check oil CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1851 of 2585
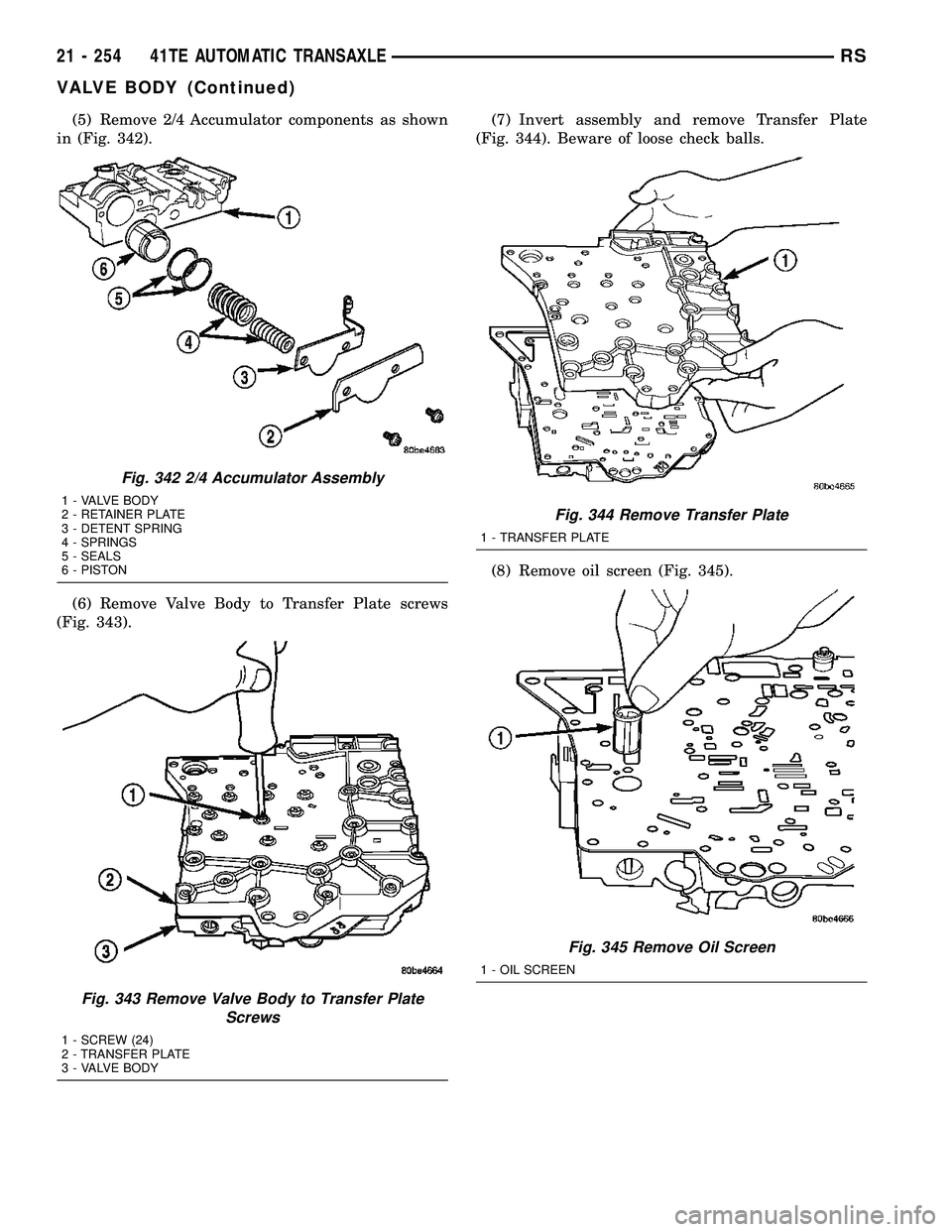
(5) Remove 2/4 Accumulator components as shown
in (Fig. 342).
(6) Remove Valve Body to Transfer Plate screws
(Fig. 343).(7) Invert assembly and remove Transfer Plate
(Fig. 344). Beware of loose check balls.
(8) Remove oil screen (Fig. 345).
Fig. 342 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - SPRINGS
5 - SEALS
6 - PISTON
Fig. 343 Remove Valve Body to Transfer Plate
Screws
1 - SCREW (24)
2 - TRANSFER PLATE
3 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 344 Remove Transfer Plate
1 - TRANSFER PLATE
Fig. 345 Remove Oil Screen
1 - OIL SCREEN
21 - 254 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1857 of 2585
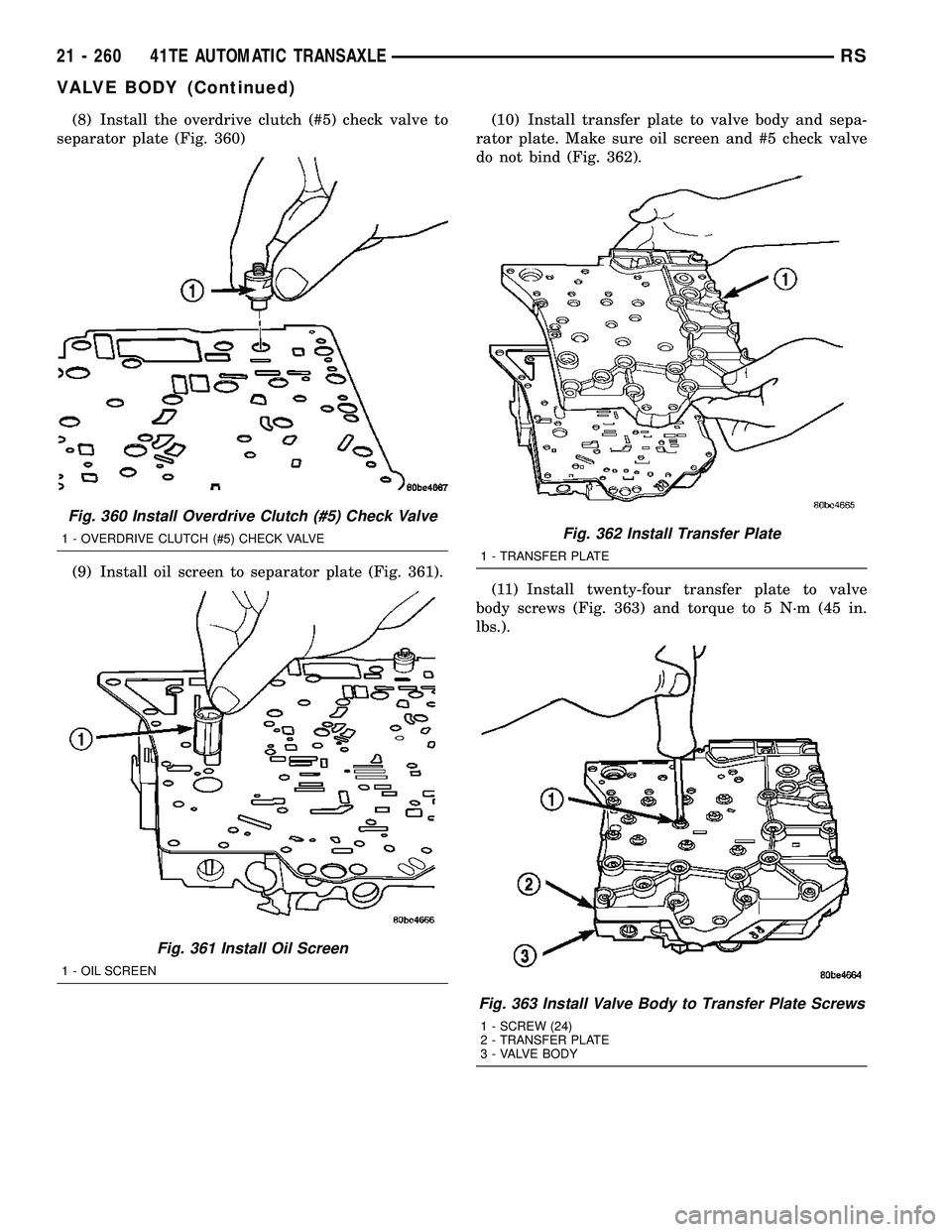
(8) Install the overdrive clutch (#5) check valve to
separator plate (Fig. 360)
(9) Install oil screen to separator plate (Fig. 361).(10) Install transfer plate to valve body and sepa-
rator plate. Make sure oil screen and #5 check valve
do not bind (Fig. 362).
(11) Install twenty-four transfer plate to valve
body screws (Fig. 363) and torque to 5 N´m (45 in.
lbs.).
Fig. 360 Install Overdrive Clutch (#5) Check Valve
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH (#5) CHECK VALVE
Fig. 361 Install Oil Screen
1 - OIL SCREEN
Fig. 362 Install Transfer Plate
1 - TRANSFER PLATE
Fig. 363 Install Valve Body to Transfer Plate Screws
1 - SCREW (24)
2 - TRANSFER PLATE
3 - VALVE BODY
21 - 260 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1885 of 2585

40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTION .........................25
OPERATION ...........................27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4XTETRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS .......27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST . . . 27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS ....................28
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR PRESSURE TESTS ....................30
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE . . . 31
REMOVAL .............................31
DISASSEMBLY .........................34
ASSEMBLY ............................51
INSTALLATION .........................73
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS 4XTE TRANSAXLE HYDRAULICSCHEMATICS ........................75
SPECIFICATIONS - 41TE TRANSAXLE .......87
SPECIAL TOOLS .......................89
ACCUMULATOR DESCRIPTION .........................94
OPERATION ...........................94
DRIVING CLUTCHES DESCRIPTION .........................95
OPERATION ...........................95
FINAL DRIVE DESCRIPTION .........................95
OPERATION ...........................96
DISASSEMBLY .........................96
ASSEMBLY ............................99
ADJUSTMENTS DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOADMEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT ......100
FLUID STANDARD PROCEDURE FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK . . . 102
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID ANDFILTER SERVICE .....................104
GEAR SHIFT CABLE REMOVAL ............................105
HOLDING CLUTCHES DESCRIPTION ........................106
OPERATION ..........................106
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY DISASSEMBLY ........................107
ASSEMBLY ...........................116 OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION ........................131
OPERATION ..........................131
DISASSEMBLY ........................131
ASSEMBLY ...........................132
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN DESCRIPTION ........................132
OPERATION ..........................132
SEAL - OIL PUMP REMOVAL ............................133
INSTALLATION ........................133
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID DESCRIPTION ........................133
OPERATION ..........................134
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/ TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID ..........................135
REMOVAL ............................135
INSTALLATION ........................136
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY DESCRIPTION ........................137
OPERATION ..........................137
REMOVAL ............................138
INSTALLATION ........................139
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT DESCRIPTION ........................140
OPERATION ..........................140
REMOVAL ............................141
INSTALLATION ........................141
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT DESCRIPTION ........................142
OPERATION ..........................142
REMOVAL ............................143
INSTALLATION ........................143
TORQUE CONVERTER DESCRIPTION ........................144
OPERATION ..........................148
REMOVAL ............................149
INSTALLATION ........................149
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY DESCRIPTION ........................150
OPERATION ..........................150
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR DESCRIPTION ........................150
OPERATION ..........................151
REMOVAL ............................151
INSTALLATION ........................152
VALVE BODY DESCRIPTION ........................152
21s - 24 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1891 of 2585

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR
PRESSURE TESTS
Inoperative clutches can be located using a series
of tests by substituting air pressure for fluid pressure
(Fig. 5) (Fig. 6). The clutches may be tested by apply-
ing air pressure to their respective passages. The
valve body must be removed and Tool 6056 installed.
To make air pressure tests, proceed as follows:
NOTE: The compressed air supply must be free of
all dirt and moisture. Use a pressure of 30 psi.
Remove oil pan and valve body. See Valve body
removal.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the overdrive clutch apply
passage and watch for the push/pull piston to move
forward. The piston should return to its starting
position when the air pressure is removed.
REVERSE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the reverse clutch apply pas-
sage and watch for the push/pull piston to move rear-
ward. The piston should return to its starting
position when the air pressure is removed.
2/4 CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the feed hole located on the
2/4 clutch retainer. Look in the area where the 2/4 piston contacts the first separator plate and watch
carefully for the 2/4 piston to move rearward. The
piston should return to its original position after the
air pressure is removed.
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the low/reverse clutch feed
hole (rear of case, between 2 bolt holes). Then, look
in the area where the low/reverse piston contacts the
first separator plate. Watch carefully for the piston to
move forward. The piston should return to its origi-
nal position after the air pressure is removed.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
Because this clutch piston cannot be seen, its oper-
ation is checked by function. Air pressure is applied
to the low/reverse and the 2/4 clutches. This locks the
output shaft. Use a piece of rubber hose wrapped
around the input shaft and a pair of clamp-on pliers
to turn the input shaft. Next apply air pressure to
the underdrive clutch. The input shaft should not
rotate with hand torque. Release the air pressure
and confirm that the input shaft will rotate.
Fig. 5 Air Pressure Test Plate
1 - TOOL 6056
2 - ACCUMULATORS
Fig. 6 Testing Reverse Clutch
1 - TOOL 6056
2 - AIR NOZZLE
21s - 30 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1962 of 2585
(5) If the turning torque is within specifications,
remove tools. Setup is complete. (6) If turning torque is not within specifications
proceed with the following steps. (a) Remove differential bearing retainer from
the transaxle case. (b) Remove the bearing cup from the differential
bearing retainer using Tool 6062A. (c) Remove the existing shim from under the
cup. (d) Measure the existing shim.
(e) If the turning torque was too high when mea-
sured, install a 0.05 mm (0.002 inch) thinner shim.
If the turning torque is was too low, install a 0.05
mm (0.002 inch) thicker shim. Repeat until 5 to 18
inch-pounds turning torque is obtained. Oil Baffle
is not required to be installed when making shim
selection. (f) Install the proper shim under the bearing
cup. Make sure the oil baffle is installed properly in the bearing retainer, below the bearing shim
and cup.
(g) Install the differential bearing retainer using
Tool 5052 and C-4171. Seal the retainer to the
housing with MOPAR tAdhesive Sealant and
torque bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(7) Using Tool L-4436A and an inch-pound torque
wrench, recheck the turning torque of the differential
(Fig. 186). The turning torque should be
between 5 and 18 inch-pounds. Shim thickness need be determined only if any of
the following parts are replaced: ² Transaxle case
² Differential carrier
² Differential bearing retainer
² Extension housing
² Differential bearing cups and cones
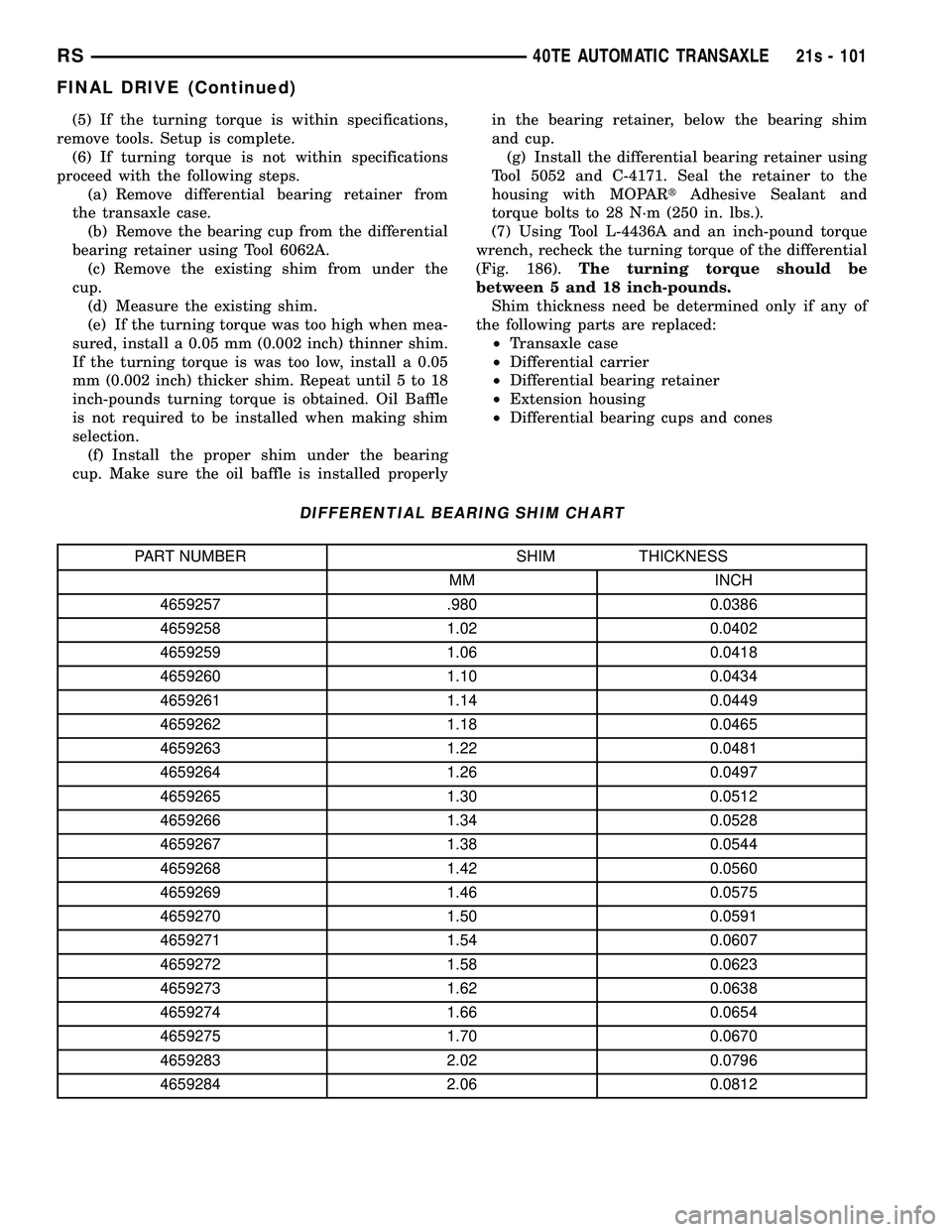
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING SHIM CHART
PART NUMBER SHIM THICKNESS
MM INCH
4659257 .980 0.0386
4659258 1.02 0.0402
4659259 1.06 0.0418
4659260 1.10 0.0434
4659261 1.14 0.0449
4659262 1.18 0.0465
4659263 1.22 0.0481
4659264 1.26 0.0497
4659265 1.30 0.0512
4659266 1.34 0.0528
4659267 1.38 0.0544
4659268 1.42 0.0560
4659269 1.46 0.0575
4659270 1.50 0.0591
4659271 1.54 0.0607
4659272 1.58 0.0623
4659273 1.62 0.0638
4659274 1.66 0.0654
4659275 1.70 0.0670
4659283 2.02 0.0796
4659284 2.06 0.0812
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 101
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)
Page 1963 of 2585

PRELOAD ADJUSTMENT W/O SHIM(1) Remove the bearing cup from the differential
bearing retainer using Miller special Tool 6062A. (2) Remove existing shim from under bearing cup.
(3) Reinstall the bearing cup into the retainer
using Miller Special Tool 6061, and C-4171.
NOTE: Oil baffle is not required when making the
shim calculation.
(4) Install the bearing retainer into the case.
Torque bolts to 28 N ²m (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Position the transaxle assembly vertically on
the support stand and install Miller Special Tool
L-4436-A into the bearing retainer. (6) Rotate the differential at least one full revolu-
tion to ensure the tapered roller bearings are fully
seated. (7) Attach a dial indicator to the case and zero the
dial. Place the tip on the end of Special Tool
L-4436-A. (8) Place a large screwdriver to each side of the
ring gear and lift. Check the dial indicator for the
amount of end play.
CAUTION: Do not damage the transaxle case and/or
differential retainer sealing surface.
(9) Using the end play measurement that was
determined, add 0.18mm (0.007 inch). This should
give you between 5 and 18 inch pounds of bearing
preload. Refer to the Differential Bearing Shim Chart
to determine which shim to use. (10) Remove the differential bearing retainer.
Remove the bearing cup. (11) Install the oil baffle. Install the proper shim
combination under the bearing cup. (12) Install the differential bearing retainer. Seal
the retainer to the housing with Mopar tSilicone
Rubber Adhesive Sealant. Torque bolts to 28 N ²m
(250 in. lbs.). (13) Using Miller Special Tool L-4436-A and an
inch-pound torque wrench, check the turning torque
of the differential (Fig. 186). The turning torque
should be between 5-18 inch-pounds.
NOTE: If turning torque is too high install a 0.05mm
(0.002 inch) thicker shim. If the turning torque is too
low, install a 0.05mm (0.002 inch) thinner shim.
Repeat until 5-18 inch-pounds of turning torque is
obtained.FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: Only transmission fluid of the type labeled
Mopar ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
should be used in this transaxle.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The transmission sump has a fluid level indicator
(dipstick) to check oil similar to most automatic
transmissions. It is located on the left side of the
engine. Be sure to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle
before removing. The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate. The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground. At normal operating temperature 82É C
(180É F), the fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT
region on the oil level indicator (Fig. 187). The fluid
level should be within the COLD region of the dip-
stick at 27É C (80É F) fluid temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK USING DRB
NOTE: Engine and Transaxle should be at normal
operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Hook up DRB scan tool and select transmis-
sion.
Fig. 187 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
21s - 102 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)
Page 1964 of 2585
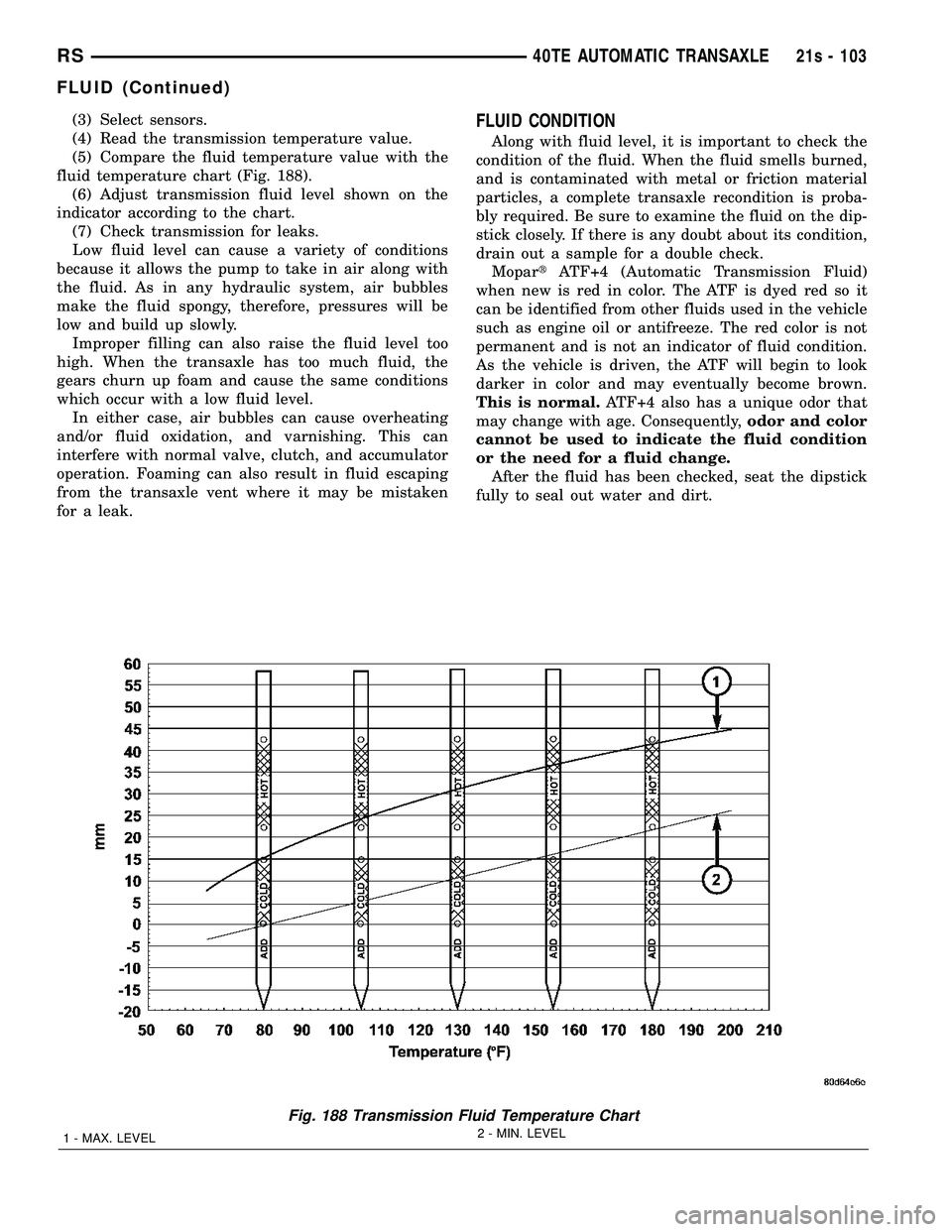
(3) Select sensors.
(4) Read the transmission temperature value.
(5) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
fluid temperature chart (Fig. 188). (6) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
indicator according to the chart. (7) Check transmission for leaks.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly. Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level. In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transaxle vent where it may be mistaken
for a leak.FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is proba-
bly required. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dip-
stick closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check. Mopar tATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed red so it
can be identified from other fluids used in the vehicle
such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red color is not
permanent and is not an indicator of fluid condition.
As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin to look
darker in color and may eventually become brown.
This is normal. ATF+4 also has a unique odor that
may change with age. Consequently, odor and color
cannot be used to indicate the fluid condition
or the need for a fluid change. After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
Fig. 188 Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart
1 - MAX. LEVEL 2 - MIN. LEVEL
RS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 103
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1965 of 2585
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
SERVICE
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in
LUBRICATION and MAINTENANCE, or the vehicle
owner's manual, for the recommended maintenance
(fluid/filter change) intervals for this transaxle.
NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled MoparTATF+4
should be used. A filter change should be made at
the time of the transmission oil change. The magnet
(on the inside of the oil pan) should also be cleaned
with a clean, dry cloth.
NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Refer to LUBRICA-
TION and MAINTENANCE for proper procedures.
Place a drain container with a large opening, under
transaxle oil pan. (2) Remove both engine mount-to-engine cross-
member cradle nuts. Using suitable screw jack and
wood block, raise engine and transmission slightly to
facilitate transaxle oil pan removal and installation. (3) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
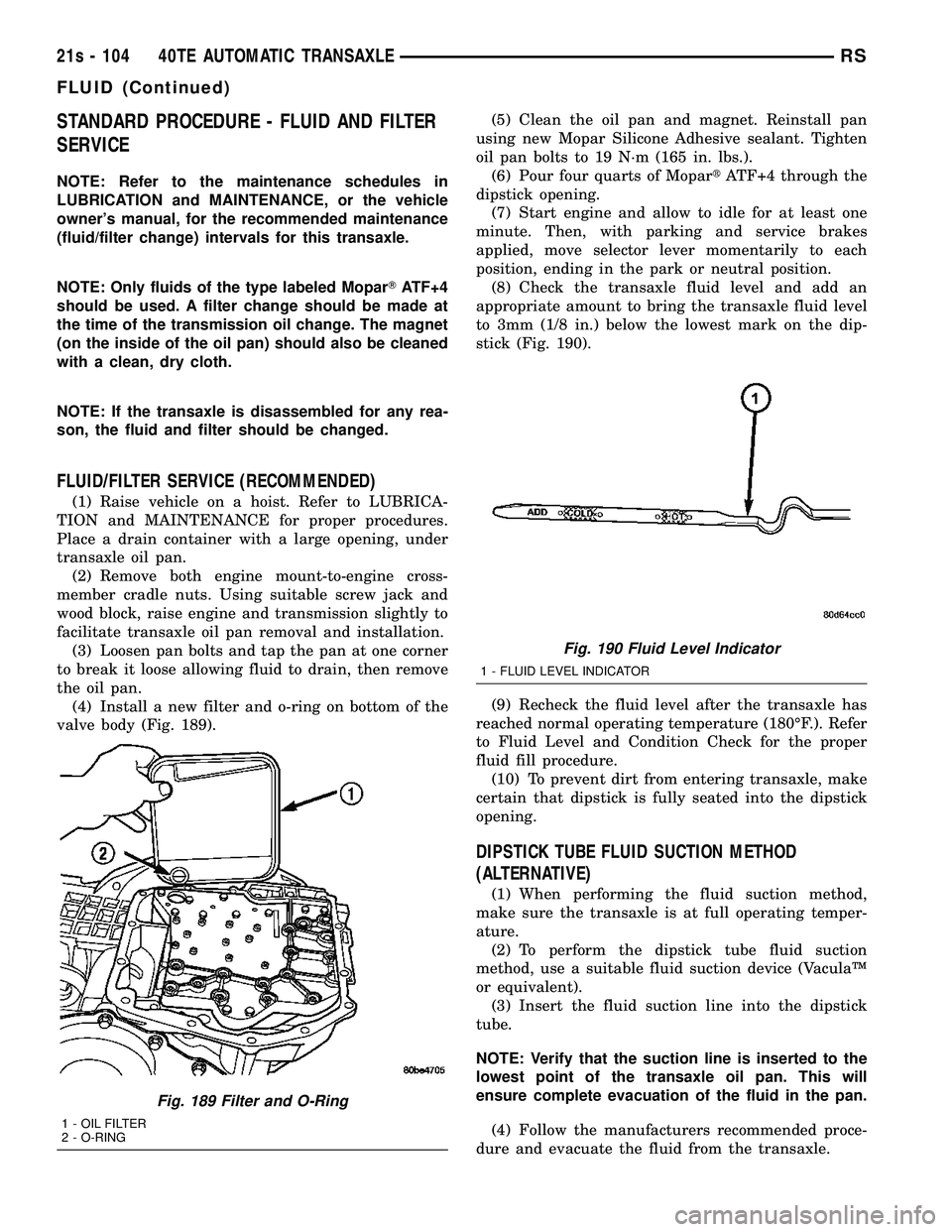
the oil pan. (4) Install a new filter and o-ring on bottom of the
valve body (Fig. 189). (5) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new Mopar Silicone Adhesive sealant. Tighten
oil pan bolts to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.). (6) Pour four quarts of Mopar tATF+4 through the
dipstick opening. (7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position. (8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 190).
(9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.). Refer
to Fluid Level and Condition Check for the proper
fluid fill procedure. (10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature. (2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent). (3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
Fig. 189 Filter and O-Ring
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
Fig. 190 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
21s - 104 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FLUID (Continued)
Page 1992 of 2585
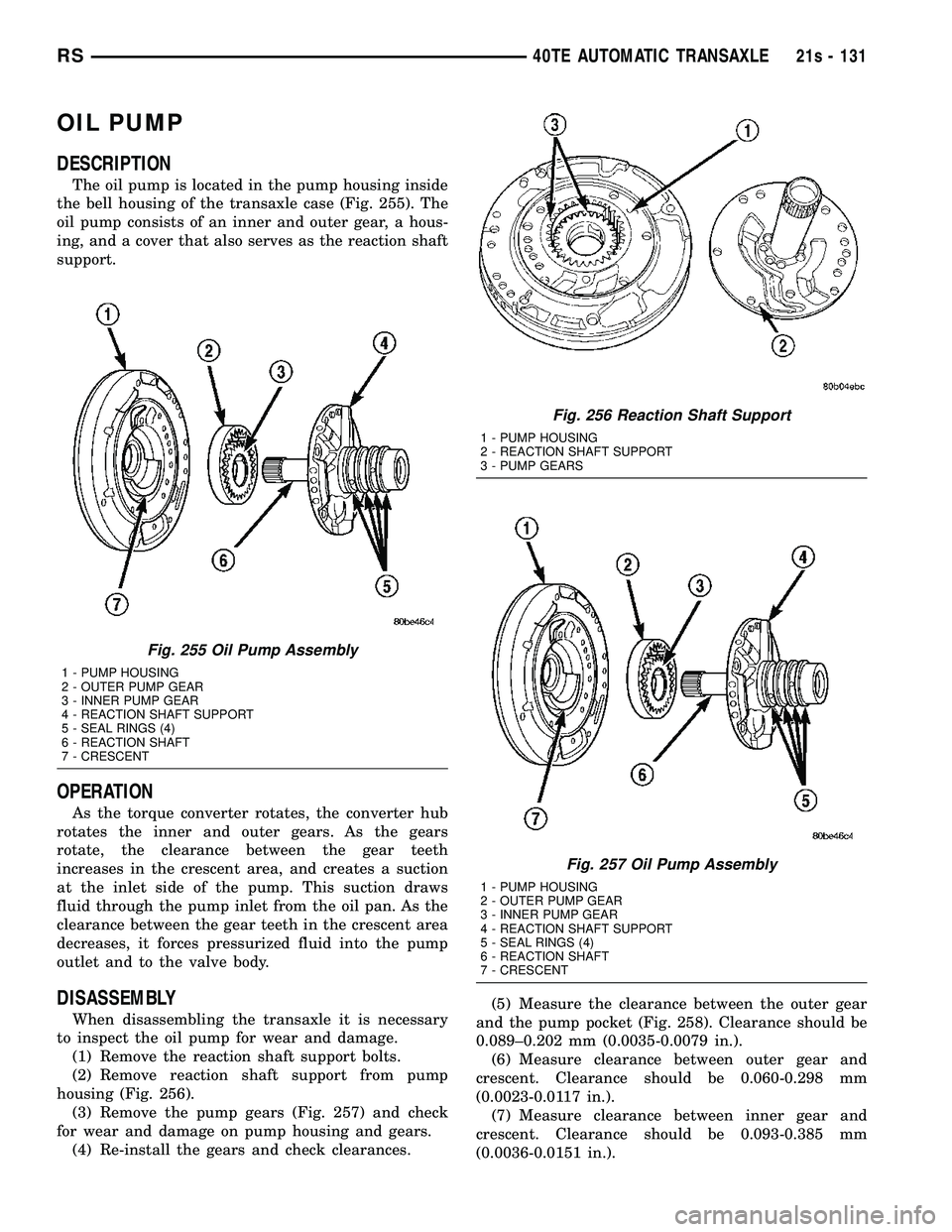
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The oil pump is located in the pump housing inside
the bell housing of the transaxle case (Fig. 255). The
oil pump consists of an inner and outer gear, a hous-
ing, and a cover that also serves as the reaction shaft
support.
OPERATION
As the torque converter rotates, the converter hub
rotates the inner and outer gears. As the gears
rotate, the clearance between the gear teeth
increases in the crescent area, and creates a suction
at the inlet side of the pump. This suction draws
fluid through the pump inlet from the oil pan. As the
clearance between the gear teeth in the crescent area
decreases, it forces pressurized fluid into the pump
outlet and to the valve body.
DISASSEMBLY
When disassembling the transaxle it is necessary
to inspect the oil pump for wear and damage. (1) Remove the reaction shaft support bolts.
(2) Remove reaction shaft support from pump
housing (Fig. 256). (3) Remove the pump gears (Fig. 257) and check
for wear and damage on pump housing and gears. (4) Re-install the gears and check clearances. (5) Measure the clearance between the outer gear
and the pump pocket (Fig. 258). Clearance should be
0.089±0.202 mm (0.0035-0.0079 in.). (6) Measure clearance between outer gear and
crescent. Clearance should be 0.060-0.298 mm
(0.0023-0.0117 in.). (7) Measure clearance between inner gear and
crescent. Clearance should be 0.093-0.385 mm
(0.0036-0.0151 in.).
Fig. 255 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - OUTER PUMP GEAR
3 - INNER PUMP GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
Fig. 256 Reaction Shaft Support
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
3 - PUMP GEARS
Fig. 257 Oil Pump Assembly
1 - PUMP HOUSING
2 - OUTER PUMP GEAR
3 - INNER PUMP GEAR
4 - REACTION SHAFT SUPPORT
5 - SEAL RINGS (4)
6 - REACTION SHAFT
7 - CRESCENT
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 131
Page 2010 of 2585
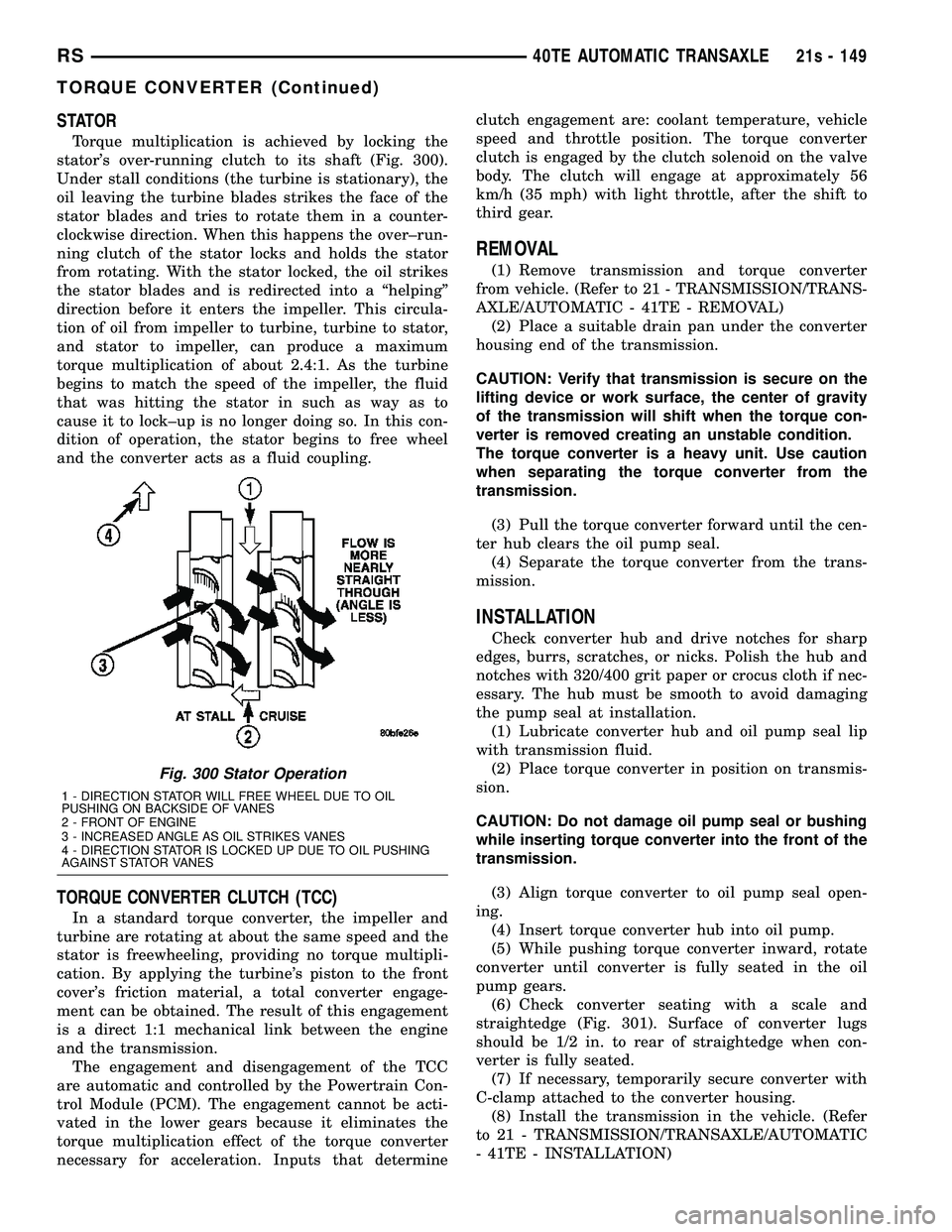
STATOR
Torque multiplication is achieved by locking the
stator's over-running clutch to its shaft (Fig. 300).
Under stall conditions (the turbine is stationary), the
oil leaving the turbine blades strikes the face of the
stator blades and tries to rotate them in a counter-
clockwise direction. When this happens the over±run-
ning clutch of the stator locks and holds the stator
from rotating. With the stator locked, the oil strikes
the stator blades and is redirected into a ªhelpingº
direction before it enters the impeller. This circula-
tion of oil from impeller to turbine, turbine to stator,
and stator to impeller, can produce a maximum
torque multiplication of about 2.4:1. As the turbine
begins to match the speed of the impeller, the fluid
that was hitting the stator in such as way as to
cause it to lock±up is no longer doing so. In this con-
dition of operation, the stator begins to free wheel
and the converter acts as a fluid coupling.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH (TCC)
In a standard torque converter, the impeller and
turbine are rotating at about the same speed and the
stator is freewheeling, providing no torque multipli-
cation. By applying the turbine's piston to the front
cover's friction material, a total converter engage-
ment can be obtained. The result of this engagement
is a direct 1:1 mechanical link between the engine
and the transmission. The engagement and disengagement of the TCC
are automatic and controlled by the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). The engagement cannot be acti-
vated in the lower gears because it eliminates the
torque multiplication effect of the torque converter
necessary for acceleration. Inputs that determine clutch engagement are: coolant temperature, vehicle
speed and throttle position. The torque converter
clutch is engaged by the clutch solenoid on the valve
body. The clutch will engage at approximately 56
km/h (35 mph) with light throttle, after the shift to
third gear.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transmission and torque converter
from vehicle. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE - REMOVAL) (2) Place a suitable drain pan under the converter
housing end of the transmission.
CAUTION: Verify that transmission is secure on the
lifting device or work surface, the center of gravity
of the transmission will shift when the torque con-
verter is removed creating an unstable condition.
The torque converter is a heavy unit. Use caution
when separating the torque converter from the
transmission.
(3) Pull the torque converter forward until the cen-
ter hub clears the oil pump seal. (4) Separate the torque converter from the trans-
mission.
INSTALLATION
Check converter hub and drive notches for sharp
edges, burrs, scratches, or nicks. Polish the hub and
notches with 320/400 grit paper or crocus cloth if nec-
essary. The hub must be smooth to avoid damaging
the pump seal at installation. (1) Lubricate converter hub and oil pump seal lip
with transmission fluid. (2) Place torque converter in position on transmis-
sion.
CAUTION: Do not damage oil pump seal or bushing
while inserting torque converter into the front of the
transmission.
(3) Align torque converter to oil pump seal open-
ing. (4) Insert torque converter hub into oil pump.
(5) While pushing torque converter inward, rotate
converter until converter is fully seated in the oil
pump gears. (6) Check converter seating with a scale and
straightedge (Fig. 301). Surface of converter lugs
should be 1/2 in. to rear of straightedge when con-
verter is fully seated. (7) If necessary, temporarily secure converter with
C-clamp attached to the converter housing. (8) Install the transmission in the vehicle. (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 300 Stator Operation
1 - DIRECTION STATOR WILL FREE WHEEL DUE TO OIL
PUSHING ON BACKSIDE OF VANES
2 - FRONT OF ENGINE
3 - INCREASED ANGLE AS OIL STRIKES VANES
4 - DIRECTION STATOR IS LOCKED UP DUE TO OIL PUSHING
AGAINST STATOR VANES
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s - 149
TORQUE CONVERTER (Continued)