coolant level CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1380 of 2585

(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.(4) Remove the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay from
the PDC.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gauge adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer (Special Tool CH7059) with cable adap-
tors to the DRBIIIt. For Special Tool identification,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIAL TOOLS).
(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gauge. Record this pressure as #1 cylin-
der pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE PRESSURE CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the pressure cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-83
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1435 of 2585

OIL COOLER & LINES
DESCRIPTION
An engine oil cooler is used on 3.3/3.8L engines
(Heavy Duty Cooling Only) (Fig. 98). The cooler is a
coolant-to-oil type and mounted between the oil filter
and engine block.
OPERATION
Engine oil travels from the oil filter and into the
oil cooler. Engine oil then exits the cooler into the
main gallery. Engine coolant flows into the cooler
from the heater return tube and exits into the water
pump inlet.
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COOLING SYSTEM
DRAINING).
(2) Disconnect oil cooler inlet and outlet hoses
(Fig. 97).
(3) Remove oil filter.
(4) Remove oil cooler attachment fitting (Fig. 98).
(5) Remove oil cooler.
INSTALLATION
(1) Lubricate seal and position oil cooler to connec-
tor fitting on oil filter adapter (Fig. 98).NOTE: Position the flat side of oil cooler parallel to
oil pan rail.
(2) Install oil cooler attachment fitting and tighten
to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 98).
(3) Install oil filter.
(4) Connect oil cooler inlet and outlet hoses (Fig.
97).
Fig. 96 Engine Oil Level Dipstick and Fill Locations
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER 3 - ENGINE OIL LEVEL DIPSTICK
2 - ENGINE OIL FILL CAP 4 - RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP
Fig. 97 Engine Oil Cooler Hoses
1 - OIL COOLER INLET TUBE
2 - INLET HOSE
3 - OIL COOLER OUTLET TUBE
4 - OUTLET HOSE
5 - WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
9 - 138 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
OIL (Continued)
Page 1721 of 2585

TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
²Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 8).
²Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: If transaxle assembly is being replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perform the TCM Quick Learn Proce-
dure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield (Fig. 9).
(3) Remove coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove fluid level indicator/tube assembly.
Plug opening to prevent debris from entering trans-
axle.
(5) Using a blade or suitable hose cutter, cut trans-
axle oil cooler lines off flush with fittings. Plug lines
and fittings to prevent debris from entering transaxle
or cooler circuit. A service splice kit will be installed
upon reassembly.
(6) Disconnect input and output shaft speed sensor
connectors (Fig. 11).
(7) Disconnect transmission range sensor (TRS)
connector (Fig. 11).
(8) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 11).
Fig. 8 Converter Leak Points - Typical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
Fig. 9 Battery Thermal Guard
1 - BATTERY THERMOWRAP (IF EQUIPPED)
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
Fig. 10 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - UPPER BOLT ATTACHING TO BATTERY TRAY
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
3 - UPPER BOLT
4 - HOSE
5 - LOWER BOLT (QTY. 2)
6 - LEFT SIDE FRAME RAIL
21 - 124 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1765 of 2585

(20) Connect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
(Fig. 166).
(21) Connect transmission range sensor connector
(Fig. 166).
(22) Connect input and output speed sensor con-
nectors (Fig. 166).
(23) Remove plugs and install transaxle oil cooler
line service splice kit. Refer to instructions included
with kit.
(24) Remove plug and Install fluid level indicator/
tube assembly.(25) Install coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 167).
(26) Install battery shield.
(27) Connect battery cables.
(28) Fill transaxle with suitable amount of ATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602). (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 166 Component Connector Location - Typical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 167 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - UPPER BOLT ATTACHING TO BATTERY TRAY
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
3 - UPPER BOLT
4 - HOSE
5 - LOWER BOLT (QTY. 2)
6 - LEFT SIDE FRAME RAIL
21 - 168 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1893 of 2585
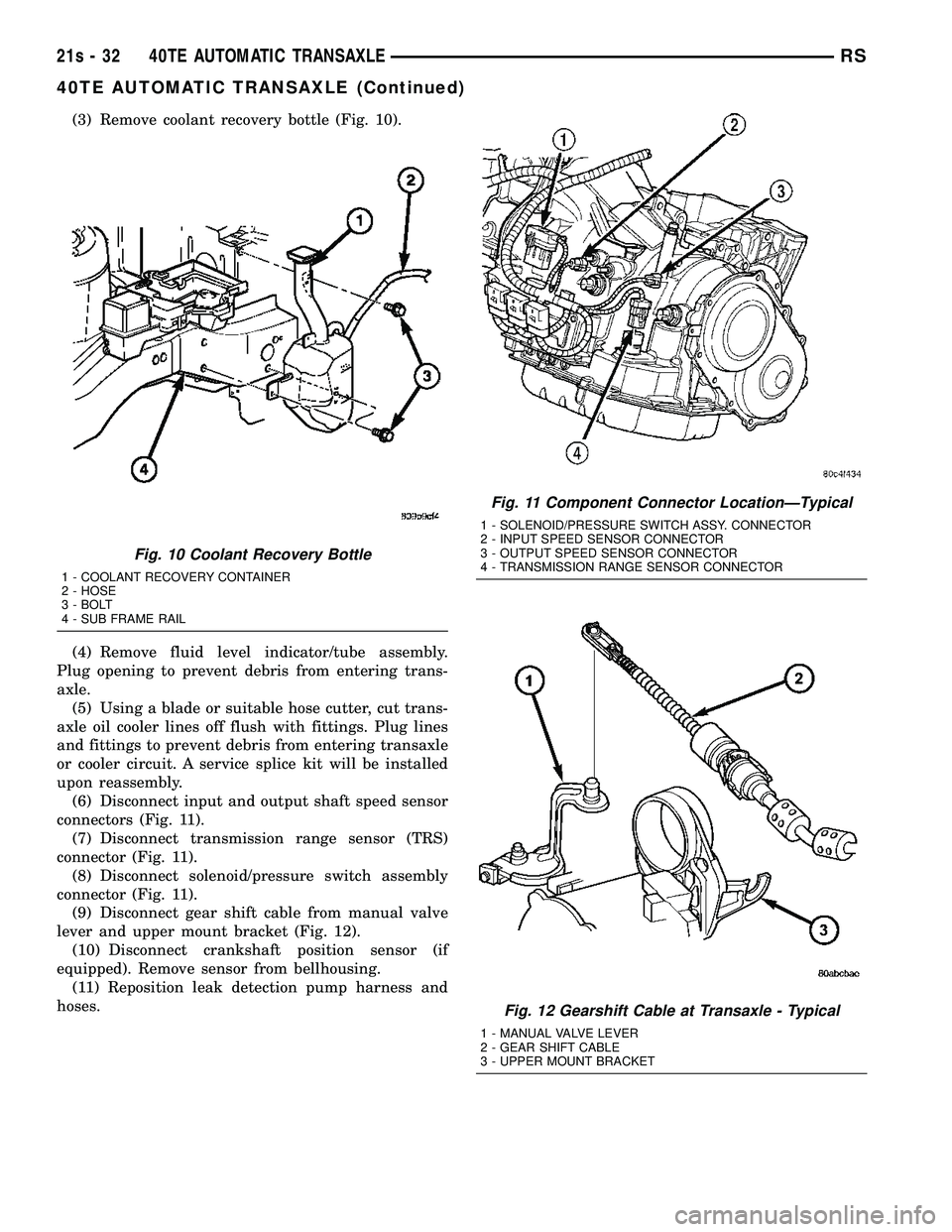
(3) Remove coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove fluid level indicator/tube assembly.
Plug opening to prevent debris from entering trans-
axle. (5) Using a blade or suitable hose cutter, cut trans-
axle oil cooler lines off flush with fittings. Plug lines
and fittings to prevent debris from entering transaxle
or cooler circuit. A service splice kit will be installed
upon reassembly. (6) Disconnect input and output shaft speed sensor
connectors (Fig. 11). (7) Disconnect transmission range sensor (TRS)
connector (Fig. 11). (8) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 11). (9) Disconnect gear shift cable from manual valve
lever and upper mount bracket (Fig. 12). (10) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor (if
equipped). Remove sensor from bellhousing. (11) Reposition leak detection pump harness and
hoses.
Fig. 10 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
2 - HOSE
3 - BOLT
4 - SUB FRAME RAIL
Fig. 11 Component Connector LocationÐTypical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 12 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
21s - 32 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1935 of 2585
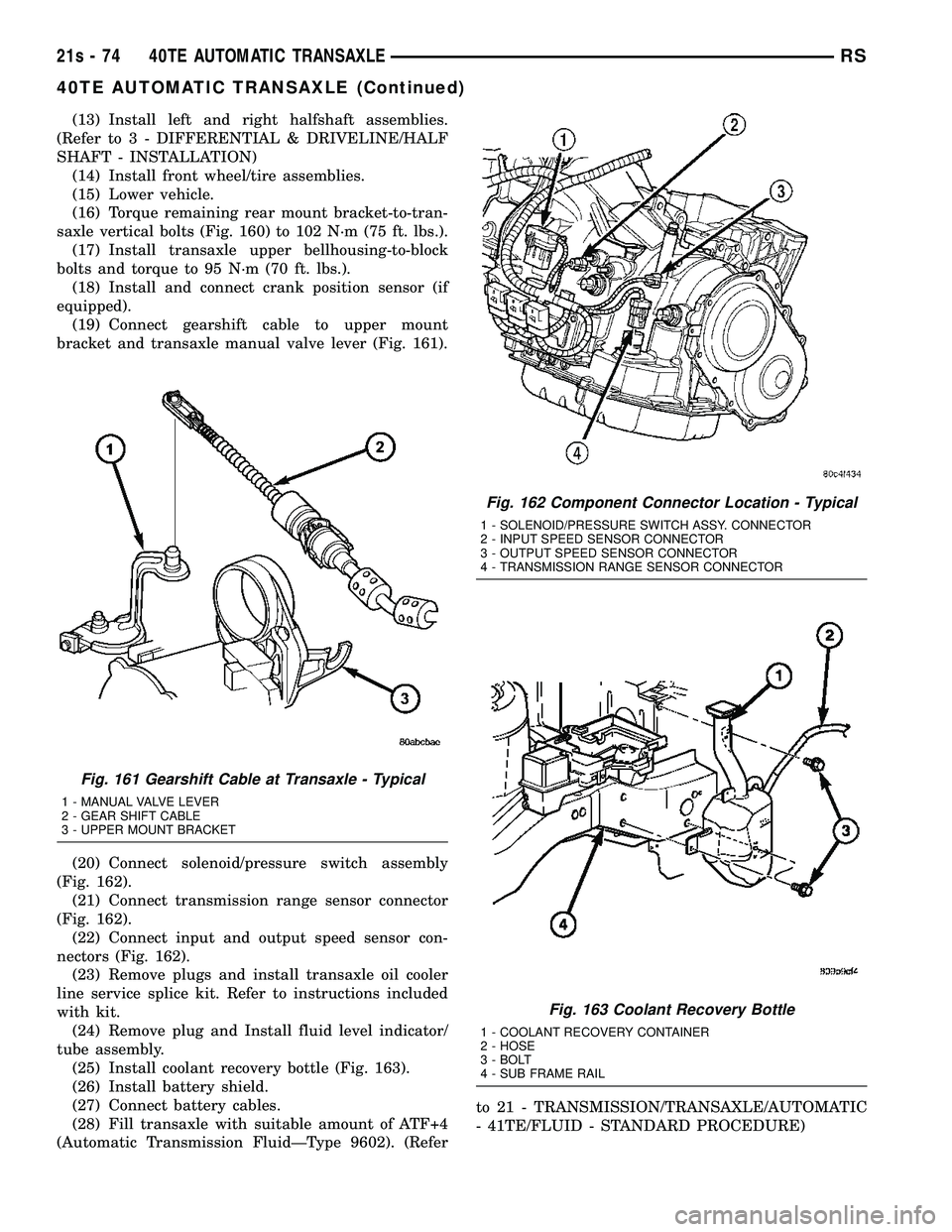
(13) Install left and right halfshaft assemblies.
(Refer t o 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF
SHAFT - INSTALLATION) (14) Install front wheel/tire assemblies.
(15) Lower vehicle.
(16) Torque remaining rear mount bracket-to-tran-
saxle vertical bolts (Fig. 160) to 102 N´m (75 ft. lbs.). (17) Install transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts and torque to 95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.). (18) Install and connect crank position sensor (if
equipped). (19) Connect gearshift cable to upper mount
bracket and transaxle manual valve lever (Fig. 161).
(20) Connect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
(Fig. 162). (21) Connect transmission range sensor connector
(Fig. 162). (22) Connect input and output speed sensor con-
nectors (Fig. 162). (23) Remove plugs and install transaxle oil cooler
line service splice kit. Refer to instructions included
with kit. (24) Remove plug and Install fluid level indicator/
tube assembly. (25) Install coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 163).
(26) Install battery shield.
(27) Connect battery cables.
(28) Fill transaxle with suitable amount of ATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602). (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 161 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
Fig. 162 Component Connector Location - Typical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 163 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
2 - HOSE
3 - BOLT
4 - SUB FRAME RAIL
21s - 74 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 2396 of 2585

HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLING
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS...............1
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................1
DESCRIPTION - SINGLE ZONE...........2
DESCRIPTION - DUAL ZONE.............2
DESCRIPTION - MANUAL THREE ZONE.....2
DESCRIPTION - AUTOMATIC THREE ZONE . . 3
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................4
OPERATION - SINGLE ZONE.............4
OPERATION - DUAL ZONE...............5
OPERATION - MANUAL THREE ZONE......5
OPERATION - THREE ZONE ATC..........5DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C COOL
DOWN TEST..........................6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE TEST..................7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE TEST.................10
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C SYSTEM.........................11
CONTROLS - FRONT.....................14
CONTROLS - REAR......................34
DISTRIBUTION - FRONT...................43
DISTRIBUTION - REAR....................56
PLUMBING - FRONT.....................64
PLUMBING - REAR......................97
CABIN HEATER........................112
HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS
To maintain the performance level of the heating,
ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) system, the
engine cooling system must be properly maintained.
The use of a bug screen is not recommended. Any
obstructions in front of the radiator or condenser will
reduce the performance of the air conditioning and
engine cooling systems.
The engine cooling system includes the radiator,
thermostat, radiator hoses and the engine coolant
pump. Refer to Cooling for more information before
opening or attempting any service to the engine cool-
ing system.
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER
A manually controlled single zone type heating-air
conditioning system, manually controlled dual zone
type heating-air conditioning system, manually con-
trolled three zone type heating-air conditioning sys-
tem or an automatic controlled three zone typeheating-air conditioning system is available on this
model.
All vehicles are equipped with a common heater,
ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) housing (Fig.
1). The system combines air conditioning, heating,
and ventilating capabilities in a single unit housing
mounted within the passenger compartment under
the instrument panel. The HVAC housing includes:
²Blower motor
²Blower motor resistor block or power module
(depending on application)
²Heater core
²Evaporator coil
²Blend door and actuator
²Mode door and actuator
²Recirculation door and actuator
Based upon the system and mode selected, condi-
tioned air can exit the HVAC housing through one or
a combination of the three main housing outlets:
defrost, panel or floor. The defrost and panel outlets
are located on the top of the housing and the floor
outlet is located on the bottom of the housing. Once
the conditioned air exits the unit housing, it is fur-
ther directed through molded plastic ducts to the var-
ious outlets in the vehicle interior. These outlets and
their locations are as follows:
²Defroster Outlet- A single large defroster out-
let is located in the center of the instrument panel
top cover, near the base of the windshield.
²Side Window Demister Outlets- There are
two side window demister outlets, one is located at
RSHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24-1
Page 2398 of 2585

REAR CONTROL PANEL
The rear A/C-heater control centrally mounted in
the headliner allows intermediate seat passengers to
adjust rear air distribution, temperature and blower
motor speed when the center knob on the front A/C-
heater control is set to the Rear position. The rear
A/C-heater control contains:
²a rotary adjustment knob for temperature.
²a rotary adjustment for fan speed control.
DESCRIPTION - AUTOMATIC THREE ZONE
The automatic temperature control (ATC), three
zone, front and rear heating and air conditioning sys-
tem allows both the driver and front occupants and
the rear intermediate occupants to select individual
comfort temperatures.
NOTE: Individual comfort temperatures are the per-
ceived temperature level at the individual seating
areas, NOT the actual passenger compartment air
temperature.
The ATC system includes a particulate air filter.
The filter element is the same size as the air condi-
tioning evaporator to ensure ample capacity. A door
at the base of the HVAC housing below the glove box
provides easy access to the filter element.
The ATC computer utilizes integrated circuitry and
information carried on the programmable communi-
cations interface (PCI) data bus network to monitor
many sensors and switch inputs throughout the vehi-
cle. In response to those inputs, the internal circuitry
and programming of the ATC computer allow it to
control electronic functions and features of the ATC
system. The inputs to the ATC computer are:
²Vehicle Speed/Engine RPM± The ATC com-
puter monitors engine rpm, vehicle speed and mani-
fold absolute pressure information from the
powertrain control module (PCM).
²Coolant Temperature± ATC computer moni-
tors coolant temperature received from the PCM and
converts it to degrees Fahrenheit.
²Ambient Temperature± ATC computer moni-
tors ambient temperature from the compass mini trip
computer (CMTC) and converts it to degrees Fahren-
heit.
²Engine Miscellaneous Sensor Status±ATC
computer monitors A/C disable information from the
PCM.
²Refrigerant Pressure± ATC computer moni-
tors barometric pressure, intake air temperature,
high side pressure and methanol content as broad-
cast by the PCM.
²Door Ajar Status± The ATC computer moni-
tors driver front door, passenger front door, left rear
door, right rear door and liftgate ajar information, asidentified by the body control module (BCM), to
determine if all in-car temperatures should be main-
tained.
²Dimming± The ATC computer monitors dim-
ming status from the BCM to determine the required
level of brightness and will dim accordingly.
²Vehicle Odometer± The ATC computer moni-
tors the vehicle odometer information from the BCM
to prevent flashing the vacuum-flourescent (VF) dig-
ital display icons if the manual motor calibration or
manual cool down tests have failed. Flashing of the
display icons will cease when the vehicle odometer is
greater than 3 miles.
²English/Metric± The ATC computer monitors
the English/Metric information broadcast by the
CMTC. The set temp displays for both the front and
rear control heads will be set accordingly.
²Vehicle Identification Number± The ATC
computer monitors the last eight characters of the
VIN broadcast by the PCM and compares it to the
information stored in EEPROM. If it is different, the
new number will be stored over the old one and a
motor calibration shall be initiated.
²A/C System Information± The ATC computer
will send a message for evaporator temperature too
low, fan blower relay status, evaporator sensor fail-
ure, rear window defogger relay and A/C select.
FRONT CONTROL PANEL
The front A/C-heater control and integral computer
is mounted in the instrument panel and contains:
²a power button which allows the system to be
completely turned off. The display is blank when the
system is off.
²a rocker switch that selects a cool-down rate.
LO-AUTO or HI-AUTO are displayed when the sys-
tem is in automatic operation.
²three rocker switches that select comfort temper-
atures from 15É to 30É C (59É to 85É F), which are
shown in the VF digital display. If the set temp is 15É
C (59É F) and the down button is pressed, the set
temp value will become 13É C (55É F) but the display
will show LO. If the set temp is 29É C (85É F) and the
up button is pressed, the set temp value will become
32É C (90É F) but the display will show HIGH. Tem-
peratures can be displayed in either metric or Fahr-
enheit, which is controlled from the overhead console.
²an air conditioning button that allows the com-
pressor to be turned off. A Snowflake symbol is illu-
minated when air conditioning is on, whether under
manual or automatic control.
²an air recirculation button. A Recirculation sym-
bol appears in the display when the button is
pressed, or when the system exceeds 80 percent cir-
culated air under automatic control due to high air
conditioning demand.
RSHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING24-3
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2405 of 2585

Condition Possible Causes Correction
The low side pressure is too
low, and the high side
pressure is too high.1. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the refrigerant lines.1. See Liquid Line, Suction Line and Discharge
Line in this group. Inspect the refrigerant lines for
kinks, tight bends or improper routing. Correct
the routing or replace the refrigerant line, if
required.
2. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the A/C expansion
valve.2. See A/C Expansion Valve in this group.
Replace the valve, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the A/C condenser.3. See A/C Condenser in this group. Replace the
restricted condenser, if required.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE TEST
WARNING: REVIEW SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND
WARNINGS IN THIS GROUP BEFORE PERFORMING
THIS PROCEDURE (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - WARNING).
Check the coolant level, drive belt tension, radiator
air flow and fan operation. Start engine and allow to
warm up to normal operating temperature.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE RADIATOR CAP
WHEN ENGINE IS HOT, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
If vehicle has been run recently, wait 15 minutes
before removing the radiator cap. Place a rag overthe cap and turn it to the first safety stop. Allow
pressure to escape through the overflow tube. When
the system pressure stabilizes, remove the cap com-
pletely.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT: TEST AND ACTION
Engine coolant is provided to the heater system by
two heater hoses. With the engine idling at normal
operating temperature, set the temperature control
to maximum heat, the mode control to the floor posi-
tion, and the blower in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged from the floor outlets. Com-
pare the test thermometer reading to the Tempera-
ture Reference chart.
TEMPERATURE REFERENCE
Ambient Temperature Minimum Floor Outlet Temperature
Celsius Fahrenheit Celsius Fahrenheit
15.5É 60É 62.2É 144É
21.1É 70É 63.8É 147É
26.6É 80É 65.5É 150É
32.2É 90É 67.2É 153É
If the floor outlet air temperature is insufficient,
check that the cooling system is operating to specifi-
cations (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE - DIAGNO-
SIS AND TESTING). Both heater hoses should be
HOT to the touch (the coolant return hose should be
slightly cooler than the supply hose). If the coolant
return hose is much cooler than the supply hose,
locate and repair the engine coolant flow obstruction
in heater system.OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW Possible locations or causes
of obstructed coolant flow are as follows:
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²Plugged heater core.
If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is insuffi-
cient, a mechanical problem may exist.
24 - 10 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGRS
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2496 of 2585

(4) Install the two screws that secure the rear A/C
expansion valve to the evaporator tube sealing plate.
Tighten the screws to 11 N´m (97 in. lbs.).
(5) Install the rear evaporator line extension onto
the expansion valve (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING/PLUMBING - REAR/EVAPORA-
TOR - INSTALLATION - EVAPORATOR LINE
EXTENSION).
(6) Install the foam insulator wrap over the rear
expansion valve.
(7) Install the rear HVAC housing (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/DISTRIBUTION/
HVAC HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
(8) Run the HVAC Cooldown Test to verify proper
operation.
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION
The rear heater core is located near the front of
the rear HVAC housing, behind the right rear wheel
house. It is a heat exchanger made of rows of tubes
and fins. One end of the core is fitted with a molded
plastic tank that includes integral heater core inlet
and outlet nipples. The rear heater core can be ser-
viced without removing the rear HVAC housing from
the vehicle.
OPERATION
Engine coolant is circulated through underbody
heater hoses to the rear heater core at all times. As
the coolant flows through the rear heater core, heat
removed from the engine is transferred to the heater
core fins and tubes. Air directed through the heater
core picks up the heat from the heater core fins. The
rear blend door allows control of the rear heater out-
put air temperature by controlling how much of the
air flowing through the rear HVAC housing is
directed through the heater core.
The rear heater core cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REAR HEATER
CORE FILLING
In its final installed position, the rear heater core
is positioned higher than the radiator fill cap. There-
fore, when the cooling system is drained and refilled,
gravity will not refill the heater core with coolant to
the proper level. This may result in two problems:1.
Insufficient coolant level in the engine cooling sys-
tem, which may result in engine overheating.2.Air
entrapped within the rear heater core, which may
result in insufficient rear heater performance. There
are two methods that may be employed to prevent
these problems:1.Pre-filling of the rear heater core.2.Thermal cycling of the engine cooling system. Fol-
lowing are descriptions of both prevention methods,
as well as a method to verify rear heater perfor-
mance.
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING
FRONT - WARNING - HEATER PLUMBING).
PRE-FILLING
If the rear heater core or the rear HVAC housing
have been removed from the vehicle for service, the
rear heater core may be pre-filled with the proper
engine coolant mixture prior to reconnecting the
heater hoses to the heater core hose fittings.
(1) The heater core should be installed in the rear
HVAC housing, and the rear HVAC housing should
be installed in the vehicle.
(2) Take the proper precautions to protect the car-
peting below the rear heater core from spilled engine
coolant and have absorbent toweling readily avail-
able to mop up any spills.
(3) Insert the small end of an appropriate funnel
into the upper hose fitting of the heater core (Fig. 4).
(4) Carefully pour the proper pre-mixed engine
coolant solution into the rear heater core through a
funnel until coolant begins to appear at the lower
hose fitting of the heater core.
(5) Use absorbent toweling to clean up any engine
coolant spills from the preceding operation.
(6) Reconnect the heater hoses to the rear heater
core (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITION-
ING/PLUMBING - REAR/HEATER HOSE - INSTAL-
LATION).
Fig. 4 Pre-Filling Heater Core - Typical
1 - REAR HEATER CORE
RSPLUMBING - REAR24 - 101
A/C EXPANSION VALVE (Continued)