fuel CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 453 of 2585

RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the PDC fuse as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the starter solenoid field coils. There should be
continuity between the cavity for relay terminal 87
and the starter solenoid terminal at all times. If OK,
go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit to the
starter solenoid as required.
(4) The coil battery terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is energized when
the ignition switch is held in the Start position and
the clutch pedal is depressed (manual trans). Check
for battery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 86
with the ignition switch in the Start position and the
clutch pedal is depressed (manual trans), and no
voltage when the ignition switch is released to the
On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, check for
an open or short circuit to the ignition switch and
repair, if required. If the circuit to the ignition switch
is OK, see the Ignition Switch Test procedure in this
group.
(5) The coil ground terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is grounded by the
PCM if the conditions are right to start the car. For
automatic trans. cars the PCM must see Park Neu-
tral switch low and near zero engine speed (rpm).
For manual trans. cars the PCM only needs to see
near zero engine speed (rpm) and low clutch inter-
lock input and see near zero engine speed (rpm). To
diagnose the Park Neutral switch of the trans range
sensor refer to the transaxle section. Check for conti-
nuity to ground while the ignition switch is in the
start position and if equipped the clutch pedal
depressed. If not OK and the vehicle has an auto-
matic trans. verify Park Neutral switch operation. If
that checks OK check for continuity between PCM
and the terminal 86. Repair open circuit as required.
Also check the clutch interlock switch operation if
equipped with a manual transmission. If OK, the
PCM may be defective.
SAFETY SWITCHES
For diagnostics of the Transmission Range Sensor,
refer to the Transaxle section for more information.
If equipped with Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch,
refer to Diagnosis and Testing in the Clutch section.
IGNITION SWITCH
After testing starter solenoid and relay, test igni-
tion switch and wiring. Refer to the Ignition Section
or Wiring Diagrams for more information. Check all
wiring for opens or shorts, and all connectors for
being loose or corroded.
BATTERY
For battery diagnosis and testing, refer to the Bat-
tery section for procedures.
ALL RELATED WIRING AND CONNECTORS
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for more information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
RESISTANCE TEST
Before proceeding with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter,
accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition and Fuel systems must be dis-
abled to prevent engine start while performing the
following tests.
(1) To disable the Ignition and Fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(2) Gain access to battery terminals.
(3) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following:
(a) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative post, and positive lead to the
battery negative cable clamp. Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between cable clamp and post.
(b) Connect positive lead of the voltmeter to the
battery positive post, and negative lead to the bat-
tery positive cable clamp. Rotate and hold the igni-
tion switch key in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between the cable clamp and post.
(c) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to battery
negative terminal, and positive lead to engine
block near the battery cable attaching point.
Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct
poor contact at ground cable attaching point. If
voltage reading is still above 0.2 volt after correct-
ing poor contacts, replace ground cable.
(4) Connect positive voltmeter lead to the starter
motor housing and the negative lead to the battery
negative terminal. Hold the ignition switch key in
8F - 32 STARTINGRS
STARTING (Continued)
Page 454 of 2585

the START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt,
correct poor starter to engine ground.
(a) Connect the positive voltmeter lead to the
battery positive terminal, and negative lead to bat-
tery cable terminal on starter solenoid. Rotate and
hold the ignition switch in the START position. If
voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct poor contact at
battery cable to solenoid connection. If reading is
still above 0.2 volt after correcting poor contacts,
replace battery positive cable.
(b) If resistance tests do not detect feed circuit
failures, replace the starter motor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
TEST
NOTE: The following results are based upon the
vehicle being at room temperature.
The following procedure will require a suitable
volt-ampere tester (Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.(1) Check battery before performing this test. Bat-
tery must be fully charged.
(2) Connect a volt-ampere tester to the battery ter-
minals. Refer to the operating instructions provided
with the tester being used.
(3) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(4) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in the PARK
and SET parking brake.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(5) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
1).
²If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 280 amps, check for engine seizing
or faulty starter.
²If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amper-
age reads 0 to 10 amps, check for corroded cables
and/or bad connections.
²Voltage below 9.6 volts and amperage draw
above 300 amps, the problem is the starter. Replace
the starter refer to starter removal.
(6) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state-of-charge and
charge battery if necessary. Disconnect all testing
equipment and connect ASD relay. Start the vehicle
several times to assure the problem has been cor-
rected.
SPECIFICATIONS
Torques
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Starter Mounting Bolts 47.4 35
Starter Solenoid Battery
Nut11.3 8.3 100
Fig. 1 Volt Ampere Tester
RSSTARTING8F-33
STARTING (Continued)
Page 489 of 2585

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION2. STARTING CIRCUIT
WIRING FAULTY. 2. REFER TO THE FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST AND
THE FEED CIRCUIT TEST IN THIS SECTION. REPAIR AS
NECESSARY.
3. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY. 3. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
4. ENGINE SEIZED. 4. REFER TO THE ENGINE SECTION, FOR DIAGNOSTIC AND SERVICE PROCEDURES.
5. LOOSE
CONNECTION AT
BATTERY, PDC,
STARTER, OR ENGINE
GROUND. 5. INSPECT FOR LOOSE CONNECTIONS.
6. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR. 6. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETH AND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
STARTER
ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT
BEFORE
ENGINE
STARTS. 1. BROKEN TEETH ON
STARTER RING GEAR.
1. REMOVE STARTER. INSPECT RING GEAR AND REPLACE
IF NECESSARY.
2. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY. 2. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
STARTER DOES
NOT
DISENGAGE. 1. STARTER
IMPROPERLY
INSTALLED. 1. INSTALL STARTER. TIGHTEN STARTER MOUNTING
HARDWARE TO CORRECT TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS.
2. STARTER RELAY
FAULTY. 2. REFER TO RELAY TEST, IN THIS SECTION. REPLACE
RELAY, IF NECESSARY.
3. IGNITION SWITCH
FAULTY. 3. REFER TO IGNITION SWITCH TEST, IN THE STEERING
SECTION. REPLACE SWITCH, IF NECESSARY.
4. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY. 4. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
5. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR. 5. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETH AND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONTROL
CIRCUIT TEST
The starter control circuit has:
²
Starter motor with integral solenoid
² Starter relay
² Transmission range sensor, or Park/Neutral
Position switch with automatic transmissions ² Ignition switch
² Battery
² All related wiring and connections
² Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled. ²
To disable ignition and fuel systems, disconnect
the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The ASD relay
is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Refer to the PDC cover for the proper relay location.
STARTER SOLENOID
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION WITH THE
PARKING BRAKE APPLIED. THIS MAY RESULT IN
PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
(1) Verify battery condition. Battery must be in
good condition with a full charge before performing
any starter tests. Refer to Battery Tests.
8Fs - 32 STARTINGRS
STARTING (Continued)
Page 491 of 2585

(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3. (3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the starter solenoid field coils. There should be
continuity between the cavity for relay terminal 87
and the starter solenoid terminal at all times. If OK,
go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit to the
starter solenoid as required. (4) The coil battery terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is energized when
the ignition switch is held in the Start position and
the clutch pedal is depressed (manual trans). Check
for battery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 86
with the ignition switch in the Start position and the
clutch pedal is depressed (manual trans), and no
voltage when the ignition switch is released to the
On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK, check for
an open or short circuit to the ignition switch and
repair, if required. If the circuit to the ignition switch
is OK, see the Ignition Switch Test procedure in this
group. (5) The coil ground terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is grounded by the
PCM if the conditions are right to start the car. For
automatic trans. cars the PCM must see Park Neu-
tral switch low and near zero engine speed (rpm).
For manual trans. cars the PCM only needs to see
near zero engine speed (rpm) and low clutch inter-
lock input and see near zero engine speed (rpm). To
diagnose the Park Neutral switch of the trans range
sensor refer to the transaxle section. Check for conti-
nuity to ground while the ignition switch is in the
start position and if equipped the clutch pedal
depressed. If not OK and the vehicle has an auto-
matic trans. verify Park Neutral switch operation. If
that checks OK check for continuity between PCM
and the terminal 86. Repair open circuit as required.
Also check the clutch interlock switch operation if
equipped with a manual transmission. If OK, the
PCM may be defective.
SAFETY SWITCHES
For diagnostics of the Transmission Range Sensor,
refer to the Transaxle section for more information. If equipped with Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch,
refer to Diagnosis and Testing in the Clutch section.
IGNITION SWITCH
After testing starter solenoid and relay, test igni-
tion switch and wiring. Refer to the Ignition Section
or Wiring Diagrams for more information. Check all
wiring for opens or shorts, and all connectors for
being loose or corroded.
BATTERY
For battery diagnosis and testing, refer to the Bat-
tery section for procedures.
ALL RELATED WIRING AND CONNECTORS
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for more information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
RESISTANCE TEST
Before proceeding with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter,
accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition and Fuel systems must be dis-
abled to prevent engine start while performing the
following tests.
(1) To disable the Ignition and Fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location. (2) Gain access to battery terminals.
(3) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following: (a) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative post, and positive lead to the
battery negative cable clamp. Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between cable clamp and post. (b) Connect positive lead of the voltmeter to the
battery positive post, and negative lead to the bat-
tery positive cable clamp. Rotate and hold the igni-
tion switch key in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between the cable clamp and post. (c) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to battery
negative terminal, and positive lead to engine
block near the battery cable attaching point.
Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct
poor contact at ground cable attaching point. If
voltage reading is still above 0.2 volt after correct-
ing poor contacts, replace ground cable.
(4) Connect positive voltmeter lead to the starter
motor housing and the negative lead to the battery
negative terminal. Hold the ignition switch key in
the START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt,
correct poor starter to engine ground. (a) Connect the positive voltmeter lead to the
battery positive terminal, and negative lead to bat-
tery cable terminal on starter solenoid. Rotate and
hold the ignition switch in the START position. If
voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct poor contact at
8Fs - 34 STARTINGRS
STARTING (Continued)
Page 492 of 2585

battery cable to solenoid connection. If reading is
still above 0.2 volt after correcting poor contacts,
replace battery positive cable.(b) If resistance tests do not detect feed circuit
failures, replace the starter motor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
TEST
NOTE: The following results are based upon the
vehicle being at room temperature.
The following procedure will require a suitable
volt-ampere tester (Fig. 1).
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
(1) Check battery before performing this test. Bat-
tery must be fully charged. (2) Connect a volt-ampere tester to the battery ter-
minals. Refer to the operating instructions provided
with the tester being used. (3) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location. (4) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in the PARK
and SET parking brake.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(5) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
1). ² If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 280 amps, check for engine seizing
or faulty starter. ² If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amper-
age reads 0 to 10 amps, check for corroded cables
and/or bad connections. ² Voltage below 9.6 volts and amperage draw
above 300 amps, the problem is the starter. Replace
the starter refer to starter removal. (6) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state-of-charge and
charge battery if necessary. Disconnect all testing
equipment and connect ASD relay. Start the vehicle
several times to assure the problem has been cor-
rected.
SPECIFICATIONS
Torques
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Starter Mounting Bolts 47.4 35
Starter Solenoid Battery Nut 11.3 8.3 100
Fig. 1 Volt Ampere Tester
RS
STARTING8Fs-35
STARTING (Continued)
Page 526 of 2585

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SELF-
DIAGNOSTICS.........................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUSTER
DIAGNOSIS...........................2REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
CLUSTER LENS
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER
DESCRIPTION
The instrumentation gauges are contained in a
subdial assembly within the instrument cluster. The
individual gauges are not serviceable. If one of the
cluster gauges becomes faulty, the entire cluster
would require replacement.
The Mechanical Instrument Cluster (MIC) with a
tachometer is equipped with a electronic vacuum flu-
orescent transmission range indicator (PRND3L),
odometer, and trip odometer display.
The MIC without a tachometer is equipped with a
Light Emitting Diode (LED) transmission range indi-
cator (PRND3L) and a vacuum fluorescent odometer
display.
The MIC is equipped with the following warning
lamps.
²Lift Gate Ajar
²Low Fuel Level
²Low Windshield Washer Fluid Level
²Cruise
²Battery Voltage
²Fasten Seat Belt
²Door Ajar
²Coolant Temperature
²Anti-Lock Brake
²Brake
²Oil Pressure
²MIL (Malfunction Indicator Lamp)
²VTSS/SKIS Indicator
²Airbag
²Traction Control
²Autostick
The MIC without a tachometer also has the follow-
ing warning lamps:
²Turns Signals
²High Beam
WATER IN FUEL LAMP - EXPORT
The Water In Fuel Lamp is located in the message
center. When moisture is found within the fuel sys-
tem, the sensor sends a message via the PCI data
bus to the instrument cluster. The MIC illuminates
the bulb in the message center, The sensor is located
underneath the vehicle, directly above the rear axle.
The sensor is housed within the fuel filter/water sep-
arator assembly cover. The sensor is not serviced sep-
arately. If found defective, the entire assembly cover
must be replaced.
OPERATION
Refer to the vehicle Owner's Manual for operation
instructions and conditions for the Instrument Clus-
ter Gauges.
WATER IN FUEL LAMP - EXPORT
The Water In Fuel Sensor is a resistive type
switch. It is calibrated to sense the different resis-
tance between diesel fuel and water. When water
enters the fuel system, it is caught in the bottom of
the fuel filter/water separator assembly, where the
sensor is located. Water has less resistance than die-
sel fuel. The sensor then sends a PCI data bus mes-
sage to the instrument cluster to illuminate the
lamp.
If the lamp is inoperative, perform the self diag-
nostic test on the instrument cluster to check the
lamp operation before continuing diagnosis.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-1
Page 527 of 2585

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SELF-DIAGNOSTICS
The instrument clusters are equipped with a self
diagnostic test feature to help identify electronic prob-
lems. Prior to any test, perform the Self-Diagnostic
Test. The self diagnostic system displays instrument
cluster stored fault codes in the odometer display,
sweeps the gauges to the calibration points, and bulb
checks the warning indicators. When the key is in the
ON position with the engine not running, the MIL will
remain illuminated for regulatory purposes.
To activate the Self-Diagnostic program:
(1) With the ignition switch in the OFF position,
depress the TRIP ODOMETER RESET button.
(2) Continue to hold the TRIP ODOMETER
RESET button untilSofand a number (software ver-
sion number (i.e.Sof 3.2) appears in the odometer
window then release the button. If a fault code is
present, the cluster will display it in the odometer
display. When all fault codes have been displayed,
the cluster will displayªendºin the odometer dis-
play. Refer to the INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DTC'S
table to determine what each trouble code means.
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DTC'S
DTC DESCRIPTION
100.0 LOOP-BACK FAILURE
100.1 ABS COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.2 BCM COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.3 EATX COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.4 FCM COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.5 ORC COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.6SBEC/DEC/MCM COMMUNICATION
FAULT
200.0 AIRBAG LED SHORT
200.1 AIRBAG LED OPEN
200.2 ABS LED SHORT
200.3 ABS LED OPEN
200.6 EL INVERTER TIME-OUT
200.7 EATX MISMATCH
400.0 EEPROM READ/WRITE FAILURE
400.1IMPROPER POWER DOWN
DETECTED
CALIBRATION TEST
The CLUSTER CALIBRATION table contains the
proper calibration points for each gauge. If the gauge
pointers are not calibrated, a problem exists in the
cluster. If any gauge is out of calibration, replace the
cluster.
CLUSTER CALIBRATION
SPEEDOMETER CALIBRATION POINT
1 0 MPH (0 KM/H)
2 20 MPH (40 KM/H)
3 60 MPH (100 KM/H)
4 100 MPH (160 KM/H)
TACHOMETER
1 0 RPM
2 1000 RPM
3 3000 RPM
4 6000 RPM
FUEL GAUGE
1 EMPTY
2 1/4 FILLED
3 1/2 FILLED
4 FULL
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE
1 COLD
2 1/4
3 3/4
4 HOT
ODOMETER SEGMENT TEST
If a segment in the odometer does not illuminate
normally, a problem exists in the display.
ELECTRONIC TRANSMISSION RANGE INDICATOR
SEGMENT TEST
If a segment in the transmission range indicator
does not illuminate normally, a problem exists in the
display.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUSTER
DIAGNOSIS
CONDITIONS
Refer to the following tables for possible problems,
causes, and corrections.
²INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS
²SPEEDOMETER DIAGNOSIS
²TACHOMETER DIAGNOSIS
²FUEL GAUGE DIAGNOSIS
²TEMPERATURE GAUGE DIAGNOSIS
²ODOMETER DIAGNOSIS
²ELECTRONIC GEAR INDICATOR DISPLAY
DIAGNOSIS
NOTE: Always check the functionality of the cluster
by running the self test prior to troubleshooting.
8J - 2 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERRS
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 532 of 2585
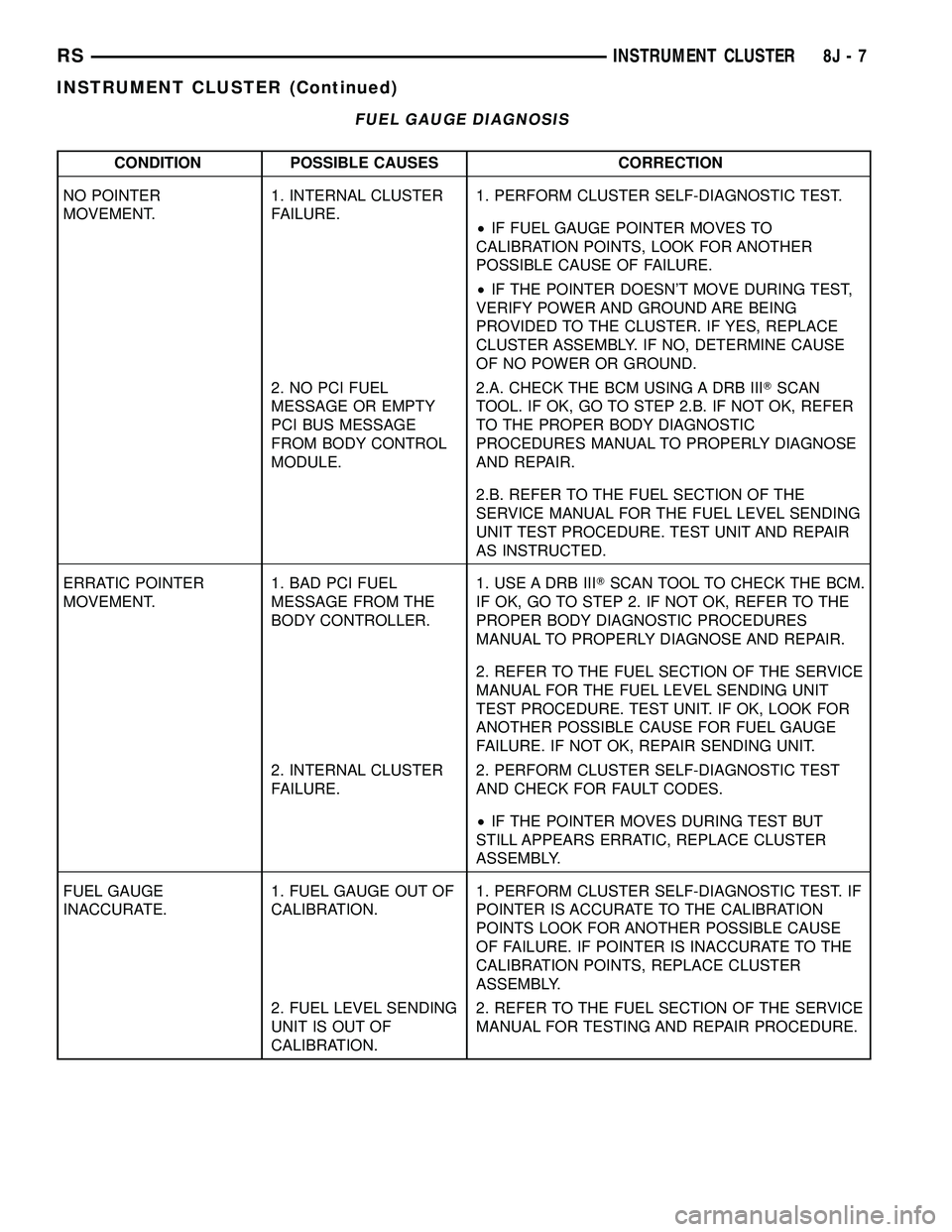
FUEL GAUGE DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO POINTER
MOVEMENT.1. INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.1. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST.
²IF FUEL GAUGE POINTER MOVES TO
CALIBRATION POINTS, LOOK FOR ANOTHER
POSSIBLE CAUSE OF FAILURE.
²IF THE POINTER DOESN'T MOVE DURING TEST,
VERIFY POWER AND GROUND ARE BEING
PROVIDED TO THE CLUSTER. IF YES, REPLACE
CLUSTER ASSEMBLY. IF NO, DETERMINE CAUSE
OF NO POWER OR GROUND.
2. NO PCI FUEL
MESSAGE OR EMPTY
PCI BUS MESSAGE
FROM BODY CONTROL
MODULE.2.A. CHECK THE BCM USING A DRB IIITSCAN
TOOL. IF OK, GO TO STEP 2.B. IF NOT OK, REFER
TO THE PROPER BODY DIAGNOSTIC
PROCEDURES MANUAL TO PROPERLY DIAGNOSE
AND REPAIR.
2.B. REFER TO THE FUEL SECTION OF THE
SERVICE MANUAL FOR THE FUEL LEVEL SENDING
UNIT TEST PROCEDURE. TEST UNIT AND REPAIR
AS INSTRUCTED.
ERRATIC POINTER
MOVEMENT.1. BAD PCI FUEL
MESSAGE FROM THE
BODY CONTROLLER.1. USE A DRB IIITSCAN TOOL TO CHECK THE BCM.
IF OK, GO TO STEP 2. IF NOT OK, REFER TO THE
PROPER BODY DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES
MANUAL TO PROPERLY DIAGNOSE AND REPAIR.
2. REFER TO THE FUEL SECTION OF THE SERVICE
MANUAL FOR THE FUEL LEVEL SENDING UNIT
TEST PROCEDURE. TEST UNIT. IF OK, LOOK FOR
ANOTHER POSSIBLE CAUSE FOR FUEL GAUGE
FAILURE. IF NOT OK, REPAIR SENDING UNIT.
2. INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.2. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
AND CHECK FOR FAULT CODES.
²IF THE POINTER MOVES DURING TEST BUT
STILL APPEARS ERRATIC, REPLACE CLUSTER
ASSEMBLY.
FUEL GAUGE
INACCURATE.1. FUEL GAUGE OUT OF
CALIBRATION.1. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST. IF
POINTER IS ACCURATE TO THE CALIBRATION
POINTS LOOK FOR ANOTHER POSSIBLE CAUSE
OF FAILURE. IF POINTER IS INACCURATE TO THE
CALIBRATION POINTS, REPLACE CLUSTER
ASSEMBLY.
2. FUEL LEVEL SENDING
UNIT IS OUT OF
CALIBRATION.2. REFER TO THE FUEL SECTION OF THE SERVICE
MANUAL FOR TESTING AND REPAIR PROCEDURE.
RSINSTRUMENT CLUSTER8J-7
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 533 of 2585

TEMPERATURE GAUGE DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO POINTER
MOVEMENT.1. INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.1. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
AND CHECK.
²IF TEMPERATURE GAUGE POINTER MOVES TO
CALIBRATION POINTS, LOOK FOR ANOTHER
POSSIBLE CAUSE OF FAILURE.
²IF THE POINTER DOESN'T MOVE DURING TEST,
VERIFY POWER AND GROUND ARE BEING
PROVIDED TO THE CLUSTER. IF YES, REPLACE
CLUSTER. IF NO, DETERMINE CAUSE OF NO
POWER OR NO GROUND.
2. NO PCI
TEMPERATURE
MESSAGE OR COLD PCI
BUS MESSAGE FROM
THE POWERTRAIN
CONTROL MODULE.2.A. CHECK PCM FAULT CODES USING A DRB IIIT
SCAN TOOL. IF THERE ARE NO FAULTS, GO TO
STEP 2.B. IF THERE ARE FAULTS, REFER TO THE
PROPER POWERTRAIN DIAGNOSTIC
PROCEDURES MANUAL TO PROPERLY DIAGNOSE
AND REPAIR.
2.B. REFER TO FUEL, COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR, DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING. REPAIR
SENSOR AS NEEDED.
ERRATIC POINTER
MOVEMENT.1. BAD PCI BUS
MESSAGE FROM THE
POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE.1.A. CHECK PCM FAULT CODES USING A DRB IIIT
SCAN TOOL. IF THERE ARE NO FAULTS, GO TO
STEP 1.B. IF THERE ARE FAULTS, REFER TO THE
PROPER POWERTRAIN DIAGNOSTIC
PROCEDURES MANUAL TO PROPERLY DIAGNOSE
AND REPAIR.
1.B. REFER TO FUEL, COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR, DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING. REPAIR
SENSOR AS NEEDED.
2. INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.2. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
AND CHECK FOR FAULT CODES.
²IF THE POINTER MOVES DURING TEST BUT
STILL APPEARS ERRATIC, REPLACE CLUSTER
ASSEMBLY.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
INACCURATE.1. TEMPERATURE
GAUGE OUT OF
CALIBRATION.1. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST.
²IF POINTER IS ACCURATE TO THE CALIBRATION
POINTS LOOK FOR ANOTHER POSSIBLE CAUSE
OF FAILURE.
²IF POINTER IS INACCURATE TO THE
CALIBRATION POINTS, REPLACE CLUSTER
ASSEMBLY.
2. COOLANT SENSOR
OUT OF CALIBRATION.2. REFER TO FUEL, COOLANT TEMPERATURE
SENSOR FOR TEST AND REPAIR PROCEDURE.
8J - 8 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERRS
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 548 of 2585

HEADLAMP SWITCH CONTINUITY
HEADLAMP
SWITCH
POSITION13-WAY
CONNECTOR
TERMINALRESISTANCE
OFF 11 TO 6 3651 - 3729V
PARKING
LAMPS ON11 TO 6 1697 - 2517V
PARKING
LAMPS WITH
FRONT FOG
LAMPS ON11 TO 6 5765 - 5886V
HEADLAMPS
ON11 TO 6 788 - 809V
AUTO ON 11 TO 6 10056 - 10264V
HEADLAMPS
ON WITH
FRONT FOG
LAMPS11 TO 6 1171 - 1200V
AUTO ON WITH
FRONT FOG
LAMPS ON11 TO 6 24278 - 24773V
DIMMER
POSITION13-WAY
CONNECTOR
TERMINALRESISTANCE
DOME 12 TO 6 15568 - 23357V
PARADE 12 TO 6 5168 - 7757V
DIM HIGH 12 TO 6 2288 - 3437V
DIM LOW 12 TO 6 688 - 1037V
OFF 12 TO 6 240 - 365V
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.(2) Remove the Instrument Panel Lower Steering
Column Cover. Refer to Body, Instrument Panel,
Lower Steering Column Cover, Removal.
(3) Reach up behind the left side of the instrument
panel and depress spring clip on top or bottom of
headlamp switch. Firmly push out on the headlamp
switch assembly.
(4) Disconnect the wiring connectors.
(5) Remove switch from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Connect the wiring connectors.
(2) Place headlamp switch assembly into position
and firmly snap into place.
(3) Install the Instrument Panel Lower Steering
Column Cover. Refer to Body, Instrument Panel,
Lower Steering Column Cover, Installation.
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
HEADLAMP UNIT
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEADLAMP UNIT
ALIGNMENT
HEADLAMP UNIT ALIGNMENT PREPARATION
(1) Verify headlamp dimmer switch and high beam
indicator operation.
(2) Inspect and correct damaged or defective com-
ponents that could interfere with proper headlamp
alignment.
(3) Verify proper tire inflation.
(4) Clean headlamp lenses.
(5) Verify that luggage area is loaded as the vehi-
cle is routinely used.
(6) Vehicles equipped with automatic load leveling
suspension should be driven normally for approxi-
mately 5 km (3 miles) before attempting a proper
headlamp unit alignment.
(7) Fuel tank should be FULL. Add 2.94 kg (6.5
lbs.) of weight over the fuel tank for each estimated
gallon of missing fuel.
ALIGNMENT SCREEN PREPARATION
(1) Position vehicle on a level surface perpendicu-
lar to a flat wall 7.62 meters (25 ft.) away from front
of headlamp lens (Fig. 13).
(2) If necessary, tape a line on the floor 7.62
meters (25 ft.) away from and parallel to the wall.
(3) Rock vehicle side-to-side three times and allow
suspension to stabilize.
(4) Jounce front suspension three times by pushing
downward on front bumper and releasing.
Fig. 12 HEADLAMP SWITCH CONNECTOR
RSLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR8L-13
HEADLAMP SWITCH (Continued)