tow CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 155 of 2585

NOTE: The following wheel sequence should be
used when bleeding the brake hydraulic system.
The use of this wheel sequence will ensure ade-
quate removal of all trapped air from the brake
hydraulic system.
²Left Rear Wheel
²Right Front Wheel
²Right Rear Wheel
²Left Front Wheel
NOTE: When bleeding the brake system, some air
may be trapped in the brake lines or valves far
upstream, as much as ten feet from the bleeder
screw (Fig. 2). Therefore, it is essential to have a
fast flow of a large volume of brake fluid when
bleeding the brakes to ensure all the air gets out.
The brakes may be manually bled or pressure bled.
Refer to the appropriate following procedure.
MANUAL BLEEDING PROCEDURE
NOTE: Correct manual bleeding of the brakes
hydraulic system will require the aid of a helper.
NOTE: To adequately bleed the brakes using the
manual bleeding procedure the rear brakes must be
correctly adjusted. Prior to the manual bleeding of
the brake hydraulic system, correctly adjust the
rear brakes.
(1) Pump the brake pedal three or four times and
hold it down before the bleeder screw is opened.
(2) Push the brake pedal toward the floor and hold
it down. Then open the left rear bleeder screw at
least 1 full turn. When the bleeder screw opens the
brake pedal will drop all the way to the floor.CAUTION: ªJust crackingº the bleeder screw often
restricts fluid flow, allowing only a slow, weak fluid
discharge of fluid. This practice will NOT get all the
air out. Make sure the bleeder is opened at least 1
full turn when bleeding.
(3) Release the brake pedal onlyafterthe bleeder
screw is closed.
(4) Repeat steps 1 through 3, four or five times, at
each bleeder screw in the proper sequence. This
should pass a sufficient amount of fluid to expel all
the trapped air from the brake system. Be sure to
monitor the fluid level in the master cylinder, so it
stays at a proper level so air will not enter the brake
system through the master cylinder.
(5) Check pedal travel. If pedal travel is excessive
or has not been improved, enough fluid has not
passed through the system to expel all the trapped
air. Continue to bleed system as necessary.
(6) Perform a final adjustment of the rear brake
shoes (when applicable), then test drive vehicle to be
sure brakes are operating correctly and that pedal is
solid.
PRESSURE BLEEDING PROCEDURE
CAUTION: Use bleeder tank Special Tool C-3496-B
or equivalent with Adapter, Special Tool 6921, to
pressurize the hydraulic system for bleeding.
Follow pressure bleeder manufacturer's instruc-
tions for use of pressure bleeding equipment.
(1) Install the Adapter Master Cylinder Pressure
Bleed Cap, Special Tool 6921 on the fluid reservoir of
the master cylinder (Fig. 3). Attach the fluid hose
from the pressure bleeder to the fitting on Special
Tool 6921.
(2) Attach a clear plastic hose to the bleeder screw
at one wheel and feed the hose into a clear jar con-
taining fresh brake fluid.
(3) Open the left rear wheel bleeder screw at least
one full turnor more to obtain an adequate flow of
brake fluid.
CAUTION: ªJust crackingº the bleeder screw often
restricts fluid flow, allowing only a slow, weak fluid
discharge of fluid. This practice will NOT get all the
air out. Make sure the bleeder is opened at least 1
full turn when bleeding.
(4) After 4 to 8 ounces of brake fluid has been bled
through the hydraulic system, and an air-free flow is
maintained in the hose and jar, this will indicate a
good bleed of the hydraulic system has been
obtained.
(5) Repeat the procedure at all the other remain-
ing bleeder screws.
Fig. 2 Trapped Air In Brake Fluid Line
1 - TRAPPED AIR
5 - 8 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 165 of 2585

(7) Remove the outboard brake shoe from the cali-
per. Brake shoe is removed by pushing the shoe
toward the piston, disengaging the two metal protru-
sions on the shoe back, then sliding the brake shoe
off the caliper.
(8) Remove inboard brake shoe from caliper.
Inboard brake shoe is removed by pulling it out of
the caliper piston, until the retaining clip is free of
the piston (Fig. 18).
CLEANING - DISC BRAKE SHOES
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ACCUMULATING ON
BRAKE PARTS DURING NORMAL USE MAY CON-
TAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS FROM PRODUCTION OR
AFTERMARKET BRAKE LININGS. BREATHING
EXCESSIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS
FIBERS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM.
EXERCISE CARE WHEN SERVICING BRAKE
PARTS. DO NOT SAND OR GRIND BRAKE LINING
UNLESS EQUIPMENT USED IS DESIGNED TO CON-
TAIN THE DUST RESIDUE. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE
PARTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING. CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE BY
DAMPENING THE BRAKE COMPONENTS WITH A
FINE MIST OF WATER, THEN WIPING THE BRAKE
COMPONENTS CLEAN WITH A DAMPENED CLOTH.
DISPOSE OF CLOTH AND ALL RESIDUE CONTAIN-
ING ASBESTOS FIBERS IN AN IMPERMEABLE
CONTAINER WITH THE APPROPRIATE LABEL. FOL-
LOW PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY THE OCCUPA-
TIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION
(OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
AGENCY (EPA) FOR THE HANDLING, PROCESSING,
AND DISPOSING OF DUST OR DEBRIS THAT MAY
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS.
INSPECTION - DISC BRAKE SHOES
Visually inspect brake shoes (pads) for uneven lin-
ing wear. Also inspect for excessive lining deteriora-
tion. Check the clearance between the tips of the
wear indicators on the shoes (if equipped) and the
brake rotors.
If a visual inspection does not adequately deter-
mine the condition of the lining, a physical check will
be necessary. To check the amount of lining wear,
remove the disc brake shoes from the calipers.
Measure each brake shoe. The combined brake
shoe and its lining material thickness should be mea-
sured at its thinnest point.
²For front disc brake shoes, when a set of brake
shoes are worn to a thickness of approximately 7.95
mm (5/16 inch), they should be replaced.
²For rear disc brake shoes, when a set of brake
shoes are worn to a thickness of approximately 7.0
mm (9/32 inch), they should be replaced.
²Typically, if front shoes are worn out, both fronts
and rears need to be replaced. Make sure to check
rears.
Replacebothdisc brake shoes (inboard and out-
board) on each caliper. It is necessary to replace the
shoes on the opposite side of the vehicle as well as
the shoes failing inspection.
Fig. 17 Correctly Supported Caliper
1 - WIRE
2 - CALIPER
3 - ADAPTER
4 - ROTOR
5 - INNER FENDER
Fig. 18 Removing Inboard Brake Shoe
1 - INBOARD BRAKE SHOE
2 - HANGER WIRE
3 - CALIPER ASSEMBLY
4 - RETAINING CLIP
5 - PISTON
5 - 18 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - REAR DISC (Continued)
Page 250 of 2585

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION4. Leaking piston seal. 4. Replace piston seal or brake caliper.
5. Suspension problem. 5. Refer to the Suspension group.
PARKING BRAKE -
EXCESSIVE HANDLE
TRAVEL 1. Rear drum brakes or rear disc
brake parking brake shoes out of
adjustment. 1. Adjust rear drum brake shoes, or
rear parking brake shoes on vehicles
with rear disc brakes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BASE BRAKE
BLEEDING
NOTE: This bleeding procedure is only for the vehi-
cle's base brakes hydraulic system. For bleeding
the antilock brakes hydraulic system, (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - ABS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
CAUTION: Before removing the master cylinder
cover, thoroughly clean the cover and master cylin-
der fluid reservoir to prevent dirt and other foreign
matter from dropping into the master cylinder fluid
reservoir.
NOTE: The following wheel sequence should be
used when bleeding the brake hydraulic system.
The use of this wheel sequence will ensure ade-
quate removal of all trapped air from the brake
hydraulic system.
² Left Rear Wheel
² Right Front Wheel
² Right Rear Wheel
² Left Front Wheel
NOTE: When bleeding the brake system, some air
may be trapped in the brake lines or valves far
upstream, as much as ten feet from the bleeder
screw (Fig. 1). Therefore, it is essential to have a
fast flow of a large volume of brake fluid when
bleeding the brakes to ensure all the air gets out. The brakes may be manually bled or pressure bled.
Refer to the appropriate following procedure.
MANUAL BLEEDING PROCEDURE
NOTE: Correct manual bleeding of the brakes
hydraulic system will require the aid of a helper.
NOTE: To adequately bleed the brakes using the
manual bleeding procedure the rear brakes must be
correctly adjusted. Prior to the manual bleeding of
the brake hydraulic system, correctly adjust the
rear brakes. (1) Pump the brake pedal three or four times and
hold it down before the bleeder screw is opened. (2) Push the brake pedal toward the floor and hold
it down. Then open the left rear bleeder screw at
least 1 full turn. When the bleeder screw opens the
brake pedal will drop all the way to the floor.
CAUTION: ªJust crackingº the bleeder screw often
restricts fluid flow, allowing only a slow, weak fluid
discharge of fluid. This practice will NOT get all the
air out. Make sure the bleeder is opened at least 1
full turn when bleeding.
(3) Release the brake pedal only afterthe bleeder
screw is closed. (4) Repeat steps 1 through 3, four or five times, at
each bleeder screw in the proper sequence. This
should pass a sufficient amount of fluid to expel all
the trapped air from the brake system. Be sure to
monitor the fluid level in the master cylinder, so it
stays at a proper level so air will not enter the brake
system through the master cylinder. (5) Check pedal travel. If pedal travel is excessive
or has not been improved, enough fluid has not
passed through the system to expel all the trapped
air. Continue to bleed system as necessary. (6) Perform a final adjustment of the rear brake
shoes (when applicable), then test drive vehicle to be
sure brakes are operating correctly and that pedal is
solid.
Fig. 1 Trapped Air In Brake Fluid Line
1 - TRAPPED AIR
RS BRAKES5s-7
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
Page 260 of 2585
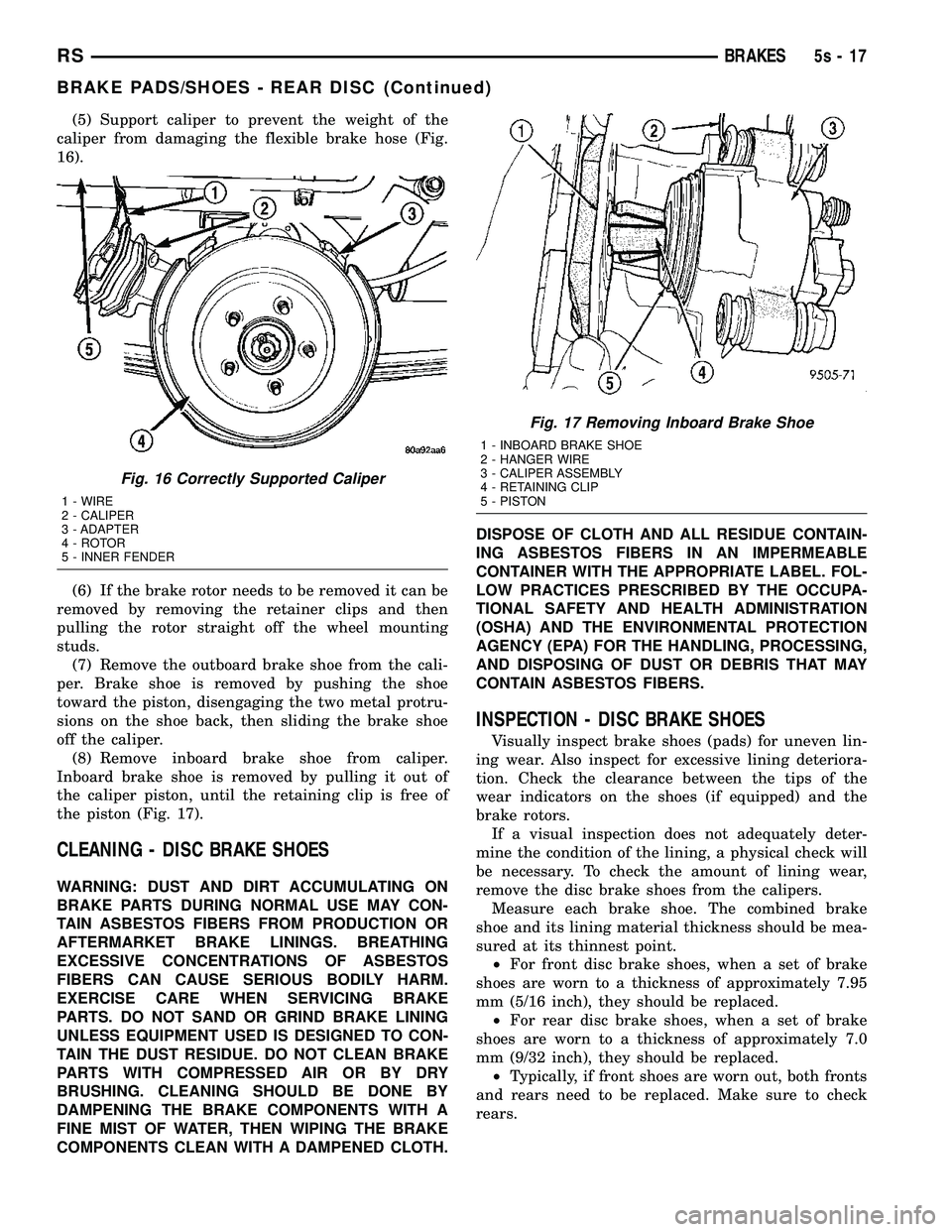
(5) Support caliper to prevent the weight of the
caliper from damaging the flexible brake hose (Fig.
16).
(6) If the brake rotor needs to be removed it can be
removed by removing the retainer clips and then
pulling the rotor straight off the wheel mounting
studs. (7) Remove the outboard brake shoe from the cali-
per. Brake shoe is removed by pushing the shoe
toward the piston, disengaging the two metal protru-
sions on the shoe back, then sliding the brake shoe
off the caliper. (8) Remove inboard brake shoe from caliper.
Inboard brake shoe is removed by pulling it out of
the caliper piston, until the retaining clip is free of
the piston (Fig. 17).
CLEANING - DISC BRAKE SHOES
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ACCUMULATING ON
BRAKE PARTS DURING NORMAL USE MAY CON-
TAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS FROM PRODUCTION OR
AFTERMARKET BRAKE LININGS. BREATHING
EXCESSIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS
FIBERS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM.
EXERCISE CARE WHEN SERVICING BRAKE
PARTS. DO NOT SAND OR GRIND BRAKE LINING
UNLESS EQUIPMENT USED IS DESIGNED TO CON-
TAIN THE DUST RESIDUE. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE
PARTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING. CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE BY
DAMPENING THE BRAKE COMPONENTS WITH A
FINE MIST OF WATER, THEN WIPING THE BRAKE
COMPONENTS CLEAN WITH A DAMPENED CLOTH. DISPOSE OF CLOTH AND ALL RESIDUE CONTAIN-
ING ASBESTOS FIBERS IN AN IMPERMEABLE
CONTAINER WITH THE APPROPRIATE LABEL. FOL-
LOW PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY THE OCCUPA-
TIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION
(OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
AGENCY (EPA) FOR THE HANDLING, PROCESSING,
AND DISPOSING OF DUST OR DEBRIS THAT MAY
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS.
INSPECTION - DISC BRAKE SHOES
Visually inspect brake shoes (pads) for uneven lin-
ing wear. Also inspect for excessive lining deteriora-
tion. Check the clearance between the tips of the
wear indicators on the shoes (if equipped) and the
brake rotors. If a visual inspection does not adequately deter-
mine the condition of the lining, a physical check will
be necessary. To check the amount of lining wear,
remove the disc brake shoes from the calipers. Measure each brake shoe. The combined brake
shoe and its lining material thickness should be mea-
sured at its thinnest point. ² For front disc brake shoes, when a set of brake
shoes are worn to a thickness of approximately 7.95
mm (5/16 inch), they should be replaced. ² For rear disc brake shoes, when a set of brake
shoes are worn to a thickness of approximately 7.0
mm (9/32 inch), they should be replaced. ² Typically, if front shoes are worn out, both fronts
and rears need to be replaced. Make sure to check
rears.
Fig. 16 Correctly Supported Caliper
1 - WIRE
2 - CALIPER
3 - ADAPTER
4 - ROTOR
5 - INNER FENDER
Fig. 17 Removing Inboard Brake Shoe
1 - INBOARD BRAKE SHOE
2 - HANGER WIRE
3 - CALIPER ASSEMBLY
4 - RETAINING CLIP
5 - PISTON
RS BRAKES5s-17
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - REAR DISC (Continued)
Page 329 of 2585
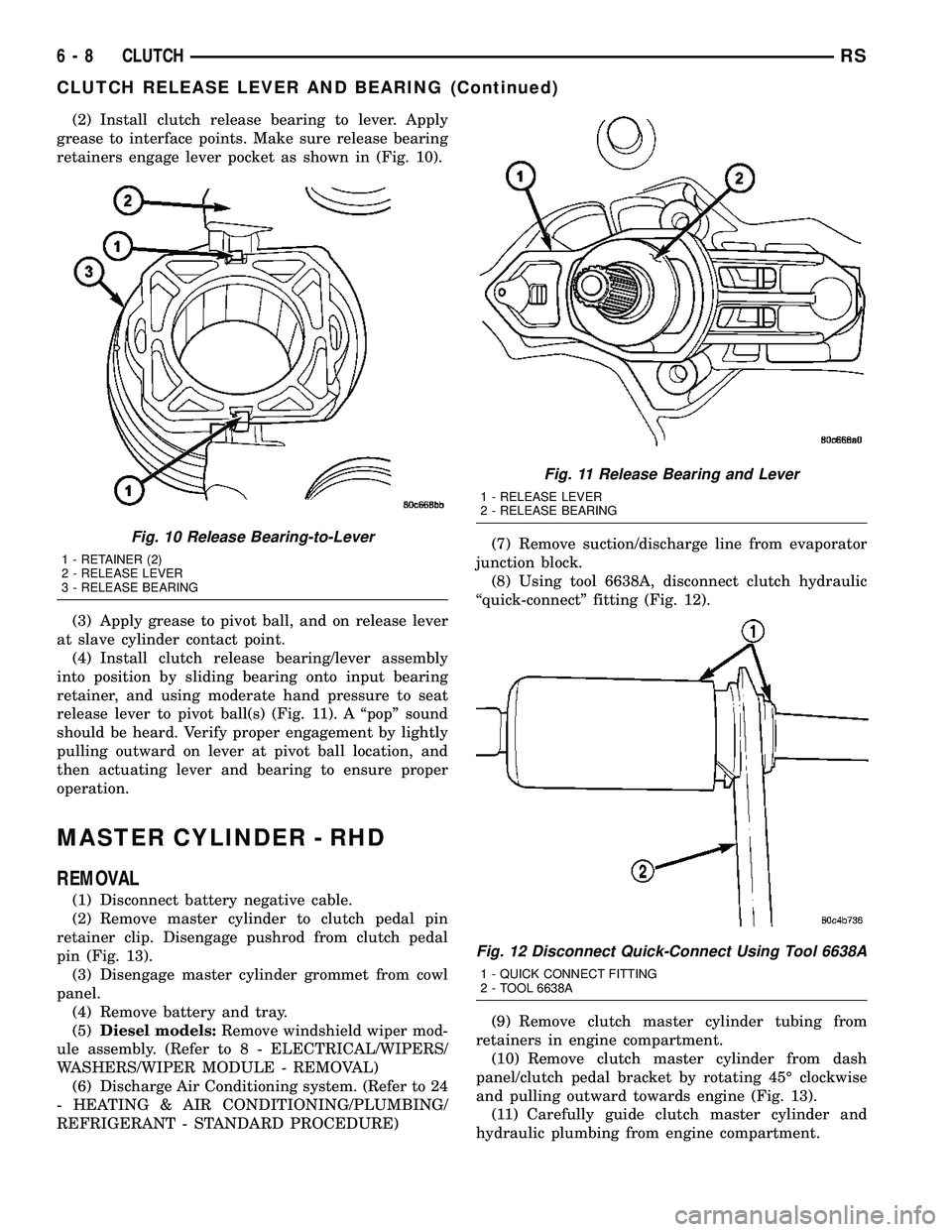
(2) Install clutch release bearing to lever. Apply
grease to interface points. Make sure release bearing
retainers engage lever pocket as shown in (Fig. 10).
(3) Apply grease to pivot ball, and on release lever
at slave cylinder contact point.
(4) Install clutch release bearing/lever assembly
into position by sliding bearing onto input bearing
retainer, and using moderate hand pressure to seat
release lever to pivot ball(s) (Fig. 11). A ªpopº sound
should be heard. Verify proper engagement by lightly
pulling outward on lever at pivot ball location, and
then actuating lever and bearing to ensure proper
operation.
MASTER CYLINDER - RHD
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove master cylinder to clutch pedal pin
retainer clip. Disengage pushrod from clutch pedal
pin (Fig. 13).
(3) Disengage master cylinder grommet from cowl
panel.
(4) Remove battery and tray.
(5)Diesel models:Remove windshield wiper mod-
ule assembly. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/
WASHERS/WIPER MODULE - REMOVAL)
(6) Discharge Air Conditioning system. (Refer to 24
- HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING/
REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)(7) Remove suction/discharge line from evaporator
junction block.
(8) Using tool 6638A, disconnect clutch hydraulic
ªquick-connectº fitting (Fig. 12).
(9) Remove clutch master cylinder tubing from
retainers in engine compartment.
(10) Remove clutch master cylinder from dash
panel/clutch pedal bracket by rotating 45É clockwise
and pulling outward towards engine (Fig. 13).
(11) Carefully guide clutch master cylinder and
hydraulic plumbing from engine compartment.
Fig. 10 Release Bearing-to-Lever
1 - RETAINER (2)
2 - RELEASE LEVER
3 - RELEASE BEARING
Fig. 11 Release Bearing and Lever
1 - RELEASE LEVER
2 - RELEASE BEARING
Fig. 12 Disconnect Quick-Connect Using Tool 6638A
1 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
2 - TOOL 6638A
6 - 8 CLUTCHRS
CLUTCH RELEASE LEVER AND BEARING (Continued)
Page 331 of 2585

(10) Using Tool 6638A, disconnect clutch master
cylinder ªquick connectº fitting (Fig. 17). Disengage
plumbing retainer from body stud.
(11) Remove master cylinder reservoir-to-strut
tower nuts (Fig. 18). Reposition reservoir off to side.
(12) Remove clutch master cylinder from dash
panel by rotating clockwise 45É and removing from
dash panel (Fig. 18).(13) Remove master cylinder and plumbing from
engine compartment. Use care not to bend or kink
plumbing. Note plumbing routing to aid in installa-
tion.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install master cylinder into position, while
routing plumbing as originally installed.
(2) Insert master cylinder pushrod through dash
panel (Fig. 18) and rotate 45É counter-clockwise to
secure.
(3) Connect master cylinder plumbing quick-con-
nect fitting. An audible ªclickº should be heard. Ver-
ify connection by pulling outward.
(4) Install master cylinder reservoir onto strut
tower. Install and tighten two (2) master cylinder
reservoir-to-strut tower nuts to 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.)
(Fig. 18).
(5) Install windshield wiper module assembly
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/WIPERS/WASHERS/
WIPER MODULE - INSTALLATION).
(6) Install battery tray.
(7) Install battery.
(8) Install battery shield.
(9) Connect master cylinder pushrod to clutch
pedal lever (Fig. 16). Install retainer clip.
(10) Install knee bolster and instrument panel
lower silencer (Fig. 15) (Fig. 14).
(11) Connect battery cables.
Fig. 16 Master Cylinder Pushrod at Pedal
1 - MASTER CYLINDER PUSHROD
2 - CLUTCH/BRAKE PEDAL ASSEMBLY
3 - PUSHROD RETAINER
Fig. 17 Disconnect Quick-Connect Using Tool 6638A
1 - QUICK CONNECT FITTING
2 - TOOL 6638A
Fig. 18 Clutch Master Cylinder Removal/Installation
1 - CLUTCH MASTER CYLINDER
2 - RESERVOIR
3 - NUT (2)
6 - 10 CLUTCHRS
MASTER CYLINDER - LHD (Continued)
Page 332 of 2585

MODULAR CLUTCH ASSY -
2.4L GAS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transaxle from vehicle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL -
REMOVAL)
(2) Remove modular clutch assembly from input
shaft (Fig. 19).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install modular clutch assembly to transaxle
input shaft (Fig. 19).
(2) Install transaxle to vehicle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL - INSTAL-
LATION)
SLAVE CYLINDER
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.Diesel models:Remove
underbody splash shield.
(2) Using Tool 6638A, disconnect hydraulic clutch
circuit quick connect fitting.
(3) Remove clutch slave cylinder (Fig. 20) by lifting
nylon tab with a small screwdriver, and then
depressing cylinder inward towards case and rotating
cylinder 60É counter-clockwise.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install clutch slave cylinder into position, not-
ing orientation of different sized lugs. While depress-
ing inward, rotate slave cylinder clockwise until
nylon locating tab rests in transaxle case cutout, and
the hydraulic tube is vertical (Fig. 20).
(2) Connect ªquick-connectº connection until an
audible ªclickº is heard. Verify connection by pulling
outward on connection.
(3)Diesel models:Install underbody splash
shield.
(4) Lower vehicle.
CLUTCH DISC AND PRESSURE
PLATE - 2.5L TD
REMOVAL
(1) Remove transaxle assembly. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/MANUAL -
REMOVAL)
(2) Remove six (6) clutch pressure plate-to-fly-
wheel bolts. Remove pressure plate and disc from fly-
wheel (Fig. 21).
(3)
Inspect flywheel. Resurface/replace as necessary.
(4) Inspect clutch release bearing and lever.
Replace as necessary. (Refer to 6 - CLUTCH/
CLUTCH RELEASE BEARING - REMOVAL)
Fig. 19 Modular Clutch Assembly
1 - MODULAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
2 - INPUT SHAFT
Fig. 20 Slave Cylinder Removal/Installation
1 - MOUNTING HOLE
2 - SLAVE CYLINDER
3 - ACCESS HOLE
4 - NYLON ANTI-ROTATION TAB
RSCLUTCH6-11
Page 334 of 2585

CLUTCH PEDAL INTERLOCK
SWITCH
REMOVAL
LHD
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
23).
(3) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 24).
(4) Disconnect interlock switch connector (Fig. 25).
(5) Remove interlock switch by depressing four (4)
plastic wing tabs, and sliding switch through mount-
ing bracket (Fig. 25). If difficulty is encountered gain-
ing access to and removing interlock switch,
removing the upstop switch/bracket assembly (Fig.25) allows for over-travel of the pedal, giving more
room for interlock switch access.
(6) Remove interlock switch harness from pedal
bracket at retainer. Remove switch.
RHD
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
23).
(3) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 24).
(4) Remove master cylinder to clutch pedal pin
retainer clip (Fig. 26). Disengage pushrod from clutch
pedal pin.
(5) Disconnect interlock and upstop switch connec-
tors.
(6) Disengage master cylinder grommet from dash
panel.
(7) Remove clutch master cylinder tubing from
retainers in engine compartment.
(8) Remove clutch master cylinder from dash pan-
el/clutch pedal bracket by rotating 45É clockwise and
pulling outward towards engine (Fig. 26).
(9) Remove clutch pedal bracket assembly (Fig.
27).
(10) Remove interlock switch harness from pedal
bracket at retainer. Remove switch (Fig. 28).
Fig. 23 Instrument Panel Lower SilencerÐLHD
Shown
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 24 Knee BolsterÐLHD Shown
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 25 Interlock/Upstop Switch Location
1 - INTERLOCK SWITCH
2 - UPSTOP SWITCH
3 - RETAINER - UPSTOP BRACKET
4 - CONNECTORS
RSCLUTCH6-13
Page 351 of 2585
ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE COOLING
SYSTEM
Establish what driving condition caused the cooling
system complaint. The problem may be caused by an
abnormal load on the system such as the following:
prolonged idle, very high ambient temperature, slight
tail wind at idle, slow traffic speed, traffic jam, high
speed, steep grade.
DRIVING TECHNIQUES
To avoid overheating the cooling system:
(1) Idle with A/C off when temperature gauge is at
end of normal range.
(2) Do not increase engine speed for more air flow
and coolant flow because the electric motor fan sys-
tems are not responsive to engine RPM. The added
cooling from higher coolant flow rate is more than
offset by increased heat rejection (engine heat added
to coolant).
TRAILER TOWING
Consult the owner's manual under Trailer Towing
and do not exceed specified limits.
VISUAL INSPECTION
If the cooling system problem is not caused by a
driving condition, perform a visual inspection to
determine if there was a recent service or accident
repair, including the following:
²Loose/damaged water pump drive belt
²Incorrect cooling system refilling (trapped air or
low level)
²Brakes possibly dragging
²Damaged hoses
²Loose/damaged hose clamps
²Damaged/incorrect engine thermostat
²Damaged cooling fan motor, fan blade and fan
shroud
²Damaged head gasket
²Damaged water pump
²Damaged radiator
²Damaged coolant recovery system
²Damaged heater core
²Open/shorted electrical circuits
If the visual inspection reveals none of the above
as cause for a cooling system complaint, refer to the
following diagnostic charts.
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
PRESSURE CAP IS BLOWING
OFF STEAM AND/OR COOLANT.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READING
MAY BE ABOVE NORMAL BUT
NOT HIGH. COOLANT LEVEL MAY
BE HIGH IN COOLANT RESERVE/
OVERFLOW TANK.1. Pressure relief valve in radiator
cap is defective, or was not
properly seated.1. Check condition of radiator cap
and cap seal. (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ENGINE/RADIATOR
PRESSURE CAP - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) Replace cap as
necessary.
2. Incorrect cap was installed. 2. Replace cap as necessary.
3. Incorrect coolant mixture. 3. Check concentration level of the
coolant. (Refer to 7 - COOLING/
ENGINE/COOLANT - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) Adjust the ethylene
glycol-to-water ratio as required.
COOLANT LOSS TO THE
GROUND WITHOUT PRESSURE
CAP BLOWOFF. GAUGE IS
READING HIGH OR HOT.1. Coolant leaks in radiator, cooling
system hoses, water pump or
engine.1. Pressure test and repair as
necessary. (Refer to 7 - COOLING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
7 - 14 ENGINERS
Page 365 of 2585

WARNING: THE WARNING WORDS ªDO NOT OPEN
HOTº ON THE RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP IS A
SAFETY PRECAUTION. WHEN HOT, PRESSURE
BUILDS UP IN COOLING SYSTEM. TO PREVENT
SCALDING OR INJURY, THE RADIATOR CAP
SHOULD NOT BE REMOVED WHILE THE SYSTEM
IS HOT OR UNDER PRESSURE.
There is no need to remove the radiator cap at any
timeexceptfor the following purposes:
(1) Check and adjust coolant freeze point.
(2) Refill system with new coolant.
(3) Conducting service procedures.
(4) Checking for vacuum leaks.
WARNING: IF VEHICLE HAS BEEN RUN RECENTLY,
WAIT 15 MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING CAP. THEN
PLACE A SHOP TOWEL OVER THE CAP AND WITH-
OUT PUSHING DOWN ROTATE COUNTERCLOCK-
WISE TO THE FIRST STOP. ALLOW FLUIDS TO
ESCAPE THROUGH THE OVERFLOW TUBE AND
WHEN THE SYSTEM STOPS PUSHING COOLANT
AND STEAM INTO THE CRS TANK AND PRESSURE
DROPS PUSH DOWN AND REMOVE THE CAP COM-
PLETELY. SQUEEZING THE RADIATOR INLET HOSE
WITH A SHOP TOWEL (TO CHECK PRESSURE)
BEFORE AND AFTER TURNING TO THE FIRST
STOP IS RECOMMENDED.
CLEANING
Use only a mild soap to clean the pressure cap.
INSPECTION
Hold the cap in your hand,top side up(Fig. 20).
The vent valve at the bottom of the cap should open.
If the rubber gasket has swollen, preventing the
valve from opening, replace the cap.Hold the cleaned cap in your hand,upside down.
If any light can be seen between vent valve and the
rubber gasket, replace the cap.Do not use a
replacement cap that has a spring to hold the
vent shut.
A replacement cap must be of the type designed for
coolant reserve systems. This design ensures coolant
return to the radiator.
RADIATOR FAN
DESCRIPTION
The dual radiator fans are mounted to the back
side of the radiator (Fig. 21). The radiator fan consist
of the fan blade, electric motor and a support shroud
which are all serviced as an assembly.
Fig. 20 Cooling System Pressure Cap
1 - OVERFLOW NIPPLE
2 - MAIN SPRING
3 - GASKET RETAINER
4 - STAINLESS-STEEL SWIVEL TOP
5 - RUBBER SEALS
6 - VENT VALVE
7 - RADIATOR
8 - FILLER NECK
7 - 28 ENGINERS
RADIATOR PRESSURE CAP (Continued)