torque CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1848 of 2585
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve is operated by the mechanical
shift linkage. Its primary responsibility is to send
line pressure to the appropriate hydraulic circuits
and solenoids. The valve has three operating ranges
or positions.
CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
The main responsibility of the converter clutch
switch valve is to control hydraulic pressure applied
to the front (off) side of the converter clutch piston.
Line pressure from the regulator valve is fed to the
torque converter regulator valve, where it passes
through the valve, and is slightly regulated. The
pressure is then directed to the converter clutch
switch valve and to the front side of the converter
clutch piston. This pressure pushes the piston back
and disengages the converter clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE
The converter clutch control valve controls the
back (on) side of the torque converter clutch. When
the PCM/TCM energizes or modulates the LR/CC
solenoid to apply the converter clutch piston, both
the converter clutch control valve and the converter
control valve move, allowing pressure to be applied to
the back side of the clutch.
T/C REGULATOR VALVE
The torque converter regulator valve slightly regu-
lates the flow of fluid to the torque converter.
LOW/REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
The low/reverse clutch is applied from different
sources, depending on whether low (1st) gear or
reverse is selected. The low/reverse switch valve
alternates positions depending on from which direc-
tion fluid pressure is applied. By design, when the
valve is shifted by fluid pressure from one channel,
the opposing channel is blocked. The switch valve
alienates the possibility of a sticking ball check, thus
providing consistent application of the low/reverse
clutch under all operating conditions.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If valve body is replaced or reconditioned,
the TCM Quick Learn Procedure must be per-
formed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect gearshift cable from manual valve
lever.
(3) Remove manual valve lever from manual shaft.
(4) Raise vehicle on hoist.
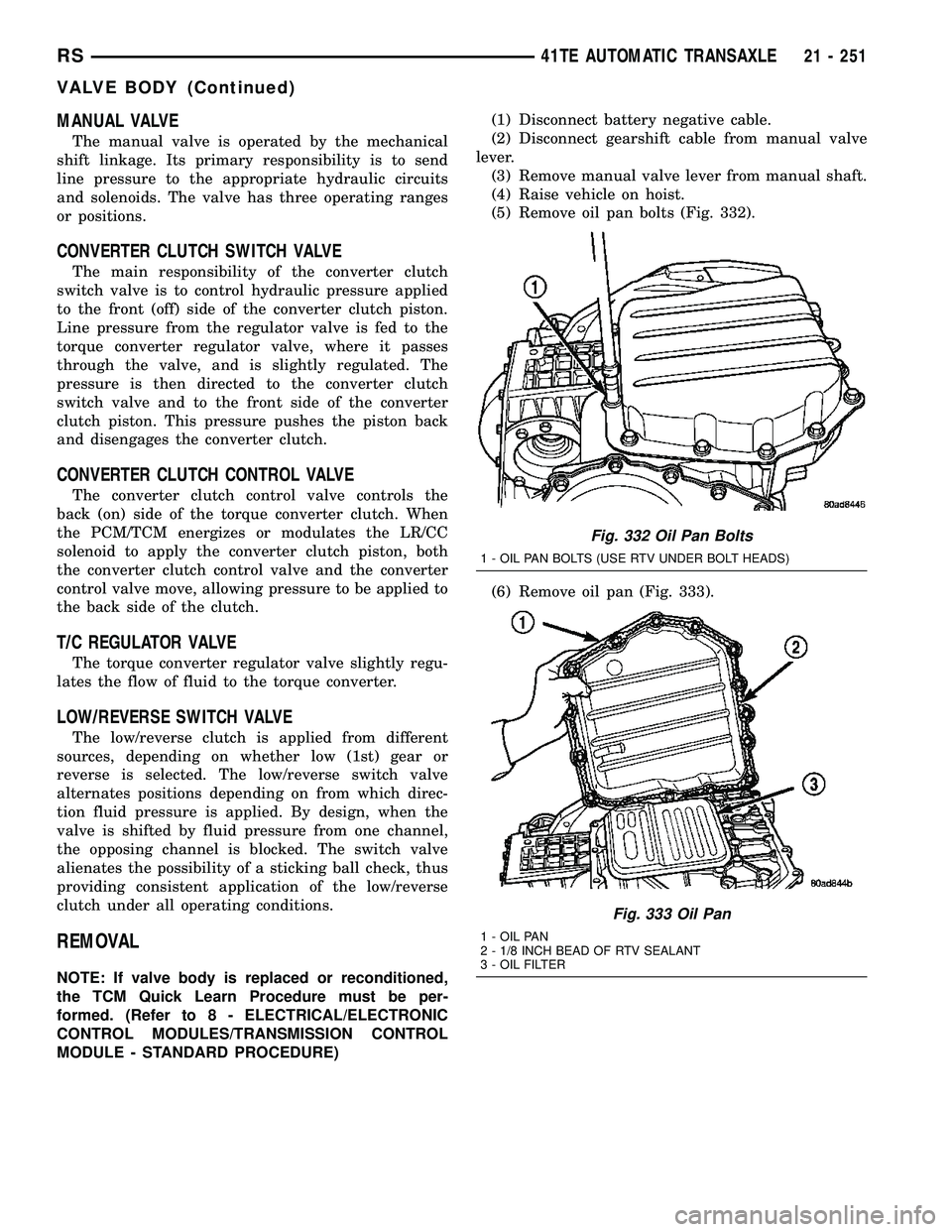
(5) Remove oil pan bolts (Fig. 332).
(6) Remove oil pan (Fig. 333).
Fig. 332 Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN BOLTS (USE RTV UNDER BOLT HEADS)
Fig. 333 Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF RTV SEALANT
3 - OIL FILTER
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 251
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1857 of 2585
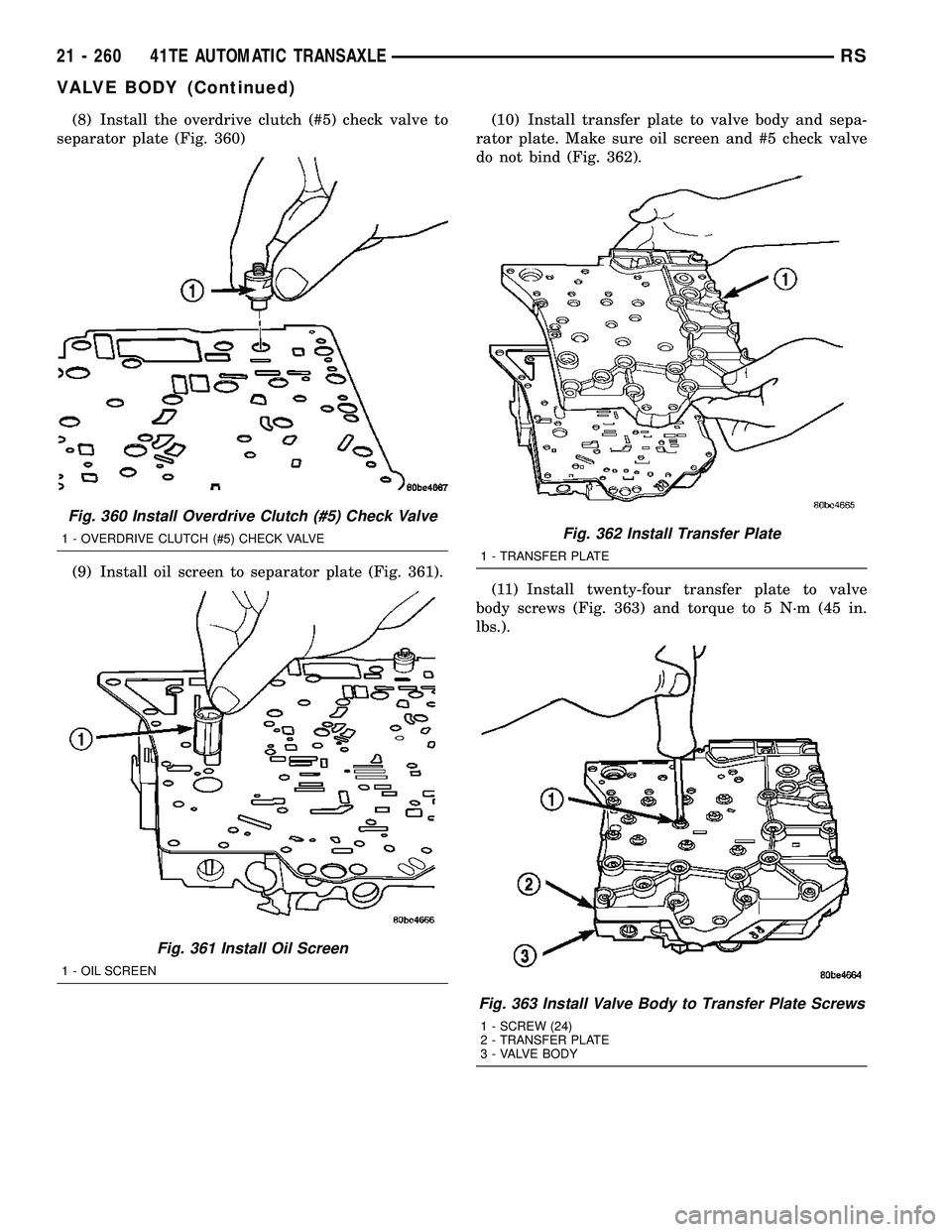
(8) Install the overdrive clutch (#5) check valve to
separator plate (Fig. 360)
(9) Install oil screen to separator plate (Fig. 361).(10) Install transfer plate to valve body and sepa-
rator plate. Make sure oil screen and #5 check valve
do not bind (Fig. 362).
(11) Install twenty-four transfer plate to valve
body screws (Fig. 363) and torque to 5 N´m (45 in.
lbs.).
Fig. 360 Install Overdrive Clutch (#5) Check Valve
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH (#5) CHECK VALVE
Fig. 361 Install Oil Screen
1 - OIL SCREEN
Fig. 362 Install Transfer Plate
1 - TRANSFER PLATE
Fig. 363 Install Valve Body to Transfer Plate Screws
1 - SCREW (24)
2 - TRANSFER PLATE
3 - VALVE BODY
21 - 260 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1858 of 2585
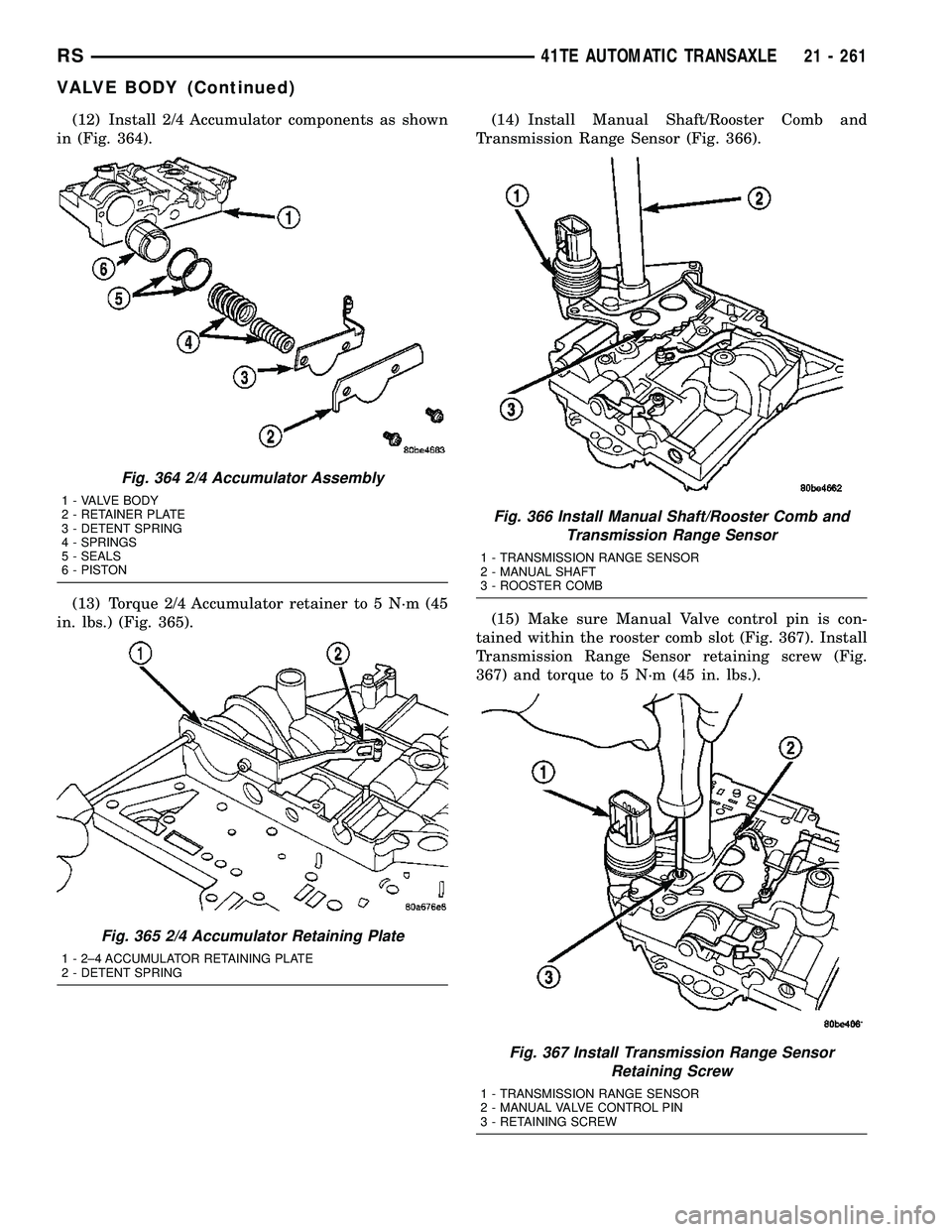
(12) Install 2/4 Accumulator components as shown
in (Fig. 364).
(13) Torque 2/4 Accumulator retainer to 5 N´m (45
in. lbs.) (Fig. 365).(14) Install Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor (Fig. 366).
(15) Make sure Manual Valve control pin is con-
tained within the rooster comb slot (Fig. 367). Install
Transmission Range Sensor retaining screw (Fig.
367) and torque to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.).
Fig. 364 2/4 Accumulator Assembly
1 - VALVE BODY
2 - RETAINER PLATE
3 - DETENT SPRING
4 - SPRINGS
5 - SEALS
6 - PISTON
Fig. 365 2/4 Accumulator Retaining Plate
1 - 2±4 ACCUMULATOR RETAINING PLATE
2 - DETENT SPRING
Fig. 366 Install Manual Shaft/Rooster Comb and
Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
3 - ROOSTER COMB
Fig. 367 Install Transmission Range Sensor
Retaining Screw
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 261
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1859 of 2585
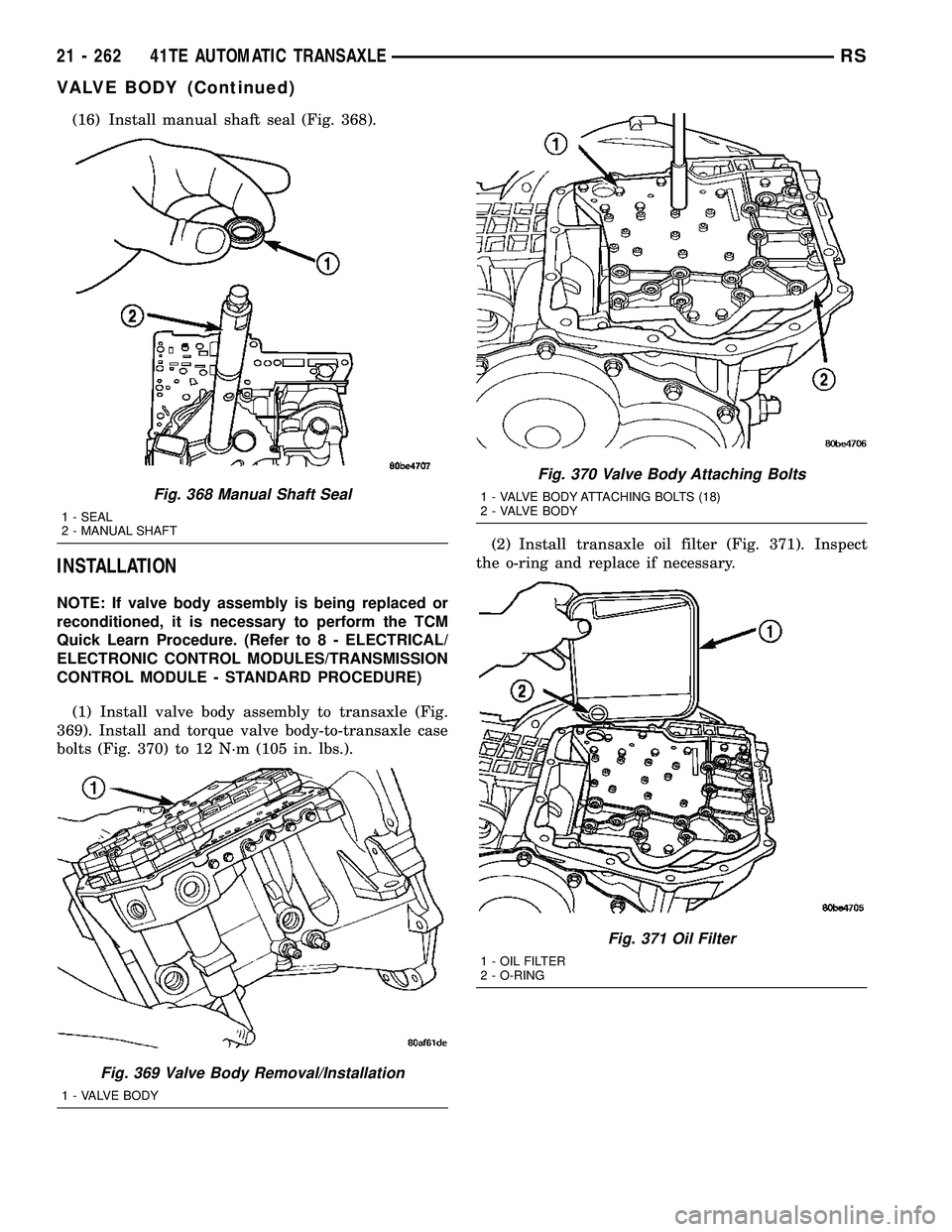
(16) Install manual shaft seal (Fig. 368).
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If valve body assembly is being replaced or
reconditioned, it is necessary to perform the TCM
Quick Learn Procedure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Install valve body assembly to transaxle (Fig.
369). Install and torque valve body-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 370) to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).(2) Install transaxle oil filter (Fig. 371). Inspect
the o-ring and replace if necessary.
Fig. 368 Manual Shaft Seal
1 - SEAL
2 - MANUAL SHAFT
Fig. 369 Valve Body Removal/Installation
1 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 370 Valve Body Attaching Bolts
1 - VALVE BODY ATTACHING BOLTS (18)
2 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 371 Oil Filter
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
21 - 262 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1860 of 2585
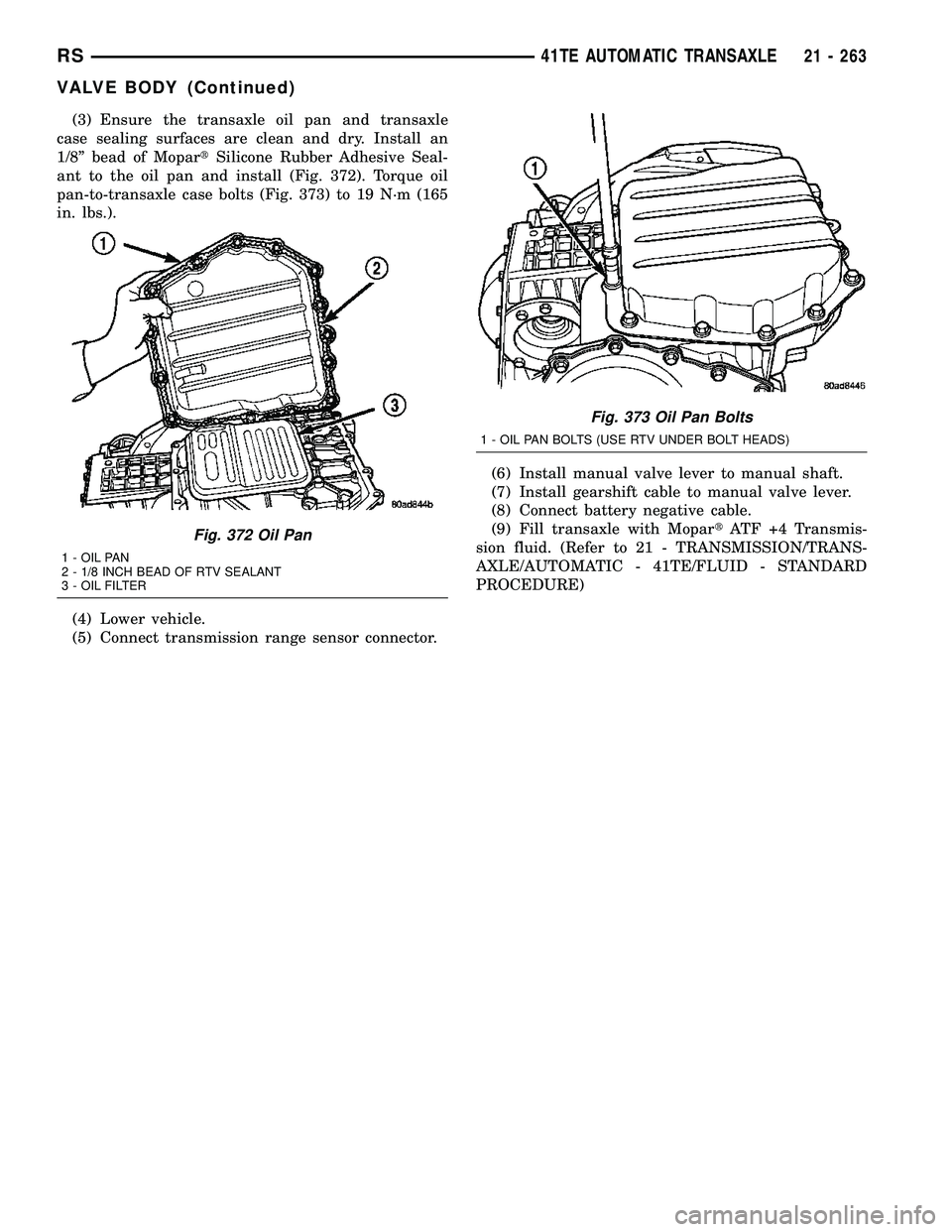
(3) Ensure the transaxle oil pan and transaxle
case sealing surfaces are clean and dry. Install an
1/8º bead of MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant to the oil pan and install (Fig. 372). Torque oil
pan-to-transaxle case bolts (Fig. 373) to 19 N´m (165
in. lbs.).
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect transmission range sensor connector.(6) Install manual valve lever to manual shaft.
(7) Install gearshift cable to manual valve lever.
(8) Connect battery negative cable.
(9) Fill transaxle with MopartATF +4 Transmis-
sion fluid. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
Fig. 372 Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF RTV SEALANT
3 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 373 Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN BOLTS (USE RTV UNDER BOLT HEADS)
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 263
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1869 of 2585
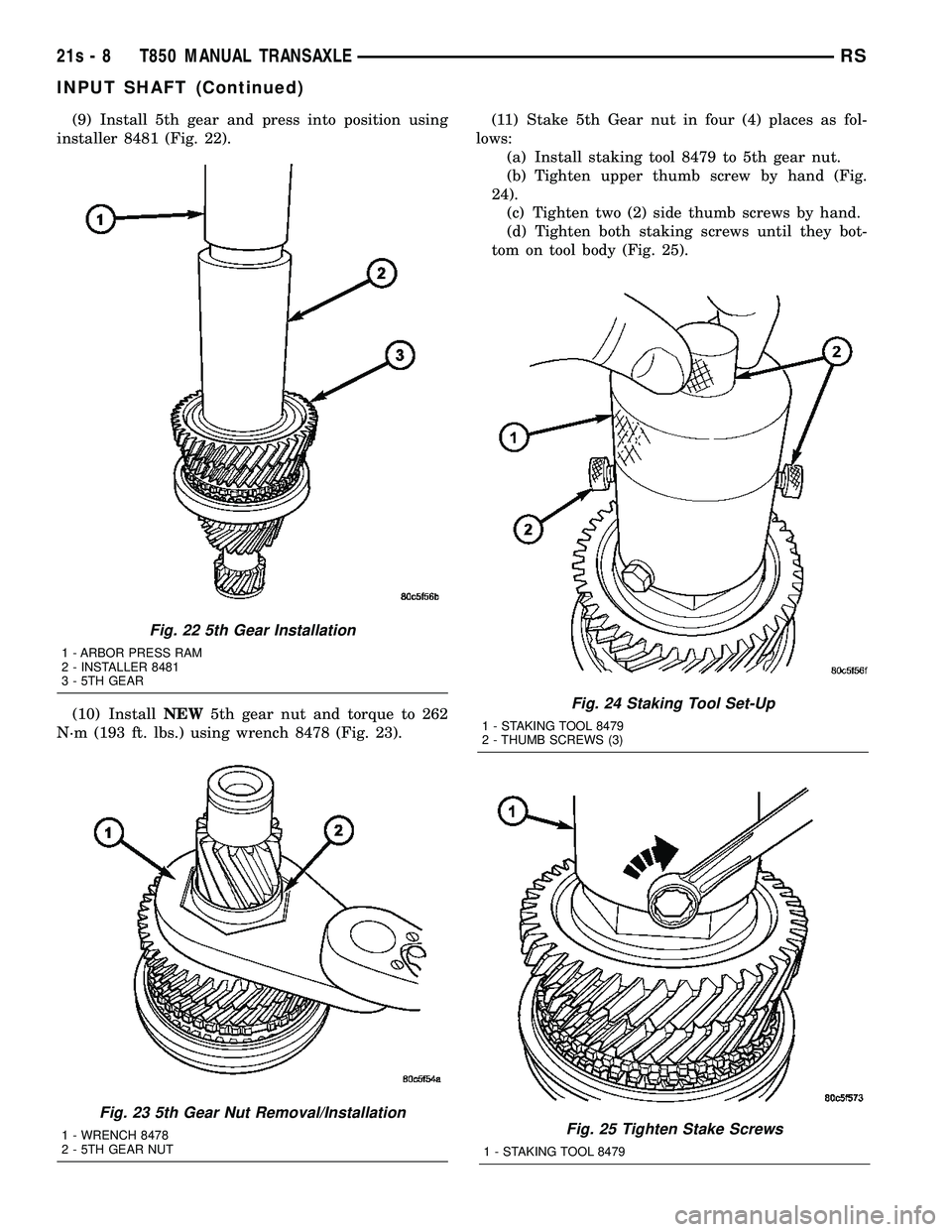
(9) Install 5th gear and press into position using
installer 8481 (Fig. 22).
(10) Install NEW5th gear nut and torque to 262
N´m (193 ft. lbs.) using wrench 8478 (Fig. 23). (11) Stake 5th Gear nut in four (4) places as fol-
lows: (a) Install staking tool 8479 to 5th gear nut.
(b) Tighten upper thumb screw by hand (Fig.
24). (c) Tighten two (2) side thumb screws by hand.
(d) Tighten both staking screws until they bot-
tom on tool body (Fig. 25).
Fig. 24 Staking Tool Set-Up
1 - STAKING TOOL 8479
2 - THUMB SCREWS (3)
Fig. 25 Tighten Stake Screws
1 - STAKING TOOL 8479
Fig. 22 5th Gear Installation
1 - ARBOR PRESS RAM
2 - INSTALLER 8481
3 - 5TH GEAR
Fig. 23 5th Gear Nut Removal/Installation
1 - WRENCH 8478
2 - 5TH GEAR NUT
21s - 8 T850 MANUAL TRANSAXLERS
INPUT SHAFT (Continued)
Page 1885 of 2585

40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE DESCRIPTION .........................25
OPERATION ...........................27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4XTETRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS .......27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST . . . 27
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS ....................28
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR PRESSURE TESTS ....................30
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE . . . 31
REMOVAL .............................31
DISASSEMBLY .........................34
ASSEMBLY ............................51
INSTALLATION .........................73
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS 4XTE TRANSAXLE HYDRAULICSCHEMATICS ........................75
SPECIFICATIONS - 41TE TRANSAXLE .......87
SPECIAL TOOLS .......................89
ACCUMULATOR DESCRIPTION .........................94
OPERATION ...........................94
DRIVING CLUTCHES DESCRIPTION .........................95
OPERATION ...........................95
FINAL DRIVE DESCRIPTION .........................95
OPERATION ...........................96
DISASSEMBLY .........................96
ASSEMBLY ............................99
ADJUSTMENTS DIFFERENTIAL BEARING PRELOADMEASUREMENT AND ADJUSTMENT ......100
FLUID STANDARD PROCEDURE FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK . . . 102
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID ANDFILTER SERVICE .....................104
GEAR SHIFT CABLE REMOVAL ............................105
HOLDING CLUTCHES DESCRIPTION ........................106
OPERATION ..........................106
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY DISASSEMBLY ........................107
ASSEMBLY ...........................116 OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION ........................131
OPERATION ..........................131
DISASSEMBLY ........................131
ASSEMBLY ...........................132
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN DESCRIPTION ........................132
OPERATION ..........................132
SEAL - OIL PUMP REMOVAL ............................133
INSTALLATION ........................133
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID DESCRIPTION ........................133
OPERATION ..........................134
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/ TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID ..........................135
REMOVAL ............................135
INSTALLATION ........................136
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY DESCRIPTION ........................137
OPERATION ..........................137
REMOVAL ............................138
INSTALLATION ........................139
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT DESCRIPTION ........................140
OPERATION ..........................140
REMOVAL ............................141
INSTALLATION ........................141
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT DESCRIPTION ........................142
OPERATION ..........................142
REMOVAL ............................143
INSTALLATION ........................143
TORQUE CONVERTER DESCRIPTION ........................144
OPERATION ..........................148
REMOVAL ............................149
INSTALLATION ........................149
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY DESCRIPTION ........................150
OPERATION ..........................150
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR DESCRIPTION ........................150
OPERATION ..........................151
REMOVAL ............................151
INSTALLATION ........................152
VALVE BODY DESCRIPTION ........................152
21s - 24 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1886 of 2585
OPERATION..........................152
REMOVAL ............................153
DISASSEMBLY ........................155 ASSEMBLY
...........................159
INSTALLATION ........................164
40TE AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION
The 40TE (Fig. 1) is a four-speed transaxle that is
a conventional hydraulic/mechanical assembly with an integral differential, and is controlled with adap-
tive electronic controls and monitors. The hydraulic
system of the transaxle consists of the transaxle
fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic valves, and various
line pressure control components. An input clutch
assembly which houses the underdrive, overdrive,
and reverse clutches is used. It also utilizes separate
Fig. 1 40TE Automatic Transaxle
1 - TRANSAXLE CASE 7 - REVERSE CLUTCH 13 - OUTPUT SHAFT GEAR
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER 8 - FRONT PLANET CARRIER 14 - TRANSFER SHAFT GEAR
3 - OIL PUMP 9 - 2/4 CLUTCH 15 - TRANSFER SHAFT
4 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR 10 - L/R CLUTCH 16 - DIFFERENTIAL
5 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH 11 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR 17 - CONVERTER DRIVE PLATE
6 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH 12 - REAR PLANET CARRIER/OUTPUT
SHAFT18 - INPUT SHAFT
RS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s-25
Page 1888 of 2585
OPERATION
Transmission output is directed to an integral dif-
ferential by a transfer gear system in the following
input-to-output ratios:
First ............................... 2.84 : 1
Second ............................. 1.57 : 1
Third .............................. 1.00 : 1
Overdrive ........................... 0.69 : 1
Reverse ............................ 2.21 : 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 4XTE TRANSAXLE
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
NOTE: Before attempting any repair on a 4XTE four-
speed automatic transaxle, check for diagnostic trou-
ble codes (DTC's) using the DRB scan tool. Refer to
the Transmission Diagnostic Procedures Manual.
Transaxle malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions: ² Poor engine performance
² Improper adjustments
² Hydraulic malfunctions
² Mechanical malfunctions
² Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin by
checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level and
condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then perform a
road test to determine if the problem has been corrected
or that more diagnosis is necessary. If the problem per-
sists after the preliminary tests and corrections are com-
pleted, hydraulic pressure checks should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, verify that the
fluid level, fluid condition, and linkage adjustment
have been approved. During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting. If the vehicle operates properly at highway speeds,
but has poor acceleration, the converter stator over-
running clutch may be slipping. If acceleration is nor-
mal, but high throttle opening is needed to maintain
highway speeds, the converter stator clutch may
have seized. Both of these stator defects require
replacement of the torque converter and thorough
transaxle cleaning. Slipping clutches can be isolated by comparing the
ªElements in Useº chart with clutch operation
encountered on a road test. This chart identifies
which clutches are applied at each position of the
selector lever.
A slipping clutch may also set a DTC and can be deter-
mined by operating the transaxle in all selector positions.
ELEMENTS IN USE AT EACH POSITION OF SELECTOR LEVER
Shift Lever Position INPUT CLUTCHES HOLDING CLUTCHES
Underdrive Overdrive Reverse 2/4 Low/Reverse
P - PARK X
R - REVERSE X X N - NEUTRAL X
OD - OVERDRIVE
First X X
Second X X Direct X X
Overdrive X X
D - DRIVE*
First X X
Second X X Direct X X
L - LOW*
First X X
Second X X
Direct X X
* Vehicle upshift and downshift speeds are increased when in these selector positions.
RS 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21s-27
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1889 of 2585
The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit which slips and to confirm proper operation
of good units. Road test analysis can diagnose slip-
ping units, but the cause of the malfunction cannot
be determined. Practically any condition can be
caused by leaking hydraulic circuits or sticking
valves.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the
diagnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most hydraulic transaxle problems. Before performing pressure tests, be certain that
fluid level and condition, and shift cable adjustments
have been checked and approved. Fluid must be at
operating temperature (150 to 200 degrees F.). Install an engine tachometer, raise vehicle on hoist
which allows front wheels to turn, and position
tachometer so it can be read. Attach 300 psi gauge (C-3293SP) to port(s)
required for test(s) being conducted. Use adapter set
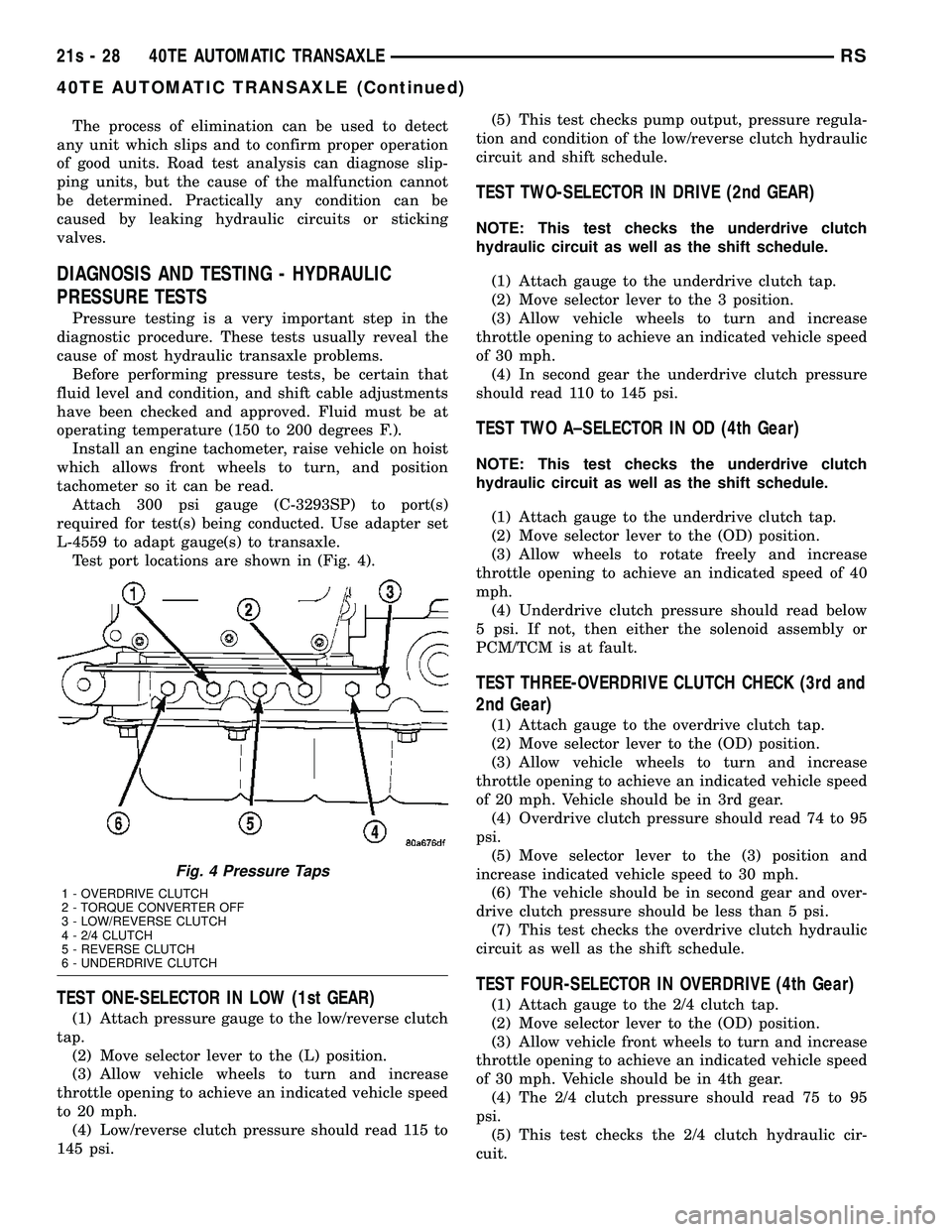
L-4559 to adapt gauge(s) to transaxle. Test port locations are shown in (Fig. 4).
TEST ONE-SELECTOR IN LOW (1st GEAR)
(1) Attach pressure gauge to the low/reverse clutch
tap. (2) Move selector lever to the (L) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
to 20 mph. (4) Low/reverse clutch pressure should read 115 to
145 psi. (5) This test checks pump output, pressure regula-
tion and condition of the low/reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit and shift schedule.
TEST TWO-SELECTOR IN DRIVE (2nd GEAR)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the 3 position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph. (4) In second gear the underdrive clutch pressure
should read 110 to 145 psi.
TEST TWO A±SELECTOR IN OD (4th Gear)
NOTE: This test checks the underdrive clutch
hydraulic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow wheels to rotate freely and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated speed of 40
mph. (4) Underdrive clutch pressure should read below
5 psi. If not, then either the solenoid assembly or
PCM/TCM is at fault.
TEST THREE-OVERDRIVE CLUTCH CHECK (3rd and
2nd Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the overdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 20 mph. Vehicle should be in 3rd gear. (4) Overdrive clutch pressure should read 74 to 95
psi. (5) Move selector lever to the (3) position and
increase indicated vehicle speed to 30 mph. (6) The vehicle should be in second gear and over-
drive clutch pressure should be less than 5 psi. (7) This test checks the overdrive clutch hydraulic
circuit as well as the shift schedule.
TEST FOUR-SELECTOR IN OVERDRIVE (4th Gear)
(1) Attach gauge to the 2/4 clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the (OD) position.
(3) Allow vehicle front wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 30 mph. Vehicle should be in 4th gear. (4) The 2/4 clutch pressure should read 75 to 95
psi. (5) This test checks the 2/4 clutch hydraulic cir-
cuit.
Fig. 4 Pressure Taps
1 - OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER OFF
3 - LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
4 - 2/4 CLUTCH
5 - REVERSE CLUTCH
6 - UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
21s - 28 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)