lock code CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 296 of 2339
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the Power Liftgate (PLG) control mod-
ule on the D-pillar and install retaining screw.
(2) Connect the wire harness connections to the
PLG control module. Be certain to slide connector
locks to the locked position.
(3) Install the D-pillar trim panel on the vehicle.
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/LEFT D-PILLAR
TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION)
(4) Connect the battery negative cable.
(5) Using an appropriate scan tool, check and
erase any PLG control module diagnostic trouble
codes.
(6) Verify PLG system operation. Cycle the PLG
through one complete open and close cycle, this will
allow the PLG control module to relearn its cycle
with the new components.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION
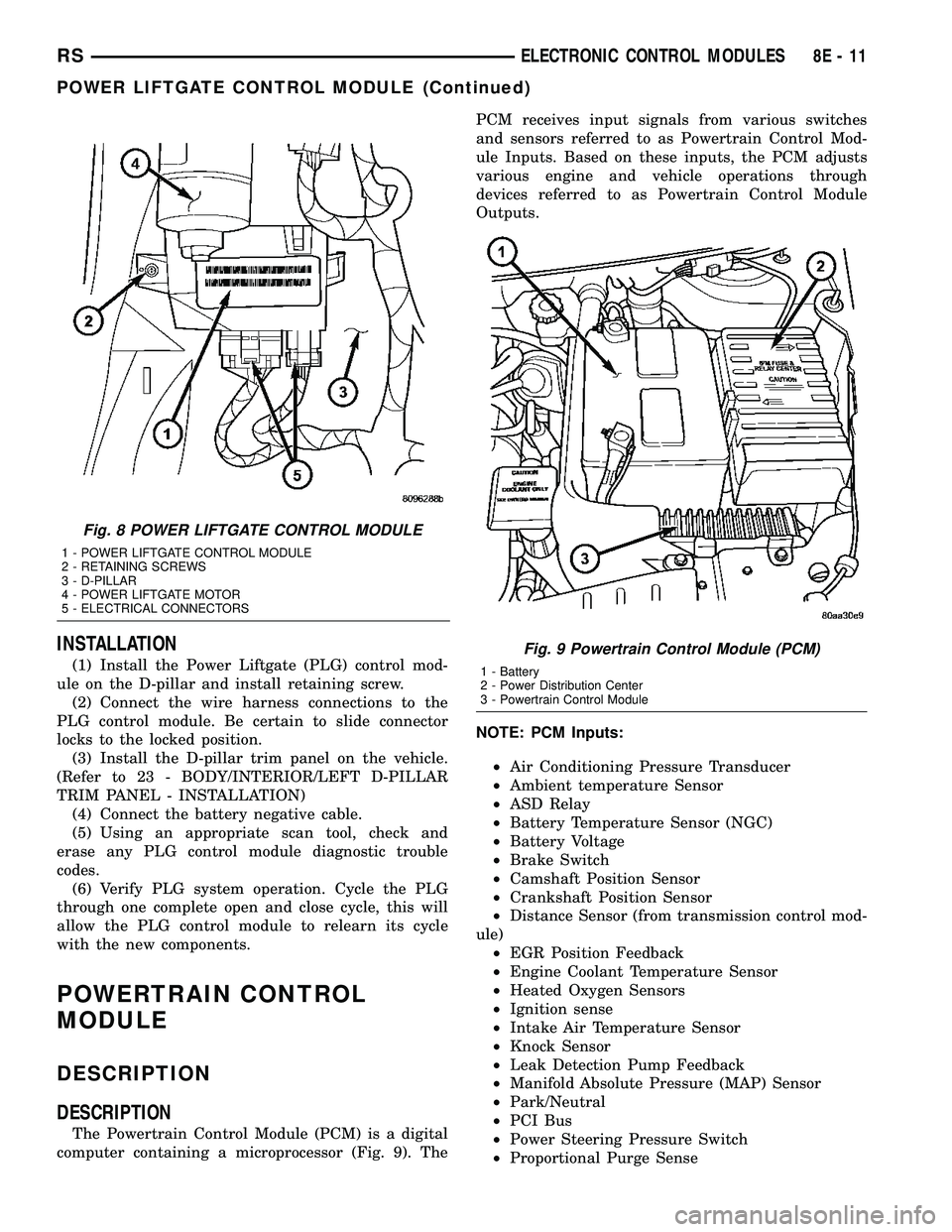
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 9). ThePCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors referred to as Powertrain Control Mod-
ule Inputs. Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts
various engine and vehicle operations through
devices referred to as Powertrain Control Module
Outputs.
NOTE: PCM Inputs:
²Air Conditioning Pressure Transducer
²Ambient temperature Sensor
²ASD Relay
²Battery Temperature Sensor (NGC)
²Battery Voltage
²Brake Switch
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Distance Sensor (from transmission control mod-
ule)
²EGR Position Feedback
²Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
²Heated Oxygen Sensors
²Ignition sense
²Intake Air Temperature Sensor
²Knock Sensor
²Leak Detection Pump Feedback
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Park/Neutral
²PCI Bus
²Power Steering Pressure Switch
²Proportional Purge Sense
Fig. 8 POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
1 - POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE
2 - RETAINING SCREWS
3 - D-PILLAR
4 - POWER LIFTGATE MOTOR
5 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
Fig. 9 Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
1 - Battery
2 - Power Distribution Center
3 - Powertrain Control Module
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-11
POWER LIFTGATE CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 302 of 2339
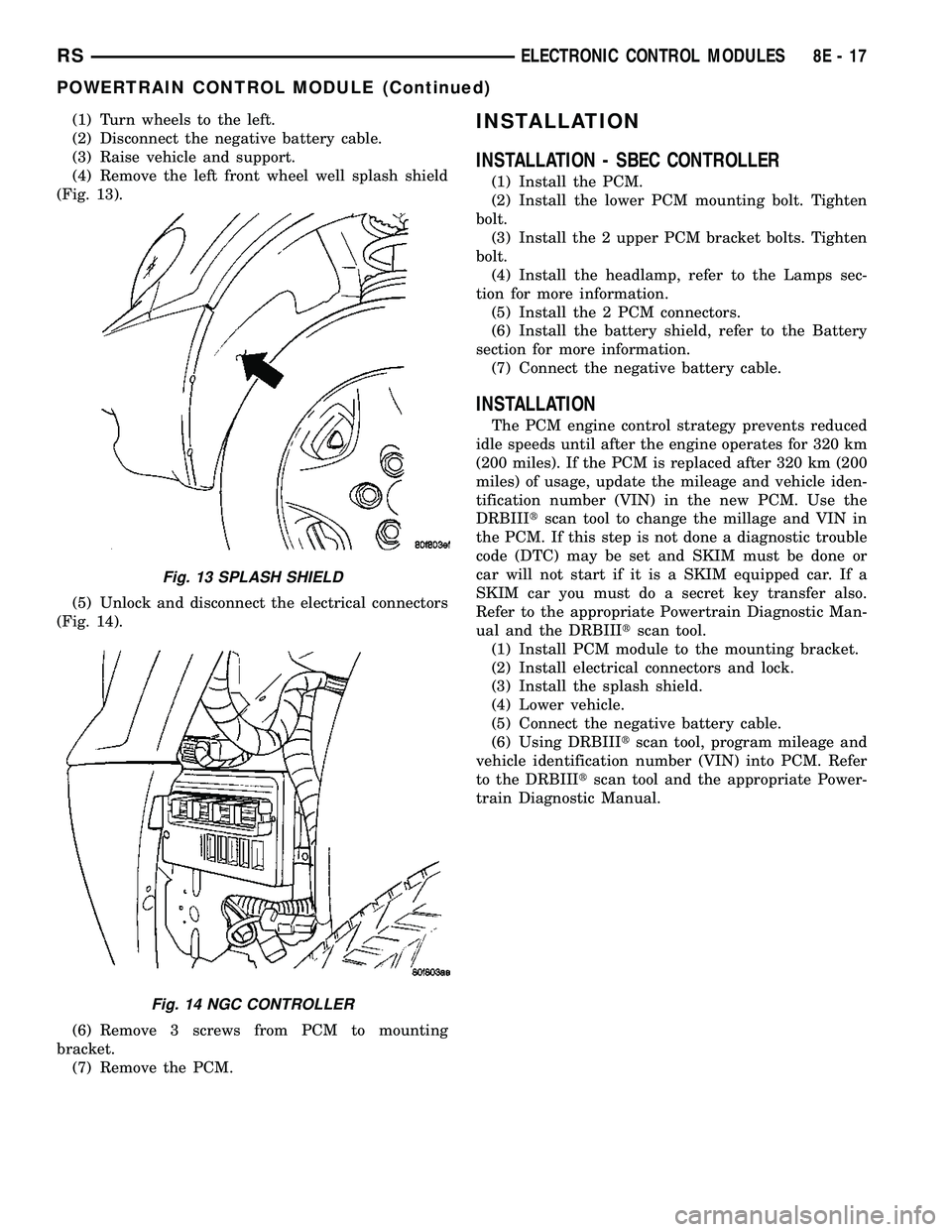
(1) Turn wheels to the left.
(2) Disconnect the negative battery cable.
(3) Raise vehicle and support.
(4) Remove the left front wheel well splash shield
(Fig. 13).
(5) Unlock and disconnect the electrical connectors
(Fig. 14).
(6) Remove 3 screws from PCM to mounting
bracket.
(7) Remove the PCM.INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - SBEC CONTROLLER
(1) Install the PCM.
(2) Install the lower PCM mounting bolt. Tighten
bolt.
(3) Install the 2 upper PCM bracket bolts. Tighten
bolt.
(4) Install the headlamp, refer to the Lamps sec-
tion for more information.
(5) Install the 2 PCM connectors.
(6) Install the battery shield, refer to the Battery
section for more information.
(7) Connect the negative battery cable.
INSTALLATION
The PCM engine control strategy prevents reduced
idle speeds until after the engine operates for 320 km
(200 miles). If the PCM is replaced after 320 km (200
miles) of usage, update the mileage and vehicle iden-
tification number (VIN) in the new PCM. Use the
DRBIIItscan tool to change the millage and VIN in
the PCM. If this step is not done a diagnostic trouble
code (DTC) may be set and SKIM must be done or
car will not start if it is a SKIM equipped car. If a
SKIM car you must do a secret key transfer also.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Man-
ual and the DRBIIItscan tool.
(1) Install PCM module to the mounting bracket.
(2) Install electrical connectors and lock.
(3) Install the splash shield.
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
(6) Using DRBIIItscan tool, program mileage and
vehicle identification number (VIN) into PCM. Refer
to the DRBIIItscan tool and the appropriate Power-
train Diagnostic Manual.
Fig. 13 SPLASH SHIELD
Fig. 14 NGC CONTROLLER
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-17
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 304 of 2339
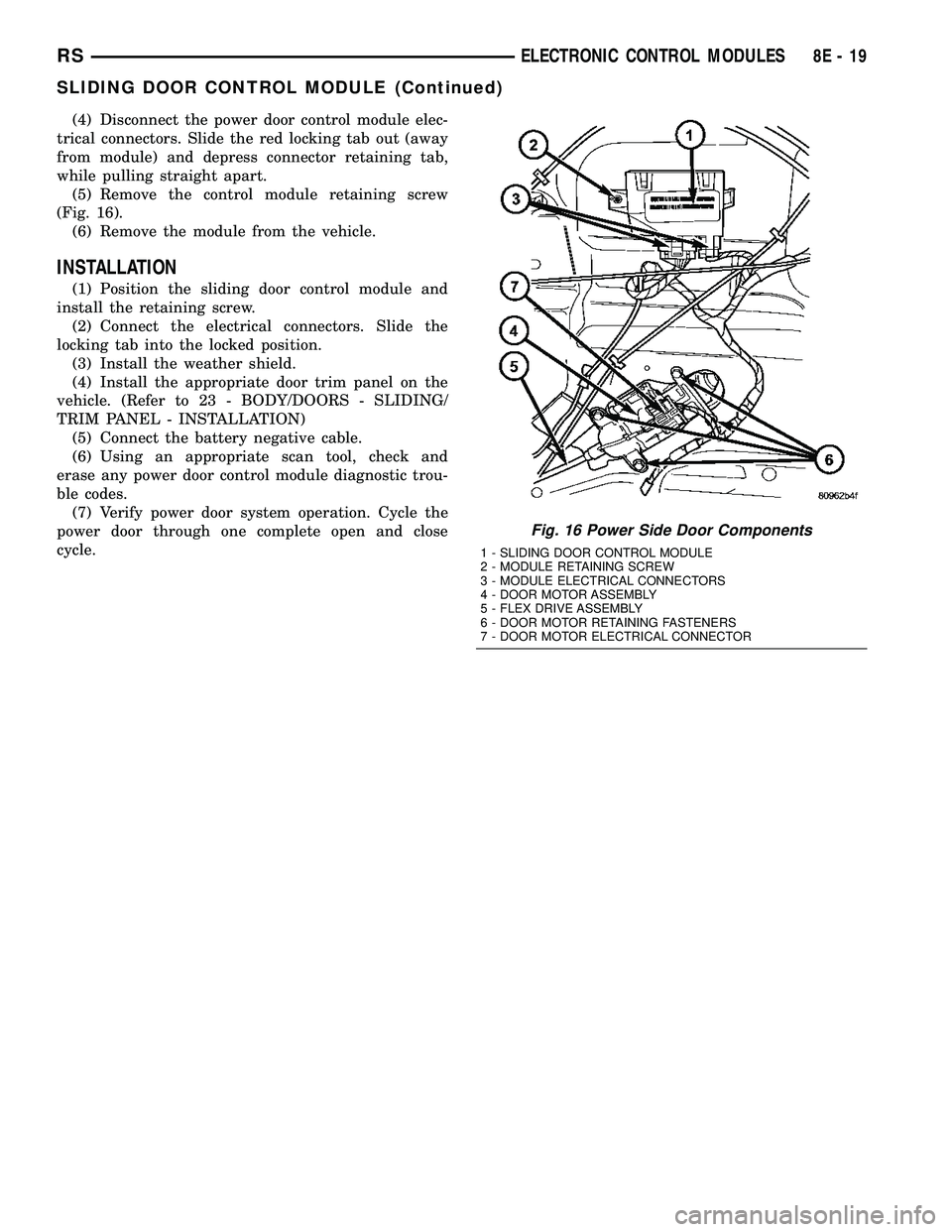
(4) Disconnect the power door control module elec-
trical connectors. Slide the red locking tab out (away
from module) and depress connector retaining tab,
while pulling straight apart.
(5) Remove the control module retaining screw
(Fig. 16).
(6) Remove the module from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the sliding door control module and
install the retaining screw.
(2) Connect the electrical connectors. Slide the
locking tab into the locked position.
(3) Install the weather shield.
(4) Install the appropriate door trim panel on the
vehicle. (Refer to 23 - BODY/DOORS - SLIDING/
TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION)
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
(6) Using an appropriate scan tool, check and
erase any power door control module diagnostic trou-
ble codes.
(7) Verify power door system operation. Cycle the
power door through one complete open and close
cycle.
Fig. 16 Power Side Door Components
1 - SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE
2 - MODULE RETAINING SCREW
3 - MODULE ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
4 - DOOR MOTOR ASSEMBLY
5 - FLEX DRIVE ASSEMBLY
6 - DOOR MOTOR RETAINING FASTENERS
7 - DOOR MOTOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-19
SLIDING DOOR CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 327 of 2339

ULES/POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE -
DESCRIPTION) section for more DTC information.
The Charging system ªBatteryº light indicates
problems with the charging system (voltage too high/
low, generator failure, etc.). If an extreme condition is
indicated, the lamp will be illuminated. The signal to
activate the lamp is sent via the PCI bus circuits.
The lamp is located on the instrument panel. Refer
to the Instrument Cluster section for additional infor-
mation.
The PCM uses the ambient air temperature sensor
to control the charge system voltage. This tempera-
ture, along with data from monitored line voltage, is
used by the PCM to vary the battery charging rate.
The system voltage is higher at cold temperatures
and is gradually reduced as the calculated battery
temperature increases.
The ambient temperature sensor is used to control
the battery voltage based upon ambient temperature
(approximation of battery temperature). The PCM
maintains the optimal output of the generator by
monitoring battery voltage and controlling it to a
range of 13.5 - 14.7 volts based on battery tempera-
ture.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
critical input and output circuits of the charging sys-
tem, making sure they are operational. A Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned to each input and
output circuit monitored by the OBD system. Some
circuits are checked continuously and some are
checked only under certain conditions.
If the OBD system senses that a monitored circuit
is bad, it will put a DTC into electronic memory. The
DTC will stay in electronic memory as long as the
circuit continues to be bad. The PCM is programmed
to clear the memory after 40 good trip if the problem
does not occur again.
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
A DTC description can be read using the DRBIIIt
scan tool. Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
nostic Procedures manual for information.
A DTC does not identify which component in a cir-
cuit is bad. Thus, a DTC should be treated as a
symptom, not as the cause for the problem. In some
cases, because of the design of the diagnostic test
procedure, a DTC can be the reason for another DTC
to be set. Therefore, it is important that the test pro-
cedures be followed in sequence, to understand what
caused a DTC to be set.ERASING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
The DRBIIItScan Tool must be used to erase a
DTC.
The following procedures may be used to diagnose
the charging system if:
²the check gauges lamp or battery lamp is illumi-
nated with the engine running
²the voltmeter (if equipped) does not register
properly
²an undercharged or overcharged battery condi-
tion occurs.
Remember that an undercharged battery is often
caused by:
²accessories being left on with the engine not
running
²a faulty or improperly adjusted switch that
allows a lamp to stay on. Refer to Ignition-Off Draw
Test (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/
BATTERY - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
²loose generator belt.
INSPECTION
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) monitors
critical input and output circuits of the charging sys-
tem, making sure they are operational. A Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) is assigned to each input and
output circuit monitored by the On-Board Diagnostic
(OBD) system. Some charging system circuits are
checked continuously, and some are checked only
under certain conditions.
Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Codes in; Powertrain
Diagnostic manual for more DTC information. This
will include a complete list of DTC's including DTC's
for the charging system.
To perform a complete test of the charging system,
refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Proce-
dures service manual and the DRBIIItscan tool.
Perform the following inspections before attaching
the scan tool.
(1) Inspect the battery condition. Refer to the Bat-
tery section (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY
SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING) for proce-
dures.
(2) Inspect condition of battery cable terminals,
battery posts, connections at engine block, starter
solenoid and relay. They should be clean and tight.
Repair as required.
(3) Inspect all fuses in both the fuseblock and
Power Distribution Center (PDC) or IPM (if
equipped) for tightness in receptacles. They should be
properly installed and tight. Repair or replace as
required.
(4) Inspect generator mounting bolts for tightness.
Replace or tighten bolts if required. Refer to the Gen-
erator Removal/Installation section of this group for
8F - 22 CHARGINGRS
CHARGING (Continued)
Page 436 of 2339
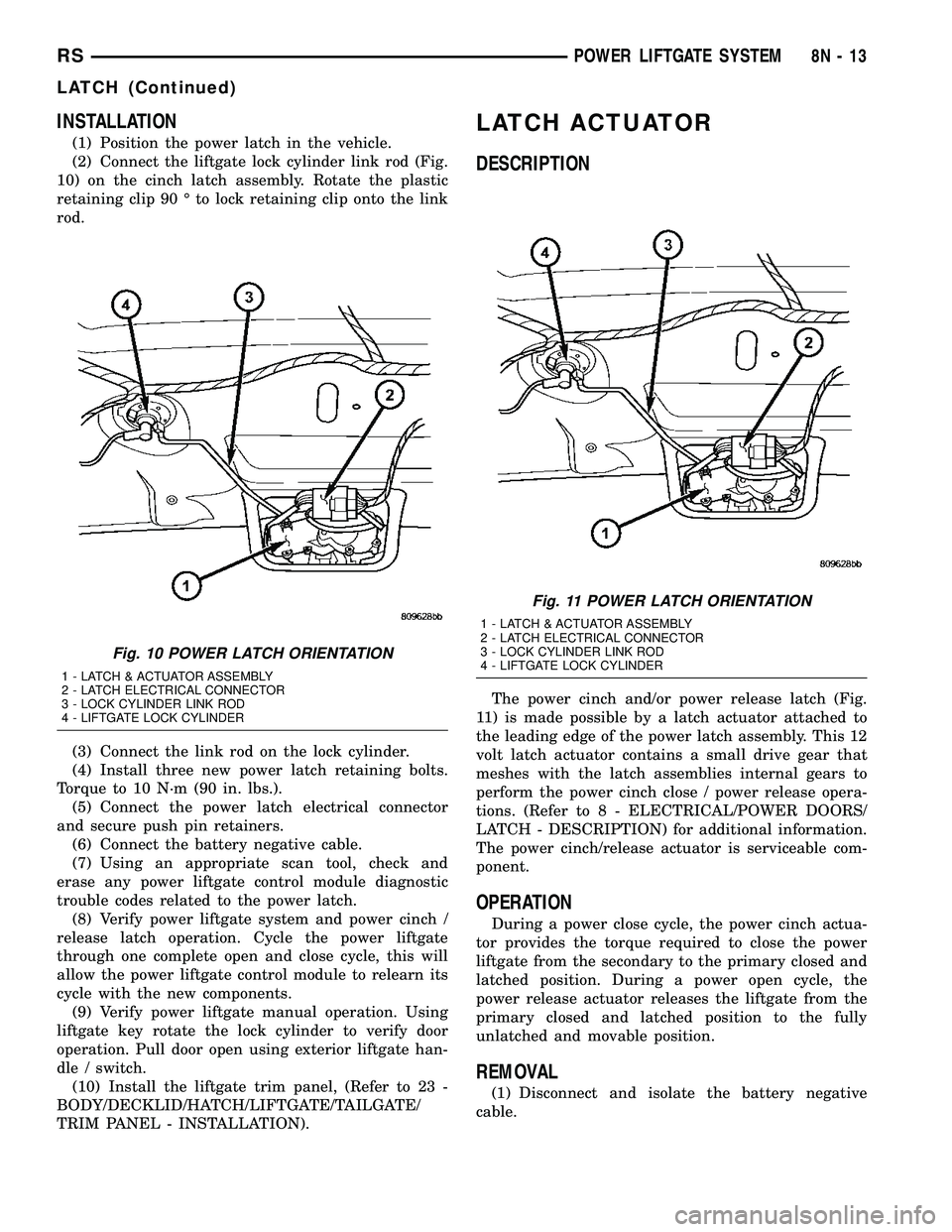
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the power latch in the vehicle.
(2) Connect the liftgate lock cylinder link rod (Fig.
10) on the cinch latch assembly. Rotate the plastic
retaining clip 90 É to lock retaining clip onto the link
rod.
(3) Connect the link rod on the lock cylinder.
(4) Install three new power latch retaining bolts.
Torque to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(5) Connect the power latch electrical connector
and secure push pin retainers.
(6) Connect the battery negative cable.
(7) Using an appropriate scan tool, check and
erase any power liftgate control module diagnostic
trouble codes related to the power latch.
(8) Verify power liftgate system and power cinch /
release latch operation. Cycle the power liftgate
through one complete open and close cycle, this will
allow the power liftgate control module to relearn its
cycle with the new components.
(9) Verify power liftgate manual operation. Using
liftgate key rotate the lock cylinder to verify door
operation. Pull door open using exterior liftgate han-
dle / switch.
(10) Install the liftgate trim panel, (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE/
TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION).
LATCH ACTUATOR
DESCRIPTION
The power cinch and/or power release latch (Fig.
11) is made possible by a latch actuator attached to
the leading edge of the power latch assembly. This 12
volt latch actuator contains a small drive gear that
meshes with the latch assemblies internal gears to
perform the power cinch close / power release opera-
tions. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER DOORS/
LATCH - DESCRIPTION) for additional information.
The power cinch/release actuator is serviceable com-
ponent.
OPERATION
During a power close cycle, the power cinch actua-
tor provides the torque required to close the power
liftgate from the secondary to the primary closed and
latched position. During a power open cycle, the
power release actuator releases the liftgate from the
primary closed and latched position to the fully
unlatched and movable position.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
Fig. 10 POWER LATCH ORIENTATION
1 - LATCH & ACTUATOR ASSEMBLY
2 - LATCH ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - LOCK CYLINDER LINK ROD
4 - LIFTGATE LOCK CYLINDER
Fig. 11 POWER LATCH ORIENTATION
1 - LATCH & ACTUATOR ASSEMBLY
2 - LATCH ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - LOCK CYLINDER LINK ROD
4 - LIFTGATE LOCK CYLINDER
RSPOWER LIFTGATE SYSTEM8N-13
LATCH (Continued)
Page 437 of 2339
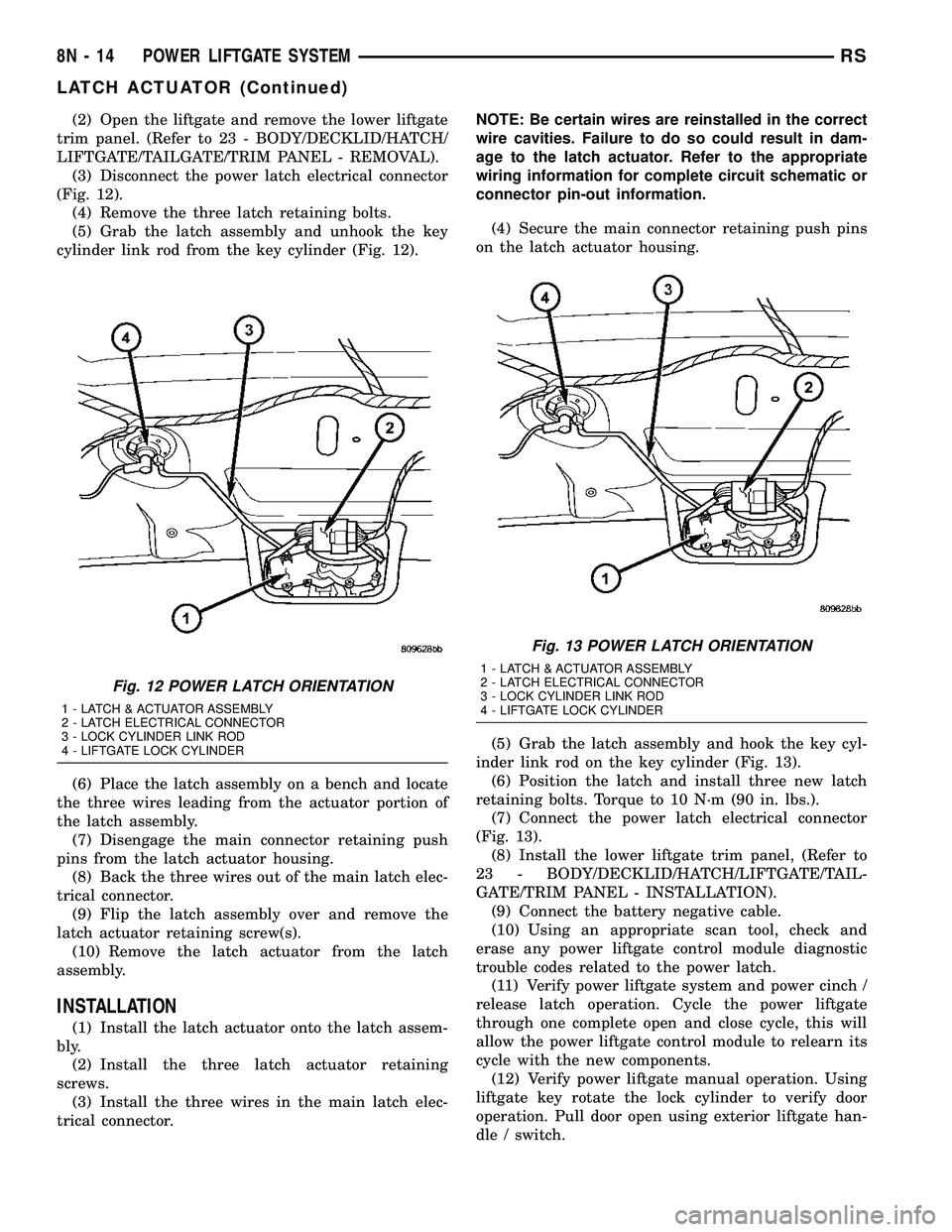
(2) Open the liftgate and remove the lower liftgate
trim panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/DECKLID/HATCH/
LIFTGATE/TAILGATE/TRIM PANEL - REMOVAL).
(3) Disconnect the power latch electrical connector
(Fig. 12).
(4) Remove the three latch retaining bolts.
(5) Grab the latch assembly and unhook the key
cylinder link rod from the key cylinder (Fig. 12).
(6) Place the latch assembly on a bench and locate
the three wires leading from the actuator portion of
the latch assembly.
(7) Disengage the main connector retaining push
pins from the latch actuator housing.
(8) Back the three wires out of the main latch elec-
trical connector.
(9) Flip the latch assembly over and remove the
latch actuator retaining screw(s).
(10) Remove the latch actuator from the latch
assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the latch actuator onto the latch assem-
bly.
(2) Install the three latch actuator retaining
screws.
(3) Install the three wires in the main latch elec-
trical connector.NOTE: Be certain wires are reinstalled in the correct
wire cavities. Failure to do so could result in dam-
age to the latch actuator. Refer to the appropriate
wiring information for complete circuit schematic or
connector pin-out information.
(4) Secure the main connector retaining push pins
on the latch actuator housing.
(5) Grab the latch assembly and hook the key cyl-
inder link rod on the key cylinder (Fig. 13).
(6) Position the latch and install three new latch
retaining bolts. Torque to 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(7) Connect the power latch electrical connector
(Fig. 13).
(8) Install the lower liftgate trim panel, (Refer to
23 - BODY/DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAIL-
GATE/TRIM PANEL - INSTALLATION).
(9) Connect the battery negative cable.
(10) Using an appropriate scan tool, check and
erase any power liftgate control module diagnostic
trouble codes related to the power latch.
(11) Verify power liftgate system and power cinch /
release latch operation. Cycle the power liftgate
through one complete open and close cycle, this will
allow the power liftgate control module to relearn its
cycle with the new components.
(12) Verify power liftgate manual operation. Using
liftgate key rotate the lock cylinder to verify door
operation. Pull door open using exterior liftgate han-
dle / switch.
Fig. 12 POWER LATCH ORIENTATION
1 - LATCH & ACTUATOR ASSEMBLY
2 - LATCH ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - LOCK CYLINDER LINK ROD
4 - LIFTGATE LOCK CYLINDER
Fig. 13 POWER LATCH ORIENTATION
1 - LATCH & ACTUATOR ASSEMBLY
2 - LATCH ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
3 - LOCK CYLINDER LINK ROD
4 - LIFTGATE LOCK CYLINDER
8N - 14 POWER LIFTGATE SYSTEMRS
LATCH ACTUATOR (Continued)
Page 444 of 2339

a second time. Pressing the Panic button also acti-
vates the courtesy lamps. Pressing the Panic button
again stops the exterior lamps from flashing and the
horn from sounding. However, the courtesy lamps
will remain illuminated until either the BCM times
out lamp operation or until the turning of the igni-
tion. The panic feature will operate if the ignition is
ON, but only if the Panic button is pressed prior to
starting the vehicle. A vehicle speed of about 25.7
km/h (15 miles-per-hour) will also cancel the panic
event.
The RKE system can also perform other functions
on this vehicle. If the vehicle is equipped with the
optional Vehicle Theft Security System (VTSS), the
RKE transmitter will arm the VTSS when the Lock
button is depressed, and disarm the VTSS when the
Unlock button is depressed.
The RKE system includes two transmitters when
the vehicle is shipped from the factory, but the sys-
tem can retain the vehicle access codes of up to a
total of eight transmitters. If an RKE transmitter is
inoperative or lost, new transmitter vehicle access
codes can be programmed into the system using a
DRB IIItscan tool.
This vehicle also offers several customer program-
mable features, which allows the selection of several
optional electronic features to suit individual prefer-
ences. Customer programmable feature options
affecting the RKE system include:
²Automatic Door Lock- Customer programma-
ble feature that allows the BCM to perform an auto-
matic door lock if the vehicle speed is above 25.7
km/h (15 miles-per-hour).
²Automatic Door Unlock On Exit- Customer
programmable feature that allows the BCM to per-
form an automatic door unlock if the vehicle speed is
0, vehicle in park and driver door is opened.
²Flash Lights with Lock and Unlock- Allows
the option of having the park lamps flash as an opti-
cal verification that the RKE system received a valid
Lock request or Unlock request from the RKE trans-
mitter, or having no optical verification.
²Programming Additional Transmitters-
Allows up to a total of four transmitter vehicle access
codes to be stored.
²Remote Unlock Sequence- Allows the option
of having only the driver side front door unlock when
the RKE transmitter Unlock button is depressed the
first time. The remaining doors unlock when the but-
ton is depressed a second time within 5 seconds of
the first unlock press. Another option is having all
doors unlock upon the first depression of the RKE
transmitter Unlock button.
²Sound Horn on Lock- Allows the option of
having the horn sound a short chirp as an audible
verification that the RKE system received a validLock request from the RKE transmitter, or having no
audible verification.
OPERATION
POWER LOCKS
The Body Control Module (BCM) locks or unlocks
the doors when an actuation input signal from a door
lock switch, Central Lock key cylinder or Remote
Keyless Entry (RKE) is received. The BCM turns on
the output drivers and provides a voltage level to the
door lock motor for a specified time.
REMOTE KEYLESS ENTRY
The RKE transmitter uses radio frequency signals
to communicate with the SKREEM module. The
SKREEM is on the PCI bus. When the operator
presses a button on the transmitter, it sends a spe-
cific request to the SKREEM. In turn, the SKREEM
sends the appropriate request over the PCI bus to
the following:
²Integrated Power Module (IPM)- to activate
the park lamps, the headlamps and the horn for the
horn chirp.
²Power Liftgate Module (PLGM)- to control
the liftgate lock and unlock functions.
After pressing the lock button on the RKE trans-
mitter, all of the door locks will lock, the illuminated
entry will turn off (if all doors are closed) and the
vehicle theft security system (if equipped) will arm.
Pressing the unlock button one time will unlock
the driver door, or all doors based on the customer
programmable feature enabled, the illuminated entry
will turn on the courtesy lamps and the vehicle theft
security system (if equipped) will disarm. Pressing
the unlock button a second time, the remaining door
locks will unlock.
If the vehicle is equipped with the memory system,
the memory message will identify which transmitter
(1 or 2) sent the signal.
ROLLING CODE
The rolling code feature changes part of the trans-
mitter message each time that it is used. The trans-
mitter message and the receiver message increment
together. Under certain conditions with a rolling code
system, such as pressing a button on the RKE trans-
mitter over 255 times outside of receiver range or
replacing the battery, the receiver and transmitter
can fall out of synchronization. To re-synchronize,
press and release the UNLOCK button on the RKE
transmitter repeatedly (it may take up to eight
cycles) while listening carefully for the power door
locks in the vehicle to cycle, indicating that resyn-
chronization has occurred.
RSPOWER LOCKS8N-21
POWER LOCKS (Continued)
Page 464 of 2339
travel. This allows the power sliding door to stop and
reverse direction any time an obstruction is felt or
any of the command switches are operated (while
closing only). Battery voltage is supplied to the power
sliding door system through a 40 amp fuse, located in
the Integrated Power Module (IPM) assembly. The
child lockout switch prevents children from opening
or actuating the power sliding door system when
desired. In the unlikely event that the power sliding
door system develops a fault, the power sliding door
can still be operated manually from the interior or
exterior door handle, just like a standard manual
sliding door.
The power sliding door control module communi-
cates on the Programmable Communication Interface
(PCI) Data Bus Circuit. Therefore, the power sliding
door control module can generate and store its own
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC). A diagnostic scan
tool, such as the DRB IIItis used to read and diag-
nose these trouble codes.
NOTE: It may be possible to generate Sliding Door
Diagnostic Trouble Codes during normal power
sliding door operation. Refer to the Body Diagnos-
tic Manual for a complete list of diagnostic routines.
For additional information, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/POWER DOORS - OPERATION). Refer to the
appropriate wiring information for complete circuit
schematic or connector pin-out information.WARNING: BE CERTAIN TO READ ALL WARNINGS
AND CAUTIONS IN POWER SLIDING DOOR OPER-
ATION BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY SERVICE OF
THE POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM OR COMPO-
NENTS.
OPERATION
With the push of a power sliding door open/close
command switch (key fob, overhead console or B-pil-
lar mounted) a signal is sent out to the Body Control
Module (BCM). The BCM then sends a signal out on
the Programmable Communication Interface (PCI)
Data Bus circuit to the power sliding door module.
The power sliding door module then signals the
power sliding door latch to release the door to the
unlatched and movable position. The motor then
starts an open cycle.
During the door cycle, if the power sliding door
module detects sufficient resistance to door travel,
such as an obstruction in the door's path, the power
sliding door module will immediately stop door move-
ment and reverse door travel to the full open or
closed position. The ability for the power sliding door
module to detect resistance to door travel is accom-
plished by hall effect sensors detecting the door
motor speed.
The power sliding door control module has the abil-
ity to learn. Anytime a door is opened or closed using
the power sliding door system the module learns
from its cycle. If a replacement power sliding door
component is installed or a door adjustment is made,
the module must re-learn the effort required to open
or close the door. A learn cycle can be performed with
a complete cycle of the door, using any one of the
command switches or with the DRB IIIt, or equiva-
lent scan tool. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
DOORS - STANDARD PROCEDURE - LEARN
CYCLE) for detailed instructions.
The power sliding door system is designed with a
number of system inhibitors. These inhibitors are
necessary for safety and/or feasibility of the power
sliding door system. The power sliding door system
inhibitors are:
²The power sliding door must be in thefullopen
or closed position in order for the power sliding door
system to start a cycle. If the door is not in this posi-
tion (based on the input from the full open, pawl or
ratchet switches) the door control module will not
respond to command switch inputs.
²The transmission must be inpark or neutral
in order for the power sliding door system to start a
cycle.
²The child lockout switch must be in the
ªUNLOCKEDº position in order for the power sliding
door systems B-pillar switches to function.
Fig. 1 KEY FOB
1 - LEFT SLIDING DOOR SWITCH
2 - RIGHT SLIDING DOOR SWITCH
3 - LIFTGATE SWITCH
RSPOWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM8N-41
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 465 of 2339

²If multiple obstacles are detected during the
same power open or close cycle the power sliding
door may go into full manual mode.
²If severe Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) are
stored in the power sliding door control module the
power sliding door may go into full manual mode.
²Due to the high pressure created in the passen-
ger compartment with the blower motor on high, the
power sliding door may not complete a power close
cycle unless a window is cracked, allowing the pres-
sure to escape. This situation will only be experi-
enced on some vehicles, or vehicles with brand new
side door weather seals installed.
²The fuel tank filler door must be in the closed
position. Due to the sliding door interference with
the open fuel tank filler door, a mechanical linkage
prevents the side door from opening and striking the
fuel door. Refer to the Body section of this manual for
detailed information on the fuel door lockout feature.
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM WARNINGS
WARNING: ALWAYS DISCONNECT THE NEGATIVE
BATTERY CABLE BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM SERVICE.
WARNING: EXTREME CARE MUST BE TAKEN TO
PREVENT OBJECTS FROM ENTERING THE DOORS
PATH ONCE THE DOOR REACHES THE CINCH
MOTOR CONTACT (APPROXIMATELY 1 INCH
BEFORE FULLY CLOSED). NEVER PLACE
OBJECTS IN THE POWER SLIDING DOOR WHEN
CINCHING CLOSED. THE OBSTACLE DETECTION
FUNCTION IS INOPERATIVE DURING THE CINCH
PHASE AND DAMAGE TO THE VEHICLE, POWER
SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM OR COMPONENTS
AND/OR PERSONAL INJURY MAY OCCUR.
WARNING: NEVER ATTEMPT TO ENTER OR EXIT
THE VEHICLE WHILE THE POWER SLIDING DOOR
IS IN MOTION. YOU COULD DAMAGE THE POWER
SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM OR COMPONENTS
AND/OR CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY.WARNING: NEVER ATTEMPT TO DRIVE AWAY WITH
THE POWER SLIDING DOOR IN MOTION. YOU
COULD DAMAGE THE POWER SLIDING DOOR SYS-
TEM OR COMPONENTS AND/OR CAUSE PER-
SONAL INJURY.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM
The power sliding door system contains many com-
ponents and modules. In order to obtain conclusive
testing, the Programmable Communications Interface
(PCI) data bus network and all of the electronic mod-
ules that provide inputs to, or receive outputs from
the power sliding door system must be checked.
The power sliding door system was designed to be
diagnosed with an appropriate diagnostic scan tool,
such as the DRB IIIt. The most reliable, efficient,
and accurate means to diagnose the power sliding
door system requires the use of a DRB IIItscan tool
and the proper Body Diagnostic Procedures manual.
The DRB IIItcan be used to observe various switch
statuses throughout the power sliding door system to
help the technician diagnose a defective switch or
component. The DRB IIItcan also be used to actuate
various components throughout the power sliding
door system to help the technician diagnose a defec-
tive component.
Before any testing of the power sliding door system
is attempted, the battery should be fully charged, all
built-in power sliding door system inhibitors read
and understood (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/POWER
DOORS - OPERATION) and all wire harness and
ground connections inspected around the affected
areas on the vehicle.
The following are quick reference diagnostic tables
to help when diagnosing and testing the power slid-
ing door system.
8N - 42 POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEMRS
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 466 of 2339
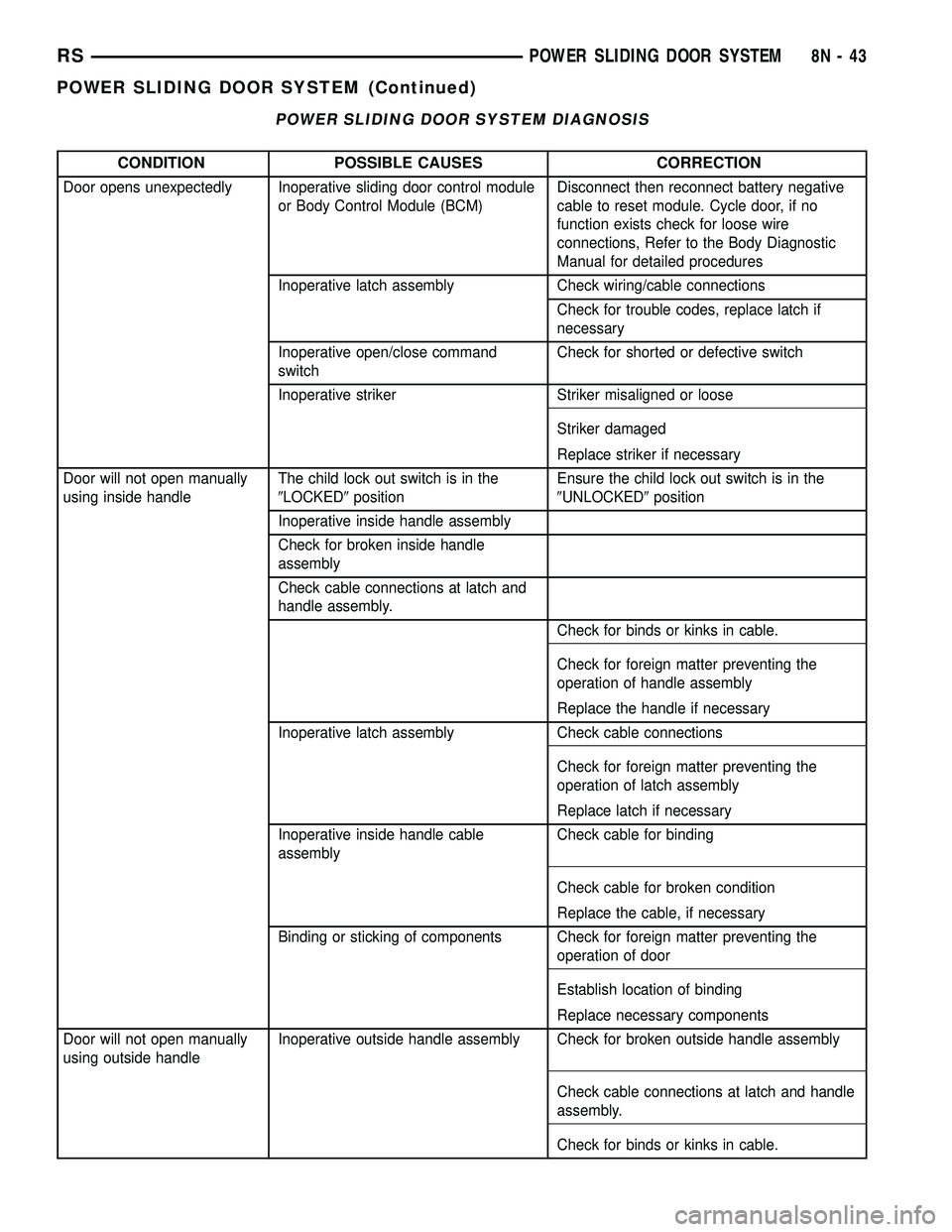
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Door opens unexpectedly Inoperative sliding door control module
or Body Control Module (BCM)Disconnect then reconnect battery negative
cable to reset module. Cycle door, if no
function exists check for loose wire
connections, Refer to the Body Diagnostic
Manual for detailed procedures
Inoperative latch assembly Check wiring/cable connections
Check for trouble codes, replace latch if
necessary
Inoperative open/close command
switchCheck for shorted or defective switch
Inoperative striker Striker misaligned or loose
Striker damaged
Replace striker if necessary
Door will not open manually
using inside handleThe child lock out switch is in the
9LOCKED9positionEnsure the child lock out switch is in the
9UNLOCKED9position
Inoperative inside handle assembly
Check for broken inside handle
assembly
Check cable connections at latch and
handle assembly.
Check for binds or kinks in cable.
Check for foreign matter preventing the
operation of handle assembly
Replace the handle if necessary
Inoperative latch assembly Check cable connections
Check for foreign matter preventing the
operation of latch assembly
Replace latch if necessary
Inoperative inside handle cable
assemblyCheck cable for binding
Check cable for broken condition
Replace the cable, if necessary
Binding or sticking of components Check for foreign matter preventing the
operation of door
Establish location of binding
Replace necessary components
Door will not open manually
using outside handleInoperative outside handle assembly Check for broken outside handle assembly
Check cable connections at latch and handle
assembly.
Check for binds or kinks in cable.
RSPOWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM8N-43
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM (Continued)