engine CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 460 of 2585
BATTERY SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
THE BATTERY SEEMS
WEAK OR DEAD WHEN
ATTEMPTING TO START
THE ENGINE. 1. The electrical system
ignition-off draw is excessive.
1. Refer to the IGNITION-OFF DRAW TEST
Standard Procedure for the proper test
procedures. Repair the excessive ignition-off
draw, as required.
2. The charging system is
faulty. 2. Determine if the charging system is performing
to specifications. Refer to Charging System for
additional charging system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the faulty charging system, as
required.
3. The battery is discharged. 3. Determine the battery state-of-charge using the Micro 420 battery tester. Refer to the Standard
Procedures in this section for additional test
procedures. Charge the faulty battery, as
required.
4. The battery terminal
connections are loose or
corroded. 4. Refer to Battery Cables for the proper battery
cable diagnosis and testing procedures. Clean
and tighten the battery terminal connections, as
required.
5. The battery has an
incorrect size or rating for
this vehicle. 5. Refer to Battery System Specifications for the
proper size and rating. Replace an incorrect
battery, as required.
6. The battery is faulty. 6. Test the battery using the Micro 420 battery tester. Refer to the Standard Procedures in this
section for additional test procedures. Replace
the faulty battery, as required.
7. The starting system is
faulty. 7. Determine if the starting system is performing
to specifications. Refer to Starting System for the
proper starting system diagnosis and testing
procedures. Repair the faulty starting system, as
required.
8. The battery is physically
damaged. 8. Inspect the battery for loose terminal posts or a
cracked and leaking case. Replace the damaged
battery, as required.
RS
BATTERY SYSTEM8Fs-3
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 463 of 2585
INSPECTION
The following information details the recommended
inspection procedures for the battery and related
components. In addition to the maintenance sched-
ules found in this service manual and the owner's
manual, it is recommended that these procedures be
performed any time the battery or related compo-
nents must be removed for vehicle service. (1) Inspect the battery cable terminal clamps for
damage. Replace any battery cable that has a dam-
aged or deformed terminal clamp. (2) Inspect the battery tray and battery holddown
hardware for damage. Replace any damaged parts. (3) Slide the thermowrap off of the battery case.
Inspect the battery case for cracks or other damage
that could result in electrolyte leaks. Also, check the
battery terminal posts for looseness. Batteries with
damaged cases or loose terminal posts must be
replaced. (4) Inspect the battery thermowrap for tears,
cracks, deformation or other damage. Replace any
battery thermal guard that has been damaged. (5) Inspect the battery built-in test indicator sight
glass(if equipped) for an indication of the battery con-
dition. If the battery is discharged, charge as
required. Refer to Standard Procedures for the
proper battery built-in indicator test procedures. Also
refer to Standard Procedures for the proper battery
charging procedures.
SPECIFICATIONS
The battery Group Size number, the Cold Cranking
Amperage (CCA) rating, and the Reserve Capacity
(RC) rating or Ampere-Hours (AH) rating can be found on the original equipment battery label. Be
certain that a replacement battery has the correct
Group Size number, as well as CCA, and RC or AH
ratings that equal or exceed the original equipment
specification for the vehicle being serviced. Battery
sizes and ratings are discussed in more detail below.
² Group Size - The outside dimensions and ter-
minal placement of the battery conform to standards
established by the Battery Council International
(BCI). Each battery is assigned a BCI Group Size
number to help identify a correctly-sized replace-
ment. ² Cold Cranking Amperage - The Cold Crank-
ing Amperage (CCA) rating specifies how much cur-
rent (in amperes) the battery can deliver for thirty
seconds at -18É C (0É F). Terminal voltage must not
fall below 7.2 volts during or after the thirty second
discharge period. The CCA required is generally
higher as engine displacement increases, depending
also upon the starter current draw requirements. ² Reserve Capacity - The Reserve Capacity (RC)
rating specifies the time (in minutes) it takes for bat-
tery terminal voltage to fall below 10.5 volts, at a
discharge rate of 25 amperes. RC is determined with
the battery fully-charged at 26.7É C (80É F). This rat-
ing estimates how long the battery might last after a
charging system failure, under minimum electrical
load. ² Ampere-Hours - The Ampere-Hours (AH) rat-
ing specifies the current (in amperes) that a battery
can deliver steadily for twenty hours, with the volt-
age in the battery not falling below 10.5 volts. This
rating is also sometimes identified as the twenty-
hour discharge rating.
BATTERY CLASSIFICATIONS & RATINGS
Part Number BCI Group Size
Classification Cold Cranking
Amperage Reserve
Capacity Ampere -
Hours Load Test
Amperage
4686158AD 34 500 110 Minutes 60 250
4727159AD 34 600 120 Minutes 66 300
4727242AD DIN H6 600 120 Minutes 66 300 4868999AA 34 700 95 Minutes 50 350
8Fs - 6 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 464 of 2585
SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY SYSTEM SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY
DESCRIPTION
There are three different batteries available on this
model. Vehicles equipped with a diesel engine utilize
a spiral wound plate designed battery with recombi-
nation technology. This is a maintenance-free battery
that is capable of delivering more power than a con-
ventional battery. This additional power is required
by a diesel engine during cold cranking. Vehicles
equipped with a gasoline engine utilize a conven-
tional battery. Refer to the following information for
detailed differences and descriptions of these batter-
ies.
SPIRAL PLATE BATTERY - DIESEL ENGINE
Spiral plate technology takes the elements of tradi-
tional batteries - lead and sulfuric acid - to the next
level. By tightly winding layers of spiral grids and
acid-permeated vitreous separators into cells, the
manufacturer has developed a battery with more
power and service life than conventional batteries the
same size. The spiral plate battery is completely, per-
manently sealed. Through gas recombination, hydro-
gen and oxygen within the battery are captured
during normal charging and reunited to form the
water within the electrolyte, eliminating the need to
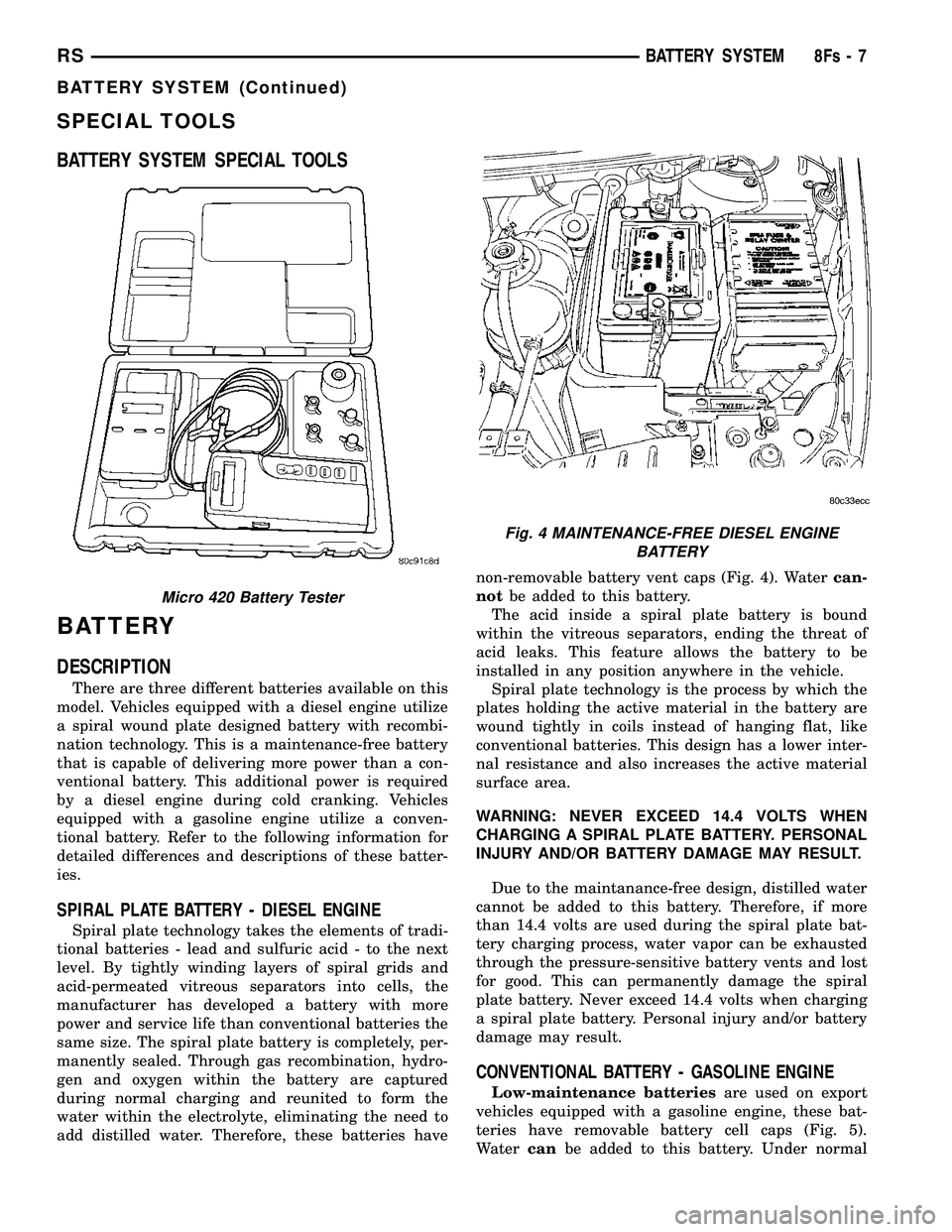
add distilled water. Therefore, these batteries have non-removable battery vent caps (Fig. 4). Water
can-
not be added to this battery.
The acid inside a spiral plate battery is bound
within the vitreous separators, ending the threat of
acid leaks. This feature allows the battery to be
installed in any position anywhere in the vehicle. Spiral plate technology is the process by which the
plates holding the active material in the battery are
wound tightly in coils instead of hanging flat, like
conventional batteries. This design has a lower inter-
nal resistance and also increases the active material
surface area.
WARNING: NEVER EXCEED 14.4 VOLTS WHEN
CHARGING A SPIRAL PLATE BATTERY. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR BATTERY DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
Due to the maintanance-free design, distilled water
cannot be added to this battery. Therefore, if more
than 14.4 volts are used during the spiral plate bat-
tery charging process, water vapor can be exhausted
through the pressure-sensitive battery vents and lost
for good. This can permanently damage the spiral
plate battery. Never exceed 14.4 volts when charging
a spiral plate battery. Personal injury and/or battery
damage may result.
CONVENTIONAL BATTERY - GASOLINE ENGINE
Low-maintenance batteries are used on export
vehicles equipped with a gasoline engine, these bat-
teries have removable battery cell caps (Fig. 5).
Water canbe added to this battery. Under normal
Micro 420 Battery Tester
Fig. 4 MAINTENANCE-FREE DIESEL ENGINE
BATTERY
RS BATTERY SYSTEM8Fs-7
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 465 of 2585
service, the composition of this battery reduces gas-
sing and water loss at normal charge rates. However
these batteries may require additional distilled water
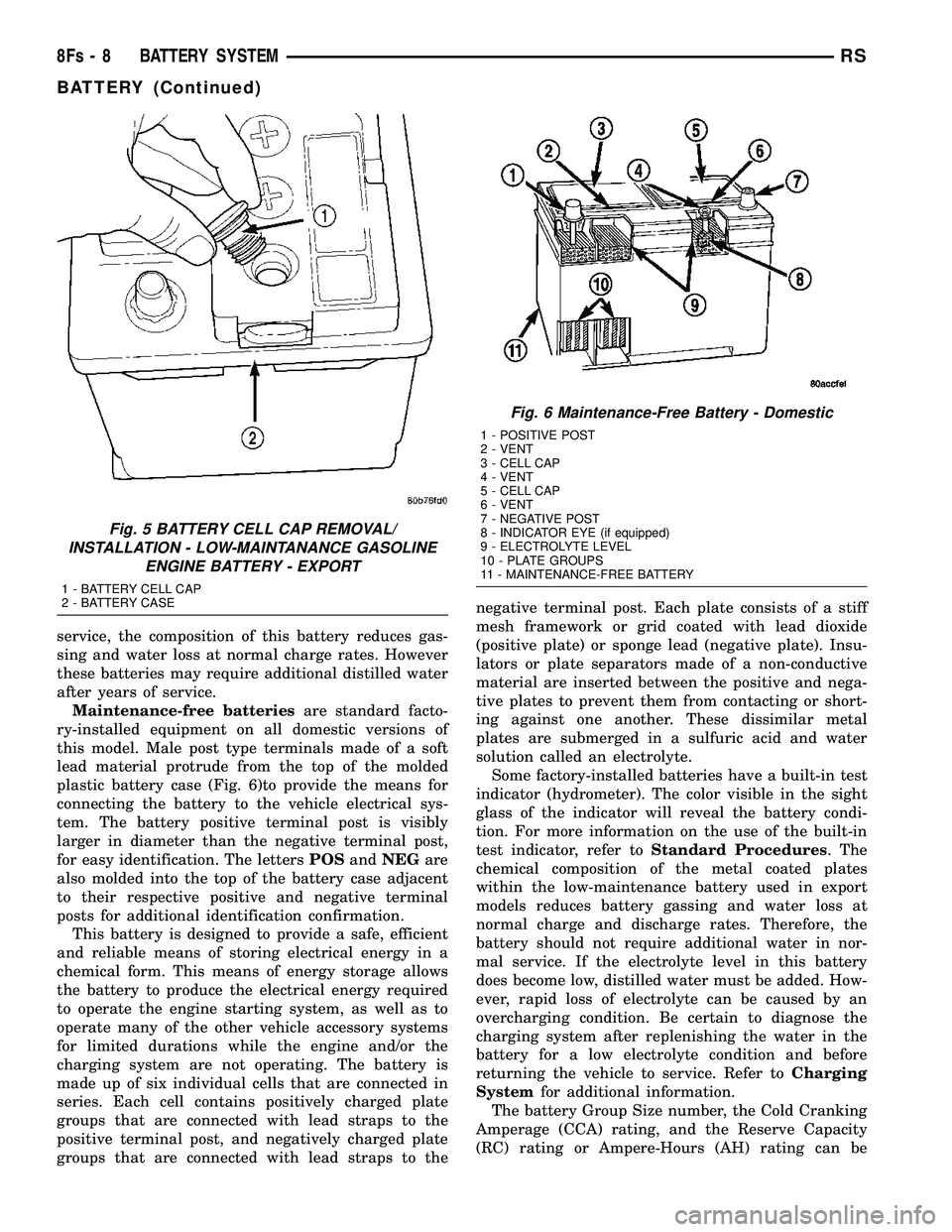
after years of service.Maintenance-free batteries are standard facto-
ry-installed equipment on all domestic versions of
this model. Male post type terminals made of a soft
lead material protrude from the top of the molded
plastic battery case (Fig. 6)to provide the means for
connecting the battery to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem. The battery positive terminal post is visibly
larger in diameter than the negative terminal post,
for easy identification. The letters POSandNEG are
also molded into the top of the battery case adjacent
to their respective positive and negative terminal
posts for additional identification confirmation. This battery is designed to provide a safe, efficient
and reliable means of storing electrical energy in a
chemical form. This means of energy storage allows
the battery to produce the electrical energy required
to operate the engine starting system, as well as to
operate many of the other vehicle accessory systems
for limited durations while the engine and/or the
charging system are not operating. The battery is
made up of six individual cells that are connected in
series. Each cell contains positively charged plate
groups that are connected with lead straps to the
positive terminal post, and negatively charged plate
groups that are connected with lead straps to the negative terminal post. Each plate consists of a stiff
mesh framework or grid coated with lead dioxide
(positive plate) or sponge lead (negative plate). Insu-
lators or plate separators made of a non-conductive
material are inserted between the positive and nega-
tive plates to prevent them from contacting or short-
ing against one another. These dissimilar metal
plates are submerged in a sulfuric acid and water
solution called an electrolyte.
Some factory-installed batteries have a built-in test
indicator (hydrometer). The color visible in the sight
glass of the indicator will reveal the battery condi-
tion. For more information on the use of the built-in
test indicator, refer to Standard Procedures . The
chemical composition of the metal coated plates
within the low-maintenance battery used in export
models reduces battery gassing and water loss at
normal charge and discharge rates. Therefore, the
battery should not require additional water in nor-
mal service. If the electrolyte level in this battery
does become low, distilled water must be added. How-
ever, rapid loss of electrolyte can be caused by an
overcharging condition. Be certain to diagnose the
charging system after replenishing the water in the
battery for a low electrolyte condition and before
returning the vehicle to service. Refer to Charging
System for additional information.
The battery Group Size number, the Cold Cranking
Amperage (CCA) rating, and the Reserve Capacity
(RC) rating or Ampere-Hours (AH) rating can be
Fig. 5 BATTERY CELL CAP REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION - LOW-MAINTANANCE GASOLINE ENGINE BATTERY - EXPORT
1 - BATTERY CELL CAP
2 - BATTERY CASE
Fig. 6 Maintenance-Free Battery - Domestic
1 - POSITIVE POST
2 - VENT
3 - CELL CAP
4 - VENT
5 - CELL CAP
6 - VENT
7 - NEGATIVE POST
8 - INDICATOR EYE (if equipped)
9 - ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
10 - PLATE GROUPS
11 - MAINTENANCE-FREE BATTERY
8Fs - 8 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 467 of 2585

STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SPIRAL PLATE
BATTERY CHARGING
Vehicles equipped with a diesel engine utilize a
unique spiral plate battery. This battery has a maxi-
mum charging voltage that must not be exceeded in
order to restore the battery to its full potential, fail-
ure to use the following spiral plate battery charging
procedure could result in damage to the battery or
personal injury. Battery charging is the means by which the bat-
tery can be restored to its full voltage potential. A
battery is fully-charged when: ² Micro 420 battery tester indicates battery is OK.
² Open-circuit voltage of the battery is 12.65 volts
or above. ² Battery passes Load Test multiple times.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS OR LOW
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL, DO NOT TEST, ASSIST-
BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY MAY ARC
INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL INJURY
AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
CAUTION: Always disconnect and isolate the bat-
tery negative cable before charging a battery.
Charge the battery directly at the battery terminals.
Do not exceed 14.4 volts while charging a battery.
CAUTION: The battery should not be hot to the
touch. If the battery feels hot to the touch, turn off
the charger and let the battery cool before continu-
ing the charging operation. Damage to the battery
may result. After the battery has been charged to 12.6 volts or
greater, perform a load test to determine the battery
cranking capacity. Refer to Battery Diagnosis and
Testing for the proper battery test procedures. If the
battery will endure a load test, return the battery to
service. If the battery will not pass a load test, it is
faulty and must be replaced. Clean and inspect the battery hold downs, tray,
terminals, posts, and top before completing battery
service. Refer to Battery System Cleaning for the
proper battery system cleaning procedures, and Bat-
tery System Inspection for the proper battery system
inspection procedures.
CHARGING A COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY ± SPIRAL PLATE BATTERY
The following procedure should be used to recharge
a completely discharged battery. Unless this proce- dure is properly followed, a good battery may be
needlessly replaced.
(1) Measure the voltage at the battery posts with a
voltmeter, accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt (Fig. 7). Refer
to Battery Removal and Installation for access
instructions. If the reading is below ten volts, the
battery charging current will be low. It could take
several hours before the battery accepts a current
greater than a few milliamperes. Such low current
may not be detectable on the ammeters built into
many battery chargers.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Connect the battery charger leads. Some bat-
tery chargers are equipped with polarity-sensing cir-
cuitry. This circuitry protects the battery charger and
the battery from being damaged if they are improp-
erly connected. If the battery state-of-charge is too
low for the polarity-sensing circuitry to detect, the
battery charger will not operate. This makes it
appear that the battery will not accept charging cur-
rent. See the instructions provided by the manufac-
turer of the battery charger for details on how to
bypass the polarity-sensing circuitry. (3) Battery chargers vary in the amount of voltage
and current they provide. The amount of time
required for a battery to accept measurable charging
current at various voltages is shown in the Charge
Rate Table. If the charging current is still not mea-
surable at the end of the charging time, the battery
is faulty and must be replaced. If the charging cur-
rent is measurable during the charging time, the bat-
tery may be good and the charging should be
completed in the normal manner.
Fig. 7 Voltmeter - Typical
8Fs - 10 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 468 of 2585

SPIRAL-PLATE BATTERY CHARGE RATE TABLEVoltage Minutes
14.4 volts maximum up to 10 minutes 13.0 to 14 volts up to 20 minutes
12.9 volts or less up to 30 minutes
CHARGING TIME REQUIRED
The time required to charge a battery will vary,
depending upon the following factors: ² Battery Capacity - A completely discharged
heavy-duty battery requires twice the charging time
of a small capacity battery. ² Temperature - A longer time will be needed to
charge a battery at -18É C (0É F) than at 27É C (80É
F). When a fast battery charger is connected to a cold
battery, the current accepted by the battery will be
very low at first. As the battery warms, it will accept
a higher charging current rate (amperage). ² Charger Capacity - A battery charger that
supplies only five amperes will require a longer
charging time. A battery charger that supplies eight
amperes will require a shorter charging time. ² State-Of-Charge - A completely discharged bat-
tery requires more charging time than a partially
discharged battery. Electrolyte is nearly pure water
in a completely discharged battery. At first, the
charging current (amperage) will be low. As the bat-
tery charges, the specific gravity of the electrolyte
will gradually rise. The Battery Charging Time Table gives an indica-
tion of the time required to charge a typical battery
at room temperature based upon the battery state-of-
charge and the charger capacity.
SPIRAL-PLATE BATTERY CHARGING TIME TABLE
Charging
Amperage 5 Amps 8 Amps
Open Circuit Voltage Hours Charging @ 21É
C (70É F)
12.25 to 12.49 6 hours 3 hours
12.00 to 12.24 10 hours 5 hours 10.00 to 11.99 14 hours 7 hours Below 10.00 18 hours 9 hours
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CONVENTIONAL
BATTERY CHARGING
Vehicles equipped with a diesel engine utilize a
unique spiral plate battery. This battery has a maxi-
mum charging voltage that must be used in order to
restore the battery to its full potential, failure to use the spiral plate battery charging procedure could
result in damage to the battery or personal injury.
Battery charging is the means by which the bat-
tery can be restored to its full voltage potential. A
battery is fully-charged when: ² Micro 420 battery tester indicates battery is OK.
² Open-circuit voltage of the battery is 12.65 volts
or above. ² Battery passes Load Test multiple times.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, DO NOT
TEST, ASSIST-BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY
MAY ARC INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE,
USE FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BAT-
TERY. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY IS EQUIPPED WITH
REMOVABLE CELL CAPS, BE CERTAIN THAT EACH
OF THE CELL CAPS IS IN PLACE AND TIGHT
BEFORE THE BATTERY IS RETURNED TO SER-
VICE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT FROM LOOSE OR MISSING
CELL CAPS.
CAUTION: Always disconnect and isolate the bat-
tery negative cable before charging a battery. Do
not exceed sixteen volts while charging a battery.
Damage to the vehicle electrical system compo-
nents may result.
CAUTION: Battery electrolyte will bubble inside the
battery case during normal battery charging. Elec-
trolyte boiling or being discharged from the battery
vents indicates a battery overcharging condition.
Immediately reduce the charging rate or turn off the
charger to evaluate the battery condition. Damage
to the battery may result from overcharging.
RS BATTERY SYSTEM8Fs-11
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 473 of 2585

(2) Remove the nut with washer that secures the
battery hold down bracket to the battery tray and
support unit. (3) Remove the battery hold down bracket from
the battery tray and support unit.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the battery hold down bracket in the
battery tray and support unit. (2) Install the nut with washer that secures the
battery hold down bracket to the battery tray and
support unit. Torque to 20 N´m (180 in. lbs.).
BATTERY CABLES
DESCRIPTION
The battery cables are large gauge, stranded cop-
per wires sheathed within a heavy plastic or syn-
thetic rubber insulating jacket. The wire used in the
battery cables combines excellent flexibility and reli-
ability with high electrical current carrying capacity.
Refer to Wiring Diagrams in the index of this ser-
vice manual for the location of the proper battery
cable wire gauge information. A clamping type female battery terminal made of
stamped metal is attached to one end of the battery
cable wire. A square headed pinch-bolt and hex nut
are installed at the open end of the female battery
terminal clamp. Large eyelet type terminals are
crimped onto the opposite end of the battery cable
wire and then solder-dipped. The battery positive
cable wires have a red insulating jacket to provide
visual identification and feature a larger female bat-
tery terminal clamp to allow connection to the larger
battery positive terminal post. The battery negative
cable wires have a black insulating jacket and a
smaller female battery terminal clamp. The battery cables cannot be repaired and, if dam-
aged or faulty they must be replaced. Both the bat-
tery positive and negative cables are available for
service replacement only as a unit with the battery
wire harness, which may include portions of the wir-
ing circuits for the generator and other components
on some models. Refer to Wiring Diagramsin the
index of this service manual for the location of more
information on the various wiring circuits included in
the battery wire harness for the vehicle being ser-
viced.
OPERATION
The battery cables connect the battery terminal
posts to the vehicle electrical system. These cables
also provide a path back to the battery for electrical
current generated by the charging system for restor-
ing the voltage potential of the battery. The female battery terminal clamps on the ends of the battery
cable wires provide a strong and reliable connection
of the battery cable to the battery terminal posts.
The terminal pinch bolts allow the female terminal
clamps to be tightened around the male terminal
posts on the top of the battery. The eyelet terminals
secured to the opposite ends of the battery cable
wires from the female battery terminal clamps pro-
vide secure and reliable connection of the battery
cables to the vehicle electrical system.
The battery positive cable terminal clamp is
attached to the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the Integrated
Power Module (IPM), and the other wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the battery positive cable
to the B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter motor
solenoid. The battery negative cable terminal clamp
is also attached to the ends of two wires. One wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the battery neg-
ative cable to the vehicle powertrain through a stud
on the left side of the engine cylinder block. The
other wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the left front fender inner shield,
near the battery.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY CABLE
A voltage drop test will determine if there is exces-
sive resistance in the battery cable terminal connec-
tions or the battery cable. If excessive resistance is
found in the battery cable connections, the connec-
tion point should be disassembled, cleaned of all cor-
rosion or foreign material, then reassembled.
Following reassembly, check the voltage drop for the
battery cable connection and the battery cable again
to confirm repair. When performing the voltage drop test, it is impor-
tant to remember that the voltage drop is giving an
indication of the resistance between the two points at
which the voltmeter probes are attached. EXAM-
PLE: When testing the resistance of the battery pos-
itive cable, touch the voltmeter leads to the battery
positive cable terminal clamp and to the battery pos-
itive cable eyelet terminal at the starter solenoid
B(+) terminal stud. If you probe the battery positive
terminal post and the battery positive cable eyelet
terminal at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud,
you are reading the combined voltage drop in the
battery positive cable terminal clamp-to-terminal
post connection and the battery positive cable.
VOLTAGE DROP TEST
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing this
8Fs - 16 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY HOLDDOWN (Continued)
Page 474 of 2585
test, be certain that the following procedures are
accomplished:² The battery is fully-charged and load tested.
Refer to Standard Procedures for the proper battery
charging and load test procedures. ² Fully engage the parking brake.
² If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic
transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in the
Park position. If the vehicle is equipped with a man-
ual transmission, place the gearshift selector lever in
the Neutral position and block the clutch pedal in the
fully depressed position. ² Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off. ² To prevent the engine from starting, remove the
Automatic Shut Down (ASD) relay. The ASD relay is
located in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), in the
engine compartment. See the fuse and relay layout
label affixed to the underside of the IPM cover for
ASD relay identification and location. (1) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative terminal post. Connect the neg-
ative lead of the voltmeter to the battery negative
cable terminal clamp (Fig. 13). Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct the poor con-
nection between the battery negative cable terminal
clamp and the battery negative terminal post.
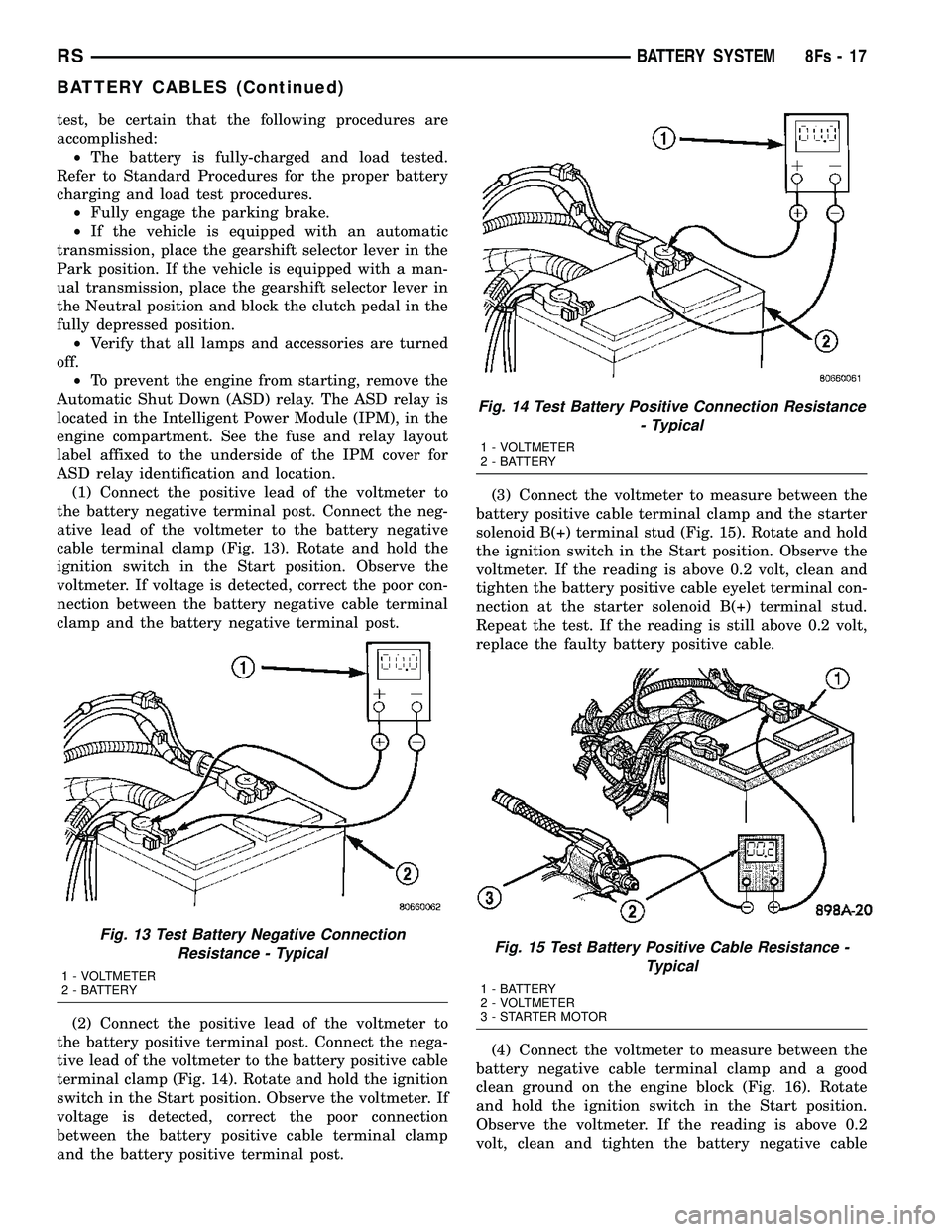
(2) Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to
the battery positive terminal post. Connect the nega-
tive lead of the voltmeter to the battery positive cable
terminal clamp (Fig. 14). Rotate and hold the ignition
switch in the Start position. Observe the voltmeter. If
voltage is detected, correct the poor connection
between the battery positive cable terminal clamp
and the battery positive terminal post. (3) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the
battery positive cable terminal clamp and the starter
solenoid B(+) terminal stud (Fig. 15). Rotate and hold
the ignition switch in the Start position. Observe the
voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2 volt, clean and
tighten the battery positive cable eyelet terminal con-
nection at the starter solenoid B(+) terminal stud.
Repeat the test. If the reading is still above 0.2 volt,
replace the faulty battery positive cable.
(4) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the
battery negative cable terminal clamp and a good
clean ground on the engine block (Fig. 16). Rotate
and hold the ignition switch in the Start position.
Observe the voltmeter. If the reading is above 0.2
volt, clean and tighten the battery negative cable
Fig. 13 Test Battery Negative Connection Resistance - Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
Fig. 14 Test Battery Positive Connection Resistance - Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
Fig. 15 Test Battery Positive Cable Resistance -Typical
1 - BATTERY
2 - VOLTMETER
3 - STARTER MOTOR
RS BATTERY SYSTEM8Fs-17
BATTERY CABLES (Continued)
Page 475 of 2585
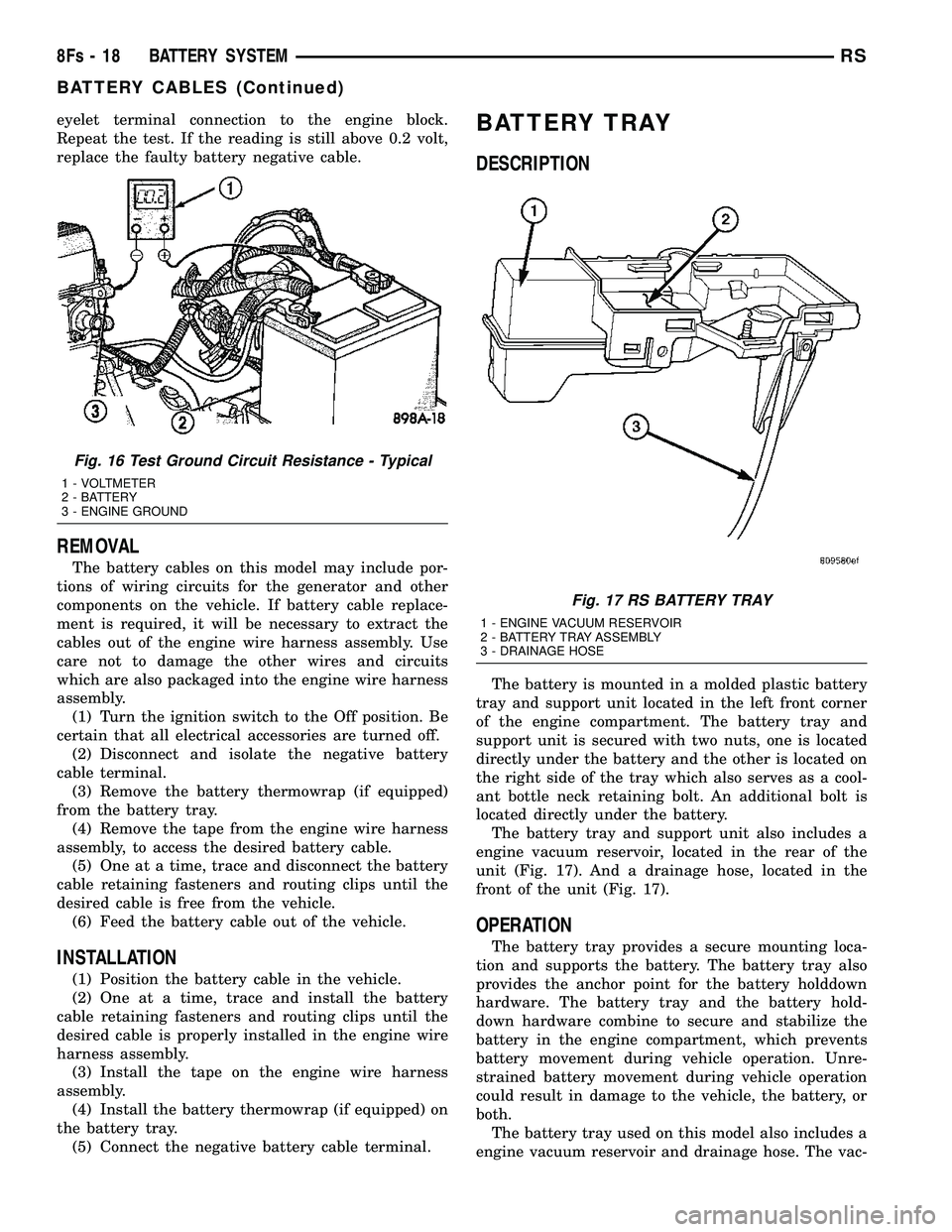
eyelet terminal connection to the engine block.
Repeat the test. If the reading is still above 0.2 volt,
replace the faulty battery negative cable.
REMOVAL
The battery cables on this model may include por-
tions of wiring circuits for the generator and other
components on the vehicle. If battery cable replace-
ment is required, it will be necessary to extract the
cables out of the engine wire harness assembly. Use
care not to damage the other wires and circuits
which are also packaged into the engine wire harness
assembly. (1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position. Be
certain that all electrical accessories are turned off. (2) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable terminal. (3) Remove the battery thermowrap (if equipped)
from the battery tray. (4) Remove the tape from the engine wire harness
assembly, to access the desired battery cable. (5) One at a time, trace and disconnect the battery
cable retaining fasteners and routing clips until the
desired cable is free from the vehicle. (6) Feed the battery cable out of the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the battery cable in the vehicle.
(2) One at a time, trace and install the battery
cable retaining fasteners and routing clips until the
desired cable is properly installed in the engine wire
harness assembly. (3) Install the tape on the engine wire harness
assembly. (4) Install the battery thermowrap (if equipped) on
the battery tray. (5) Connect the negative battery cable terminal.
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION
The battery is mounted in a molded plastic battery
tray and support unit located in the left front corner
of the engine compartment. The battery tray and
support unit is secured with two nuts, one is located
directly under the battery and the other is located on
the right side of the tray which also serves as a cool-
ant bottle neck retaining bolt. An additional bolt is
located directly under the battery. The battery tray and support unit also includes a
engine vacuum reservoir, located in the rear of the
unit (Fig. 17). And a drainage hose, located in the
front of the unit (Fig. 17).
OPERATION
The battery tray provides a secure mounting loca-
tion and supports the battery. The battery tray also
provides the anchor point for the battery holddown
hardware. The battery tray and the battery hold-
down hardware combine to secure and stabilize the
battery in the engine compartment, which prevents
battery movement during vehicle operation. Unre-
strained battery movement during vehicle operation
could result in damage to the vehicle, the battery, or
both. The battery tray used on this model also includes a
engine vacuum reservoir and drainage hose. The vac-
Fig. 16 Test Ground Circuit Resistance - Typical
1 - VOLTMETER
2 - BATTERY
3 - ENGINE GROUND
Fig. 17 RS BATTERY TRAY
1 - ENGINE VACUUM RESERVOIR
2 - BATTERY TRAY ASSEMBLY
3 - DRAINAGE HOSE
8Fs - 18 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY CABLES (Continued)
Page 476 of 2585

uum reservoir provides a storage container for engine
vacuum. Refer to the engine section of the service
manual for more engine vacuum information. The
drainage hose provides means for any liquid that
might collect in the bottom of the battery tray to
drain under the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable. (2) Remove the battery from the vehicle. Refer to
the procedure in this section. (3) Remove the battery tray retaining fasteners
(Fig. 18).
(4) Pull battery tray up far enough to disconnect
the engine vacuum harness hose from the battery
tray mounted, vacuum reservoir. (5) Remove the battery tray from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the battery tray in the vehicle.
(2) Connect the engine vacuum harness hose on
the battery tray mounted vacuum reservoir. (3) Position drainage hose and install the battery
tray retaining fasteners (Fig. 18). (4) Install the battery in the vehicle. Refer to the
procedure in this section. (5) Connect the negative battery cable.
THERMOWRAP
DESCRIPTION
A one-piece slip-on thermowrap unit shields the
battery case from engine compartment heat. The
thermowrap slips over the battery case and due to its
one piece design, the battery cables must be removed
in order to install or remove the thermowrap.
OPERATION
The thermowrap protects the battery from engine
compartment temperature extremes. The tempera-
ture of the battery can affect battery life. The air
trapped in the padded material of the thermowrap
creates a dead air space, which helps to insulate the
sides of the battery case from the air temperature
found in the surrounding engine compartment.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable. (2) Disconnect the positive battery cable.
(3) Lift the battery thermowrap straight up to
remove from the battery.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the thermowrap on the battery.
(2) Connect the negative and positive battery
cables.
Fig. 18 BATTERY TRAY POSITION & ORIENTATION
1 - BATTERY TRAY RETAINING FASTENERS
RS BATTERY SYSTEM8Fs-19
BATTERY TRAY (Continued)