Power system CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 249 of 2585
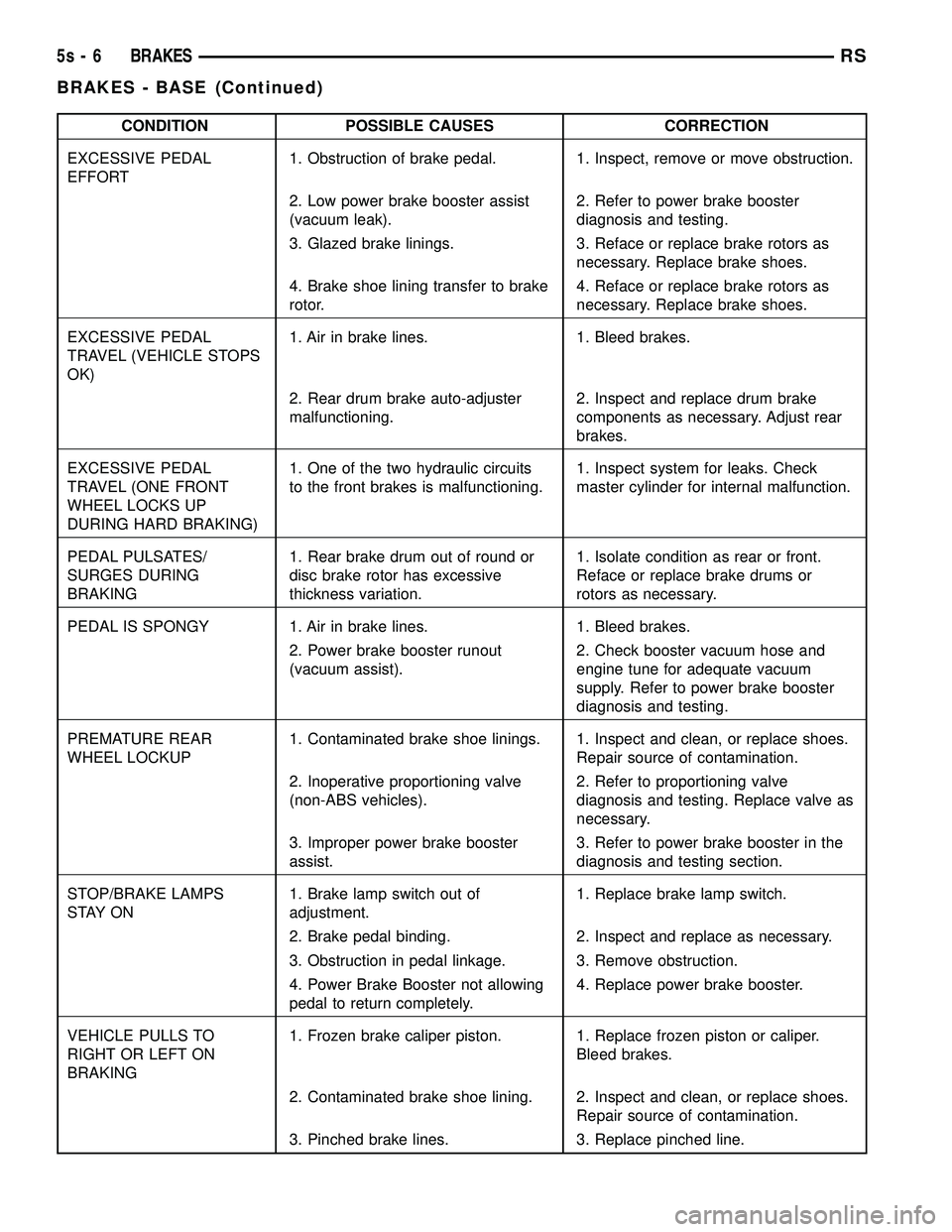
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
EFFORT 1. Obstruction of brake pedal. 1. Inspect, remove or move obstruction.
2. Low power brake booster assist
(vacuum leak). 2. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
3. Glazed brake linings. 3. Reface or replace brake rotors as necessary. Replace brake shoes.
4. Brake shoe lining transfer to brake
rotor. 4. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (VEHICLE STOPS
OK) 1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Rear drum brake auto-adjuster
malfunctioning.
2. Inspect and replace drum brake
components as necessary. Adjust rear
brakes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (ONE FRONT
WHEEL LOCKS UP
DURING HARD BRAKING) 1. One of the two hydraulic circuits
to the front brakes is malfunctioning.
1. Inspect system for leaks. Check
master cylinder for internal malfunction.
PEDAL PULSATES/
SURGES DURING
BRAKING 1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation. 1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or
rotors as necessary.
PEDAL IS SPONGY 1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes. 2. Power brake booster runout
(vacuum assist). 2. Check booster vacuum hose and
engine tune for adequate vacuum
supply. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
PREMATURE REAR
WHEEL LOCKUP 1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Inoperative proportioning valve
(non-ABS vehicles). 2. Refer to proportioning valve
diagnosis and testing. Replace valve as
necessary.
3. Improper power brake booster
assist. 3. Refer to power brake booster in the
diagnosis and testing section.
STOP/BRAKE LAMPS
S TAY O N 1. Brake lamp switch out of
adjustment. 1. Replace brake lamp switch.
2. Brake pedal binding. 2. Inspect and replace as necessary.
3. Obstruction in pedal linkage. 3. Remove obstruction.
4. Power Brake Booster not allowing
pedal to return completely. 4. Replace power brake booster.
VEHICLE PULLS TO
RIGHT OR LEFT ON
BRAKING 1. Frozen brake caliper piston. 1. Replace frozen piston or caliper.
Bleed brakes.
2. Contaminated brake shoe lining. 2. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes. Repair source of contamination.
3. Pinched brake lines. 3. Replace pinched line.
5s - 6 BRAKESRS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 251 of 2585

PRESSURE BLEEDING PROCEDURE
CAUTION: Use bleeder tank Special Tool C-3496-B
or equivalent with Adapter, Special Tool 6921, to
pressurize the hydraulic system for bleeding.Follow pressure bleeder manufacturer's instruc-
tions for use of pressure bleeding equipment. (1) Install the Adapter Master Cylinder Pressure
Bleed Cap, Special Tool 6921 on the fluid reservoir of
the master cylinder (Fig. 2). Attach the fluid hose
from the pressure bleeder to the fitting on Special
Tool 6921.
(2) Attach a clear plastic hose to the bleeder screw
at one wheel and feed the hose into a clear jar con-
taining fresh brake fluid. (3) Open the left rear wheel bleeder screw at least
one full turn or more to obtain an adequate flow of
brake fluid.
CAUTION: ªJust crackingº the bleeder screw often
restricts fluid flow, allowing only a slow, weak fluid
discharge of fluid. This practice will NOT get all the
air out. Make sure the bleeder is opened at least 1
full turn when bleeding.
(4) After 4 to 8 ounces of brake fluid has been bled
through the hydraulic system, and an air-free flow is
maintained in the hose and jar, this will indicate a
good bleed of the hydraulic system has been
obtained. (5) Repeat the procedure at all the other remain-
ing bleeder screws. (6) Check pedal travel. If pedal travel is excessive
or has not been improved, enough fluid has not
passed through the system to expel all the trapped
air. Be sure to monitor the fluid level in the pressure bleeder, so it stays at a proper level so air will not
enter the brake system through the master cylinder.
(7) Perform a final adjustment of the rear brake
shoes (when applicable), then test drive vehicle to be
sure brakes are operating correctly and that pedal is
solid.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FASTENER TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft.
Lbs. In.
Lbs.
ABS ICU Mounting Bolts To
Bracket 11 Ð 9 7
ABS ICU Mounting
Bracket-To-Cradle Bolts 28 21 250
ABS CAB-To-HCU Mounting
Screws 2Ð17
ABS Wheel Speed Sensor
Head Mounting Bolt - Front 13 Ð 115
ABS Wheel Speed Sensor
Head Mounting Bolt - Rear 10 Ð 90
Adjustable Pedal Position
Sensor Mounting Screws 7.5 66 Ð
Adjustable Pedal Module
Mounting Screws 2.0 15 Ð
Brake Tube Nuts 17 Ð 145
Brake Hose Intermediate
Bracket Bolt 12 Ð 105
Brake Hose-To-Caliper
Mounting Bolt 47 35 Ð
Disc Brake Caliper Guide
Pin Bolts 35 26 Ð
Disc Brake Caliper Bleeder
Screw 15 Ð 125
Drum Brake Wheel Cylinder
Mounting Bolts 8Ð75
Drum Brake Wheel Cylinder
Mounting Bleeder screw 10 Ð 80
Drum Brake Support Plate
Mounting Bolts 130 95 Ð
Junction Block (Non-ABS
Brakes) Mounting Bolts 28 21 250
Master Cylinder Mounting
Nuts 25 19 225
Power Brake Booster
Mounting Nuts 28 21 250
Fig. 2 Tool 6921 Installed On Master Cylinder
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 6921
2 - FLUID RESERVOIR
5s - 8 BRAKESRS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 253 of 2585

line in the master cylinder fluid reservoir, the
entire brake hydraulic system should be
checked for evidence of a leak.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove wiring harness connector from brake
fluid reservoir level switch (Fig. 3).
(2) Using fingers, compress the retaining tabs on
the opposite end of brake fluid level switch. (3) With retaining tabs compressed, grasp the con-
nector end of brake fluid level switch and pull it out
of master cylinder brake fluid reservoir.
INSTALLATION
(1) Insert brake fluid level switch into left side of
brake fluid reservoir. Be sure switch is pushed in
until retaining tabs lock it to brake fluid reservoir. (2) Connect vehicle wiring harness connector to
brake fluid level switch (Fig. 3).
ADJUSTABLE PEDALS
SWITCH
REMOVAL
(1) Remove steering column lower shroud. (Refer
to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/LOWER SHROUD -
REMOVAL) (2) Depress retaining tabs on top and bottom of
switch and remove switch from lower shroud.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the switch into the lower shroud, snap-
ping it into place. (2) Connect wiring harness connector to switch,
then install lower shroud on steering column. (Refer
to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/LOWER SHROUD -
INSTALLATION) (3) Ensure proper operation of adjustable pedals.
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - DISC BRAKES (FRONT)
Each front disc brake consists of the following com-
ponents: ² Brake Rotor
² Brake Caliper
² Brake Caliper Adapter
² Shoes (Pads)
There are two non-interchangeable front disc brake
systems. One is manufactured by TRW and the other
by Continental Teves.
CAUTION: Components used on the TRW brakes
are not interchangeable with the Continental Teves
brakes. The two different systems must not be
mixed. Improper performance, noise and increased
stopping distance can occur.
The TRW front brake caliper is a one piece casting
containing a single 64 mm diameter piston bore (Fig.
4) with a phenolic piston. The caliper mounts to a
caliper adapter using two guide pin bolts that thread
into guide pins slid into the caliper adapter (Fig. 5).
The pins are lubricated and have boots that seal
them in place in the adapter. The Continental Teves front brake caliper is a one
piece casting containing a single piston 66 mm diam-
eter bore (Fig. 4) with a phenolic piston. The caliper
mounts to a caliper adapter using two guide pin bolts
that thread into the caliper adapter and slide on
bushings mounted in the caliper.
CAUTION: TRW and Continental Teves calipers are
not interchangeable. Each caliper is specifically
designed for the unique brake system. If calipers
are interchanged, improper performance, noise and
increased stopping distance can occur.
Fig. 3 MASTER CYLINDER AND BOOSTER
1 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
2 - BOOSTER IDENTIFICATION LABEL
3 - FLUID LEVEL SWITCH CONNECTOR
4 - PRIMARY BRAKE TUBE NUT
5 - SECONDARY BRAKE TUBE NUT
6 - MASTER CYLINDER
5s - 10 BRAKESRS
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH (Continued)
Page 275 of 2585

Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container. DO NOT use petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage will result. Petroleum based fluids would be
items such as engine oil, transmission fluid, power
steering fluid etc.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications (DOT 4 and DOT 4+ are
acceptable) and SAE J1703 standards. No other type
of brake fluid is recommended or approved for usage
in the vehicle brake system. Use only Mopar tBrake
Fluid or equivalent from a tightly sealed container.
CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container of brake fluid will absorb moisture
from the air and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-based
fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of such
type fluids will result in seal damage of the vehicle
brake hydraulic system causing a failure of the
vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids would
be items such as engine oil, transmission fluid,
power steering fluid, etc.
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
A junction block is used on vehicles that are not
equipped with antilock brakes (ABS). The junction
block mounts in the same location as the integrated
control unit (ICU) does on vehicles equipped with
ABS. This allows for use of the same brake tube con-
figuration on all vehicles. The junction block is located
on the driver's side of the front suspension cradle/
crossmember below the master cylinder (Fig. 44).
It has six threaded ports to which the brake tubes
connect. Two are for the primary and secondary
brake tubes coming from the master cylinder. The
remaining four are for the chassis brake tubes going
to each brake assembly.
OPERATION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
The junction block distributes the brake fluid com-
ing from the master cylinder primary and secondary
ports to the four chassis brake tubes leading to the
brakes at each wheel. Since the junction block
mounts in the same location as the ABS integrated control unit (ICU), it allows for the common use of
brake tubes going to the brakes whether the vehicle
is equipped with or without ABS.
NOTE: Although the brake tubes coming from the
master cylinder to the junction block or ABS ICU
may appear to be the same, they are not. They are
unique to each brake system application.
REMOVAL - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
(1) Using a brake pedal depressor, move and lock
the brake pedal to a position past its first 1 inch of
travel. This will prevent brake fluid from draining
out of the master cylinder when the brake tubes are
removed from the junction block. (2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) If the vehicle is equipped with speed control,
perform the following: (a) Disconnect the battery positive cable.
(b) Remove the battery (Refer t o 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - REMOVAL). (c) Disconnect the vacuum hose connector at the
tank built into the battery tray. (d) Remove the screw securing the coolant filler
neck to the battery tray. (e) Remove the battery tray (Refer t o 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - REMOVAL). (f) Remove the fasteners and move the speed
control servo off to the side, out of the way.
CAUTION: Before removing the brake tubes from
the junction block, the junction block and the brake
tubes must be thoroughly cleaned. This is required
to prevent contamination from entering the brake
hydraulic system. (4) Remove the four chassis brake tubes from the
top of the junction block (Fig. 44). (5) Remove the primary and secondary brake
tubes from the top of the junction block. (6) Remove the bolts attaching the junction block
mounting bracket to the front suspension crossmem-
ber (Fig. 44), then remove the junction block.
INSTALLATION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
(1) Install the junction block and mounting bracket
on the front suspension crossmember (Fig. 44).
Install the mounting bolts and tighten to a torque of
28 N´m (250 in. lbs.). (2) Install the primary and secondary brake tubes
from the master cylinder in their ports. Tighten tube
nuts to a torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.). Take care
not to twist tubes when tightening tube nuts.
They must be properly positioned to allow free
movement with rubber isolated suspension
crossmember.
5s - 32 BRAKESRS
FLUID (Continued)
Page 276 of 2585

(3) Install the four chassis brake tubes into the
outlet ports of the junction block. Tighten all 6 tube
nuts to a torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.). (4) If the vehicle is equipped with speed control,
perform the following: (a) Install the speed control servo with its
mounting nuts. (b) Connect the wiring harness to the speed con-
trol servo. (c) Install the battery tray (Refer t o 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - INSTALLA-
TION). (d) Install the screw securing the coolant filler
neck to the battery tray. (e) Reconnect the vacuum hose connector at the
tank built into the battery tray. (f) Install the battery (Refer t o 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - INSTALLA-
TION). (g) Install the battery shield.
(5) Remove the brake pedal holder.
(6) Connect negative cable back on negative post of
the battery. (7) Bleed the brake system thoroughly to ensure
that all air has been expelled from the hydraulic sys-
tem. (Refer t o 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE). (8) Road test the vehicle to verify proper operation
of the brake system.
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
The master cylinder is located on the power brake
booster in the engine compartment on the driver's
side (Fig. 45). This vehicle uses 3 different master
cylinders. Master cylinder usage depends on what
type of brake system the vehicle is equipped with.
CAUTION: Master cylinders are not interchangeable
between systems. Performance and stopping dis-
tance issues will result if the incorrect master cyl-
inder is installed on the vehicle.
For information on master cylinder application,
bore and type, view the following table:
BRAKE SYSTEM MASTER CYLINDER
BORE/TYPE
Disc/Drum - ABS 23.8 mm (15/16 in.)
Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Drum - Non-ABS 23.8 mm (15/16 in.)
Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Disc - ABS 25.4 mm (1.0 in.)
Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Disc ABS With
Traction Control 25.4 mm (1.0 in.) Dual
Center Port
Fig. 44 NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
1 - MASTER CYLINDER
2 - JUNCTION BLOCK
3 - SUSPENSION CROSSMEMBER
4 - MOUNTING BOLTS
Fig. 45 Master Cylinder And Booster Location
1 - MASTER CYLINDER
2 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
RS BRAKES5s-33
JUNCTION BLOCK (Continued)
Page 277 of 2585

CAUTION: When replacing a master cylinder, be
sure to use the correct master cylinder for the type
of brake system the vehicle is equipped with.The body of the master cylinder is an anodized alu-
minum casting. It has a machined bore to accept the
master cylinder pistons and threaded ports with
seats for the hydraulic brake line connections. The brake fluid reservoir is mounted on the top of
the master cylinder. It is made of a see-through
polypropylene type plastic for easy fluid level view-
ing. A brake fluid level switch is attached to the
brake fluid reservoir. The master cylinder is not a repairable component
and must be replaced if diagnosed to be functioning
improperly. The brake fluid reservoir and brake fluid
level switch can be replaced separately.
CAUTION: Do not hone the bore of the cylinder as
this will remove the anodized surface from the bore.
DESCRIPTION - RHD
The master cylinder used on right hand drive
(RHD) vehicles functions similarly to that used on
left hand drive (LHD) vehicles. The RHD master cyl-
inder, as well as the RHD power brake booster, is
located in the same area, but lower in the engine
compartment than LHD models (Fig. 46). For that
reason an extension manifold is placed between the
fluid reservoir and master cylinder housing allowing
the fluid reservoir to be positioned in the same loca-
tion as on LHD models.
OPERATION
When the brake pedal is depressed, the master cyl-
inder primary and secondary pistons apply brake
pressure through the chassis tubes to the brakes at
each tire and wheel assembly. The master cylinder primary outlet port supplies
hydraulic pressure to the right front and left rear
brakes. The secondary outlet port supplies hydraulic
pressure to the left front and right rear brakes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER CYLINDER
BLEEDING
CAUTION: When clamping master cylinder in vise,
only clamp master cylinder by its mounting flange.
Do not clamp master cylinder piston rod, reservoir,
seal or body.
(1) Clamp master cylinder in a vise.
NOTE: Use correct bleeder tubes when bleeding
master cylinder. Master cylinder outlet ports vary in
size and type depending on whether master cylin-
der is for a vehicle equipped with traction control or
not. Traction control equipped master cylinders
require the additional use of ISO style flare adapt-
ers supplied in Special Tool Package 8822 to be
used in conjunction with Bleeder Tubes, Special
Tool Package 8358. (2) Attach special tools for bleeding master cylin-
der in the following fashion: (a)For non-traction control equipped mas-
ter cylinders , thread a Bleeder Tube, Special Tool
8358±1, into each outlet port. Tighten each tube to
17 N´m (145 in. lbs.) torque. Flex bleeder tubes and
place open ends into mouth of fluid reservoir as far
down as possible (Fig. 47). (b) For traction control equipped master
cylinders , thread one Adapter, Special Tool
8822±2, in each outlet port. Tighten Adapters to 17
N´m (145 in. lbs.) torque. Next, thread a Bleeder
Tube, Special Tool 8358±1, into each Adapter.
Tighten each tube to 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.) torque.
Flex bleeder tubes and place open ends into mouth
of fluid reservoir as far down as possible (Fig. 47).
NOTE: Make sure open ends of bleeder tubes stay
below surface of brake fluid once reservoir is filled
to proper level. (3) Fill brake fluid reservoir with Mopar tbrake
fluid or equivalent conforming to DOT 3 (DOT 4 and
DOT 4+ are acceptable) specifications. Make sure
fluid level is above tips of bleeder tubes in reservoir
to ensure no air is ingested during bleeding.
Fig. 46 RHD MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
1 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
2 - BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
3 - FLUID RESERVOIR
4 - MASTER CYLINDER
5s - 34 BRAKESRS
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 280 of 2585
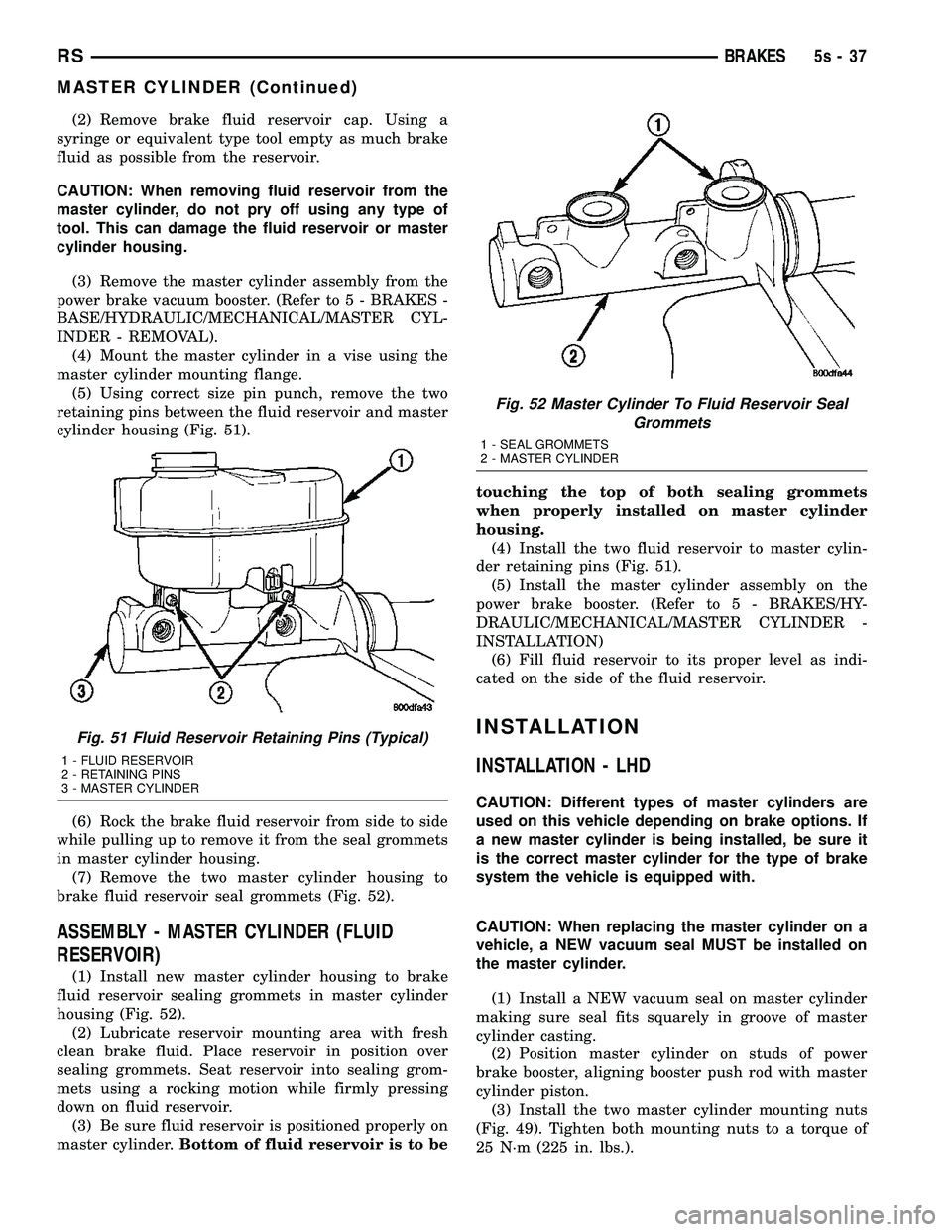
(2) Remove brake fluid reservoir cap. Using a
syringe or equivalent type tool empty as much brake
fluid as possible from the reservoir.
CAUTION: When removing fluid reservoir from the
master cylinder, do not pry off using any type of
tool. This can damage the fluid reservoir or master
cylinder housing.
(3) Remove the master cylinder assembly from the
power brake vacuum booster. (Refer t o 5 - BRAKES -
BASE/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/MASTER CYL-
INDER - REMOVAL). (4) Mount the master cylinder in a vise using the
master cylinder mounting flange. (5) Using correct size pin punch, remove the two
retaining pins between the fluid reservoir and master
cylinder housing (Fig. 51).
(6) Rock the brake fluid reservoir from side to side
while pulling up to remove it from the seal grommets
in master cylinder housing. (7) Remove the two master cylinder housing to
brake fluid reservoir seal grommets (Fig. 52).
ASSEMBLY - MASTER CYLINDER (FLUID
RESERVOIR)
(1) Install new master cylinder housing to brake
fluid reservoir sealing grommets in master cylinder
housing (Fig. 52). (2) Lubricate reservoir mounting area with fresh
clean brake fluid. Place reservoir in position over
sealing grommets. Seat reservoir into sealing grom-
mets using a rocking motion while firmly pressing
down on fluid reservoir. (3) Be sure fluid reservoir is positioned properly on
master cylinder. Bottom of fluid reservoir is to be touching the top of both sealing grommets
when properly installed on master cylinder
housing.
(4) Install the two fluid reservoir to master cylin-
der retaining pins (Fig. 51). (5) Install the master cylinder assembly on the
power brake booster. (Refer t o 5 - BRAKES/HY-
DRAULIC/MECHANICAL/MASTER CYLINDER -
INSTALLATION) (6) Fill fluid reservoir to its proper level as indi-
cated on the side of the fluid reservoir.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LHD
CAUTION: Different types of master cylinders are
used on this vehicle depending on brake options. If
a new master cylinder is being installed, be sure it
is the correct master cylinder for the type of brake
system the vehicle is equipped with.
CAUTION: When replacing the master cylinder on a
vehicle, a NEW vacuum seal MUST be installed on
the master cylinder.
(1) Install a NEW vacuum seal on master cylinder
making sure seal fits squarely in groove of master
cylinder casting. (2) Position master cylinder on studs of power
brake booster, aligning booster push rod with master
cylinder piston. (3) Install the two master cylinder mounting nuts
(Fig. 49). Tighten both mounting nuts to a torque of
25 N´m (225 in. lbs.).
Fig. 51 Fluid Reservoir Retaining Pins (Typical)
1 - FLUID RESERVOIR
2 - RETAINING PINS
3 - MASTER CYLINDER
Fig. 52 Master Cylinder To Fluid Reservoir Seal Grommets
1 - SEAL GROMMETS
2 - MASTER CYLINDER
RS BRAKES5s-37
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 281 of 2585

CAUTION: When tightening the primary and sec-
ondary brake tube nuts at master cylinder, be sure
brake tubes do not contact any other components
within the vehicle and that there is slack in the flex-
ible sections of the tubes. This is required due to
the movement between the ABS ICU and the master
cylinder while the vehicle is in motion.(4) Connect primary and secondary brake tubes to
master cylinder primary and secondary ports (Fig.
48). Brake tubes must be held securely when tight-
ened to control orientation of flex section. Tighten
tube nuts to a torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.). (5) Install wiring harness connector to brake fluid
level switch mounted in brake fluid reservoir (Fig.
48). (6) Install battery, clamp and nut.
(7) Install battery shield.
(8) Connect positive battery terminal.
(9) Connect negative battery terminal.
(10) Fill master cylinder with clean, fresh Mopar t
Brake Fluid or equivalent. (11) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation of
brakes.
INSTALLATION - RHD
CAUTION: Different types of master cylinders are
used on this vehicle depending on brake options. If
a new master cylinder is being installed, be sure it
is the correct master cylinder for the type of brake
system the vehicle is equipped with.
CAUTION: When replacing the master cylinder on a
vehicle, a NEW vacuum seal MUST be installed on
the master cylinder.
(1) Install a NEW vacuum seal on master cylinder
making sure seal fits squarely in groove of master
cylinder casting. (2) Position master cylinder on studs of power
brake booster, aligning booster push rod with master
cylinder piston. (3) Install the two master cylinder mounting nuts
(Fig. 50). Tighten both mounting nuts to a torque of
25 N´m (225 in. lbs.).
CAUTION: When tightening the primary and sec-
ondary brake tube nuts at master cylinder, be sure
brake tubes do not contact any other components
within the vehicle and that there is slack in the flex-
ible sections of the tubes. This is required due to
the movement between the ABS ICU and the master
cylinder while the vehicle is in motion. (4) Connect primary and secondary brake tubes to
master cylinder primary and secondary ports (Fig.
50). Brake tubes must be held securely when tight-
ened to control orientation of flex section. Tighten
tube nuts to a torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.). (5) Install wiring harness connector to brake fluid
level switch mounted in brake fluid reservoir (Fig.
46). (6) Install battery, clamp and nut.
(7) Install battery shield.
(8) Connect positive battery terminal.
(9) Connect negative battery terminal.
(10) Fill master cylinder with clean, fresh Mopar t
Brake Fluid or equivalent. (11) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation of
brakes.
PEDALS - ADJUSTABLE
REMOVAL
NOTE: Before proceeding, review all Steering Col-
umn and Airbag Warnings and Cautions. (Refer to
19 - STEERING/COLUMN - WARNING)(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - WARNING)
(1) Move driver's seat to full rearward position.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
post and isolate. (3) Remove throttle cable from throttle body lever.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE - REMOVAL) (4) Remove screws securing lower steering column
cover/knee blocker, then remove it (Fig. 53). (5) Disconnect parking brake release link at
release handle. (6) Compress tabs on sides of data link diagnostic
connector and remove it from knee blocker reinforce-
ment plate. (7) Remove screws securing knee blocker reinforce-
ment plate in place, then remove reinforcement plate
(Fig. 53). (8) Remove hood release from lower left reinforce-
ment. (9) Remove screws securing instrument panel
lower left reinforcement in place, then remove rein-
forcement (Fig. 54). (10) Remove brake lamp switch. Discard original
switch; it must not be reused. (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR/BRAKE
LAMP SWITCH - REMOVAL) (11) Remove upper and lower steering column
shrouds. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/
LOWER SHROUD - REMOVAL)
5s - 38 BRAKESRS
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 285 of 2585
(24) Install knee blocker reinforcement plate (Fig.
53). (25) Connect parking brake release link to release
handle. (26) Install data link diagnostic connector to
mounting hole in reinforcement plate. (27) Install lower steering column cover/knee
blocker (Fig. 53). (28) Install throttle cable onto throttle body lever.
(Refer to 14 - FUEL SYSTEM/FUEL INJECTION/
THROTTLE CONTROL CABLE - INSTALLATION)
NOTE: When reconnecting the battery on a vehicle
that has had the airbag module removed, the fol-
lowing procedure should be used.
(29) Reconnect ground cable to negative post of
battery following special Diagnosis And Testing pro-
cedure. (Refer t o 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) (30) Test operation of adjustable pedals and all
functions that are steering column operated. If appli-
cable, reset radio and clock. (31) Road test the vehicle to ensure proper opera-
tion of steering and brake systems.
PEDAL TORQUE SHAFT - RHD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the instrument panel. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/INSTRUMENT
PANEL ASSEMBLY - REMOVAL) (2) Remove the HVAC housing. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
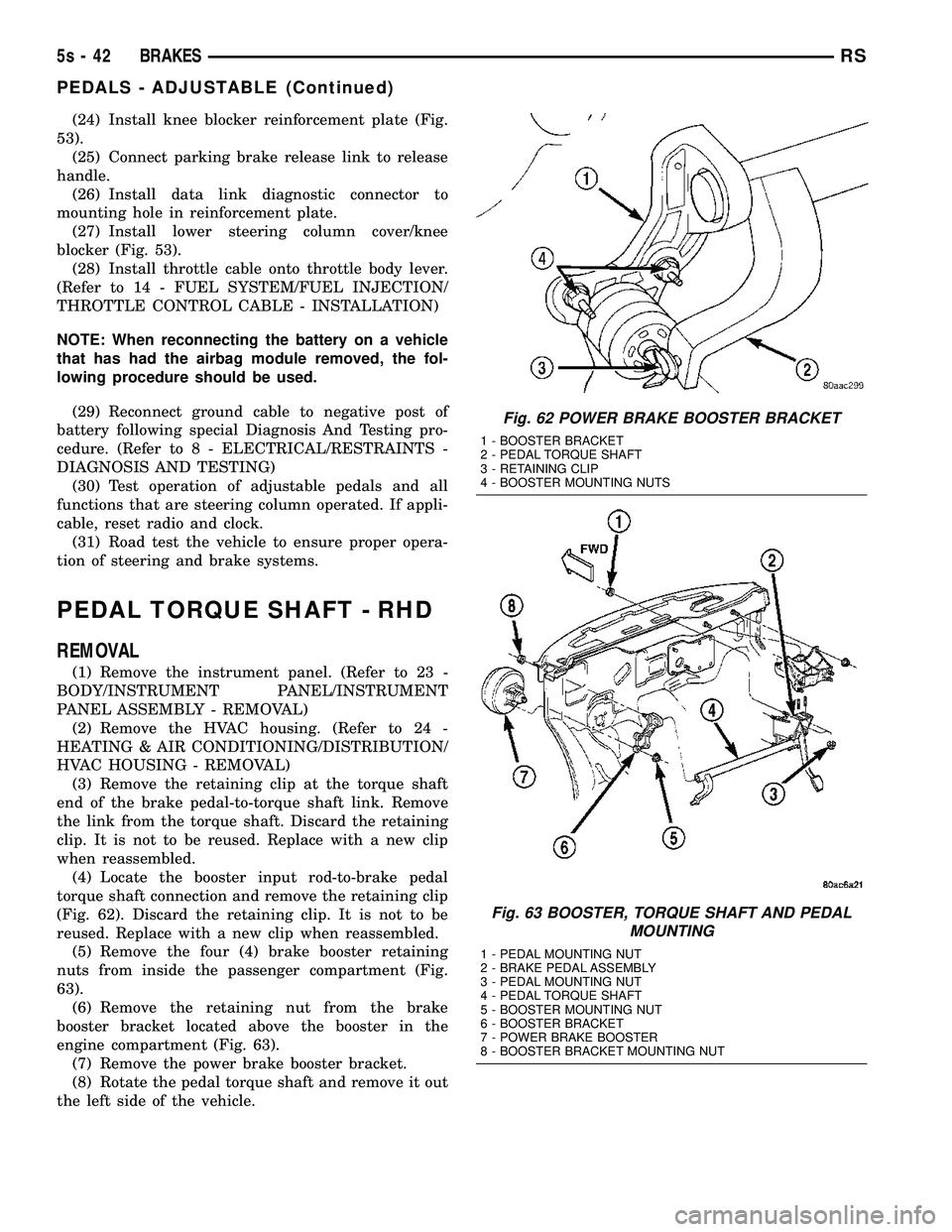
HVAC HOUSING - REMOVAL) (3) Remove the retaining clip at the torque shaft
end of the brake pedal-to-torque shaft link. Remove
the link from the torque shaft. Discard the retaining
clip. It is not to be reused. Replace with a new clip
when reassembled. (4) Locate the booster input rod-to-brake pedal
torque shaft connection and remove the retaining clip
(Fig. 62). Discard the retaining clip. It is not to be
reused. Replace with a new clip when reassembled. (5) Remove the four (4) brake booster retaining
nuts from inside the passenger compartment (Fig.
63). (6) Remove the retaining nut from the brake
booster bracket located above the booster in the
engine compartment (Fig. 63). (7) Remove the power brake booster bracket.
(8) Rotate the pedal torque shaft and remove it out
the left side of the vehicle.
Fig. 62 POWER BRAKE BOOSTER BRACKET
1 - BOOSTER BRACKET
2 - PEDAL TORQUE SHAFT
3 - RETAINING CLIP
4 - BOOSTER MOUNTING NUTS
Fig. 63 BOOSTER, TORQUE SHAFT AND PEDAL MOUNTING
1 - PEDAL MOUNTING NUT
2 - BRAKE PEDAL ASSEMBLY
3 - PEDAL MOUNTING NUT
4 - PEDAL TORQUE SHAFT
5 - BOOSTER MOUNTING NUT
6 - BOOSTER BRACKET
7 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
8 - BOOSTER BRACKET MOUNTING NUT
5s - 42 BRAKESRS
PEDALS - ADJUSTABLE (Continued)
Page 287 of 2585

NOTE: The power brake booster assembly is not a
repairable component and must be replaced as a
complete assembly if found to be faulty in any way.
The check valve located on the power brake
booster face is not repairable, but it can be
replaced separately from the power brake booster.The different engine combinations used in this
vehicle require different vacuum hose routings to the
power brake booster. All vacuum hoses must be
routed from the engine to the power brake booster
without kinks or excessively tight bends.
OPERATION
The power brake booster reduces the amount of
force required by the driver to obtain the necessary
hydraulic pressure to stop a vehicle. The power brake booster is vacuum operated. The
vacuum is supplied from the intake manifold on the
engine through a vacuum hose and the power brake
booster check valve (Fig. 64). As the brake pedal is depressed, the power brake
booster's input rod moves forward (Fig. 64). This
opens and closes valves in the power booster allowing
atmospheric pressure to enter on one side of a dia-
phragm. Engine vacuum is always present on the
other side. This difference in pressure forces the out-
put rod of the power brake booster out against the
primary piston of the master cylinder. As the pistons
in the master cylinder move forward this creates the
hydraulic pressure in the brake system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - POWER BRAKE
BOOSTER
BASIC TEST
(1) With engine off, depress and release the brake
pedal several times to purge all vacuum from the
power brake booster. (2) Depress and hold the pedal with light effort (15
to 25 lbs. pressure), then start the engine. The pedal should fall slightly, then hold. Less effort
should be needed to apply the pedal at this time. If
the pedal fell as indicated, perform the VACUUM
LEAK TEST listed after the BASIC TEST. If the
pedal did not fall, continue on with this BASIC
TEST. (3) Disconnect the vacuum hose on the vacuum
check valve, then place a vacuum gauge in line
between the vacuum hose and the valve. (4) Start the engine.
(5) When the engine is at warm operating temper-
ature, allow it to idle and check the vacuum at the
gauge. If the vacuum supply is 12 inches Hg (40.5 kPa) or
more, the power brake booster is defective and must
be replaced. If the vacuum supply is below 12 inches
Hg, continue on with this BASIC TEST. (6) Shut off the engine.
(7) Connect the vacuum gauge to the vacuum ref-
erence port on the engine intake manifold. (8) Start the engine and observe the vacuum
gauge. If the vacuum is still low, check the engine tune
and repair as necessary. If the vacuum is above 12
inches Hg, the hose or check valve to the booster has
a restriction or leak. Once an adequate vacuum supply is obtained,
repeat the BASIC TEST.
VACUUM LEAK TEST
(1) Disconnect the vacuum hose on the vacuum
check valve, then place a vacuum gauge in line
between the vacuum hose and the valve. (2) Start the engine.
(3) Allow the engine to warm up to normal operat-
ing temperature and engine idle. (4) Using vacuum line pliers, close off the vacuum
supply hose near the booster, but before the vacuum
gauge, then observe the vacuum gauge. If the vacuum drop exceeds 1.0 inch Hg (3.3 kPa)
in one minute, repeat the above steps to confirm the
reading. The vacuum loss should be less than 1.0
inch Hg in one minute time span. If the loss is more
than 1.0 inch Hg, replace the power brake booster. If
it is not, continue on with this test. (5) Remove the pliers from the hose temporarily.
Fig. 65 MASTER CYLINDER AND BOOSTER
1 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
2 - BOOSTER IDENTIFICATION LABEL
3 - FLUID LEVEL SWITCH CONNECTOR
4 - PRIMARY BRAKE TUBE NUT
5 - SECONDARY BRAKE TUBE NUT
6 - MASTER CYLINDER
5s - 44 BRAKESRS
POWER BRAKE BOOSTER (Continued)