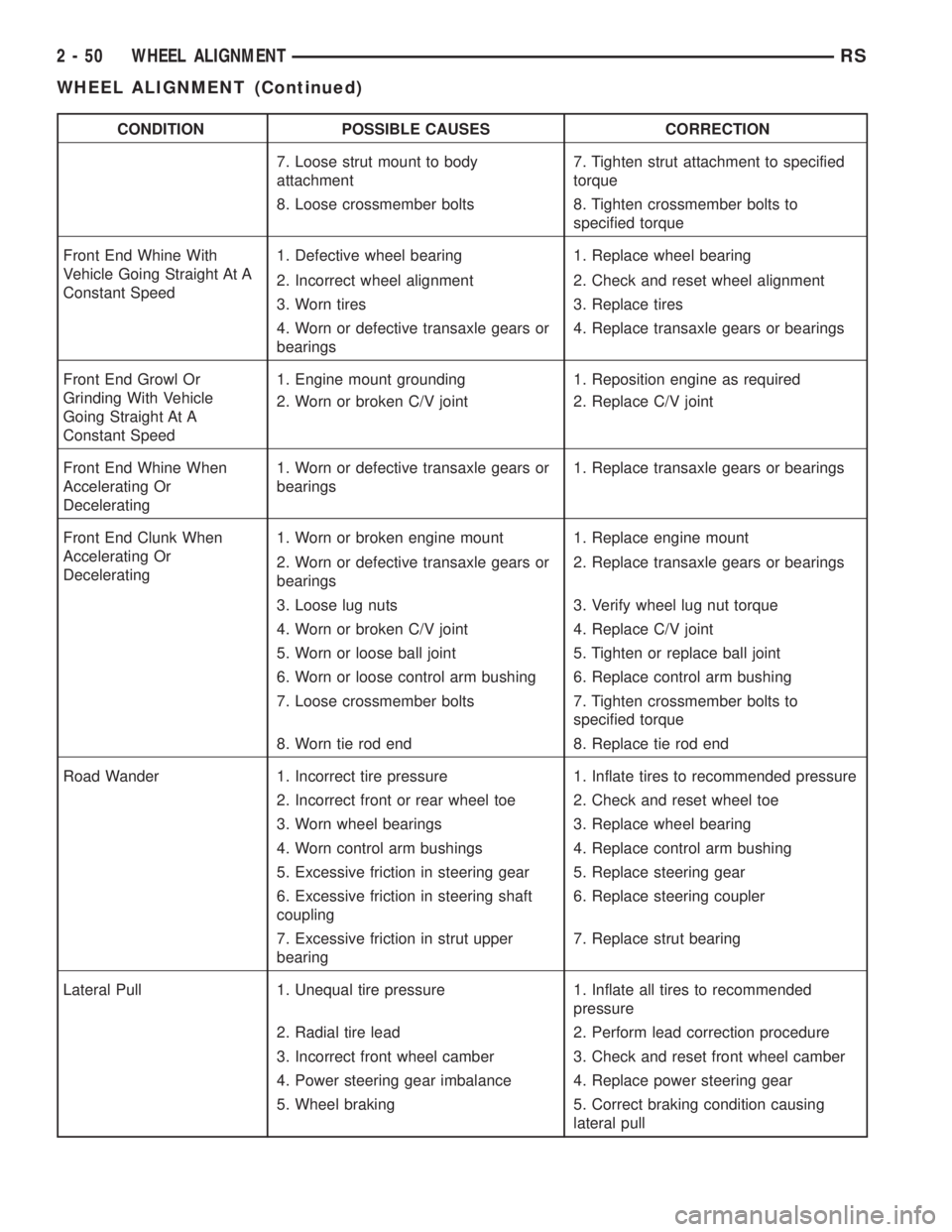
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
7. Loose strut mount to body
attachment7. Tighten strut attachment to specified
torque
8. Loose crossmember bolts 8. Tighten crossmember bolts to
specified torque
Front End Whine With
Vehicle Going Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Incorrect wheel alignment 2. Check and reset wheel alignment
3. Worn tires 3. Replace tires
4. Worn or defective transaxle gears or
bearings4. Replace transaxle gears or bearings
Front End Growl Or
Grinding With Vehicle
Going Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Engine mount grounding 1. Reposition engine as required
2. Worn or broken C/V joint 2. Replace C/V joint
Front End Whine When
Accelerating Or
Decelerating1. Worn or defective transaxle gears or
bearings1. Replace transaxle gears or bearings
Front End Clunk When
Accelerating Or
Decelerating1. Worn or broken engine mount 1. Replace engine mount
2. Worn or defective transaxle gears or
bearings2. Replace transaxle gears or bearings
3. Loose lug nuts 3. Verify wheel lug nut torque
4. Worn or broken C/V joint 4. Replace C/V joint
5. Worn or loose ball joint 5. Tighten or replace ball joint
6. Worn or loose control arm bushing 6. Replace control arm bushing
7. Loose crossmember bolts 7. Tighten crossmember bolts to
specified torque
8. Worn tie rod end 8. Replace tie rod end
Road Wander 1. Incorrect tire pressure 1. Inflate tires to recommended pressure
2. Incorrect front or rear wheel toe 2. Check and reset wheel toe
3. Worn wheel bearings 3. Replace wheel bearing
4. Worn control arm bushings 4. Replace control arm bushing
5. Excessive friction in steering gear 5. Replace steering gear
6. Excessive friction in steering shaft
coupling6. Replace steering coupler
7. Excessive friction in strut upper
bearing7. Replace strut bearing
Lateral Pull 1. Unequal tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Radial tire lead 2. Perform lead correction procedure
3. Incorrect front wheel camber 3. Check and reset front wheel camber
4. Power steering gear imbalance 4. Replace power steering gear
5. Wheel braking 5. Correct braking condition causing
lateral pull
2 - 50 WHEEL ALIGNMENTRS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 1604 of 4284

²Tires
²Road surfaces
²Wheel bearings
²Engine
²Transmission
²Exhaust
²Propeller shaft (vibration)
²Vehicle body (drumming)
Driveline module noises are normally divided into
two categories: gear noise or bearing noise. A thor-
ough and careful inspection should be completed to
determine the actual source of the noise before
replacing the driveline module.
The rubber mounting bushings help to dampen-out
driveline module noise when properly installed.
Inspect to confirm that no metal contact exists
between the driveline module case and the body. The
complete isolation of noise to one area requires
expertise and experience. Identifying certain types of
vehicle noise baffles even the most capable techni-
cians. Often such practices as:
²Increase tire inflation pressure to eliminate tire
noise.
²Listen for noise at varying speeds with different
driveline load conditions
²Swerving the vehicle from left to right to detect
wheel bearing noise.
All driveline module assemblies produce noise to a
certain extent. Slight carrier noise that is noticeable
only at certain speeds or isolated situations should be
considered normal. Carrier noise tends to peak at a
variety of vehicle speeds. Noise isNOT ALWAYSan
indication of a problem within the carrier.
TIRE NOISE
Tire noise is often mistaken for driveline module
noise. Tires that are unbalanced, worn unevenly or
are worn in a saw-tooth manner are usually noisy.
They often produce a noise that appears to originate
in the driveline module.
Tire noise changes with different road surfaces, but
driveline module noise does not. Inflate all four tires
with approximately 20 psi (138 kPa) more than the
recommended inflation pressure (for test purposes
only). This will alter noise caused by tires, but will
not affect noise caused by the differential. Rear axle
noise usually ceases when coasting at speeds less
than 30 mph (48 km/h); however, tire noise contin-
ues, but at a lower frequency, as the speed is
reduced.
After test has been completed lower tire pressure
back to recommended pressure.
GEAR NOISE (DRIVE PINION AND RING GEAR)
Abnormal gear noise is rare and is usually caused
by scoring on the ring gear and drive pinion. Scoringis the result of insufficient or incorrect lubricant in
the carrier housing.
Abnormal gear noise can be easily recognized. It
produces a cycling tone that will be very pronounced
within a given speed range. The noise can occur dur-
ing one or more of the following drive conditions:
²Drive
²Road load
²Float
²Coast
Abnormal gear noise usually tends to peak within
a narrow vehicle speed range or ranges. It is usually
more pronounced between 30 to 40 mph (48 to 64
km/h) and 50 to 60 mph (80 to 96 km/h). When objec-
tionable gear noise occurs, note the driving condi-
tions and the speed range.
BEARING NOISE (DRIVE PINION AND
DIFFERENTIAL)
Defective bearings produce a rough growl that is
constant in pitch and varies with the speed of vehi-
cle. Being aware of this will enable a technician to
separate bearing noise from gear noise.
Drive pinion bearing noise that results from defec-
tive or damaged bearings can usually be identified by
its constant, rough sound. Drive pinion front bearing
is usually more pronounced during a coast condition.
Drive pinion rear bearing noise is more pronounced
during a drive condition. The drive pinion bearings
are rotating at a higher rate of speed than either the
differential side bearings or the axle shaft bearing.
Differential side bearing noise will usually produce
a constant, rough sound. The sound is much lower in
frequency than the noise caused by drive pinion bear-
ings.
Bearing noise can best be detected by road testing
the vehicle on a smooth road (black top). However, it
is easy to mistake tire noise for bearing noise. If a
doubt exists, the tire treads should be examined for
irregularities that often causes a noise that resem-
bles bearing noise.
ENGINE AND TRANSMISSION NOISE
Sometimes noise that appears to be in the driv-
eline module assembly is actually caused by the
engine or the transmission. To identify the true
source of the noise, note the approximate vehicle
speed and/or RPM when the noise is most noticeable.
Stop the vehicle next to a flat brick or cement wall
(this will help reflect the sound). Place the transaxle
inNEUTRAL. Accelerate the engine slowly up
through the engine speed that matches the vehicle
speed noted when the noise occurred. If the same
noise is produced, it usually indicates that the noise
is being caused by the engine or transaxle.
3 - 28 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
Page 1614 of 4284

lock the front wheels first. Any torque transfer from
the rear axle to the front axle disturbs the ABS/brak-
ing system and causes potential instabilities on a
slippery surface. The BOC de-couples the rear driv-
eline as soon the rear wheels begin to spin faster
than the front wheels (front wheels locked) in order
to provide increased braking stability. Furthermore
the BOC also reduces the likelihood of throttle off
over-steer during cornering. In a throttle off maneu-
ver, the BOC once again de-couples the rear driveline
forcing all the engine brake torque to the front
wheels. This eliminates the chance of lateral slip on
the rear axle and increases it on the front. The vehi-
cle will therefore tend to understeer, a situation
which is considered easier to manage in most circum-
stances. During this maneuver, and during the ABS
braking event, the BOC does not transmit torque
through to the rear wheels. The rear driveline mod-
ule, with the BOC, will perform the same as a front
wheel drive vehicle during these events. The gear
ratio offset between the front and rear differentials
force the BOC into the overrunning mode most of the
time. This allows BOC to significantly reduce the
rolling resistance of the vehicle, which improves fuel
consumption, allows the downsizing of the driveline
components, and prevents the PTU and propshaft
joints from overheating.
OPERATION
In order to achieve all-wheel drive operation in
reverse, the overrunning clutch locking functional
direction must be reversible. The bi-directional over-
running clutch (BOC) changes the operational mode
direction depending on the propeller shaft direction.
The propeller shaft rotates in the clockwise (when
viewed from the front) direction when the vehicle is
moving forward, which indexes the BOC to the for-
ward overrunning position. When the vehicle is in
reverse, the propeller shaft will rotate counter-clock-
wise and index the BOC to the reverse overrunning
position.
The BOC acts as a mechanical stator. It is active
(transmitting torque), or it is not active and in over-
running mode (not transmitting torque). This ªall or
nothingº approach to torque transfer would cause a
sudden application of all available power to the rear
wheels, which is not desirable. Therefore it is run in
series with a viscous coupler to smooth, dampen, and
limit the transmission of torque to the rear axle and
to prevent a step style torque input to the rear axle.
STEADY STATE, LOW TO MODERATE SPEED, NO
FRONT WHEEL SLIP, FORWARD DIRECTION
During normal driving conditions, (no wheel slip),
the inner shaft (front axle) and outer race (viscous
coupler) are running at different speeds due to the
different gear ratios between the front and rear dif-
ferentials. In this condition, the outer race is always
spinning faster (overdriving between 5-32 rpm) than
the inner shaft. When the BOC (Fig. 29) is running
under these conditions, at low vehicle speeds the
drag shoes and the cage keep the rollers up on the
left side (forward side) of the inner shaft flats. This is
what is known as ªoverrunning mode.º Notice that
when the clutch is in overrunning mode, the rollers
are spinning clockwise and with the outer race, thus
no torque is being transferred.
NOTE: Low speed, forward and reverse operation is
identical, just in opposite directions. (Fig. 29)
shows forward direction in reverse the rollers are
on the other side of the flats due to a reversal of
the cage force.
TRANSIENT CONDITION (BOC LOCKED), FRONT
WHEEL SLIP, FORWARD DIRECTION
When the front wheels lose traction and begin to
slip, the propeller shaft and rear axle pinion speed
difference decreases to zero. At this point the input
shaft (cam) becomes the driving member of the BOC
(Fig. 30), compressing the rollers against the outer
race. This locks the input shaft with the outer race
and transmits torque to the housing of the viscous
coupler, that in turn transmits torque to the rear
axle pinion. It should also be noted that when the
device is locked, the inner shaft and the outer race
are rotating at the same speed. The rollers are
pinched at this point and will stay locked until a
torque reversal (no front wheel slip) occurs. When
locked, the viscous coupler slips during the torque
transfer and the amount of torque transferred is
dependent on the coupling characteristic and the
amount of front wheel slip.
3 - 38 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (Continued)
Page 1632 of 4284

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (ONE FRONT
WHEEL LOCKS UP
DURING HARD
BRAKING)1. One of the two hydraulic circuits to
the front brakes is malfunctioning.1. Inspect system for leaks. Check
master cylinder for internal malfunction.
PEDAL PULSATES/
SURGES DURING
BRAKING1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation.1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or
rotors as necessary.
PEDAL IS SPONGY 1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Power brake booster runout
(vacuum assist).2. Check booster vacuum hose and
engine tune for adequate vacuum
supply. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
PREMATURE REAR
WHEEL LOCKUP1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Inoperative proportioning valve
(non-ABS vehicles).2. Refer to proportioning valve
diagnosis and testing. Replace valve as
necessary.
3. Improper power brake booster
assist.3. Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
STOP/BRAKE LAMPS
S TAY O N1. Brake lamp switch out of
adjustment.1. Replace brake lamp switch.
2. Brake pedal binding. 2. Inspect and replace as necessary.
3. Obstruction in pedal linkage. 3. Remove obstruction.
4. Power Brake Booster not allowing
pedal to return completely.4. Replace power brake booster.
VEHICLE PULLS TO
RIGHT OR LEFT ON
BRAKING1. Frozen brake caliper piston. 1. Replace frozen piston or caliper.
Bleed brakes.
2. Contaminated brake shoe lining. 2. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
3. Pinched brake lines. 3. Replace pinched line.
4. Leaking piston seal. 4. Replace piston seal or brake caliper.
5. Suspension problem. 5. Refer to the Suspension group.
PARKING BRAKE -
EXCESSIVE HANDLE
TRAVEL1. Rear drum brakes or rear disc
brake parking brake shoes out of
adjustment.1. Adjust rear drum brake shoes, or
rear parking brake shoes on vehicles
with rear disc brakes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BASE BRAKE
BLEEDING
NOTE: This bleeding procedure is only for the vehi-
cle's base brakes hydraulic system. For bleeding
the antilock brakes hydraulic system, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - ABS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)CAUTION: Before removing the master cylinder
cover, thoroughly clean the cover and master cylin-
der fluid reservoir to prevent dirt and other foreign
matter from dropping into the master cylinder fluid
reservoir.
5 - 6 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 1639 of 4284

observed if the automatic adjuster is working prop-
erly. If one or more adjusters do not function prop-
erly, the respective drum must be removed for
adjuster servicing.
BRAKE LINES
DESCRIPTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
The brake tubes are steel with a corrosion-resis-
tant nylon coating applied to the external surfaces.
The flex hoses are made of reinforced rubber with fit-
tings at each end.
The primary and secondary brake tubes leading
from the master cylinder to the ABS ICU Hydraulic
Control Unit (HCU) or the non-ABS junction block
have a special flexible section. This flexible section is
required due to cradle movement while the vehicle is
in motion (The ICU and non-ABS junction block are
mounted to the cradle).If replacement of these
lines is necessary, only the original factory
brake line containing the flexible section must
be used.
OPERATION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
The purpose of the chassis brake tubes and flex
hoses is to transfer the pressurized brake fluid devel-
oped by the master cylinder to the wheel brakes of
the vehicle. The flex hoses are made of rubber to
allow for the movement of the vehicle's suspension.
INSPECTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes
and at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses
should be performed whenever the brake system is
serviced and every 7,500 miles or 12 months, which-
ever comes first (every engine oil change). Inspect
hydraulic brake hoses for surface cracking, scuffing,
or worn spots. If the fabric casing of the rubber hose
becomes exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the
rubber hose cover, the hose should be replaced imme-
diately. Eventual deterioration of the hose can take
place with possible burst failure. Faulty installation
can cause twisting, resulting in wheel, tire, or chassis
interference.
The brake tubing should be inspected periodically
for evidence of physical damage or contact with mov-
ing or hot components.
The flexible brake tube sections used on this vehi-
cle in the primary and secondary tubes from the
master cylinder to the ABS hydraulic control unit
connections must also be inspected. This flexible tub-
ing must be inspected for kinks, fraying and contact
with other components or with the body of the vehi-
cle.
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - FRONT
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES
(DISC/DISC BRAKES)
(1) Raise the vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(2) Remove both front wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Begin on one side of the vehicle.
(4) Remove the anti-rattle clip from the outboard
side of the caliper and adapter.
(5) Remove the two caliper guide pin bolts.
(6) Remove caliper from caliper adapter and brake
rotor.
CAUTION: Supporting weight of caliper by the flex-
ible brake fluid hose can damage the hose.
(7) Using wire or cord, hang the caliper from the
front strut assembly (Fig. 12). Support the caliper
firmly to prevent weight of caliper from being sup-
ported by the brake fluid hose.
(8) Remove the outboard brake shoe from the cali-
per adapter.
(9) Pull the inboard brake shoe away from the cal-
iper piston until the retaining clip on shoe is free
from the cavity in the caliper piston (Fig. 13).
(10) Repeat the above procedure on other side of
the vehicle.
Fig. 12 Stored Front Disc Brake Caliper
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - BRAKE FLEX HOSE
3 - CALIPER ASSEMBLY
4 - WIRE HANGER
5 - STRUT ASSEMBLY
RSBRAKES - BASE5-13
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 1658 of 4284

STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL CHECKING
Check master cylinder reservoir fluid level a mini-
mum of twice annually.
Fluid reservoirs are marked with the words FULL
and ADD to indicate proper brake fluid fill level of
the master cylinder.
If necessary, add brake fluid to bring the level to
the bottom of the FULL mark on the side of the mas-
ter cylinder fluid reservoir.
Use only Mopartbrake fluid or equivalent from a
sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT 3
specifications (DOT 4 or DOT 4+ are acceptable).
DO NOTuse brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking.
Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container.
DO NOTuse petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage will result. Petroleum based fluids would be
items such as engine oil, transmission fluid, power
steering fluid etc.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications (DOT 4 and DOT 4+ are
acceptable) and SAE J1703 standards. No other type
of brake fluid is recommended or approved for usage
in the vehicle brake system. Use only MopartBrake
Fluid or equivalent from a tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container of brake fluid will absorb moisture
from the air and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-based
fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of such
type fluids will result in seal damage of the vehicle
brake hydraulic system causing a failure of the
vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids would
be items such as engine oil, transmission fluid,
power steering fluid, etc.
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
A junction block is used on vehicles that are not
equipped with antilock brakes (ABS). The junction
block mounts in the same location as the integrated
control unit (ICU) does on vehicles equipped withABS. This allows for use of the same brake tube con-
figuration on all vehicles. The junction block is
located on the driver's side of the front suspension
cradle/crossmember below the master cylinder (Fig.
46).
It has six threaded ports to which the brake tubes
connect. Two are for the primary and secondary
brake tubes coming from the master cylinder. The
remaining four are for the chassis brake tubes going
to each brake assembly.
OPERATION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
The junction block distributes the brake fluid com-
ing from the master cylinder primary and secondary
ports to the four chassis brake tubes leading to the
brakes at each wheel. Since the junction block
mounts in the same location as the ABS integrated
control unit (ICU), it allows for the common use of
brake tubes going to the brakes whether the vehicle
is equipped with or without ABS.
NOTE: Although the brake tubes coming from the
master cylinder to the junction block or ABS ICU
may appear to be the same, they are not. They are
unique to each brake system application.
REMOVAL - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
(1) Using a brake pedal depressor, move and lock
the brake pedal to a position past its first 1 inch of
travel. This will prevent brake fluid from draining
out of the master cylinder when the brake tubes are
removed from the junction block.
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) If the vehicle is equipped with speed control,
perform the following:
(a) Disconnect the battery positive cable.
(b) Remove the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - REMOVAL).
(c) Disconnect the vacuum hose connector at the
tank built into the battery tray.
(d) Remove the screw securing the coolant filler
neck to the battery tray.
(e) Remove the battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - REMOVAL).
(f) Remove the fasteners and move the speed
control servo off to the side, out of the way.
CAUTION: Before removing the brake tubes from
the junction block, the junction block and the brake
tubes must be thoroughly cleaned. This is required
to prevent contamination from entering the brake
hydraulic system.
5 - 32 BRAKES - BASERS
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1659 of 4284

(4) Remove the four chassis brake tubes from the
top of the junction block (Fig. 46).
(5) Remove the primary and secondary brake
tubes from the top of the junction block.
(6) Remove the bolts attaching the junction block
mounting bracket to the front suspension crossmem-
ber (Fig. 46), then remove the junction block.
INSTALLATION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
(1) Install the junction block and mounting bracket
on the front suspension crossmember (Fig. 46).
Install the mounting bolts and tighten to a torque of
28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(2) Install the primary and secondary brake tubes
from the master cylinder in their ports. Tighten tube
nuts to a torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.).Take care
not to twist tubes when tightening tube nuts.
They must be properly positioned to allow free
movement with rubber isolated suspension
crossmember.
(3) Install the four chassis brake tubes into the
outlet ports of the junction block. Tighten all 6 tube
nuts to a torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.).
(4) If the vehicle is equipped with speed control,
perform the following:
(a) Install the speed control servo with its
mounting nuts.
(b) Connect the wiring harness to the speed con-
trol servo.
(c) Install the battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - INSTALLA-
TION).(d) Install the screw securing the coolant filler
neck to the battery tray.
(e) Reconnect the vacuum hose connector at the
tank built into the battery tray.
(f) Install the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - INSTALLA-
TION).
(g) Install the battery shield.
(5) Remove the brake pedal holder.
(6) Connect negative cable back on negative post of
the battery.
(7) Bleed the brake system thoroughly to ensure
that all air has been expelled from the hydraulic sys-
tem. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(8) Road test the vehicle to verify proper operation
of the brake system.
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION
The master cylinder is located on the power brake
booster in the engine compartment on the driver's
side (Fig. 47). This vehicle uses 3 different master
cylinders. Master cylinder usage depends on what
type of brake system the vehicle is equipped with.
CAUTION: Master cylinders are not interchangeable
between systems. Performance and stopping dis-
tance issues will result if the incorrect master cyl-
inder is installed on the vehicle.
Fig. 46 NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
1 - MASTER CYLINDER
2 - JUNCTION BLOCK
3 - SUSPENSION CROSSMEMBER
4 - MOUNTING BOLTS
Fig. 47 MASTER CYLINDER AND BOOSTER
LOCATION
1 - MASTER CYLINDER
2 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
RSBRAKES - BASE5-33
JUNCTION BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1660 of 4284

For information on master cylinder application,
bore and type, view the following table:
BRAKE SYSTEMMASTER CYLINDER
BORE/TYPE
Disc/Drum - ABS23.8 mm Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Drum - Non-ABS23.8 mm Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Disc - ABS25.4 mm (1-1/16 in.)
Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Disc ABS With
Traction Control25.4 mm (1-1/16 in.) Dual
Center Port
CAUTION: When replacing a master cylinder, be
sure to use the correct master cylinder for the type
of brake system the vehicle is equipped with.
The body of the master cylinder is an anodized alu-
minum casting. It has a machined bore to accept the
master cylinder pistons and threaded ports with
seats for the hydraulic brake line connections.
The brake fluid reservoir is mounted on the top of
the master cylinder. It is made of a see-through
polypropylene type plastic for easy fluid level view-
ing. A brake fluid level switch is attached to the
brake fluid reservoir.
The master cylinder is not a repairable component
and must be replaced if diagnosed to be functioning
improperly. The brake fluid reservoir and brake fluid
level switch can be replaced separately.
CAUTION: Do not hone the bore of the cylinder as
this will remove the anodized surface from the bore.
OPERATION
When the brake pedal is depressed, the master cyl-
inder primary and secondary pistons apply brake
pressure through the chassis tubes to the brakes at
each tire and wheel assembly.
The master cylinder primary outlet port supplies
hydraulic pressure to the right front and left rear
brakes. The secondary outlet port supplies hydraulic
pressure to the left front and right rear brakes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER CYLINDER
BLEEDING
CAUTION: When clamping master cylinder in vise,
only clamp master cylinder by its mounting flange,
do not clamp on primary piston, seal or body of
master cylinder.(1) Clamp the master cylinder in a vise using only
the mounting flange.
NOTE: Two different size bleeding tubes need to be
used depending on which type of master cylinder
the vehicle is equipped with. Vehicles equipped
with traction control have different size brake tubes
and nuts at the master cylinder than the non-trac-
tion control equipped vehicles. Be sure the correct
size bleeding tubes are used when bleeding the
master cylinder.
(2) Thread Bleeding Tubes, Special Tool 8358, for a
non-traction control master cylinder or Special Tool
8129 for a traction control master cylinder into mas-
ter cylinder primary and secondary ports. Position
outlet ends of bleeding tubes in reservoir with the
outlets below surface of brake fluid when reservoir is
filled to its proper level.
(3) Fill brake fluid reservoir with Mopartbrake
fluid or equivalent conforming to DOT 3 (DOT 4 and
DOT 4+ are acceptable) specifications.
(4) Using a wooden dowel, depress push rod slowly,
and then allow pistons to return to released position.
Repeat several times until all air bubbles are
expelled from master cylinder.
(5) Remove bleeding tubes from master cylinder
outlet ports, and then plug outlet ports and install
fill cap on reservoir.
(6) Remove master cylinder from vise.
(7) Install the filler cap on master cylinder fluid
reservoir.
(8) Install master cylinder. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES -
BASE/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/MASTER CYL-
INDER - INSTALLATION)
REMOVAL - MASTER CYLINDER
CAUTION: Vacuum in the power brake booster must
be pumped down (removed) before removing mas-
ter cylinder from power brake booster. This is nec-
essary to prevent the power brake booster from
sucking in any contamination as the master cylin-
der is removed. This can be done simply by pump-
ing the brake pedal, with the vehicle's engine not
running, until a firm feeling brake pedal is achieved.
(1) With engine not running, pump brake pedal
until a firm pedal is achieved (4-5 strokes).
(2) Disconnect negative battery terminal.
(3) Disconnect positive battery terminal.
(4) Remove battery shield.
(5) Remove nut and clamp securing battery to tray,
remove battery.
5 - 34 BRAKES - BASERS
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 1663 of 4284

POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
DESCRIPTION
The power brake booster mounts on the engine
compartment side of the dash panel. It is connected
to the brake pedal by the input (push) rod (Fig. 52).
The master cylinder is bolted to the front of the
booster. A vacuum line connects the power brake
booster to the intake manifold.
All vehicles use a 270 mm single diaphragm vac-
uum power brake booster.
Vehicles equipped with Disc/Disc brakes use a dif-
ferent power brake booster than vehicles equipped
with Disc/Drum brakes. Differences between the two
are internal. Service is the same for all boosters.
The power brake booster can be identified by the
tag attached to the body of the booster (Fig. 53). This
tag contains the production part number, the date it
was built, and who the manufacturer of the power
brake booster is.
NOTE: The power brake booster assembly is not a
repairable component and must be replaced as a
complete assembly if found to be faulty in any way.
The check valve located on the power brakebooster face is not repairable, but it can be
replaced separately from the power brake booster.
The different engine combinations used in this
vehicle require different vacuum hose routings to the
power brake booster. All vacuum hoses must be
routed from the engine to the power brake booster
without kinks or excessively tight bends.
OPERATION
The power brake booster reduces the amount of
force required by the driver to obtain the necessary
hydraulic pressure to stop a vehicle.
The power brake booster is vacuum operated. The
vacuum is supplied from the intake manifold on the
engine through a vacuum hose and the power brake
booster check valve (Fig. 52).
As the brake pedal is depressed, the power brake
booster's input rod moves forward (Fig. 52). This
opens and closes valves in the power booster allowing
atmospheric pressure to enter on one side of a dia-
phragm. Engine vacuum is always present on the
other side. This difference in pressure forces the out-
put rod of the power brake booster out against the
primary piston of the master cylinder. As the pistons
in the master cylinder move forward this creates the
hydraulic pressure in the brake system.
Fig. 52 Power Brake Booster (Typical)
1 - VACUUM CHECK VALVE
2 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER ASSEMBLY
3 - INPUT ROD
4 - POWER BOOSTER ASSEMBLY TO DASH PANEL MOUNTING
STUDS (4)
5 - MASTER CYLINDER MOUNTING STUDS (2)
6 - OUTPUT ROD
Fig. 53 MASTER CYLINDER AND BOOSTER
1 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
2 - BOOSTER IDENTIFICATION LABEL
3 - FLUID LEVEL SWITCH CONNECTOR
4 - PRIMARY BRAKE TUBE NUT
5 - SECONDARY BRAKE TUBE NUT
6 - MASTER CYLINDER
RSBRAKES - BASE5-37