lock CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 1245 of 2339
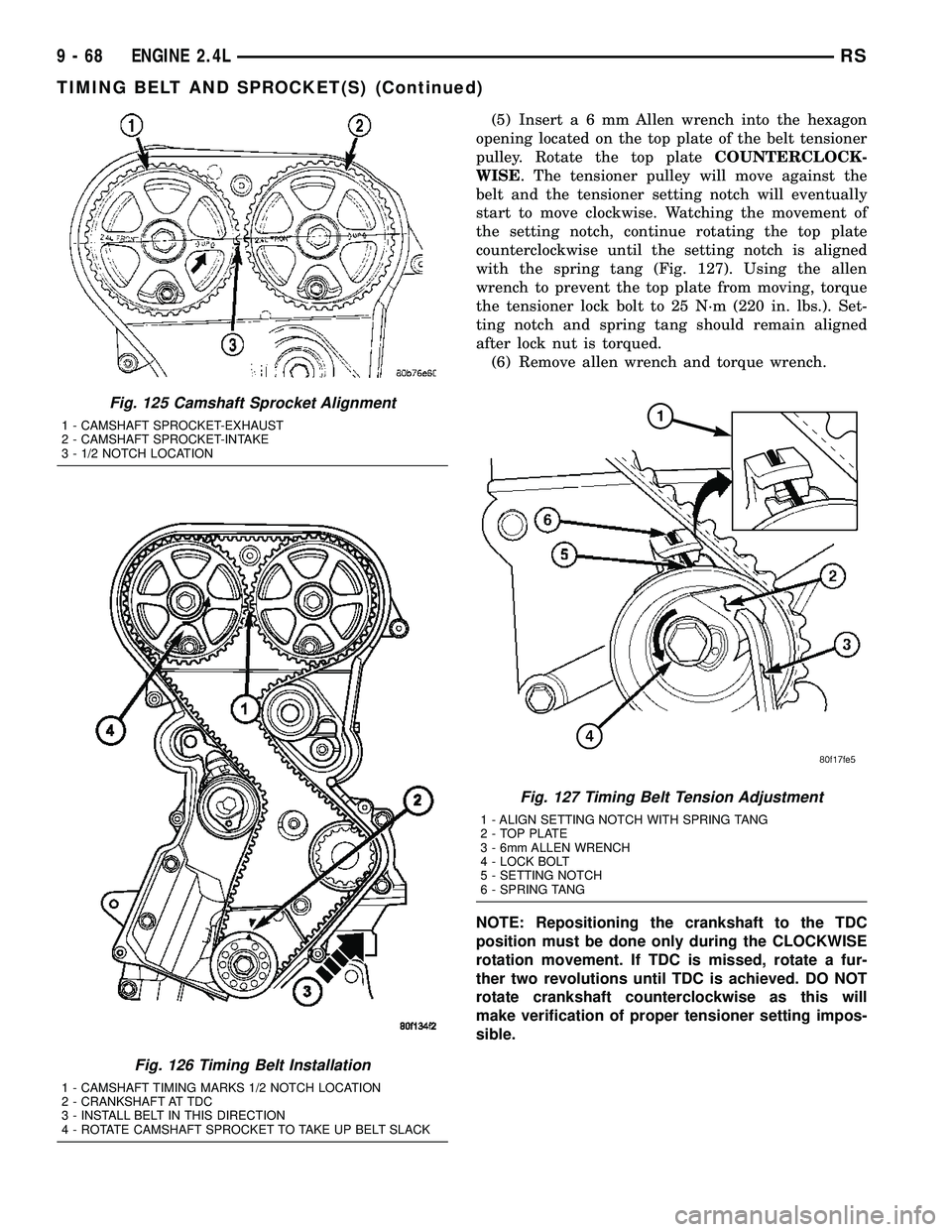
(5) Inserta6mmAllen wrench into the hexagon
opening located on the top plate of the belt tensioner
pulley. Rotate the top plateCOUNTERCLOCK-
WISE. The tensioner pulley will move against the
belt and the tensioner setting notch will eventually
start to move clockwise. Watching the movement of
the setting notch, continue rotating the top plate
counterclockwise until the setting notch is aligned
with the spring tang (Fig. 127). Using the allen
wrench to prevent the top plate from moving, torque
the tensioner lock bolt to 25 N´m (220 in. lbs.). Set-
ting notch and spring tang should remain aligned
after lock nut is torqued.
(6) Remove allen wrench and torque wrench.
NOTE: Repositioning the crankshaft to the TDC
position must be done only during the CLOCKWISE
rotation movement. If TDC is missed, rotate a fur-
ther two revolutions until TDC is achieved. DO NOT
rotate crankshaft counterclockwise as this will
make verification of proper tensioner setting impos-
sible.
Fig. 125 Camshaft Sprocket Alignment
1 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET-EXHAUST
2 - CAMSHAFT SPROCKET-INTAKE
3 - 1/2 NOTCH LOCATION
Fig. 126 Timing Belt Installation
1 - CAMSHAFT TIMING MARKS 1/2 NOTCH LOCATION
2 - CRANKSHAFT AT TDC
3 - INSTALL BELT IN THIS DIRECTION
4 - ROTATE CAMSHAFT SPROCKET TO TAKE UP BELT SLACK
Fig. 127 Timing Belt Tension Adjustment
1 - ALIGN SETTING NOTCH WITH SPRING TANG
2 - TOP PLATE
3 - 6mm ALLEN WRENCH
4 - LOCK BOLT
5 - SETTING NOTCH
6 - SPRING TANG
9 - 68 ENGINE 2.4LRS
TIMING BELT AND SPROCKET(S) (Continued)
Page 1246 of 2339

(7) Rotate the crankshaft CLOCKWISE two com-
plete revolutions manually for seating of the belt,
until the crankshaft is repositioned at the TDC posi-
tion. Verify that the camshaft and crankshaft timing
marks are in proper position (Fig. 128).
(8) Check if the spring tang is within the tolerance
window (Fig. 129). If the spring tang is within the
tolerance window, the installation process is complete
and nothing further is required. If the spring tang is
not within the tolerance window, repeat Steps 5
through 7.
(9) Install engine mount bracket to engine (Fig.
119).
(10) Install timing belt front covers and bolts
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING
BELT COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
(11) Install air conditioning/generator belt ten-
sioner and pulley (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ACCES-
SORY DRIVE/BELT TENSIONERS -
INSTALLATION).
(12) Install right engine mount (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE MOUNTING/RIGHT MOUNT -
INSTALLATION).
(13) Install crankshaft vibration damper (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/VIBRATION
DAMPER - INSTALLATION).(14) Install accessory drive belts (Refer to 7 -
COOLING/ACCESSORY DRIVE/DRIVE BELTS -
INSTALLATION).
(15) Install drive belt splash shield.
(16) Install right front wheel.
(17) Connect make-up air hose to cylinder head
cover.
(18) Install air cleaner housing, upper cover, and
clean air tube.
TIMING BELT TENSIONER &
PULLEY
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT AND SPROCKETS -
REMOVAL).
(2) Remove timing belt idler pulley (Fig. 130).
(3) Hold camshaft sprocket with Special Tool 6847
while removing bolt (Fig. 131). Remove both cam
sprockets.
(4) Remove rear timing belt cover fasteners and
remove cover from engine (Fig. 132).
(5) Remove lower bolt attaching timing belt ten-
sioner assembly to engine and remove tensioneras
an assembly(Fig. 133).
Fig. 128 Crankshaft and Camshaft Timing
1 - CAMSHAFT TIMING MARKS
2 - CRANKSHAFT TDC MARKS
3 - TRAILING EDGE OF SPROCKET TOOTH
Fig. 129 Timing Belt Tension Verification
1 - SPRING TANG
2 - TOLERANCE WINDOW
RSENGINE 2.4L9-69
TIMING BELT AND SPROCKET(S) (Continued)
Page 1248 of 2339

BALANCE SHAFTS AND
CARRIER ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The 2.4L engine is equipped with two nodular cast
iron balance shafts installed in a cast aluminum car-
rier attached to the lower cylinder block (Fig. 134).
OPERATION
The balance shafts are driven by the crankshaft
via a roller chain and sprockets. The balance shafts
are connected by helical gears. The dual counter
rotating shafts decrease second order vertical shak-
ing forces caused by component movement.
REMOVAL
BALANCE SHAFTS/CHAIN/SPROCKETS
NOTE: For service procedures requiring only tem-
porary relocation of carrier assembly refer to BAL-
ANCE SHAFT CARRIER procedure below.
(1) Drain engine oil.
(2) Remove the oil pan and pick-up tube (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(3) If replacing crankshaft sprocket, remove oil
pump (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL
PUMP - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove chain cover, guide and tensioner. Dis-
card pivot screw and adjuster screw. (Fig. 135).
(5) Remove screw retaining balance shaft drive
sprocket (Fig. 136). Remove chain and sprocket.
(6) Using two wide pry bars, work the crankshaft
sprocket back and forth until it is off the crankshaft-
shaft.
(7) Remove gear cover retaining stud (double
ended to also retain chain guide). Remove cover and
balance shaft gears (Fig. 137).
(8) Remove rear cover and balance shafts (Fig.
138).
(9) Remove four carrier to crankcase attaching
bolts to separate carrier from engine bedplate.
BALANCE SHAFT CARRIER
The following components will remain intact dur-
ing carrier removal: Gear cover, gears, balance shafts
and the rear cover (Fig. 134).
(1) Drain engine oil.
(2) Remove the oil pan and pick-up tube (Refer to
9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove chain cover, guide and tensioner (Fig.
135).
(4) Remove screw retaining balance shaft drive
sprocket (Fig. 136).
(5) Move balance shaft inboard through drive
chain sprocket. Sprocket will hang in lower chain
loop.
(6) Remove carrier to crankcase attaching bolts to
remove carrier.
Fig. 133 Timing Belt Tensioner/Bracket Assembly
1 - BOLT
2 - TENSIONER ASSEMBLY
3 - BOLT-INSTALL FOR PROPER ALIGNMENT
RSENGINE 2.4L9-71
TIMING BELT TENSIONER & PULLEY (Continued)
Page 1251 of 2339

(6) Turn crankshaft until number 1 cylinder is at
top dead center (TDC). The timing marks on the
chain sprocket should line up with the parting line
on the left side of number one main bearing cap.
(Fig. 142).(7) Place chain over crankshaft sprocket so that
the plated link of the chain is over the number 1 cyl-
inder timing mark on the balance shaft crankshaft
sprocket (Fig. 142).
(8) Place balance shaft sprocket into the timing
chain (Fig. 142) and align the timing mark on the
sprocket (dot) with the (lower) plated link on the
chain.
NOTE: The lower plated link is 8 links from the
upper link.
(9) With balance shaft keyways pointing up (12
o'clock) slide the balance shaft sprocket onto the nose
of the balance shaft. The balance shaft may have to
be pushed in slightly to allow for clearance.
Fig. 140 Balance Shaft Sprocket Alignment to
Crankshaft
1 - ALIGN FLATS
Fig. 141 Balance Shaft Drive
1 - SPROCKET
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6052Fig. 142 Balance Shaft Timing
1 - MARK ON SPROCKET
2 - KEYWAYS UP
3 - ALIGN MARKS
4 - PLATED LINK
5 - PARTING LINE (BEDPLATE TO BLOCK)
6 - PLATED LINK
9 - 74 ENGINE 2.4LRS
BALANCE SHAFTS AND CARRIER ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1252 of 2339

NOTE: THE TIMING MARK ON THE SPROCKET, THE
(LOWER) NICKEL PLATED LINK, AND THE ARROW
ON THE SIDE OF THE GEAR COVER SHOULD LINE
UP WHEN THE BALANCE SHAFTS ARE TIMED
CORRECTLY.
(10) If the sprockets are timed correctly, install the
balance shaft bolts and tighten to 28 N´m (250 in.
lbs.). A wood block placed between crankcase and
crankshaft counterbalance will prevent crankshaft
and gear rotation.
(11)CHAIN TENSIONING:
(a) Install chain tensioner loosely assembled
withnewshouldered pivot screw and adjuster
screw.
(b) Position guide on double ended stud making
sure tab on the guide fits into slot on the gear
cover. Install and tighten nut/washer assembly to
12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(c) Place a shim 1 mm (0.039 in.) thick x 70 mm
(2.75 in.) long between tensioner and chain. Push
tensioner and shim up against the chain.Apply
firm pressure 2.5±3 Kg (5.5±6.6 lbs.) directly
behind the adjustment slot to take up all
slack.Chain must have shoe radius contact as
shown in (Fig. 143).
(d) With the load applied, tighten top tensioner
bolt first, then bottom pivot bolt. Tighten bolts to
12 N´m (105 in. lbs.). Remove shim.
(e) Install carrier covers and tighten screws to
12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(12) If removed, install oil pump (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PUMP - INSTALLA-
TION).(13) Install pick-up tube and oil pan (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLA-
TION).
(14) Fill engine crankcase with proper oil to cor-
rect level.
Fig. 143 Chain Tension Adjustment
1 - 1MM (0.039 IN.) SHIM
2 - TENSIONER (ADJUSTER) BOLT
3 - PIVOT BOLT
RSENGINE 2.4L9-75
BALANCE SHAFTS AND CARRIER ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 1253 of 2339

ENGINE 3.3/3.8L
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L
DESCRIPTION.........................78
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION...........78
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE...........80
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL.............82
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
LEAK INSPECTION....................84
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST........85
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST...............................85
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING
PLASTIGAGE........................86
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS AND SEALERS . 86
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE
GASKET SURFACE PREPARATION........87
HYDROSTATIC LOCKED ENGINE.........87
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS.........88
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE
AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS..............88
REMOVAL - ENGINE ASSEMBLY...........88
INSTALLATION - ENGINE ASSEMBLY........91
SPECIFICATIONS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE......................93
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE............97
SPECIAL TOOLS
3.3/3.8L ENGINE......................98
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL............................101
INSTALLATION........................101
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL............................101
INSTALLATION........................102
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION........................102
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET...........................102
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD............103
CLEANING...........................103
INSPECTION.........................104
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD.........104CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION........................105
CYLINDER HEAD COVER - RIGHT
REMOVAL............................106
INSTALLATION........................106
CYLINDER HEAD COVER - LEFT
REMOVAL............................107
INSTALLATION........................107
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS
DESCRIPTION........................107
OPERATION..........................107
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFACING
VALVESANDVALVESEATS ............107
REMOVAL............................108
CLEANING...........................108
INSPECTION.........................108
INSTALLATION........................109
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION........................109
OPERATION..........................109
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF.......109
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD ON........111
INSPECTION..........................111
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD OFF . . . 111
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD ON....111
ROCKER ARMS
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ROCKER ARMS.........112
DESCRIPTION - PUSHRODS............112
OPERATION
OPERATION - ROCKER ARMS..........112
OPERATION - PUSHRODS.............112
REMOVAL - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT....112
DISASSEMBLY - ROCKER ARMS
AND SHAFT.........................113
ASSEMBLY - ROCKER ARMS AND SHAFT . . . 113
INSTALLATION - ROCKER ARMS
AND SHAFT.........................113
VALVE STEM SEALS
DESCRIPTION........................114
REMOVAL............................115
INSTALLATION........................115
ENGINE BLOCK
DESCRIPTION........................115
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER BORE
HONING............................115
CLEANING...........................115
9 - 76 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
Page 1254 of 2339

INSPECTION..........................115
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN BLOCK)
DESCRIPTION........................116
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
LIFTERS...........................116
REMOVAL............................117
INSTALLATION........................117
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK)
DESCRIPTION........................118
OPERATION..........................118
REMOVAL............................118
INSPECTION..........................118
INSTALLATION........................118
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION........................119
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
CONNECTING RODS..................119
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
PISTONS...........................120
REMOVAL............................120
INSTALLATION........................121
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CONNECTING ROD BEARING
CLEARANCE........................123
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING............................124
REMOVAL............................124
INSTALLATION........................124
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MAIN BEARING
FITTING............................125
REMOVAL - CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS . 127
INSTALLATION - CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS..........................127
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 3.3L..................128
DESCRIPTION - 3.8L..................128
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY..............128
REMOVAL............................128
INSTALLATION........................129
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
REMOVAL............................130
INSTALLATION........................130
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
REMOVAL............................131
INSTALLATION........................131
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER
REMOVAL............................132
INSTALLATION........................132
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL............................132
INSTALLATION........................132FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL............................133
INSTALLATION........................133
ENGINE MOUNTING
DESCRIPTION........................134
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................134
INSTALLATION........................134
LEFT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................136
INSTALLATION........................136
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL............................136
INSTALLATION........................137
RIGHT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................138
INSTALLATION........................138
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION........................138
OPERATION..........................138
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE.........................138
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
AND FILTER CHANGE.................139
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
LEVEL CHECK.......................140
OIL COOLER & LINES
DESCRIPTION........................141
OPERATION..........................141
REMOVAL............................141
INSTALLATION........................141
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL............................141
INSTALLATION........................141
OIL FILTER ADAPTER
REMOVAL............................142
INSTALLATION........................142
OIL PAN
REMOVAL............................142
CLEANING...........................142
INSPECTION.........................143
INSTALLATION........................143
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
REMOVAL............................143
INSTALLATION........................144
OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................144
OPERATION..........................144
REMOVAL............................144
INSTALLATION........................144
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................144
REMOVAL............................144
DISASSEMBLY........................145
CLEANING...........................145
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-77
Page 1255 of 2339

INSPECTION.........................145
ASSEMBLY...........................146
INSTALLATION........................146
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION........................147
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS....................147
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANIFOLD
STRIPPED THREAD REPAIR............147
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INTAKE
MANIFOLD VACUUM PORT REPAIR......148
REMOVAL - UPPER INTAKE MANIFOLD.....148
CLEANING...........................148
INSPECTION.........................149
INSTALLATION - UPPER INTAKE MANIFOLD . 149
INTAKE MANIFOLD - LOWER
REMOVAL - LOWER INTAKE MANIFOLD....150
CLEANING...........................151
INSPECTION.........................151
INSTALLATION - LOWER INTAKE MANIFOLD . 151
EXHAUST MANIFOLD - RIGHT
REMOVAL............................152
CLEANING...........................153
INSPECTION.........................153INSTALLATION........................153
EXHAUST MANIFOLD - LEFT
REMOVAL............................154
CLEANING...........................154
INSPECTION.........................155
INSTALLATION........................155
VALVE TIMING
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VALVE TIMING
VERIFICATION.......................155
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
TIMING CHAIN WEAR.................155
TIMING CHAIN COVER
REMOVAL............................156
INSTALLATION........................157
TIMING CHAIN AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - TIMING CHAIN AND
CAMSHAFT SPROCKET...............159
REMOVAL - CRANKSHAFT SPROCKET . . . 159
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CRANKSHAFT
SPROCKET.........................160
INSTALLATION - TIMING CHAIN AND
CAMSHAFT SPROCKET...............160
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L
DESCRIPTION
The 3.3 Liter (201 cu. in.) and 3.8 Liter (231 cu.
in.) engines are 60É V-6 engines with cast iron cylin-
der blocks and aluminum cylinder heads (Fig. 1). The
engine uses a single, block mounted camshaft with
pushrods to actuate the valves. These engines do not
have provisions for a free wheeling valve train.
The firing order is 1±2±3±4±5±6. The cylinders are
numbered from the front of the engine to the rear.
The front cylinder bank is numbered 2, 4, and 6. The
rear cylinder bank is numbered 1, 3, and 5.
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block just below the cylinder
head (Fig. 2).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE
DIAGNOSIS - INTRODUCTION
Engine diagnosis is helpful in determining the
causes of malfunctions not detected and remedied by
routine maintenance.These malfunctions may be classified as either
mechanical (e.g., a strange noise), or performance
(e.g., engine idles rough and stalls).
Refer to the Engine Mechanical and the Engine
Performance diagnostic charts, for possible causes
and corrections of malfunctions (Refer to 9 - ENGINE
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MECHANICAL)
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
- PERFORMANCE).
For fuel system diagnosis, (Refer to 14 - FUEL
SYSTEM/FUEL DELIVERY - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING).
Additional tests and diagnostic procedures may be
necessary for specific engine malfunctions that can-
not be isolated with the Service Diagnosis charts.
Information concerning additional tests and diagno-
sis is provided within the following:
²Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
²Cylinder Combustion Pressure Leakage Test
²Engine Cylinder Head Gasket Failure Diagnosis
²Intake Manifold Leakage Diagnosis
²Hydraulic Lash Adjuster Noise Diagnosis
²Engine Oil Leak Inspection
9 - 78 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
Page 1261 of 2339

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL CONSUMPTION OR SPARK
PLUGS FOULED1. PCV system malfunction. 1. Check system and repair as
necessary. (Refer to 25 -
EMISSIONS CONTROL/
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/PCV
VALVE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
2. Worn, scuffed or broken rings. 2. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings.
3. Carbon in oil ring slots. 3. Install new rings.
4. Rings fitted too tightly in grooves. 4. Remove rings and check
grooves. If groove is not proper
width, replace piston.
5. Worn valve guide(s). 5. Replace cylinder head assembly.
6. Valve stem seal(s) worn or
damaged.6. Replace seal(s).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
INSPECTION
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair as necessary.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(5)If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method as follows:
²Disconnect the fresh air hose (make-up air) at
the cylinder head cover and plug or cap the outlet on
the cover.
²Remove the PCV valve hose from the cylinder
head cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve outlet on the
cover.
²Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and reg-
ulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.²Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provides the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
²If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil
seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear
Seal Area Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply.
Remove the air hose, all plugs, and caps. Install the
PCV valve and fresh air hose (make-up air). Proceed
to next step.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
NOTE: If oil leakage is observed at the dipstick tube
to block location; remove the tube, clean and reseal
using MoparTStud & Bearing Mount (press fit tube
applications only), and for O-ring style tubes,
remove tube and replace the O-ring seal.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
9 - 84 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1262 of 2339

(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.(4) Remove the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay from
the PDC.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gauge adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer (Special Tool CH7059) with cable adap-
tors to the DRBIIIt. For Special Tool identification,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIAL TOOLS).
(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gauge. Record this pressure as #1 cylin-
der pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE PRESSURE CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the pressure cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-85
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)