dead battery CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001Pages: 4284, PDF Size: 83.53 MB
Page 1857 of 4284
BATTERY SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
THE BATTERY SEEMS
WEAK OR DEAD WHEN
ATTEMPTING TO START
THE ENGINE.1. The battery has an
incorrect size or rating for
this vehicle.1. Refer to Battery Specifications for the proper
size and rating. Replace an incorrect battery, as
required.
2. The battery is physically
damaged.2. Inspect the battery for loose terminal posts or a
cracked and leaking case. Replace the damaged
battery, as required.
3. The battery terminal
connections are loose or
corroded.3. Refer to Battery Cable for the proper cable
diagnosis and testing procedures. Clean and
tighten the battery terminal connections, as
required.
4. The battery is discharged. 4. Determine the battery state-of-charge. Refer to
Standard Procedures for the proper test
procedures. Charge the faulty battery, as
required.
5. The electrical system
ignition-off draw is excessive.5. Refer to Standard Procedures for the proper
test procedures. Repair the faulty electrical
system, as required.
6. The battery is faulty. 6. Determine the battery cranking capacity. Refer
to Standard Procedures for the test procedures.
Replace the faulty battery, as required.
7. The starting system is
faulty.7. Determine if the starting system is performing
to specifications. Refer to Starting System for the
proper starting system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the faulty starting system, as
required.
8. The charging system is
faulty.8. Determine if the charging system is performing
to specifications. Refer to Charging System for
the proper charging system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the faulty charging system, as
required.
RSBATTERY SYSTEM8F-3
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 1874 of 4284

(4) Install the battery in the vehicle. Refer to the
procedure in this section.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
THERMAL GUARD
DESCRIPTION
A one-piece molded plastic clam shell-type thermal
guard unit shields the battery case from engine com-
partment heat (Fig. 22). Two molded latches secure
the side of the thermal guard to the battery tray. The
front is secured by a retaining fastener at the radia-
tor closure panel and the rear by a push pin type
retainer, near the cowl panel.
OPERATION
The thermal guard protects the battery from
engine compartment temperature extremes. The tem-
perature of the battery can affect battery perfor-
mance. The air trapped between the plastic plies of
the thermal guard create a dead air space, which
helps to insulate the sides of the battery case from
the air temperature found in the surrounding engine
compartment.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the battery thermal guard retaining
fastener on the radiator closure panel (Fig. 22).
(2) Remove the push pin retainer near the cowl
trim panel.
(3) Lift the battery thermal guard straight up to
remove from the engine compartment.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the thermal guard on the battery tray
molded retaining latches.
(2) Install the battery thermal guard retaining fas-
tener on the radiator closure panel.
(3) Install the push pin retainer near the cowl trim
panel.
Fig. 21 BATTERY TRAY POSITION & ORIENTATION
1 - BATTERY TRAY RETAINING FASTENERS
Fig. 22 BATTERY POSITION & ORIENTATION
1 - BATTERY THERMAL GUARD
2 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
8F - 20 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY TRAY (Continued)
Page 1919 of 4284

AUTO SHUT DOWN RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). For the location of the relay within the
PDC, refer to the PDC cover for location. Check elec-
trical terminals for corrosion and repair as necessary
OPERATION
The ASD sense circuit informs the PCM when the
ASD relay energizes. A 12 volt signal at this input
indicates to the PCM that the ASD has been acti-
vated. This input is used only to sense that the ASD
relay is energized.
When energized, the ASD relay supplies battery
voltage to the fuel injectors, ignition coils and the
heating element in each oxygen sensor. If the PCM
does not receive 12 volts from this input after
grounding the ASD relay, it sets a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC).
When energized, the ASD relay provides power to
operate the injectors, ignition coil, generator field, O2
sensor heaters (both upstream and downstream), and
also provides a sense circuit to the PCM for diagnos-
tic purposes. The PCM energizes the ASD any time
there is a Crankshaft Position sensor signal that
exceeds a predetermined value. The ASD relay can
also be energized after the engine has been turned
off to perform an O2 sensor heater test, if vehicle is
equipped with OBD II diagnostics.
As mentioned earlier, the PCM energizes the ASD
relay during an O2 sensor heater test. This test is
performed only after the engine has been shut off.
The PCM still operates internally to perform several
checks, including monitoring the O2 sensor heaters.
CAMSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The camshaft position sensorfor the 3.3/3.8L is
mounted in the front of the timing case cover (Fig. 7)
and the camshaft position sensor for the 2.4L is
mounted on the end of the cylinder head (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
The camshaft position sensor provides cylinder
identification to the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) (Fig. 2). The sensor generates pulses as
groups of notches on the camshaft sprocket pass
underneath it (Fig. 3). The PCM keeps track of
crankshaft rotation and identifies each cylinder by
the pulses generated by the notches on the camshaftsprocket. Four crankshaft pulses follow each group of
camshaft pulses.
When the PCM receives 2 cam pulses followed by
the long flat spot on the camshaft sprocket, it knows
that the crankshaft timing marks for cylinder 1 are
next (on driveplate). When the PCM receives one
camshaft pulse after the long flat spot on the
sprocket, cylinder number 2 crankshaft timing marks
are next. After 3 camshaft pulses, the PCM knows
cylinder 4 crankshaft timing marks follow. One cam-
shaft pulse after the 3 pulses indicates cylinder 5.
The 2 camshaft pulses after cylinder 5 signals cylin-
der 6 (Fig. 3). The PCM can synchronize on cylinders
1or4.
When metal aligns with the sensor, voltage goes
low (less than 0.3 volts). When a notch aligns with
the sensor, voltage switches high (5.0 volts). As a
group of notches pass under the sensor, the voltage
switches from low (metal) to high (notch) then back
to low. The number of notches determine the amount
of pulses. If available, an oscilloscope can display the
square wave patterns of each timing event.
Top Dead Center (TDC) does not occur when
notches on the camshaft sprocket pass below the cyl-
inder. TDC occurs after the camshaft pulse (or
pulses) and after the 4 crankshaft pulses associated
with the particular cylinder. The arrows and cylinder
call outs on Figure 4 represent which cylinder the
flat spot and notches identify, they do not indicate
TDC position.
REMOVAL - 2.4L
The camshaft position sensor is mounted to the
rear of the cylinder head.
(1) Remove the negative battery cable.
Fig. 2 Camshaft Position Sensor
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 - O-RING
3 - PAPER SPACER
RSIGNITION CONTROL8I-3
Page 2880 of 4284

pump outlet, maintains pump pressure during engine
off conditions. The fuel pump relay provides voltage
to the fuel pump.
The fuel pump has a maximum deadheaded pres-
sure output of approximately 880 kPa (130 psi). The
regulator adjusts fuel system pressure to approxi-
mately 400634 kPa (5865 psi).
FUEL PUMP ELECTRICAL CONTROL
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay. For an electrical opera-
tional description of the fuel pump refer to fuel Pump
RelayÐPCM Output.
ELECTRICAL PUMP REPLACEMENT
The electric fuel pump is not serviceable. If the
fuel pump or electrical wiring harness needs replace-
ment, the complete fuel pump module must be
replaced. Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release
procedure before servicing the fuel pump.
REMOVAL
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from auxiliary
jumper terminal.
(3) Drain fuel tank, refer to the Fuel Tank proce-
dure in the Fuel Delivery section.
(4) Remove fuel tank, refer to the Fuel Tank
removal section.
(5) Clean top of tank to remove loose dirt and
debris.
(6) Using a brass punch and hammer remove lock-
nut to release pump module (Fig. 11).
WARNING: THE FUEL RESERVOIR OF THE FUEL
PUMP MODULE DOES NOT EMPTY OUT WHEN THE
TANK IS DRAINED. THE FUEL IN THE RESERVOIR
MAY SPILL OUT WHEN THE MODULE IS REMOVED.
(7) Remove fuel pump module and O-ring from
tank (Fig. 12). Discard O-ring.
INSTALLATION
(1) Wipe seal area of tank clean and place a new
O-ring seal in position on pump.
(2) Position fuel pump module in tank.
(3) Tighten locknut using a brass punch and ham-
mer to install the locknut (Fig. 11).
(4) Install fuel tank, refer to the Fuel Tank instal-
lation section.(5) Lower vehicle.
(6) Connect negative cable battery.
(7) Fill fuel tank. Check for leaks.
(8) Install fuel filler cap.
Fig. 11 FUEL PUMP MODULE LOCKING RING
Fig. 12 Fuel Pump Module Removal
1 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
2 - O-RING
14 - 8 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL PUMP MODULE (Continued)
Page 3079 of 4284
A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions. When the ignition key is in the
OFF position, the gearshift lever is unrestricted, and
able to move into any gear position (during towing,
dead battery, etc.).
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
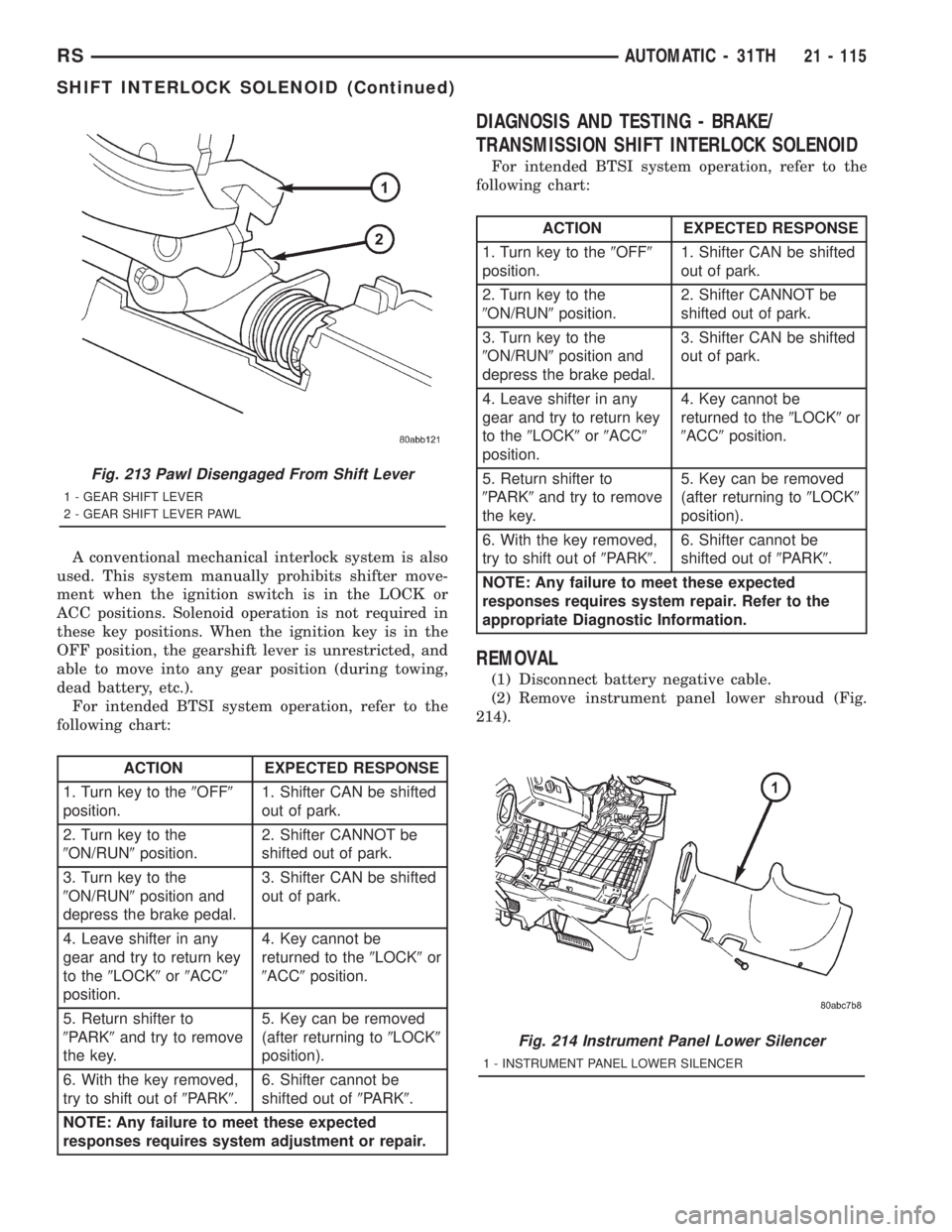
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
214).
Fig. 213 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 214 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
RSAUTOMATIC - 31TH21 - 115
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 3237 of 4284

OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid prevents the transmission shift lever from
being moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal
is applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and
controlled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM).
Battery voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid
with the ignition key is in either the ON/RUN or
START positions (Fig. 306). The ground side of the
solenoid is controlled by a driver within the IPM. It
relies on voltage supplied from the stop lamp switch
to the stop lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell
when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake
pedal is depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-ener-
gizing the solenoid. When the brake pedal is
released, the ground circuit is closed, energizing the
solenoid.
When the ignition key is in either the ON/RUN or
START positions, the BTSI solenoid is energized, and
the solenoid plunger hook pulls the shift lever pawl
into position, prohibiting the shift lever from moving
out of PARK (P) (Fig. 307). When the brake pedal is
depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-energizing
the solenoid. This moves the gearshift lever pawl out
of the way (Fig. 308), allowing the shift lever to be
moved into any gear position.
A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions. When the ignition key is in the
OFF position, the gearshift lever is unrestricted, and
able to move into any gear position (during towing,
dead battery, etc.).
Fig. 306 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 307 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 308 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
RSAUTOMATIC - 41TE21 - 273
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 4047 of 4284

Symptom:
*ENGINE CRANKS DOES NOT START
POSSIBLE CAUSES
FUEL PUMP RELAY
NO START PRE-TEST
POWERTRAIN FUSES OPEN
FUEL PRESSURE OUT OF SPECS
RESTRICTED FUEL SUPPLY LINE
FUEL PUMP INLET STRAINER PLUGGED
FUEL PUMP MODULE
FUEL PUMP CAPACITY (VOLUME) OUT OF SPECS
FUEL PUMP RELAY FUSED B+ CIRCUIT
OTHER POSSIBLE CAUSES FOR NO START
FUEL PUMP RELAY OUTPUT CIRCUIT OPEN
FUEL PUMP GROUND CIRCUIT OPEN/HIGH RESISTANCE
IPM FUSE & RELAY CENTER
FUEL PUMP MODULE
TEST ACTION APPLICABILITY
1Note: The following list of items must be checked before continuing with
any no start tests.
The battery must be fully charged and in good condition. A low charged battery may
produce invalid test results. If the battery is low, charge the battery and then attempt
to start the vehicle by cranking the engine for 15 seconds, 3 consecutive times.
This will allow any DTC's to set that may have been erased due to a dead battery.
Ensure the Powers and Ground to the PCM are ok.
Make sure the PCM communicates with the DRB and that there are no DTC's stored
in the PCM memory. If the PCM reports a No Response condition, refer to the
Communication category for the proper tests.
Read the PCM DTC's with the DRB. If any DTC's are present, they must be repaired
before continuing with any other No Start diagnostic tests. Refer to the Symptom list
for the related P-code that is reported by the PCM.
Ensure that the PCI bus is functional. Attempt to communicate with the Instrument
Cluster and SKIM, If you are unable to establish communicate refer to the
Communication category for the proper symptoms.
The Sentry Key Immobilizer System must be operating properly. Check for proper
communication with the DRB and check for DTC's that may be stored in the Sentry
Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM). repair the DTC(s) before continuing.
If no DTC's are found, using the DRB select Clear PCM (Batt Disconnect).
Crank the engine several times. Using the DRB, read DTC's. If a DTC is present
perform the DTC diagnostics before continuing.
Were any problems found?All
Ye s®Repair as necessary.
Perform POWERTRAIN VERIFICATION TEST VER-1.
No®Go To 2
253
STARTING
Page 4109 of 4284

DTC P-Code Name of Code Limp-in MIL
71 P1797 Manual shift overheat No No
73 P1798 Worn out/burnt transmission fluid No No
74 P1799 Calculated Oil temperature in use No No
75 P1738 High temperature operation activated No No
76 P1739 Power up at speed No No
77 P1717 No communication with the MIC No No
78 P0600 Serial communication link malfunction No No
79 P1714 Low battery voltage Yes Yes
Yes (underlined) indicates that this DTC can take up to five minutes of problem identification before
illuminating the MIL.
3.3.7 DTC DESCRIPTIONS
Name of code:P1792(12) - Battery was Discon-
nected (Informational code Only)
When monitored:Whenever the key is in the
Run/Start position.
Set condition:This code is set whenever the
Transmission Control Module (TCM) is discon-
nected from battery power (B+) or ground. It will
also be set during the DRBIIItBattery Disconnect
procedure.
Theory of operation:A battery backed RAM
(Random Access Memory) is used to maintain some
learned values. When the battery B(+) is discon-
nected, the memory is lost. When the B(+) is re-
stored, this memory loss is detected by the TCM.
The code is set and the learned values are initial-
ized to known constants or previously learned val-
ues from EEPROM (Electronic Erasable Program-
mable Read Only Memory). This results in the
initialization of some parameters.
Transmission Effects:Loss of trouble code data.
Immediate limp-in mode if power is lost while
operating the vehicle. Normal operation is resumed
if the power is restored during the same key start.
Possible causes:
> Battery voltage removed from TCM
> TCM disconnected
> Dead Battery
> Low battery voltage during cranking
> Battery Disconnect by DRBIIItor MDS
> Bad TCM ground circuit.
Name of code:P1767(14) - Relay Output Always
On
When monitored:Ignition key is turned from off
position to run position and/or ignition key is
turned from crank position to run position.
Set condition:This code is set if the Transmission
Control Module (TCM) senses greater than 3 voltsat the Trans Relay Output (switched battery) ter-
minal of the TCM prior to the TCM energizing the
relay.
Theory of operation:The transmission control
relay is used to supply power to the solenoid pack
when the transmission is in normal operating
mode. When the relay is off, no power is supplied to
the solenoid pack and the transmission is in limp-in
mode. The relay output is fed back to the TCM
through pins 16 and 17. It is referred to as the
Trans Relay Output circuit or switched battery.
Transmission Effects:The MIL will illuminate
and the transmission system defaults to Logical
limp-in mode. Logical Limp-in mode results in the
same modes of operation as Relay Open Limp-in.
Since the relay is stuck9on9, the TCM can not open
the relay, and the TCM shifts to 2nd gear.
Possible causes:
> Relay failure (welded contacts)
> Short to battery in 12-volt supply and/or Trans-
mission Control Relay Output circuit(s)
> Short to voltage
> TCM connector problems
> TCM
Name of code:P1768(15) - Relay Output Always
Off
When monitored:Continuously
Set condition:This code is set when less than 3
volts are present at the Trans Relay Output
(switched battery) terminals at the Transmission
Control Module (TCM) when the TCM is energizing
the relay.
Theory of operation:The transmission control
relay is used to supply power to the solenoid pack
when the transmission is in normal operating
mode. When the relay is off, no power is supplied to
the solenoid pack and the transmission is in limp-in
mode. The relay output is fed back to the TCM
through pins 16 and 17. It is referred to as the
Trans Relay Output circuit or a switched battery.
5
GENERAL INFORMATION