Servo CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 124 of 2339
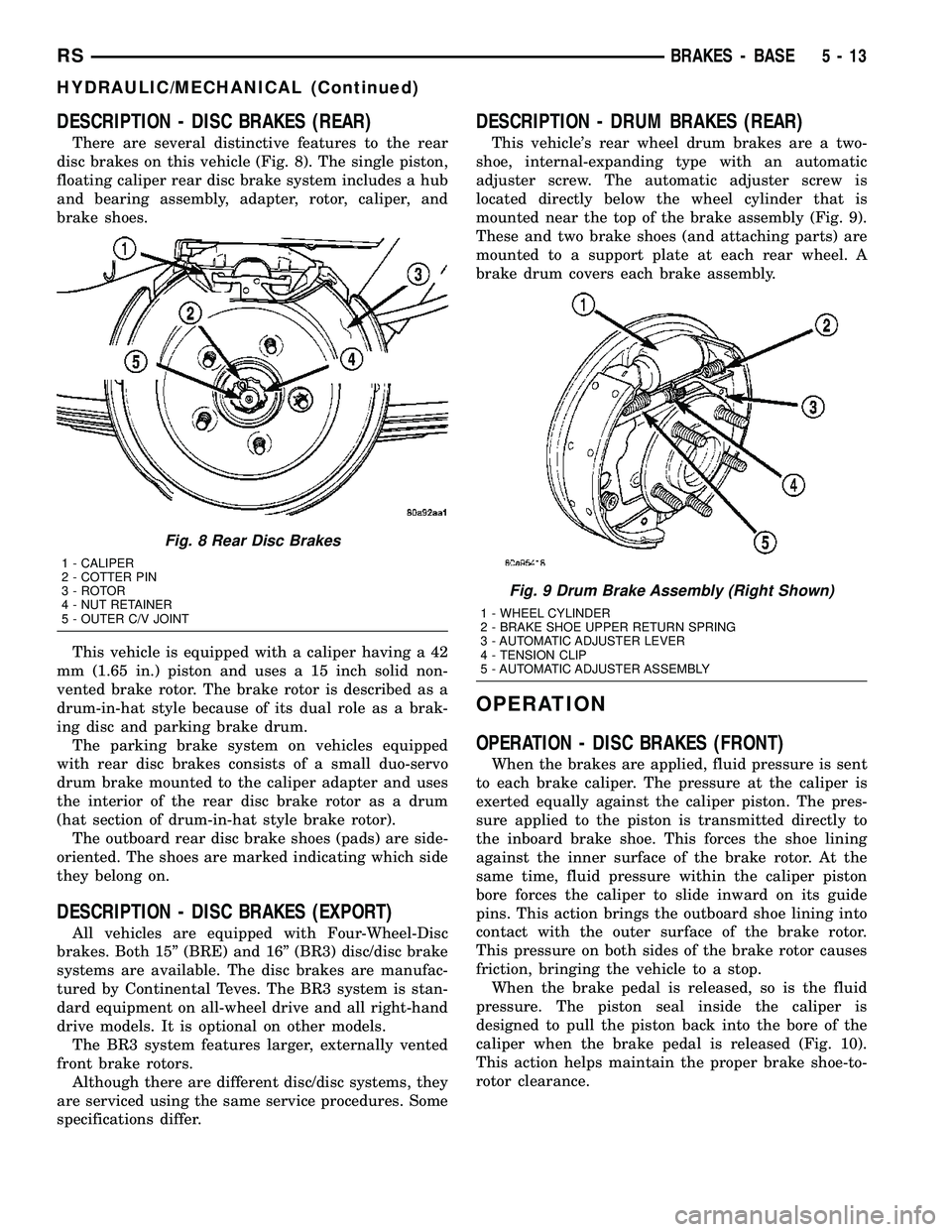
DESCRIPTION - DISC BRAKES (REAR)
There are several distinctive features to the rear
disc brakes on this vehicle (Fig. 8). The single piston,
floating caliper rear disc brake system includes a hub
and bearing assembly, adapter, rotor, caliper, and
brake shoes.
This vehicle is equipped with a caliper having a 42
mm (1.65 in.) piston and uses a 15 inch solid non-
vented brake rotor. The brake rotor is described as a
drum-in-hat style because of its dual role as a brak-
ing disc and parking brake drum.
The parking brake system on vehicles equipped
with rear disc brakes consists of a small duo-servo
drum brake mounted to the caliper adapter and uses
the interior of the rear disc brake rotor as a drum
(hat section of drum-in-hat style brake rotor).
The outboard rear disc brake shoes (pads) are side-
oriented. The shoes are marked indicating which side
they belong on.
DESCRIPTION - DISC BRAKES (EXPORT)
All vehicles are equipped with Four-Wheel-Disc
brakes. Both 15º (BRE) and 16º (BR3) disc/disc brake
systems are available. The disc brakes are manufac-
tured by Continental Teves. The BR3 system is stan-
dard equipment on all-wheel drive and all right-hand
drive models. It is optional on other models.
The BR3 system features larger, externally vented
front brake rotors.
Although there are different disc/disc systems, they
are serviced using the same service procedures. Some
specifications differ.
DESCRIPTION - DRUM BRAKES (REAR)
This vehicle's rear wheel drum brakes are a two-
shoe, internal-expanding type with an automatic
adjuster screw. The automatic adjuster screw is
located directly below the wheel cylinder that is
mounted near the top of the brake assembly (Fig. 9).
These and two brake shoes (and attaching parts) are
mounted to a support plate at each rear wheel. A
brake drum covers each brake assembly.
OPERATION
OPERATION - DISC BRAKES (FRONT)
When the brakes are applied, fluid pressure is sent
to each brake caliper. The pressure at the caliper is
exerted equally against the caliper piston. The pres-
sure applied to the piston is transmitted directly to
the inboard brake shoe. This forces the shoe lining
against the inner surface of the brake rotor. At the
same time, fluid pressure within the caliper piston
bore forces the caliper to slide inward on its guide
pins. This action brings the outboard shoe lining into
contact with the outer surface of the brake rotor.
This pressure on both sides of the brake rotor causes
friction, bringing the vehicle to a stop.
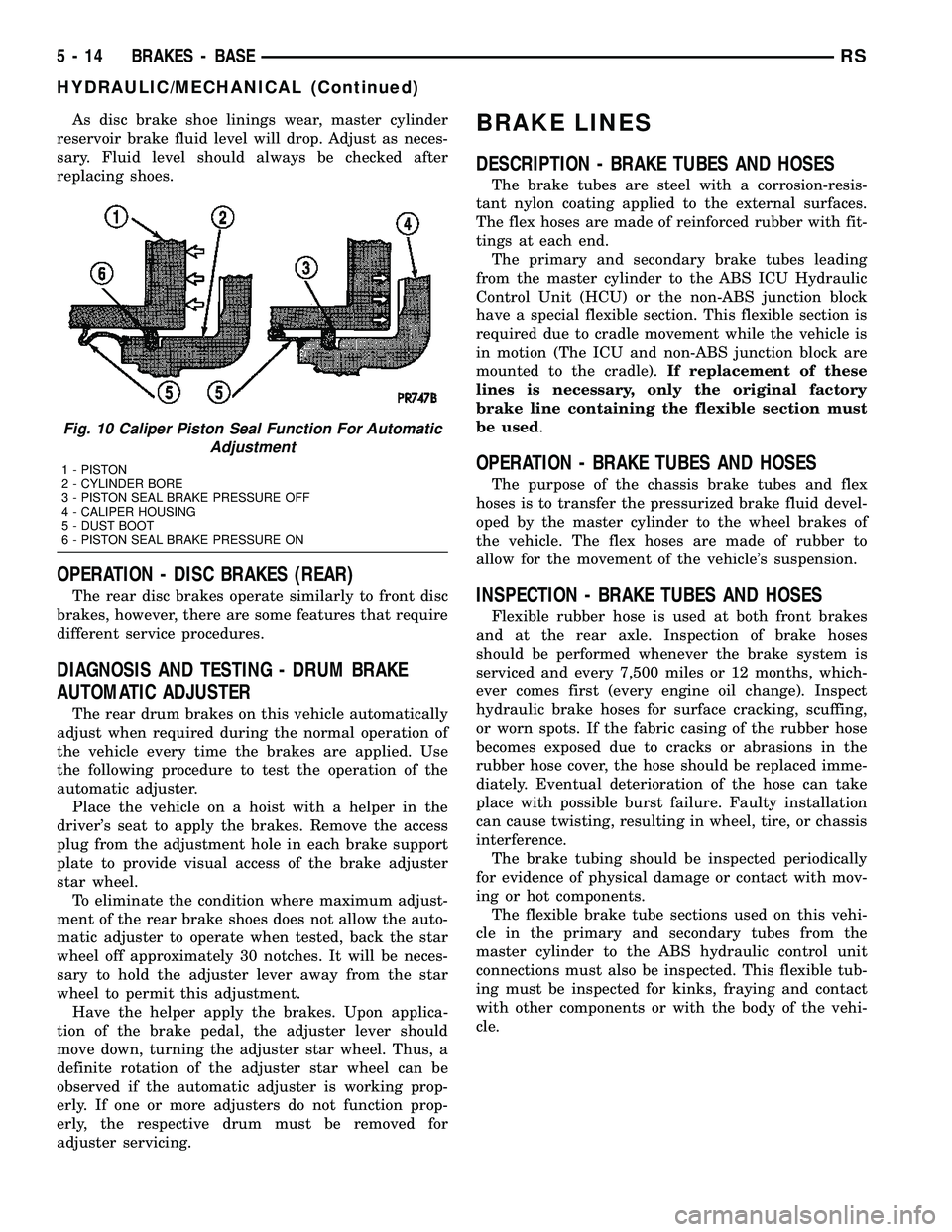
When the brake pedal is released, so is the fluid
pressure. The piston seal inside the caliper is
designed to pull the piston back into the bore of the
caliper when the brake pedal is released (Fig. 10).
This action helps maintain the proper brake shoe-to-
rotor clearance.
Fig. 8 Rear Disc Brakes
1 - CALIPER
2 - COTTER PIN
3 - ROTOR
4 - NUT RETAINER
5 - OUTER C/V JOINT
Fig. 9 Drum Brake Assembly (Right Shown)
1 - WHEEL CYLINDER
2 - BRAKE SHOE UPPER RETURN SPRING
3 - AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER LEVER
4 - TENSION CLIP
5 - AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER ASSEMBLY
RSBRAKES - BASE5-13
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 125 of 2339
As disc brake shoe linings wear, master cylinder
reservoir brake fluid level will drop. Adjust as neces-
sary. Fluid level should always be checked after
replacing shoes.
OPERATION - DISC BRAKES (REAR)
The rear disc brakes operate similarly to front disc
brakes, however, there are some features that require
different service procedures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRUM BRAKE
AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER
The rear drum brakes on this vehicle automatically
adjust when required during the normal operation of
the vehicle every time the brakes are applied. Use
the following procedure to test the operation of the
automatic adjuster.
Place the vehicle on a hoist with a helper in the
driver's seat to apply the brakes. Remove the access
plug from the adjustment hole in each brake support
plate to provide visual access of the brake adjuster
star wheel.
To eliminate the condition where maximum adjust-
ment of the rear brake shoes does not allow the auto-
matic adjuster to operate when tested, back the star
wheel off approximately 30 notches. It will be neces-
sary to hold the adjuster lever away from the star
wheel to permit this adjustment.
Have the helper apply the brakes. Upon applica-
tion of the brake pedal, the adjuster lever should
move down, turning the adjuster star wheel. Thus, a
definite rotation of the adjuster star wheel can be
observed if the automatic adjuster is working prop-
erly. If one or more adjusters do not function prop-
erly, the respective drum must be removed for
adjuster servicing.
BRAKE LINES
DESCRIPTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
The brake tubes are steel with a corrosion-resis-
tant nylon coating applied to the external surfaces.
The flex hoses are made of reinforced rubber with fit-
tings at each end.
The primary and secondary brake tubes leading
from the master cylinder to the ABS ICU Hydraulic
Control Unit (HCU) or the non-ABS junction block
have a special flexible section. This flexible section is
required due to cradle movement while the vehicle is
in motion (The ICU and non-ABS junction block are
mounted to the cradle).If replacement of these
lines is necessary, only the original factory
brake line containing the flexible section must
be used.
OPERATION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
The purpose of the chassis brake tubes and flex
hoses is to transfer the pressurized brake fluid devel-
oped by the master cylinder to the wheel brakes of
the vehicle. The flex hoses are made of rubber to
allow for the movement of the vehicle's suspension.
INSPECTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes
and at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses
should be performed whenever the brake system is
serviced and every 7,500 miles or 12 months, which-
ever comes first (every engine oil change). Inspect
hydraulic brake hoses for surface cracking, scuffing,
or worn spots. If the fabric casing of the rubber hose
becomes exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the
rubber hose cover, the hose should be replaced imme-
diately. Eventual deterioration of the hose can take
place with possible burst failure. Faulty installation
can cause twisting, resulting in wheel, tire, or chassis
interference.
The brake tubing should be inspected periodically
for evidence of physical damage or contact with mov-
ing or hot components.
The flexible brake tube sections used on this vehi-
cle in the primary and secondary tubes from the
master cylinder to the ABS hydraulic control unit
connections must also be inspected. This flexible tub-
ing must be inspected for kinks, fraying and contact
with other components or with the body of the vehi-
cle.
Fig. 10 Caliper Piston Seal Function For Automatic
Adjustment
1 - PISTON
2 - CYLINDER BORE
3 - PISTON SEAL BRAKE PRESSURE OFF
4 - CALIPER HOUSING
5 - DUST BOOT
6 - PISTON SEAL BRAKE PRESSURE ON
5 - 14 BRAKES - BASERS
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 130 of 2339
shoes on the opposite side of the vehicle as well as
the shoes failing inspection.
If the brake shoe assemblies do not require
replacement, be sure to reinstall the brake shoes in
the original position they were removed from.
INSTALLATION - REAR DISC BRAKE SHOES
(1) Completely retract caliper piston back into pis-
ton bore of caliper assembly.
(2) Lubricate both adapter abutments where the
shoes contact with a liberal amount of MopartMul-
tipurpose Lubricant, or equivalent.
(3) If removed, install the brake rotor on the hub,
making sure it is squarely seated on the face of the
hub.
(4) Install the inboard brake shoe into the caliper
piston by firmly pressing it into the piston bore using
your thumbs. Be sure inboard brake shoe is posi-
tioned squarely against the face of the caliper piston.
NOTE: The outboard shoes are different left to
right. They can be identified by a L or R stamped on
the clip.
(5) Install the outboard brake shoe on the disc
brake caliper. Be sure the outboard shoe is positioned
squarely against the outboard fingers of the caliper.
CAUTION: Use care when installing the caliper
assembly onto the adapter, so the caliper guide pin
bushings do not get damaged by the mounting
bosses.
(6) Carefully lower caliper and brake shoes over
rotor and onto adapter, reversing the removal proce-
dure (Fig. 15).
CAUTION: When installing the caliper guide pin
bolts extreme caution should be taken not to
crossthread the guide pin bolts.
(7) Install the caliper guide pin bolts. Tighten the
guide pin bolts to a torque of 35 N´m (26 ft. lbs.).
(8) Install the wheel and tire assembly. Tighten
the wheel mounting nuts in proper sequence until all
nuts are torqued to half specification. Then repeat
the tightening sequence to the full specified torque of
135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(9) Lower vehicle.
CAUTION: Before moving vehicle, pump the brake
pedal several times to insure the vehicle has a firm
brake pedal to adequately stop the vehicle.
(10) Pump brake pedal several times to set brake
shoes to rotors.
(11) Check fluid level in reservoir.(12) Road test the vehicle and make several stops
to wear off any foreign material on the brakes and to
seat the brake shoe linings.
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - REAR
DRUM
REMOVAL - REAR DRUM BRAKE SHOES
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(2) Remove the rear wheel and tire assemblies
from the vehicle.
(3) Remove rear brake drum to hub retaining clips
(if equipped), then remove rear brake drums. (Refer
to 5 - BRAKES/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/DRUM
- REMOVAL)
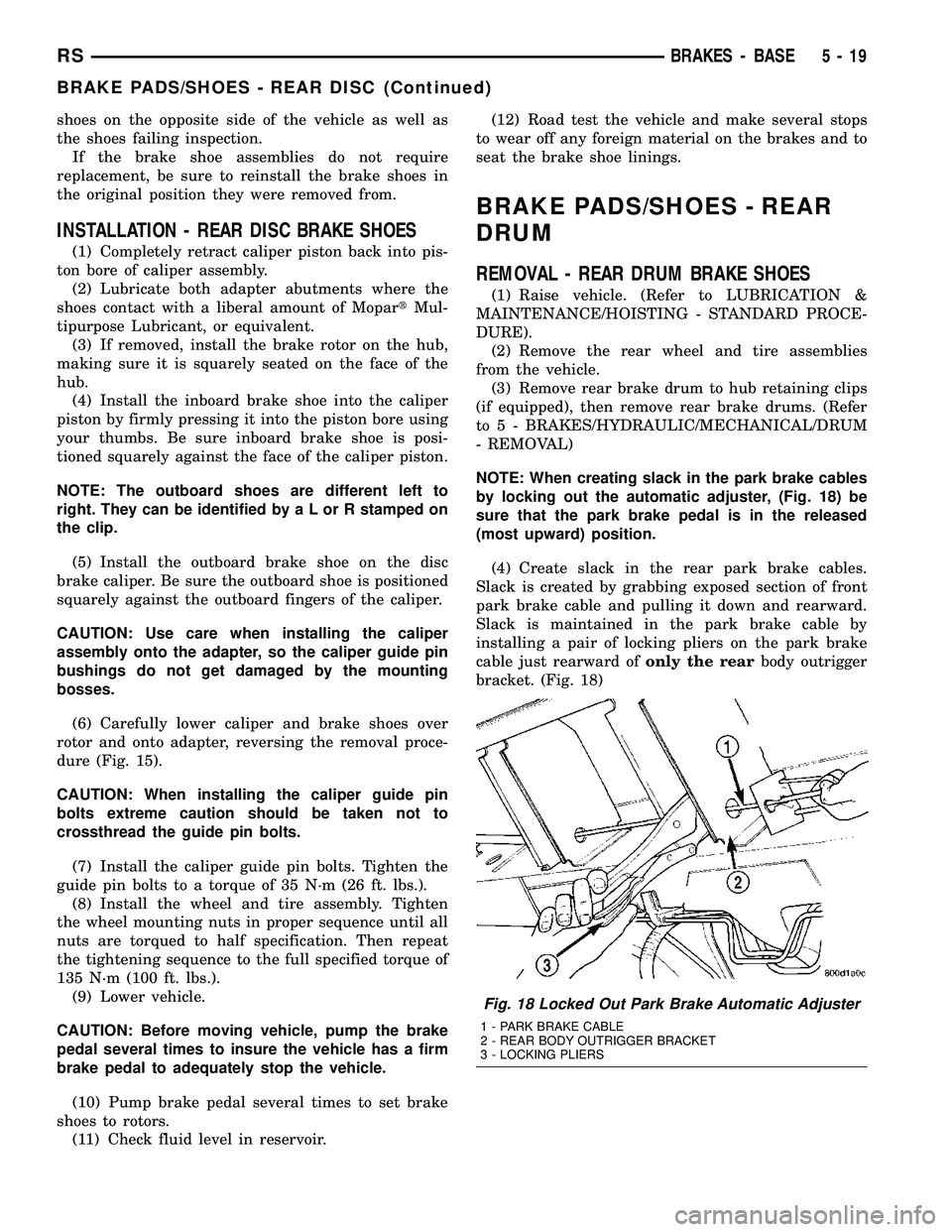
NOTE: When creating slack in the park brake cables
by locking out the automatic adjuster, (Fig. 18) be
sure that the park brake pedal is in the released
(most upward) position.
(4) Create slack in the rear park brake cables.
Slack is created by grabbing exposed section of front
park brake cable and pulling it down and rearward.
Slack is maintained in the park brake cable by
installing a pair of locking pliers on the park brake
cable just rearward ofonly the rearbody outrigger
bracket. (Fig. 18)
Fig. 18 Locked Out Park Brake Automatic Adjuster
1 - PARK BRAKE CABLE
2 - REAR BODY OUTRIGGER BRACKET
3 - LOCKING PLIERS
RSBRAKES - BASE5-19
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - REAR DISC (Continued)
Page 135 of 2339

DISC BRAKE CALIPER -
FRONT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER
(CONTINENTAL TEVES BRAKES)
(1) Depress the brake pedal past its first inch of
travel and hold it in this position using a brake pedal
depressor (holding) tool. This is done to isolate the
master cylinder from the brake hydraulic system dis-
allowing the brake fluid to completely drain out of
the brake fluid reservoir.
(2) Raise the vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(3) Remove front wheel and tire assembly.
(4) Remove the banjo bolt connecting the brake
hose to the brake caliper. There are two washers (one
on each side of the brake hose fitting) that will come
off with the banjo bolt. Discard these washers.
(5) Remove the 2 caliper guide pin bolts.
(6) Remove the brake caliper from the adapter.
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER
(TRW BRAKES)
(1) Using a brake pedal holding tool, depress the
brake pedal past its first one inch of travel and hold
it in this position. This will isolate the master cylin-
der from the brake hydraulic system and will not
allow the brake fluid to drain out of the master cyl-
inder reservoir when the lines are opened.
(2) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE.
(3) Remove the front tire and wheel assembly.
(4) Remove the banjo bolt connecting the brake
hose to the brake caliper (Fig. 31). There are two
washers (one on each side of the flex hose fitting)
that will come off with the banjo bolt. Discard the
washers.
(5) Remove the two brake caliper guide pin bolts
(Fig. 31).
(6) Remove the disc brake caliper from the disc
brake adapter.
DISASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY - CALIPER GUIDE PIN
BUSHINGS (CONTINENTAL TEVES BRAKES)
Before disassembling the brake caliper, clean and
inspect it. Refer to CLEANING or INSPECTION in
this section.(1) Using your fingers, collapse one side of the rub-
ber guide pin bushing. Pull the guide pin bushing out
the other side of the brake caliper mounting boss.
(2) Repeat this procedure on the remaining bush-
ing.
DISASSEMBLY - CALIPER PISTON AND SEAL
WARNING: UNDER NO CONDITION SHOULD HIGH
PRESSURE AIR EVER BE USED TO REMOVE A PIS-
TON FROM A CALIPER BORE. PERSONAL INJURY
COULD RESULT FROM SUCH A PRACTICE.
NOTE: Before disassembling the brake caliper,
clean and inspect it. Refer to CLEANING AND
INSPECTION in this section.
NOTE: The safest way to remove the piston from
the caliper bore is to use the hydraulic pressure of
the vehicle's brake system.
(1) Following the removal procedure in DISC
BRAKE SHOES found in this section, remove the
caliper from the brake rotor and hang the assembly
on a wire hook away from rotor and body of the vehi-
cle so brake fluid cannot get on these components.
Remove the brake shoes, and place a small piece of
wood between the piston and caliper fingers.
(2) Carefully depress the brake pedal to hydrauli-
cally push piston out of its bore. Once completed,
apply and hold down the brake pedal to any position
beyond the first inch of pedal travel using a brake
pedal holding tool. This will prevent the fluid in the
Fig. 31 Brake Caliper Mounting (Typical)
1 - BRAKE HOSE
2 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - BANJO BOLT
4 - CALIPER GUIDE PIN BOLTS
5 - 24 BRAKES - BASERS
Page 136 of 2339

master cylinder reservoir from completely draining
out.
(3) Disconnect the brake fluid flex hose from the
caliper assembly and remove it from the vehicle.
CAUTION: Do not use excessive force when clamp-
ing caliper in vise. Excessive vise pressure will
cause bore distortion.
(4) Mount the caliper in a vise equipped with pro-
tective jaws.
(5) Remove the piston dust boot from the caliper
and discard.
NOTE: Do not use a screw driver or other metal tool
for seal removal. Using such tools can scratch the
bore or leave burrs on the seal groove edges.
(6) Using a soft tool such as a plastic trim stick,
work the piston seal out of its groove in caliper pis-
ton bore (Fig. 32). Discard the old seal.
(7) Clean the piston bore and drilled passage ways
using alcohol or a suitable solvent. Wipe it dry using
only a lint-free cloth.
(8) Inspect the piston bore for scoring or pitting.
Bores that show light scratches or corrosion can usu-
ally be cleared of the light scratches or corrosion
using crocus cloth.CLEANING - CALIPER
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ACCUMULATING ON
BRAKE PARTS DURING NORMAL USE MAY CON-
TAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS FROM PRODUCTION OR
AFTERMARKET BRAKE LININGS. BREATHING
EXCESSIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS
FIBERS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM.
EXERCISE CARE WHEN SERVICING BRAKE
PARTS. DO NOT SAND OR GRIND BRAKE LINING
UNLESS EQUIPMENT USED IS DESIGNED TO CON-
TAIN THE DUST RESIDUE. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE
PARTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING. CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE BY
DAMPENING THE BRAKE COMPONENTS WITH A
FINE MIST OF WATER, THEN WIPING THE BRAKE
COMPONENTS CLEAN WITH A DAMPENED CLOTH.
DISPOSE OF CLOTH AND ALL RESIDUE CONTAIN-
ING ASBESTOS FIBERS IN AN IMPERMEABLE
CONTAINER WITH THE APPROPRIATE LABEL. FOL-
LOW PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY THE OCCUPA-
TIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION
(OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
AGENCY (EPA) FOR THE HANDLING, PROCESSING,
AND DISPOSING OF DUST OR DEBRIS THAT MAY
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS.
To clean or flush the internal passages of the brake
caliper, use fresh brake fluid or MopartNon-Chlori-
nated Brake Parts Cleaner. Never use gasoline, ker-
osene, alcohol, oil, transmission fluid or any fluid
containing mineral oil to clean the caliper. These flu-
ids will damage rubber cups and seals.
INSPECTION - CALIPER
Inspect the disc brake caliper for the following:
²Brake fluid leaks in and around boot area and
inboard lining
²Ruptures, brittleness or damage to the piston
dust boot
²Damaged, dry or brittle guide pin dust boots
If caliper fails inspection, disassemble and recondi-
tion caliper, replacing the seals and dust boots.
ASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY - CALIPER GUIDE PIN BUSHINGS
(CONTINENTAL TEVES BRAKES)
(1) Fold the guide pin bushing in half lengthwise.
NOTE: To avoid damage to the bushing, do not use
a sharp object to install the guide pin bushing.
(2) Insert the folded bushing into the caliper
mounting boss using your fingers from the rear of
the caliper.
Fig. 32 Removing Piston Seal
1 - PLASTIC TRIM STICK
2 - CALIPER
3 - PISTON SEAL GROOVE
4 - PISTON SEAL
RSBRAKES - BASE5-25
DISC BRAKE CALIPER - FRONT (Continued)
Page 139 of 2339

DISC BRAKE CALIPER - REAR
REMOVAL - REAR DISC BRAKE CALIPER
NOTE: Handling of the rotor and caliper, must be
done in such a way as to avoid damage to the rotor
and scratching or nicking of lining on the brake
shoes.
(1) Depress the brake pedal past its first inch of
travel and hold it in this position using a brake pedal
depressor (holding) tool. This is done to isolate the
master cylinder from the brake hydraulic system dis-
allowing the brake fluid to completely drain out of
the brake fluid reservoir.
(2) Raise the vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(3) Remove rear wheel and tire assembly from
vehicle.
(4) Remove the banjo bolt connecting the brake
hose to the brake caliper. There are two washers (one
on each side of the brake hose fitting) that will come
off with the banjo bolt. Discard these washers.
(5) Remove the disc brake caliper to adapter guide
pin bolts (Fig. 36).
(6) Remove rear caliper from adapter using the fol-
lowing procedure. First rotate front of caliper up
from the adapter. Then pull the rear of the caliper
and the outboard brake shoe anti-rattle clip out from
under the rear abutment on the adapter (Fig. 37).
(7) If the brake rotor requires removal, it can now
be removed by first removing the retainer clips fromthe wheel mounting studs, then pulling the rotor
straight off the studs.
DISASSEMBLY - CALIPER PISTON AND SEAL
WARNING: UNDER NO CONDITION SHOULD HIGH
PRESSURE AIR EVER BE USED TO REMOVE A PIS-
TON FROM A CALIPER BORE. PERSONAL INJURY
COULD RESULT FROM SUCH A PRACTICE.
NOTE: Before disassembling the brake caliper,
clean and inspect it. Refer to CLEANING AND
INSPECTION in this section.
NOTE: The safest way to remove the piston from
the caliper bore is to use the hydraulic pressure of
the vehicle's brake system.
(1) Following the removal procedure in DISC
BRAKE SHOES found in this section, remove the
caliper from the brake rotor and hang the assembly
on a wire hook away from rotor and body of the vehi-
cle so brake fluid cannot get on these components.
Remove the brake shoes, and place a small piece of
wood between the piston and caliper fingers.
(2) Carefully depress the brake pedal to hydrauli-
cally push piston out of its bore. Once completed,
apply and hold down the brake pedal to any position
beyond the first inch of pedal travel using a brake
pedal holding tool. This will prevent the fluid in the
master cylinder reservoir from completely draining
out.
Fig. 36 Caliper Guide Pin Bolts
1 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
2 - ADAPTER
3 - AXLE
4 - GUIDE PIN BOLTS
5 - DRIVESHAFT (AWD MODELS ONLY)
Fig. 37 Removing/Installing Caliper
1 - LIFT THIS END OF CALIPER AWAY FROM ADAPTER FIRST
2 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
3 - ADAPTER ABUTMENT
4 - OUTBOARD BRAKE SHOE HOLD DOWN CLIP
5 - OUTBOARD BRAKE SHOE
6 - ROTOR
7 - ADAPTER
5 - 28 BRAKES - BASERS
Page 144 of 2339

FLUID
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts.
Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of
petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush system. Replace master cylinder, propor-
tioning valve, caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals,
Antilock Brake hydraulic unit and all hydraulic fluid
hoses.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BRAKE FLUID
LEVEL CHECKING
Check master cylinder reservoir fluid level a mini-
mum of twice annually.
Fluid reservoirs are marked with the words FULL
and ADD to indicate proper brake fluid fill level of
the master cylinder.
If necessary, add brake fluid to bring the level to
the bottom of the FULL mark on the side of the mas-
ter cylinder fluid reservoir.
Use only Mopartbrake fluid or equivalent from a
sealed container. Brake fluid must conform to DOT 3
specifications (DOT 4 or DOT 4+ are acceptable).
DO NOTuse brake fluid with a lower boiling
point, as brake failure could result during prolonged
hard braking.
Use only brake fluid that was stored in a tightly-
sealed container.
DO NOTuse petroleum-based fluid because seal
damage will result. Petroleum based fluids would be
items such as engine oil, transmission fluid, power
steering fluid etc.
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FLUID
The brake fluid used in this vehicle must conform
to DOT 3 specifications (DOT 4 and DOT 4+ are
acceptable) and SAE J1703 standards. No other type
of brake fluid is recommended or approved for usage
in the vehicle brake system. Use only MopartBrake
Fluid or equivalent from a tightly sealed container.CAUTION: Never use reclaimed brake fluid or fluid
from an container which has been left open. An
open container of brake fluid will absorb moisture
from the air and contaminate the fluid.
CAUTION: Never use any type of a petroleum-based
fluid in the brake hydraulic system. Use of such
type fluids will result in seal damage of the vehicle
brake hydraulic system causing a failure of the
vehicle brake system. Petroleum based fluids would
be items such as engine oil, transmission fluid,
power steering fluid, etc.
JUNCTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
A junction block is used on vehicles that are not
equipped with antilock brakes (ABS). The junction
block mounts in the same location as the integrated
control unit (ICU) does on vehicles equipped with
ABS. This allows for use of the same brake tube con-
figuration on all vehicles. The junction block is
located on the driver's side of the front suspension
cradle/crossmember below the master cylinder (Fig.
44).
It has six threaded ports to which the brake tubes
connect. Two are for the primary and secondary
brake tubes coming from the master cylinder. The
remaining four are for the chassis brake tubes going
to each brake assembly.
OPERATION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
The junction block distributes the brake fluid com-
ing from the master cylinder primary and secondary
ports to the four chassis brake tubes leading to the
brakes at each wheel. Since the junction block
mounts in the same location as the ABS integrated
control unit (ICU), it allows for the common use of
brake tubes going to the brakes whether the vehicle
is equipped with or without ABS.
NOTE: Although the brake tubes coming from the
master cylinder to the junction block or ABS ICU
may appear to be the same, they are not. They are
unique to each brake system application.
RSBRAKES - BASE5-33
Page 145 of 2339

REMOVAL - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
(1) Using a brake pedal depressor, move and lock
the brake pedal to a position past its first 1 inch of
travel. This will prevent brake fluid from draining
out of the master cylinder when the brake tubes are
removed from the junction block.
(2) Disconnect the battery negative cable.
(3) If the vehicle is equipped with speed control,
perform the following:
(a) Disconnect the battery positive cable.
(b) Remove the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - REMOVAL).
(c) Disconnect the vacuum hose connector at the
tank built into the battery tray.
(d) Remove the screw securing the coolant filler
neck to the battery tray.
(e) Remove the battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - REMOVAL).
(f) Remove the fasteners and move the speed
control servo off to the side, out of the way.
CAUTION: Before removing the brake tubes from
the junction block, the junction block and the brake
tubes must be thoroughly cleaned. This is required
to prevent contamination from entering the brake
hydraulic system.
(4) Remove the four chassis brake tubes from the
top of the junction block (Fig. 44).(5) Remove the primary and secondary brake
tubes from the top of the junction block.
(6) Remove the bolts attaching the junction block
mounting bracket to the front suspension crossmem-
ber (Fig. 44), then remove the junction block.
INSTALLATION - NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
(1) Install the junction block and mounting bracket
on the front suspension crossmember (Fig. 44).
Install the mounting bolts and tighten to a torque of
28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(2) Install the primary and secondary brake tubes
from the master cylinder in their ports. Tighten tube
nuts to a torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.).Take care
not to twist tubes when tightening tube nuts.
They must be properly positioned to allow free
movement with rubber isolated suspension
crossmember.
(3) Install the four chassis brake tubes into the
outlet ports of the junction block. Tighten all 6 tube
nuts to a torque of 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.).
(4) If the vehicle is equipped with speed control,
perform the following:
(a) Install the speed control servo with its
mounting nuts.
(b) Connect the wiring harness to the speed con-
trol servo.
(c) Install the battery tray (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/TRAY - INSTALLA-
TION).
(d) Install the screw securing the coolant filler
neck to the battery tray.
(e) Reconnect the vacuum hose connector at the
tank built into the battery tray.
(f) Install the battery (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY - INSTALLA-
TION).
(g) Install the battery shield.
(5) Remove the brake pedal holder.
(6) Connect negative cable back on negative post of
the battery.
(7) Bleed the brake system thoroughly to ensure
that all air has been expelled from the hydraulic sys-
tem. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(8) Road test the vehicle to verify proper operation
of the brake system.
Fig. 44 NON-ABS JUNCTION BLOCK
1 - MASTER CYLINDER
2 - JUNCTION BLOCK
3 - SUSPENSION CROSSMEMBER
4 - MOUNTING BOLTS
5 - 34 BRAKES - BASERS
JUNCTION BLOCK (Continued)
Page 146 of 2339
MASTER CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
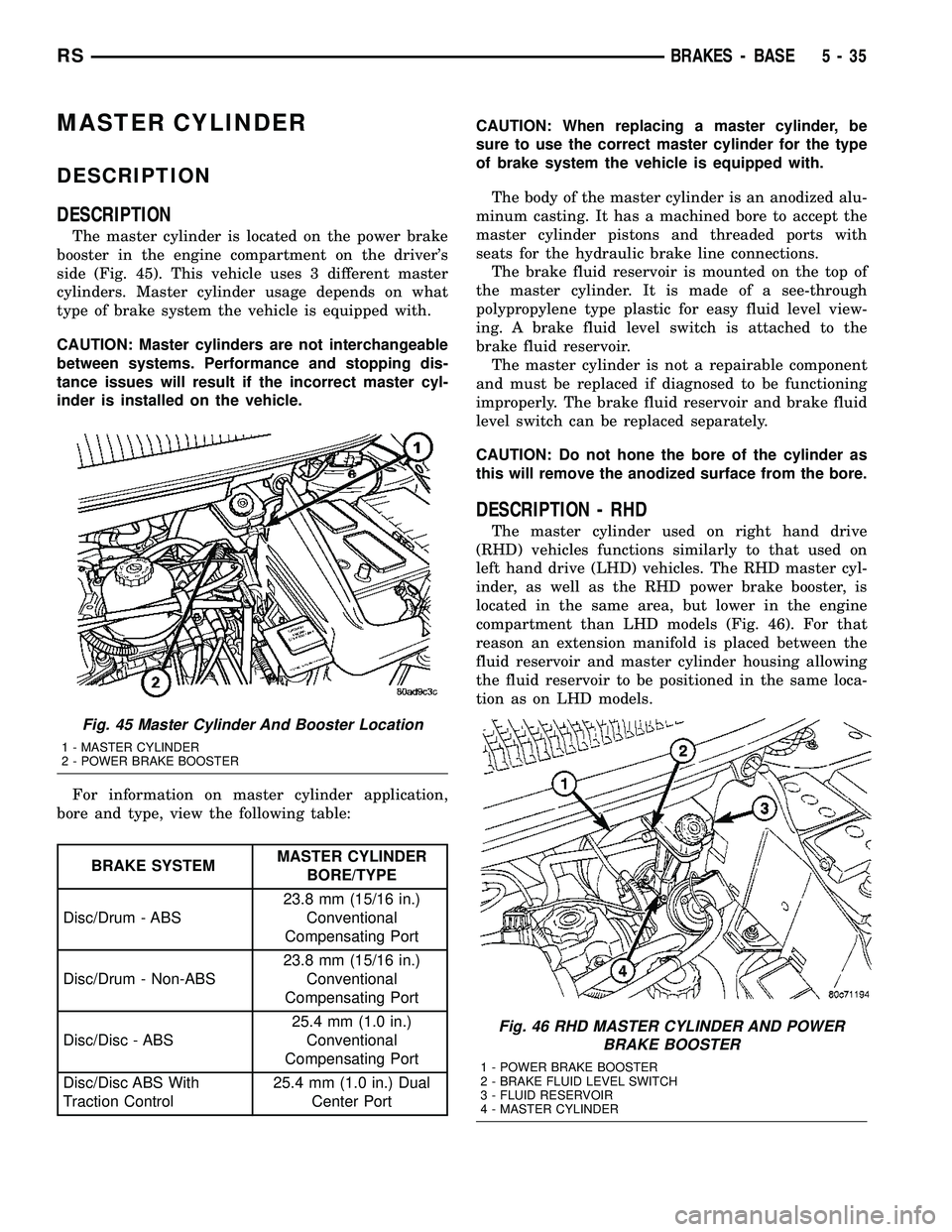
The master cylinder is located on the power brake
booster in the engine compartment on the driver's
side (Fig. 45). This vehicle uses 3 different master
cylinders. Master cylinder usage depends on what
type of brake system the vehicle is equipped with.
CAUTION: Master cylinders are not interchangeable
between systems. Performance and stopping dis-
tance issues will result if the incorrect master cyl-
inder is installed on the vehicle.
For information on master cylinder application,
bore and type, view the following table:
BRAKE SYSTEMMASTER CYLINDER
BORE/TYPE
Disc/Drum - ABS23.8 mm (15/16 in.)
Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Drum - Non-ABS23.8 mm (15/16 in.)
Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Disc - ABS25.4 mm (1.0 in.)
Conventional
Compensating Port
Disc/Disc ABS With
Traction Control25.4 mm (1.0 in.) Dual
Center PortCAUTION: When replacing a master cylinder, be
sure to use the correct master cylinder for the type
of brake system the vehicle is equipped with.
The body of the master cylinder is an anodized alu-
minum casting. It has a machined bore to accept the
master cylinder pistons and threaded ports with
seats for the hydraulic brake line connections.
The brake fluid reservoir is mounted on the top of
the master cylinder. It is made of a see-through
polypropylene type plastic for easy fluid level view-
ing. A brake fluid level switch is attached to the
brake fluid reservoir.
The master cylinder is not a repairable component
and must be replaced if diagnosed to be functioning
improperly. The brake fluid reservoir and brake fluid
level switch can be replaced separately.
CAUTION: Do not hone the bore of the cylinder as
this will remove the anodized surface from the bore.
DESCRIPTION - RHD
The master cylinder used on right hand drive
(RHD) vehicles functions similarly to that used on
left hand drive (LHD) vehicles. The RHD master cyl-
inder, as well as the RHD power brake booster, is
located in the same area, but lower in the engine
compartment than LHD models (Fig. 46). For that
reason an extension manifold is placed between the
fluid reservoir and master cylinder housing allowing
the fluid reservoir to be positioned in the same loca-
tion as on LHD models.
Fig. 45 Master Cylinder And Booster Location
1 - MASTER CYLINDER
2 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
Fig. 46 RHD MASTER CYLINDER AND POWER
BRAKE BOOSTER
1 - POWER BRAKE BOOSTER
2 - BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
3 - FLUID RESERVOIR
4 - MASTER CYLINDER
RSBRAKES - BASE5-35
Page 147 of 2339

OPERATION
When the brake pedal is depressed, the master cyl-
inder primary and secondary pistons apply brake
pressure through the chassis tubes to the brakes at
each tire and wheel assembly.
The master cylinder primary outlet port supplies
hydraulic pressure to the right front and left rear
brakes. The secondary outlet port supplies hydraulic
pressure to the left front and right rear brakes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MASTER CYLINDER
BLEEDING
CAUTION: When clamping master cylinder in vise,
only clamp master cylinder by its mounting flange.
Do not clamp master cylinder piston rod, reservoir,
seal or body.
(1) Clamp master cylinder in a vise.
NOTE: Use correct bleeder tubes when bleeding
master cylinder. Master cylinder outlet ports vary in
size and type depending on whether master cylin-
der is for a vehicle equipped with ABS or not. ABS
equipped master cylinders require the additional
use of ISO style flare adapters supplied in Special
Tool Package 8822 to be used in conjunction with
Bleeder Tubes, Special Tool Package 8358.
(2) Attach special tools for bleeding master cylin-
der in the following fashion:
(a)For non-ABS control equipped master
cylinders, thread a Bleeder Tube, Special Tool
8358±1, into each outlet port. Tighten each tube to
17 N´m (145 in. lbs.) torque. Flex bleeder tubes and
place open ends into mouth of fluid reservoir as far
down as possible (Fig. 47).
(b)For ABS equipped master cylinders,
thread one Adapter, Special Tool 8822±2, in each
outlet port. Tighten Adapters to 17 N´m (145 in.
lbs.) torque. Next, thread a Bleeder Tube, Special
Tool 8358±1, into each Adapter. Tighten each tube
to 17 N´m (145 in. lbs.) torque. Flex bleeder tubes
and place open ends into mouth of fluid reservoir
as far down as possible (Fig. 47).
NOTE: Make sure open ends of bleeder tubes stay
below surface of brake fluid once reservoir is filled
to proper level.
(3) Fill brake fluid reservoir with Mopartbrake
fluid or equivalent conforming to DOT 3 (DOT 4 and
DOT 4+ are acceptable) specifications. Make sure
fluid level is above tips of bleeder tubes in reservoir
to ensure no air is ingested during bleeding.
(4) Using a wooden dowel as a pushrod (Fig. 47),
slowly depress master cylinder pistons, then releasepressure, allowing pistons to return to released posi-
tion. Repeat several times until all air bubbles are
expelled. Make sure fluid level stays above tips of
bleeder tubes in reservoir while bleeding.
(5) Remove bleeder tubes from master cylinder
outlet ports, then plug outlet ports and install fill cap
on reservoir.
(6) Remove master cylinder from vise.
(7) Install master cylinder on vehicle. (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - BASE/HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/MAS-
TER CYLINDER - INSTALLATION)
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LHD
CAUTION: Vacuum in the power brake booster must
be pumped down (removed) before removing mas-
ter cylinder from power brake booster. This is nec-
essary to prevent the power brake booster from
sucking in any contamination as the master cylin-
der is removed. This can be done simply by pump-
ing the brake pedal, with the vehicle's engine not
running, until a firm feeling brake pedal is achieved.
(1) With engine not running, pump brake pedal
until a firm pedal is achieved (4-5 strokes).
(2) Disconnect negative battery terminal.
(3) Disconnect positive battery terminal.
(4) Remove battery shield.
Fig. 47 Master Cylinder Set Up For Bleeding
1 - BLEEDER TUBES 8358
2 - WOODEN DOWEL
3 - ADAPTER 8822-2 (USE ONLY ON ABS EQUIPPED MASTER
CYLINDERS)
4 - ADAPTER 8822-2 (USE ONLY ON ABS EQUIPPED MASTER
CYLINDERS)
5 - 36 BRAKES - BASERS
MASTER CYLINDER (Continued)