Temperature CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1306 of 2585

(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.(4) Remove the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay from
the PDC.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gauge adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer (Special Tool CH7059) with cable adap-
tors to the DRBIIIt. For Special Tool identification,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIAL TOOLS).
(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gauge. Record this pressure as #1 cylin-
der pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE PRESSURE CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the pressure cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
RSENGINE 2.4L9-9
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1321 of 2585

AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Unsnap 2 clips.
(2) Lift cover and pull toward the engine and
remove cover tabs from air box.
(3) Lift cover and remove the element (Fig. 11).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the air filter element into air box (Fig.
11).
(2) Move cover so that the tabs insert into the air
box.
(3) Push cover down and snap the 2 clips.
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(2) Disconnect the inlet air temperature sensor
(Fig. 12).
(3) Remove the inlet hose to throttle body (Fig. 11).
(4) Remove the bolt for air box at upper radiator
cross member.
(5) Pull air box up and off over the single locating
pin.
(6) Remove air box from vehicle
INSTALLATION
(1) Install air box into vehicle and onto the locat-
ing pin.(2) Install bolt to hold air box to the upper radia-
tor cross member.
(3) Install the inlet hose to the throttle body.
(4) Connect the inlet air temperature sensor (Fig.
12).
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The cross flow designed, aluminum cylinder head
contains dual over-head camshafts with four valves
per cylinder (Fig. 13). The valves are arranged in two
in-line banks. The intake valves face toward the
front of the vehicle. The exhaust valves face the dash
panel. The cylinder head incorporates powdered
metal valve guides and seats. The cylinder head is
sealed to the block using a multi-layer steel head
gasket and retaining bolts.
Integral oil galleries provide lubrication passages
to the hydraulic lash adjusters, camshafts, and valve
mechanisms.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
Fig. 11 AIR BOX COVER
Fig. 12 IAT SENSOR 2.4L
9 - 24 ENGINE 2.4LRS
Page 1331 of 2585

HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTERS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC LASH
ADJUSTER NOISE DIAGNOSIS
A tappet-like noise may be produced from several
items. Check the following items.
(1) Engine oil level too high or too low. This may
cause aerated oil to enter the adjusters and cause
them to be spongy.
(2) Insufficient running time after rebuilding cylin-
der head. Low speed running up to 1 hour may be
required.
(3) During this time, turn engine off and let set for
a few minutes before restarting. Repeat this several
times after engine has reached normal operating
temperature.
(4) Low oil pressure.
(5) The oil restrictor (integral to the head gasket)
in the vertical oil passage to the cylinder head is
plugged with debris.
(6) Air ingested into oil due to broken or cracked
oil pump pick up.
(7) Worn valve guides.
(8) Rocker arm ears contacting valve spring
retainer.
(9) Rocker arm loose, adjuster stuck or at maxi-
mum extension and still leaves lash in the system.
(10) Faulty lash adjuster.
²Check lash adjusters for sponginess while
installed in cylinder head. Depress part of rocker
arm over adjuster. Normal adjusters should feel very
firm. Spongy adjusters can be bottomed out easily.
²Remove suspected lash adjusters, and replace as
necessary.
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure is for in-vehicle service with
camshafts installed.
(1) Remove cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove rocker arm. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - REMOVAL)
(3) Remove hydraulic lash adjuster (Fig. 37).
(4) Repeat removal procedure for each hydraulic
lash adjuster.
(5) If reusing, mark each hydraulic lash adjuster
for reassembly in original position. Lash adjusters
are serviced as an assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install hydraulic lash adjuster (Fig. 37).
Ensure the lash adjusters are at least partially full of
engine oil. This is indicated by little or no plunger
travel when the lifter is depressed.
(2) Install rocker arm. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYL-
INDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS - INSTALLATION)
(3) Repeat installation procedure for each hydrau-
lic lash adjuster.
(4) Install cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
ROCKER ARMS
REMOVAL
NOTE: This procedure is for in-vehicle service with
camshafts installed.
(1) Remove cylinder head cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove spark plugs.
(3) Rotate engine until the camshaft lobe, on the
follower being removed, is positioned on its base cir-
cle (heel). Also, the piston should be a minimum of
6.3 mm (0.25 in) below TDC position.
CAUTION: If cam follower assemblies are to be
reused, always mark position for reassembly in
their original positions.
(4) Using Special Tools 8215A and 8436 slowly
depress valve assembly until rocker arm can be
removed (Fig. 38).
(5) Repeat removal procedure for each rocker arm.
Fig. 37 Hydraulic Lash Adjuster
9 - 34 ENGINE 2.4LRS
Page 1333 of 2585

(4) A controlled hone motor speed between
200±300 RPM is necessary to obtain the proper cross-
hatch angle. The number of up and down strokes per
minute can be regulated to get the desired 40±60
degree angle. Faster up and down strokes increase
the cross-hatch angle.
(5) After honing, it is necessary that the block be
cleaned again to remove all traces of abrasive.
CAUTION: Ensure all abrasives are removed from
engine parts after honing. It is recommended that a
solution of soap and hot water be used with a
brush and the parts then thoroughly dried. The bore
can be considered clean when it can be wiped
clean with a white cloth and cloth remains clean.
Oil the bores after cleaning to prevent rusting.
CLEANING
Clean cylinder block thoroughly using a suitable
cleaning solvent.
INSPECTION
ENGINE BLOCK
(1) Clean cylinder block thoroughly and check all
core hole plugs for evidence of leaking.
(2) If new core plugs are to be installed, (Refer to 9
- ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE
CORE AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS).
(3) Examine block and cylinder bores for cracks or
fractures.(4) Check block deck surfaces for flatness. Deck
surface must be within service limit of 0.1 mm (0.004
in.).
CYLINDER BORE
NOTE: The cylinder bores should be measured at
normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C119 or equivalent (Fig.
42) (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS). If
the cylinder walls are badly scuffed or scored, the
cylinder block should be replaced, and new pistons
and rings fitted.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 42). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 in.) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 in.) up from bottom of bore.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS).
CRANKSHAFT
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CRANKSHAFT END
PLAY
(1) Using Dial Indicator C-3339 and Mounting
Post L-4438, attach to front of engine, locating probe
perpendicular on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 43).
(2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.
(3) Zero the dial indicator.
Fig. 41 Cylinder Bore Cross-Hatch Pattern
1 - CROSS-HATCH PATTERN
2 - 40ɱ60É
Fig. 42 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
9 - 36 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE BLOCK (Continued)
Page 1339 of 2585
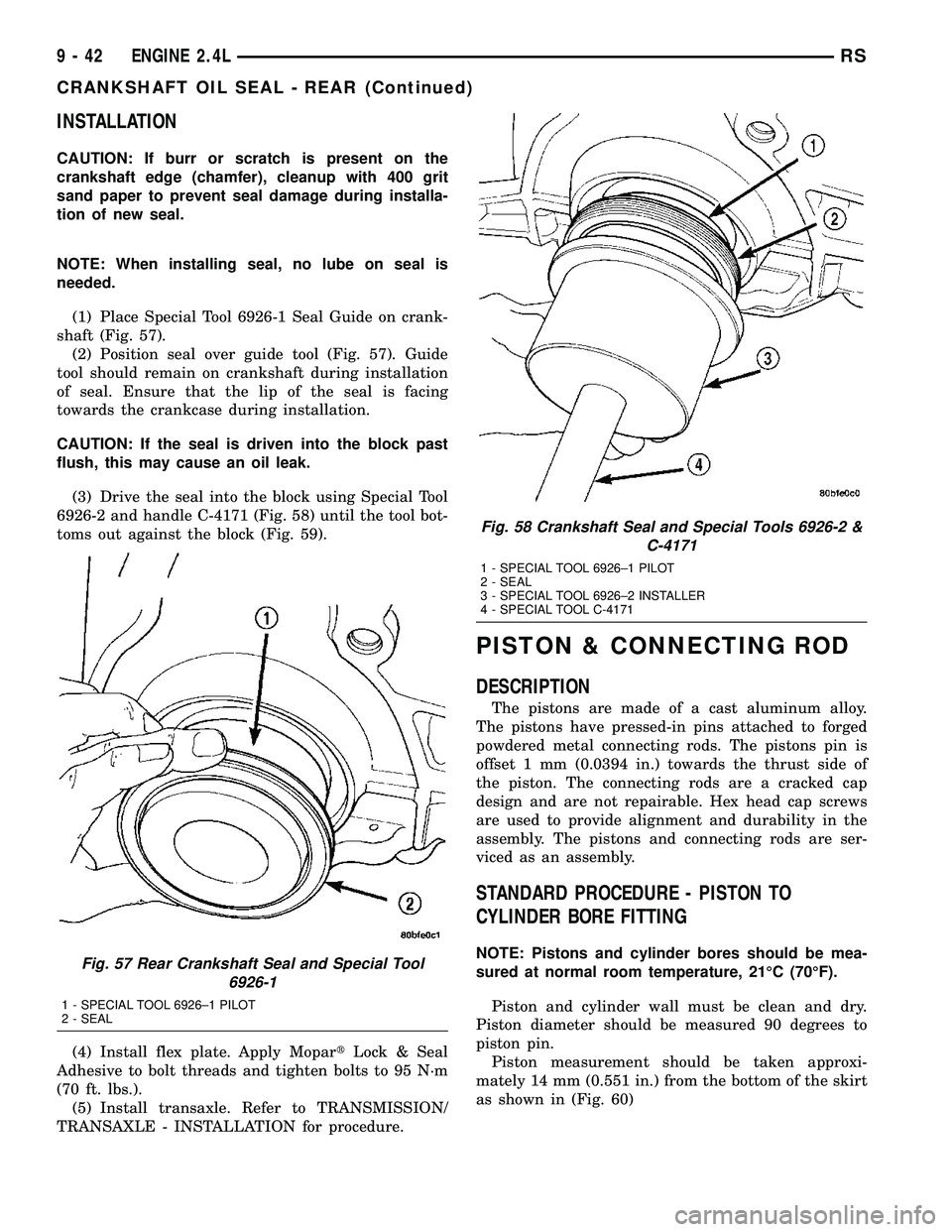
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: If burr or scratch is present on the
crankshaft edge (chamfer), cleanup with 400 grit
sand paper to prevent seal damage during installa-
tion of new seal.
NOTE: When installing seal, no lube on seal is
needed.
(1) Place Special Tool 6926-1 Seal Guide on crank-
shaft (Fig. 57).
(2) Position seal over guide tool (Fig. 57). Guide
tool should remain on crankshaft during installation
of seal. Ensure that the lip of the seal is facing
towards the crankcase during installation.
CAUTION: If the seal is driven into the block past
flush, this may cause an oil leak.
(3) Drive the seal into the block using Special Tool
6926-2 and handle C-4171 (Fig. 58) until the tool bot-
toms out against the block (Fig. 59).
(4) Install flex plate. Apply MopartLock & Seal
Adhesive to bolt threads and tighten bolts to 95 N´m
(70 ft. lbs.).
(5) Install transaxle. Refer to TRANSMISSION/
TRANSAXLE - INSTALLATION for procedure.
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are made of a cast aluminum alloy.
The pistons have pressed-in pins attached to forged
powdered metal connecting rods. The pistons pin is
offset 1 mm (0.0394 in.) towards the thrust side of
the piston. The connecting rods are a cracked cap
design and are not repairable. Hex head cap screws
are used to provide alignment and durability in the
assembly. The pistons and connecting rods are ser-
viced as an assembly.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON TO
CYLINDER BORE FITTING
NOTE: Pistons and cylinder bores should be mea-
sured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees to
piston pin.
Piston measurement should be taken approxi-
mately 14 mm (0.551 in.) from the bottom of the skirt
as shown in (Fig. 60)Fig. 57 Rear Crankshaft Seal and Special Tool
6926-1
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6926±1 PILOT
2 - SEAL
Fig. 58 Crankshaft Seal and Special Tools 6926-2 &
C-4171
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6926±1 PILOT
2 - SEAL
3 - SPECIAL TOOL 6926±2 INSTALLER
4 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
9 - 42 ENGINE 2.4LRS
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR (Continued)
Page 1355 of 2585
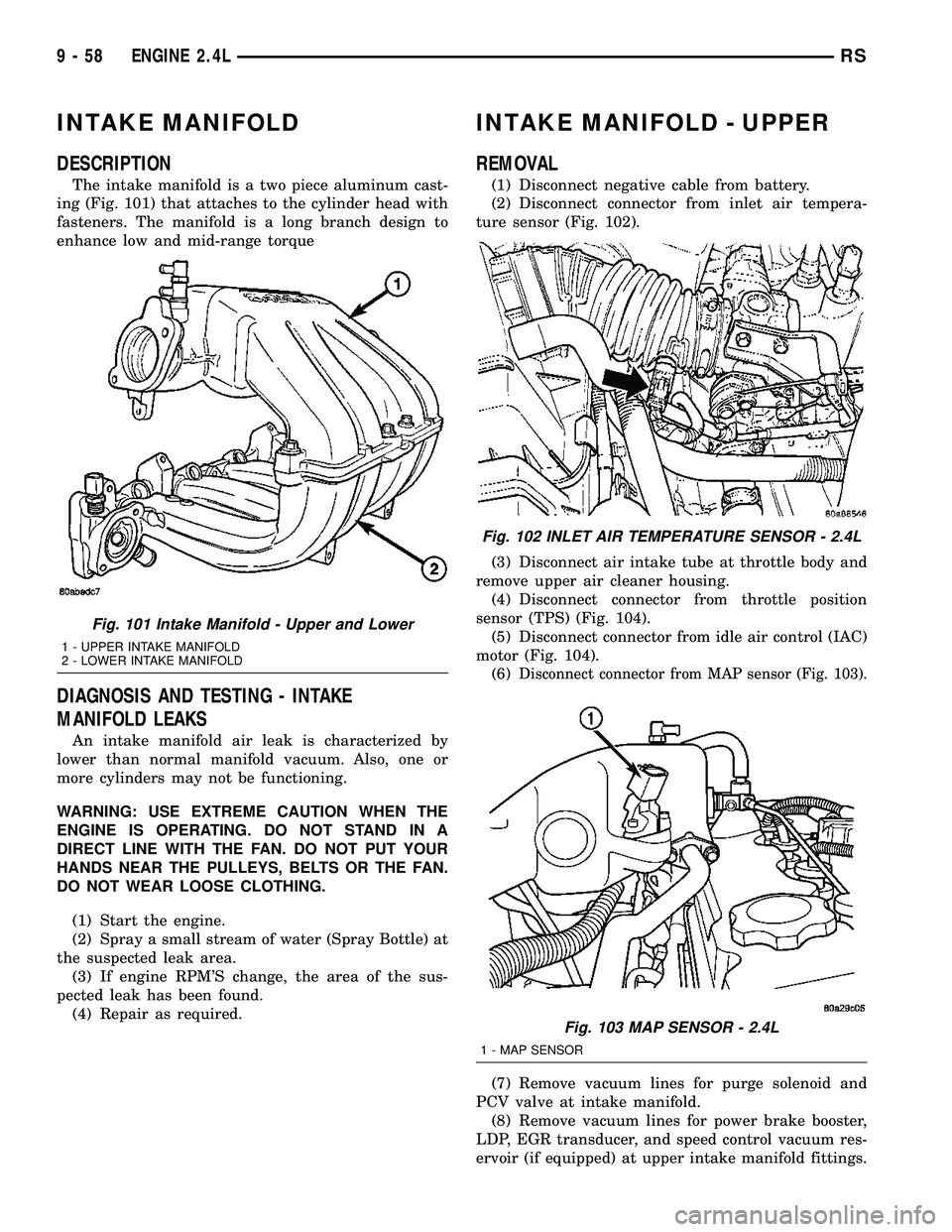
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The intake manifold is a two piece aluminum cast-
ing (Fig. 101) that attaches to the cylinder head with
fasteners. The manifold is a long branch design to
enhance low and mid-range torque
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If engine RPM'S change, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Disconnect connector from inlet air tempera-
ture sensor (Fig. 102).
(3) Disconnect air intake tube at throttle body and
remove upper air cleaner housing.
(4) Disconnect connector from throttle position
sensor (TPS) (Fig. 104).
(5) Disconnect connector from idle air control (IAC)
motor (Fig. 104).
(6)
Disconnect connector from MAP sensor (Fig. 103).
(7) Remove vacuum lines for purge solenoid and
PCV valve at intake manifold.
(8) Remove vacuum lines for power brake booster,
LDP, EGR transducer, and speed control vacuum res-
ervoir (if equipped) at upper intake manifold fittings.
Fig. 101 Intake Manifold - Upper and Lower
1 - UPPER INTAKE MANIFOLD
2 - LOWER INTAKE MANIFOLD
Fig. 102 INLET AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR - 2.4L
Fig. 103 MAP SENSOR - 2.4L
1 - MAP SENSOR
9 - 58 ENGINE 2.4LRS
Page 1356 of 2585
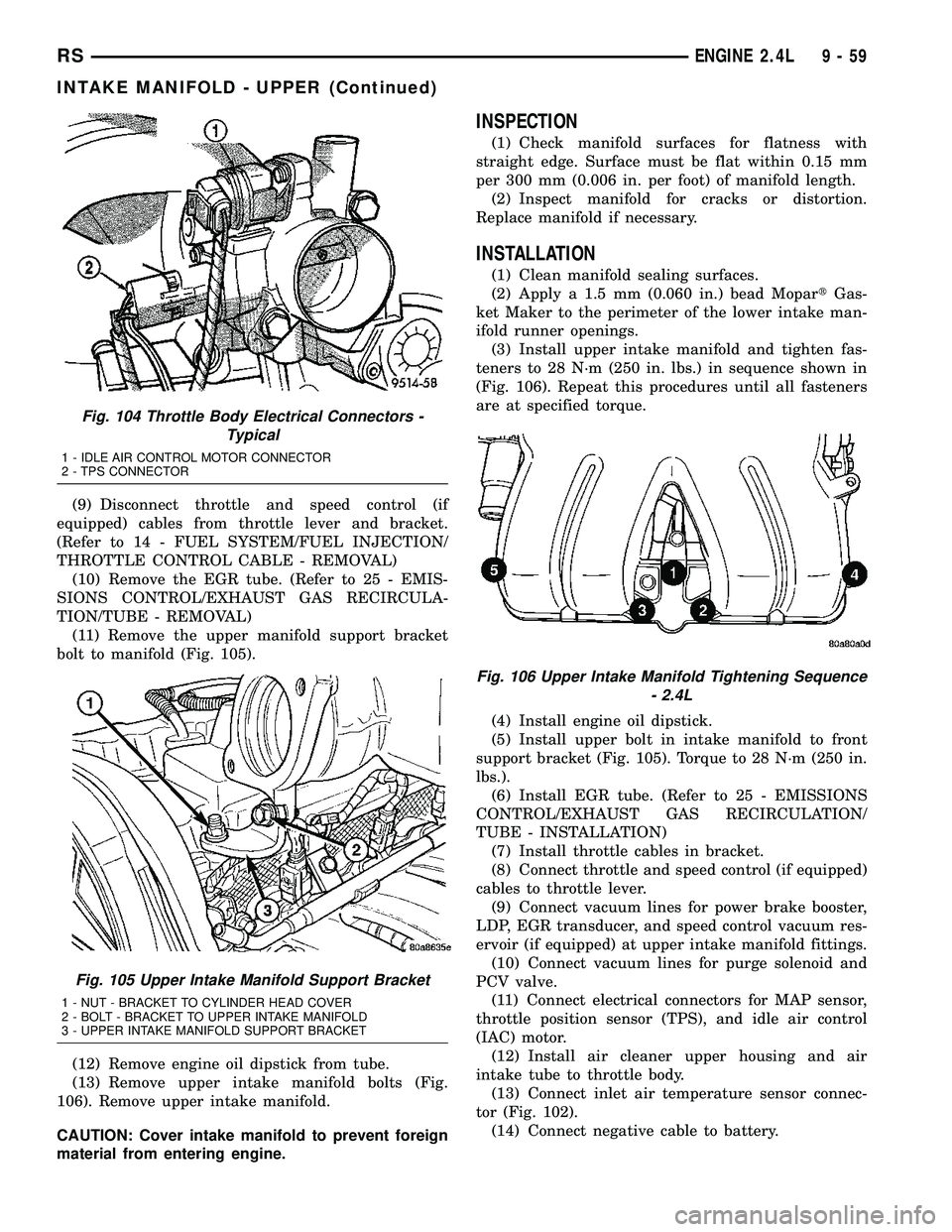
(9) Disconnect throttle and speed control (if
equipped) cables from throttle lever and bracket.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE - REMOVAL)
(10) Remove the EGR tube. (Refer to 25 - EMIS-
SIONS CONTROL/EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULA-
TION/TUBE - REMOVAL)
(11) Remove the upper manifold support bracket
bolt to manifold (Fig. 105).
(12) Remove engine oil dipstick from tube.
(13) Remove upper intake manifold bolts (Fig.
106). Remove upper intake manifold.
CAUTION: Cover intake manifold to prevent foreign
material from entering engine.
INSPECTION
(1) Check manifold surfaces for flatness with
straight edge. Surface must be flat within 0.15 mm
per 300 mm (0.006 in. per foot) of manifold length.
(2) Inspect manifold for cracks or distortion.
Replace manifold if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean manifold sealing surfaces.
(2) Apply a 1.5 mm (0.060 in.) bead MopartGas-
ket Maker to the perimeter of the lower intake man-
ifold runner openings.
(3) Install upper intake manifold and tighten fas-
teners to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) in sequence shown in
(Fig. 106). Repeat this procedures until all fasteners
are at specified torque.
(4) Install engine oil dipstick.
(5) Install upper bolt in intake manifold to front
support bracket (Fig. 105). Torque to 28 N´m (250 in.
lbs.).
(6) Install EGR tube. (Refer to 25 - EMISSIONS
CONTROL/EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION/
TUBE - INSTALLATION)
(7) Install throttle cables in bracket.
(8) Connect throttle and speed control (if equipped)
cables to throttle lever.
(9) Connect vacuum lines for power brake booster,
LDP, EGR transducer, and speed control vacuum res-
ervoir (if equipped) at upper intake manifold fittings.
(10) Connect vacuum lines for purge solenoid and
PCV valve.
(11) Connect electrical connectors for MAP sensor,
throttle position sensor (TPS), and idle air control
(IAC) motor.
(12) Install air cleaner upper housing and air
intake tube to throttle body.
(13) Connect inlet air temperature sensor connec-
tor (Fig. 102).
(14) Connect negative cable to battery.
Fig. 104 Throttle Body Electrical Connectors -
Typical
1 - IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR CONNECTOR
2 - TPS CONNECTOR
Fig. 105 Upper Intake Manifold Support Bracket
1 - NUT - BRACKET TO CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - BOLT - BRACKET TO UPPER INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 - UPPER INTAKE MANIFOLD SUPPORT BRACKET
Fig. 106 Upper Intake Manifold Tightening Sequence
- 2.4L
RSENGINE 2.4L9-59
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER (Continued)
Page 1357 of 2585

INTAKE MANIFOLD - LOWER
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release proce-
durebefore attempting any repairs.(Refer to 14 -
FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(2) Remove upper intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
CAUTION: Cover intake manifold openings to pre-
vent foreign material from entering engine.
(3) Disconnect fuel line. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FIT-
TING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(4) Drain the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(5) Remove heater supply and radiator upper
hoses at intake manifold.
(6) Disconnect coolant temperature sensor/fuel
injector wire harness connector.
(7) Remove lower intake manifold support bracket
upper bolts (Fig. 107).
(8) Loosen the lower intake manfold support
bracket lower bolt (Fig. 107).
(9) Disconnect fuel injector harness.
(10) Remove the bolts attaching the power steering
reservoir to manifold. Set reservoir aside.Do not
disconnect line from reservoir.
(11) Remove lower intake manifold fasteners (Fig.
108). Remove the manifold from engine.
(12) Inspect the manifold. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - INSPECTION)
INSPECTION
(1) Check manifold surfaces for flatness with
straight edge. Surface must be flat within 0.15 mm
per 300 mm (0.006 in. per foot) of manifold length.
(2) Inspect manifold for cracks or distortion.
Replace manifold if necessary.
INSTALLATION
If the following items were removed, install and
torque to specifications:
²Fuel rail bolts - 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.)
²Coolant outlet connector bolts - 28 N´m (250 in.
lbs.)
²Coolant temperature sensor - 7 N´m (60 in. lbs.)
(1) Position a new gasket on cylinder head and
install lower manifold.
(2) Install and tighten intake manifold fasteners to
28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) in the sequence shown in (Fig.
108). Repeat procedure until all bolts are at specified
torque.
(3) Install lower intake manifold support bracket
bolts (Fig. 107) and tighten to:
²Bolts to intake 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.)
²Bolt to engine block 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.)
(4) Position power steering reservoir on manifold
and install bolts.
(5) Connect the fuel line. (Refer to 14 - FUEL SYS-
TEM/FUEL DELIVERY/QUICK CONNECT FIT-
TING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(6) Connect coolant temperature sensor/fuel injec-
tor wiring harness electrical connector.
(7) Install the radiator upper and heater supply
hoses.
(8) Install the upper intake manifold. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)
(9) Fill the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOLING
- STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 107 Lower Intake Manifold Support Bracket
1 - SUPPORT BRACKET
2 - BOLTS - UPPER TO MANIFOLD
3 - BOLT - LOWER TO ENGINE BLOCK
Fig. 108 Lower Intake Manifold Tightening
Sequence
9 - 60 ENGINE 2.4LRS
Page 1377 of 2585

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. Check and correct engine oil
level.
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil to correct viscosity.
3. Thick oil 3. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
4. Low oil pressure. 4. Check and correct engine oil
pressure problem.
5. Dirt in hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.5. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
6. Worn rocker arms. 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms.
7. Worn hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.7. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
8. Worn valve guides. 8. Replace cylinder head assembly.
9. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.9. Grind valve seats and valves.
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.6. Replace crankshaft or grind
surface.
7. Misaligned connecting rods. 7. Replace bent connecting rods.
9 - 80 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1378 of 2585

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Excessive end play. 6. Check thrust bearing for wear on
flanges.
7. Crankshaft journal out-of-round
or worn.7. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals.
8. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.8. Tighten to correct torque.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sensor/switch. 2. Replace oil pressure sensor/
switch.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pressure sensor/switch
and main bearing oil clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Install new oil filter.
5. Worn parts in oil pump. 5. Replace worn parts or pump.
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil to correct viscosity.
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 7. Remove valve and inspect, clean,
or replace.
8. Oil pump suction tube loose. 8. Remove oil pan and install new
tube or clean, if necessary.
9. Oil pump cover warped or
cracked.9. Install new oil pump.
10. Excessive bearing clearance. 10. Measure bearings for correct
clearance.
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated
gaskets.1. Replace gasket(s).
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part.2. Tighten, repair or replace the
part.
3. Misaligned or deteriorated cup or
threaded plug.3. Replace as necessary.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-81
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)