tow CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 379 of 2585

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
HEADPHONES
WILL NOT HOLD
A CHANNEL OR
HAVE STATIC1. WEAK BATTERIES IN
THE HEADPHONES.1. REPLACE BATTERIES.
2. CLOSENESS TO
RADIO TRANSMITTER
SUCH AS A RADIO
TOWER, AIRPORT
TRANSMITTER OR
SOME MOBILE
RADIOS.2. MOVE TO AN AREA AWAY FREE FROM THESE
CONDITIONS.
REMOTE
CONTROL
INOPERATIVE1. WEAK BATTERIES IN
THE REMOTE
CONTROL.1. REPLACE BATTERIES.
2. OPERATION
CONSTRAINT OF
SYSTEM2. MAKE SURE THAT REAR AUDIO IS IN A DIFFERENT MODE
THAN FRONT SPEAKERS. REMOTE CONTROL WILL NOT
WORK WHEN BOTH ARE IN THE SAME MODE.
ANTENNA BODY AND CABLE
DESCRIPTION
All models use a fixed-length stainless steel rod-
type antenna mast, installed at the right front fender
of the vehicle. The antenna mast is connected to the
center wire of the coaxial antenna cable, and is not
grounded to any part of the vehicle.
OPERATION
To minimize static, the antenna base must have a
good ground. The coaxial antenna cable shield (the
outer wire mesh of the cable) is grounded to the
antenna base and the radio chassis.
The antenna coaxial cable has an additional dis-
connect, located near the right end of the instrument
panel. This additional disconnect allows the instru-
ment panel assembly to be removed and installed
without removing the radio.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ANTENNA BODY
AND CABLE
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO ELECTRICAL, RESTRAINTS
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. FAILURE
TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
The ohmmeter test lead connections for each test
are shown in (Fig. 1).
TEST 1
Test 1 determines of the antenna mast is insulated
from the base. Proceed as follows:
(1) Unplug the antenna coaxial cable from the
radio chassis and isolate. Remove the antenna mast.
(2) Connect an ohmmeter test lead to the inside
center of the antenna base. Connect the other test
lead to a metallic portion on the outside of the
antenna base. Check for continuity.
(3) There should be no continuity. If continuity is
found, replace the faulty or damaged antenna base
and cable assembly.
Fig. 1 Antenna Test Points
8A - 4 AUDIORS
AUDIO/VIDEO (Continued)
Page 403 of 2585

INSTALLATION
(1) Connect the module wire harness connectors.
(2) Snap the module on the seat cushion pan.
(3) Install the appropriate front seat in the vehicle
(Refer to 23 - BODY/SEATS/SEAT - INSTALLA-
TION).
(4) Connect and isolate the negative battery cable.
MEMORY SEAT/MIRROR
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the memory seat/mirror
option, utilize a memory module located under the
drivers front seat. This module is basically wired in-
line between the power seat switch and the power
seat track/adjuster motors, or in-line between the
power mirror switch and the power side view mir-
ror(s) motor(s). The MSMM contains a central pro-
cessing unit that communicates with other modules
on the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus network.
The Memory Seat/Mirror Module (MSMM) receives
hard wired inputs from the driver power seat switch
and the potentiometers on each of the driver side
power seat track motors, or from the power mirror
switch and the potentiometers on the side view mir-
ror. The MSMM receives messages over the PCI data
bus from the Body Control Module (BCM) (memory
switch status), the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
(vehicle speed status). The MSMM will prevent the
seat memory recall function from being initiated if
the driver side seat belt is buckled, if the transmis-
sion gear selector lever is not in the Park or Neutral
positions, or if the vehicle is moving.
For diagnosis of the MSMM or the PCI data bus, a
DRB IIItscan tool and the proper Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual are recommended. The MSMM cannot
be repaired and, if faulty or damaged, it must be
replaced. Refer toMemory Systemin the Power
Seat or Power Mirror section of this manual for more
information on the memory system option.
OPERATION
When memory system operation is requested
(depressing of the memory switch), a resistor multi-
plexed signal is sent from the memory switch to the
body control module (BCM). The body control module
will then send the appropriate signals out to the
memory/mirror seat module, the memory/mirror seat
module then applies the voltage supply to the power
seat track or side-view mirror if the proper require-
ments are met. The vehicle speed must equal zero
and the transmission must be in park or neutral in
order for the memory system to function.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MEMORY
SEAT/MIRROR MODULE
Visually inspect the related wiring harness connec-
tors. Look for broken, bent, pushed out, or corroded
terminals. If any of the above conditions are present,
repair as necessary. If not, use a DRB IIItscan tool
and the proper Diagnostic Procedures Manual to test
the memory/mirror seat module. For complete circuit
diagrams, refer toWiring Diagrams.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the driver side front bucket seat
retaining nuts from under the vehicle (Refer to 23 -
BODY/SEATS/SEAT - REMOVAL).
(3) Lift the drivers seat up and out of the mount-
ing holes in the floor pan and lay the seat rearward
to access the module located under the seat. It is not
necessary to disconnect the seat electrical, just use
care not to damage the wiring by over-extending.
(4) Disconnect the memory/mirror seat module
electrical connectors. Depress the retaining tab and
pull straight apart.
(5) Remove the module retaining bolts and remove
the module from the bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position and install the module retaining bolts.
(2) Connect the memory/mirror seat module elec-
trical connectors.
(3) Position the drivers seat in the mounting holes
in the floor pan.
(4) Install the driver side front bucket seat retain-
ing nuts from under the vehicle (Refer to 23 - BODY/
SEATS/SEAT - INSTALLATION).
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with a power liftgate (PLG) uti-
lize a PLG control module. This module is located on
the vehicles left side D-pillar just below the motor
assembly (Fig. 8) and contains a microprocessor,
which is used to communicate to the vehicles body
control module. The PLG control module receives and
monitors logic inputs from all the PLG system
switches except for the outside handle switch. This
module also contains the software technology to
detect liftgate obstructions and stop and/or reverse
the door accordingly.
8E - 10 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
HEATED SEAT MODULE (Continued)
Page 412 of 2585

(6) Rotate the SKIM upwards and then to the side
away from the steering column to slide the SKIM
antenna ring from around the ignition switch lock
cylinder housing.
(7) Remove the SKIM from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Slip the SKIM antenna ring around the igni-
tion switch lock cylinder housing. Rotate the SKIM
downwards and then towards the steering column.
(2) Install the one screws securing the SKIM to
the steering column.
(3) Engage the steering column wire harness from
the Sentry Key Immobilizer Module (SKIM).
(4) Install the steering column upper and lower
shrouds. Refer to Steering, Column, Column Shroud,
Installation.
(5) Install the Lower Instrument Panel Cover.
Refer to Body, Instrument Panel, Lower Instrument
Panel Cover, Installation.
(6) Connect the battery negative cable.
SLIDING DOOR CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with a power sliding door utilize
a sliding door control module. The sliding door con-
trol module is located behind the sliding door trim
panel in the center of the door, just above the sliding
door motor (Fig. 15). This module controls the opera-
tion of the door through the Programmable Commu-
nication Interface (PCI) J1850 data bus circuit and
the Body Control Module. The sliding door control
module contains software technology which enables it
to detect resistance to door travel and to reverse door
travel in order to avoid damage to the door or to
avoid possible personal injury if the obstruction is a
person. This feature functions in both the opening
and closing cycles. If the power sliding door system
develops any problems the control module will store
and recall Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC). The use
of a diagnostic scan tool, such as the DRB IIItis
required to read and troubleshoot these trouble
codes. The sliding door control module can be
reflashed if necessary. Refer to the latest Technical
Service Bulletin (TSB) Information for any updates.
The power door control module is a replaceable
component and cannot be repaired, if found to be
faulty it must be replaced. Consult your MoparŸ
parts catalog for a specific part number.
OPERATION
The power sliding door control module serves as
the main computer for the power sliding side doorsystem. All power door functions are processed
through the power door control module and/or the
vehicles body control module (BCM). At the start of a
power open command, a signal is sent to the BCM
and then to the power door control module via the
J1850 data bus circuit. This signal, generated by any
of the power door command switches, tells the power
door control module to activate a power latch release,
engage the clutch assembly and drive the door into
the full open position. If an obstacle is felt during
this power open cycle, the module will reverse direc-
tion and close the door. This process is also enabled
during a power close cycle. This process will repeat
three times, and if a fourth obstacle is detected, the
door will go into full manual mode. Once the full
open position is obtained, a hold open latch assembly
mounted full open switch tells the control module
that the door has reached the full open position. If
the power sliding door system develops any problems
the control module will store and recall Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTC). The use of a diagnostic scan
tool, such as the DRB IIItis required to read and
troubleshoot these trouble codes.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
Fig. 15 Power Side Door Components
1 - SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE
2 - MODULE RETAINING SCREW
3 - MODULE ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
4 - DOOR MOTOR ASSEMBLY
5 - FLEX DRIVE ASSEMBLY
6 - DOOR MOTOR RETAINING FASTENERS
7 - DOOR MOTOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-19
SENTRY KEY IMMOBILIZER MODULE (Continued)
Page 437 of 2585

NOTE: Never operate a vehicle without a battery
holddown device properly installed. Damage to the
vehicle, components and battery could result.
REMOVAL
All of the battery hold down hardware can be ser-
viced without removal of the battery or the battery
tray and support unit.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position. Be
certain that all electrical accessories are turned off.
(2) Remove the nut with washer that secures the
battery hold down bracket to the battery tray and
support unit.
(3) Remove the battery hold down bracket from
the battery tray and support unit.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the battery hold down bracket in the
battery tray and support unit.
(2) Install the nut with washer that secures the
battery hold down bracket to the battery tray and
support unit. Torque to 20 N´m (180 in. lbs.).
BATTERY CABLES
DESCRIPTION
The battery cables are large gauge, stranded cop-
per wires sheathed within a heavy plastic or syn-
thetic rubber insulating jacket. The wire used in the
battery cables combines excellent flexibility and reli-
ability with high electrical current carrying capacity.
Refer toWiring Diagramsin the index of this ser-
vice manual for the location of the proper battery
cable wire gauge information.
A clamping type female battery terminal made of
stamped metal is attached to one end of the battery
cable wire. A square headed pinch-bolt and hex nut
are installed at the open end of the female battery
terminal clamp. Large eyelet type terminals are
crimped onto the opposite end of the battery cable
wire and then solder-dipped. The battery positive
cable wires have a red insulating jacket to provide
visual identification and feature a larger female bat-
tery terminal clamp to allow connection to the larger
battery positive terminal post. The battery negative
cable wires have a black insulating jacket and a
smaller female battery terminal clamp.
The battery cables cannot be repaired and, if dam-
aged or faulty they must be replaced. Both the bat-
tery positive and negative cables are available for
service replacement only as a unit with the battery
wire harness, which may include portions of the wir-
ing circuits for the generator and other components
on some models. Refer toWiring Diagramsin theindex of this service manual for the location of more
information on the various wiring circuits included in
the battery wire harness for the vehicle being ser-
viced.
OPERATION
The battery cables connect the battery terminal
posts to the vehicle electrical system. These cables
also provide a path back to the battery for electrical
current generated by the charging system for restor-
ing the voltage potential of the battery. The female
battery terminal clamps on the ends of the battery
cable wires provide a strong and reliable connection
of the battery cable to the battery terminal posts.
The terminal pinch bolts allow the female terminal
clamps to be tightened around the male terminal
posts on the top of the battery. The eyelet terminals
secured to the opposite ends of the battery cable
wires from the female battery terminal clamps pro-
vide secure and reliable connection of the battery
cables to the vehicle electrical system.
The battery positive cable terminal clamp is
attached to the ends of two wires. One wire has an
eyelet terminal that connects the battery positive
cable to the B(+) terminal stud of the Integrated
Power Module (IPM), and the other wire has an eye-
let terminal that connects the battery positive cable
to the B(+) terminal stud of the engine starter motor
solenoid. The battery negative cable terminal clamp
is also attached to the ends of two wires. One wire
has an eyelet terminal that connects the battery neg-
ative cable to the vehicle powertrain through a stud
on the left side of the engine cylinder block. The
other wire has an eyelet terminal that connects the
battery negative cable to the vehicle body through a
ground screw on the left front fender inner shield,
near the battery.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY CABLE
A voltage drop test will determine if there is exces-
sive resistance in the battery cable terminal connec-
tions or the battery cable. If excessive resistance is
found in the battery cable connections, the connec-
tion point should be disassembled, cleaned of all cor-
rosion or foreign material, then reassembled.
Following reassembly, check the voltage drop for the
battery cable connection and the battery cable again
to confirm repair.
When performing the voltage drop test, it is impor-
tant to remember that the voltage drop is giving an
indication of the resistance between the two points at
which the voltmeter probes are attached.EXAM-
PLE:When testing the resistance of the battery pos-
itive cable, touch the voltmeter leads to the battery
positive cable terminal clamp and to the battery pos-
itive cable eyelet terminal at the starter solenoid
8F - 16 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY HOLDDOWN (Continued)
Page 457 of 2585

(7) Connect battery negative cable.
(8) Verify starter operation.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Place starter spacer in position on transaxle
bellhousing, flange toward flywheel.
(2) Place starter in position on bellhousing.(3) Install bolts and ground wire (Fig. 4) to hold
starter to transaxle bellhousing.
(4) Connect solenoid connector into starter.
(5) Install nut to hold B+ terminal to starter sole-
noid.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Connect battery negative cable.
(8) Verify starter operation.
8F - 36 STARTINGRS
STARTER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 494 of 2585

(5) Remove the starter mounting bolts (Fig. 9).
(6) Remove the starter.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Place starter in position on vehicle.
(2) Install the lower bolts to hold starter to trans-
axle bellhousing. (3) Install the upper bolt and ground wire (Fig. 4). (4) Place solenoid and B+ wires in position on
starter terminals (Fig. 3). (5) Install nut to hold B+ wire to terminal.
(6) Connect solenoid wire connector onto terminal.
(7) Connect battery negative cable.
(8) Verify starter operation.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Place starter spacer in position on transaxle
bellhousing, flange toward flywheel. (2) Place starter in position on bellhousing.
(3) Install bolts and ground wire (Fig. 4) to hold
starter to transaxle bellhousing. (4) Connect solenoid connector into starter.
Fig. 4 Upper Bolt and Ground Wire
Fig. 5 Starter
1 - SOLENOID CONNECTOR
2 - B+ CONNECTOR
Fig. 6 Starter Bolts
1-STARTER
2 - STARTER BOLTS
3 - TRANSAXLE
4 - ENGINE MOUNT
Fig. 7 STARTER 3.3/3.8L
1 - BELL HOUSING PLATE
2 - FLYWHEEL
3 - ENGINE MOUNT
4-STARTER
5 - SPACER
RS STARTING8Fs-37
STARTER MOTOR (Continued)
Page 496 of 2585
HEATED SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED GLASS........................... 1
HEATED MIRRORS......................... 6HEATED SEAT SYSTEM..................... 7
HEATED GLASS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATED GLASS
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER SYSTEM...................2
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER RELAY
DESCRIPTION..........................3
OPERATION............................3REMOVAL.............................3
INSTALLATION..........................3
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................4
OPERATION............................4
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER GRID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - GRID LINE AND
TERMINAL REPAIR.....................4
HEATED GLASS
DESCRIPTION
CAUTION: Grid lines can be damaged or scraped
off with sharp instruments. Care should be taken in
cleaning glass or removing foreign materials,
decals or stickers. Normal glass cleaning solvents
or hot water used with rags or toweling is recom-
mended.
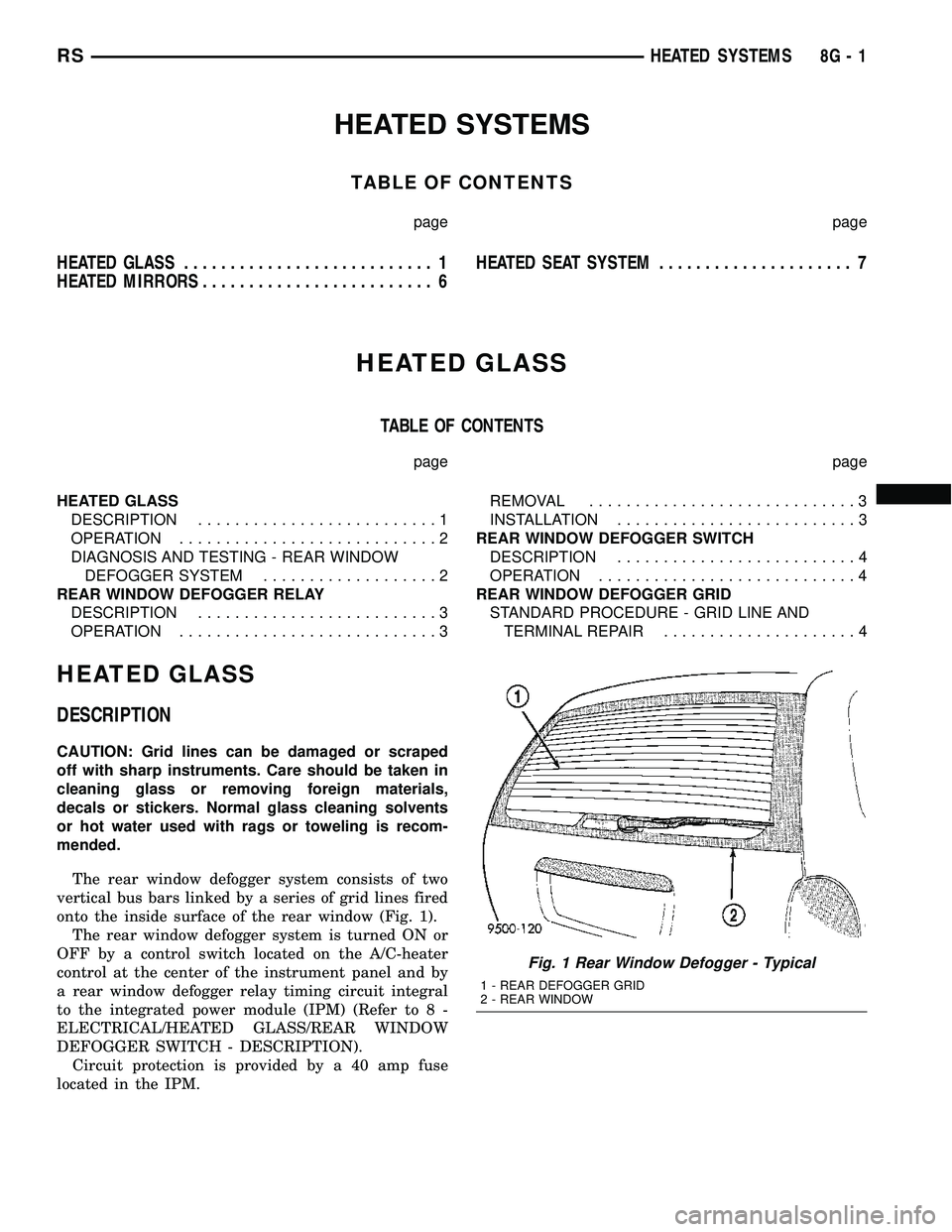
The rear window defogger system consists of two
vertical bus bars linked by a series of grid lines fired
onto the inside surface of the rear window (Fig. 1).
The rear window defogger system is turned ON or
OFF by a control switch located on the A/C-heater
control at the center of the instrument panel and by
a rear window defogger relay timing circuit integral
to the integrated power module (IPM) (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/HEATED GLASS/REAR WINDOW
DEFOGGER SWITCH - DESCRIPTION).
Circuit protection is provided by a 40 amp fuse
located in the IPM.
Fig. 1 Rear Window Defogger - Typical
1 - REAR DEFOGGER GRID
2 - REAR WINDOW
RSHEATED SYSTEMS8G-1
Page 503 of 2585
Refer to the description of the heated seat switch
later in this section for additional information.
Hard wired circuitry connects the heated seat sys-
tem components to each other through the electrical
system of the vehicle. These hard wired circuits are
integral to several wire harnesses, which are routed
throughout the vehicle and retained by many differ-
ent methods. These circuits may be connected to each
other, to the vehicle electrical system and to the
heated seat system components through the use of a
combination of soldered splices and splice block con-
nectors. Refer to Wiring for complete system wiring
schematics. The wiring information also includes the
proper wire and connector repair procedures, further
details on wire harness routing and retention, as well
as pin-out and location views for the various wire
harness connectors, splices and grounds.
OPERATION
The heated seat system components operate on
battery current received through a fuse in the Inte-
grated Power Module (IPM) on a fused ignition
switch output (run) circuit from the Body Control
Module. The system will only operate when the igni-
tion switch is in the On position. The heated seat
system will be turned Off automatically whenever
the ignition switch is turned to any position except
On. Also, the heated seat system will not operate
when the surface temperature of the seat cushion
cover at either heated seat sensor is above the
designed temperature set points of the system. See
the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for more
information on the features, use and operation of the
heated seat system.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SYSTEM
The most reliable, efficient, and accurate means to
diagnose the heated seat system requires the use of a
DRBIIItscan tool and the proper Diagnostic Proce-
dures manual. The DRBIIItscan tool can provide
confirmation that the PCI data bus is functional, that
all of the electronic modules are sending and receiv-
ing the proper messages on the PCI data bus, and
that the heated seat modules are receiving the
proper hard wired inputs from and relaying the
proper hard wired outputs to the Body Control Mod-
ule in order to perform its functions. Refer toWiring
Diagramsfor complete wiring schematics. The wir-
ing information also includes the proper wire and
connector repair procedures, further details on wire
harness routing and retention, as well as pin-out and
location views for the various wire harness connec-
tors, splices and grounds.
DRIVER HEATED SEAT
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
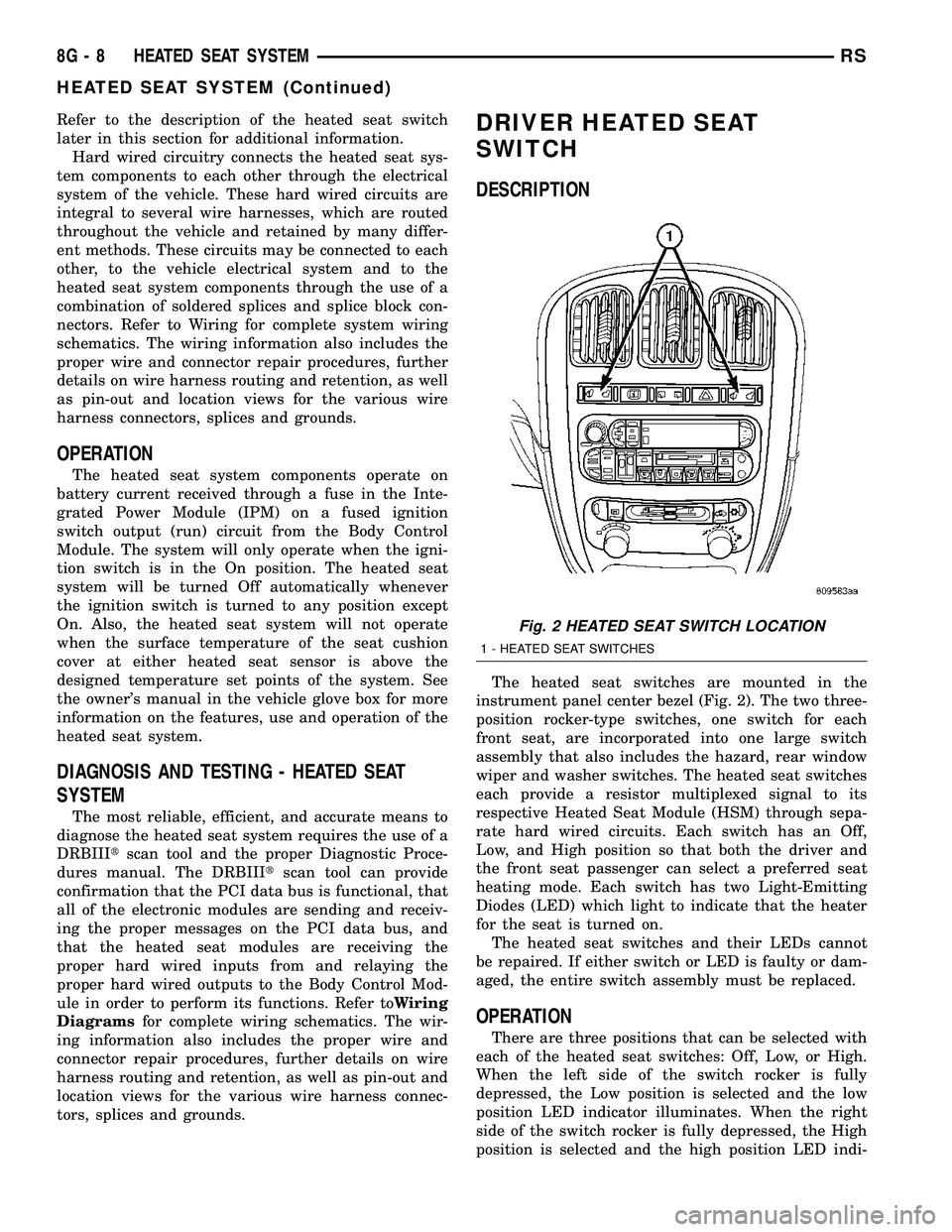
The heated seat switches are mounted in the
instrument panel center bezel (Fig. 2). The two three-
position rocker-type switches, one switch for each
front seat, are incorporated into one large switch
assembly that also includes the hazard, rear window
wiper and washer switches. The heated seat switches
each provide a resistor multiplexed signal to its
respective Heated Seat Module (HSM) through sepa-
rate hard wired circuits. Each switch has an Off,
Low, and High position so that both the driver and
the front seat passenger can select a preferred seat
heating mode. Each switch has two Light-Emitting
Diodes (LED) which light to indicate that the heater
for the seat is turned on.
The heated seat switches and their LEDs cannot
be repaired. If either switch or LED is faulty or dam-
aged, the entire switch assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
There are three positions that can be selected with
each of the heated seat switches: Off, Low, or High.
When the left side of the switch rocker is fully
depressed, the Low position is selected and the low
position LED indicator illuminates. When the right
side of the switch rocker is fully depressed, the High
position is selected and the high position LED indi-
Fig. 2 HEATED SEAT SWITCH LOCATION
1 - HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
8G - 8 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMRS
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 504 of 2585
cator illuminates. When the switch rocker is moved
to its neutral position (middle), Off is selected and
both LED indicators are extinguished.
Each switch provides separate resistor multiplexed
hard wire inputs to its respective Heated Seat Mod-
ule (HSM) to indicate the selected switch position.
The heated seat module responds to the heated seat
switch status messages by controlling the output to
the seat heater elements of the selected seat. The
Low heat position set point is about 36É C (97É F),
and the High heat position set point is about 41É C
(105É F).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRIVER HEATED
SEAT SWITCH
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toWiring
Diagrams.
WARNING: REFER TO THE RESTRAINTS SECTION
OF THIS MANUAL BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
STEERING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, SEAT OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
CHECKING SWITCH SIGNAL AND WIRING AT THE
MODULE
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Access and disconnect the gray 4-way connector
from the heated seat module. Visually inspect wiring
terminals for damage that would prevent positive
connection. If not OK, repair or replace the necessary
components.
(3) Place the heated seat switch in the LO posi-
tion. Using an Ohmmeter, check the resistance
between cavities 2 and 3 of the gray connector noted
above. Resistance should be about 3.5 kilohms (3500
ohms). If not OK, check resistance directly at switch,
as noted below. If OK, proceed to the next step. If not
OK, replace the faulty switch.
(4) Place the heated seat switch in the HI position.
Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance between
cavities 2 and 3 of the gray connector noted above.
Resistance should be about 1.4 kilohms (1400 ohms).
If not OK, check resistance directly at switch, as
noted below. If OK, proceed. If not OK replace the
faulty switch.
(5) With the system ON in the HI position, check
for battery voltage and ground at cavities 4 and 1. If
OK, proceed with testing remaining components. If
not OK, repair open or shorted wiring.
CHECKING SWITCH ONLY
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Remove the center bezel from the instrument
panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL -
REMOVAL). Check for continuity between the
ground circuit cavity (#10) of the instrument panel
switch bank electrical connector and a good ground.
There should be continuity. If OK, go to Step 2. If not
OK, repair the open ground circuit to ground as
required.
(2) Reconnect the battery negative cable. Turn the
ignition switch to the On position. Check for battery
voltage at the fused ignition switch output (run) cir-
cuit cavity of the instrument panel switch bank con-
nector (#4). If OK, turn the ignition switch to the Off
position, and go to Step 3. If not OK, repair the open
fused ignition switch output (run) circuit as required.
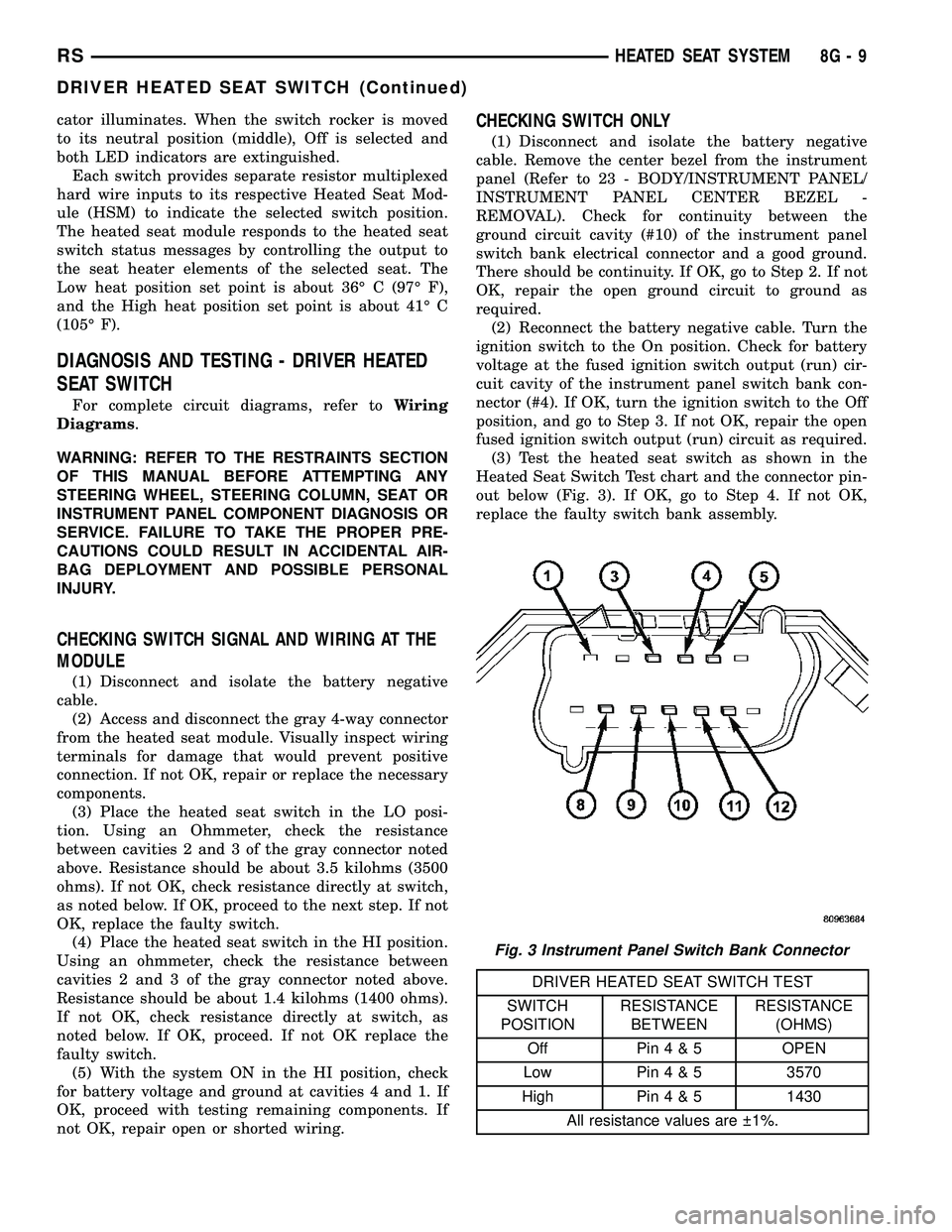
(3) Test the heated seat switch as shown in the
Heated Seat Switch Test chart and the connector pin-
out below (Fig. 3). If OK, go to Step 4. If not OK,
replace the faulty switch bank assembly.
DRIVER HEATED SEAT SWITCH TEST
SWITCH
POSITIONRESISTANCE
BETWEENRESISTANCE
(OHMS)
Off Pin4&5OPEN
Low Pin4&53570
High Pin4&51430
All resistance values are 1%.
Fig. 3 Instrument Panel Switch Bank Connector
RSHEATED SEAT SYSTEM8G-9
DRIVER HEATED SEAT SWITCH (Continued)
Page 507 of 2585
(3) Connect the negative battery cable.
(4) Verify heated seat system operation.
(5) Install the appropriate seat cushion or seat
back trim cover. Make certain the seat wire harness
is correctly routed through the seat and seat back.
The excess wire between the cushion and back ele-
ments should be securely tucked between the rear of
the cushion foam and the rear carpet flap of the trim
cover.
HEATED SEAT SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Two heated seat sensors are used per vehicle, one
in each front seat cushion heating element. The
heated seat temperature sensor is a Negative Tem-
perature Coefficient (NTC) thermistor.
The heated seat sensors cannot be repaired or
adjusted and if found to be faulty, the complete
heated seat cushion element must be replaced.
OPERATION
The temperature sensor is a NTC thermistor.
When the temperature of the seat cushion cover
rises, the resistance of the sensor decreases. The
heated seat module supplies a five-volt current to one
side of each sensor, and monitors the voltage drop
through the sensor on a return circuit. The heated
seat module uses this temperature sensor input to
monitor the temperature of the seat, and regulates
the current flow to the seat heating elements accord-
ingly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SENSOR
For complete circuit diagrams, refer toWiring
Diagrams.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the green 4-way heated seat mod-
ule wire harness connector.
(2) Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance
between cavities 2 and 3. The sensor resistance
should be between 50 kilohms at 15É C (60É F) and 2
kilohms at 30É C (85É F). If not OK, replace the
faulty seat element and sensor assembly.
PASSENGER HEATED SEAT
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
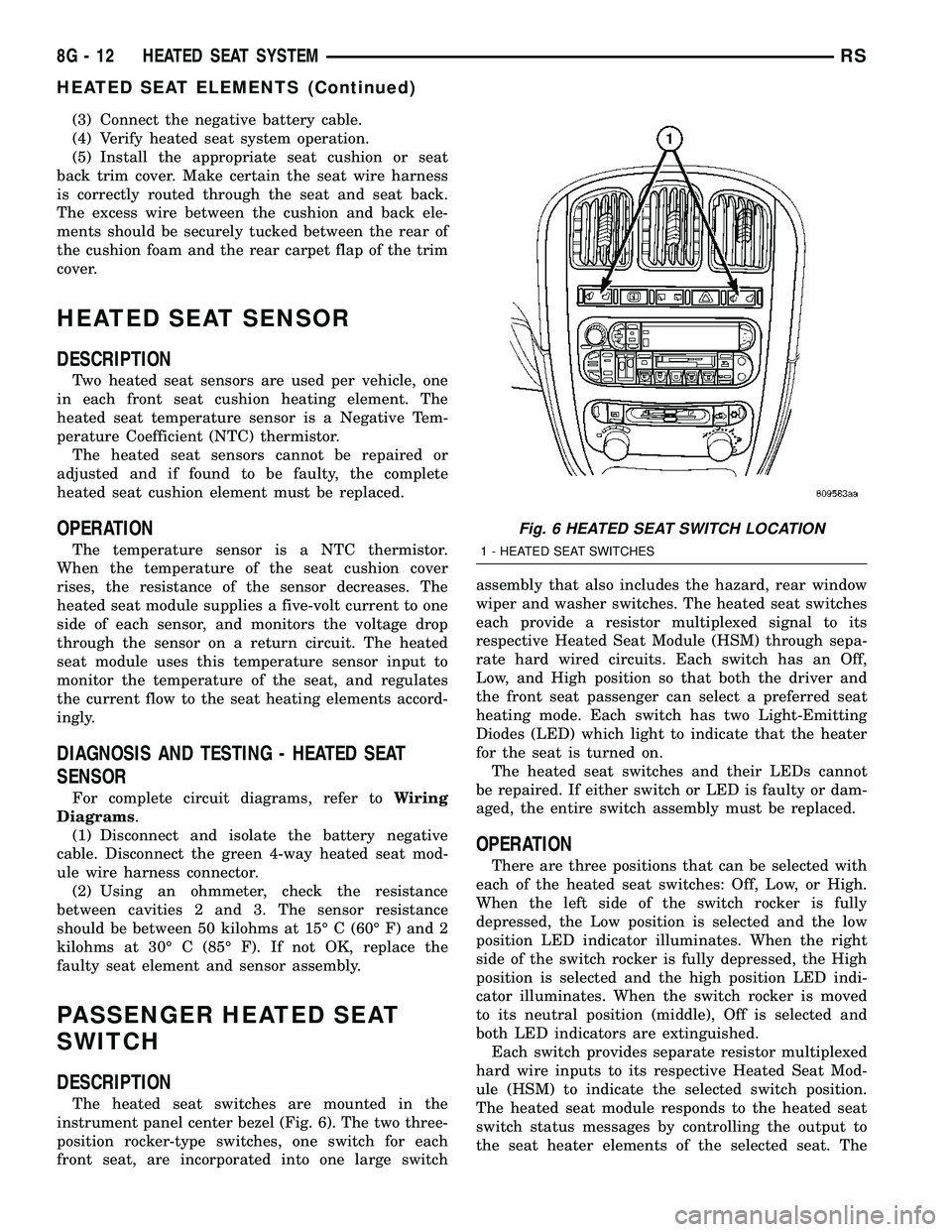
The heated seat switches are mounted in the
instrument panel center bezel (Fig. 6). The two three-
position rocker-type switches, one switch for each
front seat, are incorporated into one large switchassembly that also includes the hazard, rear window
wiper and washer switches. The heated seat switches
each provide a resistor multiplexed signal to its
respective Heated Seat Module (HSM) through sepa-
rate hard wired circuits. Each switch has an Off,
Low, and High position so that both the driver and
the front seat passenger can select a preferred seat
heating mode. Each switch has two Light-Emitting
Diodes (LED) which light to indicate that the heater
for the seat is turned on.
The heated seat switches and their LEDs cannot
be repaired. If either switch or LED is faulty or dam-
aged, the entire switch assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
There are three positions that can be selected with
each of the heated seat switches: Off, Low, or High.
When the left side of the switch rocker is fully
depressed, the Low position is selected and the low
position LED indicator illuminates. When the right
side of the switch rocker is fully depressed, the High
position is selected and the high position LED indi-
cator illuminates. When the switch rocker is moved
to its neutral position (middle), Off is selected and
both LED indicators are extinguished.
Each switch provides separate resistor multiplexed
hard wire inputs to its respective Heated Seat Mod-
ule (HSM) to indicate the selected switch position.
The heated seat module responds to the heated seat
switch status messages by controlling the output to
the seat heater elements of the selected seat. The
Fig. 6 HEATED SEAT SWITCH LOCATION
1 - HEATED SEAT SWITCHES
8G - 12 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMRS
HEATED SEAT ELEMENTS (Continued)