engine CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 404 of 2585

OPERATION
The PLG control module contains the electronic cir-
cuitry and software used to control the sequence of
events for the PLG system. This module comunicates
on the PCI bus circuit with the vehicles body control
module to monitor many different inputs and outputs
such as door lock status, transmission gear selector
position and vehicle speed. Refer to PLG system
operation for more information.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove left D-pillar trim panel from the vehi-
cle. Refer to Body for the procedure.
(3) Disconnect the wire harness connections from
the PLG motor assembly (Fig. 8).
(4) Remove the screw holding the PLG control
module to the D-pillar (Fig. 8).
(5) Remove the PLG control module from the vehi-
cle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the PLG control module on the D-pillar
and install retaining screw. Torque the screw to 14.5
in. lbs.(2) Connect the wire harness connections on the
PLG control module. Be certain to slide connector
locks to the locked position.
(3) Install the D-pillar trim panel on the vehicle.
Refer to the Body section for the procedure.
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
(5) Using an appropriate scan tool, check any
erase any PLG control module diagnostic trouble
codes.
(6) Verify PLG system operation. Cycle the PLG
through one complete open and close cycle, this will
allow the PLG control module to relearn its cycle
with the new components.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 9). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors referred to as Powertrain Control Mod-
ule Inputs. Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts
various engine and vehicle operations through
devices referred to as Powertrain Control Module
Outputs.Fig. 8 POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
1 - POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
2 - RETAINING SCREWS
3 - D-PILLAR
4 - POWER LIFTGATE MOTOR
5 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
Fig. 9 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - Battery
2 - Power Distribution Center
3 - Powertrain Control Module
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-11
POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 405 of 2585

NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²Air Conditioning Pressure Transducer
²Ambient temperature Sensor
²ASD Relay
²Battery Temperature Sensor (NGC)
²Battery Voltage
²Brake Switch
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Distance Sensor (from transmission control mod-
ule)
²EGR Position Feedback
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Heated Oxygen Sensors
²Ignition sense
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock Sensor
²Leak Detection Pump Feedback
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Park/Neutral
²PCI Bus
²Power Steering Pressure Switch
²Proportional Purge Sense
²SCI Receive
²Speed Control
²Throttle Position Sensor
²Torque Management Input
²Transaxle Control Module (3.3/3.8L Only)
²Transmission Control Relay (Switched B+) (2.4L
Only)
²Transmission Pressure Switches (2.4L Only)
²Transmission Temperature Sensor (2.4L Only)
²Transmission Input Shaft Speed Sensor (2.4L
Only)
²Transmission Output Shaft Speed Sensor (2.4L
Only)
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Vehicle Speed
NOTE: PCM Outputs:
²Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
²Automatic Shut Down (ASD) and Fuel Pump
Relays
²Data Link Connector (PCI and SCI Transmit)
²Double Start Override
²EGR Solenoid
²Fuel Injectors
²Generator Field
²High Speed Fan Relay
²Idle Air Control Motor
²Ignition Coils
²Leak Detection Pump
²Low Speed Fan Relay
²MTV Actuator
²Proportional Purge Solenoid²SRV Valve
²Speed Control Relay
²Speed Control Vent Relay
²Speed Control Vacuum Relay
²8 Volt Output
²5 Volt Output
²Torque Reduction Request
²Transmission Control Relay (2.4L Only)
²Transmission Solenoids (2.4L Only)
²Vehicle Speed
Based on inputs it receives, the powertrain control
module (PCM) adjusts fuel injector pulse width, idle
speed, ignition timing, and canister purge operation.
The PCM regulates the cooling fans, air conditioning
and speed control systems. The PCM changes gener-
ator charge rate by adjusting the generator field.
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel
ratio) based on the following inputs.
²Battery Voltage
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Exhaust Gas Oxygen Content (heated oxygen
sensors)
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Throttle Position
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control motor based on the following inputs.
²Brake Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Park/Neutral
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
²Vehicle Speed
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
²Intake Air Temperature
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Engine Speed (crankshaft position sensor)
²Knock Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure
²Park/Neutral
²Transaxle Gear Engagement
²Throttle Position
The automatic shut down (ASD) and fuel pump
relays are mounted externally, but turned on and off
by the powertrain control module through the same
circuit.
The camshaft and crankshaft signals are sent to
the powertrain control module. If the PCM does not
receive both signals within approximately one second
of engine cranking, it deactivates the ASD and fuel
pump relays. When these relays are deactivated,
power is shut off to the fuel injectors, ignition coils,
8E - 12 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 406 of 2585
fuel pump and the heating element in each oxygen
sensor.
The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the camshaft position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the engine
coolant temperature sensor, intake air temperature
sensor, manifold absolute pressure sensor and throt-
tle position sensor.
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage in new PCM. Use
the DRBIIItscan tool to change the mileage in the
PCM. Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Manual and the DRBIIItscan tool.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL (2.4L MODELS ONLY)
CLUTCH VOLUME INDEX (CVI)
An important function of the PCM is to monitor
Clutch Volume Index (CVI). CVIs represent the vol-
ume of fluid needed to compress a clutch pack.
The PCM monitors gear ratio changes by monitor-
ing the Input and Output Speed Sensors. The Input,
or Turbine Speed Sensor sends an electrical signal to
the PCM that represents input shaft rpm. The Out-
put Speed Sensor provides the PCM with output
shaft speed information.
By comparing the two inputs, the PCM can deter-
mine transaxle gear ratio. This is important to the
CVI calculation because the PCM determines CVIs
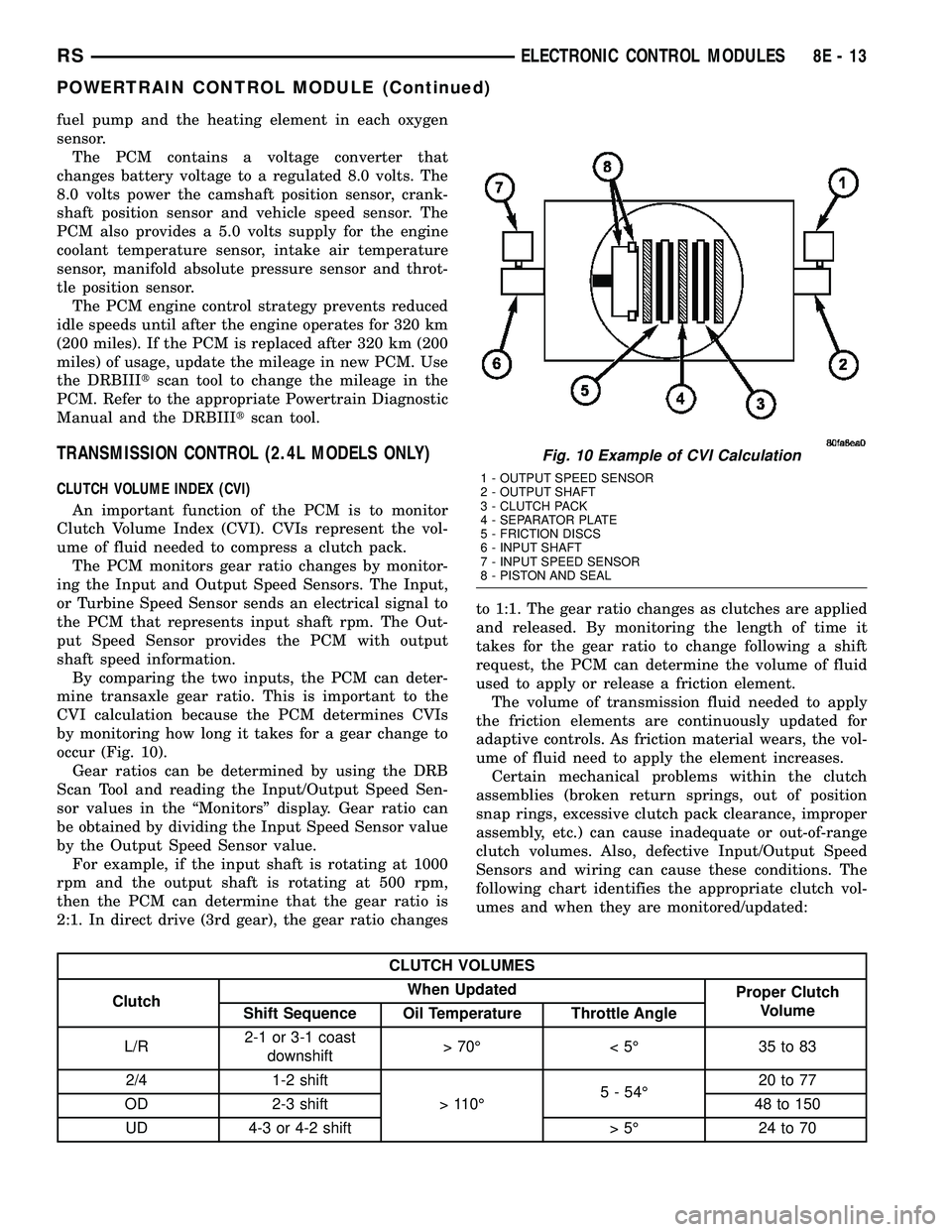
by monitoring how long it takes for a gear change to
occur (Fig. 10).
Gear ratios can be determined by using the DRB
Scan Tool and reading the Input/Output Speed Sen-
sor values in the ªMonitorsº display. Gear ratio can
be obtained by dividing the Input Speed Sensor value
by the Output Speed Sensor value.
For example, if the input shaft is rotating at 1000
rpm and the output shaft is rotating at 500 rpm,
then the PCM can determine that the gear ratio is
2:1. In direct drive (3rd gear), the gear ratio changesto 1:1. The gear ratio changes as clutches are applied
and released. By monitoring the length of time it
takes for the gear ratio to change following a shift
request, the PCM can determine the volume of fluid
used to apply or release a friction element.
The volume of transmission fluid needed to apply
the friction elements are continuously updated for
adaptive controls. As friction material wears, the vol-
ume of fluid need to apply the element increases.
Certain mechanical problems within the clutch
assemblies (broken return springs, out of position
snap rings, excessive clutch pack clearance, improper
assembly, etc.) can cause inadequate or out-of-range
clutch volumes. Also, defective Input/Output Speed
Sensors and wiring can cause these conditions. The
following chart identifies the appropriate clutch vol-
umes and when they are monitored/updated:
CLUTCH VOLUMES
ClutchWhen Updated
Proper Clutch
Volume
Shift Sequence Oil Temperature Throttle Angle
L/R2-1 or 3-1 coast
downshift>70É <5É 35to83
2/4 1-2 shift
> 110É5 - 54É20 to 77
OD 2-3 shift 48 to 150
UD 4-3 or 4-2 shift > 5É 24 to 70
Fig. 10 Example of CVI Calculation
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - OUTPUT SHAFT
3 - CLUTCH PACK
4 - SEPARATOR PLATE
5 - FRICTION DISCS
6 - INPUT SHAFT
7 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
8 - PISTON AND SEAL
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-13
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 407 of 2585

SHIFT SCHEDULES
As mentioned earlier, the PCM has programming
that allows it to select a variety of shift schedules.
Shift schedule selection is dependent on the follow-
ing:
²Shift lever position
²Throttle position²Engine load
²Fluid temperature
²Software level
As driving conditions change, the PCM appropri-
ately adjusts the shift schedule. Refer to the follow-
ing chart to determine the appropriate operation
expected, depending on driving conditions.
Schedule Condition Expected Operation
Extreme ColdOil temperature at start-up below
-16É FPark, Reverse, Neutral and 2nd
gear only (prevents shifting which
may fail a clutch with frequent
shifts)
ColdOil temperature at start-up above
-12É F and below 36É F± Delayed 2-3 upshift
(approximately 22-31 mph)
± Delayed 3-4 upshift (45-53 mph)
± Early 4-3 costdown shift
(approximately 30 mph)
± Early 3-2 coastdown shift
(approximately 17 mph)
± High speed 4-2, 3-2, 2-1 kickdown
shifts are prevented
± No EMCC
WarmOil temperature at start-up above
36É F and below 80 degree F± Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
± No EMCC
HotOil temperature at start-up above
80É F± Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
± Full EMCC, no PEMCC except to
engage FEMCC (except at closed
throttle at speeds above 70-83 mph)
OverheatOil temperature above 240É F or
engine coolant temperature above
244É F± Delayed 2-3 upshift (25-32 mph)
± Delayed 3-4 upshift (41-48 mph)
± 3rd gear FEMCC from 30-48 mph
± 3rd gear PEMCC from 27-31 mph
Super OverheatOil temperature above 260É F ± All9Overheat9shift schedule
features apply
± 2nd gear PEMCC above 22 mph
± Above 22 mph the torque
converter will not unlock unless the
throttle is closed or if a wide open
throttle 2nd PEMCC to 1 kickdown
is made
8E - 14 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 408 of 2585

OPERATION - SENSOR RETURN - PCM INPUT
The sensor return circuit provides a low electrical
noise ground reference for all of the systems sensors.
The sensor return circuit connects to internal ground
circuits within the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
OPERATION - DATA BUS COMMUNICATION
RECEIVE - PCM INPUT
The PCM uses the SCI communication bus to pre-
form engine diagnostics and flash operations. The
transmission side of the PCM uses the SCI commu-
nication bus to flash new software. However, diagnos-
tics is performed via the vehicles J1850 bus for the
transmission side of the PCM.
OPERATION - IGNITION SENSE - PCM INPUT
The ignition sense input informs the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) that the ignition switch is in
the crank or run position.
OPERATION - PCM GROUND
Ground is provided through multiple pins of the
PCM connector. Depending on the vehicle there may
be as many as two different ground pins. There are
power grounds and sensor grounds.
The power grounds are used to control the ground
side relays, solenoids, ignition coil or injectors. The
signal ground is used for any input that uses sensor
return for ground, and the ground side of any inter-
nal processing component.
The PCM case is shielded to prevent RFI and EMI.
The PCM case is grounded and must be firmly
attached to a good, clean body ground.
Internally all grounds are connected together, how-
ever there is noise suppression on the sensor ground.
For EMI and RFI protection the housing and cover
are also grounded separately from the ground pins.
OPERATION
OPERATION - 8-VOLT SUPPLY - PCM OUTPUT
- SBEC CONTROLLER
The PCM supplies 8 volts to the crankshaft posi-
tion sensor, camshaft position sensor.
OPERATION - 5 VOLT SUPPLY - PCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies 5 volts to the following sensors:
²A/C pressure transducer
²Ambient Temperature sensor
²Battery temperature
²Camshaft Position Sensor (NGC)
²Crankshaft Position Sensor (NGC)
²Electronic Throttle Control (1.6L)²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Inlet Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock sensor
²Linear EGR solenoid (if equipped)
²Manifold absolute pressure sensor
²Oil Pressure Switch
²Pedal Position Sensor (1.6L)
²Throttle position sensor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OBTAINING
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
BULB CHECK
Key on: Bulb illuminated until vehicle starts, as
long as all once per trip (readiness) monitors com-
pleted. If monitors havenotbeen completed, then:
Key on: bulb check for about 5 to 8 seconds, lamp
then flashes if once per trip (readiness) monitors
havenotbeen completed until vehicle is started,
then MIL is extinguished.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
(4) To erase DTC's, use the ªErase Trouble Codeº
data screen on the DRB scan tool.Do not erase any
DTC's until problems have been investigated
and repairs have been performed.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PINION FACTOR
SETTING
NOTE: This procedure must be performed if the
PCM/TCM has been replaced with a NEW or
replacement unit. Failure to perform this procedure
will result in an inoperative or improperly calibrated
speedometer.
The vehicle speed readings for the speedometer are
taken from the output speed sensor. The PCM/TCM
must be calibrated to the different combinations of
equipment (final drive and tires) available. Pinion
Factor allows the technician to set the Powertrain/
Transmission Control Module initial setting so that
the speedometer readings will be correct. To properly
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-15
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 409 of 2585

read and/or reset the Pinion Factor, it is necessary to
use a DRBIIItscan tool.
(1) Plug the DRBIIItscan tool into the diagnostic
connector located under the instrument panel.
(2) Select the Transmission menu.
(3) Select the Miscellaneous menu.
(4) Select Pinion Factor. Then follow the instruc-
tions on the DRBIIItscan tool screen.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - QUICK LEARN
PROCEDURE
The quick learn procedure requires the use of the
DRBIIItscan tool. This program allows the PCM/
TCM to recalibrate itself. This will provide the best
possible transaxle operation.
NOTE: The quick learn procedure should be per-
formed if any of the following procedures are per-
formed:
²Transaxle Assembly Replacement
²Powertrain/Transmission Control Module
Replacement
²Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly Replacement
²Clutch Plate and/or Seal Replacement
²Valve Body Replacement or Recondition
To perform the Quick Learn Procedure, the follow-
ing conditions must be met:
²The brakes must be applied
²The engine speed must be above 500 rpm
²The throttle angle (TPS) must be less than 3
degrees
²The shift lever position must stay until
prompted to shift to overdrive
²The shift lever position must stay in overdrive
after the Shift to Overdrive prompt until the
DRBIIItindicates the procedure is complete
²The calculated oil temperature must be above
60É and below 200É
(1) Plug the DRBIIItscan tool into the diagnostic
connector. The connector is located under the instru-
ment panel.
(2) Go to the Transmission screen.
(3) Go to the Miscellaneous screen.
(4) Select Quick Learn Procedure. Follow the
instructions of the DRBIIItto perform the Quick
Learn Procedure.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - SBEC CONTROLLER
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the battery shield, refer to the Battery
section for more information.
(3) Remove the 2 upper PCM bracket bolts (Fig.
11).(4) Remove the 2 PCM connectors.
(5) Remove the headlamp, refer to the Lamps sec-
tion for more information.
(6) Remove the lower PCM mounting bolt (Fig. 12).
(7) Remove PCM.
Fig. 11 PCM
1 - Attaching Bolts
Fig. 12 PCM LOWER BOLT
8E - 16 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 410 of 2585

REMOVAL - NGC CONTROLLER
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage and vehicle iden-
tification number (VIN) in the new PCM. Use the
DRBIIItscan tool to change the millage and VIN in
the PCM. If this step is not done a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC) may be set. Refer to the appropriate
Powertrain Diagnostic Manual and the DRBIIItscan
tool.
(1) Turn wheels to the left.
(2) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(3) Raise vehicle and support.
(4) Remove the left front wheel well splash shield
(Fig. 13).
(5) Unlock and disconnect the electrical connectors
(Fig. 14).
(6) Remove 3 screws from PCM to mounting
bracket.
(7) Remove the PCM.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - SBEC CONTROLLER
(1) Install the PCM.
(2) Install the lower PCM mounting bolt. Tighten
bolt.
(3) Install the 2 upper PCM bracket bolts. Tighten
bolt.
(4) Install the headlamp, refer to the Lamps sec-
tion for more information.
(5) Install the 2 PCM connectors.(6) Install the battery shield, refer to the Battery
section for more information.
(7) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage and vehicle iden-
tification number (VIN) in the new PCM. Use the
DRBIIItscan tool to change the millage and VIN in
the PCM. If this step is not done a diagnostic trouble
code (DTC) may be set and SKIM must be done or
car will not start if it is a SKIM equipped car. If a
SKIM car you must do a secret key transfer also.
NGC CONTROLLER LOCATION
Fig. 13 SPLASH SHIELD
Fig. 14 NGC CONTROLLER
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-17
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 411 of 2585

Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Man-
ual and the DRBIIItscan tool.
(1) Install PCM module to the mounting bracket.
(2) Install electrical connectors and lock.
(3) Install the splash shield.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
(6) Using DRBIIItscan tool, program mileage and
vehicle identification number (VIN) into PCM. Refer
to the DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Manual.
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM) con-
tains a Radio Frequency (RF) transceiver and a
microprocessor. The SKIM retains in memory the ID
numbers of any Sentry Key that is programmed to it.
The maximum number of keys that may be pro-
grammed to each module is eight (8). The SKIM also
communicates over the Programmable Communica-
tion Interface (PCI) data bus with the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM), the Body Control Module
(BCM), the Mechanical Instrument Cluster (MIC),
and the DRB IIItscan tool. The SKIM transmits and
receives RF signals through a tuned antenna
enclosed within a molded plastic ring formation that
is integral to the SKIM housing. When the SKIM is
properly installed on the steering column, the
antenna ring fits snugly around the circumference of
the ignition lock cylinder housing. If this ring is not
mounted properly, communication problems may
arise in the form of transponder-related faults.
For added system security, each SKIM is pro-
grammed with a unique9Secret Key9code. This code
is stored in memory and is sent over the PCI bus to
the PCM and to each key that is programmed to
work with the vehicle. The9Secret Key9code is there-
fore a common element found in all components of
the Sentry Key Immobilizer System (SKIS). In the
event that a SKIM replacement is required, the
9Secret Key9code can be restored from the PCM by
following the SKIM replacement procedure found in
the DRB IIItscan tool. Proper completion of this
task will allow the existing ignition keys to be repro-
grammed. Therefore, new keys will NOT be needed.
In the event that the original9Secret Key9code can
not be recovered, new ignition keys will be required.
The DRB IIItscan tool will alert the technician if
key replacement is necessary. Another security code,
called a PIN, is used to gain secured access to the
SKIM for service. The SKIM also stores in its mem-
ory the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), which itlearns through a bus message from the assembly
plant tester. The SKIS scrambles the information
that is communicated between its components in
order to reduce the possibility of unauthorized SKIM
access and/or disabling.
OPERATION
When the ignition switch is moved to the RUN
position, the Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM)
transmits an Radio Frequency (RF) signal to the
transponder in the ignition key. The SKIM then
waits for a response RF signal from the transponder
in the key. If the response received identifies the key
as valid, the SKIM sends a9valid key9message to
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) over the Pro-
grammable Communication Interface (PCI) data bus.
If the response received identifies the key as invalid
or no response is received from the transponder in
the ignition key, the SKIM sends an9invalid key9
message to the PCM. The PCM will enable or disable
engine operation based upon the status of the SKIM
messages. It is important to note that the default
condition in the PCM is9invalid key.9Therefore, if no
response is received by the PCM, the engine will be
immobilized after two (2) seconds of running.
The SKIM also sends indicator light status mes-
sages to the Mechanical Instrument Cluster (MIC) to
operate the light. This is the method used to turn the
light ON solid or to flash it after the indicator light
test is complete to signify a fault in the SKIS. If the
light comes ON and stays ON solid after the indica-
tor light test, this signifies that the SKIM has
detected a system malfunction and/or that the SKIS
has become inoperative. If the SKIM detects an
invalid keyORa key-related fault exists, the indica-
tor light will flash following the indicator light test.
The SKIM may also request an audible chime if the
customer key programming feature is available and
the procedure is being utilized (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/VEHICLE THEFT SECURITY/TRANSPON-
DER KEY - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove Lower Instrument Panel Cover. Refer
to Body, Instrument Panel, Lower Instrument Panel
Cover, Removal.
(3) Remove the steering column upper and lower
shrouds. Refer to Steering, Column, Column Shroud,
Removal.
(4) Disengage the steering column wire harness
from the Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM).
(5) Remove the one screws securing the SKIM to
the steering column.
8E - 18 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 413 of 2585

(2) Remove the appropriate door trim panel from
the vehicle. Refer to Body for the procedure.
(3) Remove the weather shield. Refer to Body for
the procedure.
(4) Disconnect the power door control module elec-
trical connectors. Slide the red locking tab out (away
from module) and depress connector retaining tab,
while pulling straight apart.
(5) Remove the control module retaining screw
(Fig. 15).
(6) Remove the module from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the control module and install the
retaining screw.
(2) Connect the control module electrical connec-
tors. Slide the locking tab into the locked position.
(3) Install the appropriate door trim panel on the
vehicle. Refer to Body for the procedure.
(4) Install the weather shield. Refer to Body for
the procedure.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
(6) Using an appropriate scan tool, check and
erase any power door control module diagnostic trou-
ble codes.
(7) Verify power door system operation. Cycle the
power door through one complete open and close
cycle.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
On models equipped with the 2.4L Engine option,
the Transmission Control Module (TCM) is located
behind the left fender and is fastened with three
screws to three clips in the left frame rail forward of
the suspension (Fig. 16). Models equipped with the
3.3/3.8L Engine option utilize a Powertrain Control
Module (PCM) which incorporates TCM functionality.
OPERATION
The TCM is the controlling unit for all electronic
operations of the transaxle. The TCM receives infor-
mation regarding vehicle operation from both direct
and indirect inputs, and selects the operational mode
of the transaxle. Direct inputs are hardwired to, and
used specifically by the TCM. Indirect inputs origi-
nate from other components/modules, and are shared
with the TCM via the J1850 communication bus.
Some examples ofdirect inputsto the TCM are:
²Battery (B+) voltage
²Ignition ªONº voltage
²Transmission Control Relay (Switched B+)
²Throttle Position Sensor²Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP)
²Transmission Range Sensor (TRS)
²Pressure Switches (L/R, 2/4, OD)
²Transmission Temperature Sensor (Integral to
TRS)
²Input Shaft Speed Sensor
²Output Shaft Speed Sensor
Some examples ofindirect inputsto the TCM
are:
²Engine/Body Identification
²Manifold Pressure
²Target Idle
²Torque Reduction Confirmation
²Speed Control ON/OFF Switch
²Engine Coolant Temperature
²Ambient/Battery Temperature
²Brake Switch Status
²DRB Communication
Based on the information received from these var-
ious inputs, the TCM determines the appropriate
shift schedule and shift points, depending on the
present operating conditions and driver demand.
This is possible through the control of various direct
and indirect outputs.
Some examples of TCMdirect outputsare:
²Transmission Control Relay
²Solenoids (LR/CC, 2/4, OD and UD)
²Vehicle Speed (to PCM)
²Torque Reduction Request (to PCM)
An example of a TCMindirect outputis:
²Transmission Temperature (to PCM)
Fig. 16 Transmission Control Module (TCM)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (TCM)
8E - 20 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 415 of 2585

SHIFT SCHEDULES
As mentioned earlier, the TCM has programming
that allows it to select a variety of shift schedules.
Shift schedule selection is dependent on the follow-
ing:
²Shift lever position
²Throttle position²Engine load
²Fluid temperature
²Software level
As driving conditions change, the TCM appropri-
ately adjusts the shift schedule. Refer to the follow-
ing chart to determine the appropriate operation
expected, depending on driving conditions.
Schedule Condition Expected Operation
Extreme ColdOil temperature at start-up below
-16É FPark, Reverse, Neutral and 2nd
gear only (prevents shifting which
may fail a clutch with frequent
shifts)
ColdOil temperature at start-up above
-12É F and below 36É F± Delayed 2-3 upshift
(approximately 22-31 mph)
± Delayed 3-4 upshift (45-53 mph)
± Early 4-3 costdown shift
(approximately 30 mph)
± Early 3-2 coastdown shift
(approximately 17 mph)
± High speed 4-2, 3-2, 2-1 kickdown
shifts are prevented
± No EMCC
WarmOil temperature at start-up above
36É F and below 80 degree F± Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
± No EMCC
HotOil temperature at start-up above
80É F± Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
± Full EMCC, no PEMCC except to
engage FEMCC (except at closed
throttle at speeds above 70-83 mph)
OverheatOil temperature above 240É F or
engine coolant temperature above
244É F± Delayed 2-3 upshift (25-32 mph)
± Delayed 3-4 upshift (41-48 mph)
± 3rd gear FEMCC from 30-48 mph
± 3rd gear PEMCC from 27-31 mph
Super OverheatOil temperature above 260É F ± All9Overheat9shift schedule
features apply
± 2nd gear PEMCC above 22 mph
± Above 22 mph the torque
converter will not unlock unless the
throttle is closed or if a wide open
throttle 2nd PEMCC to 1 kickdown
is made
8E - 22 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)